Abstract
In the context of a complex and volatile domestic and global environment, Chinese enterprises face frequent risks of supply chain disruption that seriously hinder their operations. The rise of the digital economy offers new opportunities to strengthen supply chain resilience. Building on supply chain collaboration and value co-creation theories, this study conceptualizes supply chain collaboration through three dimensions, namely information collaboration, governance collaboration, and innovation collaboration, and explores their role in enhancing resilience. Using panel data of Chinese A-share listed firms from 2011 to 2023, this study investigates the impact of focal firm digitalization on supply chain resilience and its underlying mechanisms. The results indicate that focal firm digitalization generates significant backward spillover effects, enhancing the resilience of its upstream suppliers. Although its positive influence on supply chain stability (measured by supply chain demand and supply fluctuations) is not statistically significant, it substantially enhances recovery (measured by supply chain efficiency) and adaptability (measured by supplier innovation). Mechanism analysis further reveals that digitalization strengthens supply chain collaboration through information, governance, and innovation channels, thereby reinforcing resilience. Moreover, the positive effects are heterogeneous, varying with industry competition intensity, the closeness of upstream–downstream relationships, and suppliers’ regional resource endowments. These findings highlight the need to design digitalization strategies centered on focal firm leadership and upstream–downstream collaboration, thereby advancing both resilience improvement and collaborative mechanism development through differentiated and targeted approaches.
1. Introduction
Since the Fifth Meeting of the Central Financial and Economic Affairs Commission in 2019, the strategic call to “strengthen the resilience of industrial and supply chains and advance their modernization” has been repeatedly emphasized in China’s national security strategy and reaffirmed in the Report to the 20th National Congress of the Communist Party of China. Enhancing industrial and supply chain resilience is not only a core driving force for China’s modernization and high-quality development but also a key foundation for ensuring economic stability in an increasingly complex domestic and international environment [1]. Although China has built a diversified and internationalized industrial and supply chain network, it still faces multiple challenges under current turbulence. Geopolitical tensions, technological bottlenecks, and the risk of being locked into low-value segments frequently expose Chinese enterprises to supply chain disruptions and shortages [2]. Against this backdrop, the rapid development of the digital economy provides a breakthrough for strengthening supply chain resilience. Digital technologies represented by big data, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence, characterized by pervasiveness, connectivity, and externalities, are reshaping the organizational models and operating logic of supply chains. Enterprise digitalization not only improves internal efficiency but also breaks down information barriers and reconfigures collaboration rules, thereby driving supply chains toward greater resilience and efficiency [3].
Within supply chain networks, focal firms typically occupy central positions with strong resource integration and network control capabilities (for example, core manufacturers like Huawei or leading retailers like Alibaba). As coordinative hubs, focal firms influence upstream and downstream decisions and collaboration modes by setting collaborative rules, allocating resources, and directing information flows [4]. Focusing on focal firm digitalization is therefore particularly meaningful. On the one hand, their hub position enables focal firms to generate backward spillover effects, encouraging upstream suppliers to adopt digital technologies, adjust production processes, and enhance capabilities [5]. On the other hand, as key orchestrators of resilience building, their digitalization practices exert direct and far-reaching impacts on the overall risk resistance, recovery efficiency, and adaptive potential of supply chains [6]. However, existing research has largely overlooked how digital transformation at the focal firm level affects the resilience of its upstream partners through such spillover channels. Empirical studies that quantify this relationship using firm-level panel data remain scarce. To fill this gap, the present study centers on a core research question: to examine in depth the impact of focal firm digitalization on supply chain resilience and to uncover the underlying mechanisms driving this relationship, with the aim of providing theoretical foundations and practical guidance for enhancing supply chain resilience in the context of the digital economy.
To address this gap, this study is theoretically grounded in supply chain collaboration theory and value co-creation theory. Supply chain collaboration theory emphasizes that firms achieve resource integration and risk sharing through multi-dimensional coordination mechanisms, thereby providing a theoretical foundation for understanding how digitalization fosters inter-organizational collaboration within supply networks. Value co-creation theory, on the other hand, focuses on how multiple actors jointly create value through interaction and knowledge sharing within open networks, offering theoretical support for analyzing the cross-organizational transmission mechanisms through which digitalization enhances supply chain resilience.
On this basis, this study conceptualizes supply chain collaboration as comprising three interrelated and progressive dimensions—information collaboration, governance collaboration, and innovation collaboration. Then, using supply chain data disclosed by Chinese A-share listed firms from 2011 to 2023, the study empirically investigates the impact of focal firm digitalization on supply chain resilience and its underlying mechanisms from the perspective of backward spillover empowerment effects within the framework of supply chain collaboration. The findings show that focal firm digitalization significantly enhances supply chain resilience, particularly by improving recovery and adaptability. Mechanism tests further reveal that focal firm digitalization strengthens supply chain resilience by reinforcing supply chain collaboration across information, governance, and innovation dimensions, thereby generating backward spillover effects. Heterogeneity analysis indicates that these effects are more pronounced under conditions of low industry competition intensity, high closeness of upstream–downstream relationships, and weaker suppliers’ regional resource endowments.
Compared with existing research, the contributions of this paper are threefold.
First, this study expands the analytical boundary beyond the firm level. Existing literature mainly focuses on the internal effects of enterprise digitalization [7,8,9], emphasizing its role in enhancing operational efficiency [7], governance quality [8], and innovation capability [9]. However, the inherent permeability, interconnectivity, and externality of digital technologies suggest that their impacts are not confined within organizational boundaries. Instead, digitalization can transmit across vertical supply chain linkages, influencing upstream and downstream operations. Nevertheless, there is a lack of empirical studies that quantitatively examine the relationship between focal firm digitalization and supply chain resilience using firm-level panel data. By incorporating a backward spillover perspective, this study constructs a “digitalization–resilience” analytical framework and provides the first firm-level empirical test of how focal firm digitalization enhances supply chain resilience, thereby broadening the theoretical understanding of cross-organizational digital transformation effects.
Second, this study deepens the theoretical understanding of collaborative mechanisms. Previous studies have primarily examined the antecedents of supply chain resilience [10,11,12,13]. Yet, how digitalization functions through inter-firm collaboration mechanisms remains insufficiently explained. In fact, digital technologies inherently possess collaborative attributes, enabling digitalization to strengthen supply chain resilience through multi-dimensional dynamic linkages such as information sharing, process coordination, and joint risk management. However, existing literature still lacks a systematic analytical framework that captures these multi-level collaborative processes. To address this gap, this study conceptualizes supply chain collaboration as comprising three progressively interrelated dimensions—information collaboration, governance collaboration, and innovation collaboration—and empirically demonstrates how digitalization enhances resilience by reinforcing these dimensions. This approach enriches the theoretical explanation of digital empowerment mechanisms and provides a structured framework for understanding the collaborative pathways through which digitalization fosters supply chain resilience.
Third, this study extends the analysis of contextual heterogeneity. Few studies have examined whether the effects of focal firm digitalization on supply chain resilience vary across different contexts. By systematically testing heterogeneity across industry competition intensity, the closeness of upstream–downstream relationships, and suppliers’ regional resource endowments, this study provides novel evidence on the boundary conditions of digital empowerment effects. The results highlight the specific scenarios in which these effects are most significant, offering new theoretical and practical insights for tailoring digitalization strategies at both firm and policy levels.
The remainder of this paper is structured as follows. Section 2 provides a literature review on firm digitalization and supply chain resilience. Section 3 presents the theoretical framework and research hypotheses. Section 4 introduces the research methodology, including the variables, data sources, and construction of the empirical regression models. Section 5 reports and discusses the empirical results. Finally, Section 6 concludes the study and offers managerial and policy implications.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Firm Digitalization
Existing studies widely acknowledge that firm digitalization not only reshapes firms’ internal operating logic but also exerts significant external influences through inter-firm and regional networks. Overall, these impacts can be categorized into internal and external effects.
At the internal level, prior research primarily examines how digital transformation enhances operational efficiency, governance effectiveness, and innovation capability. Digital technologies enable systemic restructuring that improves operational efficiency and cash flow management, optimizes resource allocation, and increases capital returns, thereby boosting firm performance across multiple dimensions [7]. Moreover, digitalization mitigates information asymmetry, reduces transaction costs, and enhances transparency, which helps optimize corporate governance structures, ease financing constraints, and strengthen productivity and innovation performance [8]. Furthermore, by transcending temporal and organizational boundaries, digital technologies enable firms to shift from supply-driven models toward demand-oriented, customer-centric value creation [9]. Collectively, these studies establish a robust theoretical foundation for understanding the internal benefits of digitalization.
In contrast, the external impacts of enterprise digitalization remain relatively underexplored. Limited evidence suggests that digital transformation generates spillover effects across supply chains, industrial ecosystems, and regional economies. At the supply chain level, digitalization enhances information coordination, resource sharing, and dynamic resource reconfiguration among upstream and downstream partners, improving environmental transparency and governance [14]. At the industrial level, digitalization reshapes competitive structures as data and algorithms replace traditional production factors, driving firms toward platform-based and ecosystem-oriented collaboration [15]. At the regional level, the agglomeration of digitalized firms facilitates regional innovation ecosystems and digital infrastructure development, fostering high-quality, digitally integrated growth [2].
In summary, although prior studies have provided extensive evidence on the internal efficiency gains from digitalization, the mechanisms through which digitalization generates external spillover effects across supply chain networks remain underexplored.
2.2. Supply Chain Resilience
Research on supply chain resilience has generally focused on two key dimensions, internal firm capabilities and external environmental factors.
From the internal perspective, firm-specific resources and capabilities constitute the foundation for building resilience. Dynamic resource coordination, flexible allocation, and efficient intra-chain collaboration enable firms to mitigate disruptions and recover from crises [10]. In the digital economy context, the quality of information sharing is recognized as a key endogenous driver of supply chain performance and risk mitigation. Enhanced information exchange improves coordination and responsiveness, thereby strengthening the system’s adaptive capacity [11].
From the external perspective, resilience is strongly shaped by systemic risks in the broader environment, such as geopolitical tensions and global value chain restructuring. Institutional heterogeneity increases the risk of supply disruptions [16], cross-cultural barriers cause relational frictions [17], and macroeconomic volatility forces supply chains to maintain dynamic adaptability [12].
Overall, supply chain resilience emerges from the interaction between internal capabilities and external pressures, emphasizing both the capacity to absorb shocks and the agility to recover and adapt.
2.3. Firm Digitalization and Supply Chain Resilience
Recent research has increasingly examined the relationship between enterprise digitalization and supply chain resilience; however, the mechanisms linking the two remain conceptually fragmented and empirically underexplored. Existing studies can generally be divided into two main perspectives, namely efficiency enhancement and spillover transmission.
From the perspective of efficiency enhancement, digital technologies such as big data analytics, cloud computing, and the Internet of Things have been shown to improve supply chain transparency, optimize resource allocation, and reduce transaction costs, thereby enhancing operational stability and responsiveness [18,19]. Nevertheless, most of these studies treat efficiency and resilience as independent outcomes. The theoretical and empirical pathways through which improvements in operational efficiency translate into greater supply chain resilience have not been sufficiently clarified.
From the perspective of spillover transmission, a small but growing body of research highlights the network externalities of digitalization. The digital transformation of focal firms can stimulate innovation among upstream and downstream partners through shared platforms, open data interfaces, and cross-organizational information collaboration [20,21]. However, few studies have extended these insights to the domain of supply chain resilience, particularly regarding backward spillover effects in which the digital capabilities of focal firms diffuse upstream to suppliers. How such spillover mechanisms enable suppliers to strengthen their adaptive capacity and recovery performance remains an open question.
