Abstract
Linear alkylbenzene sulfonates (LAS) are one of the organic pollutants of most concern in sewage sludge due to their widespread occurrence in domestic sewage. In this work, the occurrence of LAS was assessed in 15 wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs), with different sludge stabilization treatments, from September 2023 to March 2024. Samples were analyzed by ultrasound-assisted extraction and LC-MS/MS. In primary sludge, LAS homologues displayed the typical fingerprint of laundry detergents, suggesting these products are a primary source in influent wastewater. There was no clear correlation between the population served and the LAS concentrations in the studied WWTPs. The highest concentrations of LAS (sum of the homologues C10–C13) were found in anaerobic lagoons, followed by aerobically (6438 mg/kg) and anaerobically digested (5521 mg/kg) sludge. The lower levels were observed in composted sludge (215 mg/kg). 100% of the composted samples showed concentrations lower than 2600 mg/kg (concentration limit currently proposed by the EU for LAS), while these percentages were reduced to 25 and 13% in the case of aerobically and anaerobically digested sludges. These results showed that composting could be an effective method for ensuring compliance with a future EU Directive on sludge application to the soil.
1. Introduction
In recent years, 15 million tons of dried sludge were approximately produced per year in the European Union (EU) [1]. About 40% of the sludge is employed as nutrients and as a source of organic matter for agricultural purposes. However, there are different percentages in its application among the Member States of the EU [2]. The EU Directive on sewage sludge provides a regulatory framework to ensure its safe agricultural use, outlining baseline requirements for environmental and public health protection [3]. Prior to land application, sludge must undergo treatment to guarantee safety and facilitate more efficient handling and transport [4,5]. Nevertheless, the existing EU Directive [3] concerning the agricultural application of sewage sludge derived from domestic and urban wastewater does not establish limits for organic pollutant concentrations. In 2000, to tackle ongoing challenges in sludge management and reduce soil pollution, the EU released the third draft of a forthcoming Sludge Directive, known as the “Working Document on Sludge” [5]. This draft was a pivotal development, as it established for the first time limits of concentration for seven groups of organic compounds. Among the organic pollutants included in this Directive draft, linear alkylbenzene sulfonates (LAS), well known for their cleaning properties, are the ones that have generated major controversy. First, because there is no consensus between the different Member States about the limited value that should be fixed. For example, Denmark has limited LAS concentrations in sewage sludge to 1300 mg/kg dry matter (dm), and Portugal limits concentrations to 5000 mg/kg dm [6], while Belgium has concentrations limits of 1500 mg/kg dm [7]. The Working Document on Sludge [5] proposed 2600 mg/kg dm as a limit value, but the draft was withdrawn in 2006 [6]. Second, data on LAS concentrations in sewage sludges have been compiled for sludges produced by sewage treatment plants with anaerobic digestors, and these are generally higher than the proposed limit value [8]. Concentrations of LAS from approximately 1000 to 30,000 mg/kg dm have been reported in anaerobically digested sludge [8,9,10,11]. For example, Aparicio et al. [9] and Cantarero et al. [10] have reported concentrations of LAS of 4208 and 8060 mg/kg dm, respectively, in this sludge. LAS levels in sludges produced by treatment plants with aerobic digestors are generally lower (normally, LAS levels are ranged from 100 to 1000 mg/kg dm [9,12]). The potential biodegradation routes of these compounds have been described in wastewater treatment processes operating under both anaerobic and aerobic conditions [13,14,15,16]. While in aerobic conditions the biodegradation of LAS occurs via the ω-oxidation pathway (alkanes > alcohol > aldehydes > carboxylic acids) followed by the β-oxidation of the formed carboxylic acid [15], the biodegradation under anaerobic conditions implies the fumarate addition to the alkyl chain, ring cleavage, β-oxidation reactions, and desulfonation [14,16]. These different degradation route coulds explain the differences in the measured concentrations in sludge from aerobic and anarobic treatments throughout the slowest biodegradation under the latter conditions. However, these studies have been carried out in wastewater treatments, while the data of these compounds in different sludge treatments are scarce, especially in sludge stabilization treatments based on aerobic digestion of sludge and in other types of sewage treatment such as dehydration plants, lagoons, and composting facilities [9,17]. Moreover, the influence of other environmental factors has been evaluated. Among them, water hardness seems to be a fundamental factor [18,19,20] in controlling the cation-bridging of Ca-LAS in aqueous solution [21], which decreases the water solubility of LAS at calcium concentrations above 0.01 g/L, influences surfactant micelle formation, and lowers the critical micelle concentration. Calcium concentrations exceeding 0.1 g/L led to rapid precipitation, resulting in the formation of sparingly soluble CaLAS2·2H2O. These processes are likely to increase LAS binding to sludge. Consequently, water hardness is a driver for LAS concentration in sewage sludge.
The main objective of this work is to establish the distribution of LAS in fresh sludge from different sludge stabilization treatments and different regions, understand their occurrence under different sludge treatment conditions, their concentrations in the final product, and the type of sludge treatment technology most suitable for their reduction to comply with a future regulation to safely apply sludge as an organic amendment.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
The chemicals and reagents used in this work are described in detail, along with their sources, in the Supplementary Materials. Working solutions were obtained by diluting a stock standard solution (4000 mg/L, LAS mixture) using a methanol:H2O mixture (1:1, v/v).
2.2. Sewage Sludge Treatment Plants and Monitoring Program
The distribution of LAS was evaluated in sludge treated with different stabilization technologies. A total of 15 wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) located in the Andalusia region (South of Spain) were studied. Wastewater treatments were based on activated sludge treatment in all studied wastewater. The sludge stabilization technologies were (i) anaerobic digestion of sludge, in four anaerobic treatment plants (AnTPs); (ii) aerobic digestion of sludge, in four aerobic treatment plants (AeTPs); (iii) dehydration, in three dehydration treatment plants (DTPs); (iv) anaerobic wastewater stabilization ponds, in three anaerobic stabilization ponds (AnWSPs) sited in the small rural towns; and (v) Composting, in a composting plant (CP1). The characteristics of the sludge treatments studied are shown in Table S1 in Supplementary Materials.
