Two-Way Causality Between Economic Growth and Environmental Quality: Scale in the New Capital of Indonesia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Sustainable Development
2.2. Economic Growth
2.3. Environmental Preservation
2.4. Conceptual Development
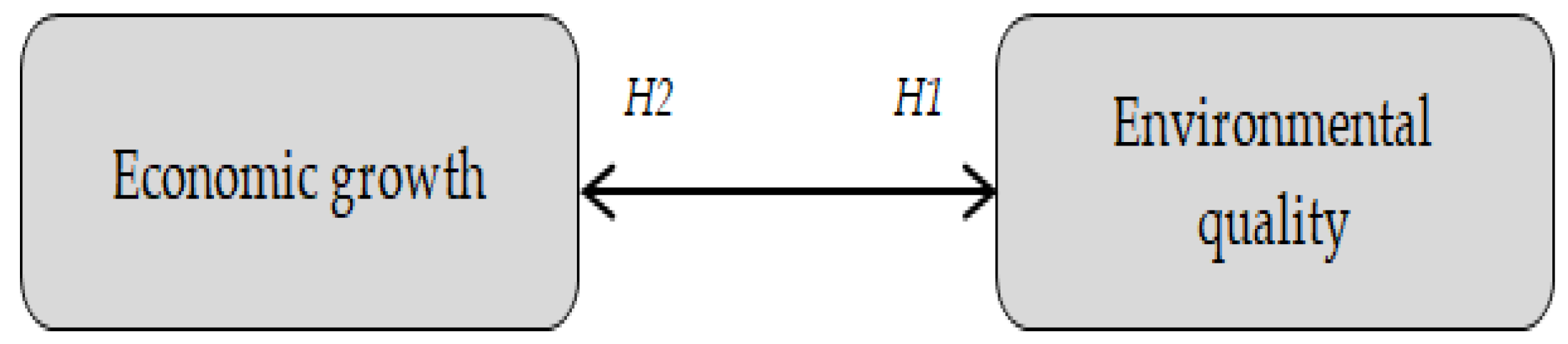
3. Methodology
3.1. Sample Data
3.2. Variables
3.3. Analysis Method
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Main Findings
4.2. Implications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Soliyev, I.I.; Ganiev, B.B. Key factors influencing economic development. Eur. J. Res. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 2, 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Mumford, K.J. Prosperity, sustainability and the measurement of wealth. Asia Pac. Pol. Stud. 2016, 3, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamah, M.; Riti, J.S.; Bin, P. Inclusive growth and environmental sustainability: The role of institutional quality in sub-Saharan Africa. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 34885–34901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krysovatyy, A.; Ptashchenko, O.; Kurtsev, O.; Ovagim, A. The concept of inclusive economy as a component of sustainable development. Probl. Ekorozwoju 2024, 19, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Gao, W.; Li, J. Can economic growth and environmental protection achieve a “win-win” situation? Empirical evidence from China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 9851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.S.; Kabir, M.N. Economic growth and environmental sustainability: Empirical evidence from East and South-East Asia. Int. J. Econ. Fin. 2013, 5, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwarya, W. Exploring the relationship between economic growth and environmental sustainability. J. Manag. Adm. Provis. 2022, 2, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obiora, S.C.; Zeng, Y.; Li, Q.; Asiedu-Ayeh, E.; Nneji, G.U.; Bamisile, O. The economic growth and environmental sustainability nexus: A metanalysis of three economic types. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2021, 65, 2556–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumming, G.S.; von Cramon-Taubadel, S. Linking economic growth pathways and environmental sustainability by understanding development as alternate social-ecological regimes. Proc. Nat. Aca. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 9533–9538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitriadi, F.; Priyagus, P.; Darma, D.C. Assessing the economic feasibility of tourism around IKN: Does it beyond the SDG standards? Indones. J. Tour. Leis. 2023, 4, 153–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiuhardi, J.; Hasid, Z.; Darma, S.; Priyagus, P.; Darma, D.C. Towards the new national capital (IKN) in Indonesia: Premises and challenges of food security. Anuário Inst. Geociências 2024, 47, 55638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyagus, P.; Rahmawati, R.; Darma, D.C. “Not viral, not popular”: What is the format for the development of iKN? In a participatory planning lens. Plan. Malays. 2024, 22, 166–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmawati, R.; Rohmah, M.; Ulfah, Y.; Juwita, R.; Noor, M.F.; Arifin, Z. Becoming a viewer again? Optimizing educational tour at IKN Nusantara to encourage community enthusiasm. J. Perspekt. Pembiayaan Dan Pembang. Drh. 2023, 11, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syaban, A.S.N.; Appiah-Opoku, S. Unveiling the complexities of land use transition in Indonesia’s new capital city IKN Nusantara: A Multidimensional Conflict Analysis. Land 2024, 13, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosyadi, R.; Hasid, Z.; Purwadi, P. Energy operations for resident and its implications for economic growth: Indonesia’s new capital city as a case study. Int. J. Energy Econ. Policy 2023, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lestari, D.; Hasid, Z.; Busari, A.; Ananda, A.A. Multiplier effect of energy infrastructure on GRDP: Horizon in 3 production areas in East Kalimantan–Indonesia. Int. J. Energy Econ. Policy 2022, 12, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adejumo, O.O. Environmental quality vs economic growth in a developing economy: Complements or conflicts. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 6163–6179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cialani, C. Economic growth and environmental quality: An econometric and a decomposition analysis. Manag. Environ. Qual. 2008, 18, 568–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donkor, M.; Kong, Y.; Manu, E.K.; Ntarmah, A.H.; Appiah-Twum, F. Economic growth and environmental quality: Analysis of government expenditure and the causal effect. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indriana, I.; Ismail, N.A.; Rahmat, S.R. Gross domestic regional product, population and environmental quality: Analysis of 33 provinces in Indonesia. J. Appl. Bus. Tax. Econ. Res. 2021, 1, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, X.; Shi, H.; Yan, Y.; Wen, X. Effect of economic growth on environmental quality: Evidence from tropical countries with different income levels. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 774, 145180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rifa’i, A.; Dewi, N.R. Environmental quality and economic growth: Evidence from 10 ASEAN countries. Sustinere J. Environ. Sustain. 2018, 2, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidi, K.; Rahman, M.M. The link between environmental quality, economic growth, and energy use: New evidence from five OPEC countries. Environ. Syst. Decis. 2021, 41, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafik, N. Economic development and environmental quality: An econometric analysis. Oxford Econ. Pap. 1994, 46, 757–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wafiq, A.N.; Suryanto, S. The impact of population density and economic growth on environmental quality: Study in Indonesia. J. Ekon. Studi Pembang. 2021, 22, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Li, H.; Li, Z. Environmental pollution and economic growth: Evidence of SO2 emissions and GDP in China. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 930780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidique, O.; Sadiawati, D.; Pratami, D. Navigating Challenges of New City Development for Nusantara, Indonesia’s Future Capital. 2025. Available online: https://www.ipsnews.net/2023/09/navigating-challenges-new-city-development-nusantara-indonesias-future-capital/ (accessed on 7 February 2025).
- Thomsen, C. Sustainability (World Commission on Environment and Development Definition). In Encyclopedia of Corporate Social Responsibility; Idowu, S.O., Capaldi, N., Zu, L., Gupta, A.D., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Abbas, J.; Sial, M.S.; Álvarez-Otero, S.; Cioca, L.-I. Achieving green innovation and sustainable development goals through green knowledge management: Moderating role of organizational green culture. J. Innov. Knowl. 2022, 7, 100272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Qing, C.; Jin, S. Environmental protection and sustainable development of enterprises in China: The moderating role of media attention. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2022, 10, 966479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langhelle, O. Sustainable development and social justice: Expanding the Rawlsian framework of global justice. Environ. Values 2000, 9, 295–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensah, J. Sustainable development: Meaning, history, principles, pillars, and implications for human action: Literature review. Cog. Soc. Sci. 2019, 5, 1653531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waaswa, A.L.; Satognon, F. Development and the environment: Overview of the development planning process in agricultural sector, in Uganda. J. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamroh, M.R.A. Pembangunan Berkelanjutan [In English: Sustainable Development]. 2020. Available online: https://geohepi.hepidev.com/2020/12/15/pembangunan-berkelanjutan/ (accessed on 25 September 2024).
