Unraveling Spatial–Temporal and Interactive Impact of Built Environment on Metro Ridership: A Case Study in Shanghai, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Built Environment Factors
2.2. Models and Methods
3. Data
3.1. Study Area
3.2. Date Resource
4. Methodology
4.1. Multiscale Geographically Weighted Regression (MGWR)
4.2. Geographical Detectors
4.2.1. Factor Detector
4.2.2. Interaction Detector
- (1)
- Weaken, nonlinear: .
- (2)
- Weaken, uni-: .
- (3)
- Enhance, bi-: .
- (4)
- Independent: .
- (5)
- Enhance, nonlinear: .
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Spatial–Temporal Variability of Metro Ridership
5.2. The Comparison of Different Models
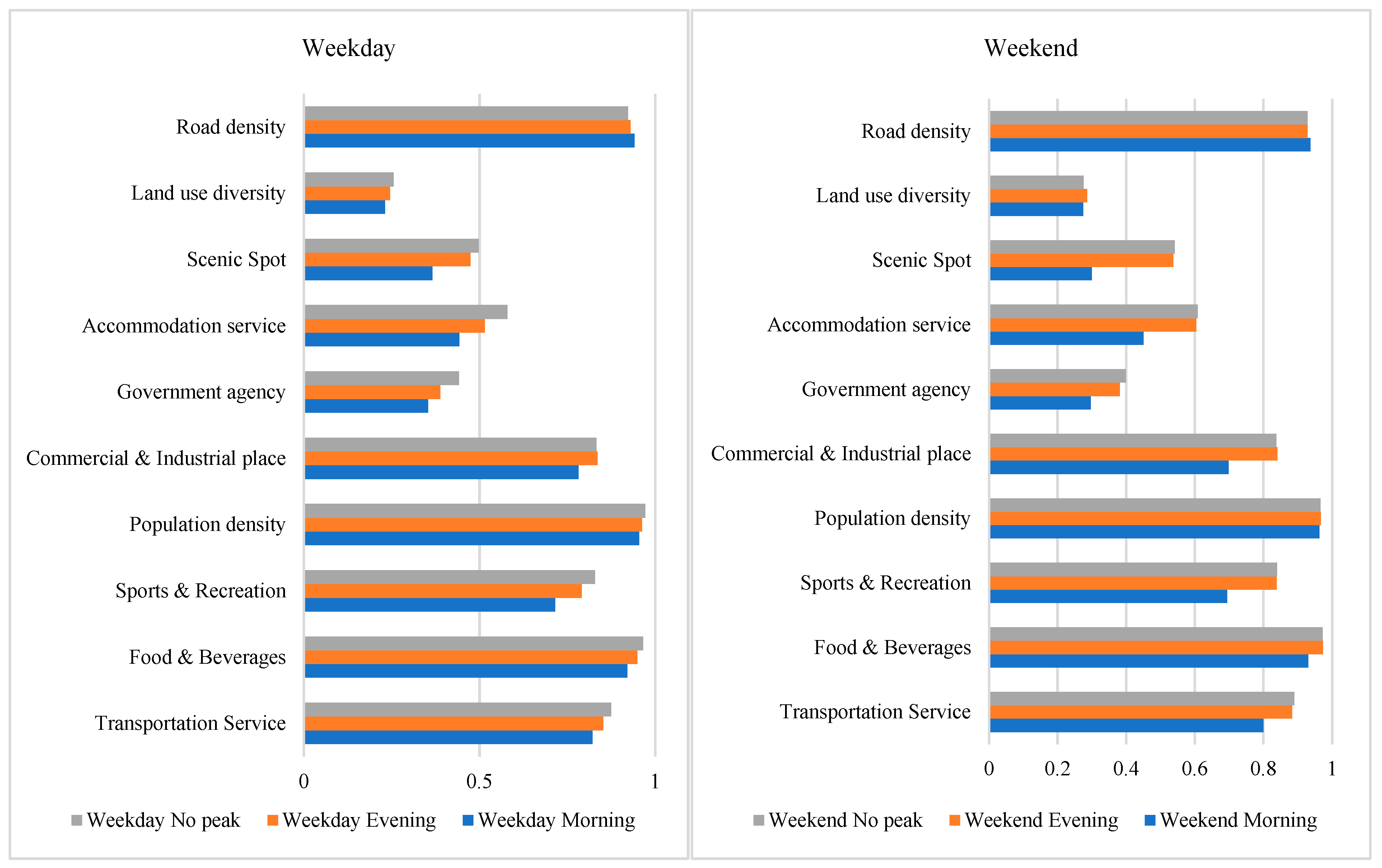
5.3. Spatial Variation in Coefficients from MGWR Model
5.4. The Interaction Influence of Factors
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ding, H.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Lu, X. Quantifying the Impact of Built Environment on Traffic Congestion: A Nonlinear Analysis and Optimization Strategy for Sustainable Urban Planning. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2025, 122, 106249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, X.; Li, Z.; Wu, Z.; Yan, Z.; Chen, Y.; Gao, F. Spatial and Temporal Dynamics of Urban Expansion Along the Guangzhou–Foshan Inter-City Rail Transit Corridor, China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Deng, W.; Song, Y.; Zhu, Y. What Influences Metro Station Ridership in China? Insights from Nanjing. Cities 2013, 35, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Zhang, L.; Li, S.; Huang, Y.; Ding, X.; Hao, J.; Huang, S.; Li, X.; Lu, F.; Zhang, H. Urban Rail Transit in China: Progress Report and Analysis (2015–2023). Urban Rail Transit 2025, 11, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Lyu, D.; Liu, X.; Tan, Z.; Gao, F.; Huang, G.; Wu, Z. The Varying Patterns of Rail Transit Ridership and Their Relationships with Fine-Scale Built Environment Factors: Big Data Analytics from Guangzhou. Cities 2020, 99, 102580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Liu, Y.; Ye, Y. Nonlinear Effects of Built Environment Features on Metro Ridership: An Integrated Exploration with Machine Learning Considering Spatial Heterogeneity. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 95, 104613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, M.-J.; Choi, K.; Jeong, J.-E.; Kwon, K.-H.; Kim, H.-J. Land Use Characteristics of Subway Catchment Areas and Their Influence on Subway Ridership in Seoul. J. Transp. Geogr. 2015, 48, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, J.; Cardozo, O.D.; García-Palomares, J.C. Transit Ridership Forecasting at Station Level: An Approach Based on Distance-Decay Weighted Regression. J. Transp. Geogr. 2011, 19, 1081–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, S.; Frank, L.F. Pedestrian Environments and Transit Ridership. J. Public Transp. 