The Urban–Rural Integration of Resources and Services Using Big Data: A Multifunctional Landscape Perspective
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Definitions and Research Methods
2.1.1. Nearest Neighbor Index
2.1.2. Kernel Density Estimation
2.1.3. Service Matching Analysis: Defining and Diagnosing Spatial Mismatch
2.2. Study Area and Data Collection
2.2.1. Study Area
2.2.2. Data Collection
2.2.3. Data Processing and Point Generation
- DEM data processing
- 2.
- Resource-based landscape attribute data point element generation
2.2.4. Service-Based Landscapes
2.3. Theoretical Framework for Understanding Spatial Functional Diversity
3. Results
3.1. Landscape Functional Diversity
3.2. Spatial Pattern
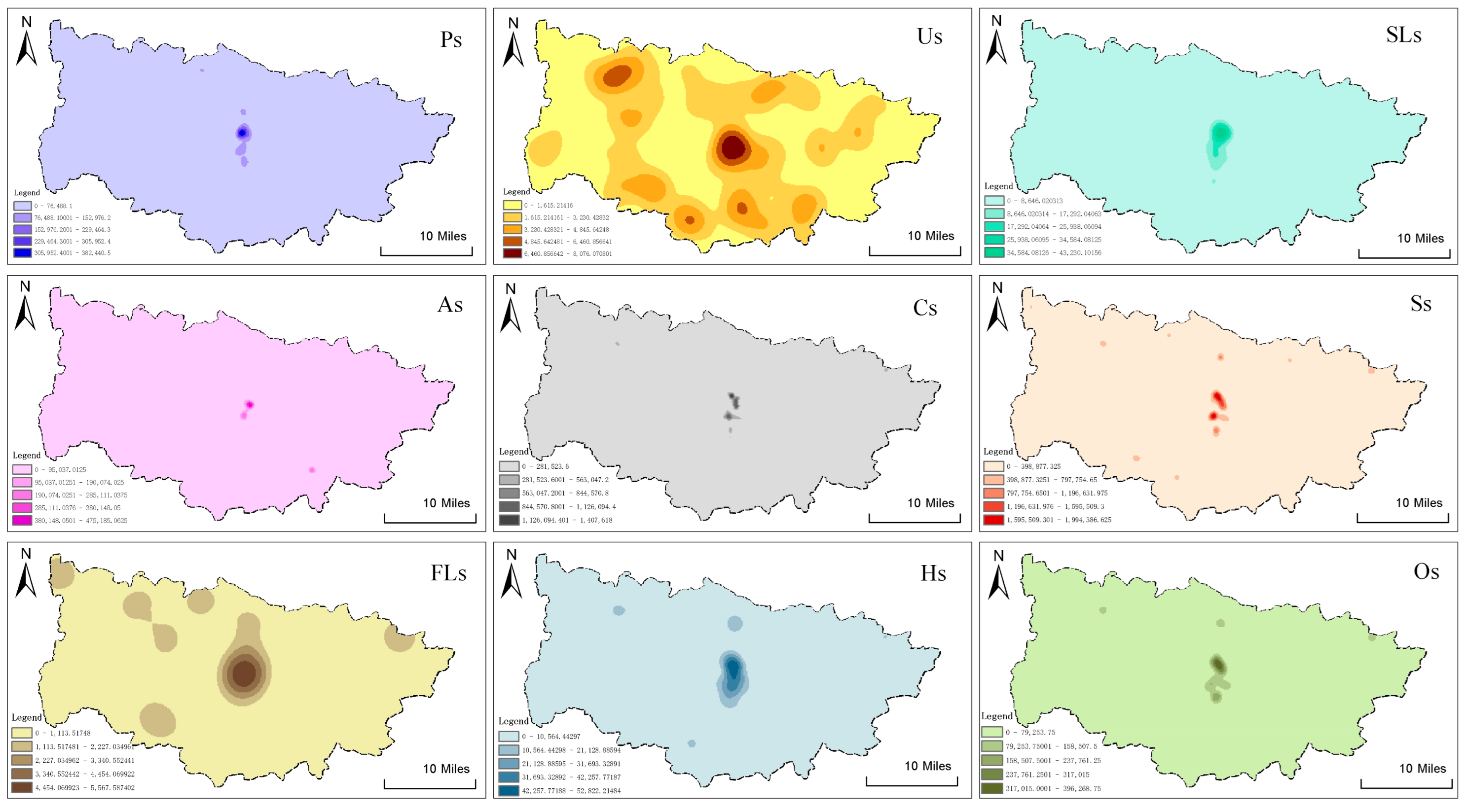
3.2.1. Resource-Oriented Landscapes
3.2.2. Service-Based Landscapes
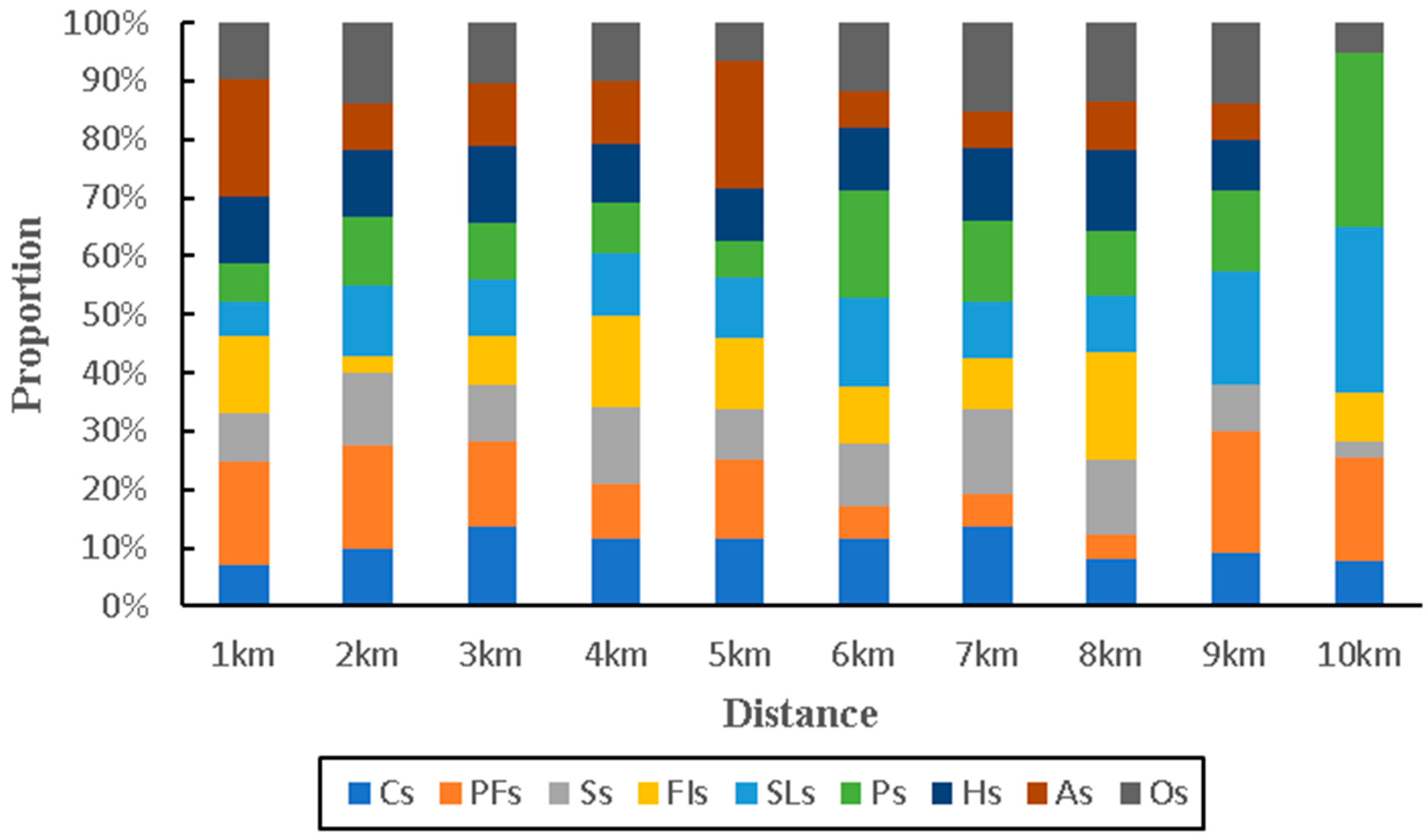
3.3. Multi-Distance Gradient Spatial Matching
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mishra, A.; Bajpai, S.; Bhadwal, S. Nature-Based Solutions for Climate-Resilient Development: A Technical, Policy, and Governance Perspective; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Ra’dI, Y.; Nefedkin, N.; Popovski, P.; Alù, A. Nonlinear, Active, and Time-Varying Metasurfaces for Wireless Communications: A perspective and opportunities. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2024, 66, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, W.; Jie, G.U.; Xie, H. Land use pattern and multifunctional evolution in Hunan Province using “production-living-ecosystem” space. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2024, 40, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wu, Z.; Zhu, L.; Li, Y. Accurate identification and trade-off analysis of multifunctional spaces of land in megacities: A case study of Guangzhou city, China. Habitat Int. 2024, 153, 103209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Marquez, R.; Xie, L.; Li, X. Evaluating the impact of