Abstract
Cultivated land (CL) is essential for human survival, as its coordinated utilization plays a crucial role in both food production and ecological protection. In this study, we focus on Aksu, a typical oasis in arid areas of Xinjiang, to explore how to improve the eco-efficiency of cultivated land utilization (ECLU) from the perspective of carbon emissions under different ownership structures. The goal is to provide policy support for the sustainable intensification of CL in Aksu. The super-efficiency slack-based measure (Super-SBM) model was used to calculate the ECLU, while the carbon emissions coefficient method was employed to estimate cultivated land carbon emissions (CLCE). Additionally, the random forest regression (RFR) model was utilized to analyze differences in CLCE between collective and state-owned cultivated lands. Finally, a Geo-detector analysis was conducted to identify driving factors of CLCE. The findings indicate that the overall ECLU values in Aksu initially increased and subsequently decreased over time. During the study period, Kalpin showed the highest ECLU, followed by Wensu and Wushi. The total CLCE in Aksu demonstrated an initial increase followed by a decrease, but the overall trend was growth, from 3.7 t in 2008 to 5.63 t in 2019, on average. It was observed that carbon emissions from state-owned cultivated land were greater than those from collective cultivated land, and carbon emissions from non-food crops were higher than those from food crops. Furthermore, spatial heterogeneity was evident in the CLCE. The single factor detection results showed that the Local_GDP (q = 0.763, representing the explanatory power of the Local_GDP on cultivated land carbon emissions) was identified as the main driver of CLCE in Aksu. The interactive detection results indicated that the Local_GDP and Farmer income (0.839) had stronger effects on CLCE in Aksu than any other two factors. It was also found that ownership of CL directly affects CLCE and indirectly affects the ECLU. In conclusion, it is necessary to formulate corresponding countermeasures for improving the ECLU involving government intervention, as well as cooperation with farmers and other stakeholders, to address these issues effectively within Aksu’s agricultural sector.
1. Introduction
Cultivated land (CL) is a land type formed through long-term human transformation of natural ecosystems and has evolved into a critical resource supporting human survival and socio-economic development [1,2]. According to a report released by the United Nations, the global population is projected to surpass 9.8 billion by 2050, which will drive a more than 50% growth in global food demand [3]. Nevertheless, China is confronted with a grim reality regarding its cultivated land resources and food security: despite accounting for only approximately 7.5% of the world’s total CL area, it bears the responsibility of feeding about 23% of the global population [4]. Meanwhile, the rapid advancement of urbanization and industrialization has led to extensive conversion of cultivated land to construction land [5,6], further aggravating this contradiction. Maintaining a dynamic balance in cultivated land quantity is essential for safeguarding food security, but this process inevitably compresses ecological space. Thus, realizing a win–win scenario between food production and ecological environmental protection to promote sustainable development has become a prominent challenge. To address these issues, intensive agricultural practices targeting yield improvement per unit cultivated land area have been widely adopted and recognized. However, numerous studies have demonstrated that agricultural intensification is a significant contributor to land degradation, soil pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, and biodiversity loss [7,8,9,10]. In recent years, the sustainable intensification of cultivated land has attracted increasing academic attention [11,12,13,14], underscoring its role as a core pathway to achieve sustainable agricultural development.
After the proposal of sustainable intensification of cultivated land, there has been a growing focus on the quantitative measurement and influencing factors of the ECLU in current academic research [13,14,15,16]. The ECLU refers to the degree to which a certain input of production factors can maximize social and economic output and minimize environmental pollution during the utilization of farmland. There is a call for researchers to conduct deeper studies on the ECLU from the perspective of sustainable land use, aiming to achieve coordination among food security, economic development, and ecological protection [17]. The ECLU serves as an important indicator for evaluating ecological civilization construction in China. It also plays a crucial role in measuring the optimal allocation of cultivated land resources and promoting high-quality agricultural development [18]. Previous studies have demonstrated that the ecological efficiency of cultivated land use in Xinjiang ranged from 0.7 to a maximum value of 1 [19], with multiple factors affecting the ECLU in this region. Furthermore, when focusing on improving the ECLU, attention should be paid to unexpected outputs such as carbon emissions caused by land-use change, which has been widely studied [20,21,22]. Our previous study indicated that the northern margin of the Tarim Basin is one of the regions with significant carbon emissions in Xinjiang over recent years [23]. The cultivated land carbon emissions (CLCE) and the eco-efficiency of cultivated land utilization under the influence of CLCE in the northwestern margin of the Tarim Basin warrant further investigation.