2009, 12, 39–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.-S.; Wang, S.-W.; Yao, L.-Y.; Rong, J.; Ma, J.-M. Estimation of Transit Ridership Based on Spatial Analysis and Precise Land Use Data. Transp. Lett. 2016, 8, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, D.; Tong, X.; Liu, K.; Chan, E.H. Understanding the Impact of Built Environment on Metro Ridership Using Open Source in Shanghai. Cities 2019, 93, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobler, W.R. A Computer Movie Simulating Urban Growth in the Detroit Region. Econ. Geogr. 1970, 46, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blainey, S. Trip End Models of Local Rail Demand in England and Wales. J. Transp. Geogr. 2010, 18, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, R.; Wu, Z.; Tong, Z.; Qin, S.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, Y. How the Built Environment Promotes Public Transportation in Wuhan: A Multiscale Geographically Weighted Regression Analysis. Travel Behav. Soc. 2022, 29, 186–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Kwan, M.-P.; Hu, W.; Li, R.; Wang, J. Examining the Effects of Station-Level Factors on Metro Ridership Using Multiscale Geographically Weighted Regression. J. Transp. Geogr. 2023, 113, 103720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Liu, T.; Yao, B.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, X. Understanding the Time-Dependent Effect of Built Environment Attributes on Station-Level Metro Ridership Uncertainty in Beijing: A Big Data Analytic Approach. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2023, 137, 105148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, J.K.; Choi, J.; Park, M.S.; Heo, T.-Y. Exploring the Catchment Area of an Urban Railway Station by Using Transit Card Data: Case Study in Seoul. Cities 2019, 95, 102364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Tsui, K.L. Modeling and Analyzing Impact Factors of Metro Station Ridership: An Approach Based on a General Estimating Equation. IEEE Intell. Transp. Syst. Mag. 2020, 12, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlin, L.A.; Singer, M.; Levine, J. Influences on Transit Ridership and Transit Accessibility in US Urban Areas. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2021, 150, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Song, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Jia, J.; Song, C. Spatial Heterogeneity Analysis for Influencing Factors of Outbound Ridership of Subway Stations Considering the Optimal Scale Range of “7D” Built Environments. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Yeh, A.G.; Yue, Y. Spatial Variation of Self-Containment and Jobs-Housing Balance in Shenzhen Using Cellphone Big Data. J. Transp. Geogr. 2018, 68, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Huang, B.; He, Q.; Chen, B.; Wei, J.; Mahmood, R. Dynamic Assessment of PM2.5 Exposure and Health Risk Using Remote Sensing and Geo-Spatial Big Data. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 253, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.Y.; Sinniah, G.K.; Li, R. Identify Impacting Factor for Urban Rail Ridership from Built Environment Spatial Heterogeneity. Case Stud. Transp. Policy 2022, 10, 1159–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Zhang, N.; Liu, Y.; Xu, W. Exploring Spatiotemporal Variation in Hourly Metro Ridership at Station Level: The Influence of Built Environment and Topological Structure. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Z.; Yang, M.; Feng, T.; Timmermans, H.J. Examining the Relationship Between Built Environment and Metro Ridership at Station-to-Station Level. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2020, 82, 102332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.; Ye, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhang, W. Discovering the Spatio-Temporal Impacts of Built Environment on Metro Ridership Using Smart Card Data. Cities 2019, 95, 102359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Zhao, X.X.; Li, C.C.; Cui, M.Y.; Wang, J.W.; Qiang, Y.J. Exploration of the Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity of Metro Ridership Prompted by Built Environment: A Multi-Source Fusion Perspective. IET Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 16, 1455–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wan, F.; Dong, C.; Yin, C.; Chen, X. Spatiotemporal Effects of Built Environment Factors on Varying Rail Transit Station Ridership Patterns. J. Transp. Geogr. 2023, 109, 103597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Ahn, Y.; Choi, S.; Kim, K. Sustainable Mobility: Longitudinal Analysis of Built Environment on Transit Ridership. Sustainability 2016, 8, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, W.; Cao, R.; Yue, Y.; Zhou, B.; Li, Q.; Li, Q. Spatial Variations in Urban Public Ridership Derived from GPS Trajectories and Smart Card Data. J. Transp. Geogr. 2018, 69, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X. Analysis of Taxi Demand and Traffic Influencing Factors in Urban Core Area Based on Data Field Theory and GWR Model: A Case Study of Beijing. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Wu, B.; Barry, M. Geographically and Temporally Weighted Regression for Modeling Spatio-Temporal Variation in House Prices. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 383–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessani, M.; Li, Z. SGWR: Similarity and Geographically Weighted Regression. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2024, 38, 1232–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotheringham, A.S.; Yang, W.; Kang, W. Multiscale Geographically Weighted Regression (MGWR). Ann. Am. Assoc. Geogr. 