special additional deductions policy on urban-rural household vulnerability: Insights from China Family Panel Studies. Econ. Anal. Policy 2025, 86, 839–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Ge, S.; Song, P.; Jombach, S.; Fekete, A.; Valánszki, I. Optimizing Urban Green Spaces for Vegetation-Based Carbon Sequestration: The Role of Landscape Spatial Structure in Zhengzhou Parks, China. Forests 2025, 16, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smardon, R.C. Beyond Greenways: The Next Step for City Trails and Walking Routes by Robert Searns (review). Landsc. J. 2024, 43, 133–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, C.M.A.; Salomao, R.P.; Ferreira, G.K.R. From green to grey: Unravelling the role of urbanization on diversity of dung beetles in an Amazonian landscape. Urban Ecosyst. 2024, 27, 773–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, Q.B.; Zucca, C.; Hermassi, T.; Diwediga, B. User-Friendly and Integrated Landscape Simulation Tool for Support Sustainable Land Management Planning in Tunisia. In Euro-Mediterranean Conference for Environmental Integration; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dacko, S.G.; Xu, W. Impact of Familiarity, Destination-Specific Relevance, and Marketing on Engagement with Augmented Reality Smart Tourism Experiences. In International Conference on Management, Tourism and Technologies; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shockley, B.; Gengler, J.J. Sharing citizenship: Economic competition, cultural threat, and immigration preferences in the rentier state. Political Sci. Res. Methods 2024, 12, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahim, E.E.M.; Abonazel, M.R.; Shalaby, O.A.; Albeltagy, W.A.A. Studying the Impact of Socioeconomic and Environmental Factors on Nitrogen Oxide Emissions: Spatial Econometric Modeling. Int. J. Energy Econ. Policy 2025, 15, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guevara-Cue, G. Revealing spatial (in) justice: Exploring the dynamics of triple spatiality in Chile and its impact on the generation of spatial barriers to social rights. GeoJournal 2024, 89, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Hu, J.; Wu, K.; Huang, M.; Hu, M. Investigating the role of green mobility in coupling coordination of urbanization and ecological environment: Evidence from high-speed rail accessibility. Transp. Policy 2025, 170, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthel, M.; Scott, J.W. Conceptualizing Place Borders as Narrative: Observations From Berlin-Wedding, a Neighbourhood in Transformation. Urban Plan. 2024, 9, 7027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Huang, T.; Zhao, H.; Li, X. Spatial and temporal dynamics of base flow in semi-arid montane watersheds and the effects of landscape patterns and topography. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamgbade, J.A.; Golly, G.N.A.; Ohueri, C.C. Sociopolitical economy and spatial accentuation of neighbourhood gentrification in East Malaysia. J. Hous. Built Environ. 2024, 39, 49–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonas, T.; Macht, G.A. Analyzing the urban-rural divide: Understanding geographic variations in charging behavior for a user-centered EVSE infrastructure. J. Transp. Geogr. 2024, 116, 103859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.Z.; Mao, R.; Zhou, Y. Rurbanomics for common prosperity: New approach to integrated urban-rural development. China Agric. Econ. Rev. 2023, 15, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Cui, J.; Zhou, L. Reflection on Popular Concepts of Landscape Design. J. Landsc. Res. 2023, 15, 67–69. [Google Scholar]
- Du, L.; Liu, H.; Liu, H.; Liu, W.; Quan, Z.; Zhang, Y. Value Assessment and Prediction of Regulating Ecosystem Services in Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park, China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Wang, L.; Huang, H. Characteristics of Urban–Rural Integration