Therefore, the relationship between focal firm digitalization and supply chain resilience, particularly in relation to cross-organizational spillover mechanisms, has not yet been systematically quantified or empirically validated.
2.4. Literature Synthesis and Research Gaps
Although prior studies have offered valuable insights into enterprise digitalization and supply chain resilience, several critical research gaps remain to be addressed.
First, existing research primarily focuses on the internal impacts of digital transformation while overlooking the vertical spillover effects transmitted through supply chain linkages. In particular, the backward spillovers from focal firms to upstream suppliers have received limited attention. To date, there has been no firm-level panel study that systematically quantifies the relationship between focal firm digitalization and supply chain resilience.
Second, although prior work has identified a range of antecedents of resilience, few studies have examined how focal firm digitalization enhances resilience through specific collaborative mechanisms. Mechanisms such as information collaboration, governance collaboration, and innovation collaboration have not been fully incorporated into an integrated analytical framework. Consequently, the transmission pathways remain conceptually ambiguous and empirically underexplored.
Third, the literature has paid insufficient attention to contextual heterogeneity, particularly regarding whether and how the digital empowerment effect varies across different environmental and relational conditions. Factors such as industry competition intensity, the closeness of supply chain relationships, and the regional resource endowment of suppliers may influence the strength of this effect, yet these contingencies remain largely unexamined.
To address these gaps, the present study adopts a backward spillover empowerment perspective, grounded in the theoretical foundations of supply chain collaboration and value co-creation. This perspective provides an integrated analytical framework for systematically examining the cross-organizational mechanisms and boundary conditions through which focal firm digitalization enhances supply chain resilience. By doing so, the study extends the theoretical understanding of digital transformation from the intra-organizational to the inter-organizational level and offers empirical evidence and practical insights for enhancing supply chain resilience in the digital economy era.
3. Theoretical Framework and Hypotheses Development
3.1. Theoretical Framework
The supply chain collaboration theory provides a foundational framework for understanding the operating logic of supply chains [15]. It posits that the supply chain, as a value-creation network, achieves efficiency through systemic collaboration that mitigates node discreteness and generates “collaborative effects.” The essence of such effects lies in interactive linkages among stakeholders, and promoting upstream–downstream collaboration is the core pathway to strengthen these effects [22].
The value co-creation theory further enriches this framework. Grounded in service-dominant logic, it emphasizes that in the diverse value co-creation networks built around customer demand by downstream firms, a shared value proposition provides the basis for mutual reliance and interaction. However, the existence of conflicting individual interests necessitates the establishment of collaborative mechanisms. Value creation, in this sense, is a process of collaborative co-creation through information exchange, service provision, and resource integration, wherein all participants share responsibilities for resource orchestration and service exchange [23]. This perspective closely echoes the central proposition of supply chain collaboration theory, namely that “collaboration creates additional value.”
Empowerment theory further elucidates how digitalization fosters collaborative mechanisms within supply chains. Structural empowerment, achieved through optimized organizational design, resource allocation, and process management, strengthens information transparency and communication efficiency, builds trust and coordination mechanisms, and promotes joint learning and innovation among partners [24]. These processes correspond to the development of information, governance, and innovation collaboration, thereby reinforcing inter-firm linkages and ultimately enhancing the cohesion, stability, and competitiveness of supply chains.
Building on these theoretical foundations, this study defines supply chain collaboration as a process in which all actors within the network, guided by the common value proposition of maximizing overall supply chain benefits and satisfying end-customer needs, share and integrate information, knowledge, and experience to sustain, consolidate, and strengthen interactive linkage effects among stakeholders [25]. The essence of this concept lies in the dynamic reinforcement of these linkages, which can be decomposed into three progressive dimensions.
First, information collaboration forms the foundation of supply chain collaboration. Its essence lies in promoting information transparency, sharing, and efficient transmission, which together reduce information asymmetry between upstream and downstream firms and create the preconditions for building trust and maintaining stable cooperative relationships. According to signaling theory and social capital theory, the authenticity and symmetry of information are key determinants of inter-firm trust. Only when information flows smoothly, transparently, and credibly can governance mechanisms among supply chain members operate effectively [26].
Second, governance collaboration develops on the basis of stable information sharing and represents an institutionalized form of cooperation. Through trust building, joint decision-making, risk sharing, and benefit alignment, supply chain members can achieve coordination and constraint balance even in the presence of incomplete contracts [27]. From the perspective of transaction cost theory, effective governance mechanisms depend on adequate information support and communication. In turn, governance collaboration enhances resource allocation efficiency and cooperative stability, thereby creating a sound institutional environment for sustained innovative collaboration.
Third, innovation collaboration constitutes the advanced and dynamic stage of supply chain collaboration. The trust and institutional foundations established through governance collaboration enable firms within the supply chain to engage in knowledge sharing, technological cooperation, and joint research and development while mitigating opportunism and coordination costs [28]. Drawing on the knowledge-based view and dynamic capability theory, innovation collaboration relies not only on information sharing and governance-based trust mechanisms but also on continuous learning and knowledge integration, which collectively drive the self-evolution and resilience enhancement of the supply chain [29].
3.2. Hypotheses Development
3.2.1. Focal Firm Digitalization and Supply Chain Resilience
Supply chain resilience refers to the comprehensive capability of a supply chain system to withstand external shocks, rapidly restore stability, and achieve structural optimization through resource integration, information sharing, and collaborative coordination among upstream and downstream firms in a complex and dynamic environment [2]. Its core connotations can be divided into three dimensions: stability, recovery, and adaptability, which together capture the staged characteristics of resilience capacity. Stability represents the foundational ability of the supply chain to maintain its structure and operational rhythm under normal conditions and initial shocks, thereby defining the system’s “risk tolerance threshold” [19]. Recovery denotes the critical ability to swiftly adjust and return to a stable state after disruptions, reflecting the “dynamic response efficiency” of the system [30]. Adaptability (evolutionary capacity) emphasizes the ability to overcome path dependence and upgrade structural configurations during long-term adaptation, determining the “sustainable improvement potential” of resilience. Together, these three dimensions form a complete resilience chain that progresses from passive defense to proactive optimization [26].
Specifically, focal firm digitalization generates backward spillover effects on supply chain resilience through three pathways.
Stability dimension. Focal firms empower upstream suppliers to enhance operational stability by building real-time information-sharing and joint risk-sensing mechanisms through digital platforms. By opening access to critical data interfaces and early-warning tools, they reduce operational fluctuations caused by information asymmetry and improve suppliers’ precision in risk identification and response [20]. Furthermore, digitalization expands supplier selection, reduces transaction switching costs, and facilitates the construction of more resilient network structures, thereby mitigating the impact of single-node failures and strengthening the overall system’s disturbance resistance [31]. However, this process may also be constrained by factors such as high technological investment costs, information security risks, and increased system dependence, which could partially weaken the positive impact of digitalization on supply chain stability [32].
Recovery dimension. Through organizational restructuring and real-time data-sharing mechanisms, focal firms improve supply chain resource integration efficiency and synchronize demand fluctuations and inventory dynamics with upstream suppliers. This breaks information silos, alleviates the bullwhip effect, and enhances supply–demand coordination accuracy [33]. At the same time, focal firms employ technologies such as digital twins and intelligent decision-making to improve their adaptive capacity, while diffusing these digital tools upstream. By co-developing blockchain-enabled risk tracing and recovery coordination mechanisms, they accelerate production adjustments and resource reallocation after disruptions, thus shortening the restoration cycle of the entire supply chain [4].
Evolutionary dimension. Focal firm digitalization disrupts path dependence in traditional linear collaboration and drives supplier development through knowledge spillovers and technological feedback [34]. By simultaneously exerting reverse pressure (e.g., raising collaboration standards) and providing positive resource-sharing (e.g., data and technical support) [13], focal firms enable suppliers to overcome technological and managerial inertia, cultivate continuous innovation capabilities, and achieve the transition from passive adaptation to proactive evolution.
These three dimensions jointly reinforce one another and contribute to the overall enhancement of supply chain resilience. Based on this reasoning, this study proposes the following hypothesis.
H1:
Focal firm digitalization generates backward spillover effects that empower upstream suppliers to enhance their operational performance, thereby improving overall supply chain resilience.
H1a:
The backward spillover effects generated by focal firm digitalization enhance the stability dimension of supply chain resilience.
H1b:
Focal firm digitalization, through backward spillover effects, significantly strengthens the recovery dimension of supply chain resilience.
H1c:
Under the backward spillover effects of focal firm digitalization, the adaptability (evolutionary capacity) dimension of supply chain resilience is effectively improved.
3.2.2. Focal Firm Digitalization, Supply Chain Collaboration, and Supply Chain Resilience
- Information Collaboration
According to information asymmetry theory, the efficiency of market transactions depends on transparent transmission and symmetric distribution of information [35]. Focal firm digitalization serves as a core driving force in breaking information barriers within supply chains and promoting information collaboration. By restructuring the logic of information flows through technological empowerment, it fundamentally alleviates the problem of information asymmetry in traditional supply chain linkages [26].
From the perspective of the information effect, focal firm digitalization enhances supply chain information collaboration in several ways. First, relying on digital technologies such as big data and cloud computing, focal firms can accurately capture market demand and consumer preferences, and share this information with upstream and downstream firms in real time via open platforms. This reduces risks of distortion in information transmission and lowers supply–demand matching costs, while opening inter-organizational information channels and transforming information flows from “delayed and fragmented” to “real-time and symmetric” [36]. Second, real-time interactions of supply–demand information mitigate the bullwhip effect, breaking the inefficient cycle of “forecast deviations–capacity redundancy–resource waste,” thereby establishing an efficiency foundation for information collaboration [37]. Third, the digital integration and synchronization of end-consumer data enable upstream suppliers to respond precisely to demand based on clear standards, reducing resource misallocation caused by ambiguous information [38].
From the perspective of the reverse pressure effect, focal firms leverage technologies such as blockchain and the industrial internet to improve the traceability and monitoring of information along the supply chain. This not only solves tracking difficulties arising from chain complexity but also provides an effective supervisory channel for all stakeholders [21]. Moreover, technology-enabled supervisory mechanisms compel upstream suppliers to disclose critical information, including production processes, quality control, and environmental compliance. This drives the transition of supply chain information from “closed and fragmented” to “transparent and shared,” thereby fostering a governance pattern based on information symmetry [39]. In addition, digital technologies foster industrial integration and cross-sectoral collaboration, requiring upstream suppliers to participate in multidimensional assessments grounded in information sharing. This further incentivizes transparency and strengthens collaboration willingness, promoting supply chain information collaboration [40].
Focal firm digitalization promotes supply chain information collaboration, which contributes to resilience in multiple ways. On the one hand, by alleviating information asymmetry, it reduces operational fluctuations caused by supply–demand mismatches and decision delays. Upstream suppliers, empowered by real-time information sharing, can optimize procurement, production, and inventory management, thereby lowering the risk of cascading failures and providing a stable foundation for supply chain operations [41]. On the other hand, when disruptions occur, the transparent and shared information networks established through collaboration become a core mechanism for rapid response. Firms can quickly locate risk sources, identify alternative resources, and, by leveraging digital twins and intelligent decision-making, accelerate resource reallocation and process adjustments. This significantly shortens the recovery cycle and improves post-disruption recovery efficiency [42]. From a long-term perspective, information collaboration facilitates the transition of supply chains from passive responses to proactive evolution. By sharing technological knowledge and market insights, firms form collaborative innovation networks that support suppliers in focusing on R&D and green transformation. At the same time, information transparency strengthens the trust foundation, promotes positive ecosystem interactions, enhances resource integration efficiency, and improves the capacity to jointly cope with long-term challenges. This drives continuous optimization and functional upgrading of supply chain structures, ultimately improving supply chain resilience [43].