- Sibe, J.P.; Chiatchoua, C.; Megne, M.N. The long run relationship between population growth and economic growth: A panel data analysis of 30 of the most populated Countries of the world. Análisis Económico 2016, 31, 205–218. [Google Scholar]
- Thornton, J. Population growth and economic growth: Long-run evidence from Latin America. South. Econ. J. 2021, 68, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, E.W.F. The role of population in economic growth. Sage Open 2017, 7, 2158244017736094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazelton, W.R. Alvin Harvey Hansen: Economic growth and a more perfect society: The economist’s role in defining the stagnation thesis and in popularizing Keynesianism. Am. J. Econ. Sociol. 1989, 48, 427–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kothe, E.J.; Ling, M.; North, M.; Klas, A.; Mullan, B.A.; Novoradovskaya, L. Protection motivation theory and pro-environmental behaviour: A systematic mapping review. Aust. J. Psychol. 2019, 71, 411–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, D. Progress on the environmental Kuznets curve? Environ. Dev. Econ. 1998, 3, 173–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhr, H. The rise of the Global South and the rise in carbon emissions. Third World Q. 2021, 42, 2724–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Huo, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Mi, Z.; Guan, D.; Feng, K. The narrowing gap in developed and developing country emission intensities reduces global trade’s carbon leakage. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Xin, L.; Lu, C.; Wu, B.; Zhong, Y. China’s CO2 emissions: A systematical decomposition concurrently from multi-sectors and multi-stages since 1980 by an extended logarithmic mean divisia index. Energy Strategy Rev. 2023, 49, 101141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrow, K.; Bolin, B.; Costanza, R.; Dasgupta, P.; Folke, C.; Holling, C.S.; Jansson, B.-O.; Levin, S.; Mäler, K.-G.; Perrings, C.; et al. Economic growth, carrying capacity, and the environment. Ecol. Econ. 1995, 15, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasid, Z.; Mire, M.S.; Rochaida, E.; Wijaya, A. Power generation infrastructure and its effect on electric energy consumption: Context in Indonesia, 2013–2020. Int. J. Energy Econ. Pol. 2023, 13, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addai, K.; Serener, B.; Kirikkaleli, D. Can environmental sustainability be decoupled from economic growth? Empirical evidence from Eastern Europe using the common correlated effect mean group test. Reg. Sustain. 2023, 4, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, A.G. Relationship between environment and sustainable economic development: A theoretical approach to environmental problems. Int. J. Asian Soc. Sci. 2013, 3, 741–761. [Google Scholar]
- Brad, S.; Mocan, B.; Brad, E.; Fulea, M. Environmentally sustainable economic growth. Amfiteatru Econ. J. 2016, 18, 446–460. [Google Scholar]
- Čábelková, I.; Smutka, L.; Mareš, D.; Ortikov, A.; Kontsevaya, S. Environmental protection or economic growth? The effects of preferences for individual freedoms. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2023, 11, 1129236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Z. Balancing environmental sustainability and economic development: Perspectives from new structural economics. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D. Environmental sustainability and economic development: A world view. J. Econ. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 6, 60–80. [Google Scholar]
- Adebayo, T.S.; Agboola, M.O.; Rjoub, H.; Adeshola, I.; Agyekum, E.B.; Kumar, N.M. Linking economic growth, urbanization, and environmental degradation in China: What is the role of hydroelectricity consumption? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2021, 18, 6975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- das Neves Almeida, T.A.; Cruz, L.; Barata, E.; García-Sánche, I.-M. Economic growth and environmental impacts: An analysis based on a composite index of environmental damage. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 76, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahuthu, A. Economic growth and environmental degradation in a global context. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2006, 8, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondaye, G.; Ondze, C.; Imongui, E. Effects of economic growth on environmental degradation in the Republic of Congo: The case of CO2 emissions. Mod. Econ. 2021, 12, 1703–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettinger, T. Environmental Impact of Economic Growth. 2021. Available online: https://www.economicshelp.org/blog/145989/economics/environmental-impact-of-economic-growth/#:~:text=The%20environmental%20impact%20of%20economic,potential%20loss%20of%20environmental%20habitats (accessed on 3 August 2024).