at the County-Scale Interface: The Case of Linqu County, China. Land 2024, 13, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhao, J.; Duan, X.; Tang, B.; Zuo, L.; Wang, X.; Guo, Q. Spatial Quantification of Cropland Soil Erosion Dynamics in the Yunnan Plateau Based on Sampling Survey and Multi-Source LUCC Data. Remote. Sens. 2024, 16, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longyin, H.U.; Cheng, J. Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Convenience of Urban Catering Industry Based on POI Data: A Case Study of Nanjing, Jiangsu Province. Geogr. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2024, 40, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Feng, Q.; Niu, B.; Chen, B.; Yan, F.; Gong, J.; Liu, J. Mapping urban villages based on point-of-interest data and a deep learning approach. Cities 2025, 156, 105549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garba, I.I.; Bell, L.W.; Chauhan, B.S.; Williams, A. Optimizing ecosystem function multifunctionality with cover crops for improved agronomic and environmental outcomes in dryland cropping systems. Agric. Syst. 2024, 214, 103821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Shao, J. Coupling mechanism for rural multifunctional development and rural settlement evolution in mountainous areas of China. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2024, 40, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y. The geographical evolution of sports cultural landscapes in historical and cultural research. GeoJournal 2025, 90, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente, M. Street Tree Redevelopment in Rome’s Historical Landscapes: From Strategic Vision to Streetscape Design. Land 2025, 14, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Vot, T.; Cohen, M.; Nowak, M.; Passy, P.; Sumera, F. Resilience of Terraced Landscapes to Human and Natural Impacts: A GIS-Based Reconstruction of Land Use Evolution in a Mediterranean Mountain Valley. Land 2024, 13, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakody, D.; Adams, V.; Pecl, G.; Lester, E. What makes a place special? Understanding drivers and the nature of place attachment. Appl. Geogr. 