Various sludge categories were included in the monitoring process, encompassing primary and secondary sludge, as well as anaerobically treated and dehydrated variants—three of which originated from AnTPs. Additionally, mixed sludge (a blend of primary and secondary), aerobically digested and dehydrated sludge (from AeTPs), mixed and dehydrated sludge (from DTPs), lagoon sludge (sourced from AnWSPs), and compost (from CP) were analyzed.
Sampling was conducted during two distinct campaigns, one in September 2023 and another in March 2024, adhering to protocols established by the United States Environmental Protection Agency [22]. The locations for each sludge type are detailed in Figure 1. Grab samples of primary, secondary, mixed, and digested sludge were collected adjacent to the stabilization treatment units at each site. For compost, composite samples were created by combining subsamples from a minimum of five locations within the composting matrix, taken at a depth of approximately 30 cm. Lagoon sludge samples were similarly composited from four distinct points at the base of each AnWSP. In total, two liters of primary, secondary, mixed, and lagoon sludge, along with one kilogram of digested/dehydrated sludge and compost, were gathered using glass containers. Upon arrival at the laboratory, all samples were freeze-dried using a Cryodos-50 lyophilizer (Telstar, Terrassa, Spain), passed through a sieve (<1 mm particle size), and stored at −30 °C until further analysis.
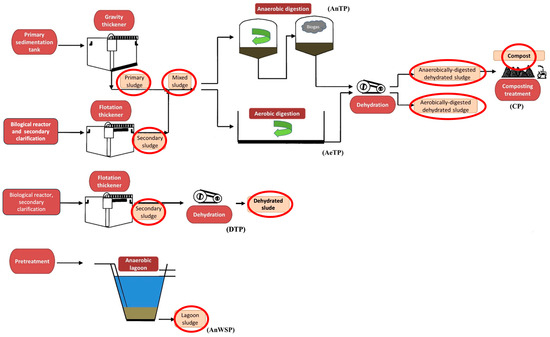
Figure 1.
Diagram of sludge treatments in the treatment plants studied and location of the sampling points (marked in red).
2.3. LAS Determination
The analysis of LAS homologues was carried out by ultrasound-assisted extraction and dispersive solid-phase extraction in a single step and determination by liquid chromatography tandem-mass spectrometry according to Martín et al. (2024) [23]. LAS homologues were analyzed by using multiple reaction monitoring mode. MS/MS parameters for each compound can be seen in Table S2 in Supplementary Materials. Quality assurance and quality control are described in detail in Supplementary Materials. A summary including recoveries and method detection, and quantification limits of target compounds are summarized in Table S3 in Supplementary Materials.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Dynamic of LAS in Sludge Stabilization Processes
The concentrations of LAS homologues in studied sludge stabilization processes are shown in Table S4. A summary of the concentrations measured in each sludge type are shown in Table 1. The highest concentrations were measured in AnWSPs, followed by AeTPs, AnTPs, DTPs, and CP, in that order. These concentrations vary from one treatment to the next and according to the type of sludge in each sludge stabilization process. There was not a clear relation between the served population and the concentrations of LAS measured in the studied WWTPs. These concentrations seem to be strongly influenced by the quality of the raw water as well as the treatment applied for sludge stabilization. The highest concentrations were measured in the case of sludge collected in small rural towns where lagoon stabilization ponds are used for wastewater treatment. However, except in the case of AeTP1, the concentrations measured in sludge from largest cities (AnTP2, AnTP3 and AnTP4) were higher than those measured in small cities as DTP2, DTP1 or DTP3.

Table 1.
Concentrations of LAS measured in studied sludge stabilization treatments.
The influence of water hardness was also analyzed. Table 2 shows a summary of the water hardness measured in the studied WWTPs. The water hardness measured in each of the studied WWTP can be found in the Supplementary Materials (Table S5).

Table 2.
Water hardness measured in the studied WWTPs.
In this work we have not found a correlation between LAS concentration levels measured in primary sludge and hardness (R2 = 0.007). In most cases influent water would be classified as very hard or hard using US Geological Survey and World Health Organization [24] criteria. These results align with the findings of Jensen et al. (2007) [25], who classified the distribution of water hardness in Spain by the percentage of the population as follows: 50% as hard water, 28% as medium, and 21% as soft. The median in Spain was 294 mg/L CaCO3. Note that authors used the following hardness definitions: soft: 0–70 mg/L CaCO3; medium: 70–212 mg/L CaCO3, hard: >212 mg/L CaCO3.
A high variability was found in the LAS measured WWTPs (the relative standard deviations of the concentrations ranged from lower than 14% for sludges from CP and AnWSPs to 48% and 146% for mixed sludges from AeTPs and DTPs, respectively), with a noteworthy influence from their original load, making it difficult to establish correlations with the hardness and even between and within technologies. There is not enough data for firm conclusions regarding the factors responsible for these variations in relative levels of LAS homologues in sludge samples. Possible factors include (1) relative levels in raw sewage, reflecting the distribution in commercial products (e.g., OECD SIDS assessment [26]); (2) binding affinity [20] and biodegradation rate [27]—both increase with alkyl chain length; and (3) extensive biodegradation during activated sludge treatment as well as possible biodegradation in raw sewage and aerobic sludge digestion [8].
3.1.1. Anaerobic Treatment Plants
The results of LAS in the sludge samples of the four AnTPs are presented in Table S4 in Supplementary Materials. Primary sludge is the result of the settling of suspended solids from wastewater during primary treatment. In all analyzed samples, homologues C10–C13 were quantified. The ΣLAS (sum of C10–C13 homologues) in primary sludge ranged from 3156 mg/kg dm in AnTP3 to 8878 mg/kg dm in AnTP1. During the initial phase of wastewater treatment, approximately 15–25% or more of LAS compounds are eliminated through adsorption onto suspended solids, primarily driven by hydrophobic interactions. Additionally, LAS may precipitate as insoluble magnesium or calcium salts, which are subsequently removed in the primary sedimentation stage [8,19,28].
