Research on the Improvement of Water Retention, Anti-Erosion and Mechanical Properties of Aeolian Sand Slopes Under the Synergistic Effect of Xanthan Gum and Water Retention Agents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Experimental Materials
2.2.1. Experimental Soil
2.2.2. Sample Preparation and Curing Process
2.2.3. Xanthan Gum and Water-Retaining Agents
- Xanthan gum
- 2.
- Water-Retention Agents
2.3. Experimental Methods
2.3.1. Evaporation Experiment
2.3.2. Erosion Experiment
2.3.3. Direct Shearing Experiment
2.3.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Results and Analyses of the Evaporation Experiment
3.1.1. Desiccation Crack Development
3.1.2. Water Evaporation
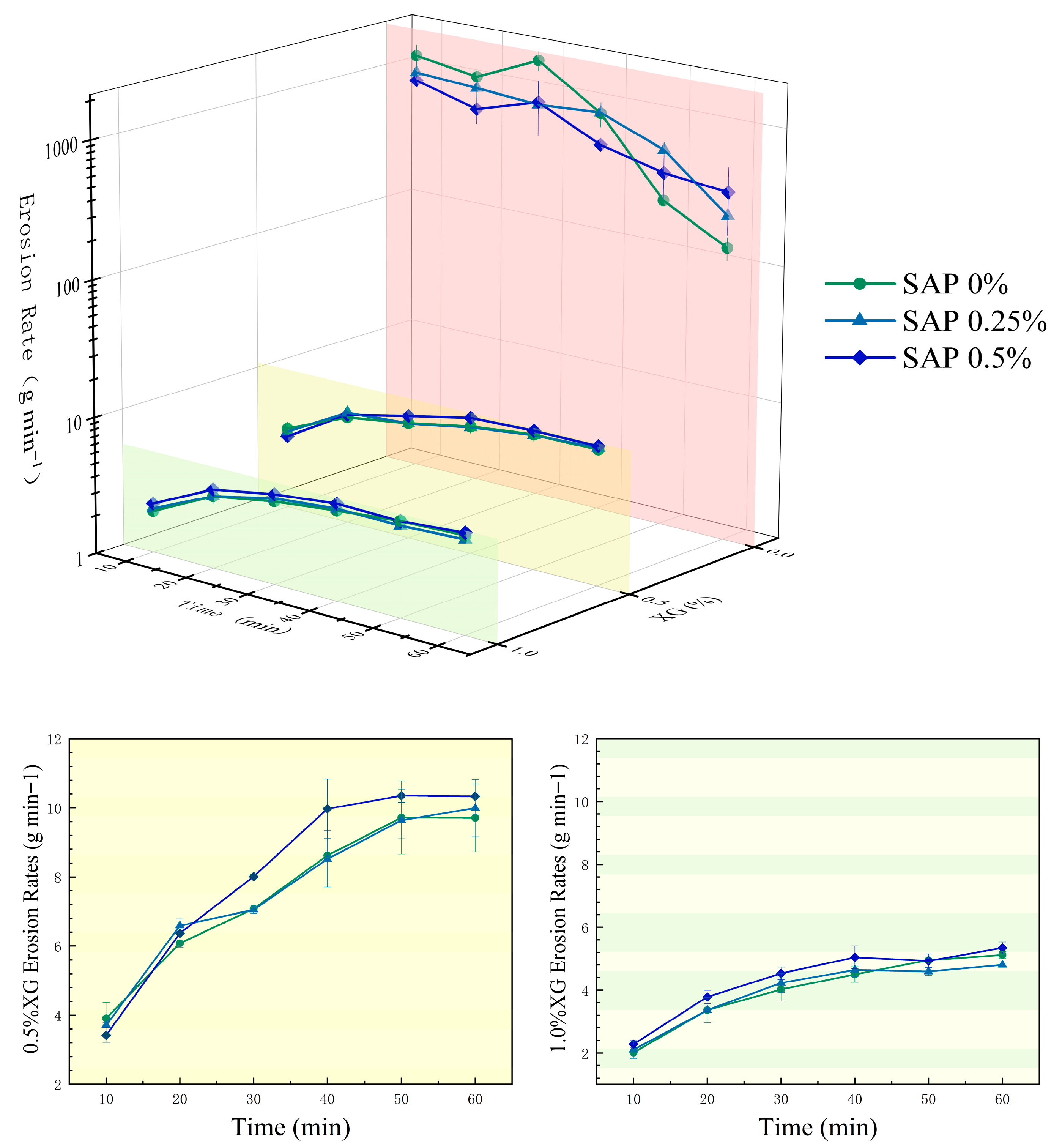
3.2. The Anti-Scour Performance of the Slope Under Different Treatments
Dynamic Characteristics During the Scouring Process
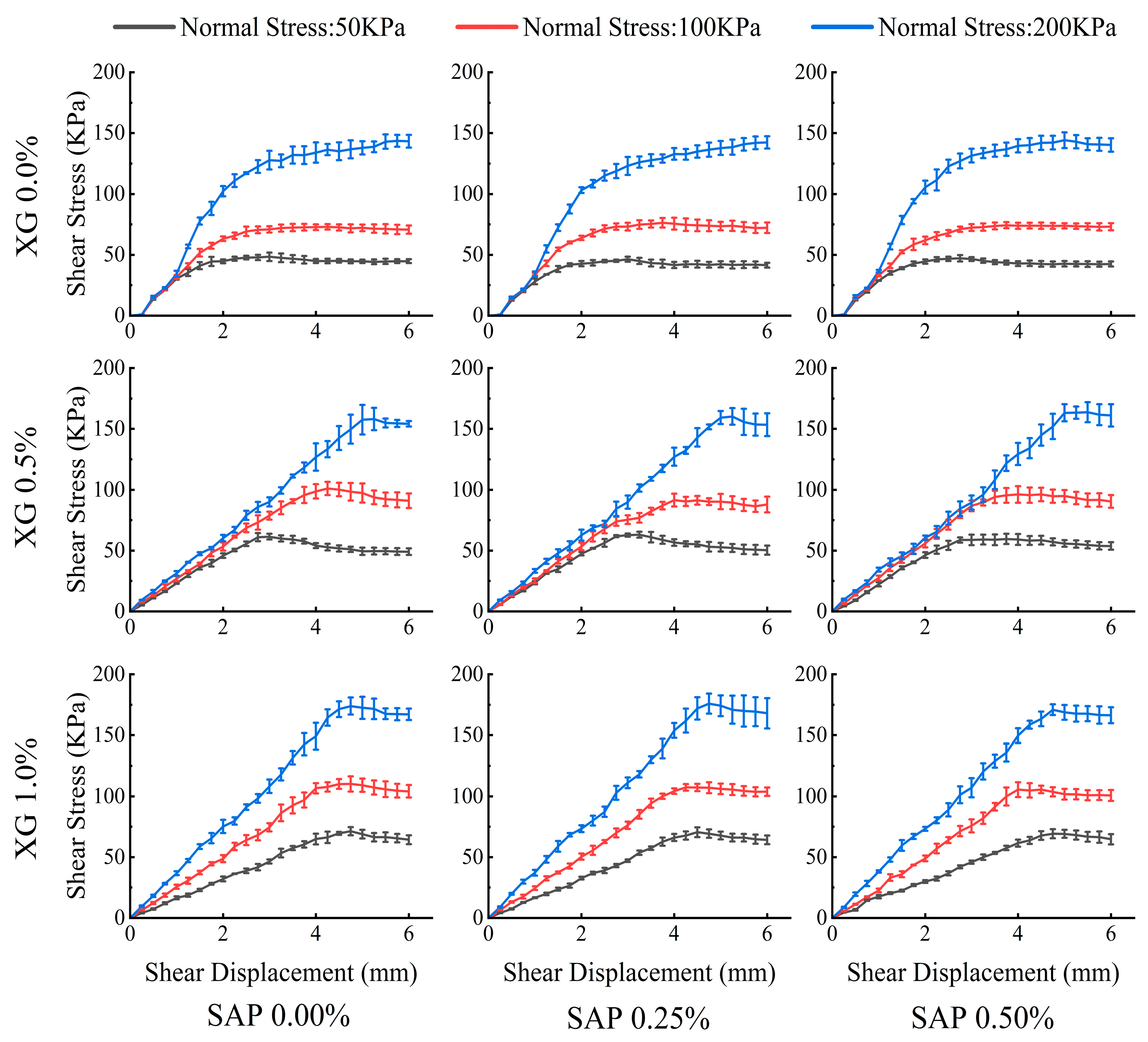
