Ozonation of Reverse Osmosis Concentrate from Municipal Wastewater Reclamation Processes: Ozone Demand, Molecular Weight Distribution, UV/Fluorescence Characteristics, and Microalgal Growth Potential
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
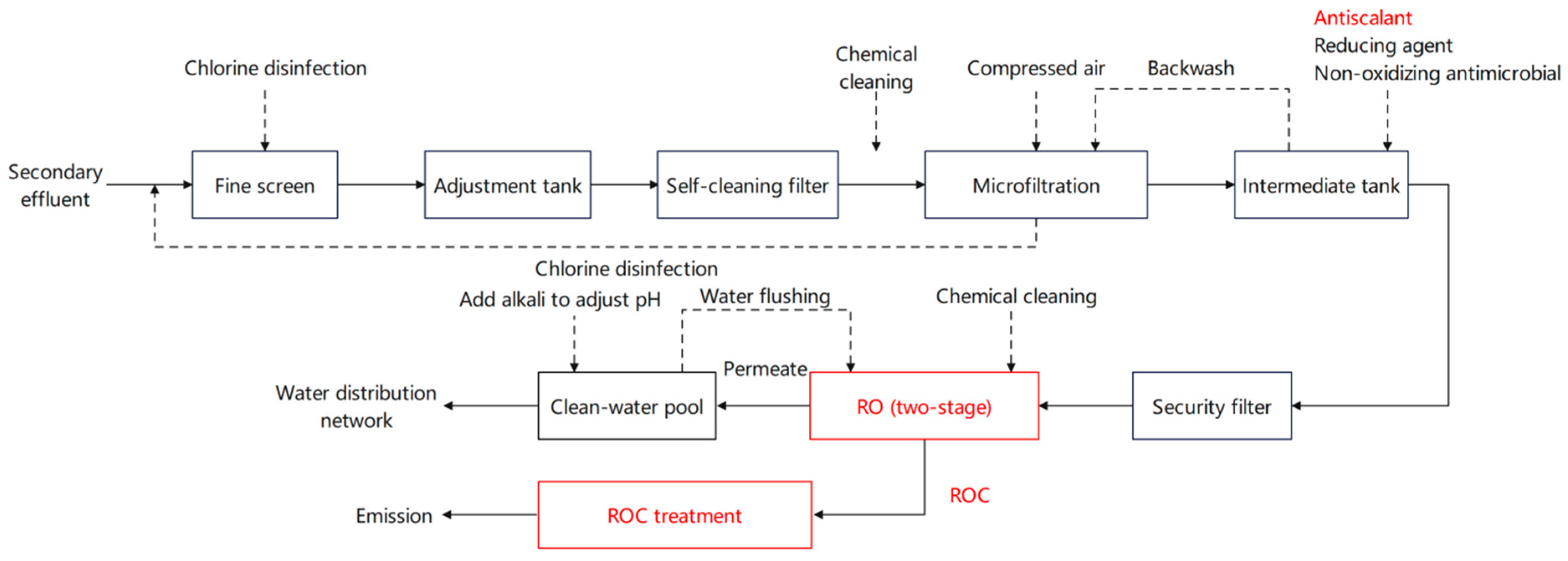
2.2. Experimental Procedure
2.2.1. Semi-Continuous Ozonation Experiment
2.2.2. Coagulation Experiment
2.2.3. Microalgae Growth Potential Experiment
2.3. Analytical Method
3. Results and Discussion
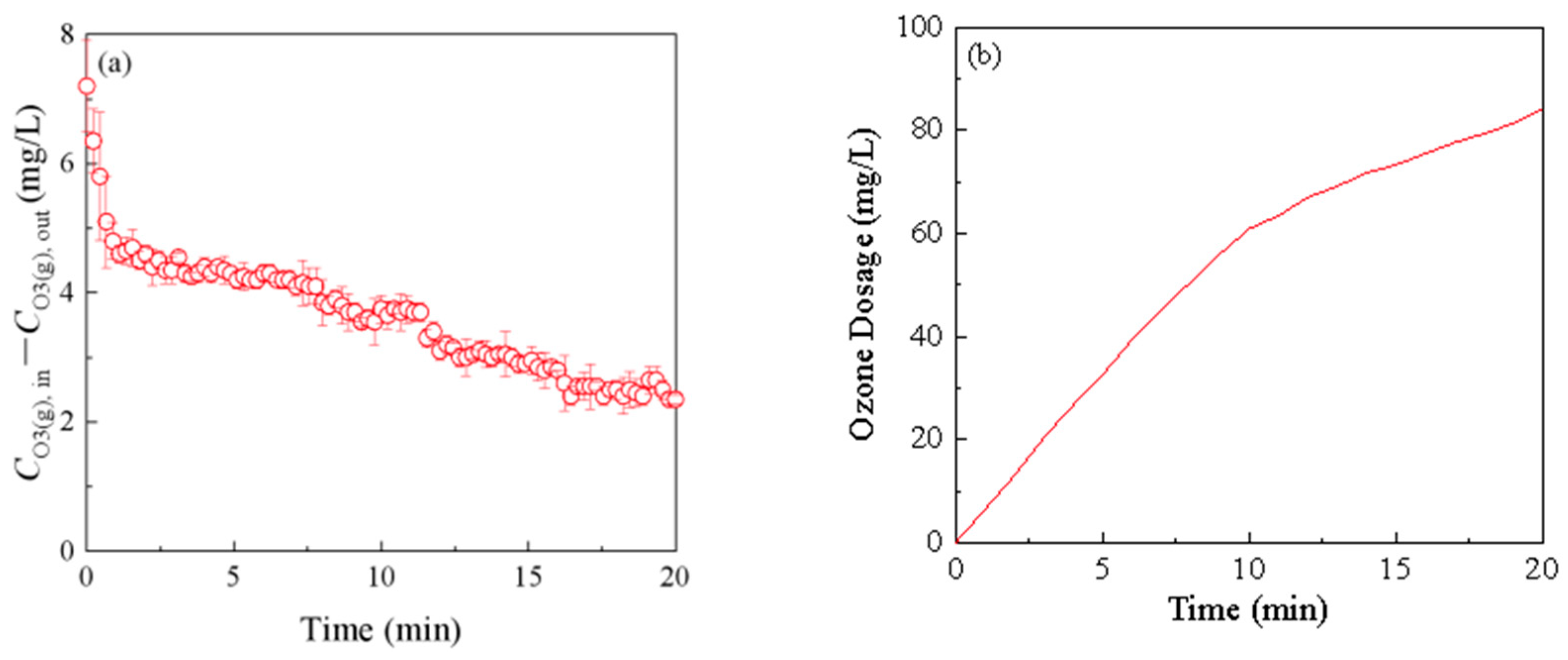
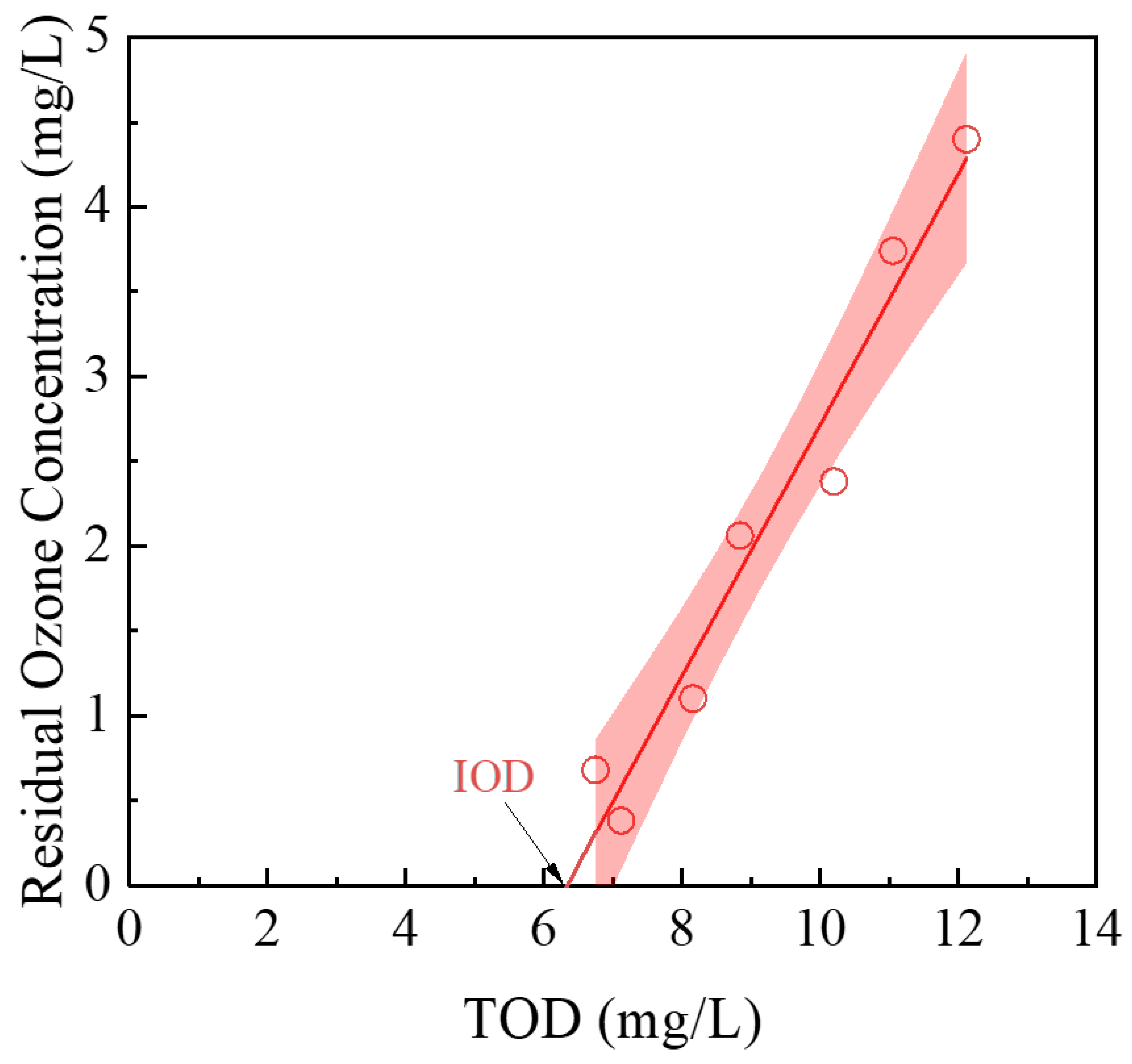
3.1. Ozone Demand of ROC
3.2. Changes in COD and BOD5
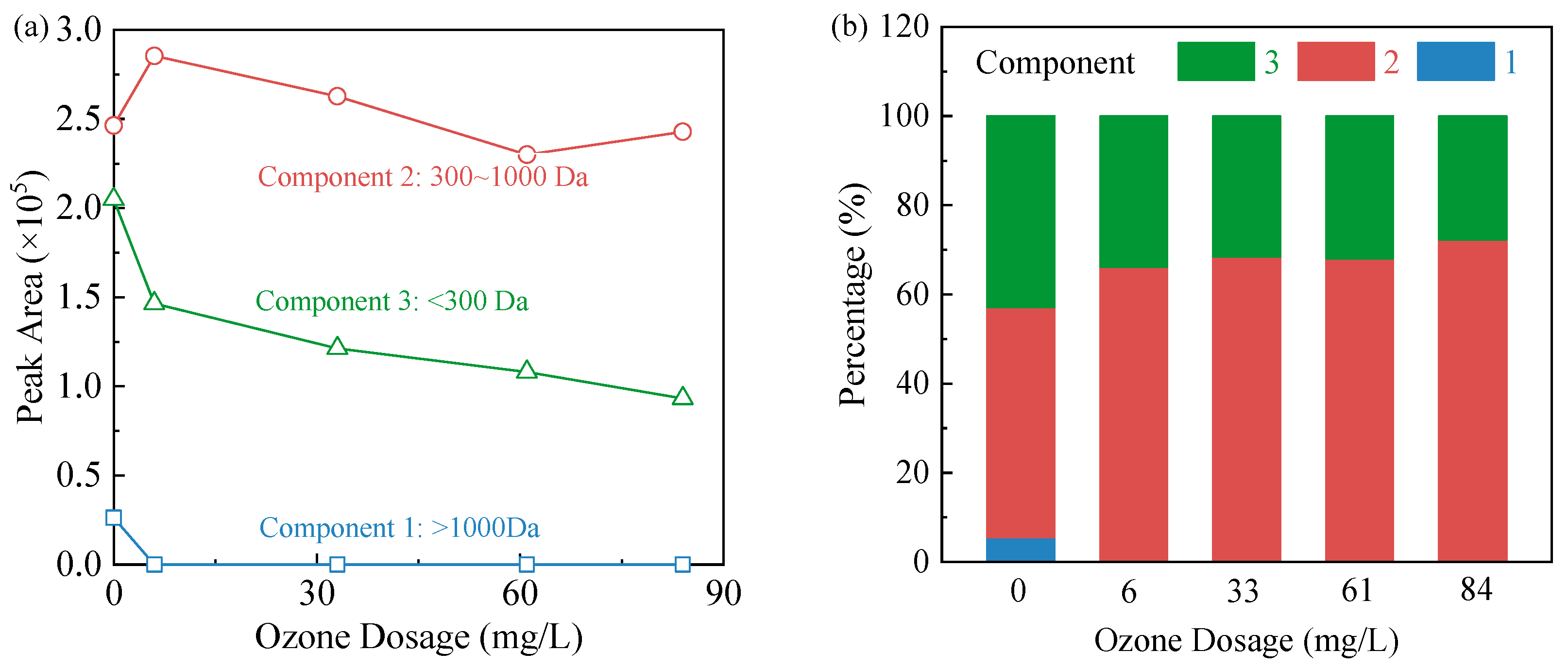
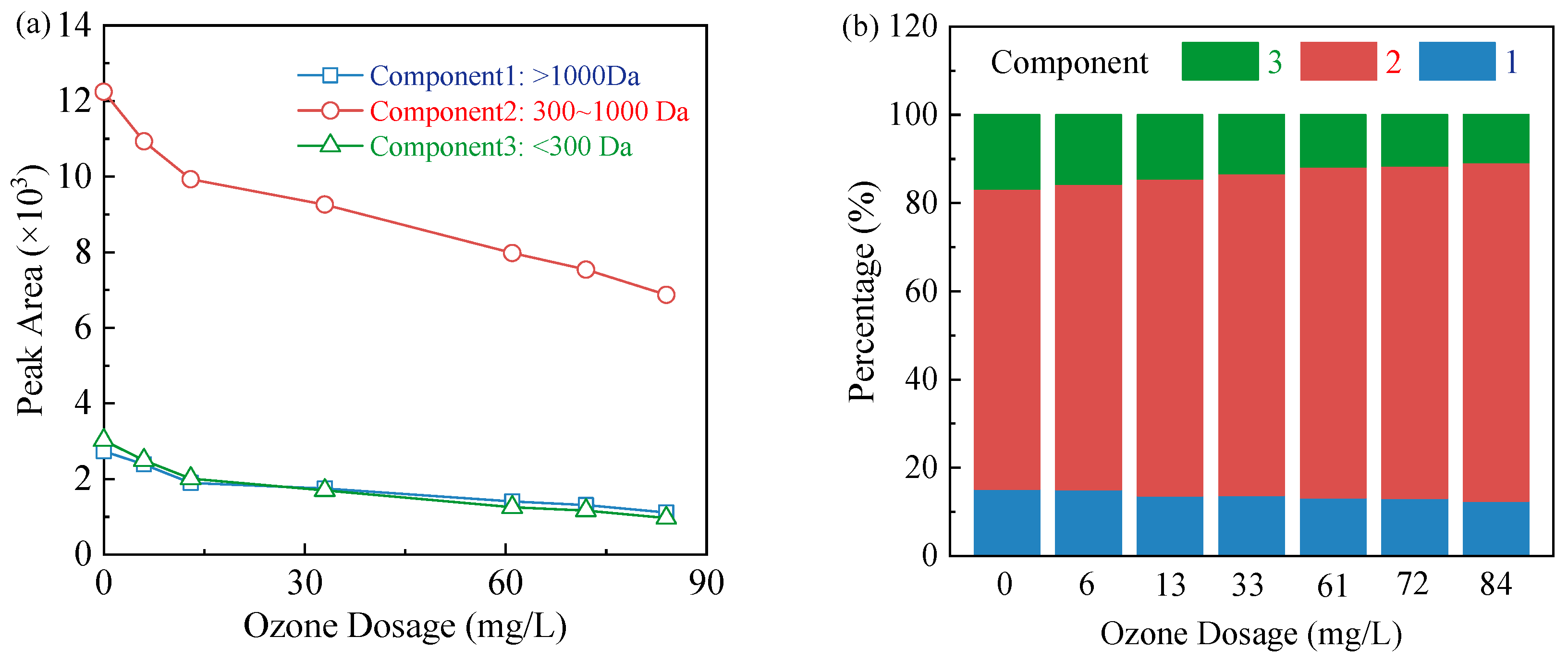
3.3. Changes in TOC and Molecular Weight Distribution of Organic Compounds
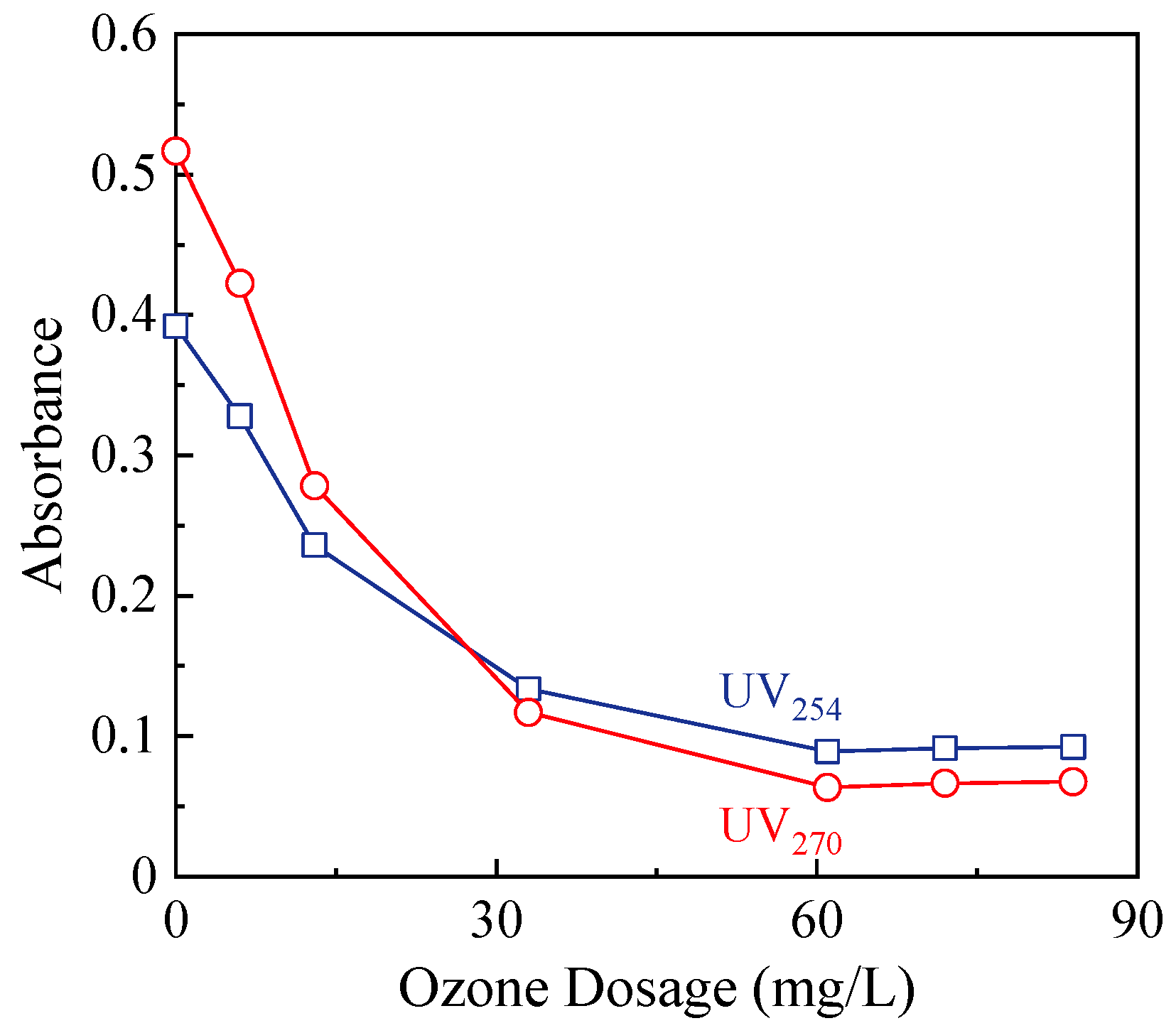
3.4. Changes in Chromophoric Organic Compounds
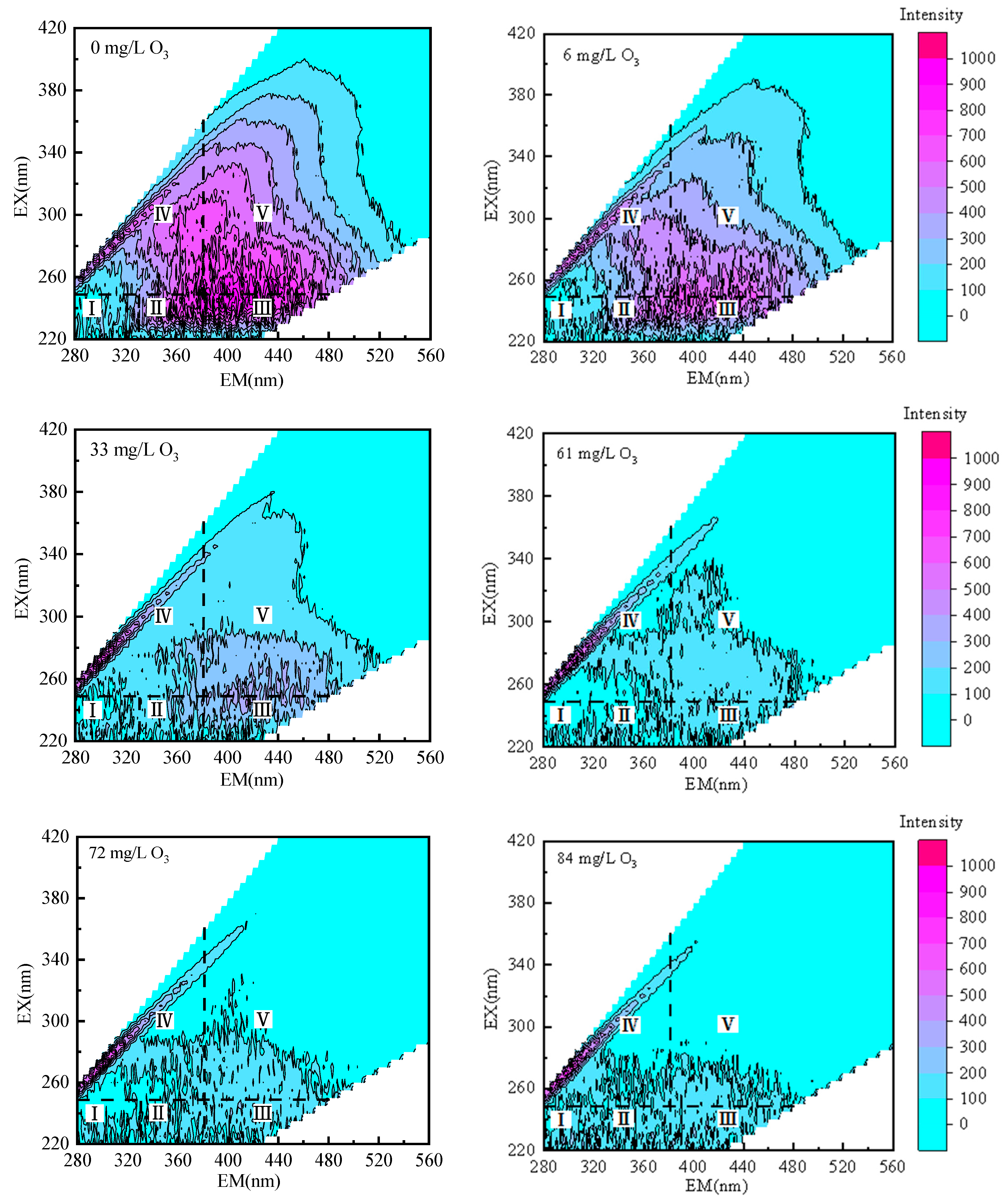
3.5. Changes in Fluorescent Organic Compounds
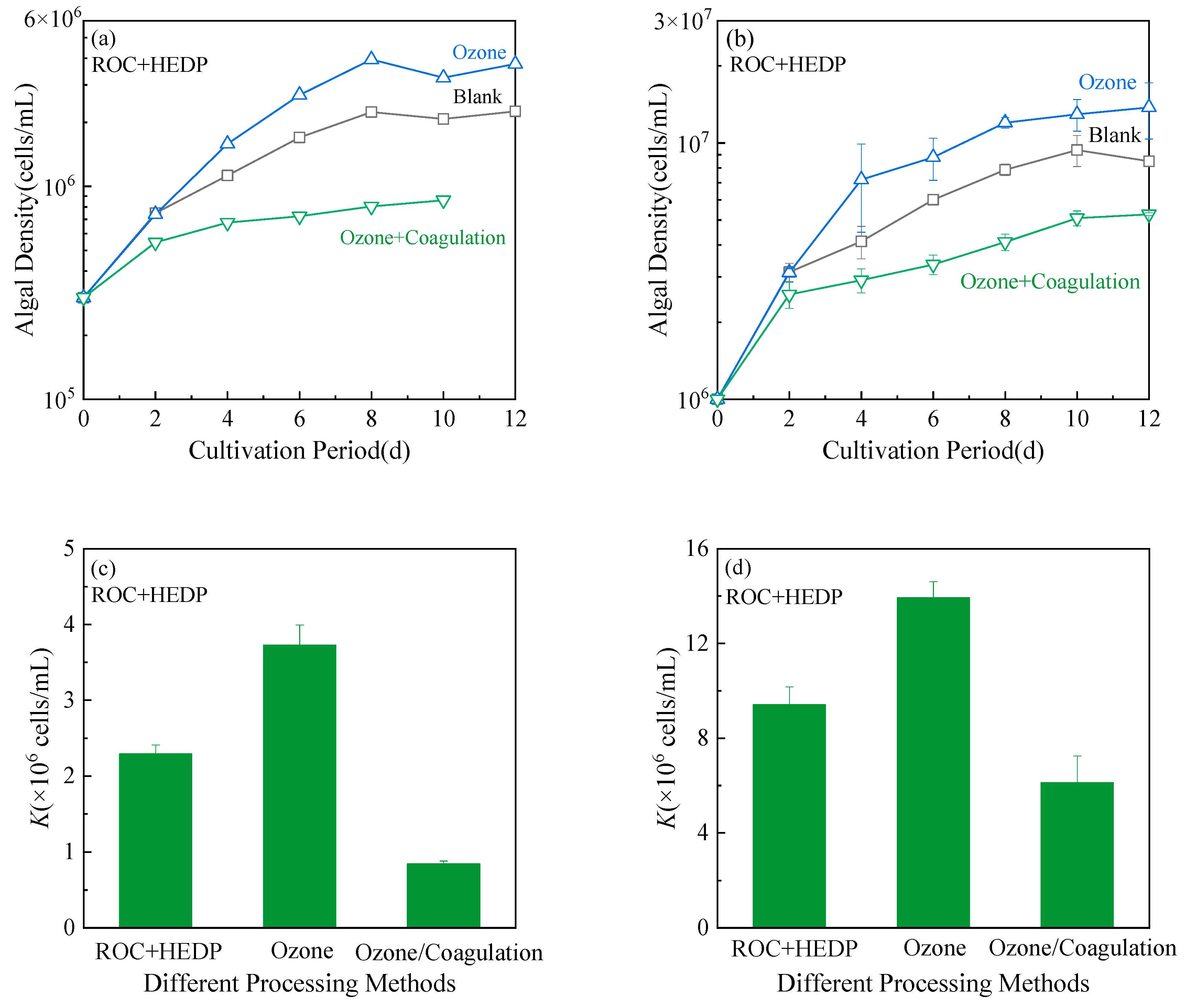
3.6. Changes in the Microalgae Growth Potential of ROC by Ozone/Coagulation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Szczuka, A.; Huang, N.; MacDonald, J.A.; Nayak, A.; Zhang, Z.; Mitch, W.A. N-Nitrosodimethylamine formation during UV/hydrogen peroxide and UV/chlorine advanced oxidation process treatment following reverse osmosis for potable reuse. