Research on the Construction and Optimization of Shenzhen’s Ecological Network Based on MSPA and Circuit Theory
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
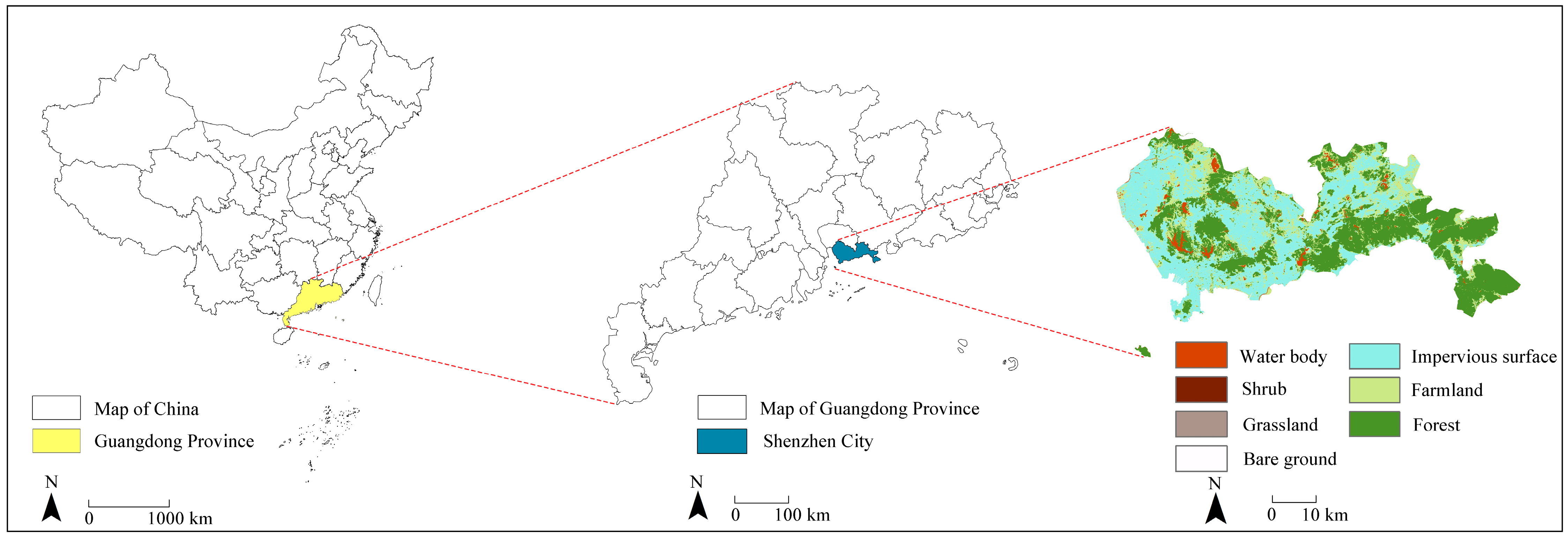
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Ecological Source Identification Based on MSPA and Landscape Connectivity Assessment
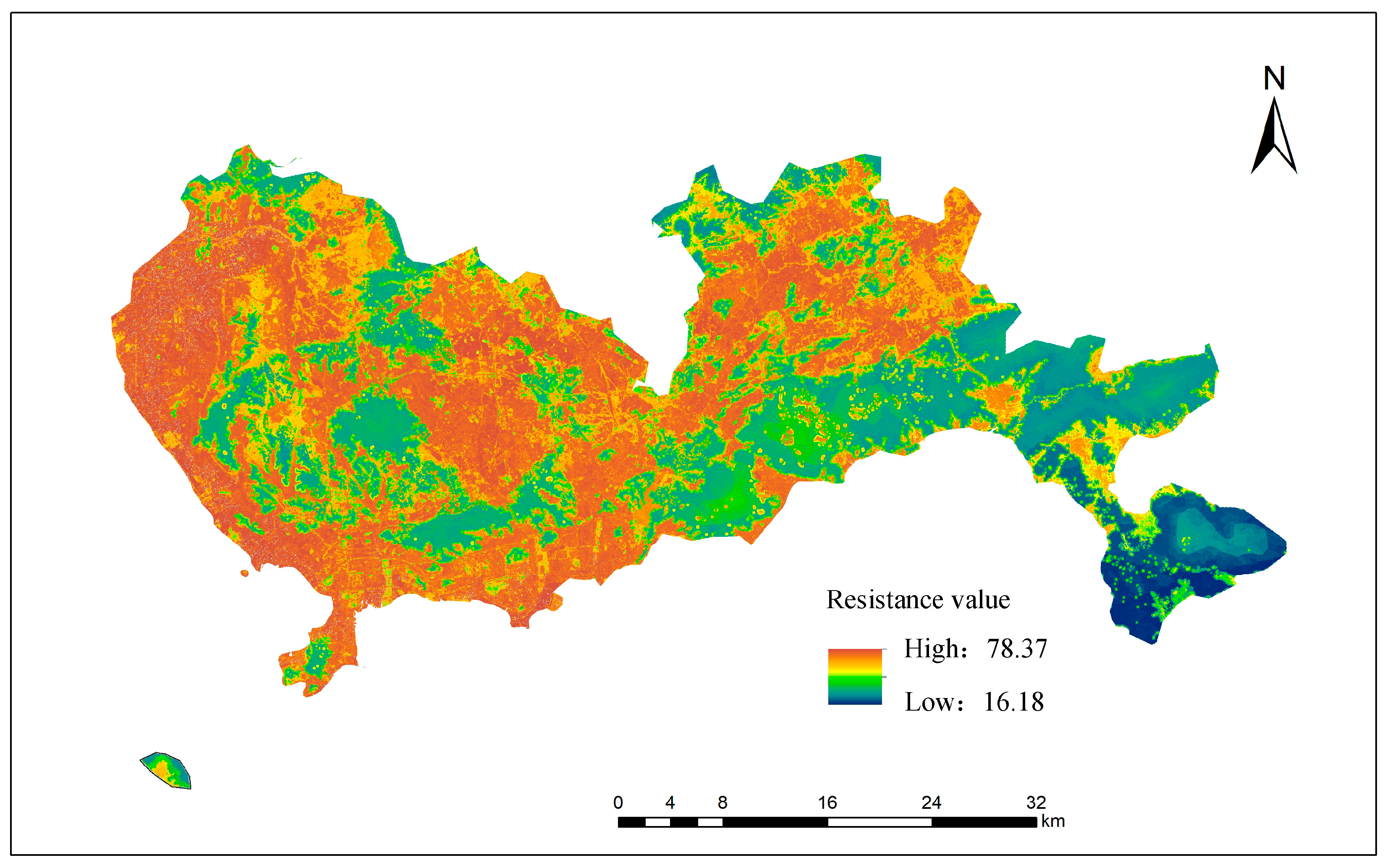
2.3.2. Ecological Resistance Surface Construction
2.3.3. Extraction of Corridors, Pinch Points, and Barrier Points Based on Circuit Theory
- (1)
- Identification of Ecological Corridors
- (2)
- Identification of Ecological Pinch Points
- (3)
- Identification of Ecological Barriers
- (4)
- Current Density Model
3. Results
3.1. Identification of Ecological Sources in Shenzhen City Area
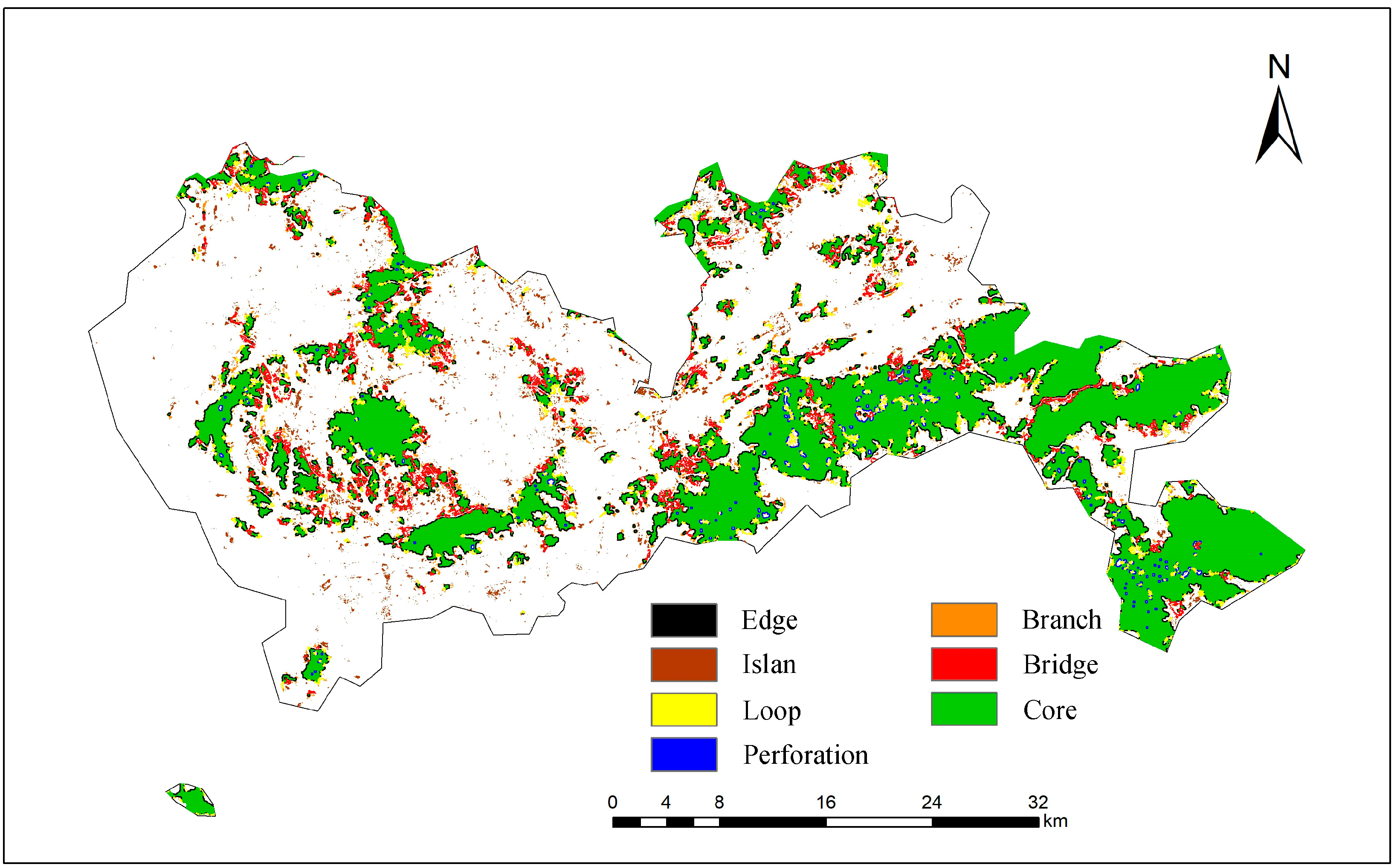
3.1.1. Landscape Pattern Analysis of Shenzhen City Area Based on MSPA
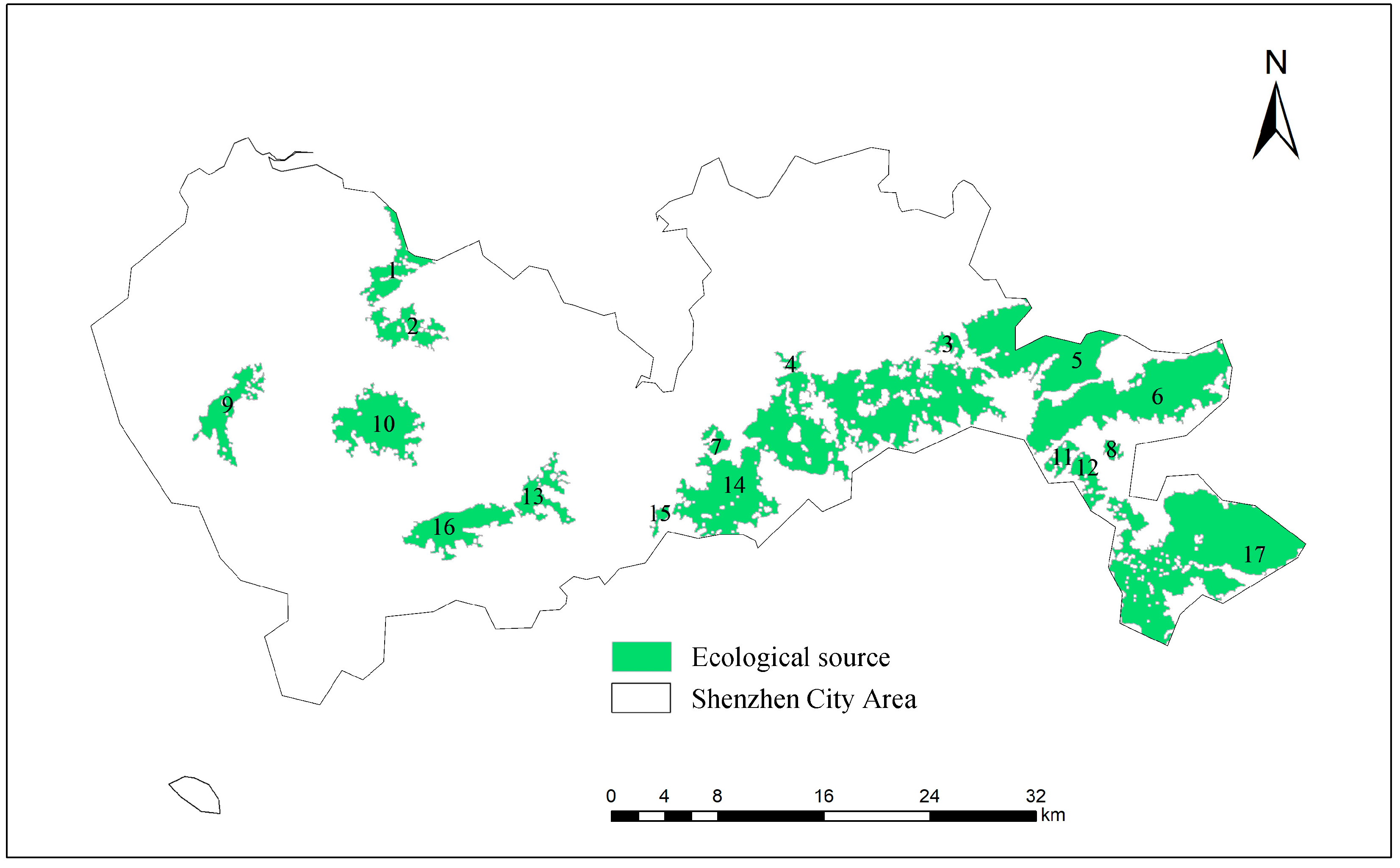
3.1.2. Identification of Ecological Sources in Shenzhen City Area
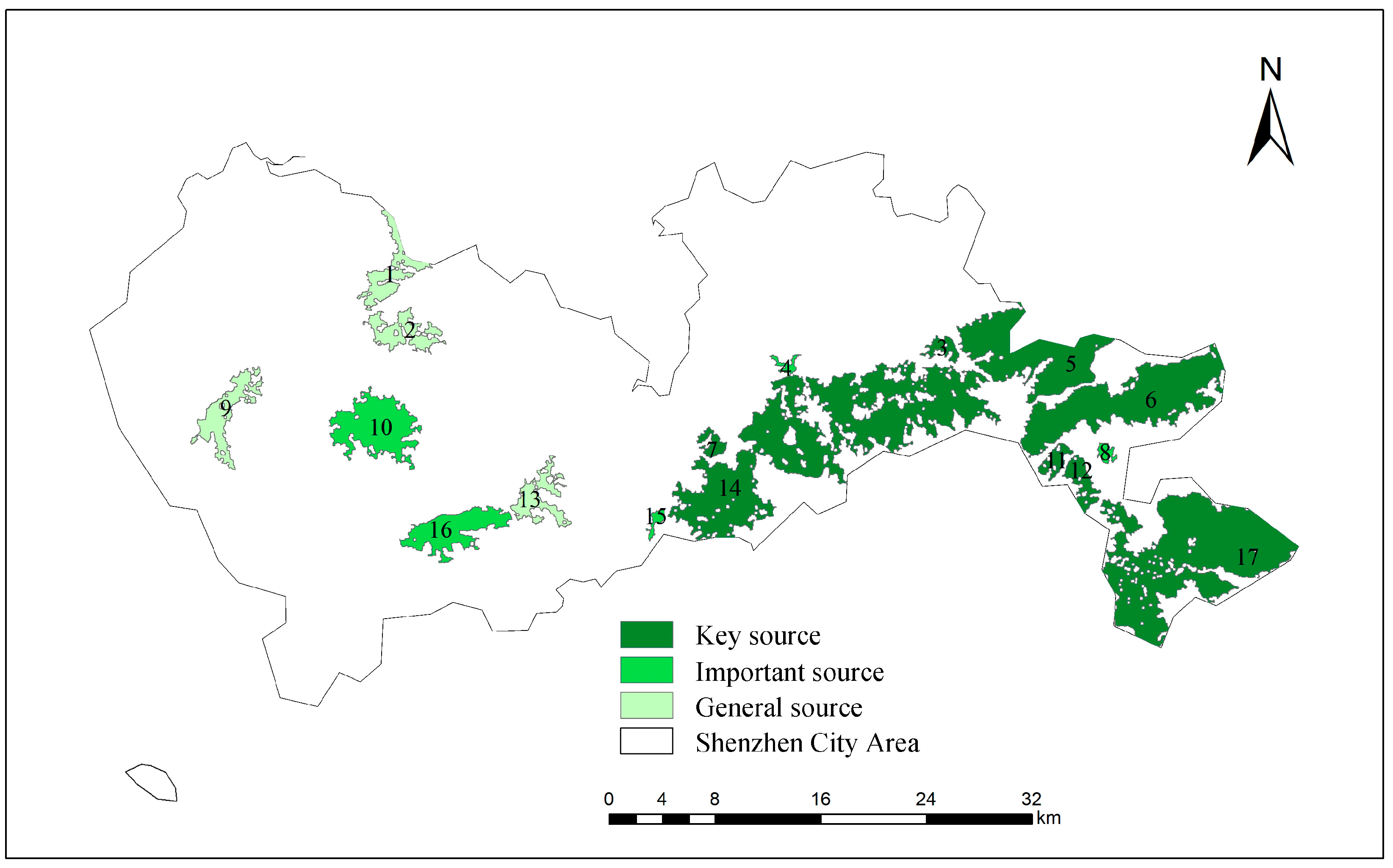
3.1.3. Classification of the Importance of Ecological Sources in Shenzhen City Area
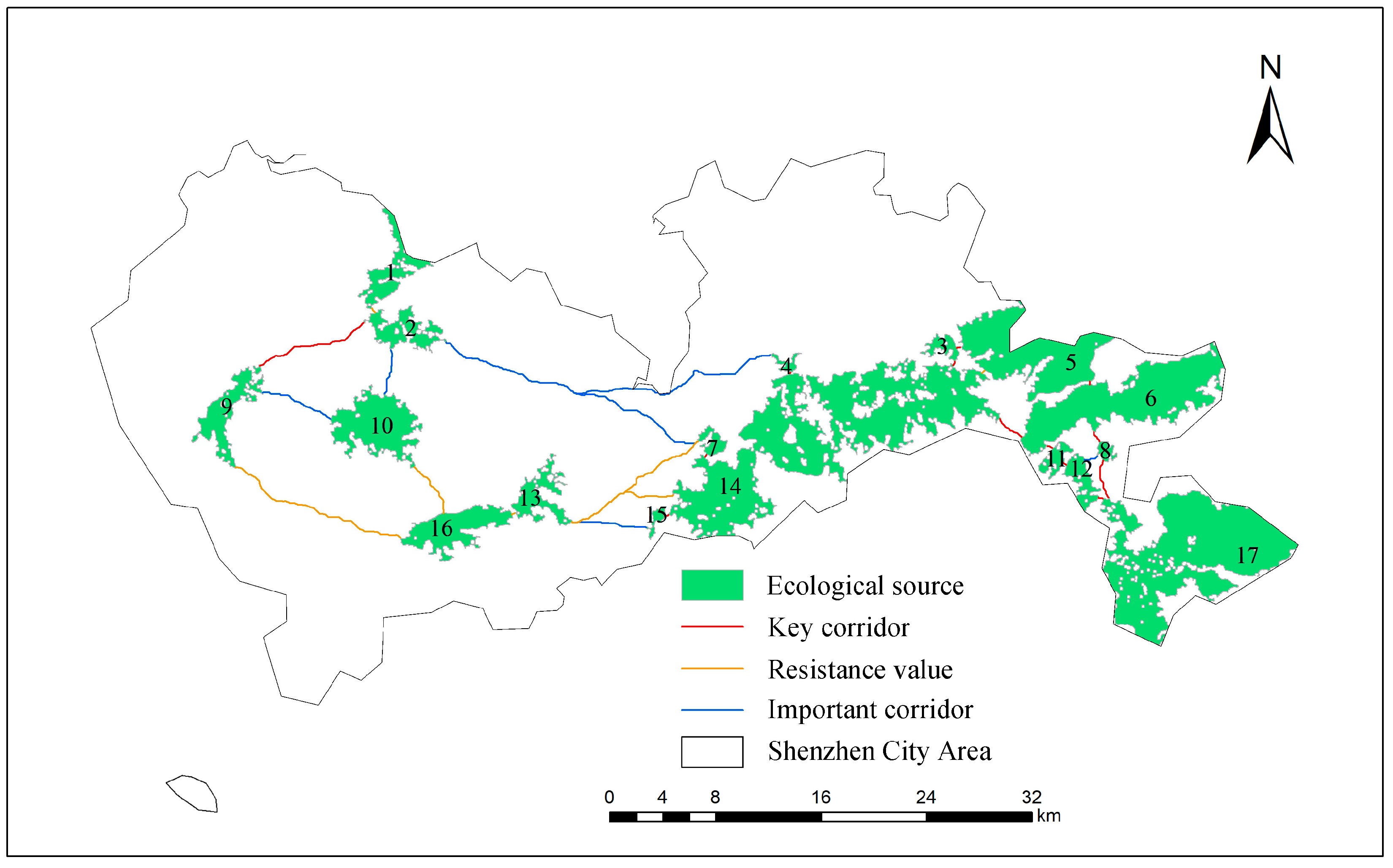
3.2. Extraction of Ecological Corridors in Shenzhen City Area
3.2.1. Construction of Ecological Resistance Surface in Shenzhen City Area
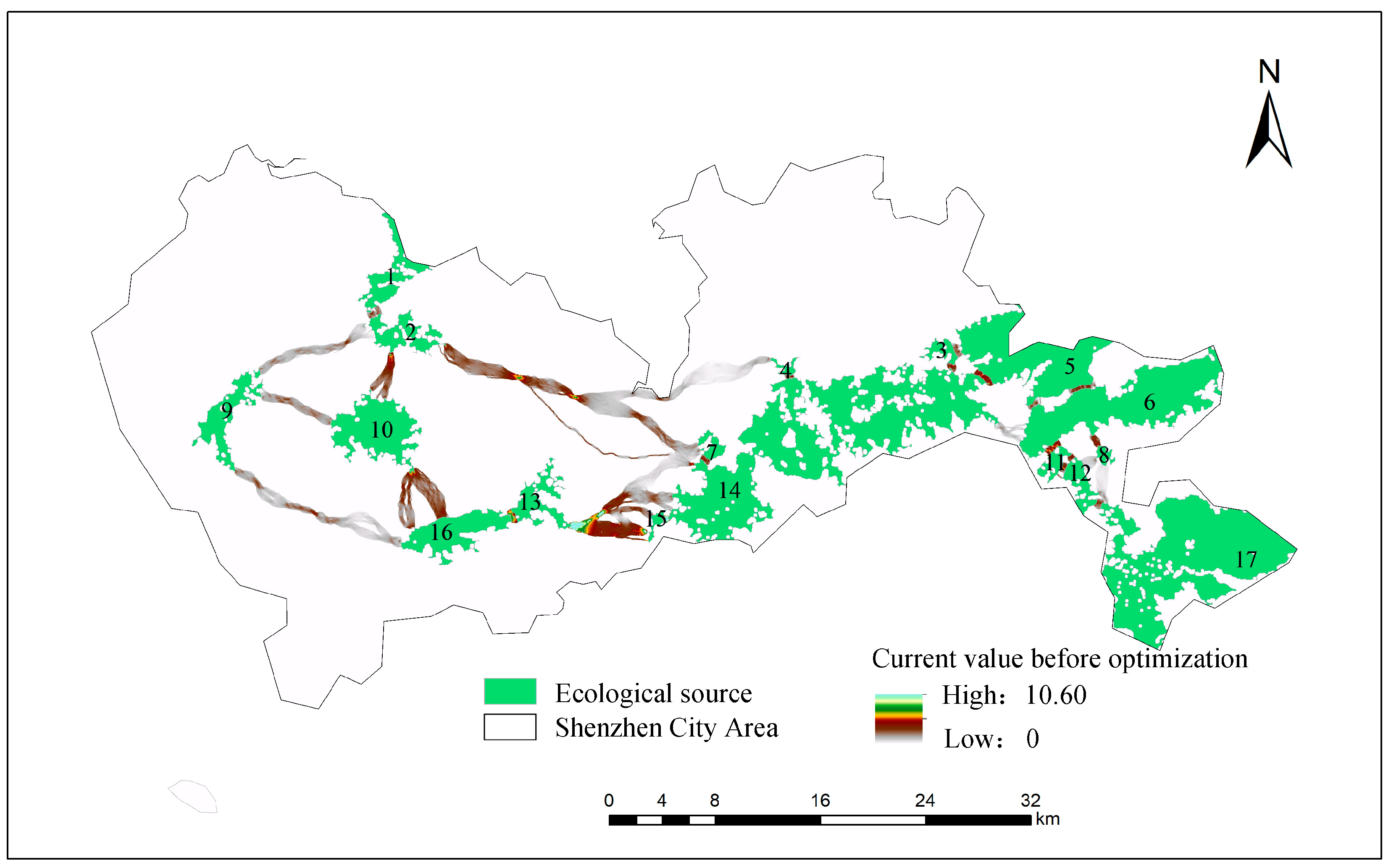
3.2.2. Extraction of Ecological Corridors in Shenzhen City Area
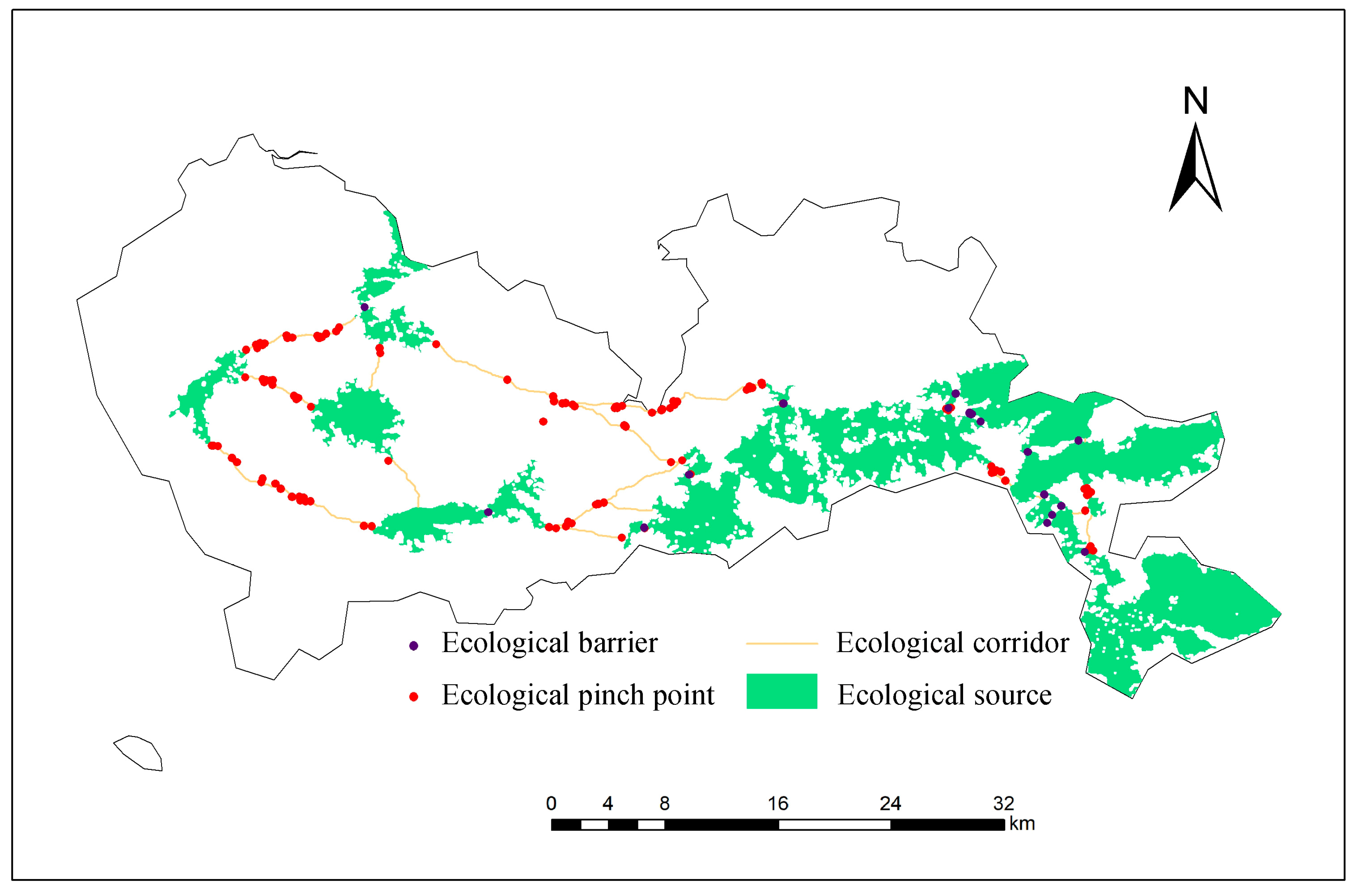
3.3. Identification of Ecological Pinch Points in Shenzhen City Area
3.4. Identification of Ecological Barriers in Shenzhen City Area
3.5. Optimization and Evaluation of the Ecological Network in Shenzhen City Area
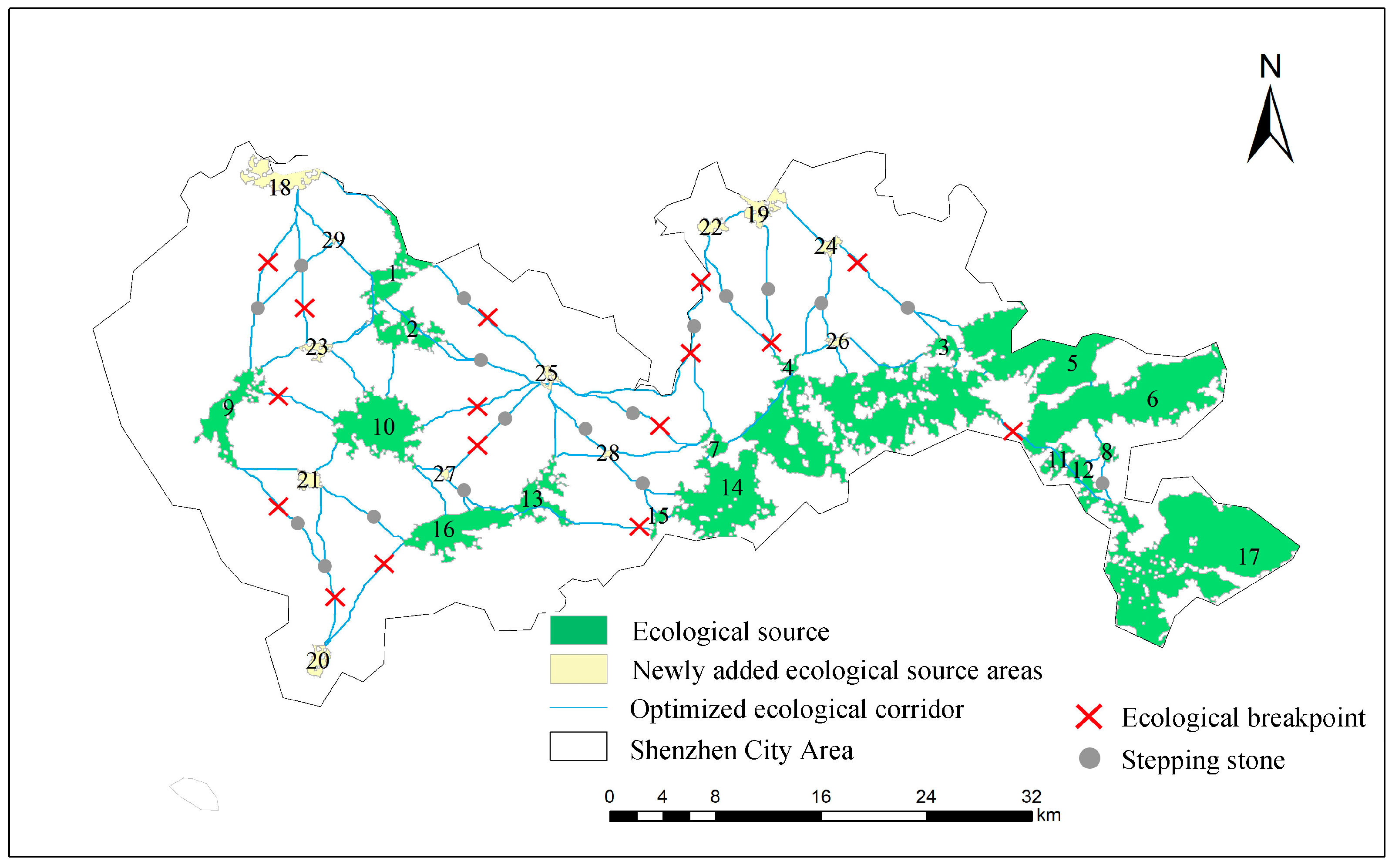
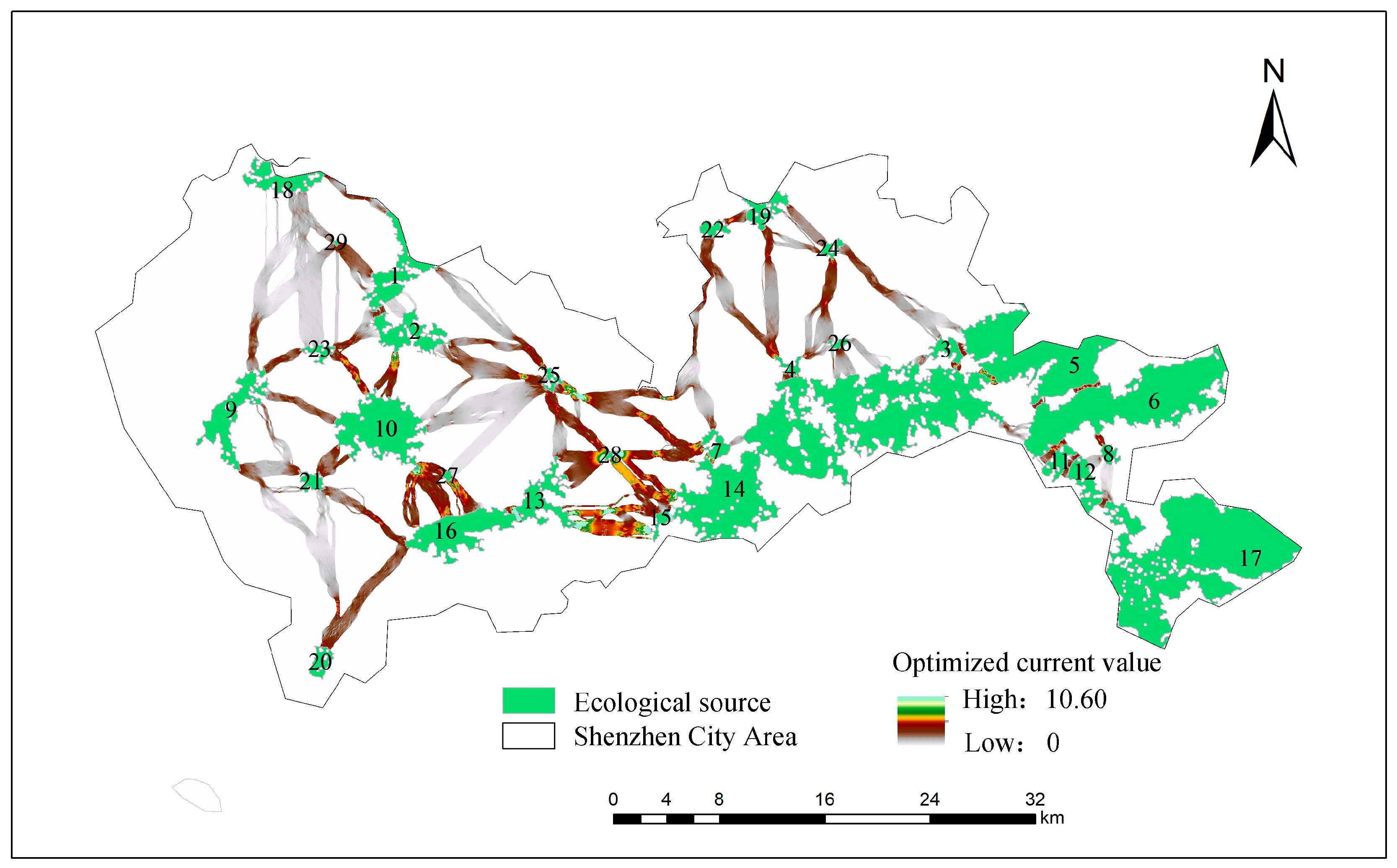
3.5.1. Network Structure Optimization by Adding Ecological Sources and Stepping Stones
3.5.2. Functional Evaluation of the Ecological Network Based on Circuit Theory
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, X.H.; Liang, K.Y. Construction of Ecological Security Pattern Based on Ecological Supply-Demand and Land Change: A Case Study of Jiangyin City, Jiangsu Province. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2025, 32, 423–434. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.Y.; Di Lire, T.; Hou, M.L.; He, Y.; Ding, X. Assessing Land Carbon Metabolism in Hubei Section of Three Gorges Reservoir Area Based on Ecological Network. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2025, 36, 2150–2158. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.Y.; Zhu, M.J.; Luan, B. Construction of Ecological Network in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area Based on ESV and Circuit Theory. Ecol. Sci. 2025, 44, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Q.; Huang, B. Construction of Urban Ecological Security Pattern Based on Multi-Source Data: A Case Study of Shenzhen. Ecol. Sci. 2025, 44, 241–253. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sallustio, L.; De Toni, A.; Strollo, A.; Di Febbraro, M.; Gissi, E.; Casella, L.; Geneletti, D.; Munafò, M.; Vizzarri, M.; Marchetti, M. Assessing habitat quality in relation to the spatial distribution of protected areas in Italy. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 201, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.X.; Gao, C.; Ren, G.Y.; Liu, D.-F. Construction of Composite Blue-Green Ecological Network in Wuhan Based on Complex Network Theory. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2025, 36, 2139–2149. [Google Scholar]
- Skokanová, H.; Netopil, P.; Havlíček, M.; Šarapatka, B. The role of traditional agricultural landscape structures in changes to green infrastructure connectivity. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 302, 107071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.L.; He, M.; Li, B.; Lei, J.; Ai, L. Construction and Optimization of Urban Ecological Network in Chongqing Main Urban Area. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2025, 34, 699–709. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, S.Q.; Huang, Y.Z.; Li, Y. Ecological Network Construction in Yunnan Province from the Perspective of Major Function-Oriented Zones. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2025, 39, 172–181+190. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kamusoko, C.; Gamba, J. Simulating urban growth using a random forest-cellular automata (RF-CA) model. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2015, 4, 447–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Feng, Q.Y.; Wang, C.X.; Yan, Y. Construction of Ecological Security Pattern in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area Based on Ecological Adaptation Theory. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2025, 45, 5769–5782. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kowe, P.; Mutanga, O.; Dube, T. Advancements in the remote sensing of landscape pattern of urban green spaces and vegetation fragmentation. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 42, 3797–3832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.J.; Lu, Y.H.; Jiang, W.; Li, T. Ecological Protection and Restoration Strategies of Territorial Space in Xianyang City Based on Ecological Network. Sci. Surv. Mapp. 2025, 50, 48–63. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.J.; Gu, Y.Y.; Xing, Z. Construction of “Biological Migration-Regional Cooling” Composite Functional Ecological Network in Wuhan Metropolitan Area. Landsc. Archit. 2025, 32, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpkins, C.E.; Dennis, T.E.; Etherington, T.R. Assessing the performance of common landscape connectivity metrics using a virtual ecologist approach. Ecol. Model. 2018, 367, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Qiao, J.J.; Liu, H.L.; Wang, G.; Feng, Y. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Optimization Strategies of Ecological Security Patterns in the Middle Reaches of the Yellow River of China. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2024, 40, 231–239. [Google Scholar]