3.3. Changes in Shear Strength of Improved Soil
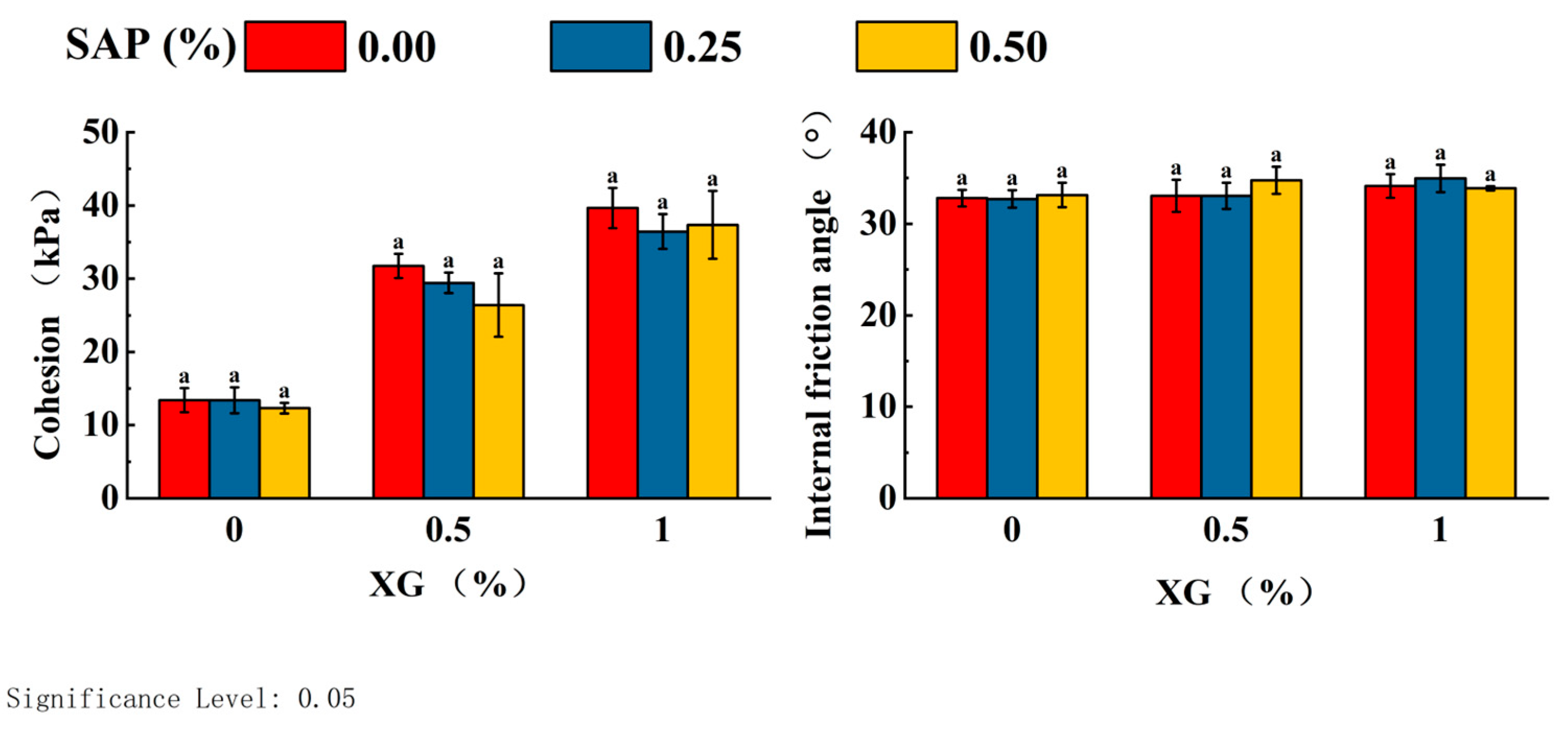
3.3.1. Influence of Additive Proportions on Shear Strength
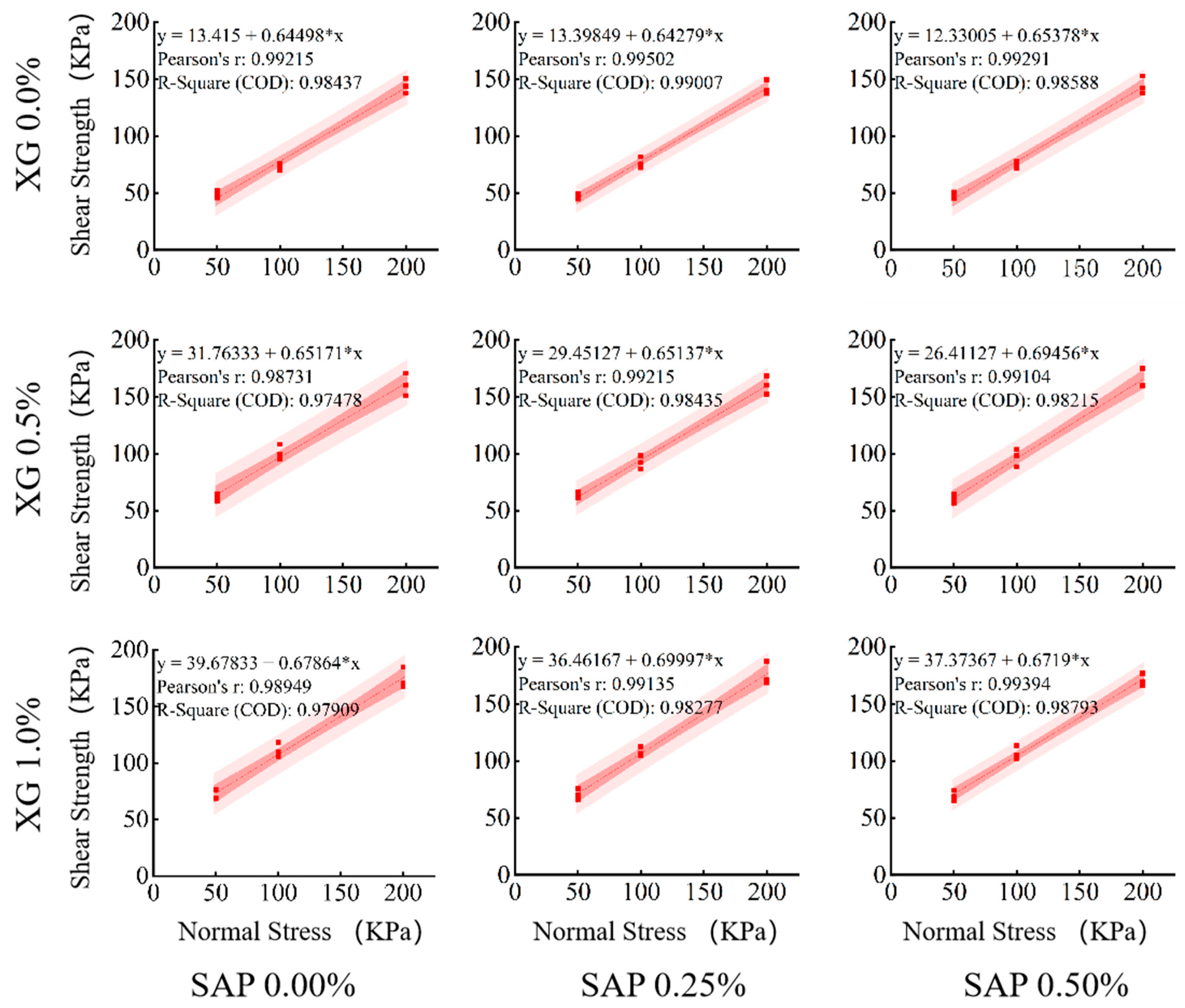
3.3.2. Regression Analysis and Significance Test of Shear Strength Parameters
4. Discussion
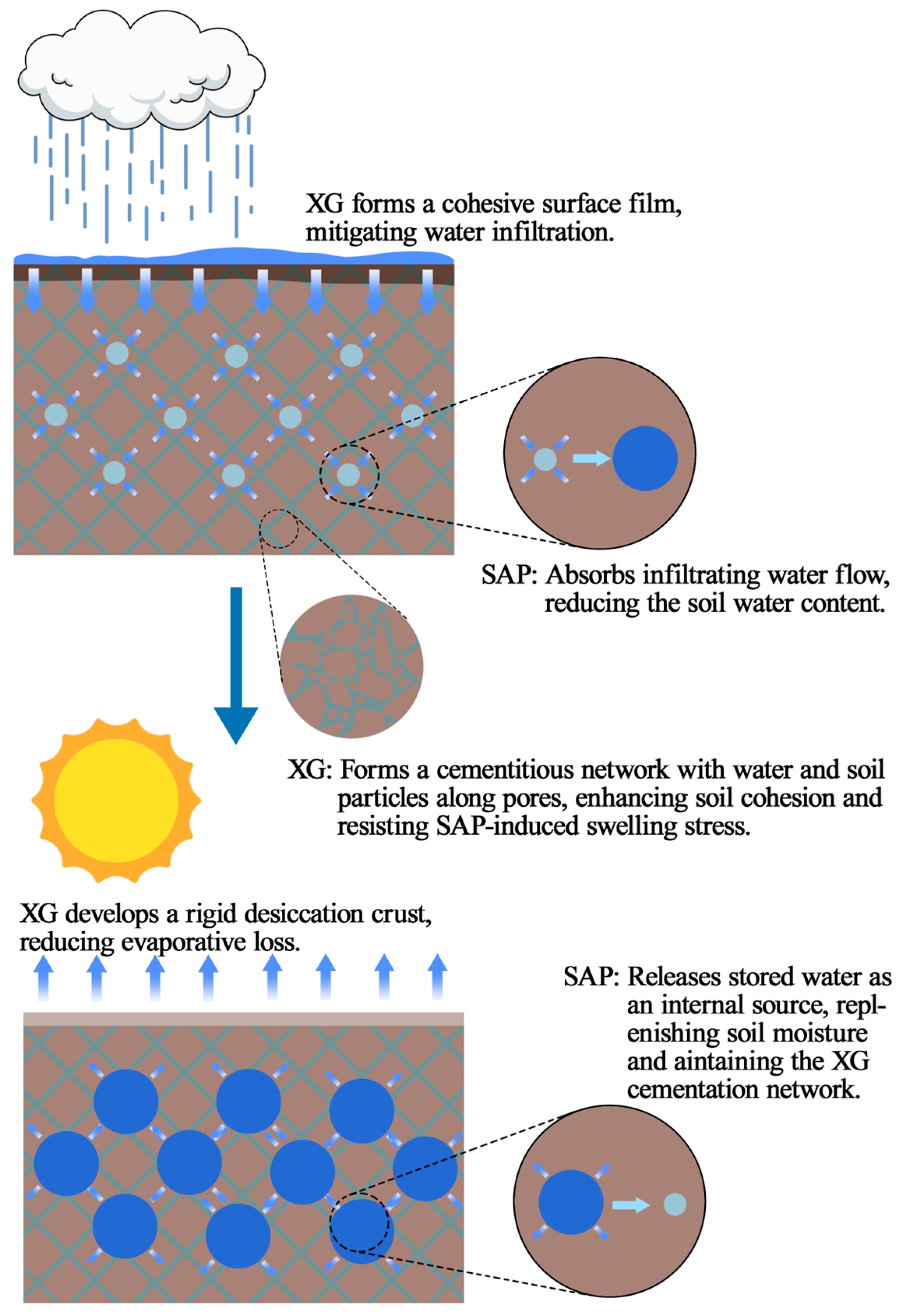
4.1. Mechanisms of Enhancing Soil Moisture Retention and Crack Resistance
4.1.1. Synergistic Mechanism of Water Retention and Cementation
4.1.2. Dynamic Processes of Water Regulation and Structural Stabilization
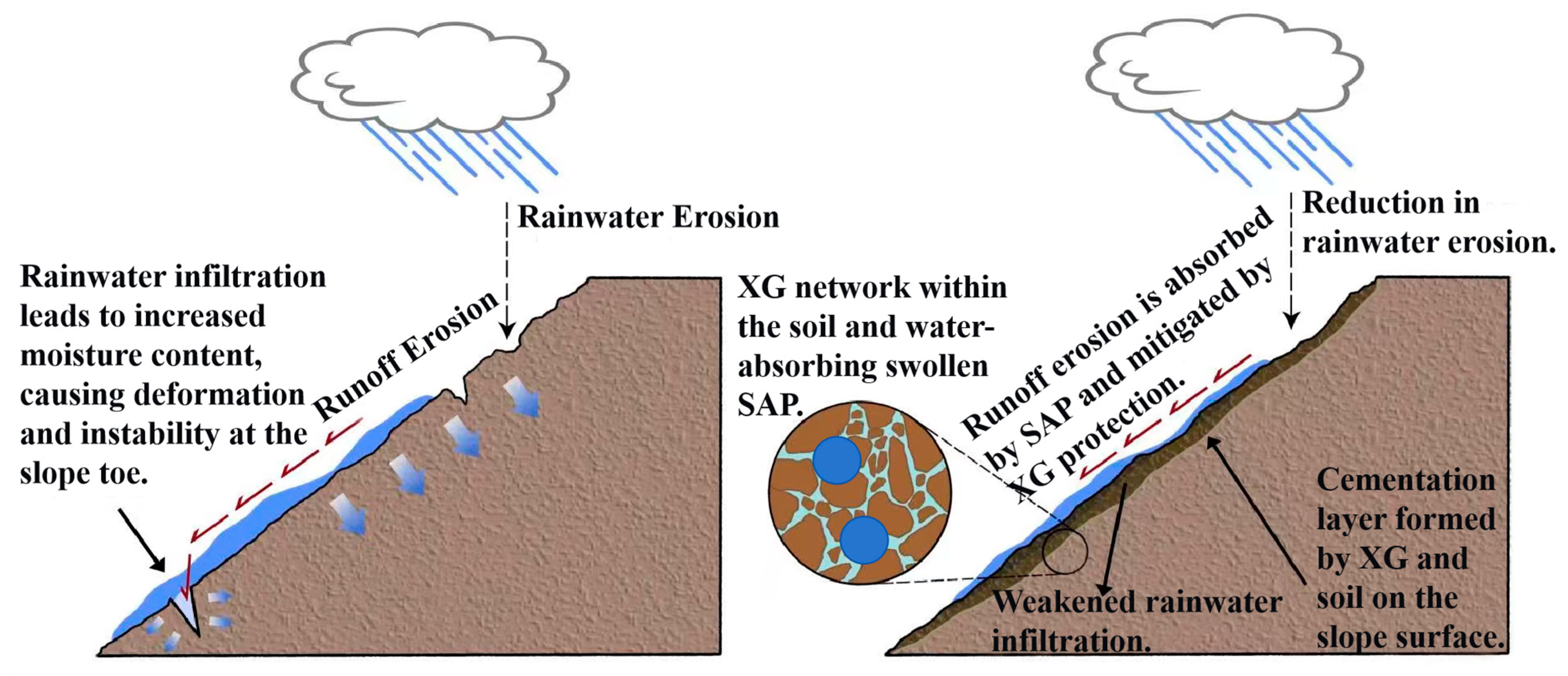
4.2. Mechanisms of Slope Resistance to Erosion
4.2.1. Synergistic Roles of XG and SAP and Quantitative Performance Comparison
4.2.2. Mechanistic Interpretation Using the Universal Soil Loss Equation (USLE) Framework
4.3. Mechanisms of Shear Strength Improvement
4.3.1. Combined Effect of XG and SAP on Shear Strength
4.3.2. Mechanism Extension Based on Soil Rheology and Polymer-Soil Interaction Models
4.3.3. Engineering Implications and Lab-Field Correlation Summary
4.4. Implications for Slope Stability
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, J.G.; Wang, T.; Yan, C.Z. The Relative Roles of Climate Change and Human Activities in the Desertification Process of Yulin City. J. Desert Res. 2012, 32, 625–630. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.C.; Wang, M.; Tao, Z.; Hu, X. Analysis of Desertification Evolution and Its Driving Forces in Yulin City. Sci. Soil Water Conserv. (Chin. Engl.) 2024, 22, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Zan, G.S.; Wang, C.P.; Li, F.; Liu, Z.; Sun, T. Main Results and Analysis of the Sixth National Survey on Desertification and Sandy Land. For. Resour. Manag. 2023, 1, 1–7. Available online: https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-LYZY202301001.htm (accessed on 17 November 2025).
