Cognitive-Inspired Multimodal Learning Framework for Hazard Identification in Highway Construction with BIM–GIS Integration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Cognitive-Inspired Approaches for Hazard Identification
2.2. Multimodal Learning for Safety Applications
2.3. Digital Twin Technologies in Construction
2.4. Integrated Safety Management Systems
3. Background and Preliminaries
3.1. Deep Learning Foundations for Cognitive-Inspired Hazard Detection
3.2. Digital Twin and BIM–GIS Integration Principles
3.3. Multimodal Data Fusion and Cognitive Modeling Frameworks
4. Cognitive-Inspired Multimodal Deep Learning Framework
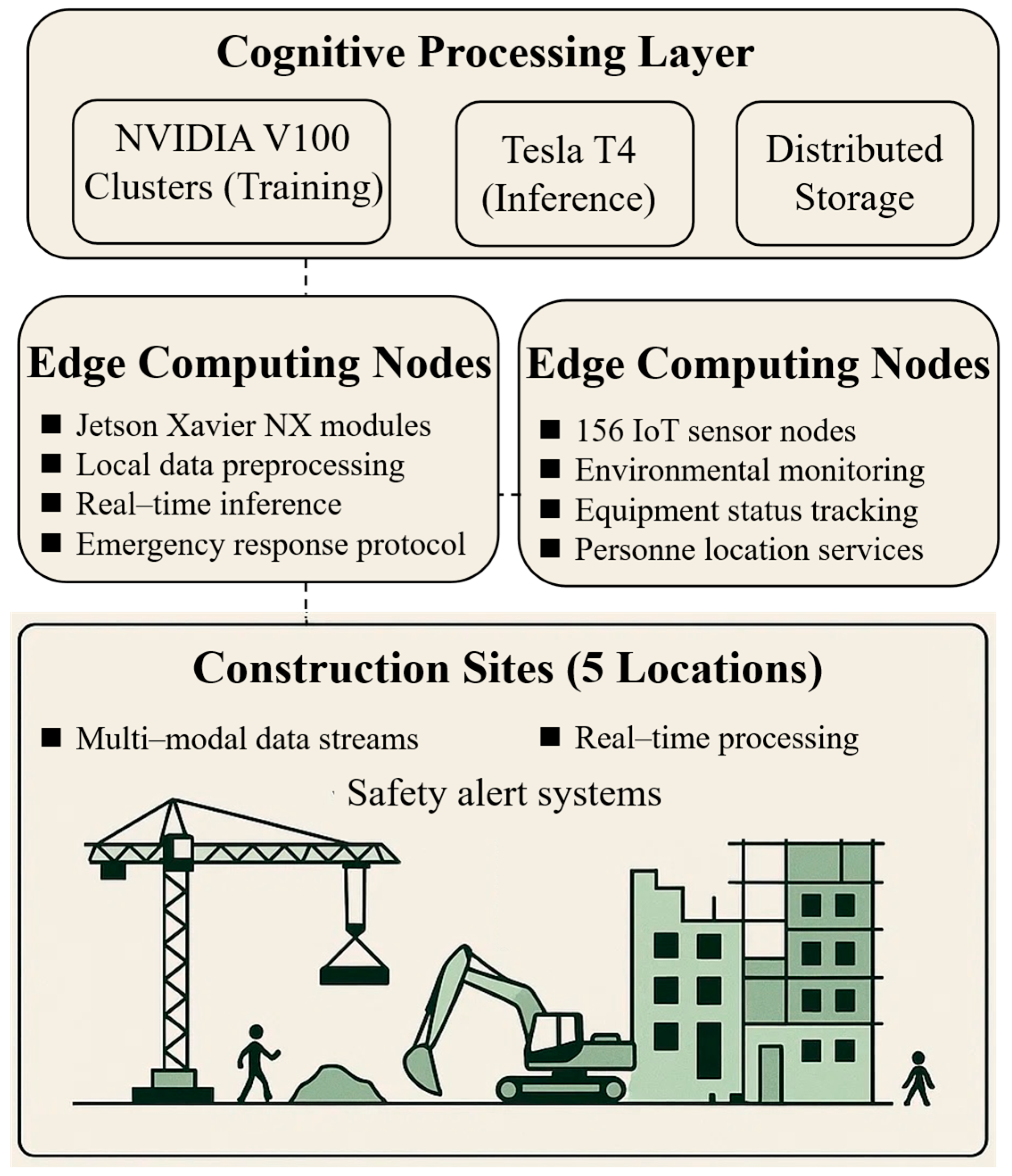
4.1. System Architecture Overview
4.2. Cognitive-Inspired Visual Attention Mechanism
4.2.1. Return Inhibition Neural Network Architecture
4.2.2. Multi-Scale Spatial Attention Integration
4.2.3. Temporal Memory and Search Strategy Learning
4.3. Multimodal Data Fusion Architecture
4.3.1. Hybrid BERT-Word2Vec Text Processing Pipeline
4.3.2. Optimized MobileNet-YOLOv5 Visual Processing
4.3.3. Adaptive Multimodal Fusion Strategy
4.4. Digital Twin Integration and Closed-Loop Management
4.4.1. Four-Layer Digital Twin Architecture
4.4.2. Adaptive Synchronization Protocols
4.4.3. Closed-Loop Feedback and Continuous Learning
5. Experimental Design and Results
5.1. Experimental Setup and Data Collection
5.1.1. Dataset Construction and Characteristics
5.1.2. Experimental Platform and Implementation Details
5.1.3. Evaluation Metrics and Baseline Methods
5.2. Component-Level Performance Analysis
5.2.1. Cognitive-Inspired Attention Mechanism Evaluation
5.2.2. Multimodal Fusion Architecture Assessment
5.2.3. Digital Twin Integration Performance
5.3. Comparative Analysis and Benchmark Results
5.3.1. Performance Comparison with Baseline Methods
5.3.2. Ablation Study Results
5.3.3. Real-World Deployment Assessment
6. Discussion
6.1. Theoretical Contributions and Implications
6.1.1. Advancement in Cognitive-Inspired Computing
6.1.2. Multimodal Learning Architecture Innovation
6.1.3. Digital Twin Paradigm Extension
6.2. Practical Implications and Industry Applications
6.2.1. Construction Safety Management Transformation
6.2.2. Scalability and Generalization Potential
6.2.3. Regulatory and Standardization Implications
6.3. Limitations and Challenges
6.3.1. Technical Limitations
6.3.2. Operational Challenges
6.3.3. Scalability and Generalization Challenges
6.4. Future Research Directions
6.4.1. Cognitive Modeling Enhancements
6.4.2. Advanced AI Integration
6.4.3. Ecosystem Integration and Standardization
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, J.; Li, Z.; Dong, S.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y. Visualization and Bibliometric Analysis of E-bike Studies: A Systematic Literature Review (1976–2023). Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2023, 122, 103891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Dong, S.; Wang, J.; Zhou, J.; Yuan, C.; Zheng, T. Capital-constrained Maintenance Scheduling for Road Networks Considering Traffic Dynamics. Transp. B Transp. Dyn. 2023, 11, 1845–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, E.; Ryan, N.; Kelly, S. Exploring the Perceived Influence of Safety Management Practices on Project Performance in the Construction Industry. Saf. Sci. 2012, 50, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Zhou, J.; Yuan, C.; Liu, D. Resilience-Based Optimization of Postdisaster Restoration Strategy for Road Networks. J. Adv. Transp. 