Technical and Economic Feasibility Investigation for the Treatment of Microplastic-Contaminated Marine Sediments Through an Environmentally Sustainable Separation Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Theoretical Basis
2.3. Experimental Apparatus and Procedures
2.3.1. Experimental Measurement of the MPs’ Settlement/Flotation Velocities
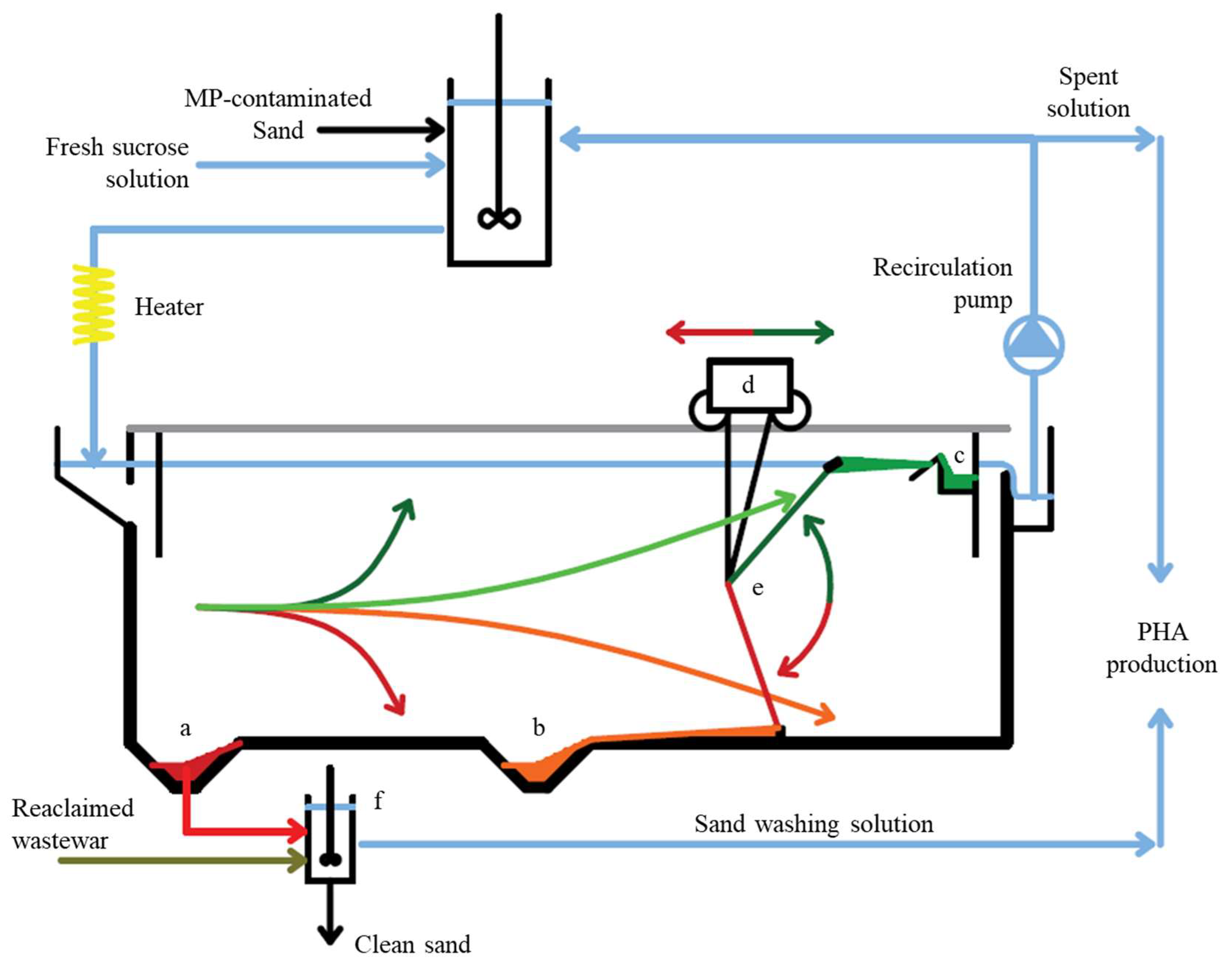
2.3.2. Experimental Density Separation Tests
3. Results and Discussion
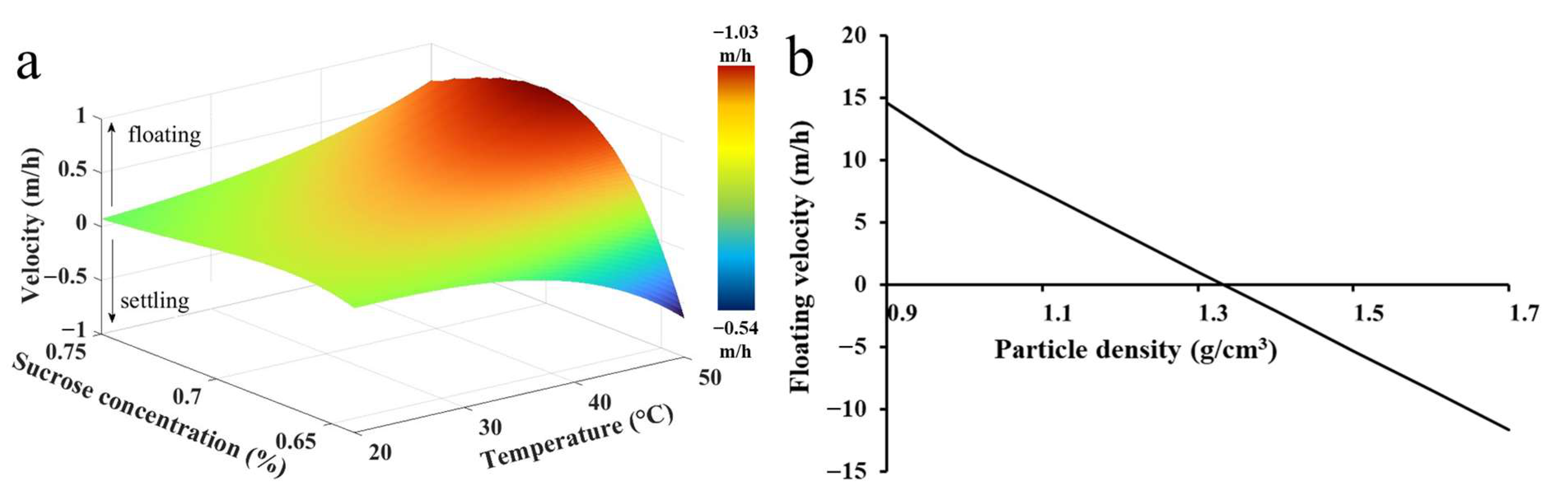
3.1. Theoretical Calculation of MPs’ Flotation/Settlement Velocities
3.2. Experimental Results
3.2.1. Experimental Determination of MPs’ Settling/Floating Velocity
3.2.2. Density Separation Tests with Artificial and Real Marine Sediments
3.3. Feasibility Study on the Density Separation Process Scale-Up
3.3.1. Potential Configuration of the Pilot/Real-Scale Separation Reactor
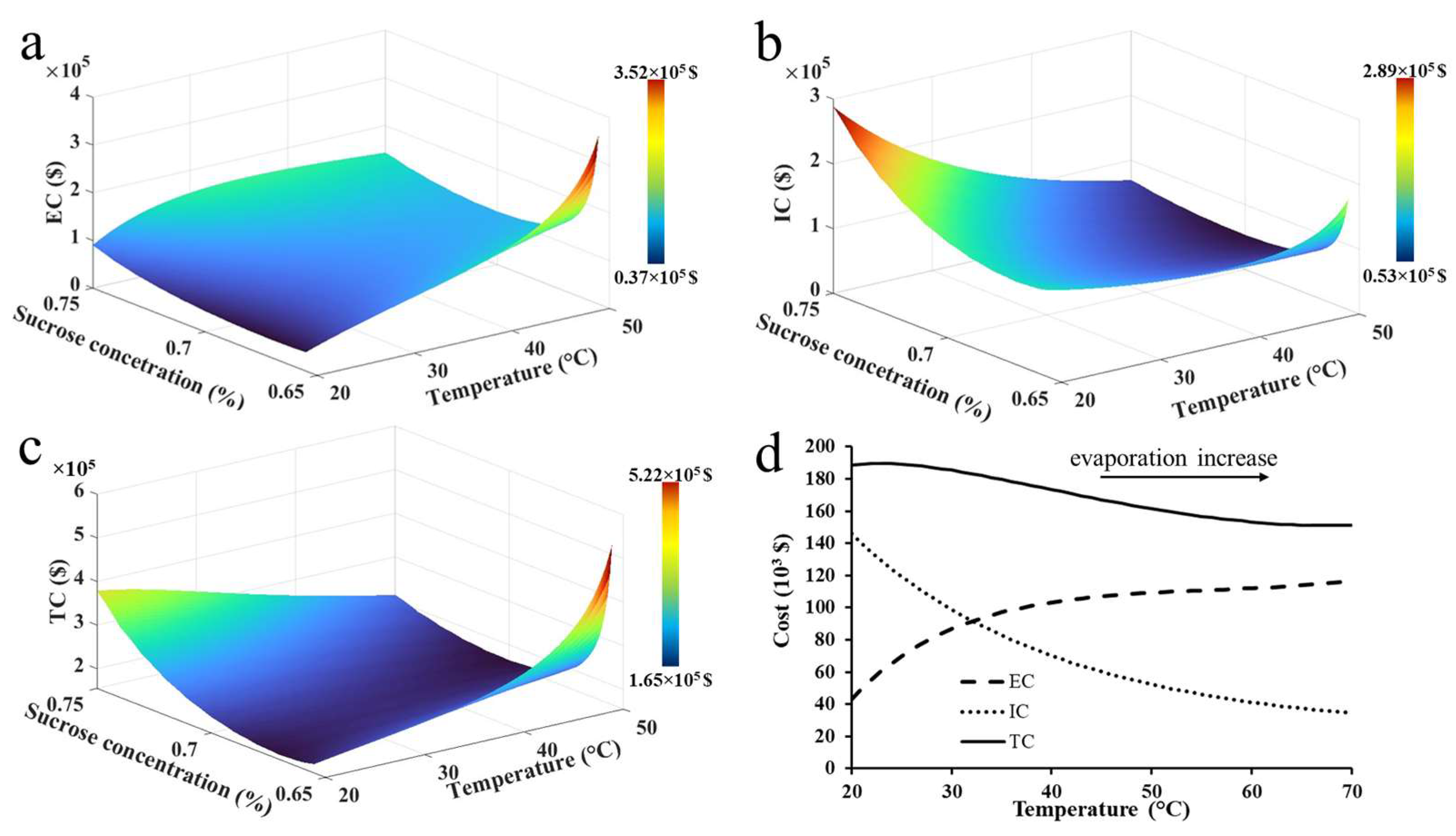
3.3.2. Process Cost Minimization and Separation Tank Design
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Napper, I.E.; Thompson, R.C. Plastic Debris in the Marine Environment: History and Future Challenges. Glob. Chall. 2020, 4, 1900081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PlasticsEurope. Plastics—The Facts 2019: An Analysis of European Plastics Production, Demand and Waste Data; PlasticsEurope: Brussel, Belgium, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Flores-Ocampo, I.Z.; Armstrong-Altrin, J.S. Abundance and composition of microplastics in Tampico beach sediments, Tamaulipas State, southern Gulf of Mexico. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 191, 114891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidu, B.C.; Xavier, K.A.M.; Shukla, S.P.; Jaiswar, A.K.; Nayak, B.B. Microplastics in the foreshore coastal waters, sediment, and coastal fauna of a highly populated megacity—A study on the effect of anthropogenic discharge on clams. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 185, 114262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edo, C.; González-Pleiter, M.; Tamayo-Belda, M.; Ortega-Ojeda, F.E.; Leganés, F.; Fernández-Piñas, F.; Rosal, R. Microplastics in sediments of artificially recharged lagoons: Case study in a Biosphere Reserve. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 138824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatramanan, S.; Chung, S.Y.; Selvam, S.; Sivakumar, K.; Soundhariya, G.R.; Elzain, H.E.; Bhuyan, M.S. Characteristics of microplastics in the beach sediments of Marina tourist beach, Chennai, India. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 176, 113409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keerthika, K.; Padmavathy, P.; Rani, V.; Jeyashakila, R.; Aanand, S.; Kutty, R. Contamination of microplastics, surface morphology and risk assessment in beaches along the Thoothukudi coast, Gulf of Mannar region. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 75525–75538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naidu, B.C.; Xavier, K.A.M.; Shukla, S.P.; Jaiswar, A.K.; Nayak, B.B. Comparative study on the microplastics abundance, characteristics, and possible sources in yellow clams of different demographic regions of the northwest coast of India. J. Hazard. Mater. Lett. 2022, 3, 100051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzi, Y.; Gedik, K.; Eryaşar, A.R.; Öztürk, R.Ç.; Şahin, A.; Yılmaz, F. Microplastic contamination and characteristics spatially vary in the southern Black Sea beach sediment and sea surface water. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 174, 113228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Ferreira, A.T.; Siegle, E.; Ribeiro, M.C.H.; Santos, M.S.T.; Grohmann, C.H. The dynamics of plastic pellets on sandy beaches: A new methodological approach. Mar. Environ. Res. 2021, 163, 105219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridson, J.H.; Patel, M.; Lewis, A.; Gaw, S.; Parker, K. Microplastic contamination in Auckland (New Zealand) beach sediments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 151, 110867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cincinelli, A.; Scopetani, C.; Chelazzi, D.; Martellini, T.; Pogojeva, M.; Slobodnik, J. Microplastics in the Black Sea sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 760, 143898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, M.; Ru, S.; Liu, X. High levels of microplastic pollution in the sediments and benthic organisms of the South Yellow Sea, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 1661–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, H.A.; Brandsma, S.H.; van Velzen, M.J.M.; Vethaak, A.D. Microplastics en route: Field measurements in the Dutch river delta and Amsterdam canals, wastewater treatment plants, North Sea sediments and biota. Environ. Int. 2017, 101, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Yang, F.; Hassan Kazmi, S.S.U.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, M.; Wang, J. A review of microplastic pollution in seawater, sediments and organisms of the Chinese coastal and marginal seas. