The Impacts of the Digital Economy on the Development of Higher Education in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. The Macroeconomic Shift: The Rise of China’s Digital Economy and Its Impacts
1.2. The Strategic Dilemma of Higher Education in the Digital Age
2. Literature Review
2.1. Connotations, Dimensions, and Measurement of the Digital Economy
2.2. The Multi-Dimensional Development of Higher Education: Scale, Structure, and Quality
2.3. The Nexus Between the Digital Economy and Higher Education: Identifying the Research Gap
3. Theoretical Framework and Research Hypotheses
3.1. Theoretical Foundation
3.2. Research Hypotheses
3.3. Integrated Theoretical Model
4. Research Design and Methodology
4.1. Measurement of Digital Economy Development Level
4.2. Measurement of Higher Education Development Level
4.3. Empirical Strategy and Model Specification
4.3.1. Baseline Regression Model
4.3.2. Mediation Effect Test
4.3.3. Addressing Endogeneity
4.4. Data Sources and Descriptive Statistics
4.4.1. Data Sources
4.4.2. Descriptive Statistics
5. Empirical Results and Analysis
5.1. Dynamic Evolution of Core Variables
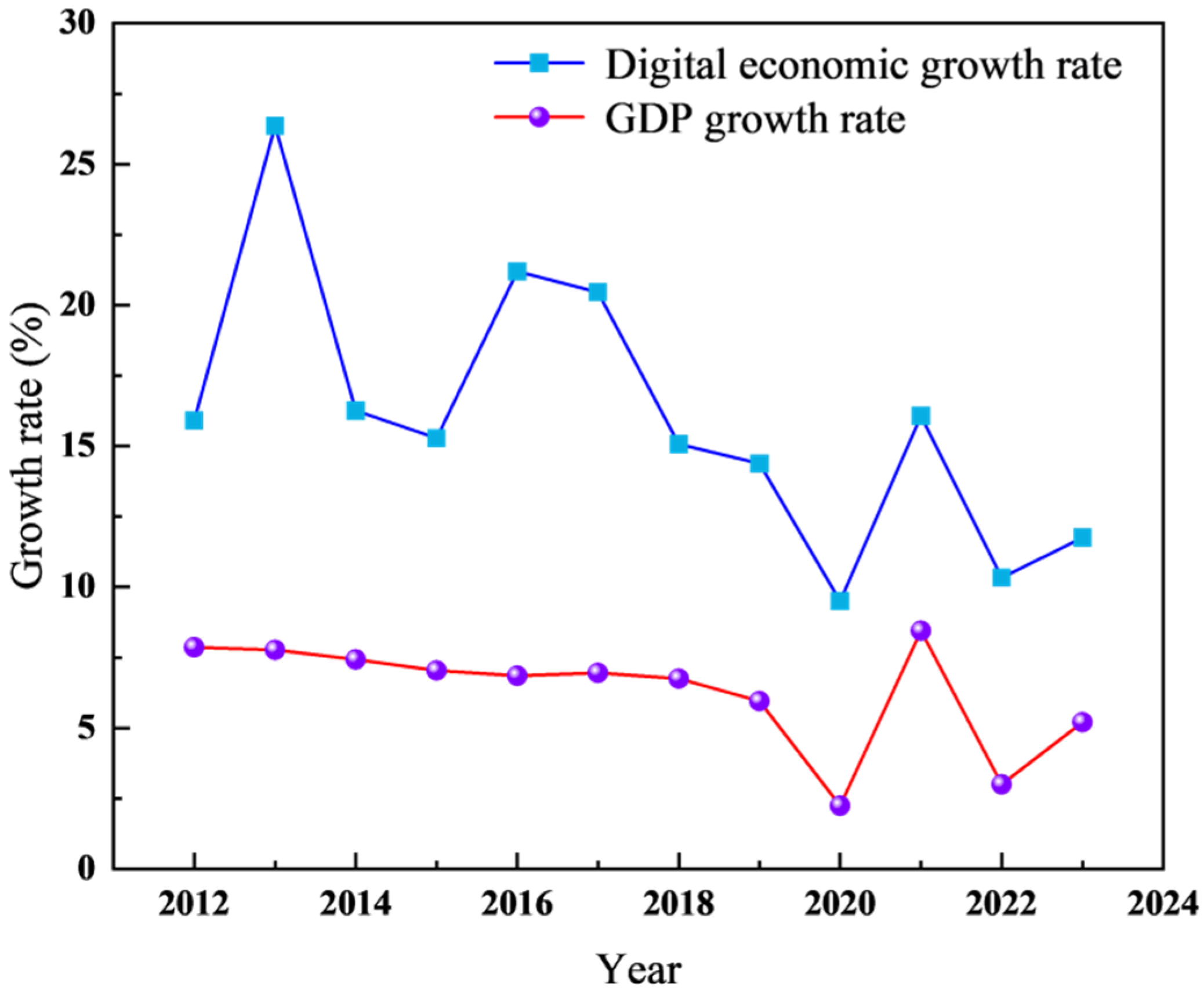
5.1.1. Dynamic Evolution of Digital Economy Development Index (DEDI)
5.1.2. Dynamic Evolution of Higher Education Development
5.2. Baseline Regression Results
5.3. Endogeneity Test Results
5.4. Mediation Effect Analysis
5.5. Robustness Checks
5.6. Regional Heterogeneity Analysis
6. Conclusions and Implications
6.1. Research Conclusions
6.2. Theoretical and Practical Implications
6.3. Policy Recommendations
6.4. Limitations and Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hong, Y.X.; Ren, B.P. The Connotation and Path of Deep Integration of Digital Economy and Real Economy. China Ind. Econ. 2023, 2, 5–16. [Google Scholar]
- Tapscott, D. The Digital Economy: Promise and Peril in the Age of Networked Intelligence. Choice Rev. 1997, 33, 33–5199. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Xie, Y.; Feng, Z.H.; Luo, Y.B.; Wang, K.; Xu, W. Better Understanding the Failure Modes of Tunnels Excavated in the Boulder-Cobble Mixed Strata by Distinct Element Method. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2020, 116, 104712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukht, R.; Heeks, R. Defining, Conceptualising and Measuring the Digital Economy. SSRN Electron. J. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwanholz, J.; Leipold, S. Sharing for A Circular Economy? An Analysis of Digital Sharing Platforms’ Principles and Business Models. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 269, 122327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development; United Nations: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2015; Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/2030agenda (accessed on 20 November 2025).
- Ministry of Education of the People’s Republic of China. China Statistical Yearbook on Education (2011–2020); China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2020. (In Chinese)