- De Montis, A.; Ganciu, A.; Cabras, M.; Bardi, A.; Mulas, M. Comparative Ecological Network Analysis: An Application to Italy. Land Use Policy 2019, 81, 714–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, D.; Pan, J. Ecological Network Identification and Connectivity Robustness Evaluation in the Yellow River Basin under a Multi-Scenario Simulation. Ecol. Modell. 2023, 482, 110384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldo, A.; Gatto, M. River networks as ecological corridors: A coherent ecohydrological perspective. Adv. Water Resour. 2018, 112, 27–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; He, Z.; Bai, W.; He, L.; Chen, X.; Chen, J. Identification of Ecological Security Patterns of Alpine Wetland Grasslands Based on Landscape Ecological Risks: A Study in Zoigê County. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 928, 172302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Du, Y.; Meersmans, J.; Qiu, S. Linking Ecosystem Services and Circuit Theory to Identify Ecological Security Patterns. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Kang, B.; Li, M.; Du, Z.; Zhang, L.; Li, H. Identification of Priority Areas for Territorial Ecological Conservation and Restoration Based on Ecological Networks: A Case Study of Tianjin City, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bombrun, M.; Dash, J.P.; Pont, D.; Watt, M.S.; Pearse, G.D.; Dungey, H.S. Forest-Scale Phenotyping: Productivity Characterisation Through Machine Learning. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Su, K.; Liang, X.; Jiang, X.; Wang, J.; You, Y.; Wang, L.; Chang, S.; Wei, C.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Identification of Priority Areas to Provide Insights for Ecological Protection Planning: A Case Study in Hechi, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Gong, Y.; Yu, Y. Integrating Pattern, Process, and Function in Urban Landscape Ecological Network Planning: A Case Study of Harbin Central City. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 159, 111671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales, F.O.; Fath, B.; Llerena, G. Quantifying a Virtual Water Metabolic Network of the Metropolitan District of Quito, Ecuador Using Ecological Network Methods. J. Ind. Ecol. 2023, 27, 1304–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Xu, H.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, W. Green Infrastructure Network Identification at a Regional Scale: The Case of Nanjing Metropolitan Area, China. Forests 2022, 13, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, J.; Shi, Z.; Zhu, W.; Li, T.; Xue, H.; Chen, X.; Yan, Y.; Ma, R. Construction and Optimization of an Ecological Network in Zhengzhou Metropolitan Area, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xia, J.; Xu, Z.; Zou, L.; Qiao, Y.; Li, P. Impact of Urban Expansion on Rain Island Effect in Jinan City, North China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlková, K.; Zýka, V.; Papp, C.