Based on the above, this study proposes the following hypothesis.
H2:
Focal firm digitalization enhances supply chain resilience by promoting upstream–downstream information collaboration and strengthening collaborative effects within supply chains, ultimately improving overall supply chain resilience.
- 2.
- Governance Collaboration
According to social reproduction theory, improving the effectiveness of supply chain collaborative governance is a core prerequisite for ensuring the smooth functioning of social reproduction processes [44]. Focal firm digitalization promotes this process through technological empowerment and mechanism reconstruction across three dimensions: network connections, information interactions, and structural forms. Its underlying logic lies in overcoming traditional barriers to collaboration with digital means, thereby reshaping the foundational operating logic and efficiency base of supply chain collaboration [45].
From the perspective of network connections, focal firm digitalization significantly lowers the technical and economic barriers for firms to access industrial internet platforms. Through the positive feedback mechanism implied by Metcalfe’s Law, the scale of participating firms continuously expands. By sharing data resources, standardized interfaces, and collaborative tools, individual firms can reduce redundant investments, achieve economies of scale, and realize value co-creation, thus strengthening cohesion and transforming upstream–downstream enterprises from fragmented cooperation into tightly connected network communities [46].
From the perspective of information interactions, digital technologies establish efficient communication channels and digital-twin-based mechanisms for information transparency. These not only break down information silos among firms but also reduce technical barriers to knowledge integration. As a result, supply chain nodes can capture environmental signals in real time and coordinate responses accordingly, significantly improving the timeliness and accuracy of information sharing and providing a solid data foundation for cross-organizational collaborative decision-making [44].
From the perspective of structural forms, digitalization drives the transformation of traditional linear supply chains into platform-based ecosystems. Open architectures not only broaden firms’ strategic options and enhance risk diversification, but also, through the mediation of data flows and the establishment of standardized protocols, construct nonlinear collaborative networks. Such networks improve cross-organizational resource allocation efficiency and enable the shift from loosely coupled, linearly connected collaborations to deeply integrated, network-based governance structures, thereby enhancing governance collaboration among upstream and downstream firms [47].
Focal firm digitalization promotes governance collaboration within supply chains, which in turn strengthens resilience through two mechanisms: business process coordination and risk governance coordination. On the one hand, supported by digital platforms, tighter network connections and resource integration mechanisms accelerate factor flows, deepen trust and resource sharing, and foster a shift toward open collaboration and community-based value creation. This also optimizes network configurations and resource allocations, strengthens structural empowerment, and reduces efficiency losses and risk exposure associated with fragmented operations, thereby stabilizing supply chain operations [44]. On the other hand, governance collaboration improves resilience by constructing mechanisms for risk-sharing and joint response. With digital technologies, risks can be monitored in real time, accurately identified, and effectively shared across the supply chain. This provides upstream suppliers with early-warning signals to formulate contingency plans and facilitates collaborative prevention mechanisms that mitigate fragmented responses caused by information asymmetry. Ultimately, this reduces the risk of supply disruptions and enhances the supply chain’s elasticity and recovery capacity when facing unexpected shocks [48].
Based on the above analysis, this study proposes the following hypothesis.
H3:
Focal firm digitalization enhances supply chain resilience by promoting upstream–downstream governance collaboration and strengthening collaborative effects within supply chains, ultimately improving overall supply chain resilience.
- 3.
- Innovation Collaboration
According to technological innovation theory, technological progress is not only a key engine of economic growth but also a fundamental driver of supply chain structural optimization and functional upgrading [49]. Focal firm digitalization, by integrating industrial technologies with digital capabilities, reconstructs the logic of innovation resource allocation and becomes a critical force for activating the overall innovation potential of supply chains.
From the perspective of innovation collaboration effects, focal firm digitalization empowers supply chain innovation in several ways. First, through digital technologies such as data collection and algorithmic modeling, focal firms transform implicit, unstructured production data and experiential knowledge into quantifiable and standardized process norms [50]. By leveraging digital platforms to break organizational boundaries, they integrate heterogeneous technological capabilities across supply chain stages, thereby enhancing knowledge spillovers and collaborative innovation capacity [51]. Second, focal firms consolidate dispersed technological resources, talent, and data assets via digital platforms to provide an efficient space for collaboration. This facilitates joint problem-solving around key technologies and drives R&D from closed, firm-centered initiatives toward open, multi-party participation, ultimately forming an innovation ecosystem encompassing upstream and downstream firms [41]. Third, focal firm digitalization stimulates demand for highly skilled labor, leading to an upgrading of the human capital structure. The knowledge and applied technological capabilities embedded in this shift provide crucial support for knowledge and technology diffusion and integration within the supply chain, improving core R&D efficiency and enabling the supply chain to move toward higher value-added activities [46].
Supply chain innovation collaboration driven by focal firm digitalization further enhances resilience through innovation spillover effects and open innovation modes. On the one hand, innovation collaboration constructs efficient networks for the flow of knowledge, information, and technological elements. These networks provide critical knowledge support for upstream suppliers’ technological and product innovation, improve transparency and timeliness of knowledge sharing, clarify suppliers’ innovation orientation, and optimize resource allocation efficiency, thereby reinforcing suppliers’ innovation willingness and capabilities. Such innovation outcomes directly contribute to improved supply quality and lay the foundation for supply chain resilience [52]. On the other hand, open innovation modes promote the establishment of technological strategic alliances between upstream and downstream firms. Under governance frameworks of shared resources, knowledge, and risk costs, upstream suppliers become deeply embedded in collaborative innovation processes and enhance supply–demand alignment quality through diverse joint innovation activities. Moreover, this open mode of innovation sustains continuous interactions and value co-creation between upstream and downstream firms, significantly enhancing the supply chain’s dynamic adaptability to technological iterations and market fluctuations, and accelerating the construction of highly resilient supply chains [17].
Based on this reasoning, this study proposes the following hypothesis.
H4:
Focal firm digitalization enhances supply chain resilience by promoting upstream–downstream innovation collaboration and strengthening collaborative effects within supply chains, ultimately improving overall supply chain resilience.
To more clearly illustrate the relationship between focal firm digitalization and supply chain resilience as well as the underlying mechanisms, this study presents a conceptual model in Figure 1.
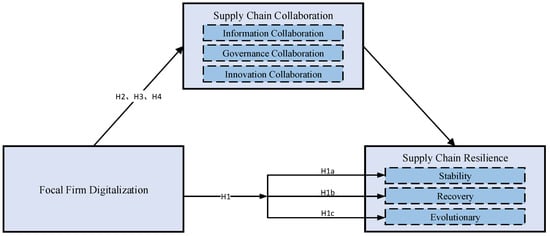
Figure 1.
Conceptual Model.
4. Research Methodology
4.1. Sample Selection and Data Sources
In 2011, the 12th Five-Year Plan for the Development of National Strategic Emerging Industries incorporated enterprise digitalization into the national strategy, marking the beginning of Chinese firms’ increasing emphasis on digital transformation. Combined with the commercialization of technologies such as the Internet of Things and big data, as well as the restructuring of corporate supply chains in the aftermath of the global financial crisis, and considering data availability and policy characteristics, this study selects Chinese A-share listed firms from 2011 to 2023 as the initial sample pool and uses Stata 18.0 for analysis.
To ensure data quality, several screening steps are applied. First, this study focuses on traditional real-sector enterprises and excludes those belonging to the digital industry. Second, this study removes firms with abnormal financial conditions such as those labeled ST (Special Treatment, indicating companies with abnormal financial status or other operational risks), *ST (Particular Special Treatment, referring to firms facing delisting risk due to severe financial distress), or PT (Pending Treatment, denoting firms under special supervision for financial irregularities or potential insolvency), and drop firms in the financial and insurance industries. Third, for cases in which the top five suppliers are unlisted firms but have listed affiliated entities, including associates, joint ventures, or subsidiaries of listed companies, this study adopts the following substitution procedure. Publicly available information from the listed affiliates is first used as the alternative data source. When multiple affiliated listed entities exist, the substitution follows the principle of decision-making participation priority, in accordance with the Accounting Standard for Business Enterprises No. 36—Related Party Disclosures. Accordingly, the listed company that exercises substantive control or holds dominant decision-making power over the supplier enterprise is manually identified and selected as the representative sample. Although affiliated listed firms may differ from their unlisted counterparts in terms of firm size and financial stability, these affiliated relationships typically reflect substantive control and shared operational decision-making structures. Therefore, this substitution approach does not materially bias the estimation results but rather ensures consistency and data completeness in capturing supply chain linkages.
After this screening process, this study obtains 4387 valid unbalanced panel observations in the form of “Ci (focal firm) − Sik (supplier) − Y (year).” To minimize the potential influence of extreme values on the results, all continuous variables are winsorized at the 1% and 99% levels.
4.2. Variable Definition and Measurement
4.2.1. Supply Chain Resilience
Based on the preceding discussion and drawing from the prior study [19], this study conceptualizes supply chain resilience in terms of three dimensions: stability, recovery, and evolutionary capacity, and employs the entropy weight method to construct a multidimensional indicator system for systematic measurement. First, supply chain stability emphasizes demand–supply matching, relationship continuity, and process smoothness under normal operating conditions. Accordingly, two dimensions are adopted to measure stability: risk bearing and demand–supply fluctuations. From the perspective of risk bearing, a firm’s ability to assume risk constitutes a critical antecedent, as it strengthens trust and resource commitment, thereby enhancing the durability of supply chain relationships—the stronger the risk-bearing capacity, the more stable the supply chain relationship. Following on relevant literature [53], this study measures this dimension by the annualized standard deviation of daily stock returns of upstream suppliers. This indicator exhibits strong exogeneity and objectively reflects the suppliers’ risk exposure under the influence of supply chain relationships. Moreover, higher volatility, within the context of stable supply chain partnerships, signifies the strengthening of joint risk-sharing mechanisms and is therefore regarded as an indicator of supply chain relationship stability. From the perspective of demand–supply fluctuations, the stability of supply chain relationships can be reflected in the inventory reserves of upstream suppliers. Excessive inventory increases costs and risks, whereas firms must optimize inventory structures to balance scale and improve turnover efficiency. Within the context of supply chain collaboration, if upstream suppliers are able to meet demand with relatively low inventory (i.e., small inventory adjustment amplitudes), this often signals stable cooperative relationships, reduces transaction uncertainty, and enhances resilience. Therefore, following the prior study [2], this study quantifies inventory adjustment amplitude as the absolute value of the natural logarithm of consecutive inventory changes (), which reflects suppliers’ inventory optimization and response efficiency. From a theoretical perspective, fluctuations in suppliers’ inventories are primarily influenced by their own operational decisions and external environmental shocks. The core explanatory variable in this study, the digitalization level of the focal firm, is not directly causally related to suppliers’ inventory adjustments, as the focal firm’s digitalization does not directly determine such decisions. Therefore, the risk of endogeneity between this variable and the core explanatory variable is relatively low. The measurement formula is as follows.
Here, denotes the net inventory value of firm at the end of year , and represents the absolute value of the variable.
Second, supply chain recovery reflects the ability of a supply chain to return to its original operational trajectory after external shocks, and the degree of deviation or fluctuation serves as an effective measure of this characteristic. From the perspective of demand–supply relationships, when external shocks disrupt the dynamic balance of the supply chain, information exchange and transaction frequency among upstream and downstream firms are weakened, thereby reducing the efficiency of product and service flows [42]. Accordingly, and following on relevant literature [50], this study employs supply chain efficiency as a proxy indicator of recovery. Specifically, this study uses the inventory turnover days of upstream supplier firms as the measurement indicator of supply chain efficiency. This measure not only captures the frequency of information exchange and the intensity of transaction collaboration among supply chain nodes, but also reflects the supply chain system’s flexible adjustment capacity and responsiveness to external shocks through changes in inventory liquidity. Moreover, the design of this indicator aligns with the practical need for supply chain efficiency optimization under the current context of industrial overcapacity. In addition, from the perspective of variable correlation, this indicator is primarily influenced by suppliers’ own operational decisions, such as inventory management strategies and production planning—as well as external environmental shocks, including market demand fluctuations and the stability of raw material supply. Its direct association with the core explanatory variable in this study is relatively weak, indicating a low potential risk of endogeneity. The calculation formula for supply chain efficiency is as follows.
