Sustainable Urbanization: Unpacking the Link Between Urban Clusters and Environmental Protection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. Variables
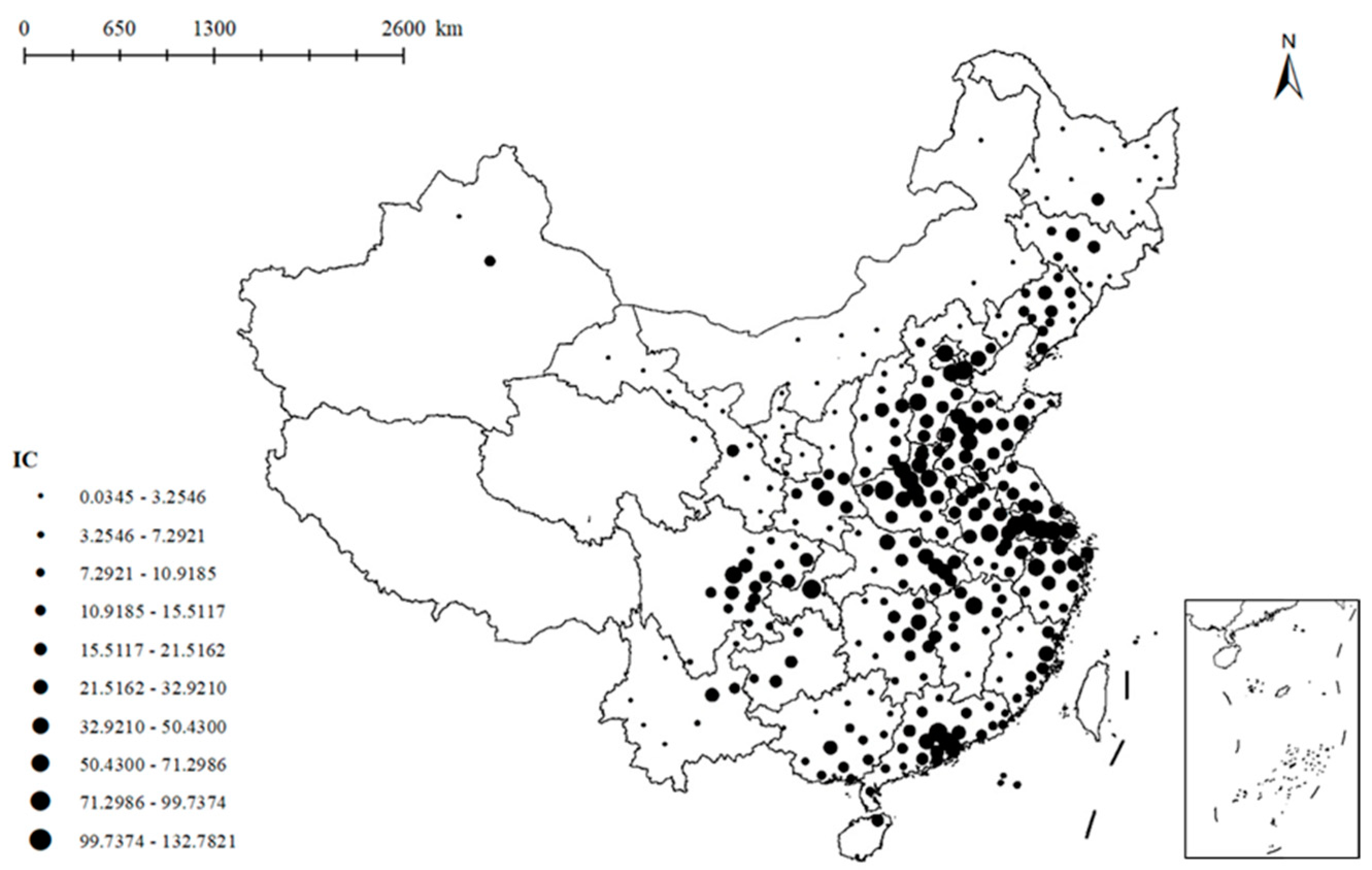
2.2.1. Dependent Variables: The Comprehensive Index of Urban Pollution
- (1)
- Normalize the pollution indicator j for city i:
- (2)
- Calculate the proportion of pollutant j of the city i to the total:
- (3)
- Calculate the entropy of the pollution indicator j:
- (4)
- Calculate the coefficient of variation of the pollution indicator j:
- (5)
- Calculate the weight of the pollution indicator j:
- (6)
- Calculate the comprehensive pollution index for city i: .