2024, 163, 103177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, N.; Sharma, A. Understanding and Recreating Historical Landscapes through Oral History, Architectural and Archival Research—A Methodology: The Case of the Royal Gardens of Rajnagar, Bundelkhand. J. Herit. Manag. 2018, 2, 202–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Liu, P.; Huang, L.; Feng, S.; Li, Y. Features of architectural landscape fragmentation in traditional villages in Western Hunan, China. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 18633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Zhou, J.; Chen, X.; Xu, Y.; Tao, J. Risk Assessment of Geological Disasters Triggered by Heavy Rainfall in Mountainous Areas: A Case Study in Hebei Province, China. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2025, 23, 5443–5460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Fan, J.; Luo, J.; Ren, R.; Li, H. Study on Urban System Relationships and Resilience Promotion Strategies in Underdeveloped Mountainous Areas Based on Social Network Analysis: A Case Study of Qiandongnan Miao and Dong Autonomous Prefecture. Land 2025, 14, 1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
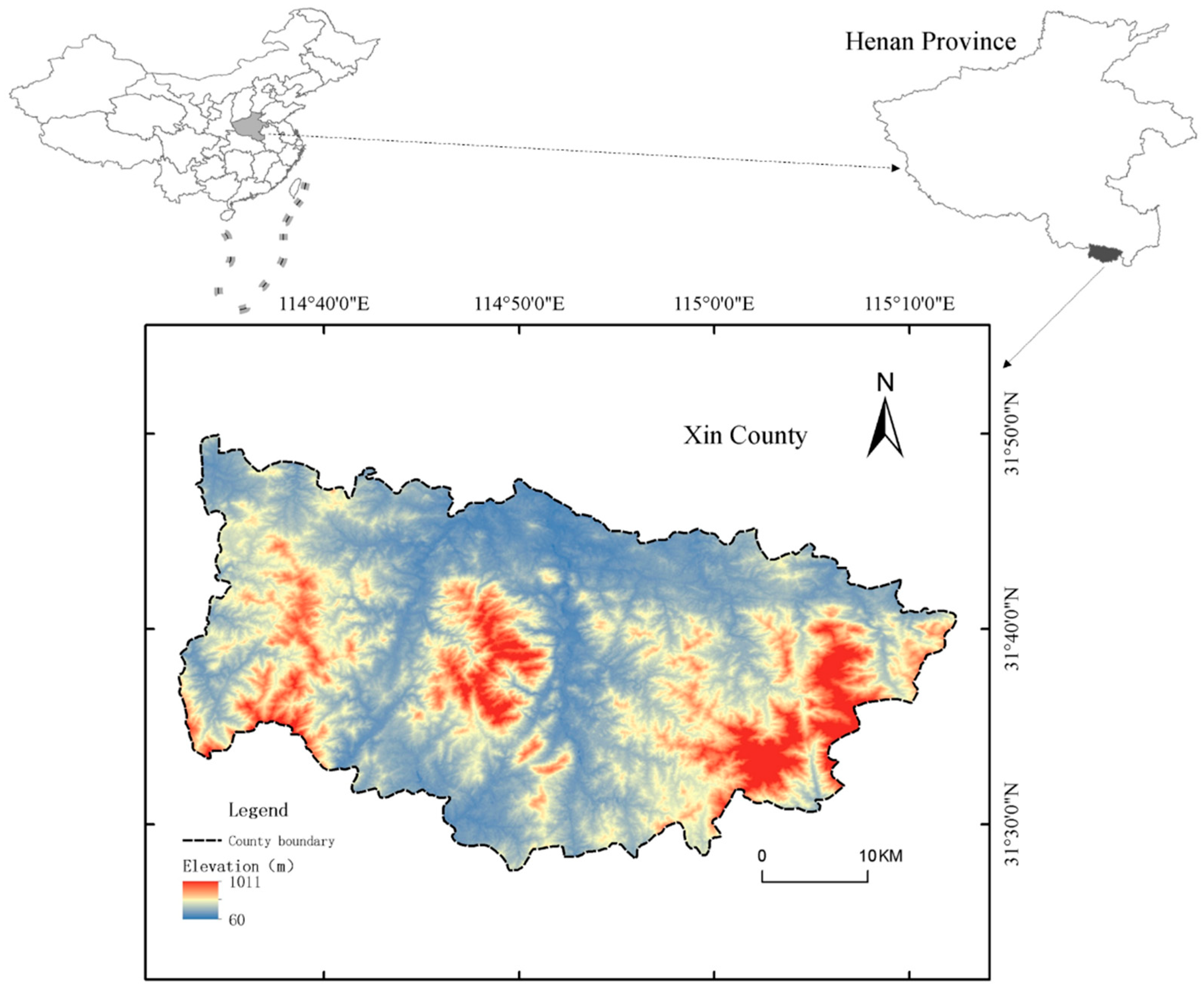


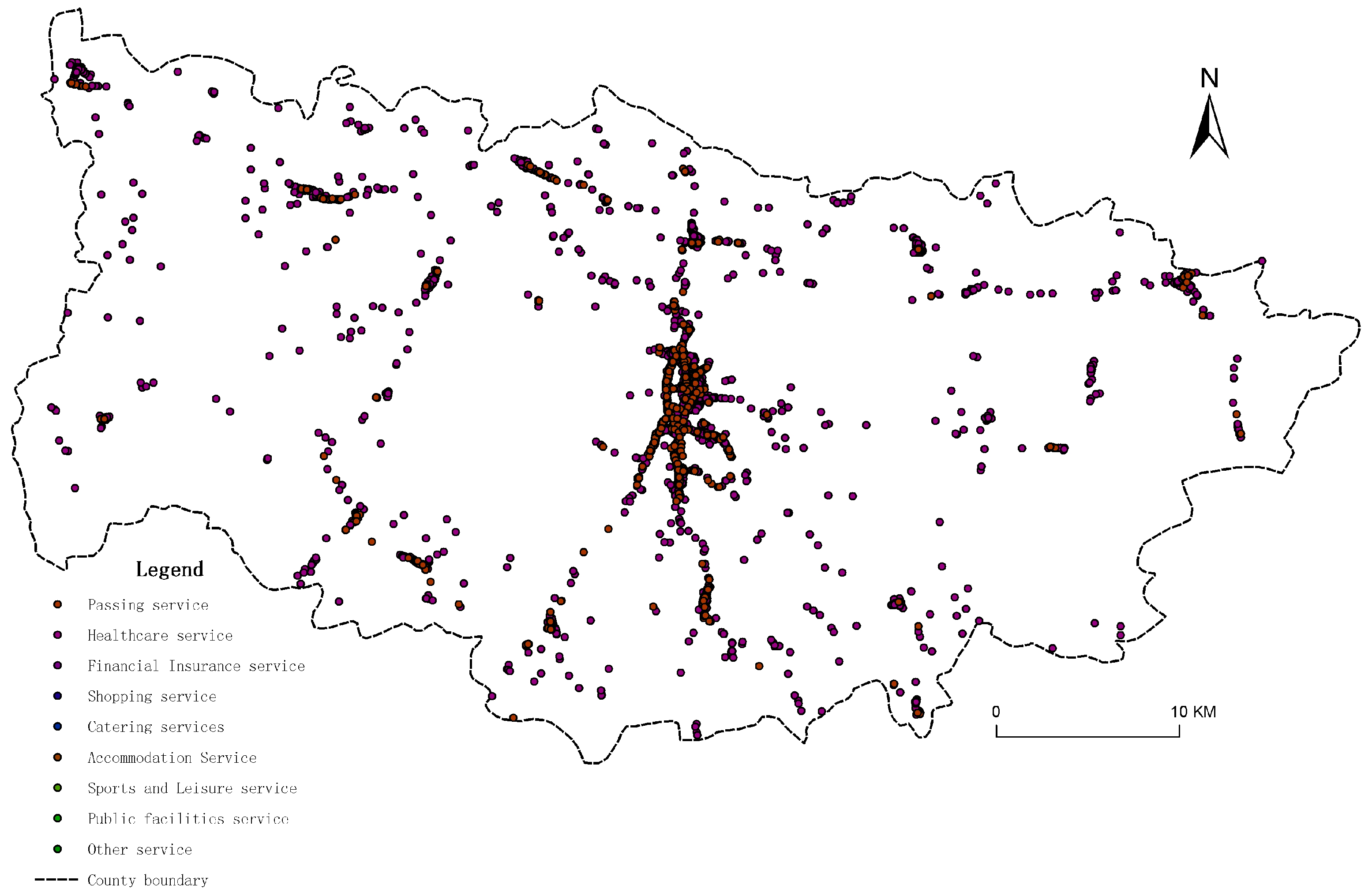


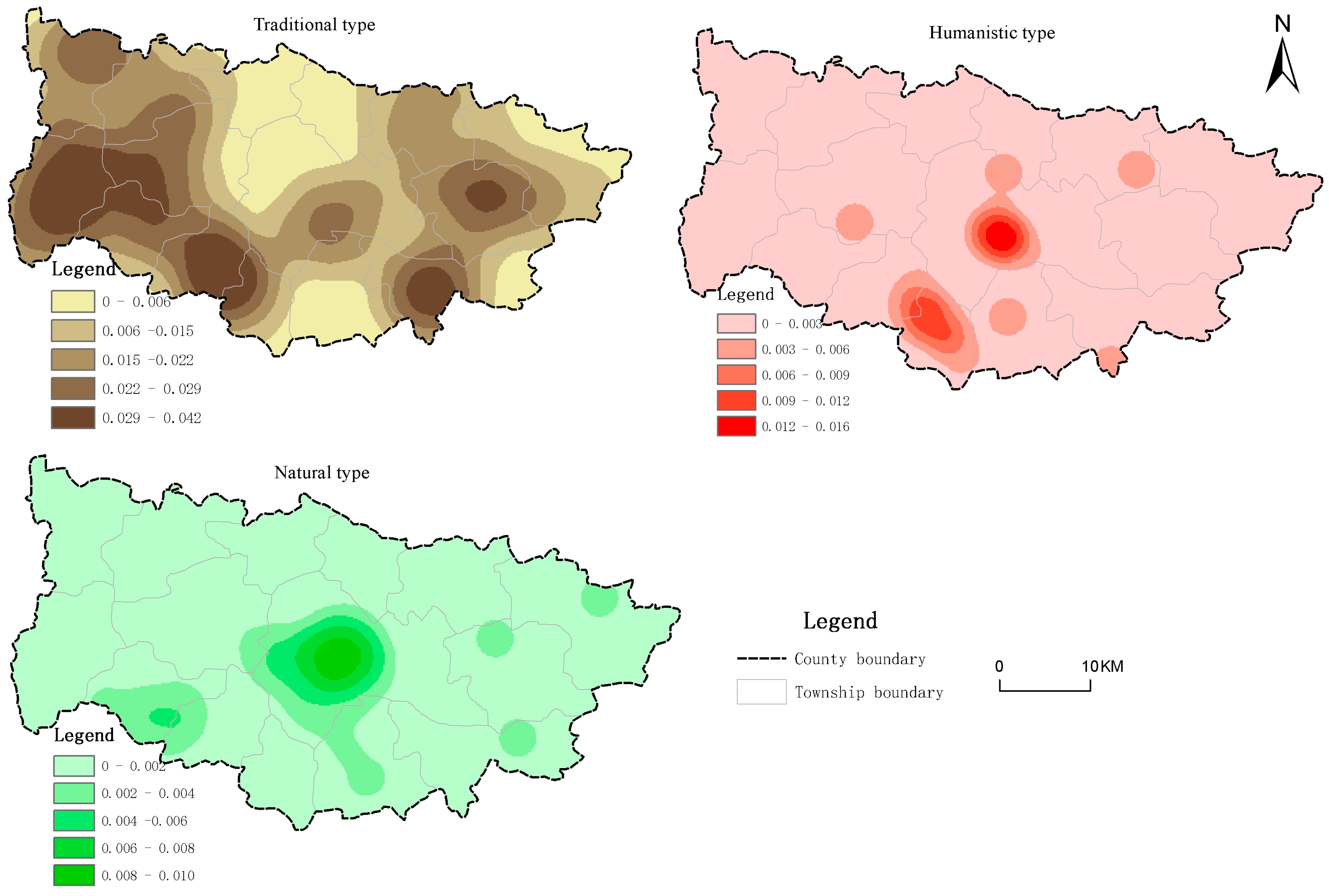


| Dataset | Data Content | Resolution | Data source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Geographic data | DEM and land-use remote sensing monitoring data | Grid | https://www.gscloud.cn/ |
| Management data | Administrative boundaries, national highways, and other spatial data | Spatial linear vector data | National Geomatics Center of China http://www.ngcc.cn |