2021, 2021, 8871876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Luo, H.; Liu, H. Deep Learning-Based Data Analytics for Safety in Construction. Autom. Constr. 2022, 140, 104302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, M.; Ding, H. An ALNS-based Approach for the Traffic-police-routine-patrol-Vehicle Assignment Problem in Resource Allocation Analysis of Traffic Crashes. Traffic Inj. Prev. 2024, 25, 688–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Chen, Q.; de Soto, B. Application of Digital Twin Technologies in Construction: An Overview of Opportunities and Challenges. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Automation and Robotics in Construction, Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 2–4 November 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Q.; Sun, C.; Li, Y.; Qi, Z.; Zhang, G. Applications of Digital Twin Technology in Construction Safety Risk Management: A Literature Review. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2025, 32, 3587–3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Shih, S.; Yen, K. An Integrated GIS, BIM and Facilities Infrastructure Information Platform Designed for City Management. J. Chin. Inst. Eng. 2021, 44, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Ding, L.; Love, P.E.D.; Luo, H.; Li, H.; Peña-Mora, F.; Zhong, B.; Zhou, C. Computer Vision Applications in Construction Safety Assurance. Autom. Constr. 2020, 110, 103013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lin, W.; Liu, M.; Rady, M.M. Multimodal Deep Learning Framework for Mental Disorder Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2020 15th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2020), Buenos Aires, Argentina, 16–20 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hakimi, O.; Liu, H.; Abudayyeh, O.; Houshyar, A.; Almatared, M.; Alhawiti, A. Data Fusion for Smart Civil Infrastructure Management: A Conceptual Digital Twin Framework. Buildings 2023, 13, 2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Ni, G.; Gao, F.; Zhang, Q.; Niu, M.; Ding, Z. Influencing Mechanism of Safety Sign Features on Visual Attention of Construction Workers: A Study Based on Eye-Tracking Technology. Buildings 2022, 12, 1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downing, P.; Liu, J.; Kanwisher, N. Testing Cognitive Models of Visual Attention with fMRI and MEG. Neuropsychologia 2001, 39, 1329–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; Zhong, G.; Yu, H. A Review on the Attention Mechanism of Deep Learning. Neurocomputing 2021, 452, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borji, A.; Itti, L. State-of-the-Art in Visual Attention Modeling. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 35, 185–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tixier, A.; Hallowell, M.; Rajagopalan, B.; Bowman, D. Automated Content Analysis for Construction Safety: A Natural Language Processing System to Extract Precursors and Outcomes from Unstructured Injury Reports. Autom. Constr. 2016, 62, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, H.; Zhao, X. Automatic Construction Site Hazard Identification Integrating Construction Scene Graphs with BERT Based Domain Knowledge. Autom. Constr. 2022, 142, 104535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Kang, S. Development of an Image Data Set of Construction Machines for Deep Learning Object Detection. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2021, 35, 05020005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, H.; Cai, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Sotelo, M.A.; Li, Z. Robust-FusionNet: Deep Multimodal Sensor Fusion for 3-D Object Detection under Severe Weather Conditions. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 71, 2513713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Sekula, P.; Ding, L. Machine Learning in Construction: From Shallow to Deep Learning. Dev. Built Environ. 2021, 6, 100045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yi, W.; Chi, H.; Wang, X.; Chan, A. A Critical Review of Virtual and Augmented Reality (VR/AR) Applications in Construction Safety. Autom. Constr. 2018, 86, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Hou, L.; Zhang, G.; Moon, S. Development of BIM, IoT and AR/VR Technologies for Fire Safety and Upskilling. Autom. Constr. 2021, 125, 103631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Zheng, A.; Yu, W.; Cao, H.; Ling, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhou, D. Digital Twin Technology in Transportation Infrastructure: A Comprehensive Survey of Current Applications, Challenges, and Future Directions. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamau, E.; Myllynen, T.; Mustapha, S.; Babatunde, G.; Alabi, A. A Conceptual Model for Real-Time Data Synchronization in Multi-Cloud Environments. Int. J. Multidiscip. Res. Growth Eval. 2024, 5, 1139–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyo, E.; Hartmann, T.; Ungureanu, L. Interoperability between BIM and GIS through Open Data Standards: An Overview of Current Literature. In Proceedings of the 9th Linked Data in Architecture and Construction Workshop, Luxembourg, Luxembourg, 11–13 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, E.; Ahn, S.; Han, S.; Abourizk, S. Identification and Association of High-Priority Safety Management System Factors and Accident Precursors for Proactive Safety Assessment and Control. J. Manag. Eng. 2018, 34, 04017041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Li, J.; Xiong, J.; Hu, M.; Zeng, R.; Sugumaran, V. Scenario Modeling for Urban Road Emergency Management: A Cognitive Digital Twin–Based Method. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2025, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Aires, M.; López-Alonso, M.; Martínez-Rojas, M. Building Information Modeling and Safety Management: A Systematic Review. Saf. Sci. 2018, 101, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niaz, A.; Khan, S.; Niaz, F.; Shoukat, M.U.; Niaz, I.; Jia, Y. Smart City IoT Application for Road Infrastructure Safety and Monitoring by Using Digital Twin. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on IT and Industrial Technologies (ICIT), Chiniot, Pakistan, 3–4 October 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Nebauer, C. Evaluation of Convolutional Neural Networks for Visual Recognition. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1998, 9, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soydaner, D. Attention Mechanism in Neural Networks: Where It Comes and Where It Goes. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 13371–13385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Dong, L.; Lapata, M. Long Short-Term Memory-Networks for Machine Reading. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1601.06733. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Yang, Y.; Cheng, X.; Zuo, H.; Zheng, C. The Development of Digital Twin Technology Review. In Proceedings of the 2020 Chinese Automation Congress (CAC), Shanghai, China, 6–8 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yevu, S.K.; Owusu, E.K.; Chan, A.P.C.; Sepasgozar, S.M.E.; Kamat, V.R. Digital Twin-Enabled Prefabrication Supply Chain for Smart Construction and Carbon Emissions Evaluation in Building Projects. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 78, 107598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardin, B.; McCool, D. BIM and Construction Management: Proven Tools, Methods, and Workflows; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mushtaha, A.W.; Alaloul, W.S.; Musarat, M.A.; Baarimah, A.O.; Rabah, F.K.; Alawag, A.M. BIM-GIS Integration for Infrastructure Management in Post-Disaster Stage. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Smart Infrastructure and Construction, Manama, Bahrain, 28–29 January 2024. [Google Scholar]
- El Yamani, S.; Hajji, R.; Billen, R. IFC-CityGML Data Integration for 3D Property Valuation. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2023, 12, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moir, S.; Paquet, V.; Punnett, L.; Buchholz, B.; Wegman, D. Making Sense of Highway Construction: A Taxonomic Framework for Ergonomic Exposure Assessment and Intervention Research. Appl. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2003, 18, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, K.; Terachi, Y.; Takagi, K.; Izumi, S.; Kawaguchi, H.; Yoshimoto, M. Architectural Study of HOG Feature Extraction Processor for Real-Time Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE 19th International Conference on Electronics, Circuits, and Systems, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 17–19 October 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Baidya, R.; Jeong, H. YOLOv5 with ConvMixer Prediction Heads for Precise Object Detection in Drone Imagery. Sensors 2022, 22, 8424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, H.; Rafieizonooz, M.; Han, S.; Lee, D. Current Status and Future Directions of Deep Learning Applications for Safety Management in Construction. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basystiuk, O.; Rybchak, Z.; Zavushchak, I.; Marikutsa, U. Evaluation of Multimodal Data Synchronization Tools. Comput. Des. Syst. Theory Pract. 2024, 6, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochovski, P.; Stankovski, V. Supporting Smart Construction with Dependable Edge Computing Infrastructures and Applications. Autom. Constr. 2018, 85, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Jin, T.; Ang, P.; Bian, X.; Chen, Y. Computer Vision-based Monitoring of the 3-D Structural Deformation of an Ancient Structure Induced by Shield Tunneling Construction. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boella, G.; Janssen, M.; Hulstijn, J.; Humphreys, L.; van der Torre, L. Managing Legal Interpretation in Regulatory Compliance. In Proceedings of the 19th ACM Symposium on Access Control Models and Technologies, London, ON, Canada, June 25–27 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, C.; Zhang, C.; Yahja, A.; Mostafavi, A. Disaster City Digital Twin: A Vision for Integrating Artificial and Human Intelligence for Disaster Management. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2021, 56, 102049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, K. Situating Workplace Surveillance: Ethics and Computer Based Performance Monitoring. Ethics Inf. Technol. 