- Wang, Y.M.; Tao, Y.C.; Cheng, Z.Y.; Li, B. Long-term protective effect of soil spraying on highway cutting slopes. J. Ecol. Environ. 2021, 30, 1724–1731. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L.P.; Qi, X.F. Research on the Stability Analysis of Windblown Sand Roadbed Slope. J. Inn. Mong. Agric. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2009, 30, 212–215. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Q.; Zhang, N.; Jin, Y.; Qin, H.; Ding, J. Slope failure of biotreated sand embankments under rainfall conditions: Experimental investigation and numerical simulation. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2020, 79, 4683–4699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eades, J.L.; Grim, R.E. Reaction of hydrated lime with pure clay minerals in soil stabilization. Highw. Res. Board Bull. 1960. Available online: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:55002825 (accessed on 17 November 2025).
- Ramana Murty, V.; Hari Krishna, P. Amelioration of expansive clay slopes using calcium chloride. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2007, 19, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahedi, M.; Cetin, B.; White, D.J. Performance evaluation of cement and slag stabilized expansive soils. Transp. Res. Rec. 2018, 2672, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayat, K.H. Viscosity-enhancing admixtures for cement-based materials—An overview. Cem. Concr. Compos. 1998, 20, 171–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezende, J.C.V.; Neto, J.O.A.; Zornberg, J.G. Shear Strength Characterization of the Interface Between Geocell Walls and Infill. Indian Geotech. J. 2025, 55, 3119–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; He, S.; Song, X.; Duan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, D.; Huang, M. The use of geocell as soil stabilization and soil erosion countermeasures. Geomatics. Nat. Hazards Risk 2021, 12, 2155–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, A. Geocell reinforced foundation beds-past findings, present trends and future prospects: A state-of-the-art review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 154, 658–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lann, T.; Bao, H.; Lan, H.; Zheng, H.; Yan, C.; Peng, J. Hydro-mechanical effects of vegetation on slope stability: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 926, 171691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, W.W.; Liu, Y.; Jia, L.Z. Review on the effects of plant functional traits on soil conservation. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 3355–3364. [Google Scholar]