Here, denotes supply chain efficiency, where a smaller value indicates better inventory liquidity, stronger collaborative efficiency in logistics, information flow, and capital flow among supply chain nodes, as well as greater recovery capacity of the supply chain; represents the inventory turnover ratio.
From the perspective of economic dynamic adjustment, when supply chains encounter external shocks, firm performance deviates from the benchmark trajectory and subsequently reconstructs a steady state through dynamic adjustment mechanisms [52]. Accordingly, this study adopts a “deviation share” analytical framework, in which the magnitude of performance deviation of supplier firms is used as a measurement indicator of supply chain recovery, thereby capturing the causal relationship between performance deviation and system resilience. Following the methodological approach of the prior study [42], this study constructs the econometric model (3) below. Within this model, the residuals between observed values and estimated values serve as the core measurement tool to quantify the dynamic adjustment trajectory of supplier firms’ economic performance over time. A larger absolute residual value indicates stronger recovery capacity of the supply chain under external shocks, whereas a smaller residual implies weaker recovery ability.
Here, denotes firm economic performance, measured by the ratio of earnings before interest and taxes to the number of employees. The model also incorporates a set of control variables that may affect firm performance, including firm size (), leverage (), revenue growth rate (), firm age (), and board size ().
Finally, supply chain evolutionary capacity emphasizes the ability of supply chains to achieve a capability leap from “passive response” to “proactive evolution” through long-term interactions such as knowledge sharing, technological innovation, resource integration, and optimization of resource allocation. Accordingly, this study measures and empirically analyzes supply chain evolutionary capacity along two key dimensions: suppliers’ technological innovation capability and resource allocation efficiency. First, technological innovation capability significantly enhances operational efficiency and systemic resilience by promoting the deep application of emerging technological tools in supply chain management. To capture this, this study employs the ratio of R&D expenditure to operating revenue as a proxy variable, which effectively reflects the intensity of a firm’s resource commitment to technology development and its potential for innovation output. Second, higher resource allocation efficiency within supply chains strengthens the ability of firms to cope with risks and challenges [46]. Therefore, this study measures supply chain resource allocation efficiency from the perspective of upstream suppliers’ total factor productivity, where higher TFP indicates greater efficiency in resource allocation across supply chain partners (Table 1).

Table 1.
Supply chain resilience measurement index system.
4.2.2. Focal Firm Digitalization
Here, the text analysis method is employed to construct a quantitative measurement system for firm digitalization based on word frequency statistics of digitalization-related terms disclosed in listed firms’ annual reports. Its underlying logic derives from the “process perspective,” which conceptualizes firm digitalization as a long-term, holistic, and systematic strategic transformation process. The frequent occurrence of digitalization-related keywords in annual reports can effectively capture the degree of commitment to and depth of implementation of digital transformation strategies. Meanwhile, by leveraging standardized data collection procedures and multidimensional classifications (e.g., digital technology applications, Internet-based business models), the text analysis method provides an operational approach for dynamically measuring the level of enterprise digitalization [8].
To mitigate subjective bias and enhance measurement objectivity, this study constructs a proxy variable for focal firm digitalization () using the text analysis method, following the approaches of relevant literature [1,51]. The specific steps are as follows: first, this study counts and aggregates the frequency of 94 digitalization-related keywords appearing in the “Management Discussion and Analysis” (MD&A) section of focal firms’ annual reports. Second, to address extreme values, this study adds one to the raw frequency counts and take the natural logarithm, and then divide the results by 100 to eliminate scale differences. Finally, considering the potential lagged transmission effect of focal firm digitalization on supply chain resilience, this study adjusts the processed digitalization indicator by one period lag. The resulting variable serves as the proxy measure of focal firm digitalization for the empirical analysis.
The digitalization keyword dictionary constructed in this study consists of two components: the underlying technologies and practical applications of four core digital technologies, namely ABCD—Artificial Intelligence (AI), Blockchain, Cloud Computing, and Big Data. The MD&A section of annual reports is selected as the object of text analysis for the following reason: under statutory disclosure requirements, this section obliges listed firms to systematically disclose the substantive impact of business strategies on operational activities. As enterprise digitalization represents a central dimension of strategic transformation, its effects on production processes and resource allocation are ultimately transmitted to financial performance. In line with the principles of compliance and materiality, firms are required to provide sufficient disclosure of the progress and potential risks of digital transformation in the MD&A section [1]. This requirement offers an authoritative and comprehensive information basis for text analysis.
4.2.3. Control Variables
Following the prior studies [12,44], this study selects a set of indicators that may affect the main effects as control variables. Detailed variable definitions are presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Definition of main variables.
Specifically, this study includes firm-level characteristics such as firm size (), return on total assets (), return on equity (), cash flow (), growth rate (), leverage (), current ratio (), total asset growth rate (), and Tobin’s Q (). In addition, this study incorporates governance-related indicators such as ownership concentration (), board size (), and the proportion of independent directors () to reflect corporate governance structure. To further ensure that the degree of digitalization of upstream firms does not bias the results, this study also includes the digitalization level of supplier firms () as a control variable.
4.3. Baseline Regression Model
To test Hypothesis H1 and examine the impact of enterprise digitalization on supply chain resilience—namely, the vertical spillover effects of focal firm digitalization on the operational performance of upstream supplier firms—this study follows the approach of relevant literature [54] and constructs the following econometric model:
Here, is the dependent variable, representing the interactive supply chain resilience between focal firm and its supplier k in year . The core explanatory variable is focal firm digitalization, denoted as , which is lagged by one period to reduce potential endogeneity concerns and to capture the delayed effect of digital transformation initiatives on supply chain resilience, as the impact of digital investments typically materializes over time. also includes a set of control variables, while and represent firm and year fixed effects, respectively, and denotes the random error term. The focal firm digitalization variable is the primary focus of this study. If the estimated coefficient is significantly positive, it indicates that focal firm digitalization contributes to improving supply chain resilience, thereby providing empirical support for Hypothesis H1.
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Descriptive Statistics and VIF Tests
5.1.1. Descriptive Statistics
Table 3 reports the descriptive statistics of the main variables. The supply chain resilience () indicator has a mean of 0.3011, a standard deviation of 0.0763, a maximum of 0.6654, and a minimum of 0.1235. Overall, the values fall within a reasonable range and are consistent with the findings of prior studies [53], which validates the rationality of the measurement. Regarding the sub-dimensions of supply chain resilience: stability () is based on 4190 observations, with a mean of 0.2951, a standard deviation of 0.1948, a minimum of 0.0000, and a maximum of 0.9314; recovery () includes 4160 observations, with a mean of 0.4276, a standard deviation of 0.0651, a minimum of 0.0528, and a maximum of 0.8079; and evolutionary capacity () is based on 3189 observations, with a mean of 0.1984, a standard deviation of 0.0867, a minimum of 0.0337, and a maximum of 0.9046. These results suggest that in the supply chain management practices of Chinese listed firms, greater emphasis is placed on supply chain stability, while relatively less attention is given to evolutionary capacity. In addition, the focal firm digitalization index () has a mean of 1.2629, a standard deviation of 1.3386, a minimum of 0.0000, and a maximum of 4.9904. The distributional characteristics and parameter values are largely consistent with those reported by relevant literature [55], further demonstrating the robustness and reliability of the digitalization measurement employed in this study. In addition, a cumulative probability plot was used to examine the normality of the residuals for the core variables, and the results indicate that they generally conform to the assumption of normal distribution.

Table 3.
Descriptive statistics.
5.1.2. VIF Tests
To test for potential multicollinearity, this study calculated the variance inflation factors (VIF) for all explanatory variables. The results, reported in Table 4, show that the mean VIF is 1.85 (with a maximum value of 4.22), both well below the conventional threshold of 5, indicating that multicollinearity is not a serious concern in the model.

Table 4.
VIF test results.
5.2. Baseline Regression
5.2.1. Focal Firm Digitalization and Supply Chain Resilience
Based on the baseline regression model (4) constructed earlier, this study examines the impact of focal firm digitalization on supply chain resilience. Table 5 reports the baseline regression results for the direct effects of focal firm digitalization on supply chain resilience. Column (1) includes only the core explanatory variable without any controls; Column (2) adds firm-level characteristics of focal firms to control for the potential influence of upstream suppliers’ digitalization; Column (3) further includes the digitalization indicator of upstream suppliers; and Column (4) additionally incorporates governance-related indicators of focal firms as control variables.

Table 5.
Benchmark regression results.
The regression results are presented in Table 5. Column (1) reports the baseline results, where the coefficient of focal firm digitalization () is 0.0035 and statistically significant at the 5% level, indicating that digitalization positively contributes to supply chain resilience. In column (2), after including firm-level control variables such as size, profitability, and capital structure, the coefficient decreases to 0.0026 and becomes significant at the 10% level. This suggests that part of the positive effect of digitalization may be mediated through firm resources and operational performance, implying that some digitalization benefits are indirectly captured by these firm attributes. In column (3), when supplier digitalization is further controlled for, the coefficient of focal firm digitalization rises again to 0.0031 and regains 5% significance, indicating a complementary relationship between focal firm and supplier digitalization. Supplier digitalization facilitates data interoperability and enhances joint information-sharing efficiency, thereby amplifying the resilience-enhancing effect of focal firm digitalization. Finally, in column (4), after controlling for corporate governance variables, the coefficient remains stable (0.0031, significant at the 5% level), confirming the robustness of the positive effect of digitalization on supply chain resilience. These findings indicate that focal firm digitalization significantly enhances supply chain resilience through backward spillover empowerment effects, thereby validating Hypothesis H1.
In addition, in Columns (3) and (4), the regression coefficient of the upstream suppliers’ digitalization indicator () is −0.0027, significant at the 10% level. This suggests a significant negative relationship between upstream suppliers’ digitalization and supply chain resilience. Two possible explanations can be offered: a reverse causality effect—when upstream suppliers exhibit weaker supply chain resilience, they tend to compensate passively by investing in digitalization (e.g., introducing risk early-warning systems), leading to an observed negative association between resilience and digitalization [8]; and short-term transformation costs—during the initial phase of digitalization, upstream suppliers face sunk costs related to technology upgrading and organizational restructuring. These short-term burdens may crowd out resources otherwise allocated to resilience building (e.g., emergency inventories), thereby exerting a suppressing effect on supply chain resilience [41].