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felsing, S.; Kochleus, C.; Buchinger, S.; Brennholt, N.; Stock, F.; Reifferscheid, G. A new approach in separating microplastics from environmental samples based on their electrostatic behavior. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelvetro, V.; Corti, A.; Bianchi, S.; Ceccarini, A.; Manariti, A.; Vinciguerra, V. Quantification of poly(ethylene terephthalate) micro- and nanoparticle contaminants in marine sediments and other environmental matrices. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 385, 121517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellasi, A.; Binda, G.; Pozzi, A.; Boldrocchi, G.; Bettinetti, R. The extraction of microplastics from sediments: An overview of existing methods and the proposal of a new and green alternative. Chemosphere 2021, 278, 130357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagter, E.; Frias, J.; Nash, R. Microplastics in Galway Bay: A comparison of sampling and separation methods. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 135, 932–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppock, R.L.; Cole, M.; Lindeque, P.K.; Queirós, A.M.; Galloway, T.S. A small-scale, portable method for extracting microplastics from marine sediments. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 230, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbreath, A.; McKee, L.; Shimabuku, I.; Lin, D.; Werbowski, L.M.; Zhu, X.; Grbic, J.; Rochman, C. Multiyear Water Quality Performance and Mass Accumulation of PCBs, Mercury, Methylmercury, Copper, and Microplastics in a Bioretention Rain Garden. J. Sustain. Water Built Environ. 2019, 5, 04019004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuelle, M.-T.; Dekiff, J.H.; Remy, D.; Fries, E. A new analytical approach for monitoring microplastics in marine sediments. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 184, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imhof, H.K.; Schmid, J.; Niessner, R.; Ivleva, N.P.; Laforsch, C. A novel, highly efficient method for the separation and quantification of plastic particles in sediments of aquatic environments. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2012, 10, 524–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalf, A.; Eddy, S. Wastewater Engineering: Treatment, Disposal, and Reuse, 3rd ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Barber, E.J. Calculation of density and viscosity of sucrose solutions as a function of concentration and temperature. Natl. Cancer Inst. Monogr. 1966, 21, 219–239. [Google Scholar]