- Hanushek, E.A.; Woessmann, L. The Knowledge Capital of Nations: Education and the Economics of Growth; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Du, Y.H.; Lai, J.X.; Qiu, J.L.; Ma, E.L.; Sun, H.; Shi, X.H. Mechanic Performance of Novel Prefabricated Inverted Arch in NATM Tunnels: Insights From Numerical Experiment and In-Situ Tests. Tunn. Under. Gr. Sp. Tech. 2026, 168, 108071. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, E.D.; Hu, H.R.; Lai, J.X.; Zhang, W.H.; He, S.Y.; Cui, G.H.; Wang, K.; Wang, L.X. Deformation Analysis of High-Speed Railway CFG Pile Composite Subgrade during Shield Tunnel Underpassing. Structures. 2025, 78, 109193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angrist, J.D.; Pischke, J.S. Mostly Harmless Econometrics: An Empiricist’s Companion; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, C.L.; Yoon, K. Multiple Attribute Decision Making: Methods and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Acemoglu, D.; Autor, D. Skills, tasks and technologies: Implications for employment and earnings. In Handbook of Labor Economics; Ashenfelter, O., Card, D., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 4, pp. 1043–1171. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Li, M. Digital transformation of higher education in China: Progress, challenges and paths. J. High. Educ. Manag. 2021, 6, 12–19. [Google Scholar]
- Harloe, M.; Perry, B. Universities, Localities and Regional Development: The Emergence of the ‘Mode 2’ University? Int. J. Urban. Int. J. Urban Reg. Res. 2004, 28, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.; Magusin, E. Exploring the Digital Library: A Guide for Online Teaching and Learning; Online Teaching and Learning Series; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; ISBN 978-0-470-59658-6. [Google Scholar]
- Van Reenen, J. The Race Between Education and Technology. Econ. J. 2010, 120, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.; Lawton, W. Universities, the Digital Divide and Global Inequality. J. High. Educ. Policy Manag. 2018, 40, 598–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Y.Q. Research on the Changes of China’s College Entrance Examination Policy: Analysis Based on “Stakeholder Theory”. J. High. Educ. Res. 2010, 31, 52. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, D.H. Strengthening Confidence in Higher Education System and Enhancing the Ability to Serve the New Development Paradigm. China High. Educ. Res. 2020, 12, 5–6. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, N. Current Situation and Analysis of Intangible Cultural Heritage Live Streaming. Mark. World. 2021, 9, 62–63. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.K. Exploring the Path of Digital Transformation in Higher Education. China High. Educ. Res. 2023, 3, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, L.J.; Liu, J.T.; Su, F.G. Digital Transformation in Higher Education: Connotation, Dilemmas and Paths. China Educ. Inf. 2022, 28, 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- Afonso, O.; Albuquerque, A.L.; Almeida, A. Wage Inequality Determinants in European Union Countries. Appl. Financ. Lett. 2013, 20, 1170–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.Y. A Comparative Study of Graduate Employment Surveys: 2003–2011. Chin. Educ. Soc. 2015, 47, 12–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, X. The impact of digital infrastructure on higher education enrollment: A provincial-level analysis of China. Educ. Econ. 2021, 3, 456–478. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Z.; Ye, B. Mediation analysis: Current practices and new recommendations. Front. Psychol. 2014, 5, 530. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, T.; Levine, R.; Levkov, A. Big bad banks? The winners and losers from bank deregulation in the United States. J. Financ. 