5.2.2. Focal Firm Digitalization and Different Dimensions of Supply Chain Resilience
In the linear regression model (4), the dependent variable is replaced by supply chain stability (), recovery (), and evolution () to examine the backward spillover empowerment effects of focal firm digitalization on each dimension of supply chain resilience. Table 6 reports the regression results. Column (1) shows that the coefficient of focal firm digitalization () on supply chain stability () is 0.0038, but not statistically significant, indicating that the impact of focal firm digitalization on supply chain stability is not evident at this stage. Column (2) shows that the coefficient of focal firm digitalization () on supply chain recovery () is 0.0041 and statistically significant at the 5% level, suggesting that the backward spillover empowerment effects of focal firm digitalization enhance supply chain recovery. Column (3) shows that the coefficient of focal firm digitalization () on supply chain evolution () is 0.0031 and statistically significant at the 5% level, indicating that focal firm digitalization also plays a positive role in strengthening supply chain evolution. Taken together, the results suggest that focal firm digitalization enhances supply chain recovery and cultivates supply chain evolution, thereby improving overall resilience and providing empirical support for Hypotheses H1b and H1c. According to the results in Column (1), although there is a positive relationship between focal firm digitalization and supply chain stability, the coefficient is not significant. This may be due to two factors: on the one hand, the rapid improvement in digitalization levels has outpaced the establishment of robust data sovereignty and security management systems within supply chain networks, which hinders the development of trust between upstream and downstream partners [13]; on the other hand, given the turbulent domestic and international economic environment, many non-focal firms in the supply chain face considerable operational pressure and lack stable business conditions, thereby limiting the stabilizing effects of focal firm digitalization on upstream supplier operations [38].

Table 6.
Empirical test results.
5.3. Endogeneity Tests
Existing studies suggest that the improvement of firm digitalization is influenced by multiple factors, raising potential concerns of endogeneity such as reverse causality—namely, focal firms embedded in highly resilient supply chain networks may find it easier to advance their digitalization processes. To address this issue, this study employs the instrumental variable approach.
Following the method of prior study [53], this study uses the average digitalization () level of other firms (excluding the focal firm) within the same region–industry classification in the same year as the instrumental variable for focal firm digitalization. The rationale is that firms in the same region and industry face similar market and industrial environments, thus exhibiting high correlation with the focal firm’s digitalization, but they are not directly related to the resilience of the focal firm’s supply chain, thereby satisfying both the relevance and exclusion restrictions.
Drawing on the idea of constructing valid internal instruments without relying on external shocks, and following the industry–province stratification framework proposed by relevant literature [56], this study constructs the cubic term of the difference between focal firm digitalization and the mean digitalization level within the same industry (two-digit code)–province classification as the instrumental variable (), while excluding samples in which upstream and downstream firms are located in the same province, in order to avoid bias from regional economic linkages.
To further ensure robustness, this study narrows the sample scope and, following on prior study [43], construct the cubic term of the difference between focal firm digitalization and the mean digitalization level within the same industry (two-digit code)–city classification as the instrumental variable (), while excluding samples in which upstream and downstream firms are located in the same city.
The regression results are reported in Table 7. Columns (1), (3), and (5) present the first-stage regressions of focal firm digitalization on the instrumental variables , and , respectively. The results show that the selected instruments are all significantly and positively correlated with focal firm digitalization at the 1% level, satisfying the relevance condition. Furthermore, in the under-identification tests, all p-values equal 0; in the weak-instrument tests, the F-statistics are 1392.15, 93.7478, and 97.8722, respectively, all well above the critical value of 16.38, thereby rejecting the null hypothesis of weak instruments. These results confirm the validity of the chosen instrumental variables. Columns (2), (4), and (6) report the second-stage regression results after controlling for endogeneity. The coefficients of focal firm digitalization are 0.0168, 0.0148, and 0.0212, respectively, all significantly positive at least at the 5% level. These findings are consistent with the baseline regression results, indicating that the positive effect of focal firm digitalization on supply chain resilience remains robust after addressing endogeneity concerns, thereby providing further support for Hypothesis H1.

Table 7.
Instrumental variables method test results.
5.4. Robustness Tests
To further strengthen the reliability of the baseline regression results and the conclusion of Hypothesis H1, this section conducts a series of robustness checks on the empirical findings regarding firm digitalization and supply chain resilience, with the results reported in Table 8.

Table 8.
Robustness test results.
Controlling for potential confounding factors. The backward spillover effects of focal firm digitalization may diffuse through nonlinear channels such as industry competition, internal resource transmission, and geographical proximity [30]. To exclude such confounding effects, following relevant literature [40], this study excludes samples with geographical clustering, industry homogeneity, and related-party transactions from Model (4) for robustness testing. Columns (1)–(3) of Table 8 show that the coefficients of are 0.0027, 0.0038, and 0.0024, respectively, all significantly positive at least at the 10% level. These results are consistent with the baseline regression findings, suggesting that the positive impact of firm digitalization on supply chain resilience remains significant after accounting for potential confounders.
Alternative measurement of the explanatory variable. Referring to prior study [1], this study uses text analysis to count the frequencies of 99 digitalization-related keywords in the MD&A section of downstream firms’ annual reports, take the natural logarithm after adding one, and then lag the variable by one period to construct an alternative proxy for focal firm digitalization (). Column (4) of Table 8 shows that the coefficient of is 0.3335, significantly positive at the 5% level. This result is consistent with the baseline regression, confirming that the positive effect remains robust under an alternative measurement approach.
Controlling for lagged dependent variables. Since there may be bidirectional causality between focal firm digitalization and supply chain resilience, this study further controls for the lagged value of supply chain resilience () as an additional covariate. Column (5) of Table 8 shows that the coefficient of is 0.0038, significantly positive at the 5% level and consistent with the baseline results, while the coefficient of is insignificant. This indicates that the positive effect remains robust after controlling for lagged effects, and there is no evidence of reverse causality between the two.
In addition, to address potential violations of the normality assumption and enhance the robustness of statistical inference, this study re-estimated the main coefficients using the bootstrap method. Specifically, based on 1000 repeated resampling iterations, the bootstrap standard errors and bias-corrected confidence intervals for the core explanatory variable were calculated. As shown in Table 9, the bootstrap estimates are consistent with the baseline regression results in terms of coefficient signs, significance levels, and confidence interval ranges, indicating that the empirical conclusions are robust under different distributional assumptions. This further suggests that the positive impact of focal firm digitalization on supply chain resilience is not driven by sample distribution characteristics or estimation methods, but is statistically reliable and robust.

Table 9.
Baseline regression bootstrap test results.
5.5. Heterogeneity Tests
To further examine contextual heterogeneity, this study investigates whether the impact of focal firm digitalization on supply chain resilience varies across different external and relational conditions. Specifically, three contextual factors are considered: industry competition intensity, upstream–downstream relationship closeness, and suppliers’ regional resource endowments.
The heterogeneity regression results are presented in Table 10. To facilitate intuitive comparison, Table 11 summarizes the regression coefficients, significance levels, and the results of group difference tests. This summary table helps to clearly illustrate the magnitude and direction of heterogeneity effects under varying conditions.

Table 10.
Heterogeneity analysis results.

Table 11.
Summary of heterogeneity test results.
5.5.1. Industry Competition Intensity of Focal Firms
When market competition is intense, firms often increase information disclosure to mitigate information asymmetry. Conversely, when industry competition is weak, disadvantaged firms are more likely to be marginalized, and their limited business transparency reduces their ability to effectively disclose operational information, thereby exacerbating information asymmetry across the supply chain [57]. As the core coordinator in the supply chain, a focal firm’s forecasting accuracy, order collaboration efficiency, and rational allocation of upstream resources are all constrained by such information barriers. Therefore, when the focal firm operates in a less competitive industry, it tends to proactively enhance its digitalization level to overcome information blockages created by weaker upstream firms. By leveraging digital technologies, focal firms not only mitigate information asymmetry within the supply chain but also strengthen overall supply chain collaboration, ensuring that real downstream market demand is accurately transmitted upstream to safeguard operational efficiency.
To examine this heterogeneity, this study follows relevant literature [57] and adopts the industry Lerner index to measure the market competition intensity of focal firms. Based on Model (4), this study constructs a grouping variable according to the median value of the Lerner index across all focal firms in the sample. If a focal firm’s Lerner index is greater than the median, this indicates stronger pricing power, higher market monopoly, and lower market competition, and the grouping variable is coded as 1; otherwise, it is coded as 0. Using this setup, this study conducts sub-sample regressions to test whether the impact of focal firm digitalization on supply chain resilience differs under varying levels of market competition. The regression results are reported in Columns (1) and (2) of Table 10.
According to the results reported in Columns (1) and (2) of Table 10, the regression coefficient of is 0.0005 in Column (1) and is not statistically significant, whereas in Column (2) the coefficient is 0.0043 and significant at the 10% level. This comparison suggests that, relative to focal firms operating in highly competitive industries, the positive effect of digitalization on supply chain resilience is more pronounced when focal firms are in less competitive markets. Furthermore, the bootstrap p-value () reported in Table 10 tests whether the coefficients of digitalization are statistically equal across the two groups—that is, whether the effect of focal firm digitalization on resilience differs significantly between high- and low-competition contexts. The empirical p-value () is 0.003, which is less than the 1% significance level, providing additional evidence of significant heterogeneity in the effect.
5.5.2. The Closeness of Upstream–Downstream Relationships
In supply chains, close upstream–downstream relationships facilitate data flows and information sharing among firms, enabling end-to-end traceability of information and improving supply chain responsiveness. Such relationships are often accompanied by long-term contracts and benefit-sharing mechanisms, which foster risk-sharing arrangements and enhance the supply chain’s ability to withstand external shocks. In addition, close collaboration encourages joint R&D in digital technologies, contributing to the establishment of a technological ecosystem and promoting the modernization of supply chains [58]. Therefore, the empowering effect of focal firm digitalization on supply chain resilience is expected to be more significant when upstream–downstream relationships are stronger.
To examine this heterogeneity, this study follows prior study [59] by identifying “stable customers” as those appearing in both the current and previous year’s supplier customer lists. The closeness of upstream–downstream relationships () is then measured by the ratio of sales to stable customers to the total sales of the top five customers. Based on Model (4), this study constructs a grouping variable according to the median value of the closeness indicator across all samples: if the indicator of a given sample is above the median, its is considered closer (coded as 1); otherwise, the value is 0. This allows us to test for heterogeneity in the backward spillover empowerment effect of focal firm digitalization on supply chain resilience under different levels of relationship closeness. The regression results are presented in Columns (3) and (4) of Table 10.
The results show that the regression coefficient of in Column (3) is 0.0146 and not statistically significant, while the coefficient in Column (4) is 0.0034 and significant at the 5% level. This indicates that compared with weaker upstream–downstream relationships, focal firm digitalization has a more pronounced positive effect on supply chain resilience when upstream–downstream relationships are stronger. Furthermore, the group coefficient difference test (Bootstrap, 1000 replications) yields an empirical p-value () is 0.007, which is less than the 1% significance level, further confirming the presence of significant heterogeneity.
5.5.3. Suppliers’ Regional Resource Endowments
When firms are located in regions with weaker resource endowments, they often face resource constraints that stimulate stronger innovation incentives [60]. Consequently, upstream suppliers in such regions are more likely to actively adopt and cooperate with the digital empowerment initiatives of focal firms. At the same time, focal firms can leverage digital technologies to overcome spatial and temporal barriers, reduce frictions in knowledge and information flows, address collaboration shortcomings, and generate innovation spillover effects, thereby strengthening innovation collaboration along the supply chain and enhancing resilience. Moreover, in regions with weaker resource endowments, local governments are more inclined to provide targeted subsidies or tax incentives (e.g., the “Eastern Data, Western Computing” initiative) to encourage focal firms to invest in the digitalization of upstream suppliers, further reinforcing the implementation of digital empowerment. Therefore, the positive effect of focal firm digitalization on supply chain resilience is expected to be more pronounced in regions with weaker resource endowments.
To examine this heterogeneity, this study follows relevant literature [61] and classifies supplier regions based on the list of 262 resource-based cities, county-level cities, or districts identified in the National Plan for the Sustainable Development of Resource-Based Cities (2013–2020). Based on Model (4), this study constructs a grouping variable for regional resource endowments: supplier cities are classified into four categories—growing, mature, declining, and regenerative resource-based cities—alongside non-resource-based cities. If an upstream supplier is located in one of the first four categories, the city is considered to have higher resource endowments, and = 1; otherwise, = 0. The regression results are reported in Columns (5) and (6) of Table 10.