2001, 3, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, N.; Cheung, S.; Li, K. Perceptive Biases in Construction Mediation: Evidence and Application of Artificial Intelligence. Buildings 2023, 13, 2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chung, S. Artificial Intelligence in Safety-Critical Systems: A Systematic Review. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2022, 122, 442–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Data Category | Volume | Specifications | Collection Sites | Annotation Quality |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Visual Data | 32,847 images | 4K resolution | Sites A–E | 85% inter-annotator agreement |
| 1247 h video | 30–60 FPS | Multi-weather | ||
| Textual Data | 15,623 reports | PDF/Word formats | All sites | Expert validation |
| 8934 incident logs | Multilingual support | Historical archives | Domain ontology | |
| 12,456 compliance docs | - | - | - | |
| Sensor Data | 156 IoT nodes | Environmental | Real-time streams | Calibrated sensors |
| Continuous monitoring | Equipment | Edge processing | Quality assurance | |
| - | Personnel tracking | - | - | |
| Ground Truth | 23 hazard categories | Hierarchical taxonomy | Expert annotations | >85% agreement |
| 87 sub-categories | Severity levels | Consensus validation | Triple annotation |
| Method | Accuracy (%) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1-Score (%) | Response Time (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Faster R-CNN | 73.5 | 78.2 | 69.1 | 73.4 | 892 |
| Standard YOLOv5 | 76.8 | 81.3 | 72.4 | 76.6 | 234 |
| Fixed Multimodal Fusion | 78.2 | 83.7 | 74.8 | 79 | 187 |
| Commercial System A | 66.9 | 71.2 | 62.8 | 66.7 | 1247 |
| Commercial System B | 69.4 | 74.6 | 65.1 | 69.5 | 956 |
| Proposed Framework | 91.7 | 94.2 | 89.4 | 91.7 | 147 |
| Site Characteristics | Site A | Site B | Site C | Site D | Site E | Average | Std Dev |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Location | Urban Highway | Rural Highway | Mountain Pass | Coastal Route | Industrial Zone | — | — |
| Climate | Temperate | Continental | Alpine | Maritime | Urban Heat | — | — |
| Detection Accuracy | 92.30% | 91.80% | 90.90% | 91.20% | 92.10% | 91.70% | ±0.6% |
| Response Time | 142 ms | 151 ms | 156 ms | 144 ms | 148 ms | 148 ms | ±5.4 ms |
| User Satisfaction | 89% | 85% | 84% | 88% | 91% | 87% | ±2.8% |
| Accident Reduction | 38% | 31% | 29% | 35% | 37% | 34% | ±3.6% |
| Efficiency Gain | 45% | 39% | 38% | 43% | 47% | 42% | ±3.8% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, J.; Li, Z.; Shi, Z.; Mao, X.; Gao, C. Cognitive-Inspired Multimodal Learning Framework for Hazard Identification in Highway Construction with BIM–GIS Integration. Sustainability 2025, 17, 9395. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219395
Zhou J, Li Z, Shi Z, Mao X, Gao C. Cognitive-Inspired Multimodal Learning Framework for Hazard Identification in Highway Construction with BIM–GIS Integration. Sustainability. 2025; 17(21):9395. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219395
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Jibiao, Zewei Li, Zhan Shi, Xinhua Mao, and Chao Gao. 2025. "Cognitive-Inspired Multimodal Learning Framework for Hazard Identification in Highway Construction with BIM–GIS Integration" Sustainability 17, no. 21: 9395. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219395
APA StyleZhou, J., Li, Z., Shi, Z., Mao, X., & Gao, C. (2025). Cognitive-Inspired Multimodal Learning Framework for Hazard Identification in Highway Construction with BIM–GIS Integration. Sustainability, 17(21), 9395. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219395