Overall, in all plants except AnTP2, the concentration levels for the ΣLAS in primary sludge measured in September were slightly higher than those found in March. This fact could be explained by the decrease in the flow rates during the summer months and, consequently, with a reduced dilution of wastewater discharges. Additionally, it is possible that the usage of LAS may be higher in September compared to March due to increased water consumption during the warmer months. However, there is no significant difference between the mean values of both months (student paired t-test: tcal = 1.88, ttab = 3.18; p > 0.05).
Total LAS concentration levels in primary sludge from the AnTP2, AnTP3, and AnTP4 were comparable to LAS levels previously determined in four AnTPs in Seville, as reported in Aparicio et al. (2009) [9]. The concentration levels measured in AnTP1 on both sampling dates were almost twice as high as those in the rest of AnTPs. This can be explained by the discharges from industries, mainly involved in olive processing, located in nearby towns whose wastewater is treated at this WWTP, in addition to the large population it serves (21 municipalities within the area).
Secondary sludges primarily consist of microbial biomass produced during the activated sludge treatment process (Figure 1). In secondary sludges, a significant decrease in LAS concentration is noted (almost 96% less). It could be explained considering the adsorption of target compounds onto settled solids during pre- and primary treatments, and the biodegradation by microorganisms in secondary (activated sludge) treatment. The ΣLAS ranges from 49 mg/kg dm to 468 mg/kg dm in AnTP2.
After the sludge treatment by anaerobic digestion, a concentration effect is observed; the ΣLAS ranged from 2487 mg/kg dm in AnTP4 to 12,161 mg/kg dm in AnTP1. The concentration levels detected in this type of sludge are comparable to those observed in primary sludge and may even exceed them in certain instances. Previous studies suggest that LAS undergoes decomposition in anaerobic bioreactors (using digestor sludge as the microbial inoculum) where LAS is the sole/main carbon source [16,29]. This poor degradation of LAS in anaerobic conditions has been previously reported [9,10,13,25]. The degradation of LAS under anaerobic conditions implies the fumarate addition to the alkyl chain, ring cleavage, β-oxidation reactions, and desulfonation [14]. Several studies have been focused on the evaluation of the factor affecting the degradation of LAS under anaerobic conditions as hydraulic retention time or the application of co-substrates. These studies showed that the addition of co-substrates as electron acceptors that favour their oxidation could strongly affect to the degradation of LAS under these conditions [13]. As a consequence, the absence of electron acceptors substances in anaerobic sludge stabilization reactors could delay the degradation of these compounds. This fact, together with the loss of weight and organic matter during the anaerobic digestion and dehydration process, could explain the concentrations of LAS in anaerobically digested and dehydrated sludge, comparable to those in primary sludge. Previous studies have also reported similar findings [9,10,13,25,30]. In Figure 2 the distribution of LAS homologues along anaerobic digestion is plotted as boxplots. Each box shows the lower percentile (≤5%), median (≤50%), upper percentile (≤95%) and means concentrations. Maximum and minimum values are represented by the whiskers.
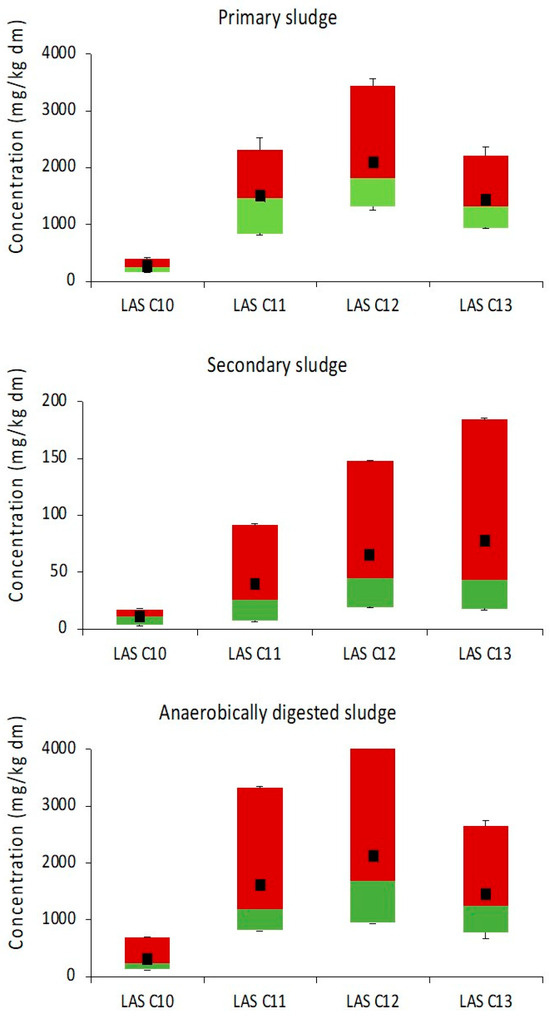
Figure 2.
LAS homologues distribution in AnTPs. Each box shows the lower percentile (≤5%), median (≤50%), upper percentile (≤95%), and mean concentrations. Maximum and minimum values are represented by the whiskers.
In primary sludge, LAS homologues present the typical fingerprint of laundry detergents (C10:C11:C12:C13/5:28:39:27), which could indicate the use of detergents as the main source of these compounds to the influent wastewater. In European laundry detergents, the homologous composition of LAS typically includes C10 at 10–15%, C11 and C12 each ranging from 25 to 35%, and C13 between 15 and 30% [24,26]. The C10 homologue was found at the lowest concentration levels in the analyzed sludge samples, consistent with its lower abundance in commercial LAS products. LAS C12 was the most prevalent homologue in primary sludge, followed by C11 and C13, respectively. The LAS C10 content (5%) was lower and the LAS C12 content (39%) higher than expected based on commercial laundry products, likely due to higher LAS partitioning to sludge with increasing carbon chain length. Lower LAS C13 in primary sludge show enhanced biodegradation, likely in sewer pipes [8]. According to Temmink and Klapwijk (2004) [31], who conducted a detailed assessment of the fate of LAS C12 in activated sludge plants, sorption is an extremely fast and reversible process, and primary biodegradation increase when the sludge is loaded with higher influent concentrations.