The results show that the regression coefficient of focal firm digitalization () is 0.0026 in Column (5) and not statistically significant, while in Column (6) it is 0.0032 and significant at the 10% level. This indicates that in regions with weaker supplier resource endowments, the empowering effect of focal firm digitalization on supply chain resilience is more pronounced. Furthermore, the empirical p-value (0.009) is less than 0.01, indicating statistical significance at the 1% level and further confirming the presence of significant heterogeneity.
5.6. Mechanism Analysis
Building on the previous analysis, the key to how focal firm digitalization enhances supply chain resilience lies in strengthening supply chain collaboration. The connotation of supply chain collaboration can be understood from three interrelated levels: information collaboration, governance collaboration, and innovation collaboration. Accordingly, following the mechanism testing approach of prior study [54], this study conducts mechanism analysis from these three dimensions.
5.6.1. Information Collaboration
In traditional supply chains, conflicts of interest among members, long chain structures, and complex networks make it difficult to track, measure, and monitor information flows. This poses significant challenges to improving information transparency and symmetry [37]. The well-known bullwhip effect originates from these problems: on the one hand, network complexity increases errors in information processing and transmission, creating supply–demand mismatches; on the other hand, factors such as price fluctuations, strategic interactions among firms, and demand volatility disrupt normal transactions, resulting in efficiency losses along the chain [26]. Only when supply chain members form an information community that enables real-time sharing and transparent, symmetric information flows can the bullwhip effect be mitigated, resource allocation optimized, and supply chain resilience enhanced. Therefore, this study adopts the bullwhip effect as a proxy variable to measure the degree of information symmetry between upstream and downstream firms, thereby capturing information collaboration.
The bullwhip effect () of upstream–downstream firms is measured following relevant studies [33,62], using supply–demand volatility to reflect the extent of the effect. In this framework, a firm’s demand () is proxied by its main business cost, while production is proxied by the change in annual net inventory combined with the firm’s main business cost and revenue ().
Here, the volatility of the annual production demand variable for focal firms and their upstream suppliers is measured by the standard deviation of the variable (). Based on this calculation, a proxy variable for the bullwhip effect () between focal firms and their upstream suppliers in a given year can be obtained. A larger value indicates lower transparency and symmetry of information between upstream and downstream in the industrial supply chain.
The bullwhip effect of the supply chain structure (). Relying solely on the supply–demand deviation of upstream firms cannot fully capture the transparency of information along the entire chain. Therefore, building on Equation (5) and following [33], this study adopts the ratio of the production–demand deviation of upstream firms to that of their corresponding downstream firms as a proxy variable for the bullwhip effect in the supply chain structure.
Here, denotes the supply–demand deviation of focal firm in year , and denotes the supply–demand deviation of its upstream supplier in the same year . Based on these measures, the bullwhip effect at the structural level of the supply chain () is constructed as a proxy variable reflecting the degree of deviation between upstream and downstream firms. A larger value of indicates a more pronounced bullwhip effect within the supply chain structure, implying greater information asymmetry between upstream and downstream firms.
The empirical results of the information collaboration mechanism are presented in Table 12. In column (1), the coefficient of focal firm digitalization () is −0.1059 and is significant at the 10% level, indicating that digitalization by focal firms can significantly reduce their own production demand fluctuations. This effect may stem from firms’ ability to leverage multi-source data integration and AI-driven demand forecasting models to improve the accuracy of demand predictions, thereby mitigating fluctuations arising from forecasting errors. Moreover, by employing digital inventory management tools, firms can achieve dynamic supply–demand alignment and optimize inventory turnover efficiency, which helps to smooth large demand variations through more effective resource allocation. Column (2) shows that the coefficient of is −0.0614 and significant at the 10% level, suggesting that focal firm digitalization also significantly reduces production demand fluctuations among upstream suppliers. This effect may arise because focal firms can use digital platforms to share real-time end-customer demand and order data with upstream suppliers, thereby reducing information delays and distortions and preventing suppliers from amplifying production demand fluctuations caused by the “bullwhip effect.” In column (3), the coefficient of is −0.1393 and significant at the 5% level, demonstrating that focal firm digitalization effectively stabilizes production demand fluctuations across the entire supply chain. Taken together, these results indicate that focal firm digitalization can significantly reduce production demand volatility in both upstream and downstream enterprises, effectively mitigate the bullwhip effect within the supply chain, and promote upstream–downstream information collaboration. This, in turn, strengthens supply chain collaboration and ultimately enhances supply chain resilience, thereby validating Hypothesis H2.

Table 12.
Information collaboration mechanism verification results.
5.6.2. Governance Collaboration
Governance collaboration primarily encompasses risk co-governance and business co-management along supply chain linkages. Following prior study [13], this study adopts risk governance and business stability as proxy variables for these two dimensions, employing multiple indicators to capture the degree of governance collaboration between upstream and downstream enterprises within the industrial supply chain.
From the perspective of risk governance, this study first draws on relevant studies [27,44], and measure trade credit risk between upstream and downstream firms using the ratio of suppliers’ accounts receivable to main business revenue (). A smaller value indicates that receivables account for a smaller proportion of transactions, suppliers face less collection pressure, and upstream–downstream transactions are more collaborative with lower cooperation risks. Second, following prior studies [47], this study uses suppliers’ accounts receivable turnover () to measure upstream firms’ risk exposure. A higher turnover rate suggests that supply chain operational risks faced by upstream and downstream enterprises are lower, thereby strengthening business collaboration.
From the perspective of business stability, this study draws on relevant literature [12], and employ the natural logarithm of suppliers’ inventory turnover days () to capture supply chain efficiency. A lower value indicates more frequent interactions between upstream and downstream firms, as well as stronger trade collaboration. Furthermore, recognizing that stable and persistent business ties help reduce external transaction costs and mitigate the risk of opportunism caused by high asset specificity, this study follows prior study [52] and use the ratio of intangible assets to total assets () to measure suppliers’ external transaction costs. A lower ratio reflects lower transaction costs, which in turn indicates more enduring business collaboration between upstream and downstream partners.
The governance collaboration mechanism test results are reported in Table 13. In column (1), the regression coefficient of focal firm digitalization () is −0.0054 and significant at the 5% level, indicating that focal firm digitalization effectively alleviates upstream–downstream trade credit pressure. This effect may stem from two mechanisms. First, focal firms integrate credit and transaction data across the supply chain through digital platforms, reducing information asymmetry and diminishing the reliance on credit sales driven by insufficient trust. Second, supply chain partners can leverage dynamic risk warning systems to optimize transaction terms and curb excessive credit extension, thereby mitigating accounts receivable risks. Column (2) shows that the coefficient of is 2.2302, significant at the 10% level, suggesting that focal firm digitalization significantly improves suppliers’ accounts receivable turnover, thereby lowering their risk exposure. This effect may arise because digital platforms established by focal firms allow upstream suppliers to shorten payment cycles and accelerate cash recovery through online settlement tools. In addition, these platforms enable dynamic risk assessment and optimization of payment terms, which helps mitigate bad debt risks across the supply chain and further improves the liquidity and financial stability of upstream firms.

Table 13.
Business collaboration mechanism verification results.
In column (3), the coefficient of is −0.0019, which is significant at the 5% level, demonstrating that digitalization significantly reduces suppliers’ external transaction costs. This effect may be explained by two factors. First, focal firms utilize digital platforms to automate and integrate key processes—such as order management, logistics tracking, and account reconciliation—replacing traditional manual coordination and thereby reducing the time and labor costs suppliers expend on documentation and communication. Second, supply chain partners rely on digital credit systems to streamline the establishment of transactional trust, minimizing the additional costs suppliers incur to mitigate risks and ultimately lowering overall external transaction costs. Column (4) reports a coefficient of −0.0431 for , significant at the 1% level, implying that digitalization significantly enhances supply chain efficiency of upstream firms. This improvement may stem from several mechanisms. First, digitalization enables the integration of internal and external multi-source data to optimize demand forecasting, thereby alleviating information asymmetry among supply chain nodes and reducing resource misallocation. Second, by digitalizing processes such as order management and logistics tracking, focal firms can shorten transaction cycles and lower coordination costs. Furthermore, digital platforms facilitate the dynamic allocation of inventory and production capacity across upstream and downstream partners, enhancing the responsiveness and adaptability of the supply chain and ultimately improving its overall operational efficiency.
Taken together, these results suggest that focal firm digitalization can effectively reduce supply chain risk levels, strengthen business collaboration between upstream and downstream firms, and improve supply chain efficiency. This enhances governance collaboration across the supply chain, thereby reinforcing supply chain coordination and ultimately empowering the improvement of supply chain resilience. Hypothesis H3 is thus supported.
5.6.3. Innovation Collaboration
Focal firm digitalization facilitates innovation collaboration within the supply chain by promoting resource sharing, knowledge flow, and joint innovation among supply chain partners [51]. This process not only reduces costs and improves efficiency but also strengthens the innovation capacity and dynamic adaptability of the supply chain, ultimately empowering resilience.
Following relevant literature [29], the innovation capability of upstream suppliers is measured by the logarithmic ratio of invention patent applications (, plus one) to invention patent grants (, plus one). To further test whether focal firm digitalization improves suppliers’ innovation efficiency through upstream–downstream collaborative innovation, this study adopts the approach of prior studies [2,41]. Specifically, joint patent applications and joint patent grants are employed as proxies for knowledge spillover in collaborative innovation. The logarithmic transformation (plus one) of the number of joint patent applications () and joint patent grants () is used to measure the quantity and quality of cooperative innovation, thereby capturing the level of knowledge diffusion.
A three-step mediation test is then employed to examine the mechanism. Drawing on the mediation model framework proposed by relevant literature [63], this study investigates whether the mechanism “focal firm digitalization → innovation spillover → innovation capability” holds, thereby verifying whether digitalization enhances resilience by promoting collaborative innovation and improving suppliers’ innovation efficiency.
The results of the innovation collaboration mechanism test are reported in Table 14. Columns (1)–(3) and columns (4)–(6) both present the results of the three-step mediation tests. The difference lies in the measurement of innovation spillover and innovation capability: for innovation spillover, column (2) uses the number of joint innovations by the focal firm, while column (5) uses the quality of those joint innovations; for innovation capability, columns (1) and (3) use upstream firms’ counts of patent applications, whereas columns (4) and (6) use counts of patents granted as an alternative metric. In Columns (1) and (4), the regression coefficients of focal firm digitalization () are 0.0686 and 0.0708, respectively, both significant at the 10% level, indicating that digitalization can effectively enhance suppliers’ innovation capability. In Columns (2) and (5), the coefficients of are positive at the 10% significance level, with values of 0.0543 and 0.0298, suggesting that focal firm digitalization contributes to improving the quantity and quality of its cooperative innovation. This effect may be attributed to two factors. First, digitalization enables focal firms to expand their collaboration networks and precisely identify technologically capable partners, thereby increasing opportunities for joint innovation. Second, digital platforms facilitate real-time monitoring of project progress, reducing information distortion during the R&D process and ensuring the reliability and effectiveness of collaborative innovation outcomes.

Table 14.
Innovation collaboration mechanism verification results.
Furthermore, Column (3) shows that the coefficient of cooperative innovation quantity () is 0.0801, significant at the 5% level, while Column (6) reports that the coefficient of cooperative innovation quality () is 0.1466, also significant at the 5% level. These findings demonstrate that focal firms can significantly enhance suppliers’ innovation capability through cooperative innovation. This effect may arise for two main reasons. First, an increase in the number of collaborative innovation projects provides suppliers with more opportunities for technological exchange and learning, enabling them to absorb advanced R&D methods and practices. Second, high-quality collaborative innovations facilitate the direct transfer of core technological achievements from focal firms to suppliers, helping them address technological gaps and rapidly strengthen their innovation capacity.