2010, 5, 1637–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanasi, S.; Ghezzi, A.; Cavallo, A.; Rangone, A. Making Sense of the Sharing Economy: A Business Model Innovation Pespective. Technol. Anal. Strateg. 2020, 32, 895–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Academy of Information and Communications Technology (CAICT). Digital Economy Development in China; China Academy of Information and Communications Technology (CAICT): Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.N.; Hu, B.B.; Wang, S.G. Research on the Evolution Mechanism and Characteristics of Digital Economy. Sci. Res. 2021, 39, 406–414. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.L. Can Digital Economy Promote Industrial Structure Transformation?—Also on Effective Market and Proactive Government. Econ. Issues. 2023, 3, 35–44. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.Y.; Guo, P.F.; Li, M. Research on the impact of digital economic development in the yangtze river economic belt on green total factor productivity. Statistics. Decis. 2025, 41, 121–125. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, G.L. The Autonomy of Chinese Universities (1952–2012): An Institutional Interpretation of Policy Changes. J. China Univ. Geosci. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2012, 12, 78–86+139–140. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.P.; Liu, L.B. Ambiguous Governance: The Logic of China’s Private Higher Education Policy Changes. Mod. Educ. Manag. 2021, 5, 52–60. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y. Accumulating Momentum and Adapting to Changes. China High. Educ. 2021, 1, 4–7. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.G. The Role of Higher Education in the New Development Paradigm. Teach. Educ. (High. Educ. Forum) 2021, 15, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Zhang, W. Exploring Path Strategies for Higher Education Institutions to Boost Digital Economy Development. China. Educ. Info. 2022, 28, 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.F.; Zhang, C. Elements and Approaches of Digital Reform in China’s Higher Education. China High. Educ. Res. 2022, 7, 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, D.K. Promoting the Integration of Digital Transformation into the Whole Process of Higher Education. China High. Educ. 2023, 2, 27–30+36. [Google Scholar]
- He, S.S. Evaluation of Coupling Coordination Degree Between Digitalization and Higher Education in China and Its Influencing Factors. J. Northeast. Univ. (Soc. Sci.) 2023, 25, 128–135. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, L.P.; Lin, L. Digital Governance in Higher Education: Internal Mechanism, Logical Framework and Implementation Path. Jianghuai. Trib. 2022, 4, 183–192. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.K. Digital Development of Higher Education: Connotation, Stages and Implementation Paths. China High. Educ. 2023, 2, 16–20. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, G.D.; Wang, Z.H. Key Areas, Content Structure and Practical Paths of Digital Transformation in Higher Education. China High. Educ. Res. 2022, 11, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, T.S. Promoting Digital Transformation in Higher Education to Strengthen Governance Effectiveness: US Experiences and Implications for China. China. Educ. Inf. 2022, 28, 13–26. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Wu, Y.L. Promoting Transformation Through Evaluation: OECD’s Top-Level Framework and Practical Measures for Digital Transformation in Higher Education. China High. Educ. Res. 2022, 7, 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Schultz, T. Education and Economic Growth. Teach. Coll. Rec. 1961, 62, 46–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romer, P.M. Endogenous Technical Change. J. Polit. Econ. 1990, 98, 71–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAfee, A.; Brynjolfsson, E. Machine, Platform, Crowd: Harnessing Our Digital Future; W. W. Norton & Company: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 153–154. ISSN 0422-2784. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.Y.; Sun, X.Y. Higher Education During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Responses and Challenges. Educ. Chang. 2022, 26, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.Y.; Wang, X.J. Digital Economy Empowering China’s “Dual Circulation” Strategy: Internal Logic and Implementation Paths. Economist 2021, 102–109. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.C.; Gu, Y.A. Industrial structure: The entry point for coordinated development of local higher education and economy—An analysis based on the Southern Jiangsu region. Jiangsu High. Educ. Res. 2015, 46–49. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Edwards, J.S.; Dwivedi, Y.K. Artificial Intelligence for Decision Making in the Era of Big Data—Evolution, Challenges and Research Agenda. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2019, 48, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.Z.; Dan, T. Digital Dividend or Digital Divide? Digital Economy and Urban-Rural Income Inequality in China. Telecommun. Policy 2023, 47, 102616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal Filho, W.; Kirby, D.A.; Sigahi, T.F.A.C.; Bella, R.L.F.; Anholon, R.; Quelhas, O.L.G. Higher Education and Sustainable Entrepreneurship: The State of the Art and a Look to the Future. Sustain. Dev. 2025, 33, 957–969. [Google Scholar]





| Research Stream | Representative Authors | Core Focus/Methodology | Relevance to This Study & Identified Gap |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digital Economy: Concepts & Measurement | Tapscott (1996) [2]; Bukht & Heeks (2017) [4]; CAICT (2020) [30] | Defining the scope and layers of the digital economy; constructing national/provincial level measurement indices. | Provides the foundational conceptual framework and methodological reference for our Digital Economy Development Index (DEDI). |
| Higher Education Development | Li et al. (2010) [19]; Zhong (2020) [20]; Wu (2021) [36] | Analyzing policy evolution, quality standards, and structural reforms in higher education. | Informs the construction of our three-dimensional (scale, structure, quality) evaluation system. |
| Digital Economy & Education (Conceptual/ Tech-focused) | Yang (2023) [22]; Ning et al. (2022) [23]; Ge (2023) [40] | Discussing the digital transformation of education, focusing on technology application, platform building, and pedagogical models. | Highlights the prevailing tech-centric discourse and clears the space for our study’s distinct focus on the digital economy as a macroeconomic driver. |