| Statistical data | Urban and rural landscape statistical data | Statistical values | Local management and statistical departments |
| Network big data | POIs | Spatial point data | Baidu Map https://map.baidu.com |
| ID | Type | Subtype | Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Catering services (Cs) | Hotels, restaurants, restaurants, fast food restaurants, tea houses, farmhouse restaurants, and other catering-related services | 836 |
| 2 | Public facility services (PFs) | Public toilets | 287 |
| 3 | Shopping services (Ss) | Shopping malls, shopping malls, supermarkets, convenience stores, farmers markets, specialty stores, etc. | 2314 |
| 4 | Financial insurance service (FIs) | Banks, ATMs, postal savings, rural credit cooperatives, etc. | 85 |
| 5 | Sports and leisure services (SLs) | Leisure venues, sports venues, theaters, resorts and recuperation venues, entertainment venues, etc. | 127 |
| 6 | Passing services (Ps) | Railway stations, bus stations, parking lots, car rental and maintenance, motorcycle rental and maintenance, high-speed exits, high-speed entrances, gas stations, etc. | 379 |
| 7 | Healthcare services (Hs) | Hospitals, disease control centers, 120 emergency centers, health centers, clinics, pharmacies, etc. | 236 |
| 8 | Accommodation services (As) | Hotels, guesthouses, hostels, homestays, etc. | 227 |
| 9 | Other services (Os) | Beauty salons, telecommunication business halls, photography shops, logistics outlets, lottery sales, other life service departments, etc. | 665 |
| Functional Category | Classification | Type Characteristics | Type Explanation | Type Content | Type Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resource-oriented landscape | Humanistic type | Uniqueness, stability, non-renewability, etc. | Humanistic-type resources are highly dependent on historical figures and events and have uniqueness; they have long-term stability and cannot be replicated or regenerated. | Cultural landscape complex with red historical activities, red historical figures, red historical relics, and other resources as the main body | 14 |