Taken together, focal firm digitalization promotes both its own cooperative innovation and the innovation capability of upstream suppliers, thereby fostering innovation collaboration across the supply chain. This, in turn, empowers the improvement of supply chain resilience, providing empirical support for Hypothesis H4.
5.6.4. Robustness Test for Mechanism Analysis
To ensure the robustness of the mechanism analysis, this study conducted a bootstrap test with 1000 resamples. The estimated indirect effects and their bias-corrected confidence intervals are reported in Table 15. The bootstrap results remain consistent with the baseline mechanism regressions, providing further evidence that the mediating effects identified through information, governance, and innovation collaboration are statistically robust and reliable.

Table 15.
Bootstrap test results.
In addition to the bootstrap approach, this study further conducts a parametric sensitivity analysis by replacing certain proxy variables to ensure the robustness of the mechanism test results. Specifically, in the information collaboration mechanism, the measure of used to construct the bullwhip effect () is replaced by using main business revenue instead of main business cost to re-estimate the proxy variable Bullwhip. The results remain consistent with those reported earlier, confirming the stability of the identified information collaboration pathway.
For governance and innovation collaboration mechanisms, several proxy variables have already been employed in the preceding analysis to measure risk governance, business stability, and innovation capability. Accordingly, no further alternative indicators are introduced for these mechanisms, since the existing specifications are sufficient to verify the robustness of the mediating effects.
6. Conclusions and Implication
6.1. Conclusions
This study yields several key findings.
Focal firm digitalization enhances supply chain resilience through backward spillover empowerment effects. At the dimensional level, its positive impact on supply chain stability is not statistically significant (mainly constrained by contradictions between digitalization and data governance, as well as external economic turbulence). However, it significantly improves both recovery and evolutionary capabilities of the supply chain.
The heterogeneity analysis reveals that the positive effect of focal firm digitalization on supply chain resilience is more pronounced in contexts characterized by lower industry competition, closer upstream–downstream relationships, and weaker regional resource endowments of suppliers.
The underlying mechanisms through which focal firm digitalization affects supply chain resilience can be summarized into three major pathways: information empowerment, governance empowerment, and innovation spillover. Specifically, information empowerment facilitates information collaboration by reducing asymmetry, improving the quality of information integration, and enhancing traceability and monitoring efficiency, thereby driving upstream suppliers to improve operational performance. Governance empowerment strengthens supply chain resilience by optimizing network structure, improving resource allocation, and fostering collaborative business and risk management. Innovation spillover promotes resilience by broadening the scope and efficiency of knowledge flows, enabling open innovation models, and cultivating a collaborative innovation ecosystem.
It should be noted that the conclusions of this study are primarily derived from analyses based on manufacturing supply chain samples. Manufacturing supply chains are typically characterized by tighter vertical linkages among firms and a relatively mature process of digital integration, which provides a specific contextual foundation for the formation of the study’s findings. Nevertheless, the backward spillover empowerment effect identified in this research may also offer theoretical implications for service-oriented or hybrid supply chains. However, the applicability and boundary conditions of this mechanism in non-manufacturing contexts warrant further empirical examination and clarification in future studies.
6.2. Practical Implication
Based on these findings, the study provides the following managerial implications.
For focal firms, it is crucial to play a leading role in the process of digital transformation by deeply integrating digital technologies into the core of supply chain strategy. Specifically, firms should develop IoT- and big data–based monitoring systems to achieve supply chain visualization and dynamic management. By deploying sensors, RFID devices, and intelligent gateways across key stages such as production, warehousing, and transportation, firms can collect real-time data on logistics, equipment, and inventory. Leveraging cloud computing and edge computing enables data integration and intelligent analysis, thereby enhancing supply chain transparency, strengthening predictive and early warning capabilities, and effectively mitigating the “bullwhip effect.”
At the same time, firms should establish a digital governance platform to optimize resource allocation and risk management within the supply chain. This platform should encompass core functions such as data governance, intelligent decision-making, risk early warning, and performance evaluation. It should enhance system compatibility and information efficiency through data standardization, apply artificial intelligence and algorithmic models to dynamically optimize procurement, production, and logistics, build real-time monitoring–based mechanisms for risk identification and emergency response, and establish a feedback system for continuous improvement and strategic adjustment.
Moreover, firms need to strengthen data security and privacy protection to ensure compliance and operational stability. Through the integration of these systems, focal firms can achieve intelligent decision-making and collaborative governance across the entire supply chain, thereby significantly enhancing operational efficiency, risk resilience, and sustainable competitiveness. Under different contextual conditions, focal firms should balance data security with coordination efficiency in highly competitive industries, deepen data interconnectivity and process integration in tightly coupled supply chains, and overcome path dependence through digital-driven innovation in resource-abundant regions.
For upstream suppliers, maintaining strategic alignment with focal firms in the digital era is essential for enhancing overall supply chain resilience and competitiveness. Specifically, suppliers should advance digital transformation through three key dimensions: information sharing, process collaboration, and innovation co-creation.
First, in terms of information sharing, suppliers should actively integrate into the digital supply chain platforms established by focal firms to achieve real-time interconnectivity of key data such as production plans, inventory levels, and order demands. By leveraging ERP systems and cloud-based data platforms, suppliers can realize multi-node information visualization and predictive analysis, thereby optimizing capacity allocation and inventory structures while reducing mismatches and resource waste. Improved information transparency also strengthens mutual trust and coordination efficiency between upstream and downstream partners.
Second, regarding process collaboration, suppliers should adopt digital tools and technological standards provided by focal firms to promote the standardization and intelligent upgrading of production processes. Through the implementation of industrial internet platforms and manufacturing execution systems (MES), suppliers can monitor equipment status, optimize production rhythms, and ensure quality traceability, thereby enhancing process stability and controllability. Additionally, digital twin technology can be applied to simulate production scenarios, enabling early risk identification and improving adaptive responses to supply chain disruptions.
Finally, in the dimension of innovation co-creation, suppliers should shift from passive response to active engagement by integrating into the digital innovation ecosystem led by focal firms. Through joint R&D participation, co-establishment of innovation platforms, and shared data resources, suppliers can collaboratively advance innovation in new materials, energy-efficient technologies, and intelligent manufacturing solutions. Such collaboration not only enhances suppliers’ own innovation capabilities but also promotes knowledge flow and evolutionary learning within the entire supply chain, thereby fostering long-term synergistic competitiveness.
Overall, digital collaboration among upstream suppliers is not only a necessary response to focal firms’ digital strategies but also a critical pathway for improving their own adaptability and innovation capacity. By strengthening information sharing, process collaboration, and innovation co-creation, suppliers can transform from passive participants into active enablers, thereby reinforcing overall supply chain resilience.
For government policymakers, establishing an institutional and ecosystem framework that enables digitally driven supply chain resilience is essential for achieving high-quality economic development and ensuring industrial chain security and stability.
First, governments should strengthen investment in digital infrastructure by promoting the application of industrial internet, 5G, and related technologies in manufacturing clusters and critical supply chain nodes. They should also develop open and shared industrial internet platforms and national-level supply chain data-sharing systems, standardize data formats and interfaces to ensure security and interoperability, and address “information silos”. In addition, fiscal subsidies and tax incentives should be used to reduce the digital transformation costs of small and medium-sized enterprises, particularly upstream suppliers.
Second, governments should improve collaborative governance mechanisms along industrial chains by establishing a Digital Supply Chain Coordination Committee composed of government agencies, focal firms, and industry associations. This committee should guide focal firms in leveraging blockchain and other trusted technologies to break down data barriers, enhance transparency, and promote deep integration of upstream and downstream partners.
Furthermore, under heterogeneous conditions, regulatory authorities should implement differentiated policy measures tailored to industry and regional characteristics: strengthening antitrust enforcement and data-sharing oversight in highly competitive industries; promoting industrial upgrading in resource-abundant regions to prevent overreliance on single resources; and using fiscal incentives and talent development programs to stimulate digital innovation. Collectively, these initiatives can provide long-term institutional support for enhancing supply chain resilience and sustaining industrial competitiveness in the digital era.
6.3. Limitations and Future Research
Although this study provides valuable theoretical and practical implications for the continuous improvement of supply chain resilience, it still has several limitations that warrant further exploration in future research. Moreover, since supply chain resilience is a key influencing factor in achieving sustainable supply chain development, the two are inherently interdependent and cannot be meaningfully separated in future theoretical and empirical investigations.
First, this study focuses on examining how enterprise digitalization enhances supply chain resilience through three collaborative mechanisms—information empowerment, governance empowerment, and innovation spillover. Although the empirical results validate the effectiveness of these mechanisms, other potential pathways—such as differences in firms’ dynamic capabilities and the proactive accountability behavior of supply chain members—may also play critical roles and merit further exploration. Specifically, enterprise digitalization can strengthen information processing and resource integration capabilities, thereby enhancing firms’ abilities to sense, seize, and reconfigure in response to environmental changes. Consequently, heterogeneity in firms’ dynamic capabilities may serve as an important conduit through which digitalization affects supply chain adaptability and recovery. At the same time, the digital practices of focal firms often promote high transparency and traceability within collaborative governance systems, encouraging supply chain members to exhibit proactive accountability behavior, such as actively participating in joint risk management and collaborative innovation. Variations in such behavior may influence the transmission efficiency of digital empowerment and the overall resilience of the supply chain. These potential mechanisms provide new theoretical insights into the multifaceted pathways through which digitalization fosters supply chain resilience.
Second, this study examines the relationship between enterprise digitalization and supply chain resilience from a linear perspective. This approach reflects the current stage of digital development in China, where the positive effects of digitalization remain dominant, and more complex nonlinear relationships have not yet fully emerged. However, from a theoretical standpoint, the relationship between enterprise digitalization and supply chain resilience may exhibit complex nonlinear characteristics. Such nonlinearity primarily arises from the progressive maturation of digital ecosystems and the accelerating pace of technological iteration, which cause the direction and intensity of digitalization’s impact on supply chain resilience to vary across different stages of development. In the early stages of digitalization, enterprises enhance information transparency, coordination efficiency, and risk response capabilities through the adoption of digital technologies, thereby significantly improving supply chain adaptability and recovery capacity. As digitalization deepens, however, the complexity of technological investment, system integration, and data governance increases substantially. Enterprises may face diminishing marginal returns, resource misallocation, and heightened system dependence, which collectively raise operational risks and maintenance costs while potentially weakening supply chain flexibility and responsiveness. Therefore, as digital ecosystems evolve and technologies continue to advance, the effect of enterprise digitalization on supply chain resilience is likely to be stage-dependent and nonlinear, potentially taking J-shaped, N-shaped, or inverted U-shaped forms. Future research exploring these underlying nonlinear dynamics would provide deeper theoretical insights and more practical implications for understanding and enhancing supply chain resilience in the digital era.
