Emotional Intelligence and Employees’ Commitment: Analyzing the Role of Brand Image and Corporate Social Responsibility Among Lebanese SMEs
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Is there a direct influence on SME employees’ EI and their commitment level?
- Can CSR initiatives of SMEs in Lebanon mediate the EI–Commitment relationship for their staff? And
- Does brand image mediate the relationship between EI and commitment in this context?
2. Literature Review
2.1. Theoretical Foundation
2.2. Hypotheses Development
2.2.1. Emotional Intelligence and Employee Commitment
2.2.2. Mediating Role of Brand Image
2.2.3. Mediating Role of Corporate Social Responsibility
3. Sampling Procedures
4. Measurements
5. Analysis and Results
6. Discussions
6.1. General Discussions
6.2. Theoretical Implications
6.3. Practical Implications
7. Conclusions
Limitations and Recommendations
- Qualitative studies can be designed to obtain in-depth information about employees’ EI and commitment to the organization.
- Longitudinal studies can address the effectiveness of CSR and branding initiatives among SMEs, enabling observation of changes through time.
- Corporate organizations and SMEs in the Middle East can be addressed with larger sample sizes to include cross-cultural results and build upon the current findings.
- Internal and external CSR activities can be compared along with different leadership styles, organizational cultures, or industry-specific settings to further build upon the current understanding of the subject.
- Multilevel and multi-source designs can address the impact of managers in such contextual settings.
- Analyzing this context in neighboring nations and within the MENA region can provide cross-cultural understanding, furthering the findings of the current research.
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al Maalouf, N.J.; Daouk, A.; Elia, J.; Ramadan, M.; Sawaya, C.; Baydoun, H.; Zakhem, N.B. The impact of emotional intelligence on the performance of employees in the Lebanese banking sector during crisis. J. Law Sustain. Dev. 2023, 11, e1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhamad, A.M.; Akyürek, M.; Baadhem, A.M.S.; Jaafar, Z.M. Examining the influence of emotional intelligence on decision-making among students: The mediating effect of Branding loyalty. Int. J. Cent. Bank. 2024, 20, 537–562. [Google Scholar]
- Farmanesh, P.; Saliba, C.; Athari, S.A.; Naaman, D.; Al Geitany, S.H.; Abualrob, J.O. Bridging Sustainable Development: The Nexus of Business Safety, Health Management, and Corporate Social Sustainability—Do Affective Commitment and Emotional Intelligence Mediate? Sustainability 2025, 17, 3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S. Development of a measure of emotional intelligence. Psychol. Stud.-Univ. Calicut 2004, 49, 136–141. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, I.; Fatma, M. Understanding the Influence of CPE on brand image and brand commitment: The mediating role of brand identification. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, K.M.; De Silva Lokuwaduge, C.S. Impact of corporate social responsibility practices on employee commitment. Soc. Responsib. J. 2021, 17, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwaiger, K.; Zehrer, A. The relationship between employer image and employee commitment in family-run hospitality firms. Int. J. Cult. Tour. Hosp. Res. 2021, 16, 352–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afolashade, I.S.; Jimoh, A.M.; Raji, N.A.; Fowowe-Ogunmilugba, B.J.; Oduola, O.Z.; Adewuyi, H.O. Emotional intelligence, job satisfaction, reward system and organizational commitment among workers. ASEAN J. Econ. Econ. Educ. 2024, 3, 45–60. [Google Scholar]