2017, 107, 1247–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Fotheringham, A.S.; Li, Z.; Oshan, T.; Kang, W.; Wolf, L.J. Inference in Multiscale Geographically Weighted Regression. Geogr. Anal. 2020, 52, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-F.; Zhang, T.-L.; Fu, B.-J. A Measure of Spatial Stratified Heterogeneity. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 67, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, P.; Yang, S.; Lei, M.; Chen, T.; Dong, N. Quantitative Analysis of the Factors Influencing Spatial Distribution of Soil Heavy Metals Based on Geographical Detector. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 664, 392–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Kuang, T.; Tao, S. Quantifying Influences of Natural Factors on Vegetation NDVI Changes Based on Geographical Detector in Sichuan, Western China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 233, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Fan, Z.; Duan, J.; Gao, W.; Wang, R.; Liu, N.; Hua, S. Assessment of Interactions Between Influencing Factors on City Shrinkage Based on Geographical Detector: A Case Study in Kitakyushu, Japan. Cities 2022, 131, 103958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, G.; Zhang, H.; Jin, L.; Su, Y.; Wu, K. Identifying the Determinants of Housing Prices in China Using Spatial Regression and the Geographical Detector Technique. Appl. Geogr. 2017, 79, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Li, X.H.; Christakos, G.; Liao, Y.L.; Zhang, T.; Gu, X.; Zheng, X.Y. Geographical Detectors-Based Health Risk Assessment and Its Application in the Neural Tube Defects Study of the Heshun Region, China. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 107–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Li, J.; Shen, Q.; Shi, C. What Determines Rail Transit Passenger Volume? Implications for Transit Oriented Development Planning. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2017, 57, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Lyu, D.; Huang, G.; Zhang, X.; Gao, F.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X. Spatially Varying Impacts of Built Environment Factors on Rail Transit Ridership at Station Level: A Case Study in Guangzhou, China. J. Transp. Geogr. 2020, 82, 102631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, H.; Qu, W. Geographical Detection of Traffic Accidents Spatial Stratified Heterogeneity and Influence Factors. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
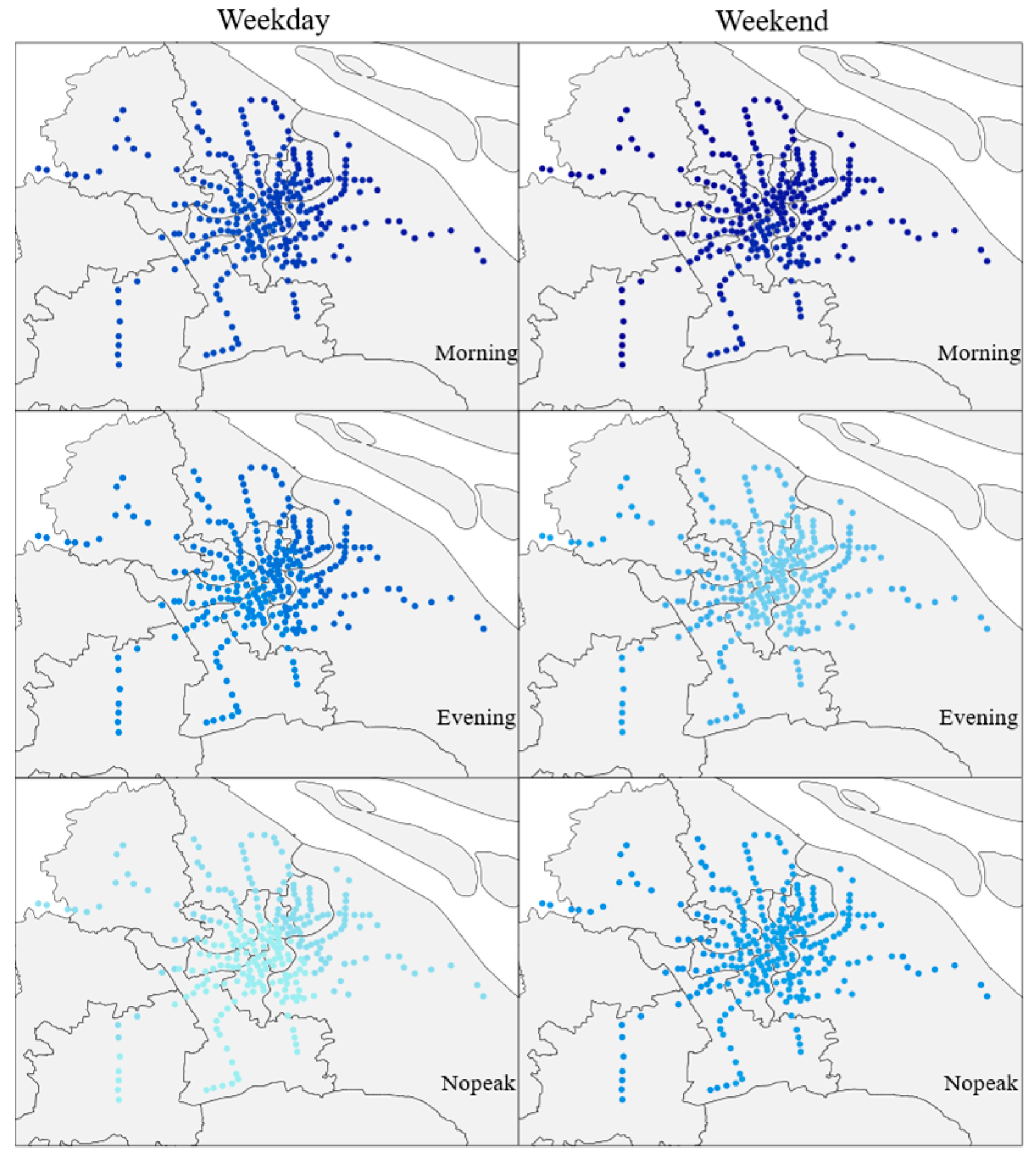

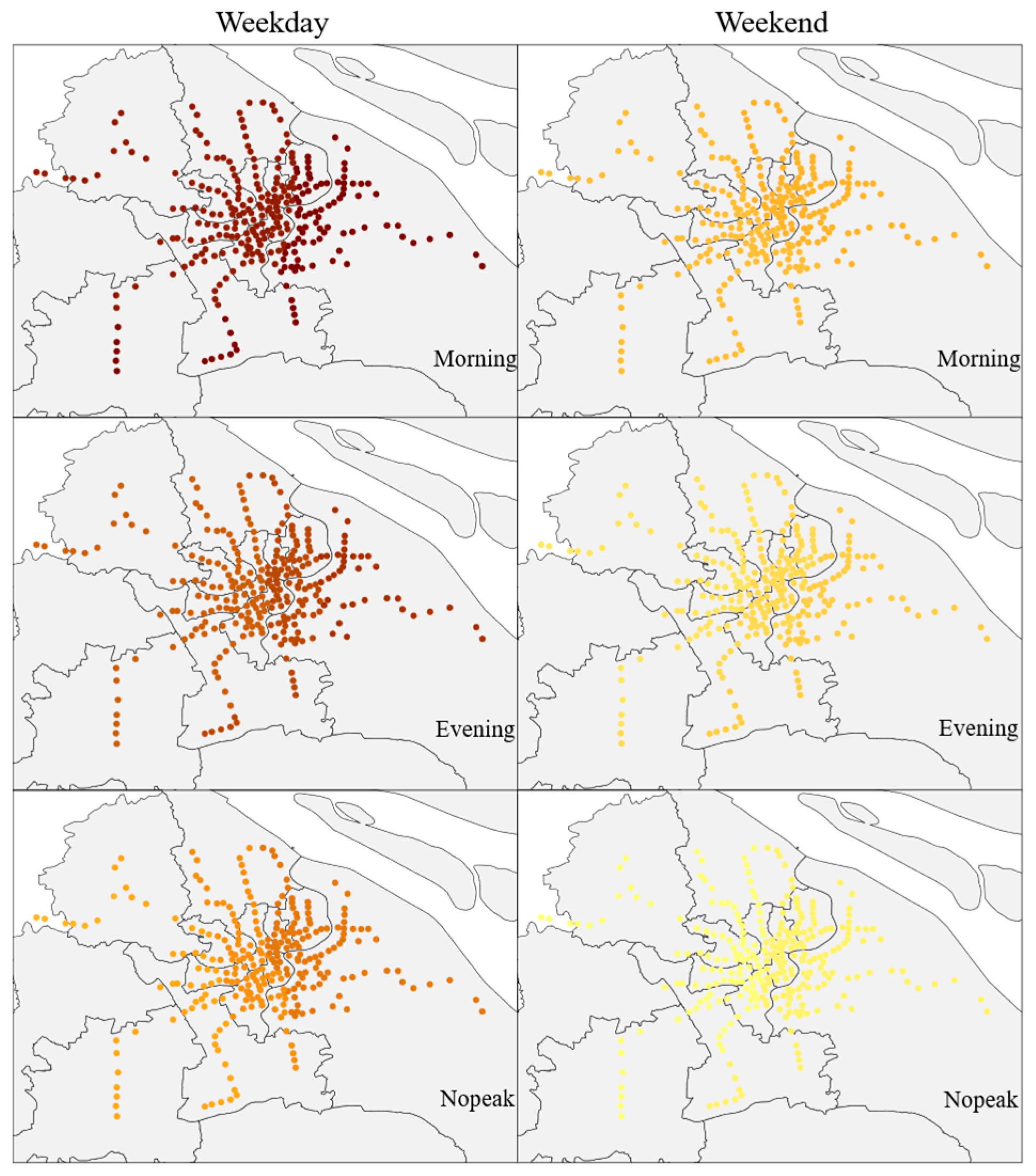
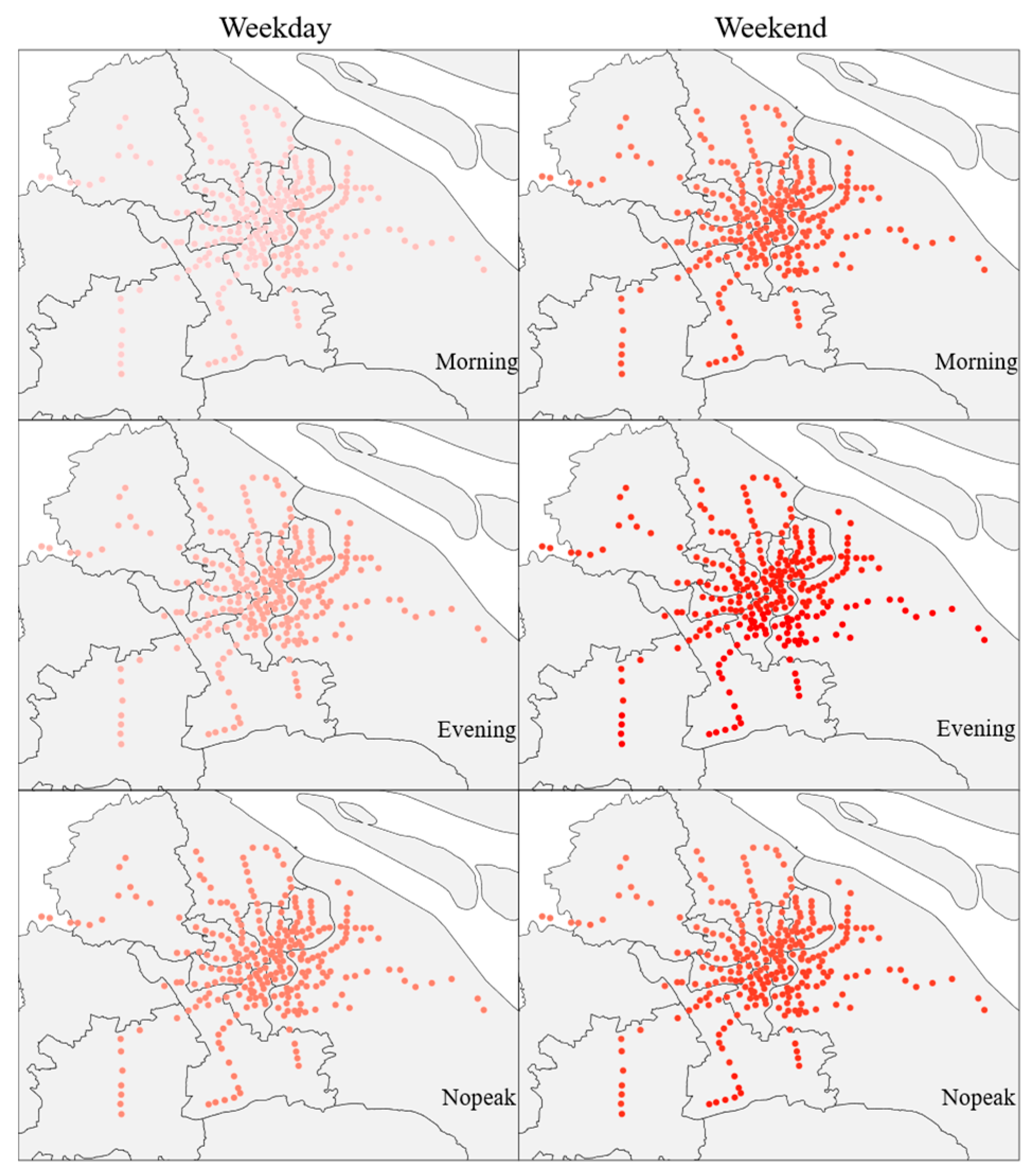
| Variables | Description | Source | Mean | STD | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metro ridership | Weekday | Morning | Metro passenger flow at different time periods | SCD from Shanghai Metro during July of 2016 | 3887.88 | 3103.68 |
| Evening | 3285.95 | 3000.55 | ||||
| No Peak | 1050.56 | 974.93 | ||||
| Weekend | Morning | 1293.28 | 1058.42 | |||