In secondary and digested sludge, the distribution profile of homologues is influenced by microbial biodegradation during activated sludge treatment. In the secondary sludge, LAS C13 was predominant, followed by LAS C12, LAS C11, and LAS C10, respectively. Higher LAS C13 in secondary sludge indicates sorption as driver of homologue distribution. Similarly, previous studies indicate the relationship between sorption rates to sludges and the length of the chain, with higher chain length homologues having higher sorption rates to sludges due to their higher hydrophobicity [19,32]. The pattern observed in digested sludge is similar to those observed in primary sludge due to its higher concentration levels in comparison to secondary levels (which make up 1% of the total). However, results indicate that there is no significant difference between the mean values of LAS C11, C12, and C13 in the three types of sludge (student paired t-test: tcal = 1.93 in primary sludge, tcal = 1.40 in secondary sludge, and tcal = 1.40 in digested sludge ttab = 2.14; p > 0.05).
The concentrations of LAS are similar to those values reported in earlier works. For example, mean concentrations of LAS (sum of C10, C11, C12, and C13 homologues) of 1549, 275, and 4208 mg/kg dm were reported in Seville twenty years ago for primary, secondary, and anaerobically digested dehydrated sludge samples, respectively [9]. Values in anaerobically digested sludge are comparable to the calculated European-wide mean value, 5600 mg/kg dm, and well within 95% confidence range of 0.49 to 15.07 g/kg dm [8]. In Madrid, the average concentration of LAS found in anaerobic sewage sludge samples was 8060 mg/kg, higher than the average values for European sludge [10]. The highest ∑LAS concentration measured in this work in AnTP1 (12,161 mg/kg dm) is well below the highest value (ca. 30,000 mg/kg dm) previously found in Alicante, Spain [18]. It should be noted, however, that the WWTP with this exceptionally high LAS concentration was reported to have very high water hardness (>500 mg/L as CaCO3), higher than the water hardness in any of the WWTPs surveyed in the present study.
3.1.2. Aerobic Treatment Plants
The results of LAS in the sludge samples of the four AeTPs are presented in Table S4 in Supplementary Materials. The LAS homologue and total concentrations in mixed sludge are expected to have average values between primary and secondary sludges as mixed sludges are composed of both primary and secondary sludges. Mixed sludges present concentrations of LAS ranging from 3147 mg/kg dm in AeTP3 to 11,727 mg/kg dm in AeTP1. It is noteworthy that significant differences in LAS concentrations in mixed sludges were found between AeTPs, (student t-test: tcal = 7.89, ttab = 2.45; p < 0.05). For instance, in AeTP1 and AeTP2 the ΣLAS exceeded 10,000 mg/kg dm, whereas in AeTP3 and AeTP4, the concentrations averaged around 5000 mg/kg dm. This difference likely represents differences in LAS concentrations in sewage influent, which range from 1 to 15 mg/L [8].
LAS levels in aerobically digested sludge from all four sampled WWTPs are higher than European-wide monitoring data, which indicates LAS concentrations <500 mg/kg dm in aerobically digested sludge [8]. Moreover, a high variability was observed in the reduction in the LAS concentration from one AeTP to the next. While AeTP1’s LAS concentration was not reduced, a slight reduction was observed in AeTP2 and 3 (16 and 15%, respectively), and a high reduction was observed in the AeTP4 (mean 67%). This could be due to process limitations or operational differences among plants. Based on the findings compiled by Jensen et al. (2007) [25], LAS concentrations tend to be significantly higher in sludge subjected to anaerobic digestion, with reported levels ranging from 3000 to 30,000 mg/kg dm. In contrast, aerobically digested sludge typically contains lower amounts (100–500 mg/kg dm), while untreated sludge shows intermediate values (400–14,000 mg/kg dm). Cantarero et al. (2012) [10] further observed that the average LAS content in aerobically digested sludge is approximately 1270 mg/kg, which remains below the concentrations identified in the present study. These authors emphasized that the type of biological treatment (whether aerobic or anaerobic) can markedly affect LAS retention, leading to notable differences in concentration. Additionally, the presence of hard water, particularly in southern Spain, may contribute to the formation of poorly soluble LAS salts with calcium and magnesium, thereby hindering biodegradation even under aerobic conditions. According to Cantarero et al. (2012) [10], the highest LAS levels in Spain have been recorded in regions with elevated water hardness, whereas the lowest concentrations are typically found in areas with soft water.
In Figure 3 the distribution of LAS homologues along aerobic digestion is plotted as boxplots. The LAS homologue abundance in mixed and aerobically digested sludge was C12 ≈ C13 > C11 > C10. The pattern observed for homologues in mixed sludges is slightly different than those observed in primary sludge from AnTPs, which could be explained by the influence of the activated sludge process in mixed sludges.
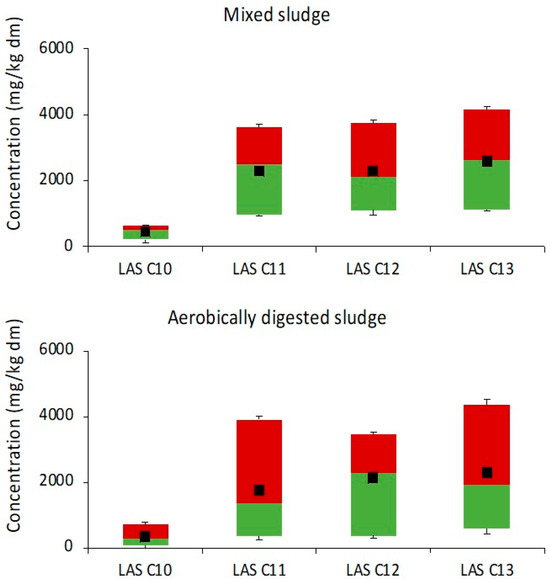
Figure 3.