Cultivated land carbon emissions are defined as the release of greenhouse gases comprising those originating from fertilizer and pesticide application, agricultural energy use, and cultivated land conversion within agricultural systems [24]. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), China’s agriculture accounts for 14% of global greenhouse gas emissions. Furthermore, the China Council for International Cooperation on Environment and Development reports that agricultural greenhouse gas emissions constitute approximately 17% of China’s national total [25]. Reducing agricultural carbon emissions represents an essential pathway to enhance cultivated land-use efficiency, a critical factor in achieving sustainable intensification of cultivated land.
In terms of measuring the ECLU, relevant studies have yielded fruitful results and promoted the continuous deepening of ECLU research. The stochastic frontier analysis (SFA) model, data envelopment analysis (DEA) model, the slacks-based model (SBM), super-efficiency SBM, and directional distance function (DDF) model have been widely used in evaluating the efficiency of cultivated land utilization [2,5,18,24,26]. Among these, the super-efficiency SBM model, particularly suitable for handling the multiple input–output framework inherent to cultivated land-use systems, has been frequently adopted for ECLU assessment [2,27]. Regarding the selection of input and output indicators for the ECLU, current research has focused more on “tangible” resource inputs such as cultivated land area, labor force, agricultural diesel, chemical fertilizers, pesticides, agricultural films, etc., as well as expected economic output, but has overlooked unexpected outputs such as carbon emission and agricultural non-point source pollution [28,29]. However, the super-efficiency SBM model can effectively address these unexpected outputs that are ignored in the process of evaluating the ECLU. Additionally, the Super-SBM model can compensate for the limitations of traditional DEA models by ranking and separating effective decision-making units. Moreover, a number of scholars have focused on specific causes for low ECLU [4,30].
However, it is crucial to recognize that the state and collective agrarian property regimes constitute the predominant forms of cultivated land tenure in China [31]. Crucially, the impact of land ownership on carbon emissions—and its consequent indirect effects on cultivated land-use efficiency (ECLU) in Aksu—remains an open question. Previous studies have demonstrated that land ownership significantly influences rice productivity and technical efficiency [32]. Similarly, studies have explored strategies for enhancing agricultural productivity through adjustments to cultivated land-tenure arrangements [33]. The potential influence of land-tenure systems on cultivated land carbon emissions has garnered increasing academic attention. Research indicates that land ownership structure can significantly alter landscape diversity and ecological productivity [34]. Empirical evidence from Shandong and Henan provinces further demonstrates that cultivated land tenure exerts a significant impact on the adoption of agricultural green control technologies [35]. Furthermore, differences in land ownership have been shown to drive variations in agricultural productivity, as evidenced by research in Zimbabwe [36], while ambiguities in land tenure have been linked to increased differentiation in cultivated land production efficiency [37]. Consequently, landowners must strategically balance immediate and long-term profitability when making decisions regarding pesticide application to optimize land productivity [38].
Apparently, the utilization of oasis cultivated land in Xinjiang is facing challenges in food, ecological, and social security, and it needs to be urgently transformed towards sustainable intensive utilization [39]. The northern margin of the Tarim Basin has shown large carbon emissions in Xinjiang over the years, which will indirectly affect the CLCE in these areas. Therefore, the Aksu region on the northern margin of the Tarim Basin was selected as the study area. In this study, we used the Super-SBM model to measure the ECLU and employed the carbon emissions coefficient method to estimate CLCE in Aksu. Subsequently, we applied a random forest regression model to analyze differences in CLCE between collective cultivated land and state-owned cultivated land. Additionally, Geo-detector was utilized to identify and quantify the driving factors of CLCE. Ultimately, we quantitatively compared carbon emissions across different cultivated land ownership regimes, aiming to provide policy recommendations for achieving sustainable intensification of cultivated land in Aksu.