- Telis, V.R.N.; Telis-Romero, J.; Mazzotti, H.B.; Gabas, A.L. Viscosity of Aqueous Carbohydrate Solutions at Different Temperatures and Concentrations. Int. J. Food Prop. 2007, 10, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swindells, J.F.; Snyder, C.F.; Hardy, R.C.; Golden, P.E. Viscosities of Sucrose Solutions at Various Temperatures: Tables of Recalculated Values; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1958. [Google Scholar]
- Geyer, R. Production, use, and fate of synthetic polymers. In Plastic Waste and Recycling; Letcher, T.M., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 13–32. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Li, M.; Deng, H.; Cai, L.; Cai, H.; Yan, B.; Hu, J.; Shi, H. A straightforward method for measuring the range of apparent density of microplastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Xiao, H.; Sun, H. Investigating the settling dynamics of cohesive silt particles with particle-resolving simulations. Adv. Water Resour. 2018, 111, 406–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Winckel, T.; Liu, X.; Vlaeminck, S.E.; Takács, I.; Al-Omari, A.; Sturm, B.; Kjellerup, B.V.; Murthy, S.N.; De Clippeleir, H. Overcoming floc formation limitations in high-rate activated sludge systems. Chemosphere 2019, 215, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Luo, J.; Wu, Y.; Qi, B.; Chen, X.; Wan, Y. Decoloration of sugarcane molasses by tight ultrafiltration: Filtration behavior and fouling control. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 204, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Jiang, H. Microbial production of value-added bioproducts and enzymes from molasses, a by-product of sugar industry. Food Chem. 2021, 346, 128860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.J.; Kim, S.H.; Shin, N.; Oh, S.-J.; Hwang, J.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, Y.-H.; Bhatia, S.K.; Jeon, J.-M.; Yoon, J.-J.; et al. Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) production from sugar cane molasses and tap water without sterilization using novel strain, Priestia sp. YH4. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 250, 126152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woods, D.R. Rules of Thumb in Engineering Practice; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; ISBN 9783527312207. [Google Scholar]