- Zhao, X.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, W. The impact of environmental pollution and economic growth on public health: Evidence from China. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 861157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prawitasari, N.; Amarullah, R.; Sari, M.A.P.; Azizah, T.N.; Sartika, D.; Kusumaningrum, M.; Wahyuni, T.; Hidayah, K.; Permadi, R.N. Public servant competency development of national capital (IKN) buffer regions as a policy approach in Indonesia. Eur. J. Bus. Manag. 2023, 15, 76–88. [Google Scholar]
- Central Statistics Agency-East Kalimantan. Laju Pertumbuhan Produk Domestik Regional Bruto Atas Dasar harga Konstan 2010 Menurut Kabupaten/Kota [In English: Growth Rate of Gross Regional Domestic Product at Constant 2010 Prices by District/City]. 2024. Available online: https://kaltim.bps.go.id/indicator/157/95/1/-seri-2010-laju-pertumbuhan-pdrb-kabupaten-kota-atas-dasar-harga-konstan-2010.html (accessed on 15 October 2024).
- Ministry of Environment and Forestry-Republic of Indonesia. Indeks Kualitas Lingkungan Hidup Indonesia [In English: Indonesian Environmental Quality Index]; Directorate General of Pollution and Environmental Damage Control: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Kurniawan, E.; Zulfikar, A.L.; Wijaya, A.; Darma, D.C. Harmonization of trading partners between Indonesia–Italy: Empirical calculations of selected agricultural commodities. Indones. J. Dev. Plan. 2024, 8, 91–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarty, D.; Mandal, S.K. Is economic growth a cause or cure for environmental degradation? Empirical evidences from selected developing economies. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 2020, 7, 100045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, G.M.; Krueger, A.B. Economic growth and the environment. Q. J. Econ. 1995, 110, 353–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyagus, P. Does economic growth efficient and environmental safety? The case of transportation sector in Indonesia. Int. J. Energy Econ. Pol. 2022, 11, 365–372. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Yuan, S.; Sun, L. The relationships between economic growth and environmental pollution based on time series data? An empirical study of Zhejiang Province. J. Camb. Stud. 2012, 7, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castiglione, C.; Infante, D.; Smirnova, J. Environment and economic growth: Is the rule of law the go-between? The case of high-income countries. Energy Sustain. Soc. 2015, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everett, T.; Ishwaran, M.; Ansaloni, G.P.; Rubin, A. Economic growth and the environment. In Paper 2: Defra Evidence and Analysis Serie; The Department for Environment, Food & Rural Affairs: London, UK, 2010. Available online: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/69195/pb13390-economic-growth-100305.pdf (accessed on 29 November 2024).
- Gedikli, A. An investigation of the reasons for the natural resource curse: Selected country cases. Buss. Econ. Res. J. 2019, 11, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabegović, A. Institutions, Economic Growth, and The “Curse” of Natural Resources. In Studies in Mining Policy; MacMahon, F., Ed.; Fraser Institute: Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2009; Available online: https://www.fraserinstitute.org/sites/default/files/CurseofNaturalResources2009.pdf (accessed on 10 December 2024).
- Moradbeigi, M.; Law, S.H. Growth volatility and resource curse: Does financial development dampen oil shocks? Res. Pol. 2016, 48, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di John, J. Is there really a resource curse? A critical survey of theory and evidence. Glob. Gov. 2021, 17, 167–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Ferranti, D.; Perry, G.E.; Lederman, D.; Maloney, W.F. From Natural Resources to Knowledge Economy; World Bank Latin American and Caribbean Studies: Washington, DC, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, G.; Czelusta, J. Resource-Based Growth: Past and Present. In Natural Resources: Neither Curse nor Destiny; Lederman, D., Maloney, W.F., Eds.; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2007; pp. 183–212. [Google Scholar]
- Sachs, J.D.; Warner, A.M. The curse of natural resources. Eur. Econ. Rev. 2001, 45, 827–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gylfason, T. Natural resources, education, and economic development. Eur. Econ. Rev. 2001, 45, 847–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gylfason, T.; Herbertsson, T.T.; Zoega, G. A mixed blessing: Natural resources and economic growth. Macroecon. Dyn. 1999, 3, 204–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, C.A.; Weidmann, J. Does Mother Nature Corrupt? Natural Resources, Corruption, and Economic Growth. IMF Working Papers, No. 99/85; IMF: Washington, DC, USA, 1999; Available online: https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/WP/Issues/2016/12/30/Does-Mother-Nature-Corrupt-Natural-Resources-Corruption-and-Economic-Growth-3126 (accessed on 4 December 2024).