2.2.2. Key Independent Variable: The Index of Urban Clusters
2.2.3. Control Variables
2.3. Empirical Method
2.3.1. Baseline Specification
2.3.2. Congestion Alleviation
2.3.3. Industry Structural Optimization
2.3.4. Technological Innovation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Baseline
3.2. Potential Mechanisms
3.2.1. Mechanism Test of Congestion Alleviation
3.2.2. Mechanism Test of Industry Structural Optimization
3.2.3. Mechanism Test of Technological Innovation
3.3. Robustness Tests
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPCC. IPCC Climate Change 2007: Synthesis Report; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Chien, F.; Sadiq, M.; Nawaz, M.A.; Hussain, M.S.; Tran, T.D.; Le Thanh, T. A step toward reducing air pollution in top Asian economies: The role of green energy, eco-innovation, and environmental taxes. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 297, 113420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IPCC. IPCC Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. IPCC Summary for Policymakers of the Sixth Assessment Report of Working Group II; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Douglas, I. The political filter in the local implementation of initiatives relating to urban ecology. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 125, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joss, S. Eco-cities and Sustainable Urbanism. In International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 829–837. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Tao, Y. Synergistic Agglomeration of Manufacturing and Logistics Industries and Urban Green Economy Efficiency: Influence and Upgrading. Math. Probl. Eng. 2023, 2023, 8118981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portnov, B.A.; Schwartz, M. Urban Clusters as Growth Foci. J. Reg. Sci. 2009, 49, 287–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Li, M.; Hou, S.; Zhang, C. Research on the Spatial Network Characteristics, Synergistic Emission Reduction Effects and Mechanisms of Carbon Emission in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijers, E.J.; Burger, M.J.; Hoogerbrugge, M.M. Borrowing size in networks of cities: City size, network connectivity and metropolitan functions in Europe. Pap. Reg. Sci. 2016, 95, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Liu, Z. A New Perspective on the Evaluation of Urbanization Sustainability: Urban Health Examination. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Yuan, E.; Yang, K.; Tao, D. Does technology innovation reduce haze pollution? An empirical study based on urban innovation index in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 24063–24076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piracha, A.; Chaudhary, M.T. Urban Air Pollution, Urban Heat Island and Human Health: A Review of the Literature. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, G.; Hu, Y.; Zhong, Y. Industrial agglomeration, spatial structure and economic growth: Evidence from urban cluster in China. Heliyon 2023, 9, e19963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perz, S.G.; Aramburu, C.; Bremner, J. Population, land use and deforestation in the Pan Amazon Basin: A comparison of Brazil, Bolivia, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru and Venezuela. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2005, 7, 23–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, S.; Punia, M.; Yu, H.; Chakraborty, S. Is dense or sprawl growth more prone to heat-related health risks? Spatial regression-based study in Delhi, India. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 81, 103808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hankey, S.; Marshall, J.D. Impacts of urban form on future US passenger-vehicle greenhouse gas emissions. Energy Policy 2010, 38, 4880–4887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, T.J.; Kenworthy, J.R.; Moy, C.; dos Santos, F. An international urban air pollution model for the transportation sector. Transp. Res. Part D-Transp. Environ. 2003, 8, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, E.A.; Andrade, J.S., Jr.; Makse, H.A. Large cities are less green. Sci. Rep. 2015, 4, 4235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satterthwaite, D. Environmental transformations in cities as they get larger, wealthier and better managed. Geogr. J. 1997, 163, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.K.; Ghuge, V.V. How urban growth dynamics impact the air quality? A case of eight Indian metropolitan cities. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 930, 172399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yan, D. Does urban sprawl exacerbate urban haze pollution? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 56522–56534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Shang, S.; Feng, X.; Kong, Y.; Bai, J. Evolution and Trend Analysis of Research Hotspots in the Field of Pollution-Intensive Industry Transfer-Based on Literature Quantitative Empirical Study of China as World Factory. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 732734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, G.M.; Krueger, A.B. Economic-growth and the environment. Q. J. Econ. 1995, 110, 353–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levinson, A. Technology, International Trade, and Pollution from US Manufacturing. Am. Econ. Rev. 2009, 99, 2177–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Guo, M. The impact of FDI on haze pollution: “Pollution paradise” or “pollution halo?”--Spatial analysis of PM2.5 concentration raster data in 283 cities. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1133178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drut, M.; Mahieux, A. Correcting agglomeration economies: How air pollution matters. Pap. Reg. Sci. 2017, 96, 381–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Mahamud, S.; Thurston, G.D. Recent spatial gradients and time trends in Dhaka, Bangladesh, air pollution and their human health implications. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2019, 69, 478–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Yang, S.; Liu, S. Asymmetrically Spatial Effects of Urban Scale and Agglomeration on Haze Pollution in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, J.; Wang, Y.; Zameer, H. Can urban spatial structure adjustment mitigate air pollution effect of economic agglomeration? New evidence from the Yangtze River Delta region, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 57302–57315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Cui, R.; Li, C.; Ge, H.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, X. Impact of urban agglomeration construction on urban air quality-empirical test based on PSM-DID model. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 15099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; Tang, X.; Xie, R.; Han, F. The effect of manufacturing agglomerations on smog pollution. Struct. Change Econ. Dyn. 2020, 54, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, F.; Li, J. Does new-type urbanization help reduce haze pollution damage? Evidence from China’s county-level panel data. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 47123–47136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Li, H.; Du, Y. Can urban cluster policies improve innovation? Evidence from China. Appl. Econ. Lett. 2023, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, J.; Jiang, J. Urban Sprawl and Haze Pollution: Based on Raster Data of Haze PM2.5 Concentrations in 283 Cities in Mainland China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 929558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Li, M.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chen, W. Economic agglomeration and emissions reduction: Does high agglomeration in China’s urban clusters lead to higher carbon intensity? Urban Clim. 2022, 43, 101174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, L.; Yu, Y. Does urban cluster promote the increase of urban eco-efficiency? Evidence from Chinese cities. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 197, 957–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q. Do Urban Clusters Promote the Development of Cities? J. World Econ. 2016, 39, 99–123. [Google Scholar]
- Hashmi, S.H.; Fan, H.; Fareed, Z.; Shahzad, F. Asymmetric nexus between urban agglomerations and environmental pollution in top ten urban agglomerated countries using quantile methods. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 13404–13424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Yu, B.; Liang, L. High-Tech Industrial Agglomeration and Urban Innovation in China’s Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration: From the Perspective of Industrial Structure Optimization and Industrial Attributes. Complexity 2022, 2022, 2555182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.K.; Antoniuk, V.S.; Lapo, A.S.; Vansovich, E.R. Managing urban agglomeration processes in Russia in the context of agglomerative and socio-economic development. Heliyon 2024, 10, e28654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Hu, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Ren, W.; Li, J. A quantitative assessment of the distribution and extent of urban clusters in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2012, 22, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Ye, Y.; Yu, H. Manufacturing agglomeration, urban form, and haze pollution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 18921–18936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, P.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, G. Empirical Study of the Relationship between FDI and Environmental Regulation: An Intergovernmental Competition Perspective. Econ. Res. 2011, 46, 133–145. [Google Scholar]
- Lecocq, F.; Hourcade, J.C.; Duong, M.H. Decision making under uncertainty and inertia constraints: Sectoral implications of the when flexibility. Energy Econ. 1998, 20, 539–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, J.P.; Silva, E.A.; Pinho, P. Spatial metrics to study urban patterns in growing and shrinking cities. Urban Geogr. 2016, 37, 246–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xu, J. Energy and resource conservation and air pollution abatement in China’s iron and steel industry. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 147, 67–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Sun, Y.; Lan, Q.; Jiang, F. Impacts of industrial agglomeration on pollution and ecological efficiency-A spatial econometric analysis based on a big panel dataset of China’s 259 cities. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Feng, S.; Chu, H.; Huang, W. The Heterogeneous Effects of Urban Form on CO2 Emissions: An Empirical Analysis of 255 Cities in China. Land 2023, 12, 981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.H.; Zeng, W.P. Path to sustainable development: Can industrial intelligence and technological innovation balance economic growth and environmental quality in China? Sustain. Dev. 2024, 32, 4486–4504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Hu, S. How Does Technological Innovation Mediate the Relationship between Environmental Regulation and High-Quality Economic Development? Empirical Evidence from China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, M.J.; Abreu, M.A.; de Groot, H.L.F. Micro-evidence on the determinants of innovation in the Netherlands: The relative importance of absorptive capacity and agglomeration externalities. Pap. Reg. Sci. 2015, 94, 249–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koengkan, M.; Kazemzadeh, E.; Fuinhas, J.A.; Tash, M.N.S. Heterogeneous impact of eco-innovation on premature deaths resulting from indoor and outdoor air pollution: Empirical evidence from EU29 countries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 2298–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, L.; Sun, F.; Huang, R. Innovation-based urbanization: Evidence from 270 cities at the prefecture level or above in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 29, 1283–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marosi, Z.; Adorean, E.