2. Study Area and Data Sources
2.1. Study Area
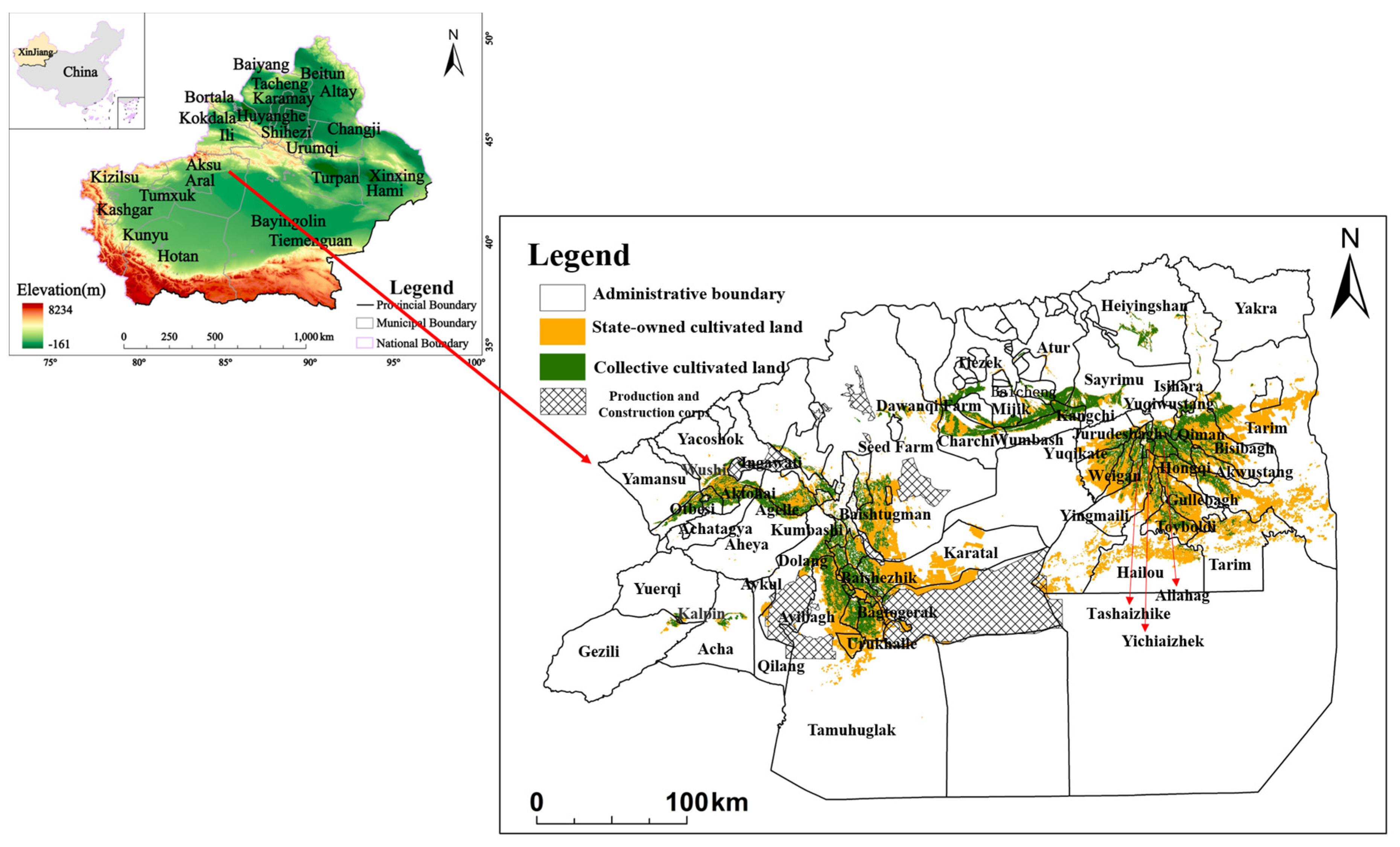
Aksu is situated at the southern foothills of the Tianshan Mountain in the southwest of Xinjiang and the northern edge of the Tarim Basin (Figure 1). The region experiences a warm temperate continental arid climate. The terrain slopes from high in the north to low in the south, with Tianshan Mountain to the north, Gobi and oasis in the middle, Taklimakan Desert to the south, Baicheng Basin to the east, and Wushi Valley to the west. There are perennial glaciers and snow in the high mountains, which are the origin of many rivers in Aksu. The development of oasis agriculture relying on these rivers has led to well-developed agriculture and animal husbandry sectors that occupy a leading position in the national economy. Aksu is considered one of Xinjiang’s main irrigated agricultural areas and serves as a production base for grain, cotton, fruit, and melon. At the end of 2019, the total cultivated land area reached 702,414.3 hm2, with a per capita cultivated land area of 0.273 hm2. In contrast, at the end of 2008, the cultivated land area was 511,135.44 hm2, with a per capita cultivated land area of 0.226 hm2. This represents an increase in the total cultivated land area of 191,278.86 hm2, and an increase in per capita cultivated land area of 0.047 hm2 compared to 2019. The expansion of both total and per capita cultivated land areas exacerbates the imbalance between supply and demand for arable land due to local natural and socio-economic constraints. This situation also gives rise to social, ecological, and environmental challenges that need to be addressed effectively.