-R.; Romportl, D. An Ecological Network for Large Carnivores as a Key Tool for Protecting Landscape Connectivity in the Carpathians. J. Maps 2023, 20, 2290858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Gao, H.; Liu, J.; Fu, T.; Qi, F.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, L. Study on the Characteristics of Ecological Network and Critical Areas of Ecological Restoration in Hebei-Tianjin Coastal Wetlands. Wetlands 2024, 44, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, S.; Good, R. The Benefits of Restored Linear Vegetation Corridors for Biodiversity Conservation: A Case Study. Australas. Plant Conserv. J. Aust. Netw. Plant Conserv. 2016, 24, 22–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.Y.; Xiu, C.; Li, L.L.; Ye, Y.H.; Chen, Y.L. Construction of Ecological-Urban Network Pattern for Ecological Synergy in Bay-Area Urban Agglomeration: A Case Study of Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 44, 11049–11064. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Modica, G.; Praticò, S.; Laudari, L.; Ledda, A.; Di, F.S. Implementation of multispecies ecological networks at the regional scale: Analysis and multi-temporal assessment. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 289, 112494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, Q.; Liang, G.; Liu, M.; Hu, X.; Lin, S.; Wu, Z. Construction of an Ecological Security Pattern Based on the PLUS and MSPA Models: A Case Study of the Fuzhou Metropolitan Area. Sustainability 2025, 17, 5830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, M.; Duo, L.; Chen, N.; Lu, J.; Yang, W. Multi-Scenario Simulation and Assessment of Ecological Security Patterns: A Case Study of Poyang Lake Eco-Economic Zone. Sustainability 2025, 17, 4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Zhang, Q.T.; Cui, Y. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Optimization of Ecological Network in Rapidly Urbanizing Area of Nanning. Chin. Landsc. Archit. 2025, 41, 125–131. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cao, W.J.; Yang, Q.K.; Jia, G.X.; Bai, H.; Guo, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Wen, L. Construction and optimization of ecological network based on ecological vulnerability in Ulanqab, Inner Mongolia, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2025, 36, 376–382. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y.; Yang, T.; Gong, J. Identification of Ecological Restoration Areas Based on “Ecological Quality-Ecological Network” Framework: A Case Study of Wuhan. China Land Sci. 2024, 38, 129–142. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zou, C.; Tang, X.; Tan, Q.; Feng, H.; Guo, H.; Mei, J. Constructing Ecological Networks for Mountainous Urban Areas Based on Morphological Spatial Pattern Analysis and Minimum Cumulative Resistance Models: A Case Study of Yongtai County. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fábos, J.G. Green way plann in gin the United States: Its origins and recent case studies. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2004, 68, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, A.T.; Sunter, E.J.; Fauvelle, C.; Bradshaw, J.L.; Ford, B.; Hutchen, J.; Phillipow, N.; Teichman, K.J. Effective corridor width: Linking the spatial ecology of wildlife with land use policy. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2020, 66, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, S.; Settele, J.; Brondízio, E.S.; Ngo, H.T.; Agard, J.; Arneth, A.; Balvanera, P.; Brauman, K.A.; Butchart, S.H.; Chan, K.M.; et al. Pervasive human-driven decline of life on Earth points to the need for transformative change. Science 2019, 366, eaax3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klar, N.; Herrmann, M.; Henning-Hahn, M.; Pott-Dörfer, B.; Hofer, H.; Kramer-Schadt, S. Between ecological theory and planning practice: (Re-) Connecting forest patches for the wildcat in Lower Saxony, Germany. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2012, 105, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lin, X.H.; Ge, S.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y. Formation Mechanism and Evolution Characteristics of Cultivated Land Carbon Flow Ecological Network in Hubei Province Under “Dual Carbon” Goals. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2025, 45, 1599–1612. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.X.; Chai, B.; Zhang, Y.; He, W.; Tan, X. Comparative Study of Ecological Networks Based on Gravity Model and Circuit Theory: A Case Study of Jining City. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2025, 45, 1684–1696. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Huang, Y.Z. Regional Ecological Network Construction in Wenshan Prefecture Based on InVEST-MSPA. Environ. Monit. Manag. Technol. 2024, 36, 41–46. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lian, H.G.; Liu, C.F.; Ni, B.W.; Qu, Z. Ecological Network Construction and Optimization of Protected Area System in Arid Northwest China: A Case Study of Hexi Corridor. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2025, 36, 259–270. [Google Scholar]
- Fortin, M.-J.; Dale, M.R.T.; Brimacombe, C. Network ecology in dynamic landscapes. Proc. R. Soc. B 2021, 288, 20201889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opdam, P.; Steingröver, E.; van Rooij, S. Ecological networks: A spatial concept for multi-actor planning of sustainable landscapes. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2006, 75, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, M.Y.; Wang, L.N.; Yu, J.; Luo, Q. Ecological Restoration Strategy of Territorial Space Based on Comparative Optimization of Ecological Network. Chin. Landsc. Archit. 