| Evening | 1528.75 | 1655.19 | ||||
| No peak | 1030.43 | 1060.84 | ||||
| Transportation Service | Number of transportation services in each PCA | POI date of Gaode Map | 124.62 | 100.82 | ||
| Food & Beverages | Number of restaurants, coffee houses, dessert houses in each PCA | POI date of Gaode Map | 409.20 | 411.83 | ||
| Sports & Recreation | Number of sports stadiums, recreation center, theaters, cinemas in each PCA | POI date of Gaode Map | 62.22 | 57.10 | ||
| Population density | Population density in each PCA (thousands person per km2) | Original data from WorldPop & measured in GIS | 19.72 | 12.93 | ||
| Commercial & Industrial place | Number of companies, financial institutions, and factories in each PCA | POI date of Gaode Map | 66.32 | 78.30 | ||
| Medical service | Number of medical services in each PCA | POI date of Gaode Map | 17.43 | 19.50 | ||
| Education | Number of schools and universities in each PCA | POI date of Gaode Map | 5.94 | 9.03 | ||
| Government agency | Number of government agencies in each PCA | POI date of Gaode Map | 10.94 | 12.48 | ||
| Accommodation service | Number of accommodation services in each PCA | POI date of Gaode Map | 11.15 | 12.26 | ||
| Scenic Spot | Number of Scenic Spots in each PCA | POI date of Gaode Map | 3.73 | 8.55 | ||
| Land use diversity | Land use diversity index | Original data from PCL (Peng Cheng Laboratory) & measured in GIS | 0.48 | 0.21 | ||
| Road density | Road density in each PCA (road length (km) per km2) | Original data from OpenStreetMap & measured in GIS | 28.78 | 12.56 | ||
| Variables | p_Value | VIF | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weekday | Weekend | ||||||
| Morning | Evening | No Peak | Morning | Evening | No Peak | ||
| (Intercept) | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | |
| Transportation Service | 0.324 * | 0.318 ** | 0.316 ** | 0.415 ** | 0.291 * | 0.296 * | 9.253 |
| Food & Beverages | 0.267 * | 0.324 ** | 0.279 ** | 0.228 | 0.336 ** | 0.337 ** | 7.845 |
| Sports & Recreation | −0.448 *** | −0.363 ** | −0.371 ** | −0.494 *** | −0.339 ** | −0.353 ** | 8.800 |
| Population density | 0.293 *** | 0.275 *** | 0.276 *** | 0.305 *** | 0.265 *** | 0.26 *** | 2.702 |
| Commercial & Industrial place | 0.510 *** | 0.452 *** | 0.355 *** | 0.313 *** | 0.252 ** | 0.226 ** | 3.408 |
| Medical service | 0.111 | 0.038 | 0.055 | 0.042 | −0.047 | −0.028 | 2.102 |
| Education | 0.059 | 0.041 | 0.052 | 0.03 | 0.008 | 0.016 | 1.502 |
| Government agency | −0.154 * | −0.198 ** | −0.136 * | −0.132 | −0.198 ** | −0.155 * | 3.089 |
| Accommodation service | 0.205 * | 0.232 ** | 0.35 *** | 0.422 *** | 0.445 *** | 0.421 *** | 3.956 |
| Scenic Spot | 0.125 * | 0.182 ** | 0.201 *** | 0.071 | 0.208 *** | 0.235 *** | 1.824 |
| Land use diversity | 0.239 ** | 0.226 ** | 0.221 ** | 0.231 ** | 0.208 ** | 0.213 ** | 1.179 |
| Road density | 0.129 * | 0.232 ** | 0.209 ** | −0.021 | 0.21 ** | 0.217 ** | 1.374 |