LAS homologues distribution during aerobic digestion. Each box shows the lower percentile (≤5%), median (≤50%), upper percentile (≤95%), and means concentrations. Maximum and minimum values are represented by the whiskers.
3.1.3. Dehydration Treatment Plant
The results of LAS in the analyzed DTP samples are presented in Table S4. In DTPs, the moisture content in the sludge produced by WWTPs is decreased without undergoing a biological digestion process. This approach is commonly used in facilities where a significant decrease in organic load is not required or where further stabilization of the sludge beyond the secondary treatment is unnecessary.
The mixed sludges analyzed from DTPs consist of secondary sludge produced during the biological phase of wastewater treatment. These facilities typically lack a primary treatment stage, primarily due to the low content of suspended solids and floatable matter in the incoming wastewater, or because the influent has already undergone preliminary processes that effectively remove most of these particulates.
The results obtained indicate that the LAS concentrations are appreciably lower compared to those of the other treatments discussed previously. This fact can be explained by the origin of this sludge, which derives from the secondary decanter and is subsequently recirculated back into the biological reactor to sustain the necessary quantity of active sludge. Consequently, these sludges primarily consist of microbial biomass produced during the depuration process. In the case of the secondary sludges collected from DTP, the ΣLAS ranges from 85 mg/kg dm in DTP1 to 1117 mg/kg dm in DTP3. DTP3 experienced a peak in LAS load in March compared to September, likely explained by a specific discharge during that time. However, there is no significant difference between the mean LAS concentration values of both months in DTPs (student paired t-test: tcal = 1.18, ttab = 4.30; p > 0.05).
In dehydrated sludges, the ΣLAS ranges from 203 mg/kg dm to 542 mg/kg dm in DTP3 in September and March, respectively. Sludge dehydration proves to be an ineffective method for eliminating LAS. Instead, it has the opposite effect and leads to a further concentration of the compound as the initial water content in the sludges is reduced. This effect is particularly pronounced in DTP1, where the presence of LAS homologues is up to four times higher in dehydrated sludge than in mixed sludge. Since these sludges are not subjected to any type of digestion, their composition depends largely on the characteristics of the secondary sludge.
In Figure 4 the distribution of LAS homologues in DTPs is plotted as boxplots. Note that the highest value measured in the mixed sludges of DTP3 during the month of March was not considered. The LAS homologue abundance in secondary and dehydrated sludge was similar: C12 > C13 ≈ C11 > C10. As happened in secondary sludges from AnTPs and mixed sludges from AeTPs, the pattern observed could be indicative of the influence of the activated sludge process. Higher concentrations of the homologues are generally observed with the increasing alkyl chain length. This observation is consistent with the increased rate of binding with increasing chain length.
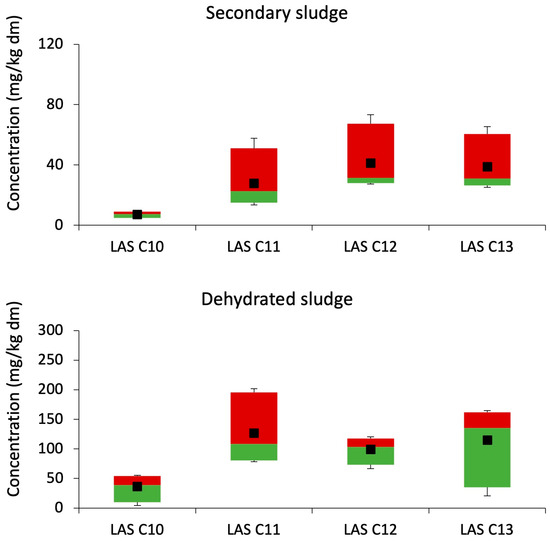
Figure 4.
LAS homologues distribution during dehydration. Each box shows the lower percentile (≤5%), median (≤50%), upper percentile (≤95%), and mean concentrations. Maximum and minimum values are represented by the whiskers.
3.1.4. Anaerobic Stabilization Pond Treatments
Wastewater treatment through anaerobic stabilization ponds is designed to treat wastewater through interaction with biomass. These ponds are constructed at shallow depths (2 to 4 m) with relatively long retention periods (usually several months). In anaerobic ponds, microorganisms break down organic matter in the absence of oxygen. Suspended particles and organic matter settle at the bottom of the pond and are decomposed by anaerobic microorganisms present.
The AnWSPs are the most common wastewater treatments applied in small communities with equivalent inhabitants in the range up to 10,000. The AnWSPs were located in small rural towns of Andalusia (South of Spain). The results of LAS in the analyzed samples are presented in Table S4 in Supplementary Materials.
The ΣLAS in the three studied treatment plants range from 10,332 mg/kg dm in AnSWP2 to 14,619 mg/kg dm in AnSWP3. The concentration levels measured in this type of sludge were the highest among all types, which is expected given that processes conducted in the absence of oxygen are inefficient in degrading these compounds. LAS concentration likely increases throughout the solid retention time of the treatment, as initially most of the LAS will be adsorbed to suspended particles and organic matter present in the wastewater. During the long retention time, particulates and organic matter that are not biodegraded undergo precipitation and accumulation in the sludge deposited at the bottom of the lagoon [33].
In Figure 5 the distribution of LAS homologues in lagoon sludge is plotted as boxplots. A different profile was found in this type of sludge. As for C10, it is found in much lower proportions, consistent with observations in all samples from other treatments, suggesting its relative sorption rates. The presence of LAS C13 in all samples is much higher compared to the other homologues, nearly double that of the C11 and C12 homologues. These two homologues are consistently present in all cases with very similar concentrations. This fact can be explained by the relationship between sorption rates to sludges and the length of the chain, with lower chain length homologues having lower sorption rates to sludges. The levels in lagoon sludge indicated very low (nil) LAS biodegradation.