- Osta, A.M. The impact of employee engagement on intention to leave in SMEs in Lebanon: The moderating role of normative commitment. Cogent Bus. Manag. 2025, 12, 2501208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrontis, D.; Chaarani, H.E.; Nemar, S.E.; Dib, H. The relationship between managers’ emotional intelligence and employees’ performance. J. Int. Bus. Entrep. Dev. 2021, 13, 177–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makdissi, R.; Attal, L.; Mekdessi, S. Resilience and adaptation: Navigating economic crisis in Lebanon-transformation of commercial company into industrial entity during uncertainty. IOSR J. Bus. Manag. (IOSR-JBM) 2023, 25, 62–76. [Google Scholar]
- Kankam, G.; Charnor, I.T. Emotional intelligence and consumer decision-making styles: The mediating role of brand trust and brand loyalty. Futur. Bus. J. 2023, 9, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salovey, P.; Mayer, J.D. Emotional intelligence. Imagin. Cogn. Personal. 1990, 9, 185–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokburger-Sauer, N.; Ratneshwar, S.; Sen, S. Drivers of consumer–brand identification. Int. J. Res. Mark. 2012, 29, 406–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, R.; Carpenter, A.; Huisingh, D. A review of ‘theories of the firm’ and their contributions to Corporate Sustainability. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 106, 430–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinson, R.; Boateng, H.; Renner, A.; Kosiba, J.P.B. Antecedents and consequences of customer engagement on Facebook: An attachment theory perspective. J. Res. Interact. Mark. 2019, 13, 204–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, R.; Simsarian, C.; Bongar, B. Attachment Theory/Style: Emotional Commitment. In Encyclopedia of Sexual Psychology and Behavior; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Deb, S.K.; Nafi, S.M.; Mallik, N.; Valeri, M. Mediating effect of emotional intelligence on the relationship between employee job satisfaction and firm performance of small business. Eur. Bus. Rev. 2023, 35, 624–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mura, L.; Zsigmond, T.; Machová, R. The effects of emotional intelligence and ethics of SME employees on knowledge sharing in Central-European countries. Oeconomia Copernic. 2021, 12, 907–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofimov, A.; Drobot, O.; Kоkаrieva, A.; Maksymova, N.; Lovochkina, A.; Kozytska, I. The influence of management style and emotional intelligence on the formation of employees’ commitment and loyalty. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Rev. 2019, 7, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.K.; Kim, B.Y. The effect of emotional intelligence on job satisfaction: A case study of SME Management Consultants in Korea. J. Asian Financ. Econ. Bus. 2021, 8, 1129–1138. [Google Scholar]
- Le, T.T.; Ikram, M. Do sustainability innovation and firm competitiveness help improve firm performance? Evidence from the SME sector in Vietnam. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2022, 29, 588–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akomea, S.Y.; Agyapong, A.; Ampah, G.; Osei, H.V. Entrepreneurial orientation, sustainability practices and performance of small and medium enterprises: Evidence from an emerging economy. Int. J. Prod. Perform. Manag. 2023, 72, 2629–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.C.; Tan, C.E.; Choong, Y.O. Occupational Safety & Health Management and Corporate Sustainability: The Mediating Role of Affective Commitment. Saf. Health Work. 2023, 14, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loor-Zambrano, H.Y.; Santos-Roldán, L.; Palacios-Florencio, B. Relationship CSR and employee commitment: Mediating effects of internal motivation and trust. Eur. Res. Manag. Bus. Econ. 2022, 28, 100185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valeri, M. Guest editorial: Managerial practices supporting the growth of small business. Eur. Bus. Rev. 2023, 35, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajzen, I. The theory of planned behavior. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 1991, 50, 179–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagozzi, R.P. Attitudes, intentions, and behavior: A test of some key hypotheses. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1981, 41, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-S. The drivers of green brand equity: Green brand image, green satisfaction, and green trust. J. Bus. Ethic. 2010, 93, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, P.; del Bosque, I.R. CSR and customer loyalty: The roles of trust, customer identification with the company and satisfaction. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2013, 35, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline, R.B. Principles and Practice of Structural Equation Modeling; Guilford Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Goleman, D. Emotional Intelligence: Issues in Paradigm Building. In The Emotionally Intelligent Workplace; Jossey-Bass: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2001; Volume 13, p. 26. [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrova, B.; Tomova, T. A Wellness lifestyle, emotional intelligence, workplace and leadership success. Int. Sci. J. Smart Innov. Recreat. Wellness Ind. Niche Tour. 2025, 6, 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Herut, A.H.; Muleta, H.D.; Lebeta, M.F. Emotional intelligence as a predictor for academic achievement of children: Evidence from primary schools of southern Ethiopia. Soc. Sci. Humanit. Open 2024, 9, 100779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johar, S.S.H.; Shah, I.M. The impact of emotional intelligence on organizational commitment through self-esteem of employee in public sector. Bus. Manag. Rev. 2014, 4, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Mekdessi, S.; El-Hawli, S.; Makdissi, R. The impact of current crises on employment-empirical study on food sector SMEs in north Lebanon. J. Econ. Financ. 2021, 12, 28–47. [Google Scholar]
- Low, G.S.; Lamb, C.W., Jr. The measurement and dimensionality of brand associations. J. Prod. Brand Manag. 2000, 9, 350–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros-Arrieta, D.; García-Cali, E. Internal branding: Conceptualization from a literature review and opportunities for future research. J. Brand Manag. 2021, 28, 133–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.K.; Nasruddin, E. Strategic Brand Equity Management for SMEs: Insights from a Comprehensive Literature Review. Int. J. Bus. Technol. Manag. 2024, 6, 264–280. [Google Scholar]
- Ramesh, K.; Saha, R.; Goswami, S.; Sekar; Dahiya, R. Consumer’s response to CSR activities: Mediating role of brand image and brand attitude. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2019, 26, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Fatma, M. Online destination brand experience and authenticity: Does individualism-collectivism orientation matter? J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2021, 20, 100597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbanzadeh, D.; Rahehagh, A. Emotional brand attachment and brand love: The emotional bridges in the process of transition from satisfaction to loyalty. Rajagiri Manag. J. 2020, 15, 16–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haris, M.; Nasir, N.; Cheema, S. The impact of social media activities on emotional attachment with the mediating role of brand image and brand commitment of retail sector. Rev. Educ. Adm. LAW 2022, 5, 173–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, S.A.; Khan, K.A.; Hakim, F. Whether organizational citizenship behavior is triggered by employee CSR perception and spiritual values: The moderating role of Islamic work ethics. Manag. Res. Rev. 2024, 47, 353–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhumoudi, H.; Alfarhan, K. The Role of Corporate Social Responsibility and Emotional Intelligence Towards Effective Management: Empirical Evidence from Saudi Arabia. J. Manag. Sustain. 