| Digital Economy & Education (Emerging Empirical) | He (2023) [41] | Measuring the coupling coordination degree between digitalization and higher education using provincial data. | Provides a preliminary correlational study but lacks a causal identification strategy, a dimensional decomposition, and an investigation into the underlying transmission mechanisms. |
| This Study | Zhao et al. | Empirically tests the causal impact of the macro-digital economy on the three dimensions of higher education, employing panel models and robust mediation analysis to uncover the income-level mechanism. | Seeks a more nuanced understanding than correlations or technological determinism alone can yield by providing a systematic, empirical, and mechanism-driven analysis. |
| Primary Dimension | Secondary Dimension | Tertiary Indicator | Entropy Weight |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digital Industrialization | Digital Infrastructure | Telecommunication User Density (households/10,000 persons) | 0.052 |
| Mobile Phone Base Stations (units/10,000 km2) | 0.045 | ||
| Internet Broadband Access Ports (ports/10,000 people) | 0.048 | ||
| Fixed Internet Bandwidth per Capita (Mbps/person) | 0.042 | ||
| 5G Base Stations Density (units/100 km2) | 0.055 | ||
| Digital Industry | Output of Electronic Information Manufacturing (100 million yuan) | 0.068 | |
| Revenue of Internet Services (100 million yuan) | 0.072 | ||
| Software Industry Revenue (100 million yuan) | 0.065 | ||
| Digital Content Industry Revenue (100 million yuan) | 0.059 | ||
| E-commerce Platform Transaction Volume (1 trillion yuan) | 0.062 | ||
| Digital Innovation | Number of High-tech Enterprises (units) | 0.048 | |
| Patents in Digital Technologies (pieces) | 0.051 | ||
| Industrial Digitalization | Agriculture Digitalization | Rural Electricity Consumption per Capita (kWh/person) | 0.032 |
| Agricultural E-commerce Transaction Volume Ratio (%) | 0.035 | ||
| Smart Agricultural Equipment Penetration (%) | 0.030 | ||
| Industry Digitalization | Industrial Robot Density (units/10,000 workers) | 0.058 | |
| Manufacturing Enterprise Digitalization Rate (%) | 0.055 | ||
| Industrial Internet Platform Number (units) | 0.049 | ||
| Service Digitalization | E-commerce Transaction Volume (1 trillion yuan) | 0.065 | |
| Online Retail Sales Ratio (%) | 0.059 | ||
| Online Catering Revenue Ratio (%) | 0.042 | ||
| Online Travel Booking Volume (10,000 person-times) | 0.045 |
| First-Level Indicator | Second-Level Indicator | Entropy Weight |
|---|---|---|
| Higher Education Scale | Total Enrollment in HEIs (10,000 persons) | 0.165 |
| Gross Enrollment Rate of Higher Education (%) | 0.145 | |
| Higher Education Structure | Proportion of STEM Disciplines (%) | 0.082 |
| Regional Balance Index (ratio) | 0.078 | |
| Proportion of Applied HEIs (%) | 0.065 | |
| Postgraduate Enrollment Ratio (%) | 0.063 | |
| Vocational Education Enrollment Ratio (%) | 0.062 | |
| Higher Education Quality | Average Faculty-Student Ratio (students/faculty member) | 0.075 |
| Government Education Expenditure per Student (yuan/student) | 0.072 | |
| Number of Patents Granted per 10,000 Students (patents/10,000 students) | 0.068 | |
| Average Years of Education of Faculty (years) | 0.065 | |
| Employment Rate of Graduates (6 months post-graduation) (%) | 0.060 |
| Control Variable Name | Abbreviation | Definition | Theoretical Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urban Disposable Income per Capita | Income | Natural logarithm of urban disposable income per capita (10,000 yuan) | Wealthier regions have stronger fiscal and household capacity to invest in higher education [30]. |