- Cammeraat, E.; Van Beek, R.; Kooijman, A. Vegetation succession and its consequences for slope stability in SE Spain. Plant Soil 2005, 278, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, C.; Merton, L.; Burger, P. Impact of vegetative cover and slope on runoff, erosion, and water quality for field plots on a range of soil and spoil materials on central Queensland coal mines. Soil Res. 2000, 38, 313–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, I.; Kwon, Y.-M.; Im, J.; Cho, G.-C. Soil consistency and interparticle characteristics of xanthan gum biopolymer–containing soils with pore-fluid variation. Can. Geotech. J. 2019, 56, 1206–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Chung, M.; Park, H.M.; Song, K.-I.; Chang, I. Xanthan gum biopolymer as soil-stabilization binder for road construction using local soil in Sri Lanka. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2019, 31, 06019012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonça, A.; Morais, P.V.; Pires, A.C.; Chung, A.P.; Oliveira, P.V. A review on the importance of microbial biopolymers such as xanthan gum to improve soil properties. Appl. Sci. 2020, 11, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghchiche, A.; Haouam, A.; Immirzi, B. Use of polymers and biopolymers for water retaining and soil stabilization in arid and semiarid regions. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 2010, 4, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Pei, X.; Huang, R. Impact of polymer mixtures on the stabilization and erosion control of silty sand slope. J. Mt. Sci. 2019, 16, 470–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.; Chaudhary, K.; Malik, A.; Punia, H.; Sewhag, M.; Berkesia, N.; Nagora, M.; Kalia, S.; Malik, K.; Kumar, D.; et al. Superabsorbent polymers as a soil amendment for increasing agriculture production with reducing water losses under water stress condition. Polymers 2022, 15, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Guo, C.; Li, S. Influence of super absorbent polymer on soil water retention, seed germination and plant survivals for rocky slopes eco-engineering. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 62, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, A.T.P.; Chang, I.; Cho, G.C. Soil water retention and vegetation survivability improvement using microbial biopolymers in drylands. Geomech. Eng. 2019, 17, 475–483. [Google Scholar]
- Ostrand, M.S.; Desutter, T.M.; Daigh, A.L.M.; Limb, R.F.; Steele, D.D. Superabsorbent polymer characteristics, properties, and applications. Agrosystems. Geosci. Environ. 2020, 3, e20074. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, B.; Guo, H.; Xiao, H.; Wei, T. The effect of super absorbent polymers on soil and water conservation on the terraces of the loess plateau. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 102, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, B.; Zhao, C.; Wu, Y.; Han, W.; Song, J.; Bai, W. Effects of different concentrations of super-absorbent polymers on soil structure and hydro-physical properties following continuous wetting and drying cycles. J. Integr. Agric. 2022, 21, 3368–3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyuan, M.; Zhang, H.G.; Deng, R.T.; Wang, G.; Xiao, J.; Zhao, Y. Study on the Evolution Law of Cracks in Expansive Soil Modified by Xanthan Gum Biopolymer. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2025, 47, 106–114. [Google Scholar]