2024, 14, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theron, M.; Cant, M.; Wiid, J. CSR communication and internal stakeholders: The overlooked market. Int. J. Res. Bus. Soc. Sci. 2024, 13, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, C.M.F.; Coelho, A.; da Ascensão Marques, A.M. Are Organizational Citizenship Behaviors for Environment (OCBEs) affected by Greenwashing? The Mediating Role of Job Satisfaction and Affective Commitment. In Proceedings of the EnANPAD 2022, Online, 21–23 December 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Situmorang, S.A. Investigating the Influence of Emotional Intelligence and Organizational Commitment on Organizational Citizenship Behavior: An Examination of the Workforce at PT XYZ. Bus. Econ. Commun. Soc. Sci. J. (BECOSS) 2024, 6, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, A. Relevance of CSR for building effective commitment of employees: A multilevel approach. J. Glob. Responsib. 2023, 14, 135–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, M.J.; Khalid, M.H. Linking corporate social responsibility to organizational commitment: The role of employee job satisfaction. J. Glob. Responsib. 2025, 16, 407–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orazalin, N.; Baydauletov, M. Corporate social responsibility strategy and corporate environmental and social performance: The moderating role of board gender diversity. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2020, 27, 1664–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casula, M.; Rangarajan, N.; Shields, P. The potential of working hypotheses for deductive exploratory re-search. Qual. Quant. 2021, 55, 1703–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hair, J.F., Jr.; Sarstedt, M.; Ringle, C.M.; Gudergan, S.P. Advanced Issues in Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bravo, R.; Buil, I.; de Chernatony, L.; Martínez, E. Managing brand identity: Effects on the employees. Int. J. Bank Mark. 2017, 35, 2–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, E.; De Chernatony, L. The effect of brand extension strategies upon brand image. J. Consum. Mark. 2004, 21, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.; Leblanc, G. Corporate image and corporate reputation in customers’ retention decisions in services. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2001, 8, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F.; Risher, J.J.; Sarstedt, M.; Ringle, C.M. When to use and how to report the results of PLS-SEM. Eur. Bus. Rev. 2019, 31, 2–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamantopoulos, A.; Sarstedt, M.; Fuchs, C.; Wilczynski, P.; Kaiser, S. Guidelines for choosing between multi-item and single-item scales for construct measurement: A predictive validity perspective. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2012, 40, 434–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, T.K.; Henseler, J. Consistent partial least squares path modeling. MIS Q. 2015, 39, 297–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jöreskog, K.G. Simultaneous factor analysis in several populations. Psychometrika 1971, 36, 409–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henseler, J.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M. A new criterion for assessing discriminant validity in variance-based structural equation modeling. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2015, 43, 115–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henseler, J.; Ringle, C.M.; Sinkovics, R.R. The use of partial least squares path modeling in international marketing. In New Challenges to International Marketing; Emerald Group Publishing Limited: Bingley, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J.F., Jr.; Hult, G.T.M.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M.; Danks, N.P.; Ray, S. Evaluation of reflective measurement models. In Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) Using R: A Workbook; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 75–90. [Google Scholar]