- Wulandari, C.; Hayati, B. The relationship between economic development and environmental degradation in Indonesia. Econ. Dev. Anal. J. 2020, 9, 328–342. Available online: https://journal.unnes.ac.id/sju/edaj/article/view/38159 (accessed on 15 December 2024).
- Raihan, A.; Begum, R.A.; Said, M.N.M.; Pereira, J.J. Relationship between economic growth, renewable energy use, technological innovation, and carbon emission toward achieving Malaysia’s Paris agreement. Environ. Syst. Decis. 2022, 42, 586–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardo, D.; Maulana, M.; Hartanto, J. Impact of economic growth and FDI on Indonesia environmental degradation: EKC and pollution hypothesis testing. J. Ekon. Pembang. 2023, 21, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humbatova, S.I.; Hajiyeva, N.; Fodor, M.G.; Sood, K.; Grima, S. The impact of economic growth on the ecological environment and renewable energy production: Evidence from Azerbaijan and Hungary. J. Risk Finan. Manag. 2024, 17, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osuntuyi, B.V.; Lean, H.H. Economic growth, energy consumption and environmental degradation nexus in heterogeneous countries: Does education matter? Environ. Sci. Eur. 2022, 34, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dardouri, N.; Smida, M. The link between economic growth and ecological footprint: What future prospects for the G7 Countries: PMG-ARDL. Migr. Let. 2023, 21, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Li, K.; Duan, S.; Song, C. Economic growth and environmental pollution in China: New evidence from government work reports. Energy Econ. 2023, 124, 106803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acheampong, A.O.; Osei Opoku, E.E. Environmental degradation and economic growth: Investigating linkages and potential pathways. Energy Econ. 2023, 123, 106734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, X.; Yuan, P.; Zhang, Y. Trade-off between environment and economy: The relationship between carbon and inflation. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1093528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velenturf, P.M.; Purnell, P. Principles for a sustainable circular economy. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 27, 1437–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qamruzzaman, M. Do natural resources bestow or curse the environmental sustainability in Cambodia? Nexus between clean energy, urbanization, and financial deepening, natural resources, and environmental sustainability. Energy Strategy Rev. 2024, 53, 101412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariram, N.P.; Mekha, K.B.; Suganthan, V.; Sudhakar, K. Sustainalism: An integrated socio-economic-environmental model to address sustainable development and sustainability. Sustainabilty 2023, 15, 10682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekins, P.; Zenghelis, D. The costs and benefits of environmental sustainability. Sustain. Sci. 2021, 16, 949–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badulescu, D.; Simut, R.; Badulescu, A.; Badulescu, A.V. The relative effects of economic growth, environmental pollution and non-communicable diseases on health expenditures in European Union Countries. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2019, 16, 5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dianjaya, A.R.; Epira, P. Indonesia green economy implementation readiness of greenhouse gas emissions reduction. J. Contemp. Gov. Public Policy 2020, 1, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijayanti, Y.R.; Sari, I.C. Reinvigorating sustainable green economics in Indonesia: Exploring the nexus between global green economy index and SDG 8. J. Indones. Sustain. Dev. Plan. 2024, 5, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suparjo, S.; Darma, S.; Kurniadin, N.; Kasuma, J.; Priyagus, P.; Darma, D.C.; Haryadi, H. Indonesia’s new SDGs agenda for green growth—Emphasis in the energy sector. Int. J. Energy Econ. Policy 2021, 11, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Region | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PPU | 3.13 | 2.64 | 4.7 | −2.9 | 2.55 | 4.48 | 6.22 |
| Paser | 5.17 | 5.07 | 5.09 | −1.82 | 4.8 | 5.07 | 4.46 |
| Balikpapan | 6.73 | 5.61 | 6.12 | −1.41 | 3.59 | 6.45 | 4.14 |