-C.; Ilovan, O.-R.; Gligor, V.; Voicu, C.-G.; Nicula, A.-S.; Dulama, M.E. Living the urban cultural landscapes in the city centre of cluj-napoca/kolozsvar/klausenburg, romania. Mitt. Osterr. Geogr. Ges. 2019, 161, 117–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Jin, M.; Chen, Y. Has the synergistic development of urban cluster improved carbon productivity?—Empirical evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 414, 137535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqin, G.; Huijuan, W. Analysis of Industrial Carbon Transfer in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei City Cluster and Surrounding Areas. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 895142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vac, M.B.; Soporan, V.F.; Cocis, E.A.; Batrînescu, G.; Nemes, O. Gas analysis of municipal landfill emissions. Stud. Univ. Babes-Bolyai Chem. 2012, 57, 23–30. [Google Scholar]
| (1) | (2) | (3) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ic | −0.165 *** (0.027) | −0.075 *** (0.021) | −0.030 *** (0.002) |
| pop | 1.288 *** (0.0906) | 0.507 *** (0.0730) | 0.218 *** (0.0553) |
| GDP per capita | −0.087 *** (0.004) | −0.023 (0.052) | 0.060 (0.039) |
| Market openness | −0.010 *** (0.002) | −0.004 * (0.002) | −0.002 (0.001) |
| Fiscal decentralization | 1.2558 *** (0.0968) | −0.0946 (0.0829) | −0.0274 (0.0630) |
| Infrastructure level | −0.002 (0.036) | −0.053 * (0.032) | 0.005 (0.023) |
| Industrialization level | 0.002 *** (0.0002) | −0.11 (0.19) | −0.07 (0.14) |
| Education level | −0.103 (0.0016) | −0.010 (0.0013) | 0.011 (0.0010) |
| Environmental regulation level | 2.4897 *** (0.0822) | 2.2745 *** (0.0668) | 1.9047 *** (0.0515) |
| L.LnS | 0.6119 *** (0.0100) | ||
| Constant | −16.5547 *** (0.5260) | −11.6360 *** (0.4244) | −4.7883 *** (0.3429) |
| City fixed effects | √ | √ | √ |
| Year fixed effects | √ | √ | |
| Observations | 4828 | 4828 | 4828 |
| R2 | 0.2214 | 0.2943 |
| Overall | Big Cities Group | Small Cities Group | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | |
| ic | 0.0643 *** (0.0094) | 0.0747 *** (0.0126) | −0.0379 (0.0306) |
| pop | 0.8823 *** (0.0869) | 0.8953 *** (0.1483) | 0.6773 *** (0.1342) |
| ic × pop | −0.0110 *** (0.0014) | −0.0119 *** (0.0019) | 0.0053 (0.0053) |
| City fixed effects | √ | √ | √ |
| Year fixed effects | √ | √ | √ |
| Observations | 4828 | 2414 | 2414 |
| R2 | 0.2893 | 0.2137 | 0.2871 |
| Overall | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | ||||
| ic | 5.2087 * (2.9515) | −0.075 *** (0.0021) | −0.073 *** (0.0021) | |||
| ind | −0.04 *** (0.01) | |||||
| City fixed effects | √ | √ | √ | |||
| Year fixed effects | √ | √ | √ | |||
| Observations | 4828 | 4828 | 4828 | |||
| R2 | 0.3607 | 0.2943 | 0.3004 | |||
| Developed Cities Group | Less Developed Cities Group | |||||
| (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | |
| ic | 6.6760 *** (2.3771) | −0.055 *** (0.0021) | −0.045 ** (0.0020) | −1.4093 (8.3682) | −0.0103 * (0.0056) | −0.0103 * (0.0056) |
| ind | −0.012 *** (0.00) | 0.001 (0.00) | ||||
| City fixed effects | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Year fixed effects | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Observations | 2414 | 2414 | 2414 | 2414 | 2414 | 2414 |
| R2 | 0.2319 | 0.3284 | 0.2531 | 0.3245 | 0.3164 | 0.3154 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ic | 1312.22 *** (61.40) | −0.075 *** (0.021) | −0.047 ** (0.022) |
| patent | −0.023 *** (0.000) | ||
| City fixed effects | √ | √ | √ |
| Year fixed effects | √ | √ | √ |
| Observations | 4828 | 4828 | 4828 |
| R2 | 0.3164 | 0.3734 | 0.3529 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ic | −0.079 *** (0.021) | −0.068 *** (0.014) | −0.059 *** (0.012) | −0.069 *** (0.022) | −0.072 *** (0.019) |
| Ln population density | −0.3880 *** (0.1071) | ||||
| Controls | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| City fixed effects | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Year fixed effects | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Observations | 4828 | 4828 | 4828 | 4828 | 4828 |
| R2 | 0.1726 | 0.2204 | 0.1722 | 0.3421 | 0.2219 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Z.; Luo, J. Sustainable Urbanization: Unpacking the Link Between Urban Clusters and Environmental Protection. Sustainability 2025, 17, 873. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17030873
Xu Z, Luo J. Sustainable Urbanization: Unpacking the Link Between Urban Clusters and Environmental Protection. Sustainability. 2025; 17(3):873. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17030873
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Zhaopeng, and Jin Luo. 2025. "Sustainable Urbanization: Unpacking the Link Between Urban Clusters and Environmental Protection" Sustainability 17, no. 3: 873. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17030873
APA StyleXu, Z., & Luo, J. (2025). Sustainable Urbanization: Unpacking the Link Between Urban Clusters and Environmental Protection. Sustainability, 17(3), 873. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17030873