- Henseler, J.; Dijkstra, T.K.; Sarstedt, M.; Ringle, C.M.; Diamantopoulos, A.; Straub, D.W.; Ketchen, D.J., Jr.; Hair, J.F.; Hult, G.T.M.; Calantone, R.J. Common beliefs and reality about PLS: Comments on Rönkkö and Evermann (2013). Organ. Res. Methods 2014, 17, 182–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmueli, G.; Ray, S.; Estrada, J.M.V.; Chatla, S.B. The Elephant in the Room: Predictive Performance of PLS Models. J. Bus. Res. 2016, 69, 4552–4564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasution, M.I.; Fahmi, M.; Prayogi, M.A. The quality of small and medium enterprises performance using the structural equation model-part least square (SEM-PLS). J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1477, 052052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purwanto, A.; Sudargini, Y. Partial least squares structural squation modeling (PLS-SEM) analysis for social and management research: A literature review. J. Ind. Eng. Manag. Res. 2021, 2, 114–123. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos, H.M.; Mustafa, M.; Caspersz, D.; Raveentheran, A. Organizational support and pro-organizational behaviors in hotel family-SMEs: The role of emotional intelligence. J. Hum. Resour. Hosp. Tour. 2021, 20, 542–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouerdian, E.G.B.; Mansour, N.; Gaha, K.; Gattoussi, M. Linking emotional intelligence to turnover intention: LMX and affective organizational commitment as serial mediators. Leadersh. Organ. Dev. J. 2021, 42, 1206–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeidan, S. Empirical investigation of the relationship between emotional intelligence, organisational commitment and turnover intentions. J. Inf. Knowl. Manag. 2020, 19, 2050012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purwanto, A.; Wafa, A.; Sanjani, M.A.F. Interpersonal Communication Strategies in Building an Image of Contigency Perspective of Accommodation. Manag. Indones. J. Educ. Manag. 2023, 5, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafait, Z.; Huang, J. Exploring the nexus of emotional intelligence and university performance: An investigation through perceived organizational support and innovative work behavior. Psychol. Res. Behav. Manag. 2023, 16, 4295–4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsughayir, A. The effect of emotional intelligence on organizational commitment: Understanding the mediating role of job satisfaction. Manag. Sci. Lett. 2021, 11, 1309–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellitteri, J. Emotional Intelligence and Leadership Styles in Education. Psychol. Its Contexts/Psychol. Její Kontexty 2021, 12, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Age | Frequency | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| 20–30 | 31 | 16.85 |
| 31–35 | 65 | 35.32 |
| 36–40 | 72 | 39.13 |
| +40 | 16 | 8.70 |
| Gender | ||
| Male | 103 | 55.98 |
| Female | 81 | 44.02 |
| Education | ||
| Diploma/Bachelor | 123 | 66.85 |
| Masters/PhD | 61 | 33.15 |
| Marital Status | ||
| Married | 131 | 71.20 |
| Single | 53 | 28.80 |
| Factors | Dimensions | Indicators | Outer Loadings | Alpha | Rho A | CR | AVE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brand Image | - | BI1 | 0.741 | 0.811 | 0.788 | 0.846 | 0.711 |
| BI2 | 0.734 | ||||||
| BI3 | 0.752 | ||||||
| BI4 | 0.762 | ||||||
| BI5 | 0.733 | ||||||
| Employee Commitment | - | EC1 | 0.721 | 0.833 | 0.810 | 0.829 | 0.701 |
| EC2 | 0.725 | ||||||