2024, 40, 43–49. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.F.; Ni, B.W.; Lian, H.G.; He, Y. Resilience Evolution and Enhancement Strategy of Ecological Network in Arid Inland River Basin: A Case Study of Shiyang River Basin. J. Nat. Resour. 2024, 39, 2087–2101. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- She, Y.C.; Chen, C.L.; Mao, S.Z.; Tan, J. Construction and Optimization of Ecological Network in Core Area of Changsha-Zhuzhou-Xiangtan Based on MSPA-Linkage Mapper. For. Grassl. Resour. Res. 2024, 4, 60–69. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Keeley, A.T.H.; Beier, P.; Gagnon, J.W. Estimating landscape resistance from habitat suitability: Effects of data source and non- linearities. Landsc. Ecol. 2016, 31, 2151–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrado, M.; Sabater, S.; Chaplin-Kramer, B.; Mandle, L.; Ziv, G.; Acuña, V. Model development for the assessment of terrestrial and aquatic habitat quality in conservation planning. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 540, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Chen, X.M.; Xie, Y.W.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, Z.; Xue, X.; Tan, D.; Li, X. Construction of Composite Green Space Ecological Network Under Multi-Objective Orientation: A Case Study of Central Urban Area of Quanzhou. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2025, 41, 308–322. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Z.H.; Zhou, Y.; Yao, J.; Ning, S.; Luo, Y.; Wang, M. Optimization of Urban Thermal Environment Ecological Network Based on Morphological Spatial Pattern Analysis and Minimum Cumulative Resistance Model. J. Zhejiang AF Univ. 2024, 41, 1085–1093. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.R.; Jiang, G.G.; Zhou, J. Construction and Optimization of Landscape Ecological Pattern in Jialing River Basin Based on ESV-ERI-MCR Evaluation. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2024, 44, 124–135. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.Q.; Wei, X.J.; Xie, M.R.; Zhong, S.; Chen, W.; Xia, Y. Nested Analysis of Ecological Network in Nanchang City Based on Comprehensive Identification of Multi-Scale Ecological Sources. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2024, 31, 408–418. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Pili, S.; Serra, P.; Salvati, L. Landscape and the city: Agro-forest systems, land fragmentation and the ecological network in Rome, Italy. Urban For. Urban Green. 2019, 41, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, N.S.; Magalhaes, M.R. Methodology for mapping the national ecological network to mainland Portugal: Aplanning tool towards a green infrastructure. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 104, 802–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, E.; Gounand, I.; Ward, C.L.; Altermatt, F. Bridging ecology and conservation: From ecological networks to ecosystem function. J. Appl. Ecol. 2017, 54, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, A.; Miranda, M.; Arellano, E.C. Landscape dynamics and their effect on the functional connectivity of a Mediterranean landscape in Chile. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.Y.; Xu, Z.H.; Ye, H.Y.; Li, T. Impact of Road Infrastructure on Ecological Network in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2024, 35, 1653–1660. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Z.; Yin, H.W.; Kong, F.H.; Su, J.; Sun, H.; Li, J. Construction and Optimization of Egret Habitat Network in Nanjing Based on Habitat Clustering Analysis and Landscape Corridor Simulation. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 44, 3303–3316. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Wang, D.R. Construction and Optimization of Ecological Network in Lanzhou-Xining Urban Agglomeration Based on Adaptive Cycle. Arid Zone Res. 2024, 41, 856–864. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Gao, Y.; Li, F.; Cheng, C. Research Progress on Urban Ecological Space Under Territorial Spatial Planning. Chin. Landsc. Archit. 2024, 40, 22–28. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
| Data Type | Data Source | Format | Year | Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Administrative division data | Standard Map Service System of the Ministry of Natural Resources of China (http://bzdt.ch.mnr.gov.cn/) | Vector data | 2024 | - |
| Land use data | Chinese Academy of Sciences Resource and Environment Science Data Center (https://www.resdc.cn/) | Raster data | 2024 | 30 m |
| DEM data | Geospatial Data Cloud Website (https://www.gscloud.cn/) | 2024 | 12.5 m | |
| Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) | China Qinghai-Tibet Plateau Scientific Data Center (https://data.tpdc.ac.cn/) | 2024 | 30 m | |
| Road data | OpenStreetMap (https://edithistory.peterboswell.net/) | Vector data | 2024 | - |
| River data | Geospatial Data Cloud Website (https://www.gscloud.cn/) | 2024 | - | |
| Soil data | Soil Science Data Center (https://soil.geodata.cn/) | Raster data | 2024 | 30 m |
| Resistance Factor | Weight | Resistance Score | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | ||
| Elevation | 0.0652 | [0, 5] | (5, 20] | (20, 35] | (35, 50] | >50 |
| Slope | 0.0358 | [0, 200] | (200, 400] | (400, 600] | (600, 800] | >800 |
| Normalized Difference Vegetation Index | 0.1221 | (0.75, 1] | (0.5, 0.75] | (0.25, 0.5] | (0, 0.25] | (0, −0.2] |
| Distance from the river | 0.0407 | [0, 350] | (350, 700] | (700, 1050] | (1050, 1400] | >1400 |
| Soil | 0.0612 | Red soil | Rice soil | Tidal soil | Red soil, Yellow-red soil | Coastal saline soil |
| Land use | 0.1828 | Forest | Grassland, Shrubs | Farmland | Bare ground, Water body | Impervious surface |
| Distance from the railway | 0.1104 | >2000 | (1500, 2000] | (1000, 1500] | (500, 1000] | [0, 500] |