Figure 1.
Geographical location and administrative division of Xinjiang. (The standard map number is GS (2024) 0650, which is sourced from the National Geographic Information Public Service Platform and the base map has not been modified).
2.2. Data Sources and Processing
The data sources are divided into four parts. Table 1 shows the data sources. In our study, the questionnaire survey, including the input–output data of cultivated land (food crops and non-food crops), was investigated for state-owned land farmers and collective land farmers in each county and city in Aksu. The survey samples were 230 random questionnaires (209 were available) from nine counties and cities in the study area. Among them, 104 questionnaires belonged to the survey data of collectively owned land farming households, and 105 questionnaires belonged to the survey results of state-owned land farming households. The survey is based on the average total sown area of 867,100 hm2 of crops in Aksu between 2018 and 2021. The food crops, including wheat, accounted for about 15%, and corn accounted for about 10%. The non-food crops, including cotton, accounted for about 59%, silage corn accounted for about 4.5%, and vegetables, including peppers and tomatoes, accounted for about 2.8%. Thus, in this study, “food crops” refers to wheat and corn, and “non-food crops” refers to cotton, silage corn, and vegetables.

Table 1.
Data description.
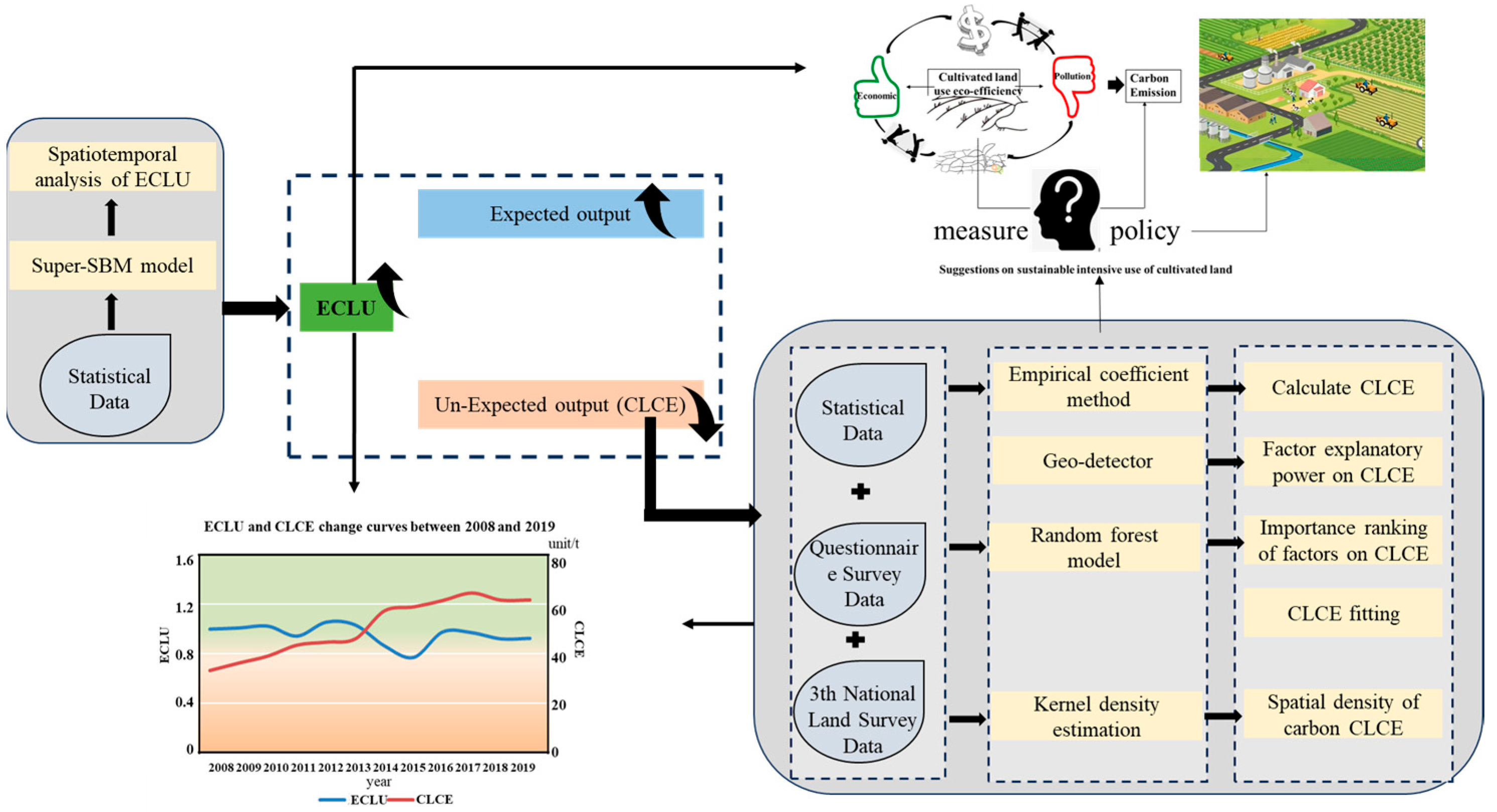
This study explored the ECLU from the perspective of CLCE and found differences in cultivated land carbon emission with different property rights (Figure 2) in order to put forward countermeasures and suggestions for oasis food security and cultivated land ecological protection.