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 15465–15475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Li, H.; Zhang, S.; Mi, X.; Guo, Y.; Song, Z.; Liu, Y.; Pan, H.; Wang, B.; Liu, Y.; et al. Effect of confined Mn oxides on regulating capability of activated coke for persulfate-based oxidation of a sweetener acesulfame. Water Cycle 2024, 5, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, B. Combining Ultrafiltration and Reverse Osmosis Technologies Key to Producing Pure Water for Power Plant Boilers [N/OL]. Available online: https://www.power-eng.com/emissions/combining-ultrafiltration-reverse-osmosis-technologies-key-producing-pure-water-power-plant-boilers/#gref (accessed on 24 September 2025).
- Lee, H.; Jin, Y.; Hong, S. Recent transitions in ultrapure water (UPW) technology: Rising role of reverse osmosis (RO). Desalination 2016, 399, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, T.A. Purification of landfill leachate with reverse osmosis and nanofiltration. Desalination 1998, 119, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Lisdonk, C.A.C.; van Paassen, J.A.M.; Schippers, J.C. Monitoring scaling in nanofiltration and reverse osmosis membrane systems. Desalination 2000, 132, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hege, K.; Verhaege, M.; Verstraete, W. Electro-oxidative abatement of low-salinity reverse osmosis membrane