- Berkane, H.A.; Della, N.; Benziane, M.M.; Denine, S.; Elroul, A.B.; Feknous, H. Laboratory investigation on the effect of a combination of xanthan gum and clay on the behavior of sandy soil. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 2022, 7, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joga, J.R.; Varaprasad, B.J.S. Effect of xanthan gum biopolymer on dispersive properties of soils. World J. Eng. 2020, 17, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Che, W.Y.; Hao, S.F.; Ma, X.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, W.; Qian, W. Study on the mechanical properties and microstructure deterioration mechanism of xanthan gum-stabilized soil under dry-wet cycles based on CT technology. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2024, 46, 1119–1126. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.F.; Zhang, C.Y.; Liu, J.; Huang, L.H.; Bu, F.; Dai, C.J. Effect of sand content on anti-crack and anti-scour property of xanthan gum composite silty clay. Adv. Sci. Technol. Water Resour. 2023, 43, 1006–7647. [Google Scholar]
- Todisco, F.; Vergni, L.; Ortenzi, S.; DIMatteo, L. Soil Loss Estimation Coupling a Modified USLE Model with a Runoff Correction Factor Based on Rainfall and Satellite Soil Moisture Data. Water 2022, 14, 2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pampalone, V.; Nicosia, A.; Palmeri, V.; Serio, M.A.; Ferro, V. Rill and Interrill Soil Loss Estimations Using the USLE-MB Equation at the Sparacia Experimental Site (South Italy). Water 2023, 15, 2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabalar, A.F.; Canakci, H. Direct shear tests on sand treated with xanthan gum. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng.—Ground Improv. 2011, 164, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wu, L.; Perdjon, M.; Huang, X.; Peng, Y. The drying effect on xanthan gum biopolymer treated sandy soil shear strength. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 197, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.Z.; Hao, S.F.; Mei, H.; Liu, J.; Ren, J.; Bu, F.; Wang, Z. Strength Characteristics of Sand Modified by Biopolymers under Dry-Wet Cycles. Acta Mater. Compos. Sin. 2023, 40, 2285–2295. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, Y.M.; Moon, J.H.; Cho, G.C.; Kim, Y.U.; Chang, I. Xanthan gum biopolymer-based soil treatment as a construction material to mitigate internal erosion of earthen embankment: A field-scale study. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 389, 131716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Chang, I.; Kang, S.J.; Lee, D.H.; Cho, G.C. Alkaline induced-cation crosslinking biopolymer soil treatment and field implementation for slope surface protection. Geomech. Eng. 2023, 33, 29–40. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.; Chang, I.; Cho, G.C. Advanced biopolymer-based soil strengthening binder with trivalent chromium–xanthan gum crosslinking for wet strength and durability enhancement. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2023, 35, 04023360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchmann, C.; Neff, J.; Meyer, M.; Bundschuh, M.; Steinmetz, Z. Superabsorbent polymers in soil: The new microplastics? Camb. Prism. Plast. 2024, 2, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