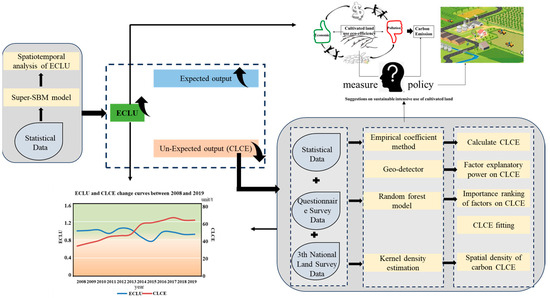
Figure 2.
Schematic of the research process.
3. Method
3.1. Calculation of the ECLU: Super-SBM Model
Based on an in-depth interpretation of the connotation of the ECLU and the research results of relevant scholars [27,40,41], an evaluation system for the ECLU in Aksu was established under the principles of rationality and objectivity (see Table 2). The index system aims to reflect the coordination among cultivated land input, economic output, and ecological environment, as well as to demonstrate the impact of cultivated land input on agricultural economic growth and rural ecological environment. In this study, for unexpected output, we only considered CLCE and temporarily did not take into account non-point source pollution in agriculture.

Table 2.
Evaluation index system of cultivated land-use eco-efficiency.
The total CLCE comprises direct emissions from six key agricultural inputs: tillage operations, synthetic fertilizer application, agricultural plastic film usage, diesel fuel consumption, irrigation energy use, and pesticide deployment. To ensure data accessibility and minimize bias caused by incomplete or omitted information, nine counties and cities in the Aksu region (Aksu, Wensu, Kuqa, Shaya, Xinhe, Baicheng, Wushi, Awat, and Kalpin) were selected for this study. The primary sources of data for this research were the Statistical Yearbook of Aksu, the Statistical Bulletin of Aksu, and county-level statistical data of Aksu spanning from 2009 to 2020.
Tone (2001) proposed the Super-SBM model, which combines the advantages of the traditional efficiency evaluation model, data envelopment analysis (DEA), and the slacks-based measure (SBM) of efficiency [42,43]. The Super-SBM model is an advanced data enveloping analysis model used to evaluate the efficiency of decision-making units (such as enterprises, regions, and farmland utilization units) [1,2,4,5]. It goes beyond the traditional input–output model by measuring the efficiency of unexpected outputs. This is achieved through the addition of slack variables in the model, overcoming the problem of measurement error in the traditional DEA model. Therefore, this paper selects the Super-SBM model to measure the ECLU in Aksu, with its principle as follows:
In the first equation, each county represents a decision unit. The symbol m denotes the total number of decision units, where X, Ye, and Yn represent the matrices of inputs, desired outputs, and undesired outputs, respectively. In Equation (2), the symbol denotes the ECLU, where [i ∈ (1~m)], r [r ∈ (1~p1)], and h [h ∈ (1~p2)] represent the number of input variables, expected output variables, and unexpected output variables. The relaxation vectors of input, expected output, and unexpected output are , , and . In Equation (3), xk, yk, and bk represent the input, expected output, and unexpected output vectors of decision unit k, respectively. λ is used to denote the weight vectors. The symbols S−, S+, and Sb− denote the relaxation matrix for inputs, expected outputs, and unexpected outputs, respectively.