concentrates. Water Res. 2004, 38, 1550–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hege, K.; Verhaege, M.; Verstraete, W. Indirect electrochemical oxidation of reverse osmosis membrane concentrates at boron-doped diamond electrodes. Electrochem. Commun. 2002, 4, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerhoff, P.; Moon, H.; Minakata, D.; Crittenden, J. Oxidation of organics in retentates from reverse osmosis wastewater reuse facilities. Water Res. 2009, 43, 3992–3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersever, I.; Ravindran, V.; Pirbazari, M. Biological denitrification of reverse osmosis brine concentrates: I. Batch reactor and chemostat studies. J. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2007, 6, 503–518. [Google Scholar]
- Badruzzaman, M.; Oppenheimer, J.; Adham, S.; Kumar, M. Innovative beneficial reuse of reverse osmosis concentrate using bipolar membrane electrodialysis and electrochlorination processes. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 326, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajbi, F.; Hammi, H.; M’Nif, A. Reuse of RO desalination plant reject brine. J. Phase Equilibria Diffus. 2010, 31, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Curcio, E.; Al Obaidani, S.; Di Profio, G.; Fontananova, E.; Drioli, E. Membrane distillation-crystallization of seawater reverse osmosis brines. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 71, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Hu, H.-Y.; Wu, Q.-Y.; Tang, X.; Sun, Y.-X.; Shi, X.-L.; Huang, J.-J. Effects of chemical agent injections on genotoxicity of wastewater in a microfiltration-reverse osmosis membrane process for wastewater reuse. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 260, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainardis, M.; Buttazzoni, M.; De Bortoli, N.; Mion, M.; Goi, D. Evaluation of ozonation applicability to pulp and paper streams for a sustainable wastewater treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-C.; Zeng, S.-S.; Ouyang, Y.; Sang, L.; Yang, S.-Y.; Zhang, X.-Q.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Ye, J.; Xiao, M.-T.; Zhang, N. An intensified ozonation system in a tank reactor with foam block stirrer: Synthetic textile wastewater treatment and mass transfer modeling. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 257, 117909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Bai, X.; Bai, Y. Exploration and case analysis of treatment processes and reuse pathways for industrial brine wastewater in China. Water Cycle 2024, 5, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granzoto, M.R.; Seabra, I.; Malvestiti, J.A.; Cristale, J.; Dantas, R.F. Integration of ozone, UV/H2O2 and GAC in a multi-barrier treatment for secondary effluent polishing: Reuse parameters and micropollutants removal. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 759, 143498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharel, S.; Stapf, M.; Miehe, U.; Ekblad, M.; Cimbritz, M.; Falås, P.; Nilsson, J.; Sehlén, R.; Bregendahl, J.; Bester, K. Removal of pharmaceutical metabolites in wastewater ozonation including their fate in different post-treatments. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 759, 143989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Huang, Y.; Zhuo, X.; He, C.; Li, Q. Molecular-level transformation characteristics of refractory organics in landfill leachate during ozonation treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 749, 141558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Chen, Z.; Lu, Y.; Shi, Q.; Wu, Y.; Hu, H.-Y. Significant increase of assimilable organic carbon (AOC) levels in MBR effluents followed by coagulation, ozonation and combined treatments: Implications for biostability control of reclaimed water. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2021, 15, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.B.; Wang, W.L.; Huang, N.; Wu, Q.Y.; Lee, M.Y.; Hu, H.Y. 2-Phosphonobutane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid (PBTCA) degradation by ozonation: Kinetics, phosphorus transformation, anti-precipitation property changes and phosphorus removal. Water Res. 2019, 148, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-J.; Halali, M.A.; Baker, T.; Sarathy, S.; de Lannoy, C.-F. A comparative study of RO mem-brane scale inhibitors in wastewater reclamation: Antiscalants versus pH adjustment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 240, 116549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Song, D.; Chen, W.; Yang, H. Antiscalants in RO membrane scaling control. Water Res. 2020, 183, 115985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gryta, M. Polyphosphates used for membrane scaling inhibition during water desalination by membrane distillation. Desalination 2012, 285, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-P.; Singer, P.C. Inhibition of calcite crystal growth by polyphosphates. Water Res. 2005, 39, 4835–4843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Q.; Du, Y.; Hu, H. Degradation of natural organic matter by UV/chlorine oxidation: Molecular decomposition, formation of oxidation byproducts and cytotoxicity. Water Res. 2017, 124, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Jiang, X.; Ji, X.; Yin, J.; Shi, B.; Li, Y.; Qi, F. Effect of phosphorus on the performance of sulfur autotrophic denitrification. Water Cycle 2024, 5, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.; Xu, Z.; Wang, W.L.; Wang, Q.; Wu, Q.Y.; Hu, H.Y. Elimination of amino trimethylene phosphonic acid (ATMP) antiscalant in reverse osmosis concentrate using ozone: Anti-precipitation property changes and phosphorus removal. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 133027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Li, X.; Hu, H.; Su, Z. Biomass production of a Scenedesmus sp. under phosphorous-starvation cultivation condition. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 112, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Xi, J.; Huang, J.J.; Hu, H.Y. Effect of inlet ozone concentration on the performance of a micro-bubble ozonation system for inactivation of Bacillus subtilis spores. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 114, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; Zhang, F.; Lu, Y.; Hu, H.-Y. A novel model simulating reclaimed water disinfection by ozonation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 179, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HJ 828-2017; Water Quality—Determination of the Chemical Oxygen Demand-Dichromate Method. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- HJ 505-2009; Water Quality—Determination of Biochemical Oxygen Demand after 5 Days (BOD5) for Dilution and Seeding Method. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2009.