- Paraschiv, L.S.; Acomi, N.; Serban, A.; Paraschiv, S. A web application for analysis of heat transfer through building walls and calculation of optimal insulation thickness. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, I.; Shafigh, P.; Abu Hassan, Z.F.B.; Mahyuddin, N.B. Thermal conductivity of concrete—A review. J. Build. Eng. 2018, 20, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung Anh, L.D.; Pásztory, Z. An overview of factors influencing thermal conductivity of building insulation materials. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 44, 102604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| PP | HDPE | PLA | PVC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Waste | turning swarf | pipeline | filament for 3D printer | pipeline |
| Color | white | black | white | gray |
| Density (g/cm3) | 0.90 | 0.94 | 1.24 | 1.42 |
| Constant | Value |
|---|---|
| A1 | 18.027525 |
| A2 | 4.8318329 · 10−4 |
| A3 | 7.7830857 · 10−5 |
| C1 | 212.57059 |
| C2 | 0.13371672 |
| C3 | −2.9276449 · 10−4 |
| Sand (g) | S/L Ratio (kg/m3) | PP (Number) | HDPE (Number) | PLA (Number) | PVC (Number) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 12.5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1.0 | 25 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 2.0 | 50 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| 3.0 | 75 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| 4.0 | 100 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| 5.0 | 125 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soufizadeh, M.; Morello, R.; Ferraro, A.; Spasiano, D.; Fratino, U. Technical and Economic Feasibility Investigation for the Treatment of Microplastic-Contaminated Marine Sediments Through an Environmentally Sustainable Separation Process. Sustainability 2025, 17, 1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17031258
Soufizadeh M, Morello R, Ferraro A, Spasiano D, Fratino U. Technical and Economic Feasibility Investigation for the Treatment of Microplastic-Contaminated Marine Sediments Through an Environmentally Sustainable Separation Process. Sustainability. 2025; 17(3):1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17031258
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoufizadeh, Maryam, Raffaele Morello, Alberto Ferraro, Danilo Spasiano, and Umberto Fratino. 2025. "Technical and Economic Feasibility Investigation for the Treatment of Microplastic-Contaminated Marine Sediments Through an Environmentally Sustainable Separation Process" Sustainability 17, no. 3: 1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17031258
APA StyleSoufizadeh, M., Morello, R., Ferraro, A., Spasiano, D., & Fratino, U. (2025). Technical and Economic Feasibility Investigation for the Treatment of Microplastic-Contaminated Marine Sediments Through an Environmentally Sustainable Separation Process. Sustainability, 17(3), 1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17031258