3.2. Carbon Emissions of Cultivated Land
Carbon emissions in agricultural production activities generally encompass six aspects: tillage (T), agricultural machinery (AM), chemical fertilizer (CF), pesticide (P), agricultural film (AF), and irrigation (I). The carbon emissions from chemical fertilizers, pesticides, and agricultural film primarily occur during their production and usage processes [44]. Carbon emissions from agricultural machinery are mainly attributed to the use of fossil fuels. Similarly, carbon emissions from agricultural irrigation are indirectly linked to the use of fossil fuels for electricity generation. Furthermore, soil organic carbon is depleted during agricultural cultivation, leading to the release of soil carbon. Consequently, the total carbon emission of cultivated land was calculated using the method of agricultural carbon emission coefficients outlined in Table 3 with Equation (4):
where C_E is the total carbon emissions of CL, Ei is the total amount of kinds of carbon emission sources of CL, and θi is the emission coefficient for each carbon emission source.

Table 3.
The coefficient of major carbon sources during the process of cultivating land.
3.3. Random Forest Regression Model
This study investigates carbon emissions from food and non-food crops on both collective-owned and state-owned farmland in Aksu, based on a questionnaire survey of 209 households. We analyzed per-unit-area carbon emission intensity differences across land ownership types and employed a random forest regression (RFR) model to assess the significance of emission contributions from (1) food crops versus non-food crops, and (2) collective versus state-owned farmland, respectively. Input variables included agricultural film (AF), chemical fertilizer (CF), pesticide (P), agricultural electricity (AE), agricultural diesel (AD), and irrigation (I). It should be noted that the CLCE indicators used in the empirical coefficient method align with the questionnaire survey, except for disaggregating the “total power of agricultural machinery” into “agricultural electricity (AE)” and “agricultural diesel (AD)” for finer-grained analysis. The findings may inform cultivated land management and production planning in arid oasis regions. Farmland tenure adjustment is highlighted as a critical strategy for enhancing land quality and advancing agricultural modernization [45].
The RFR model is an ensemble machine-learning algorithm based on decision trees. The basic idea of its algorithm is to construct a certain number of decision trees and combine them according to certain criteria to generate a random forest [45,46,47]. The RF model offers distinct advantages in the algorithm due to its capacity for processing high-dimensional data, random sample selection, and the ability to assess variable importance [46,47]. In this study, the RFR model was employed to rank the significance of key factors influencing carbon emissions from cultivated land in Aksu and identify the primary influencing factors across different ownership categories. Evaluation indicators included the coefficient of determination (R2) and root mean square error (RMSE). The importance ranking was determined using the IncMSE method, with calculation formulas as follows in Equations (5)–(7):
The variables Oi and Pi represent the i-th measured value and fitting value, respectively. They also represent the average values of measured and fitted values, respectively. I represents the root mean square error increased by the influencing factor. Error1i refers to the data that does not participate in decision tree training when the decision tree is selected, while Error2i refers to the data that does not participate in decision tree training when random interference is added. A higher R2 value closer to 1 indicates a lower RMSE value closer to 0, signifying higher model interpretation accuracy. Using R software (R4.2.3), 60% of the data are used as training samples and 40% as test samples. After repeated tests, it was determined that the optimal number of leaves for the decision tree is 42, with a total of 500 trees.
3.4. Kernel Density Estimation
The kernel density estimation (KDE) method [48] is a non-parametric approach used to estimate unknown density functions. It is primarily employed for estimating the probability density of random variables [23] and can effectively capture the distance attenuation effect in the spatial distribution of geographical phenomena. In this study, based on the data of cultivated land attributes from the Third National Land Survey and 209 household survey data points, the KDE was used to reveal the spatial aggregation characteristics of CLCE. The kernel density estimator for the density function is as follows:
In the above formula, f(x) is the probability density function, n is the sample size, h is the bandwidth, whose value affects the smoothness of the kernel density distribution, and x − xi represents the distance from the estimate point to the output grid. K is the kernel function. The kernel function mainly includes the Gaussian kernel, quadratic kernel, double-weight kernel, and so on. In this study, we adopt the commonly used Gaussian kernel function, defined as .