| Variables | Weekday | Weekend | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moran’s I | p | z | Moran’s I | p | z | ||
| Metro ridership | Morning | 0.26 | 0.001 | 7.7125 | 0.173 | 0.001 | 5.0781 |
| Evening | 0.289 | 0.001 | 8.3621 | 0.222 | 0.001 | 6.661 | |
| No peak | 0.297 | 0.001 | 8.7019 | 0.24 | 0.001 | 7.1648 | |
| Transportation Service | 0.774 | 0.001 | 21.5453 | 0.774 | 0.001 | 21.5453 | |
| Food & Beverages | 0.632 | 0.001 | 18.2026 | 0.632 | 0.001 | 18.2026 | |
| Sports & Recreation | 0.707 | 0.001 | 19.4424 | 0.707 | 0.001 | 19.4424 | |
| Population density | 0.801 | 0.001 | 21.9514 | 0.801 | 0.001 | 21.9514 | |
| Commercial & Industrial place | 0.508 | 0.001 | 14.5214 | 0.508 | 0.001 | 14.5214 | |
| Government agency | 0.65 | 0.001 | 19.1416 | 0.65 | 0.001 | 19.1416 | |
| Accommodation service | 0.606 | 0.001 | 17.2693 | 0.606 | 0.001 | 17.2693 | |
| Scenic Spot | 0.395 | 0.001 | 11.6727 | 0.395 | 0.001 | 11.6727 | |
| Land use diversity | 0.139 | 0.001 | 4.1564 | 0.139 | 0.001 | 4.1564 | |
| Road density | 0.344 | 0.001 | 10.1992 | 0.344 | 0.001 | 10.1992 | |
| Model | Index | Weekday | Weekend | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Morning | Evening | No Peak | Morning | Evening | No Peak | ||
| OLS | RSS | 127.824 | 105.432 | 100.053 | 156.697 | 114.379 | 110.574 |
| Log-likelihood | −283.251 | −257.059 | −249.938 | −310.949 | −268.136 | −263.536 | |
| Degree of freedom | 259 | 259 | 259 | 259 | 259 | 259 | |
| AIC | 588.502 | 536.118 | 521.875 | 643.898 | 558.273 | 549.072 | |
| AICC | 591.706 | 539.322 | 525.08 | 647.103 | 561.478 | 552.276 | |
| R2 | 0.53 | 0.612 | 0.632 | 0.424 | 0.579 | 0.593 | |
| Adj. R2 | 0.512 | 0.598 | 0.618 | 0.402 | 0.563 | 0.578 | |
| GWR | RSS | 97.682 | 88.198 | 84.639 | 127.785 | 111.864 | 108.099 |
| Log-likelihood | −246.676 | −232.785 | −227.184 | −283.21 | −265.112 | −260.456 | |
| Degree of freedom | 240.027 | 245.083 | 245.485 | 244.222 | 257.383 | 257.362 | |
| RMSE | 0.638 | 0.6 | 0.587 | 0.835 | 0.659 | 0.949 | |
| AIC | 559.298 | 521.403 | 509.397 | 623.976 | 561.458 | 552.189 | |
| AICC | 568.71 | 528.045 | 515.842 | 631.052 | 563.49 | 554.227 | |
| R2 | 0.641 | 0.676 | 0.689 | 0.53 | 0.589 | 0.603 | |
| Adj. R2 | 0.593 | 0.64 | 0.655 | 0.477 | 0.565 | 0.58 | |
| MGWR | RSS | 97.087 | 87.709 | 81.771 | 126.556 | 101.486 | 97.724 |
| Log-likelihood | −245.845 | −232.03 | −222.496 | −281.896 | −251.871 | −246.734 | |
| Degree of freedom | 234.927 | 243.837 | 244.222 | 241.791 | 250.692 | 250.692 | |
| RMSE | 0.643 | 0.6 | 0.579 | 0.82 | 0.882 | 0.882 | |
| AIC | 567.835 | 522.386 | 502.548 | 626.209 | 548.359 | 538.085 | |
| AICC | 580.608 | 529.661 | 509.623 | 634.594 | 552.541 | 542.266 | |
| R2 | 0.643 | 0.678 | 0.699 | 0.535 | 0.627 | 0.641 | |
| Adj. R2 | 0.586 | 0.64 | 0.665 | 0.476 | 0.595 | 0.61 | |