| New Senior Secondary School Enrolment | Eligible_Pop | Natural logarithm of new enrolment in regular senior secondary schools (10,000 persons) | Proxies for the size of the immediate demand pool for higher education [36]. |
| Tertiary Sector Share of GDP | Ind_Structure | Value-added of the tertiary sector as a share of GDP (%) | A more advanced industrial structure increases demand for high-skilled talent, stimulating higher education development [20]. |
| Provincial Marketization Index | Institutions | Provincial Marketization Index (0–12) | Better institutional quality reduces transaction costs and optimizes education resource allocation [41]. |
| Government Education Expenditure per Student | GovEduPerStu | Fiscal education expenditure per student in higher education institutions (10,000 yuan/student) | Directly reflects public investment in higher education, a key determinant of educational quality [38]. |
| Baseline Secondary Education Quality | SecEduQuality | Average college entrance exam score (out of 750) | Proxies for the quality of the student pool for higher education, avoiding misattributing basic education advantages to the digital economy [39]. |
| Variable Category | Variable Name | Mean | Std. Dev. | Min | Max | Unit/Definition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent Variables | Higher Education Scale | 122.8 | 44.9 | 27.9 | 285.6 | 10,000 persons (total enrollment) |
| Higher Education Structure | 38.1 | 5.1 | 28.8 | 50.9 | % (share of STEM enrollment) | |
| Higher Education Quality | 12.2 | 4.1 | 3.0 | 24.8 | Patents/10,000 students | |
| Core Explanatory Variable | Digital Economy Development Index | 0.45 | 0.20 | 0.11 | 0.92 | Index (0–1, entropy-weighted) |
| Mediator Variables | Regional Income Level | 5.5 | 2.2 | 2.0 | 12.5 | 10,000 yuan (urban disposable income per capita) |
| Institutional Quality | 7.8 | 2.2 | 0.2 | 11.5 | Marketization index (0–12) | |
| Innovation Capacity | 48.2 | 21.5 | 5.8 | 120.7 | Patents per 10,000 persons | |
| Public Education Spending | 1.8 | 0.9 | 0.5 | 5.2 | 10,000 yuan (fiscal education expenditure per capita) | |
| Control Variables | Urban Disposable Income per Capita | 2.9 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 6.8 | 10,000 yuan |
| New Senior Secondary School Enrolment | 45.6 | 18.7 | 8.9 | 98.2 | 10,000 persons | |
| Tertiary Sector Share of GDP | 47.5 | 9.8 | 30.1 | 84.2 | % | |
| Provincial Marketization Index | 7.7 | 2.1 | 0.2 | 11.5 | Index (0–12) | |
| Government Education Expenditure per Student | 2.5 | 1.2 | 0.8 | 6.9 | 10,000 yuan/student | |
| Baseline Secondary Education Quality | 685.2 | 58.7 | 520.1 | 820.5 | Average college entrance exam score (out of 750) |
| Dependent Variable | (1) HE-Scale (RE) | (2) HEStruc-ture (RE) | (3) HEQuality (FE) | (4) HE-Scale (2011–2015) | (5) HE-Scale (2016–2020) | (6) HEQuality (2011–2015) | (7) HEQuality (2016–2020) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DEDI | 0.321 *** | 0.256 *** | 0.089 | 0.318 *** | 0.323 *** | 0.085 | 0.092 |
| (0.045) | (0.038) | (0.062) | (0.051) | (0.049) | (0.068) | (0.065) | |
| Income | 0.124 ** | 0.098 * | 0.105 ** | 0.119 ** | 0.128 ** | 0.099 * | 0.112 ** |
| (0.058) | (0.052) | (0.048) | (0.063) | (0.059) | (0.053) | (0.051) | |