Third, the empirical analysis is limited by sample scope. By focusing on Chinese A-share listed firms and simplifying the supply chain network into first-tier structures, the study does not account for firms in other institutional and regional contexts. Future studies could expand the sample to include enterprises from other countries or regions, thereby enhancing the generalizability and applicability of the findings on how digitalization influences supply chain resilience.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, writing—original draft preparation, J.-X.D.; software, validation, formal analysis, investigation, resources, W.-X.H.; data curation, writing—review and editing, visualization, supervision, project administration, Z.-G.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the “Shaanxi Provincial Special Support Program for Leading Talents in Philosophy and Social Sciences (No. 2020063005SX)”.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets of this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| MD&A | Management Discussion and Analysis |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
References
- Yavuz, M.S.; Tatlı, H.S.; Bozkurt, G. Exploring the financial impact of digital transformation: A comprehensive analysis on firms. J. Innov. Knowl. 2025, 10, 100795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opoku, R.K.; Light, O.; Bonney, B.; Abboah, C.K.B.; Mawusi, S.K. Ameliorating sustainable performance through supply chain resilience and technology innovation: An empirical mediation analysis in a manufacturing industry. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2024, 36, 1565–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strimovskaya, A.; Barykin, S.; Volkova, E.; Tsyplakova, E.; Sinko, G.; Kuzmenkova, V.; Krasilnikov, A. Multi-level conceptual model of efficiency control in supply chain management. IFAC-Pap. 2023, 56, 1809–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guntuka, L.; Cantor, D.E.; Corsi, T.M.; D’oria, L.; Grover, A. Do Supply Chain Characteristics Influence a Rival Firm’s Responses to a Focal Firm’s Product Preannouncements? A Competitive Dynamics Perspective. J. Bus. Logist. 2024, 45, e12395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Mo, H.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, T. The effect of stability and concentration of upstream and downstream relationships of focal firms on two-level trade credit. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2024, 270, 109173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heldt, L.; Pikuleva, E. When upstream suppliers drive traceability: A process study on blockchain adoption for sustainability. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2025, 55, 196–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunila, M.; Rantala, T.; Ukko, J. Artificial intelligence-driven digital servitization: The importance of platform characteristics and firm-level factors. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2025, 130, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, J.M.; Wang, S.; Xu, L. Digitalization and the performance of non-technological firms: Evidence from the COVID-19 and natural disaster shocks. J. Corp. Financ. 2024, 89, 102670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, F.; Ahmad, M.; Irfan, M.; Wang, Z.; Fareed, Z. Analyzing the influence of smart and digital manufacturing on cost stickiness: A study of U.S. manufacturing firms. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2024, 95, 103473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emrouznejad, A.; Abbasi, S.; Sıcakyüz, Ç. Supply chain risk management: A content analysis-based review of existing and emerging topics. Supply Chain Anal. 2023, 3, 100031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottoni, P.; Di Ciccio, C.; Pareschi, R.; Tortola, D.; Gessa, N.; Massa, G. Blockchain-as-a-Service and Blockchain-as-a-Partner: Implementation options for supply chain optimization. Blockchain: Res. Appl. 2023, 4, 100119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, D. Two views of supply chain resilience. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2024, 62, 4031–4045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, S.; Mohamadpour Tosarkani, B. An analytical approach for evaluating the impact of blockchain technology on sustainable supply chain performance. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2022, 246, 108429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Tang, Z. The Impact of Enterprise Digital Capability on Supply Chain Digitalization—From the Perspective of Supply Chain Cooperation. J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2024, 19, 3051–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buranasiri, B.; Lai, P.-L.; Woo, S.; Piboonrungroj, P. Impact of sustainable development goal orientation on supply chain collaboration and sustained competitive advantage: Evidence from the tea and coffee industry. Asian J. Shipp. Logist. 2024, 40, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahachi, M.; Moukala, H.; Ismail, A.; Hopf, A.; Ehm, H. Simulating the COVID19-pandemic and its impact on the semiconductor supply chain: Enabling a supply chain risk management framework. IFAC-Pap. 2022, 55, 2215–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahmar, A.; Zekhnini, K.; Masmoudi, M.; Siddiqui, A.A. Navigating the sustainable supply chain realm: Revolutionizing from 3.0 to 5.0. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2025, 208, 111380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, J.; He, C.; Jiang, X.; An, Q. Sewage Treatment Equipment Supply Chain Collaboration and Resilience Improvement Path Analysis: Collaborative Decision-Making, Information Sharing, Risk Management. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, E.D.; Smyth, C.; Gupta, S.; Dennehy, D. Artificial intelligence and big data analytics for supply chain resilience: A systematic literature review. Ann. Oper. Res. 2023, 327, 605–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Wang, X. Enterprise digital transformation empowers supply Chain stability. Financ. Res. Lett. 2024, 66, 105693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Li, H.; He, Z. The effect of blockchain technology on supply chain collaboration: A case study of lenovo. Systems 2023, 11, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafique, M.N.; Yeo, S.F.; Tan, C.L. Roles of top management support and compatibility in big data predictive analytics for supply chain collaboration and supply chain performance. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2024, 199, 123074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saarijärvi, H.; Kannan, P.; Kuusela, H. Value co-creation: Theoretical approaches and practical implications. Eur. Bus. Rev. 2013, 25, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, D.D.; Zimmerman, M.A. Empowerment theory, research, and application. Am. J. Community Psychol. 1995, 23, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veile, J.W.; Schmidt, M.-C.; Müller, J.M.; Voigt, K.I. The transformation of supply chain collaboration and design through Industry 4.0. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2024, 27, 986–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazal, T.; Alzoubi, H. Modelling supply chain information collaboration empowered with machine learning technique. Intell. Autom. Soft Comput. 2021, 29, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansell, C.; Gash, A. Collaborative governance in theory and practice. J. Public Adm. Res. Theory 2008, 18, 543–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermicelli, S.; Cricelli, L.; Grimaldi, M. How can crowdsourcing help tackle the COVID-19 pandemic? An explorative overview of innovative collaborative practices. Rd Manag. 2021, 51, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksoy, C. Digital business ecosystems: An environment of collaboration, innovation, and value creation in the digital age. J. Bus. Trade 2023, 4, 156–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-khatib, A.; Al-Shboul, M.; Khattab, M. How can generative artificial intelligence improve digital supply chain performance in manufacturing firms? Analyzing the mediating role of innovation ambidexterity using hybrid analysis through CB-SEM and PLS-SEM. Technol. Soc. 2024, 78, 102676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badhan, I.A.; Neeroj, M.H.; Rahman, S. Currency rate fluctuations and their impact on supply chain risk management: An empirical analysis. Int. J. Bus. Manag. Sci. 2024, 4, 6–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamah, E.; Alzubi, A.; Yinal, A. Unveiling the impact of digitalization on supply chain performance in the post-COVID-19 era: The mediating role of supply chain integration and efficiency. Sustainability 2023, 16, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán Peña, J.A.; Ortiz Bas, Á.; Reyes Maldonado, N.M. Impact of bullwhip effect in quality and waste in perishable supply chain. Processes 2021, 9, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDougall, N.; Davis, A. The local supply chain during disruption: Establishing resilient networks for the future. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 462, 142743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavlanova, T.; Benbunan-Fich, R.; Koufaris, M. Signaling theory and information asymmetry in online commerce. Inf. Manag. 2012, 49, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raweewan, M.; Ferrell Jr, W.G. Information sharing in supply chain collaboration. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2018, 126, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panahifar, F.; Byrne, P.J.; Salam, M.A.; Heavey, C. Supply chain collaboration and firm’s performance: The critical role of information sharing and trust. J. Enterp. Inf. Manag. 2018, 31, 358–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baah, C.; Opoku Agyeman, D.; Acquah, I.S.K.; Agyabeng-Mensah, Y.; Afum, E.; Issau, K.; Ofori, D.; Faibil, D. Effect of information sharing in supply chains: Understanding the roles of supply chain visibility; agility; collaboration on supply chain performance. Benchmarking Int. J. 2022, 29, 434–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, T.K.; Angelis, J.; Khilji, W.A.; Kalaiarasan, R.; Wiktorsson, M. Demonstration of a blockchain-based framework using smart contracts for supply chain collaboration. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2023, 61, 1497–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejeb, A.; Keogh, J.G.; Simske, S.J.; Stafford, T.; Treiblmaier, H. Potentials of blockchain technologies for supply chain collaboration: A conceptual framework. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2021, 32, 973–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhadi, A.; Mani, V.; Kamble, S.S.; Khan, S.A.R.; Verma, S. Artificial intelligence-driven innovation for enhancing supply chain resilience and performance under the effect of supply chain dynamism: An empirical investigation. Ann. Oper. Res. 2024, 333, 627–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guntuka, L.; Corsi, T.M.; Cantor, D.E. Recovery from plant-level supply chain disruptions: Supply chain complexity and business continuity management. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2024, 44, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, A.; Rasheed, R.; Ngah, A.H.; Pradeepa Jayaratne, M.D.R.; Rahi, S.; Tunio, M.N. Role of information processing and digital supply chain in supply chain resilience through supply chain risk management. J. Glob. Oper. Strateg. Sourc. 2024, 17, 429–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statsenko, L.; Scholten, K.; Stevenson, M. The influence of global value chain governance on supply network resilience. Supply Chain Manag. Int. J. 2025, 30, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Li, J. How does digital collaboration impact supply chain resilience. Financ. Res. Lett. 2024, 66, 105684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherrafi, A.; Chiarini, A.; Belhadi, A.; El Baz, J.; Chaouni Benabdellah, A. Digital technologies and circular economy practices: Vital enablers to support sustainable and resilient supply chain management in the post-COVID-19 era. TQM J. 2022, 34, 179–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, P.; Ellram, L.; Formentini, M.; Ries, J.-M. Guest editorialEmerging research and future pathways in digital supply chain governance. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2021, 41, 1021–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadegan, A.; Dooley, K. A typology of supply network resilience strategies: Complex collaborations in a complex world. J. Supply Chain Manag. 2021, 57, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenken, K. Technological innovation and complexity theory. Econ. Innov. New Technol. 2006, 15, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan, P.; Philsoophian, M. Improving of supply chain collaboration and performance by using block chain technology as a mediating role and resilience as a moderating variable. J. Knowl. Econ. 2023, 14, 4561–4582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostini, L.; Galati, F.; Gastaldi, L. The digitalization of the innovation process: Challenges and opportunities from a management perspective. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2020, 23, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, R.H. Leveraging business analytics and digital business management to optimize supply chain resilience: A strategic approach to enhancing US economic stability in a post-pandemic era. World, J. Adv. Res. Rev. 2024, 23, 2774–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Q. Developing supply chain resilience through integration: An empirical study on an e-commerce platform. J. Oper. Manag. 2023, 69, 477–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T. Mediation Effect and Moderation Effect in Empirical Studies of Causal Inference. China Ind. Econ. 2022, 5, 100–120. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, X.; Zheng, L.; Fan, S.; Zuo, S. Green innovation and carbon emission performance: The role of digital economy. Energy Policy 2024, 195, 114344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Xu, Q. Impacts of carbon emissions allowance limitations on carbon price with power generation rights trading in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 470, 143312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakandala, D.; Chen, J.; Chikweche, T. SME supply chain resilience in disruptive times: The effects of supply chain robustness; access to government assistance and disruption intensity. Bus. Process Manag. J. 2025, 31, 467–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfi, M.; Larmour, A. Supply chain resilience in the face of uncertainty: How horizontal and vertical collaboration can help? Contin. Resil. Rev. 2022, 4, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, F.; Siegler, J. The role of visibility in supply chain resiliency: Applying the Nexus supplier index to unveil hidden critical suppliers in deep supply networks. Decis. Support Syst. 2024, 176, 114063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, A. Risk; reward; and resilience framework: Integrative policy making in a complex world. J. Int. Econ. Law 2023, 26, 233–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, H.H.; Lao, K.; Ren, Z. The impacts of resource endowment; and environmental regulations on sustainability—Empirical evidence based on data from renewable energy enterprises. Energies 2022, 15, 4678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osadchiy, N.; Schmidt, W.; Wu, J. The bullwhip effect in supply networks. Manag. Sci. 2021, 67, 6153–6173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.L.; Zhang, L.; Hou, J.T.; Liu, H.Y. Procedures for testing mediating effects and their applications. Acta Psychol. Sin. 2004, 5, 614–620. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).