| Time | Morning | Evening | No Peak | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | GWR | MGWR | GWR | MGWR | GWR | MGWR | ||||||
| Index | BW | Mean | BW | Mean | BW | Mean | BW | Mean | BW | Mean | BW | Mean |
| Intercept | 155 | 0.05 | 92 | 0.105 | 192 | 0.025 | 269 | 0.088 | 194 | 0.001 | 262 | 0.05 |
| Transportation Service | 155 | 0.325 | 271 | 0.329 | 192 | 0.267 | 271 | 0.277 | 194 | 0.21 | 271 | 0.202 |
| Food & Beverages | 155 | 0.26 | 46 | 0.434 | 192 | 0.289 | 48 | 0.493 | 194 | 0.243 | 48 | 0.434 |
| Sports & Recreation | 155 | −0.381 | 271 | −0.439 | 192 | −0.287 | 259 | −0.414 | 194 | −0.256 | 244 | −0.372 |
| Population density | 155 | 0.297 | 271 | 0.243 | 192 | 0.278 | 271 | 0.271 | 194 | 0.25 | 271 | 0.231 |
| Commercial & Industrial place | 155 | 0.491 | 271 | 0.503 | 192 | 0.457 | 270 | 0.457 | 194 | 0.399 | 260 | 0.383 |
| Government agency | 155 | −0.146 | 271 | −0.157 | 192 | −0.209 | 271 | −0.211 | 194 | −0.138 | 271 | −0.135 |
| Accommodation service | 155 | 0.257 | 271 | 0.25 | 192 | 0.277 | 271 | 0.266 | 194 | 0.398 | 271 | 0.37 |
| Scenic Spot | 155 | 0.117 | 271 | 0.121 | 192 | 0.179 | 271 | 0.168 | 194 | 0.188 | 271 | 0.169 |
| Land use diversity | 155 | 0.227 | 251 | 0.232 | 192 | 0.215 | 251 | 0.204 | 194 | 0.219 | 271 | 0.207 |
| Road density | 155 | 0.137 | 271 | 0.127 | 192 | 0.239 | 271 | 0.237 | 194 | 0.206 | 271 | 0.22 |
| Time | Morning | Evening | No Peak | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | GWR | MGWR | GWR | MGWR | GWR | MGWR | ||||||
| Index | BW | Mean | BW | Mean | BW | Mean | BW | Mean | BW | Mean | BW | Mean |
| Intercept | 194 | −0.009 | 271 | 0.094 | 230 | −0.008 | 262 | 0.007 | 230 | −0.006 | 262 | 0.011 |
| Transportation Service | 194 | 0.292 | 271 | 0.342 | 230 | 0.167 | 271 | 0.228 | 230 | 0.173 | 271 | 0.236 |
| Food & Beverages | 194 | 0.185 | 48 | 0.392 | 230 | 0.284 | 186 | 0.291 | 230 | 0.288 | 186 | 0.276 |
| Sports & Recreation | 194 | −0.393 | 260 | −0.5 | 230 | −0.276 | 271 | −0.31 | 230 | −0.283 | 271 | −0.304 |
| Population density | 194 | 0.271 | 96 | 0.336 | 230 | 0.253 | 271 | 0.255 | 230 | 0.246 | 271 | 0.247 |
| Commercial & Industrial place | 194 | 0.378 | 271 | 0.347 | 230 | 0.313 | 271 | 0.282 | 230 | 0.285 | 271 | 0.255 |
| Government agency | 194 | −0.137 | 271 | −0.114 | 230 | −0.221 | 271 | −0.216 | 230 | −0.171 | 271 | −0.169 |
| Accommodation service | 194 | 0.46 | 271 | 0.455 | 230 | 0.493 | 271 | 0.476 | 230 | 0.468 | 269 | 0.46 |
| Scenic Spot | 194 | 0.061 | 271 | 0.058 | 230 | 0.202 | 271 | 0.207 | 230 | 0.227 | 271 | 0.234 |
| Land use diversity | 194 | 0.234 | 271 | 0.217 | 230 | 0.202 | 271 | 0.200 | 230 | 0.209 | 271 | 0.208 |
| Road density | 194 | −0.018 | 268 | −0.019 | 230 | 0.209 | 271 | 0.213 | 230 | 0.215 | 271 | 0.218 |
| Days | Time | Ranks | Factors | Single q | Interactive q | Enhancement |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weekday | Morning | 1 | Commercial & Industrial place ∩ Transportation Service | 0.821996 | 0.99966 | 21.61% |