- Deng, H. Ozonation mechanism of carbamazepine and ketoprofen in RO concentrate from municipal wastewater treatment: Kinetic regimes, removal efficiency and matrix effect. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 137150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.Y.; Wang, W.L.; Du, Y.; Wu, Q.Y.; Huang, N.; Xu, Z.B.; Hu, H.Y. Comparison of UV/H2O2 and UV/PS processes for the treatment of reverse osmosis concentrate from municipal wastewater reclamation. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 388, 124260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guvenc, S.Y.; Bayat, M.E.; Can-Gueven, E.; Varank, G. Hybrid and combined electro-oxidation and peroxi-coagulation processes in effective treatment of textile reverse osmosis concentrate. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2024, 298, 120365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, F.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Lai, B. Treatment of reverse osmosis (RO) concentrate from an old landfill site by Fe0/PS/O3 process. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2017, 92, 2616–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.L.; Lee, M.Y.; Du, Y.; Zhou, T.H.; Yang, Z.W.; Wu, Q.Y.; Hu, H.Y. Understanding the influence of pre-ozonation on the formation of disinfection byproducts and cytotoxicity during post-chlorination of natural organic matter: UV absorbance and electron-donating-moiety of molecular weight fractions. Environ. Int. 2021, 157, 106793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.J.; Wu, Y.P.; Ye, B.; Wu, D.X.; Lee, M.Y.; Wu, Q.Y.; Wang, W.L. Molecular weight fraction-specific transformation of natural organic matter during hydroxyl radical and sulfate radical oxidation. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 498, 155397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Wu, Q.-Y.; Zhao, X.; Du, Y.; Huang, H.; Shi, X.-L.; Hu, H.-Y. Transformation of anti-estrogenic-activity related dissolved organic matter in secondary effluents during ozonation. Water Res. 2014, 48, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Wu, Q.Y.; Du, Y.; Yang, Y.; Hu, H.Y. Anti-estrogenic activity formation potential assessment and precursor analysis in reclaimed water during chlorination. Water Res. 2014, 48, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Zhang, H. Exploring the Reaction Mechanism for Ozone Oxidation of Petrochemical Reverse Osmosis Concentrate by Resin Adsorption Chromatography. In Proceedings of the AASRI International Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications (IEA 2015), London, UK, 27–28 June 2015; Atlantis Press: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 700–706. [Google Scholar]
- Loh, W.H.; Cai, Q.Q.; Li, R.; Jothinathan, L.; Lee, B.C.; Ng, O.H.; Guo, J.; Ong, S.L.; Hu, J.Y. Reverse osmosis concentrate treatment by microbubble ozonation-biological activated carbon process: Organics removal performance and environmental impact assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 798, 149289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Westerhoff, P.; Leenheer, J.A.; Booksh, K. Fluorescence excitation-Emission matrix regional integration to quantify spectra for dissolved organic matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 5701–5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Fang, F.; Shao, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Huang, J.; Guo, J. The biotransformation of soil phosphorus in the water level fluctuation zone could increase eutrophication in reservoirs. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 763, 142976. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Shen, S.; Xu, Y.; Guo, T.; Dai, H.; Lu, X. Application of membrane separation processes in phosphorus recovery: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 767, 144346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanjung, R.H.R.; Indrayani, E.; Agamawan, L.P.; Hamuna, B. Water quality assessment to determine the trophic state and suitability of Lake Sentani (Indonesia) for various utilisation purposes. Water Cycle 2024, 5, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.X.; Wu, Y.H.; Zhang, T.Y.; Xu, X.Q.; Dao, G.H.; Hu, H.Y. Simultaneous nitrogen, phosphorous, and hardness removal from reverse osmosis concentrate by microalgae cultivation. Water Res. 2016, 94, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.X.; Zhang, T.Y.; Dao, G.H.; Xu, Z.B.; Wu, Y.H.; Hu, H.Y. Assessment and mechanisms of microalgae growth inhibition by phosphonates: Effects of intrinsic toxicity and complexation. Water Res. 2020, 186, 116333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogard, S.; Pearce, R.; Gonzalez, R.; Yetka, K.; Bott, C. Optimizing ozone disinfection in water reuse: Controlling bromate formation and enhancing trace organic contaminant oxidation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 18499–18508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameters | Concentration (mg/L) | Parameters | Concentration (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| COD | 141 | Na+ | 285 |
| BOD5 | 29.7 | K+ | 65 |
| TOC | 41 | Ca2+ | 338 |
| Alkalinity | 607 | Mg2+ | 104 |
| Acidity | 3.8 | NH4+ | 1.2 |
| Total Nitrogen | 37 | Cl− | 652 |
| Total phosphorus | 0.5 | SO42− | 365 |
| Inorganic phosphorus | 0.3 | NO3− | 113 |
| Region | Corresponding Substance |
|---|---|
| I | Tyrosine-containing aromatic proteins |
| II | Tryptophan-containing aromatic proteins |
| III | Fulvic acid humic substances |
| IV | Aromatic proteins, soluble microbial metabolites |
| V | Humic acid-type humus |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chi, Y.; Xu, Z.; Huang, N. Ozonation of Reverse Osmosis Concentrate from Municipal Wastewater Reclamation Processes: Ozone Demand, Molecular Weight Distribution, UV/Fluorescence Characteristics, and Microalgal Growth Potential. Sustainability 2025, 17, 9564. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219564
Chi Y, Xu Z, Huang N. Ozonation of Reverse Osmosis Concentrate from Municipal Wastewater Reclamation Processes: Ozone Demand, Molecular Weight Distribution, UV/Fluorescence Characteristics, and Microalgal Growth Potential. Sustainability. 2025; 17(21):9564. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219564
Chicago/Turabian StyleChi, Yuchang, Zibin Xu, and Nan Huang. 2025. "Ozonation of Reverse Osmosis Concentrate from Municipal Wastewater Reclamation Processes: Ozone Demand, Molecular Weight Distribution, UV/Fluorescence Characteristics, and Microalgal Growth Potential" Sustainability 17, no. 21: 9564. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219564
APA StyleChi, Y., Xu, Z., & Huang, N. (2025). Ozonation of Reverse Osmosis Concentrate from Municipal Wastewater Reclamation Processes: Ozone Demand, Molecular Weight Distribution, UV/Fluorescence Characteristics, and Microalgal Growth Potential. Sustainability, 17(21), 9564. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219564