| Natural type | Restrictiveness, centralization, compatibility, etc. | Natural-type resources generally have ecological characteristics and limitations in their utilization. They have a strong dependence on natural geographical conditions and are relatively concentrated in space. In terms of utilization, they have strong compatibility with other types of tourism resources. | Natural landscape resources mainly composed of geographical landscapes, water landscapes, etc. | 15 | |
| Traditional type | Potentiality, scarcity, adaptability, etc. | The internal and external value of traditional-type resources is constantly being explored and has potential. Antique tourism resources with certain regional characteristics are relatively scarce. The development of traditional villages requires protective transformation to be revitalized. | Traditional landscape resources mainly consisting of traditional villages, rural cultural and historical relics, rural buildings and facilities, etc. | 30 | |
| Service-oriented landscape | Service-oriented type | Universality, scalability, variability, etc. | Service-oriented type spaces are widely present in urban and rural landscape resource spaces, often on a large scale, and their utilization types change under certain conditions. | A functional space that provides services for tourism activities such as catering, public facilities, shopping, transportation, and medical care | 5156 |
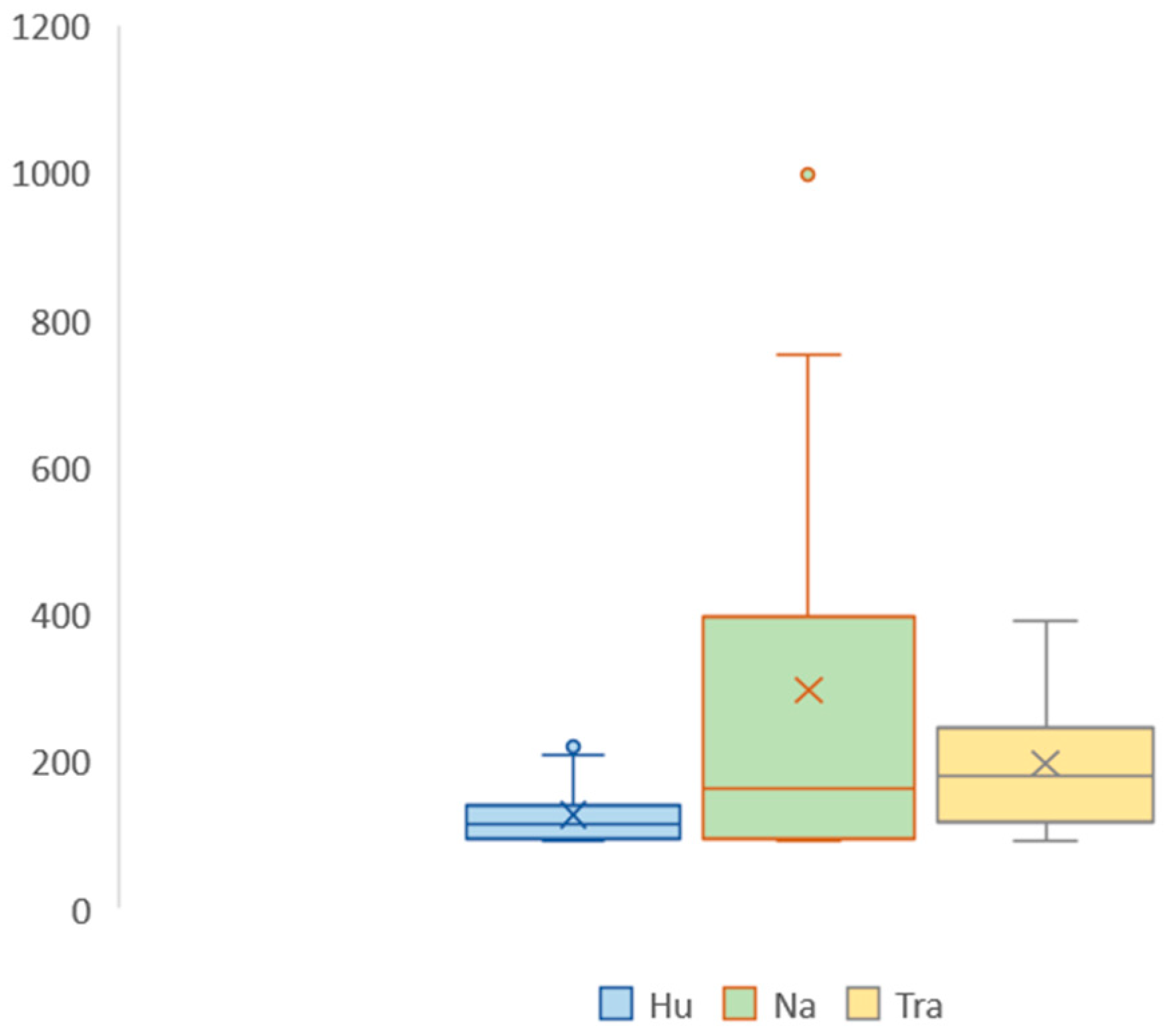
| Type | Samples | Average Nearest Neighbor Distance (m) | Expected Average Nearest Neighbor Distance (m) | Nearest Neighbor Index (NNI) | Distribution Pattern |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Humanistic resource-oriented | 14 | 4426.0287 | 3306.3901 | 1.338629 | Low dispersion type |
| Natural resource-oriented | 15 | 4882.9526 | 3545.49 | 1.377229 | Low dispersion type |
| Traditional resource-oriented | 30 | 3581.3006 | 3590.4654 | 0.997447 | Random type |