| Distance to highway | 0.0798 | >2000 | (1500, 2000] | (1000, 1500] | (500, 1000] | [0, 500] |
| Distance from major city roads | 0.0644 | [0, 350] | (350, 700] | (700, 1050] | (1050, 1400] | >1400 |
| MSPA landscape type | 0.2376 | Core | Bridge | Branch, Loop | Edge, Islet | Perforation, Background |
| Landscape Type | Foreground (Woodland) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Area (km2) | Proportion of Woodland (%) | Proportion of the Study Area (%) | |
| Core | 426.69 | 60.70% | 21.99% |
| Islan | 27.68 | 3.94% | 1.43% |
| Loop | 40.85 | 5.81% | 2.10% |
| Bridge | 65.44 | 9.31% | 3.37% |
| Edge | 95.91 | 13.64% | 4.94% |
| Perforation | 11.13 | 1.58% | 0.57% |
| Branch | 28.84 | 4.10% | 1.49% |
| Importance Level of Ecological Source Areas | Quantity | Percentage of Total Ecological Source Areas (%) | Area (km2) | Proportion of Total Ecological Source Area (%) | Connectivity Index (dPC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Key source | 8 | 47.06% | 277.48 km2 | 78.72% | dPC > 1 |
| Important source | 5 | 29.41% | 39.59 km2 | 11.23% | 1 > dPC > 0.5 |
| General source | 4 | 23.53% | 35.43 km2 | 10.05% | dPC < 0.5 |
| Category | Optimized State | Quantity | Area (km2) | Length (km) | Current Density (A) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ecological sources | Before optimization | 17 | 352.50 | - | - |
| After optimization | 29 | 415.98 | - | - | |
| Ecological corridor | Before optimization | 26 | - | 127.44 | - |
| After optimization | 46 | - | 358.73 | - | |
| Ecological pinch point | Before optimization | 0 | 0 | - | - |
| After optimization | 120 | 41.64 | - | - | |
| Ecological barrier | Before optimization | 0 | 0 | - | - |
| After optimization | 26 | 27.87 | - | - | |
| Ecological network current density | Before optimization | - | - | - | 10.60 |
| After optimization | - | - | - | 20.50 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Tang, X.; Zou, C.; Guo, H. Research on the Construction and Optimization of Shenzhen’s Ecological Network Based on MSPA and Circuit Theory. Sustainability 2025, 17, 9779. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219779
Li H, Tang X, Zou C, Guo H. Research on the Construction and Optimization of Shenzhen’s Ecological Network Based on MSPA and Circuit Theory. Sustainability. 2025; 17(21):9779. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219779
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Hao, Xiaoxiang Tang, Cheng Zou, and Huanyu Guo. 2025. "Research on the Construction and Optimization of Shenzhen’s Ecological Network Based on MSPA and Circuit Theory" Sustainability 17, no. 21: 9779. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219779
APA StyleLi, H., Tang, X., Zou, C., & Guo, H. (2025). Research on the Construction and Optimization of Shenzhen’s Ecological Network Based on MSPA and Circuit Theory. Sustainability, 17(21), 9779. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219779