| Samarinda | 5.28 | 5.08 | 4.09 | 1.82 | 3.48 | 5.11 | 4.84 |
| Kutai Kartanegara | 6.8 | 5.36 | 6.89 | −1.09 | 3.99 | 5.32 | 4.94 |
| Indonesia | 5.07 | 5.17 | 5.02 | −2.07 | 3.7 | 5.31 | 5.05 |
| Region | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PPU | 75.65 | 85.9 | 80.87 | 76.45 | 75.06 | 74.46 | 76.15 |
| Paser | 74.17 | 73.09 | 65.92 | 70.07 | 73.22 | 62.39 | 62.9 |
| Balikpapan | 71.47 | 75.71 | 74.2 | 72.74 | 75.29 | 73.97 | 73.41 |
| Samarinda | 69.38 | 68.78 | 61.94 | 68.43 | 71.03 | 68.43 | 73.5 |
| Kutai Kartanegara | 81.87 | 86.88 | 78.98 | 78.49 | 75.06 | 74.46 | 80.95 |
| Indonesia | 66.46 | 71.67 | 66.55 | 70.27 | 71.43 | 72.42 | 72.54 |
| Variable Name | Source | Parameter | Observation Period |
|---|---|---|---|
| Economic growth | Central Statistics Agency-East Kalimantan [59] | Percent (%) | 2017–2023 |
| Environmental quality | Ministry of Environment and Forestry-Republic of Indonesia [60] | Index (points) | 2017–2023 |
| Items | Economic Growth | Environmental Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Mean | 4.05 | 73.75 |
| Median | 4.84 | 74.17 |
| Maximum | 6.89 | 86.88 |
| Minimum | −2.90 | 61.94 |
| Std. deviation | 2.45 | 5.80 |
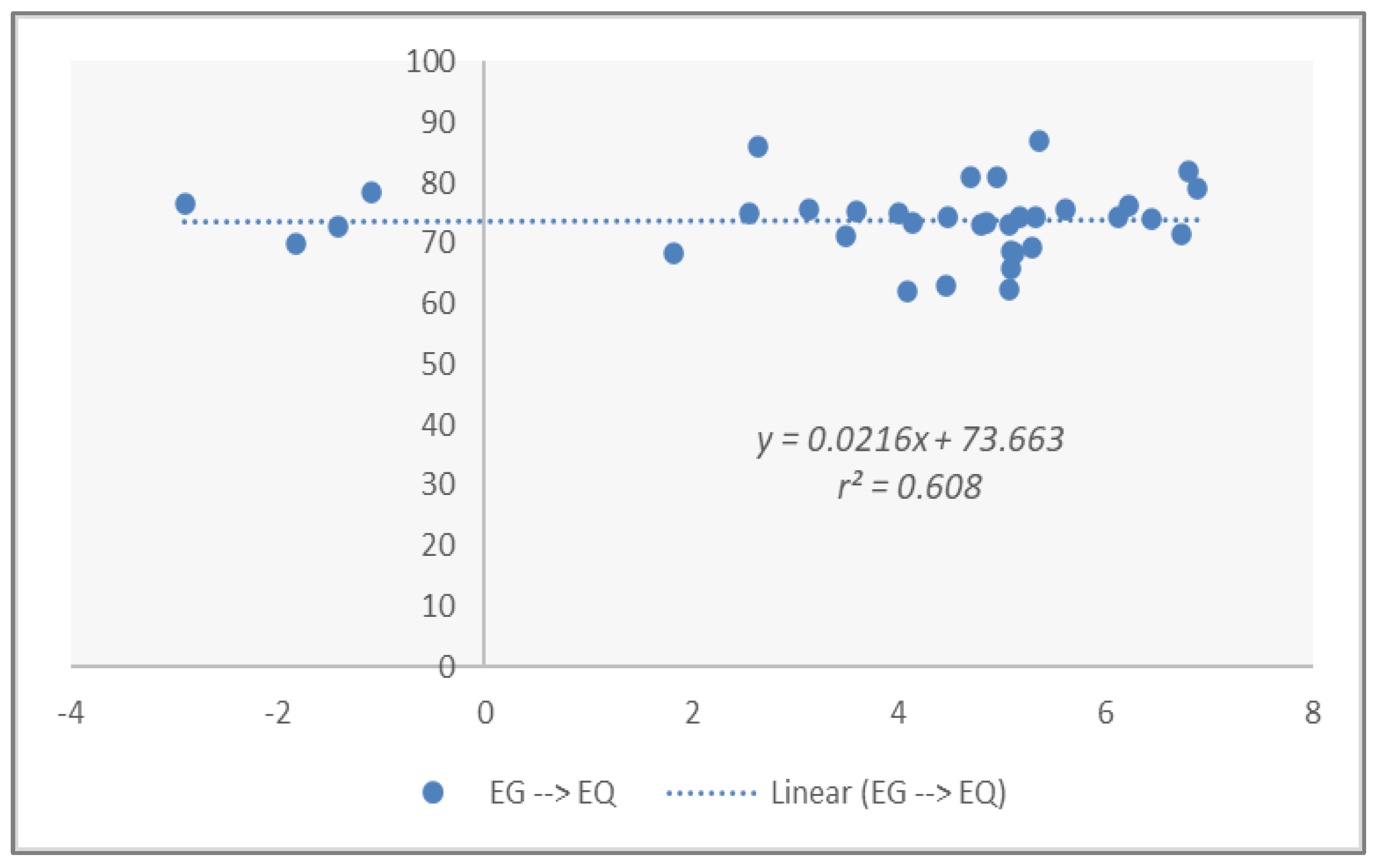
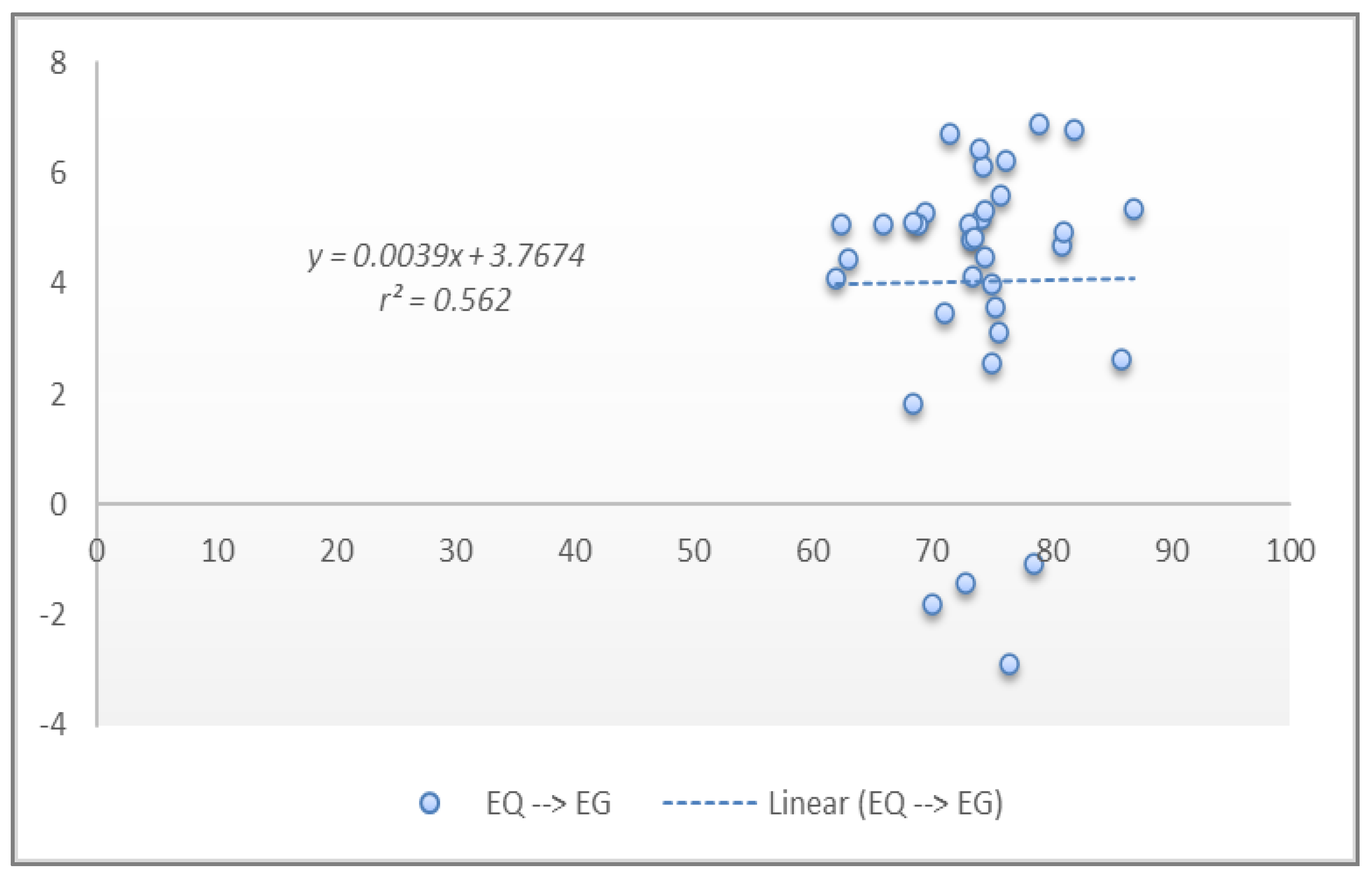
| Pearson | 0.959 (0.009) ** | |
| Kendall’s tau | 0.580 (0.016) * | |
| Spearman’s rho | 0.587 (0.037) * | |
| Obs. | 35 | 35 |
| Items | Model 1 (Economic Growth → Environmental Quality) | Model 2 (Environmental Quality → Economic Growth) |
|---|---|---|
| Constant | 37.909 (0.000) ** | 8.693 (0.043) * |
| Coefficients | 0.959 | 0.493 |
| t-statistics | 3.052 | 2.693 |
| Prob. | 0.009 ** | 0.027 * |
| Lower bound | −0.817 | −0.146 |
| Upper bound | 0.860 | 0.153 |
| F-statistics | 4.605 | 2.485 |
| Prob. | 0.003 ** | 0.023 * |
| Std. error | 5.883 | 3.767 |
| Obs. | 35 | 35 |
| Authorships | Variables (Substance) | Model | Sign |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wulandari and Hayati [78] | Economic growth → Environmental degradation | Vector Error Correction Model (VECM) | + |
| Liu et al. [21] | GDP per capita → Terrestrial carbon sequestration | Panel Model | + |