| 2 | Land use diversity ∩ Transportation Service | 0.821996 | 0.99895 | 21.53% | ||
| 3 | Land use diversity ∩ Commercial & Industrial place | 0.782282 | 0.996781 | 27.42% | ||
| Evening | 1 | Commercial & Industrial place ∩ Transportation Service | 0.851932 | 0.999823 | 17.36% | |
| 2 | Land use diversity ∩ Transportation Service | 0.851932 | 0.998827 | 17.24% | ||
| 3 | Land use diversity ∩ Commercial & Industrial place | 0.83608 | 0.99818 | 19.39% | ||
| No peak | 1 | Commercial & Industrial place ∩ Transportation Service | 0.87528 | 0.999767 | 14.22% | |
| 2 | Land use diversity ∩ Transportation Service | 0.87528 | 0.999157 | 14.15% | ||
| 3 | Land use diversity ∩ Commercial & Industrial place | 0.832894 | 0.998841 | 19.92% | ||
| Weekend | Morning | 1 | Commercial & Industrial place ∩ Transportation Service | 0.799317 | 0.999264 | 25.01% |
| 2 | Land use diversity ∩ Transportation Service | 0.799317 | 0.998591 | 24.93% | ||
| 3 | Land use diversity ∩ Sports & Recreation | 0.698638 | 0.997424 | 42.77% | ||
| Evening | 1 | Commercial & Industrial place ∩ Transportation Service | 0.883352 | 0.999737 | 13.18% | |
| 2 | Land use diversity ∩ Transportation Service | 0.883352 | 0.999043 | 13.10% | ||
| 3 | Land use diversity ∩ Sports & Recreation | 0.838603 | 0.999028 | 19.13% | ||
| No peak | 1 | Commercial & Industrial place ∩ Transportation Service | 0.889219 | 0.999768 | 12.43% | |
| 2 | Land use diversity ∩ Sports & Recreation | 0.839402 | 0.999391 | 19.06% | ||
| 3 | Land use diversity ∩ Transportation Service | 0.889219 | 0.999384 | 12.39% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xue, Q.; Cheng, L.; Li, Z.; Xing, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, H.; Peng, Y. Unraveling Spatial–Temporal and Interactive Impact of Built Environment on Metro Ridership: A Case Study in Shanghai, China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 9479. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219479
Xue Q, Cheng L, Li Z, Xing Y, Wang H, Li H, Peng Y. Unraveling Spatial–Temporal and Interactive Impact of Built Environment on Metro Ridership: A Case Study in Shanghai, China. Sustainability. 2025; 17(21):9479. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219479
Chicago/Turabian StyleXue, Qingwen, Lingzhi Cheng, Zhichao Li, Yingying Xing, Hongwei Wang, Hongwei Li, and Yichuan Peng. 2025. "Unraveling Spatial–Temporal and Interactive Impact of Built Environment on Metro Ridership: A Case Study in Shanghai, China" Sustainability 17, no. 21: 9479. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219479
APA StyleXue, Q., Cheng, L., Li, Z., Xing, Y., Wang, H., Li, H., & Peng, Y. (2025). Unraveling Spatial–Temporal and Interactive Impact of Built Environment on Metro Ridership: A Case Study in Shanghai, China. Sustainability, 17(21), 9479. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219479