3.5. Geo-Detector Model
The Geo-detector model is a statistical method used to detect spatial heterogeneity and reveal the driving forces behind it [49]. Its principle is to determine the similarity of the spatial distribution of two variables through the perspective of spatial stratification heterogeneity, which consists of factor detection, interaction detection, risk detection, and ecological detection. In recent years, it has been widely applied in the fields of climate change, ecological engineering, and urban research [50,51,52,53]. In this paper, the Geo-detector was utilized to explore the causes of spatial differentiation of CLCE from a holistic perspective in Aksu based on data from the Third National Land Survey. The factor detection module was employed to test the explanatory power of each factor (Table 3) on the spatial and temporal differentiation pattern of CLCE effects. The interactive detection module was used to identify the coupling mode of each factor (Table 3) and its influence intensity on the spatial differentiation of CLCE effects. Furthermore, the factor detector was used to further analyze the effects of CLCE on the spatial differentiation of the ECLU.
(1) The results of factor detection were utilized to assess the impact of environmental factors on CLCE, with the q value representing the explanatory power of influencing factors on CLCE in Aksu. The expression for the q value is as follows:
In Equation (9), where q represents the influence index of influencing factors on CLCE, h = 1, 2, … L denotes the stratification of variable Y (carbon emissions from cultivated land) or factor X (Local_GDP, Farmer income (FI), Proportion of effective irrigated area (PEI), Degree of chemicalization of agriculture per unit area (DCA), Degree of fiscal policies for agricultural support (DFP), Intensity of investment in agriculture (IIA), Multiple cropping index (MCI), and Operation scale of cultivated land (PSCL)). N is the number of samples in the entire region, Nh is the number of samples in layer h, σ2 signifies the variance of carbon emissions from cultivated land in the whole region, and σh2 indicates the variance of carbon emissions from cultivated land in layer h. In Equation (10), SSW and SST represent the sum of variances within the layer and across the entire region, respectively. The value range for q is [0, 1], with a larger value indicating a stronger explanatory power of the factor to CLCE. The value of q = 1 suggests an optimal interpretative effect, while a value of q = 0 indicates no correlation between the factor and CLCE.
(2) Interaction detector, which is used to determine if the combined action of the two factors will lead to a rise, a drop, or no change at all in the influence degree of the CLCE. By comparing the q value of the single factor, the sum of the q value of two factors, and the q value of the interaction of two factors, respectively. The five types of relationships between the two factors are as follows:
- ➀
- Weaken, nonlinear: q(X1∩X2) < Min(q(X1), q(X2)).
- ➁
- Weaken, nonlinear Single-factor: Min(q(X1), q(X2)) < q(X1∩X2) < Max(q(X1)), q(X2)).