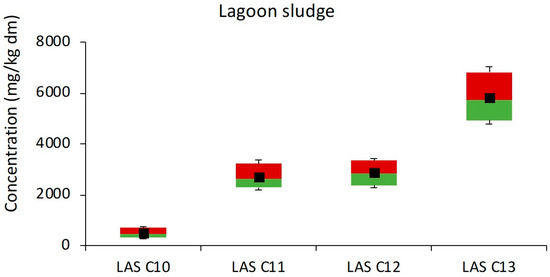
Figure 5.
LAS homologues distribution in lagoon sludge. Each box shows the lower percentile (≤5%), median (≤50%), upper percentile (≤95%) and means concentrations. Maximum and minimum values are represented by the whiskers.
3.1.5. Composting
Composting was performed in thermally regulated, dynamic full-scale batteries. Peak temperatures, ranging from 40 to 49 °C, were observed during the initial fermentation phase. Mechanical turning ensured adequate aeration by regularly mixing and loosening the material, which prevented compaction and promoted oxygen diffusion. The biosolid piles underwent composting for a duration of 4 to 5 months. This type of stabilization treatment involves the controlled biological decomposition of organic matter present in the sludge, providing oxygen to aerobic microorganisms throughout the composting process, which are responsible for degrading and eliminating this matter. Composting platforms allow production of sludges with homogeneous quality that are stabilized and, most of the time, also sanitized.
Composting resulted the most effective method in the LAS reduction from sludge. The ΣLAS was generally less than 236 mg/kg dm (Table S4). During the composting process sludge is exposed to the sunlight and undergoes periodic mechanical rotation. This treatment method entails a highly aerated process, facilitating efficient degradation of the compound by aerobic bacteria. LAS degradation commences through Ω-oxidation, targeting the terminal methyl group and facilitating subsequent b-oxidation steps. In the following phase, the sulfonate moiety is removed, initiating aromatic ring cleavage and resulting in the formation of carbon dioxide, water, sulfate ions, and microbial biomass [14,34,35].
In Figure 6 the distribution of LAS homologues in compost samples is plotted as boxplots. LAS C13 was found to be the most abundant homologue, followed by C12, C11, and C10, respectively. The pattern indicates that the homologue distribution of the residual levels in compost is driven by relative sorption rates.
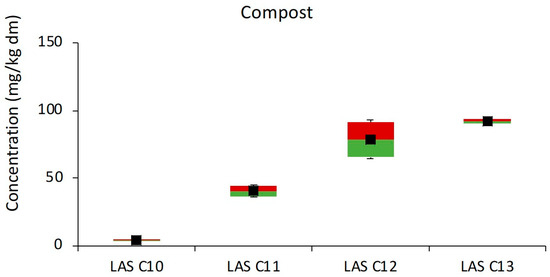
Figure 6.
LAS homologues distribution in compost. Each box shows the lower percentile (≤5%), median (≤50%), upper percentile (≤95%), and means concentrations. Maximum and minimum values are represented by the whiskers.
3.2. Implications of the EU Directive
The application of sewage sludge onto the soil is a usual practice in the EU. Particularly, in Spain, 84% of the sludges generated in 2017 and 2018 were applied to the soil, and this reuse is even more pronounced in Andalusia (South of Spain) [1].
Directive 86/278/EEC, established by the EU to safeguard environmental quality—particularly soil health—during the agricultural use of sewage sludge [3], was originally designed to encourage its application while preventing adverse effects on ecosystems, human health, and animal welfare. However, the Directive has become outdated and is currently undergoing a revision process to better align with contemporary environmental standards [36,37]. Notably, the third draft of the revision, released in 2000, introduced more stringent thresholds for heavy metals and, for the first time, proposed concentration limits for organic contaminants in sludge. As of now, the Directive remains under review, with potential inclusion of cut-off values for selected organic compounds under consideration.
Regarding LAS, the homologues C10–C13 are the most relevant compounds in detergents and laundry formulations. For these compounds, the 3rd draft of the working document on sludge [5] proposed a concentration limit value of 2600 mg/kg on sludge applied to the soil.
Considering the concentrations measured in this work (Figure 7), the highest concentration levels were found in the anaerobic lagoons, followed by the anaerobically digested sludges and the aerobically digested sludges, and with a lesser contribution in the dehydrated sludges and the composted sludges. Around 88%, 75%, and 100% of the sludge samples digested anaerobically, aerobically, and in anaerobic tanks, respectively, exceeded the limit of 2600 mg/kg dm established in the working paper, while none of the samples of dehydrated and composted sludge exceeded this limit. Nevertheless, DTP proves to be an ineffective method for LAS degradation while composting resulted the most effective method.
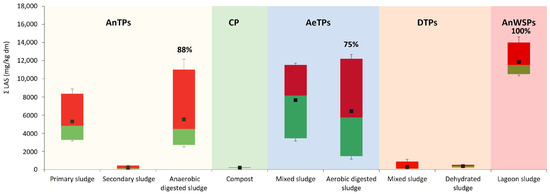
Figure 7.
Concentration levels of LAS in sludge stabilization processes. Each box shows the lower percentile (≤5%), median (≤50%), upper percentile (≤95%), and mean concentrations. Maximum and minimum values are represented by the whiskers. The red line shows the limit value proposed for the LAS concentrations by the 3rd draft of the working document on sludge. In bold is the percentage of samples exceeding the proposed value.
4. Conclusions
The distribution of LAS homologues alongside different sludge stabilization treatments, including anaerobic and aerobic digestion, dehydration, composting, and anaerobic wastewater stabilization ponds, has been evaluated. The highest concentrations of LAS were observed in anaerobic lagoons, followed by anaerobically digested sludges and aerobically digested sludges, with lesser contributions from dehydrated and composted sludges. There was no clear relationship between the served population and the concentrations of LAS measured in the studied WWTPs. A high variability was found in the measured concentrations among WWTPs, making it difficult to establish correlations with hardness and even between different treatment technologies.