| Raihan et al. [79] | Economic growth → CO2 emissions | Dynamic Ordinary Least Squares (DOLS) | + |
| Leonardo et al. [80] | Economic growth → Environmental degradation | Error Correction Model (ECM) | + |
| Humbatova et al. [81] | Economic growth → Ecological environment | Autoregressive Distributed Lag (ARDL) | + |
| Osuntuyi and Lean [82] | Economic growth ↔ Environmental damage | Fully Modified Ordinary Least Squares (FMOLS), DLOS, PMG-Autoregressive Distributed Lag (PMG-ARDL), and Common Correlated Effects Mean Group (CCEMG) | + |
| Dardouri and Smida [83] | GDP → Ecological footprint | PMG-ARDL | + |
| Yu et al. [84] | Economic growth → Environmental damage | Two-Stage Least Square (2SLS) | + |
| Acheampong and Opoku [85] | Environmental degradation → Economic growth | Moments Technique Method with Global Panel | - |
| Xu et al. [86] | Carbon → Inflation | Ordinary Least Square (OLS) Regression | + |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nurjanana, N.; Darma, D.C.; Suparjo, S.; Kustiawan, A.; Wasono, W. Two-Way Causality Between Economic Growth and Environmental Quality: Scale in the New Capital of Indonesia. Sustainability 2025, 17, 1656. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17041656
Nurjanana N, Darma DC, Suparjo S, Kustiawan A, Wasono W. Two-Way Causality Between Economic Growth and Environmental Quality: Scale in the New Capital of Indonesia. Sustainability. 2025; 17(4):1656. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17041656
Chicago/Turabian StyleNurjanana, Nurjanana, Dio Caisar Darma, Suparjo Suparjo, Andriawan Kustiawan, and Wasono Wasono. 2025. "Two-Way Causality Between Economic Growth and Environmental Quality: Scale in the New Capital of Indonesia" Sustainability 17, no. 4: 1656. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17041656
APA StyleNurjanana, N., Darma, D. C., Suparjo, S., Kustiawan, A., & Wasono, W. (2025). Two-Way Causality Between Economic Growth and Environmental Quality: Scale in the New Capital of Indonesia. Sustainability, 17(4), 1656. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17041656