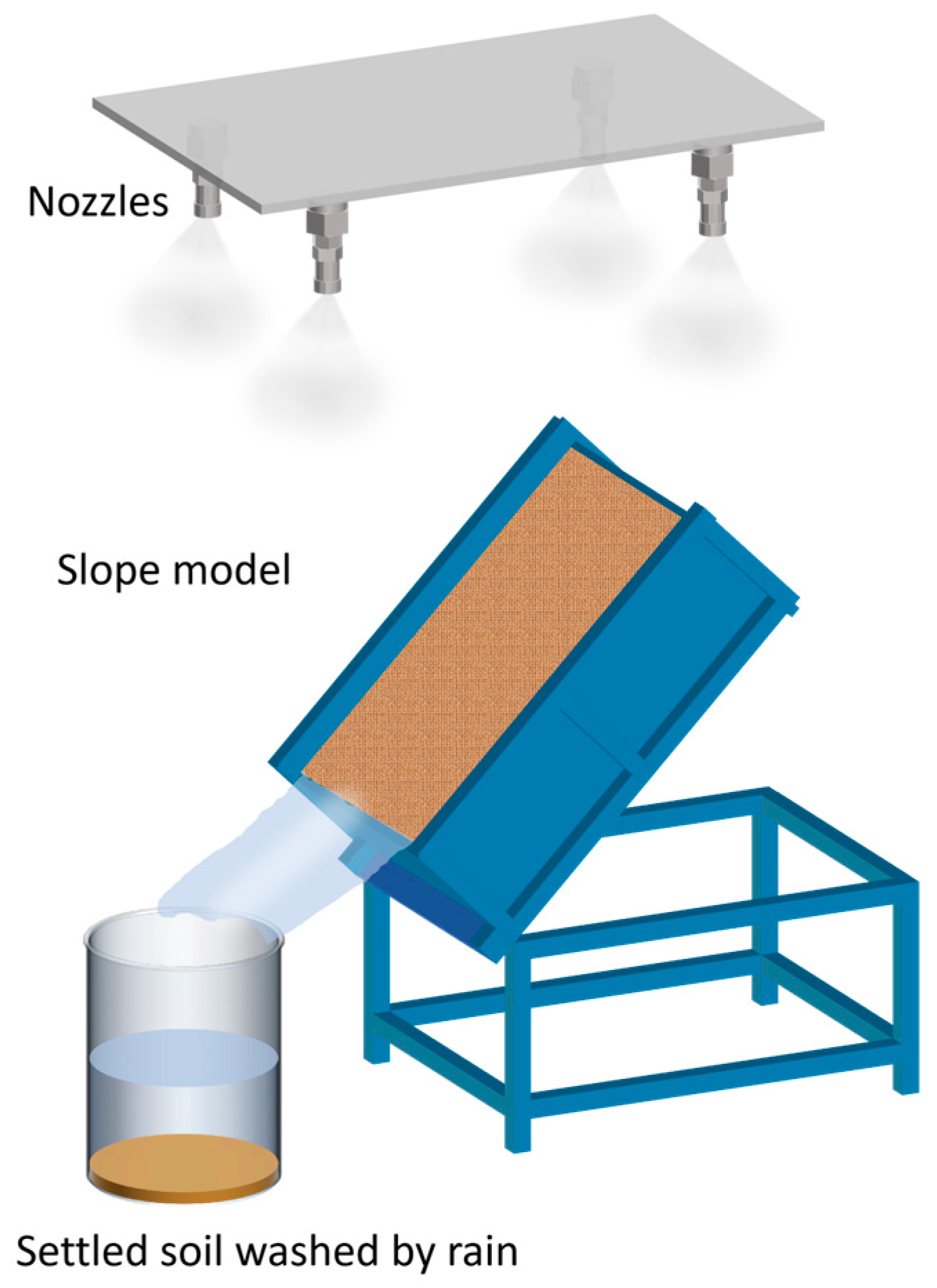

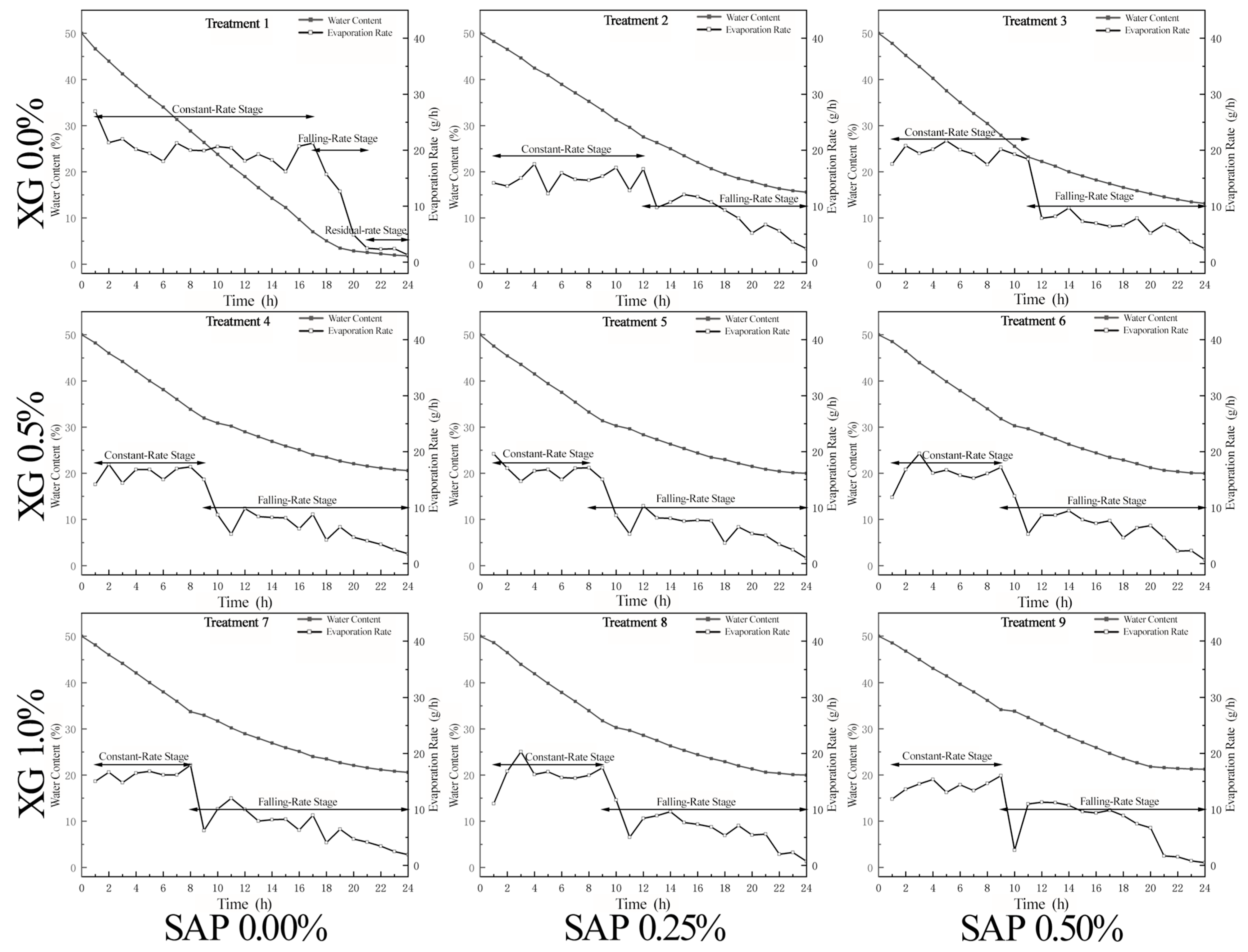
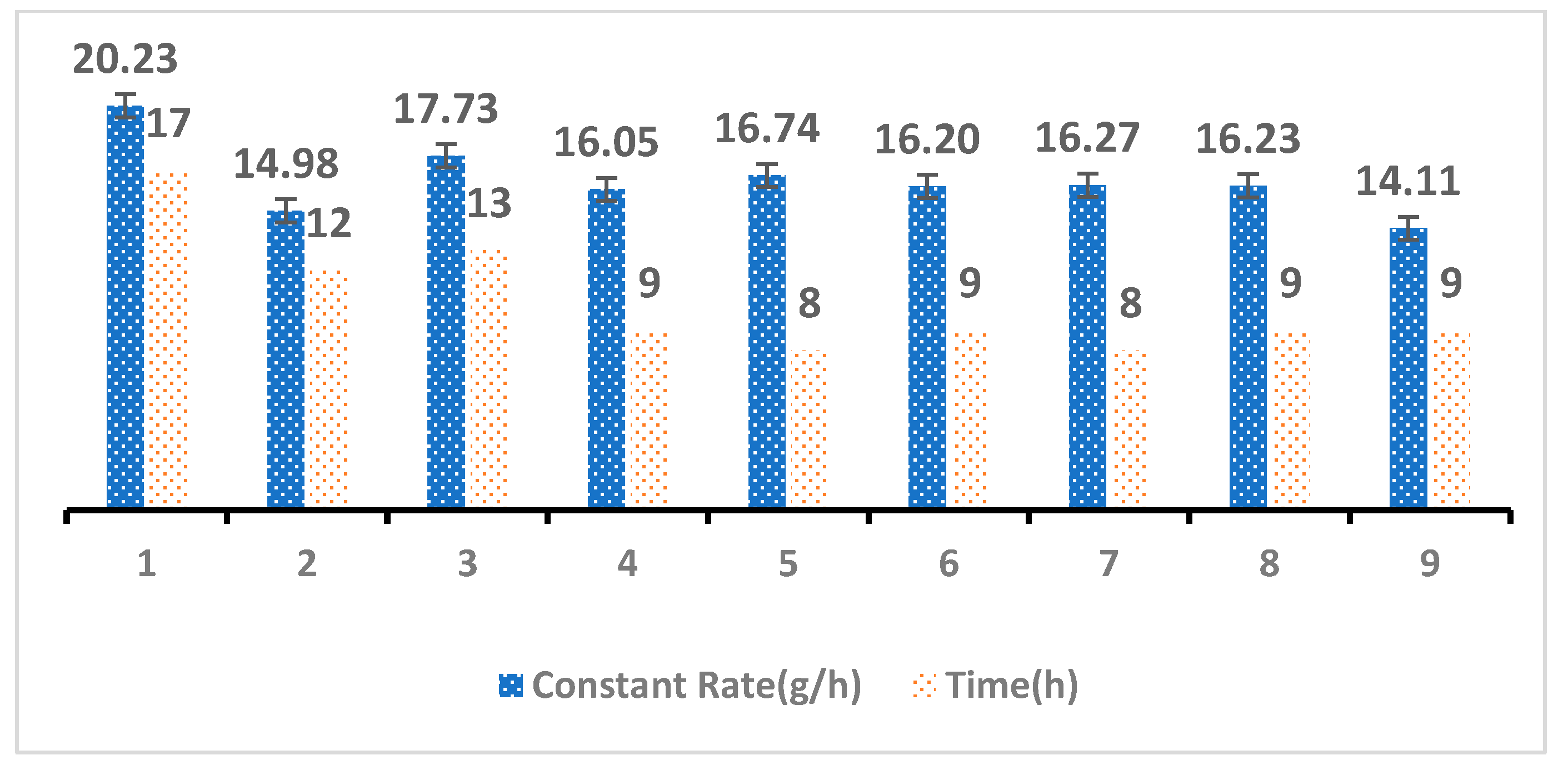

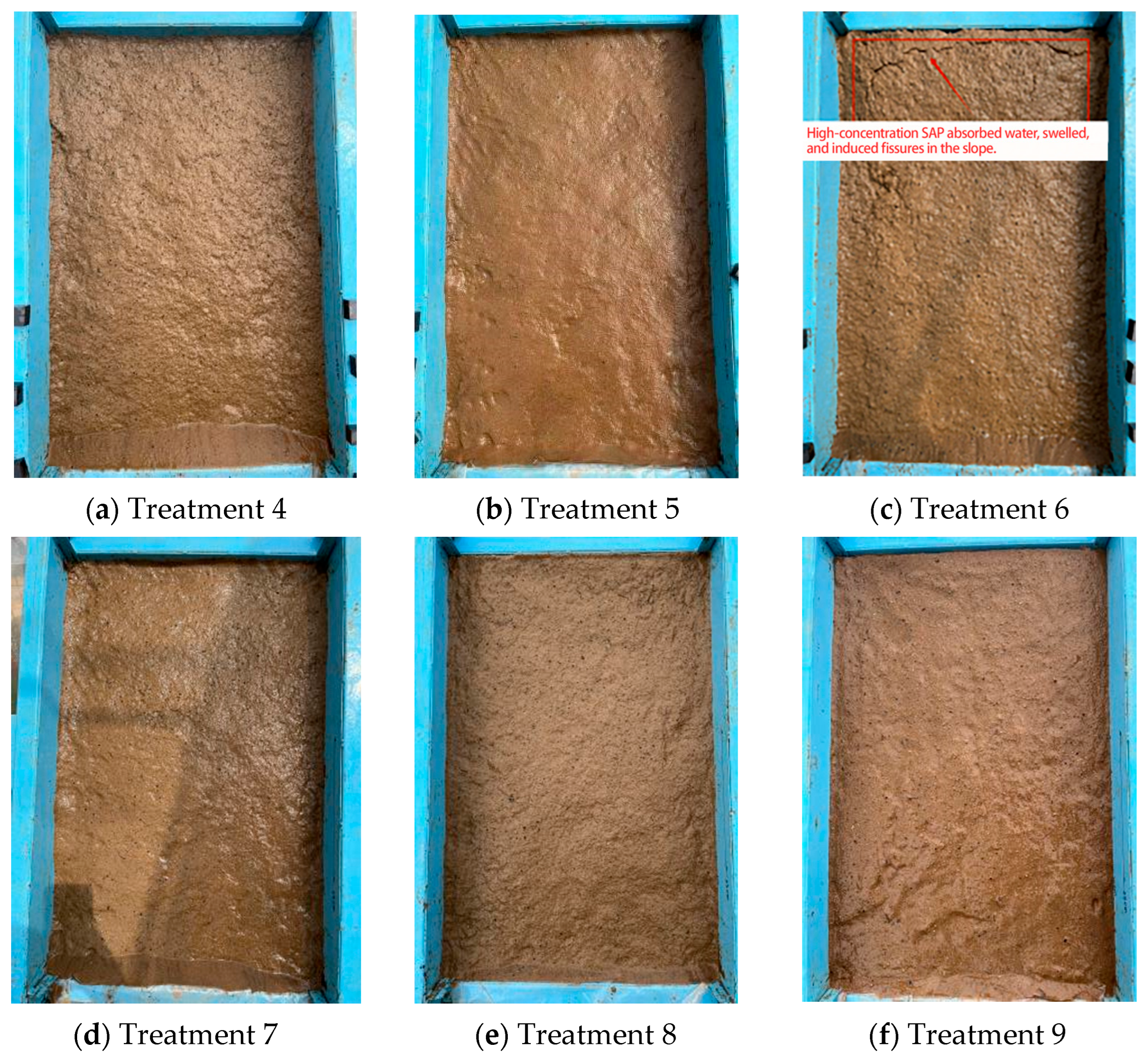
| Treatment Number | XG Concentration (% w/w) | SAP Concentration (% w/w) | Number of Replicates |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| 2 | 0 | 0.25 | 3 |
| 3 | 0 | 0.5 | 3 |
| 4 | 0.5 | 0 | 3 |
| 5 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 3 |
| 6 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 3 |
| 7 | 1 | 0 | 3 |
| 8 | 1 | 0.25 | 3 |
| 9 | 1 | 0.5 | 3 |
| Plastic Limit (%) | Liquid Limit (%) | Plasticity Index | Optimum Moisture Content (%) | Natural Density (g/cm3) | Maximum Dry Density (g/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12.16 | 14.55 | 2.39 | 13.10 | 1.75 | 2.1 |
| Treatment | Total Crack Area (mm2) | Crack Area Ratio (%) | Maximum Width (mm) | Maximum Length (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 13.30 | 0.08% | 0.09 | 25.86 |
| 2 | 686.82 | 4.29% | 6.38 | 185.26 |
| 3 | 785.76 | 4.91% | 4.22 | 187.80 |
| 4 | 599.00 | 3.74% | 3.96 | 247.85 |
| 5 | 161.12 | 1.01% | 1.59 | 58.77 |
| 6 | 458.04 | 2.86% | 4.82 | 193.50 |
| 7 | 406.47 | 2.54% | 3.79 | 94.67 |
| 8 | 179.66 | 1.12% | 2.26 | 72.57 |
| 9 | 147.66 | 0.92% | 1.61 | 57.38 |
| Treatment | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
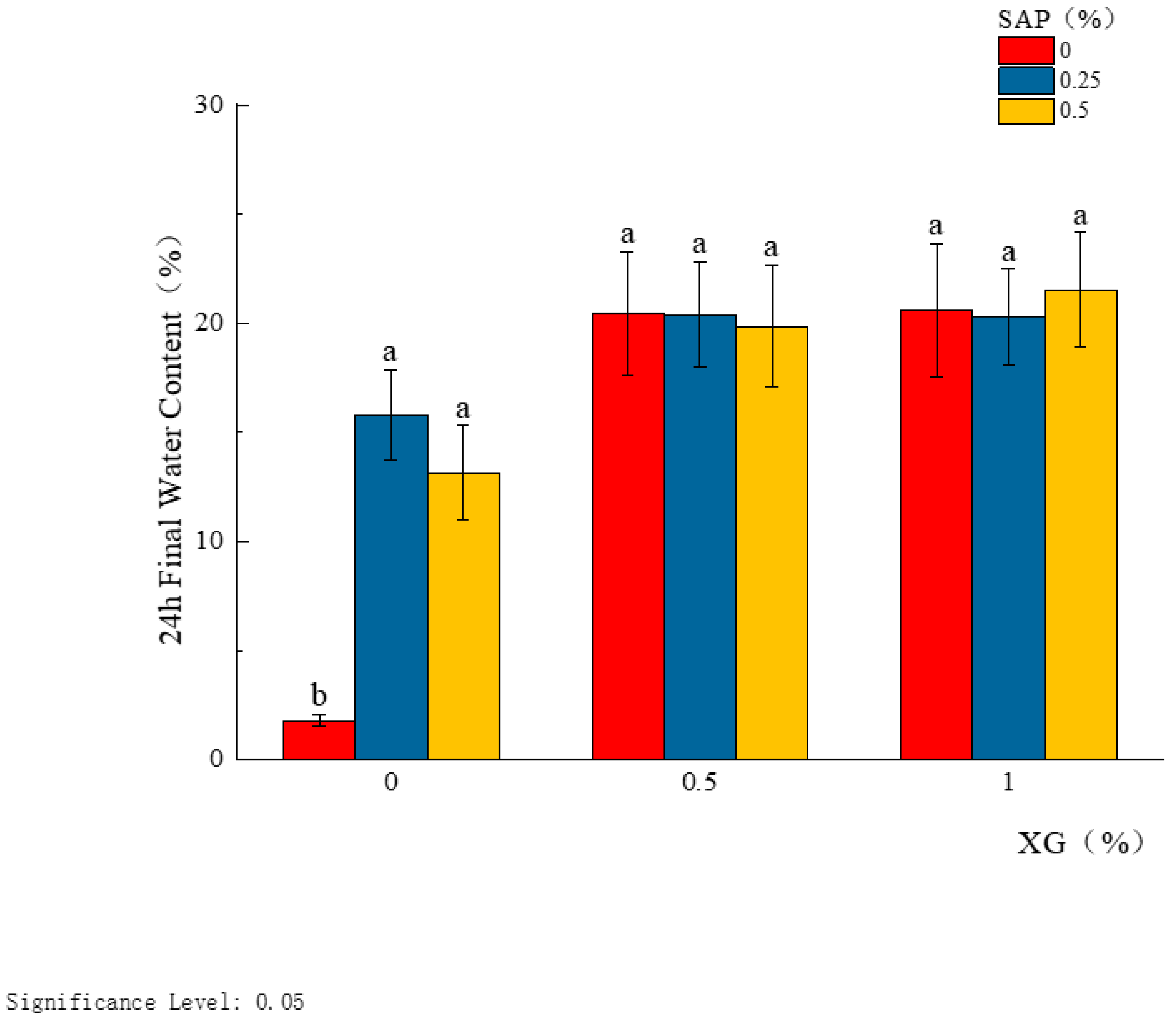
| Water content % | 1.80 ± 0.22 | 15.80 ± 1.67 | 13.14 ± 1.77 | 20.43 ± 2.32 | 20.40 ± 1.98 | 19.87 ± 2.29 | 20.59 ± 2.51 | 20.27 ± 1.81 | 21.53 ± 2.15 |
| SAP Concentration (%) | Water Content (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| XG 0.0% | 0.00 | 1.80 ± 0.22 b |
| 0.25 | 15.80 ± 1.67 a | |
| 0.50 | 13.14 ± 1.77 a | |
| XG 0.5% | 0.00 | 20.43 ± 2.32 a |
| 0.25 | 20.40 ± 1.98 a | |
| 0.50 | 19.87 ± 2.29 a | |
| XG 1.0% | 0.00 | 20.59 ± 2.51 a |
| 0.25 | 20.27 ± 1.81 a | |
| 0.50 | 21.53 ± 2.15 a | |
| XG | F | 54.817 |
| p | <0.01 ** | |
| SAP | F | 9.442 |
| p | 0.02 * | |
| XG × SAP | F | 9.77 |
| p | <0.01 ** |
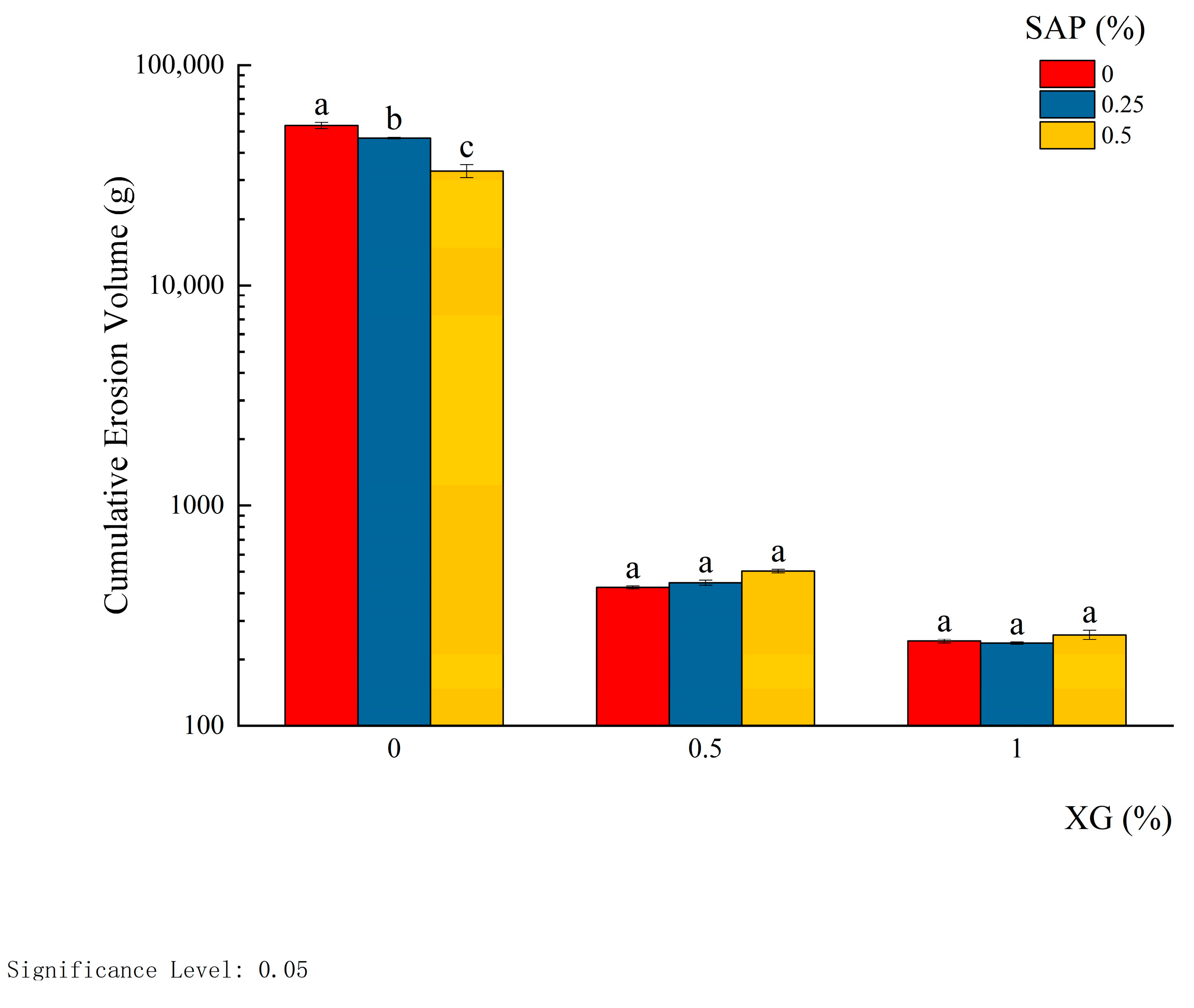
| Treatment | XG (%) | SAP (%) | Cumulative Scouring Volume (kg) | Relative to the Proportion in Treatment 1 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 53.36 ± 5.4130 a | 100.00 |
| 2 | 0.25 | 43.56 ± 6.3927 b | 81.62 | |
| 3 | 0.5 | 35.63 ± 2.9440 c | 66.77 | |
| 4 | 0.5 | 0 | 0.45 ± 0.0192 a | 0.85 |
| 5 | 0.25 | 0.45 ± 0.0194 a | 0.85 | |
| 6 | 0.5 | 0.48 ± 0.0080 a | 0.91 | |
| 7 | 1 | 0 | 0.24 ± 0.0040 a | 0.45 |
| 8 | 0.25 | 0.24 ± 0.0078 a | 0.44 | |
| 9 | 0.5 | 0.25 ± 0.0037 a | 0.47 | |
| XG | F | 484.654 | ||
| p | <0.001 *** | |||