In primary sludge, LAS homologues present the typical fingerprint of laundry detergents (C10:C11:C12:C13/5:28:39:27), which could indicate the use of these products as the main source of these compounds to the influent wastewater. The C10 homologue was found at the lowest concentration levels in all types of sludge samples, consistent with its lower abundance in commercial products. Long-chain LAS are preferentially adsorbed onto the sludge due to their greater hydrophobic character as well as their precipitation as insoluble Mg/Ca-salts. In secondary and digested sludge, the distribution profile of homologues is also influenced by microbial biodegradation during activated sludge treatment. In lagoon sludge, compost and secondary sludge, LAS C13 was predominant, followed by LAS C12, LAS C11, and LAS C10, respectively. This fact indicates sorption as main driver of homologue distribution, with longer-chain LAS preferentially adsorbed due to their higher hydrophobicity.
At the European Union level, the Sewage Sludge Directive outlines a regulatory framework to ensure the safe application of sludge in agriculture, defining baseline criteria for safeguarding both environmental and human health. However, requirements vary across Member States, and further environmental assessment at the EU concentrations limit of LAS in sludge would be needed to establish whether these concentrations led to unequal environmental and health protection across the EU. In this base, further research on land application of sewage sludge is required to ensure safe use and optimize efficient transport and recovery of nutrients, as well as to determine the more effective technology for the disposal of these contaminants. Regardless, the results obtained in this work showed that the application of a composting post-treatment process to sludge mitigates the concentration levels of organic compounds like LAS and would be an effective method for ensuring that LAS levels in sludge do not exceed the limit of 2600 mg/kg dm in the EC working paper. In addition, composting allows production of sludges with homogeneous quality, that are stabilized and most of the time also sanitized. Furthermore, composting plants such as CP1 have the capacity to treat sludge from the entire province as well as surrounding areas.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/su172210034/s1. Table S1: Characteristics of the studied sludge stabilization plants; Table S2: MS/MS parameters.; Table S3: Validation parameters.; Table S4: Concentrations of LAS C10-C13 in studied sludge stabilization processes.; Table S5: Water hardness for all of the WWTPs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.M.; methodology, J.L.S.; validation, I.A.; formal analysis, C.M.; investigation, N.G.-C.; resources, N.G.-C.; data curation, J.L.S.; writing—original draft preparation, C.M.; writing—review and editing, J.H., E.A., I.A., J.L.S., and J.M.; visualization, C.M.; supervision, J.L.S.; project administration, E.A.; funding acquisition, J.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Council for LAB/LAS Environmental Research (CLER).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
Authors acknowledge the oversight by Victoria Ochoa of Moeve. N.G.C. gratefully thanks the Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación (MICIU/AEI/10.13039/501100011033) for her predoctoral contract (PRE2021-100799).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AeTPs | Aerobic treatment plants |
| AnTPs | Anaerobic treatment plants |
| AnWSPs | Anaerobic wastewater stabilization ponds |
| CPs | Composting plants |
| dm | Dry matter |
| DTPs | Dehydration treatment plants |
| LAS | Linear alkylbenzene sulfonates |
| WWTPs | Wastewater treatment plants |
References
- Mejías, C.; Martín, J.; Santos, J.L.; Aparicio, I.; Alonso, E. Occurrence of pharmaceuticals and their metabolites in sewage sludge and soil: A review on their distribution and environmental risk assessment. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 30, e00125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fijalkowski, K.; Rorat, A.; Grobelak, A.; Kacprzak, M.J. The presence of contaminations in sewage sludge: The current situation. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 203, 1126–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union (EU). Council directive 86/278/EEC of 12 June 1986 on the protection of the environment, and in particular of the soil, when sewage sludge is used in agriculture. Off. J. Eur. Union L Ser. 1986, 181, 6–12. [Google Scholar]
- Fytili, D.; Zabaniotou, A. Utilization of sewage sludge in EU application of old and new methods-A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2008, 12, 116–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission (EC). Working Document on Sludge; 3rd Draft; DG Environment, European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2000. Available online: https://www.isprambiente.gov.it/it/progetti/cartella-progetti-in-corso/suolo-e-territorio-1/uso-dei-fanghi-di-depurazione-in-agricoltura-attivita-di-controllo-e-vigilanza-del-territorio/files/3rd_Draft_sludge_en.pdf (accessed on 16 September 2025).
- Hudcová, H.; Vymazal, J.; Rozkošný, M. Present restrictions of sewage sludge application in agriculture within the European Union. Soil Water Res. 2019, 14, 104–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mininni, G.; Blanch, A.R.; Lucena, F.; Berselli, S. EU policy on sewage sludge utilization and perspectives on new approaches of sludge management. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 7361–7374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HERA Project, Human and Environmental Risk Assessment on Ingredients of Household Cleaning Products. LAS, Linear Alkylbenezene Sulphonate (CAS No. 68411-30-3). 2013. Available online: https://www.heraproject.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/HERA-LAS-revised-April-2013-Final1.pdf (accessed on 5 October 2025).