| Eligible_Pop | 0.087 * | 0.065 | 0.052 | 0.082 * | 0.091 * | 0.048 | 0.056 |
| (0.046) | (0.041) | (0.039) | (0.049) | (0.047) | (0.042) | (0.040) | |
| Ind_Structure | 0.076 | 0.082 * | 0.069 | 0.071 | 0.080 * | 0.063 | 0.074 |
| (0.049) | (0.044) | (0.041) | (0.053) | (0.050) | (0.045) | (0.043) | |
| Institutions | 0.102 ** | 0.085 * | 0.092 ** | 0.097 ** | 0.106 ** | 0.088 * | 0.096 ** |
| (0.043) | (0.039) | (0.042) | (0.047) | (0.045) | (0.046) | (0.044) | |
| GovEduPerStu | 0.189 ** | 0.123 * | 0.215 *** | 0.182 ** | 0.195 ** | 0.208 *** | 0.221 *** |
| (0.078) | (0.065) | (0.059) | (0.083) | (0.080) | (0.064) | (0.061) | |
| SecEduQuality | 0.098 * | 0.076 | 0.156 ** | 0.093 * | 0.102 * | 0.149 ** | 0.162 ** |
| (0.052) | (0.048) | (0.063) | (0.056) | (0.054) | (0.067) | (0.065) | |
| Constant | 25.341 *** | 7.826 *** | 1.985 | 24.872 *** | 25.793 *** | 1.852 | 2.108 |
| (4.826) | (1.653) | (1.589) | (5.134) | (4.962) | (1.695) | (1.632) | |
| Provincial/Year FE | Yes/Yes | Yes/Yes | Yes/Yes | Yes/Yes | Yes/Yes | Yes/Yes | Yes/Yes |
| R2 | 0.78 | 0.72 | 0.69 | 0.76 | 0.79 | 0.67 | 0.70 |
| N | 300 | 300 | 300 | 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 |
| Mediator | DEDI→Mediator (α) | Mediator→HE (β) | Total Indirect Effect (α × β) | Sobel Test (p-Value) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HEScale | ||||
| RegIncome | 0.448 *** | 0.062 * | 0.028 * | 0.092 |
| InstQuality | 0.315 *** | 0.058 | 0.018 | 0.176 |
| HEStructure | ||||
| RegIncome | 0.448 *** | 0.045 | 0.020 | 0.185 |
| InstQuality | 0.315 *** | 0.076 * | 0.024 * | 0.087 |
| HEQuality | ||||
| RegIncome | 0.452 *** | 0.212 *** | 0.096 *** | 0.009 |
| InstQuality | 0.318 *** | 0.041 | 0.013 | 0.243 |
| InnCapacity | 0.508 *** | 0.030 | 0.015 | 0.315 |
| PubEduSpend | 0.385 *** | 0.054 | 0.021 | 0.259 |
| Test Method | Dependent Variable | Coefficient (DEDI) | Std. Error | p-Value | N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Alternative DEDI (PCA) | HEScale | 0.308 *** | 0.047 | 0.000 | 300 |
| HEStructure | 0.241 *** | 0.040 | 0.000 | 300 | |
| HEQuality | 0.089 | 0.064 | 0.170 | 300 | |
| 2. Exclude Municipali-ties | HEScale | 0.305 *** | 0.054 | 0.000 | 260 |
| HEStructure | 0.235 *** | 0.046 | 0.000 | 260 | |
| HEQuality | 0.092 | 0.070 | 0.188 | 260 | |
| 3. Full Two-Way FE Model | HEScale | 0.332 *** | 0.051 | 0.000 | 300 |
| HEStructure | 0.264 *** | 0.044 | 0.000 | 300 | |
| HEQuality | 0.083 | 0.060 | 0.165 | 300 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, J.; Li, Q.; Chen, J. The Impacts of the Digital Economy on the Development of Higher Education in China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 11266. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172411266
Zhao J, Li Q, Chen J. The Impacts of the Digital Economy on the Development of Higher Education in China. Sustainability. 2025; 17(24):11266. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172411266
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Junjing, Qi Li, and Jinfeng Chen. 2025. "The Impacts of the Digital Economy on the Development of Higher Education in China" Sustainability 17, no. 24: 11266. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172411266
APA StyleZhao, J., Li, Q., & Chen, J. (2025). The Impacts of the Digital Economy on the Development of Higher Education in China. Sustainability, 17(24), 11266. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172411266