| SAP | F | 6.411 | ||
| p | 0.008 ** | |||
| XG*SAP | F | 6.459 | ||
| p | 0.002 ** | |||
| Treatment | XG% | SAP% | Cohesion (c) kPa | Internal Friction Angle (φ) | Increase Rate of c Value % | Increase Rate of φ Value % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 13.42 | 32.82 | 0.00% | 0.00% |
| 2 | 0.25 | 13.40 | 32.73 | −0.12% | −0.27% | |
| 3 | 0.5 | 12.33 | 33.18 | −8.09% | 1.08% | |
| 4 | 0.5 | 0 | 31.76 | 33.09 | 136.77% | 0.83% |
| 5 | 0.25 | 29.45 | 33.08 | 119.54% | 0.79% | |
| 6 | 0.5 | 26.41 | 34.78 | 96.88% | 5.98% | |
| 7 | 1 | 0 | 39.68 | 34.16 | 195.78% | 4.09% |
| 8 | 0.25 | 36.46 | 34.99 | 171.80% | 6.61% | |
| 9 | 0.5 | 37.37 | 33.90 | 178.60% | 3.28% |
| Treatment | XG% | SAP% | Cohesion (c) kPa | Internal Friction Angle (φ)° | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 13.42 ± 1.352 a | 32.81 ± 0.747 a | |||
| 2 | 0.25 | 13.40 ± 1.444 a | 32.73 ± 0.776 a | ||||
| 3 | 0.5 | 12.33 ± 0.601 a | 33.16 ± 1.100 a | ||||
| 4 | 0.5 | 0 | 31.76 ± 1.340 a | 33.07 ± 1.440 a | |||
| 5 | 0.25 | 29.45 ± 1.150 a | 33.06 ± 1.158 a | ||||
| 6 | 0.5 | 26.41 ± 3.550 a | 34.76 ± 1.204 a | ||||
| 7 | 1 | 0 | 39.68 ± 2.244 a | 34.15 ± 1.048 a | |||
| 8 | 0.25 | 36.46 ± 1.941 a | 34.97 ± 1.226 a | ||||
| 9 | 0.5 | 37.37 ± 3.773 a | 33.90 ± 0.191 a | ||||
| Cohesion | XG | F | 198.687 | Internal friction angle | XG | F | 2.832 |
| p | <0.001 *** | p | 0.085 | ||||
| SAP | F | 2.727 | SAP | F | 0.492 | ||
| p | 0.092 | p | 0.619 | ||||
| XG × SAP | F | 0.798 | XG × SAP | F | 0.967 | ||
| p | 0.542 | p | 0.450 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, N.; Bai, X.; Xu, C.; Liang, Y.; Mao, Z.; Bai, M. Research on the Improvement of Water Retention, Anti-Erosion and Mechanical Properties of Aeolian Sand Slopes Under the Synergistic Effect of Xanthan Gum and Water Retention Agents. Sustainability 2025, 17, 10441. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310441
Deng N, Bai X, Xu C, Liang Y, Mao Z, Bai M. Research on the Improvement of Water Retention, Anti-Erosion and Mechanical Properties of Aeolian Sand Slopes Under the Synergistic Effect of Xanthan Gum and Water Retention Agents. Sustainability. 2025; 17(23):10441. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310441
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Niandong, Xuejian Bai, Chong Xu, Yixuan Liang, Zhuxin Mao, and Ming Bai. 2025. "Research on the Improvement of Water Retention, Anti-Erosion and Mechanical Properties of Aeolian Sand Slopes Under the Synergistic Effect of Xanthan Gum and Water Retention Agents" Sustainability 17, no. 23: 10441. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310441
APA StyleDeng, N., Bai, X., Xu, C., Liang, Y., Mao, Z., & Bai, M. (2025). Research on the Improvement of Water Retention, Anti-Erosion and Mechanical Properties of Aeolian Sand Slopes Under the Synergistic Effect of Xanthan Gum and Water Retention Agents. Sustainability, 17(23), 10441. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310441