- Aparicio, I.; Santos, J.L.; Alonso, E. Limitation of the concentration of organic pollutants in sewage sludge for agricultural purposes: A case study in South Spain. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 1747–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantarero, S.; Prieto, C.A.; López, I. Occurrence of high-tonnage anionic surfactants in Spanish sewage sludge. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 95, S149–S153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogh, P.H.; Lopez, C.V.; Cassani, G.; Jensen, J.; Holmstrup, M.; Schraepen, N.; Jørgensen, E.; Gavor, Z.; Temara, A. Risk assessment of linear alkylbenzene sulphonates, LAS, in agricultural soil revisited: Robust chronic toxicity tests for Folsomia candida (Collembola), Aporrectodea caliginosa (Oligochaeta) and Enchytraeus crypticus (Enchytraeidae). Chemosphere 2007, 69, 872–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schowanek, D.; David, H.; Francaviglia, R.; Hall, J.; Kirchmann, H.; Krogh, P.H.; Smith, S.; Schraepen, N. Probabilistic risk assessment for linear alkylbenzene sulfonate (LAS) in sewage sludge used on agricultural soil. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2007, 49, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.L.; Silva, L.G.; Veras, S.T.S.; Gavazza, S.; Florencio, L.; Motteran, F.; Kato, M.T. Use of nitrate, sulphate, and iron (III) as electron acceptors to improve the anaerobic degradation of linear alkylbenzene sulfonate: Effects on removal potential and microbiota diversification. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2025, 32, 16640–16655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara-Martin, P.A.; Gomez-Parra, A.; Sanz, J.L.; González-Mazo, E. Anaerobic degradation pathway of linear alkylbenzene sulfonates (LAS) in sulfate-reducing marine sediments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1670–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.K.; Lee, S.H.; Yoon, H.; Jeong, G.; Jung, Y.J.; Hur, M.; Lee, B.H.; Park, H.D. Microbiome degrading linear alkylbenzene sulfonate in activated sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 418, 126365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delforno, T.P.; Macedo, T.Z.; Midoux, C.; Lacerda, G.V.; Rué, O.; Mariadassou, M.; Loux, V.; Varesche, M.B.A.; Bouchez, T.; Bize, A.; et al. Comparative metatranscriptomic analysis of anaerobic digesters treating anionic surfactant contaminated wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 482–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, J.; Mejías, C.; Arenas, M.; Santos, J.L.; Aparicio, I.; Alonso, E. Occurrence of Linear Alkylbenzene Sulfonates, Nonylphenol Ethoxylates and Di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate in Composting Processes: Environmental Risks. Sustainability 2022, 14, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berna, J.L.; Ferrer, J.; Moreno, A.; Prats, D.; Bevia, F.R. The fate of LAS in the environment. Tenside Surfactants Deterg. 1989, 26, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, L.; Gellera, A.; Landone, A. LAS removal and biodegradation in a wastewater treatment plant. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1993, 12, 1777–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, M.T.; Campos, E.; Dalmau, M.; Ribosa, I.; Sanchez-Leal, J. Structure–activity relationships for association of linear alkyl- benzene sulfonates with activated sludge. Chemosphere 2002, 49, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adám, A.A.; Ziegenheim, S.; Janovák, L.; Szabados, M.; Bús, C.; Kukovecz, Á.; Kónya, Z.; Dékány, I.; Sipos, P.; Kutus, B. Binding of Ca2+ Ions to Alkylbenzene Sulfonates: Micelle Formation, Second Critical Concentration and Precipitation. Materials 2023, 16, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). POTW Sludge Sampling and Analysis Guidance Document. 2018. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/biosolids/potw-sludge-sampling-and-analysis-guidance-document (accessed on 16 September 2025).
- Martín, J.; Mejías, C.; Santos, J.L.; Aparicio, I.; Alonso, E.; Heinze, J. Quantification of linear alkylbenzene sulphonates in complex sludge samples: Influence of matrix effects in calibration methods. Microchem. J. 2024, 204, 111089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Programme, United Nations Environment. Linear Alkylbenzene Sulfonates & Related Compounds. In Environmental Health Criteria Series; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996; ISBN 9789241571692. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, J.; Smith, S.R.; Krogh, P.H.; Versteeg, D.J.; Temara, A. European risk assessment of LAS in agricultural soil revisited: Species sensitivity distribution and risk estimates. Chemosphere 2007, 69, 880–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development Screening Information Data Sets (OECD SIDS). Initial Assessment Report on LAS. 2005. Available online: https://www.cleaninginstitute.org/sites/default/files/research-pdfs/LAS_SIAR.pdf (accessed on 16 September 2025).
- Swisher, R.D. Surfactant Biodegradation, 2nd ed.; Revised and Expanded, Surfactant Science Series; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 1987; Volume 18, ISBN 9780824769383. [Google Scholar]
- Fauser, P.; Vikelsøe, J.; Sørensen, P.B.; Carlsen, L. Phthalates, nonylphenols and LAS in an alternately operated wastewater treatment plant—Fate modelling based on measured concentrations in wastewater and sludge. Water Res. 2003, 37, 1288–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinze, J.E. Understanding the Biodegradation of LAS in the Absence of Oxygen. CLER Rev. 2015, 15, 20–59. [Google Scholar]
- García, M.T.; Campos, E.; Ribosa, I.; Latorre, A.; Sánchez-Leal, J. Anaerobic digestion of linear alkyl benzene sulfonates: Biodegradation kinetics and metabolite analysis. Chemosphere 2005, 60, 1636–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temmink, H.; Klapwijk, B. Fate of linear alkylbenzene sulfonate (LAS) in activated sludge plants. Water Res. 2004, 38, 903–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiCorcia, A.; Samperi, R.; Bellioni, A.; Marcomini, A.; Zanette, M.; Lenr, K.; Cavalli, L. LAS Pilot study at the “Roma-Nord” sewage treatment plant and in the Tiber river. Riv. Ital. Sostanze Gr. 1994, 71, 467–475. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez, P.S. Contribución Al Estudio de la Degradación Anaerobia de Tensioactivos Aniónicos Alquilbencenosulfonatos lineales, Alquilsufatos Y Alcoholes Etoxilados Sulfatos. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Alicante, San Vicente del Raspeig, Alicante, Spain, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Kuntze, K.; Shinoda, Y.; Moutakki, H.; Mcinerney, M.J.; Vogt, C.; Richnow, H.H.; Boll, M. 6-Oxocyclohex-1-ene-1-carbonyl-coenzyme A hydrolases from obligately anaerobic bacteria: Characterization and identification of its gene as a functional marker for aromatic compounds degrading anaerobes. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 1547–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mungray, A.K.; Kumar, P. Fate of Linear Alkylbenzene Sulfonates in the Environment: A Review. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2009, 63, 981–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seleiman, M.F.; Arja, S.; Pirjo, S.A.M. Recycling sludge on cropland as fertilizer–Advantages and risks. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 155, 105647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, R.M.; Cummins, E. Evaluation of ‘classic’ and emerging contaminants resulting from the application of biosolids to agricultural lands: A Review. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2015, 21, 492–5134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).