| EC3 | 0.744 | ||||||
| EC4 | 0.759 | ||||||
| EC5 | 0.753 | ||||||
| CSR | Social | CSS1 | 0.762 | 0.816 | 0.801 | 0.818 | 0.674 |
| CSS2 | 0.753 | ||||||
| CSS3 | 0.733 | ||||||
| Economic | CSE4 | 0.731 | 0.814 | 0.774 | 0.805 | 0.688 | |
| CSE5 | 0.744 | ||||||
| CSE6 | 0.735 | ||||||
| Environmental | CSG7 | 0.728 | 0.807 | 0.788 | 0.806 | 0.693 | |
| CSG8 | 0.736 | ||||||
| CSG9 | 0.741 | ||||||
| Emotional Intelligence | Self-Awareness | SA1 | 0.744 | 0.811 | 0.817 | 0.807 | 0.671 |
| SA2 | 0.759 | ||||||
| SA3 | 0.747 | ||||||
| Self-Regulation | SR1 | 0.731 | 0.813 | 0.816 | 0.786 | 0.706 | |
| SR2 | 0.766 | ||||||
| SR3 | 0.712 | ||||||
| Empathy | EP1 | 0.759 | 0.794 | 0.773 | 0.771 | 0.677 | |
| EP2 | 0.763 | ||||||
| EP3 | 0.731 | ||||||
| Motivation | MT1 | 0.741 | 0.788 | 0.762 | 0.782 | 0.703 | |
| MT2 | 0.744 | ||||||
| MT3 | 0.755 | ||||||
| Social Skills | SS1 | 0.761 | 0.805 | 0.788 | 0.811 | 0.710 | |
| SS2 | 0.770 | ||||||
| SS3 | 0.748 |
| SA | SR | EP | MT | SS | CSS | CSE | CSG | BI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SR | 0.684 | - | |||||||
| EP | 0.563 | 0.572 | - | ||||||
| MT | 0.611 | 0.623 | 0.637 | - | |||||
| SS | 0.612 | 0.644 | 0.651 | 0.667 | - | ||||
| CSS | 0.622 | 0.614 | 0.650 | 0.661 | 0.677 | - | |||
| CSE | 0.549 | 0.563 | 0.613 | 0.611 | 0.594 | 0.619 | - | ||
| CSG | 0.577 | 0.544 | 0.610 | 0.579 | 0.588 | 0.579 | 0.596 | - | |
| BI | 0.572 | 0.549 | 0.589 | 0.586 | 0.603 | 0.594 | 0.547 | 0.610 | - |
| EC | 0.593 | 0.588 | 0.579 | 0.601 | 0.589 | 0.602 | 0.613 | 0.608 | 0.610 |
| Construct | Items | Convergent Validity | Weights | VIF | t-Statistics |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EI | Self-Awareness | 0.715 | 0.342 | 1.923 | 3.011 |
| Self-Regulation | 0.333 | 1.880 | 3.024 | ||
| Empathy | 0.341 | 1.865 | 3.029 | ||
| Motivation | 0.338 | 1.844 | 3.022 | ||
| Social Skills | 0.340 | 1.829 | 3.018 | ||
| CSR | Social | 0.719 | 0.337 | 1.944 | 2.814 |
| Economic | 0.344 | 1.938 | 2.822 | ||
| Environmental | 0.336 | 1.933 | 2.819 |
| Effects | Relations | β | t-Statistics | p-Value | Hypothesis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct | |||||
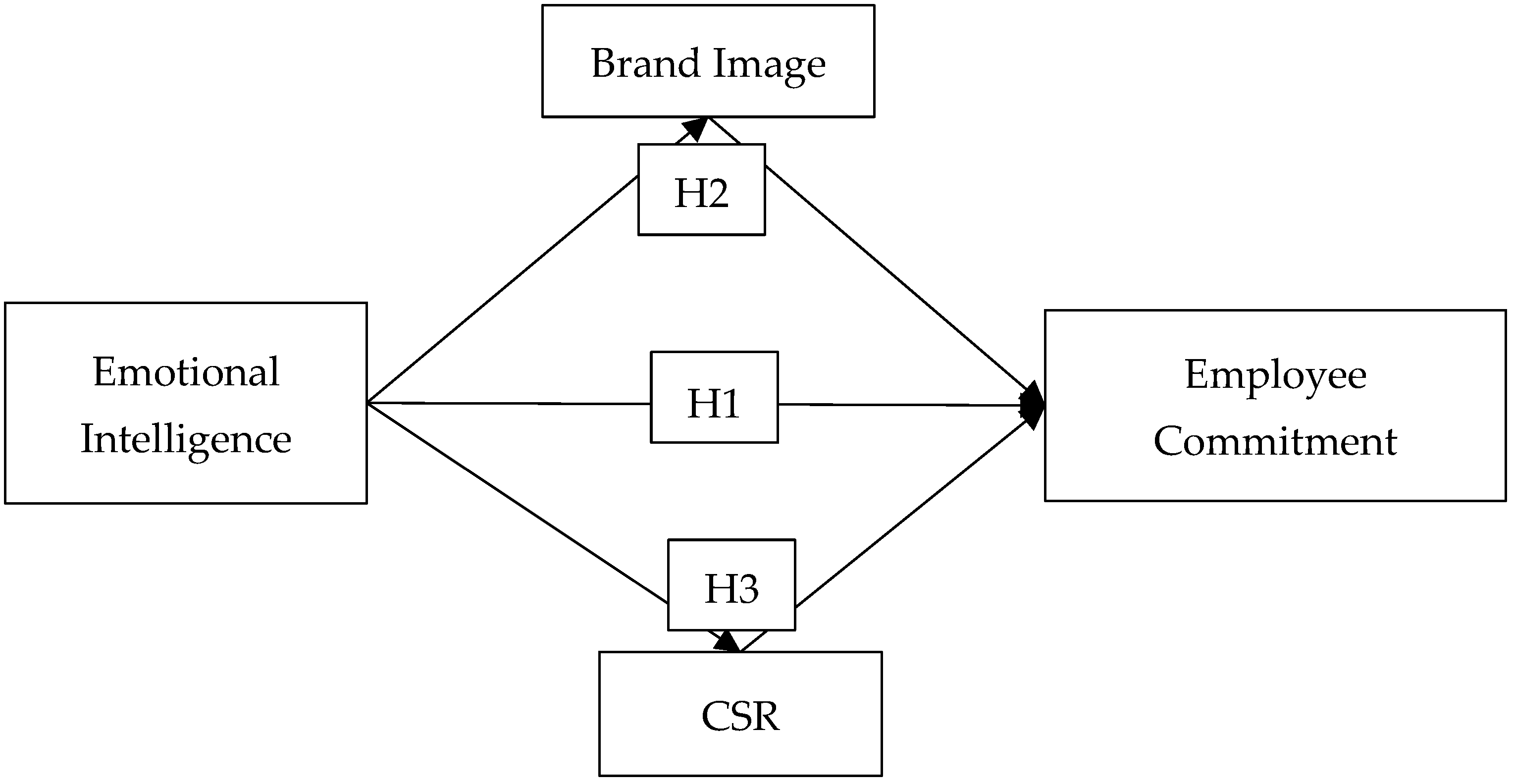
| H1 | EI → EC | 0.343 | 3.433 ** | 0.001 | Supported |
| Mediation | |||||
| H2 | EI → BI → EC | 0.307 | 2.877 * | 0.009 | Supported |
| H3 | EI → CSR → EC | 0.312 | 2.985 * | 0.009 | Supported |
| Control Variables | |||||
| Gender → EC | 0.122 | 2.114 * | |||
| Age → EC | 0.116 | 2.133 * | |||
| Education → EC | 0.119 | 2.096 * | |||
| Marital Status → EC | 0.121 | 2.122 * | |||
| R2EC = 0.729/Q2EC = 0.563/RMSE = 0.663/MAE = 0.512 R2CSR = 0.577/Q2CSR = 0.558/RMSE = 0.664/MAE = 0.538 R2BI = 0.565/Q2BI = 0.533/RMSE = 0.661/MAE = 0.564 SRMR: 0.033; NFI: 0.925; CFI: 0.981 | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tahhan, S.A. Emotional Intelligence and Employees’ Commitment: Analyzing the Role of Brand Image and Corporate Social Responsibility Among Lebanese SMEs. Sustainability 2025, 17, 9602. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219602
Tahhan SA. Emotional Intelligence and Employees’ Commitment: Analyzing the Role of Brand Image and Corporate Social Responsibility Among Lebanese SMEs. Sustainability. 2025; 17(21):9602. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219602
Chicago/Turabian StyleTahhan, Suha Ali. 2025. "Emotional Intelligence and Employees’ Commitment: Analyzing the Role of Brand Image and Corporate Social Responsibility Among Lebanese SMEs" Sustainability 17, no. 21: 9602. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219602
APA StyleTahhan, S. A. (2025). Emotional Intelligence and Employees’ Commitment: Analyzing the Role of Brand Image and Corporate Social Responsibility Among Lebanese SMEs. Sustainability, 17(21), 9602. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219602