| Catering service type | 836 | 145.381692 | 705.024581 | 0.206208 | High concentration type |
| Public facility service type | 287 | 835.066928 | 1262.964413 | 0.661196 | Low agglomeration type |
| Shopping service type | 2314 | 56.416709 | 437.632926 | 0.128913 | High concentration type |
| Financial and insurance service type | 85 | 394.95815 | 2021.975651 | 0.195333 | High concentration type |
| Sports and leisure service type | 127 | 916.139887 | 1667.047208 | 0.549558 | Low agglomeration type |
| Passing service type | 379 | 224.770372 | 1071.408888 | 0.20979 | High concentration type |
| Healthcare service type | 236 | 481.798545 | 1262.775821 | 0.381539 | High concentration type |
| Accommodation service type | 227 | 358.531457 | 1214.831753 | 0.295128 | High concentration type |
| Other service type | 665 | 142.755136 | 769.672179 | 0.185475 | High concentration type |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Yang, Q. The Urban–Rural Integration of Resources and Services Using Big Data: A Multifunctional Landscape Perspective. Sustainability 2025, 17, 9934. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17229934
Wang Y, Wang B, Yang Q. The Urban–Rural Integration of Resources and Services Using Big Data: A Multifunctional Landscape Perspective. Sustainability. 2025; 17(22):9934. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17229934
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yayun, Baoshun Wang, and Qing Yang. 2025. "The Urban–Rural Integration of Resources and Services Using Big Data: A Multifunctional Landscape Perspective" Sustainability 17, no. 22: 9934. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17229934
APA StyleWang, Y., Wang, B., & Yang, Q. (2025). The Urban–Rural Integration of Resources and Services Using Big Data: A Multifunctional Landscape Perspective. Sustainability, 17(22), 9934. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17229934