- ➂
- Enhance, double factor: q(X1∩X2) > Max(q(X1), q(X2)).
- ➃
- Independent: q(X1∩X2) = q(X1) + q(X2).
- ➄
- Enhance, nonlinear: q(X1∩X2) > q(X1) + q(X2).
4. Results
4.1. Analysis of the ECLU of Aksu
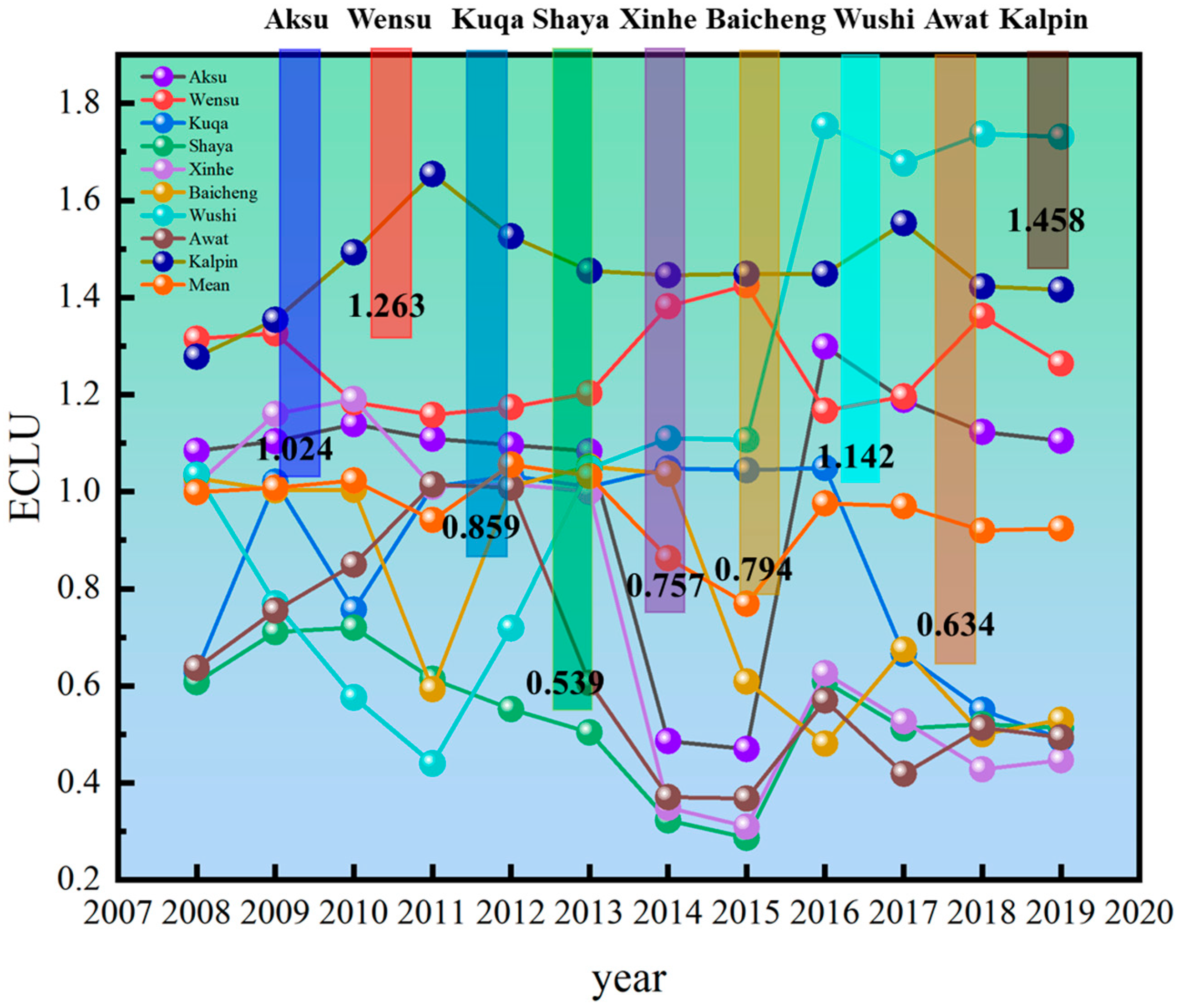
Based on the Super-SBM model with undesired output, the ECLU of the nine cities and counties in Aksu from 2008 to 2019 was calculated using MATLAB 2022a software. We obtained the ECLU of the Aksu region from 2008 to 2019, as seen in Figure 3.

Figure 3.
ECLU of Aksu from 2008 to 2019.
Firstly, through the comparison of agricultural input and output data for each city and county in Aksu, it is evident that the number of employees in agriculture, usage of chemical fertilizers, pesticides, agricultural diesel, agricultural films, and effective irrigated area has continued to increase with the expansion of cultivated land. The expansion of cultivated land coincides with a steady increase in production factors, and it has driven rapid agricultural development in Aksu. Consequently, this growth has resulted in an expected increase in cultivated land output, but it also contributes to unexpected output growth. As shown in Figure 3, the ECLU in Aksu is approximately 0.95 and exhibited fluctuating changes during the study period. The ECLU fluctuated around 1 from 2008 to 2013, then began to decline to its lowest point of 0.769 in 2015, and finally rose again to 0.957 in 2019. This indicates that there remains substantial room for enhancing resource conservation and environmental protection in the production of cultivated land in Aksu. When comparing the average ECLU of each city and county between 2008 and 2019, Kalpin had the highest at 1.458, while Shaya had the lowest at 0.539. Additionally, it was observed that Wensu and Kalpin maintained stable ECLU values. However, there was a noticeable fluctuation of ECLU values in other cities and counties across the region. Overall, these findings highlight the necessity of further prioritizing efforts to enhance resource conservation and environmental protection in the region’s cultivated land production. Notably, substantial disparities exist in the level of cultivated land production technology across cities and counties in Aksu. It was observed that the sown areas of Shaya and Kuqa were similar, but during the study period, the average ECLU of Kuqa was 0.32 higher than that of Shaya. This difference can be attributed to the fact that the number of pesticides used in Shaya is much higher than that in Kuqa, which is the main reason for the low ECLU in Shaya. The characteristics of ECLU changes in Aksu from 2008 to 2019 reflect a relatively extensive mode of agricultural economic development, accompanied by a backward level of cultivated land production technology. Specifically, agricultural economic growth has been achieved through the continuous expansion of various production factors, while the green and sustainable development of agriculture has been overlooked.
4.2. Carbon Emission Analysis of Cultivated Land in Various Counties and Cities in Aksu
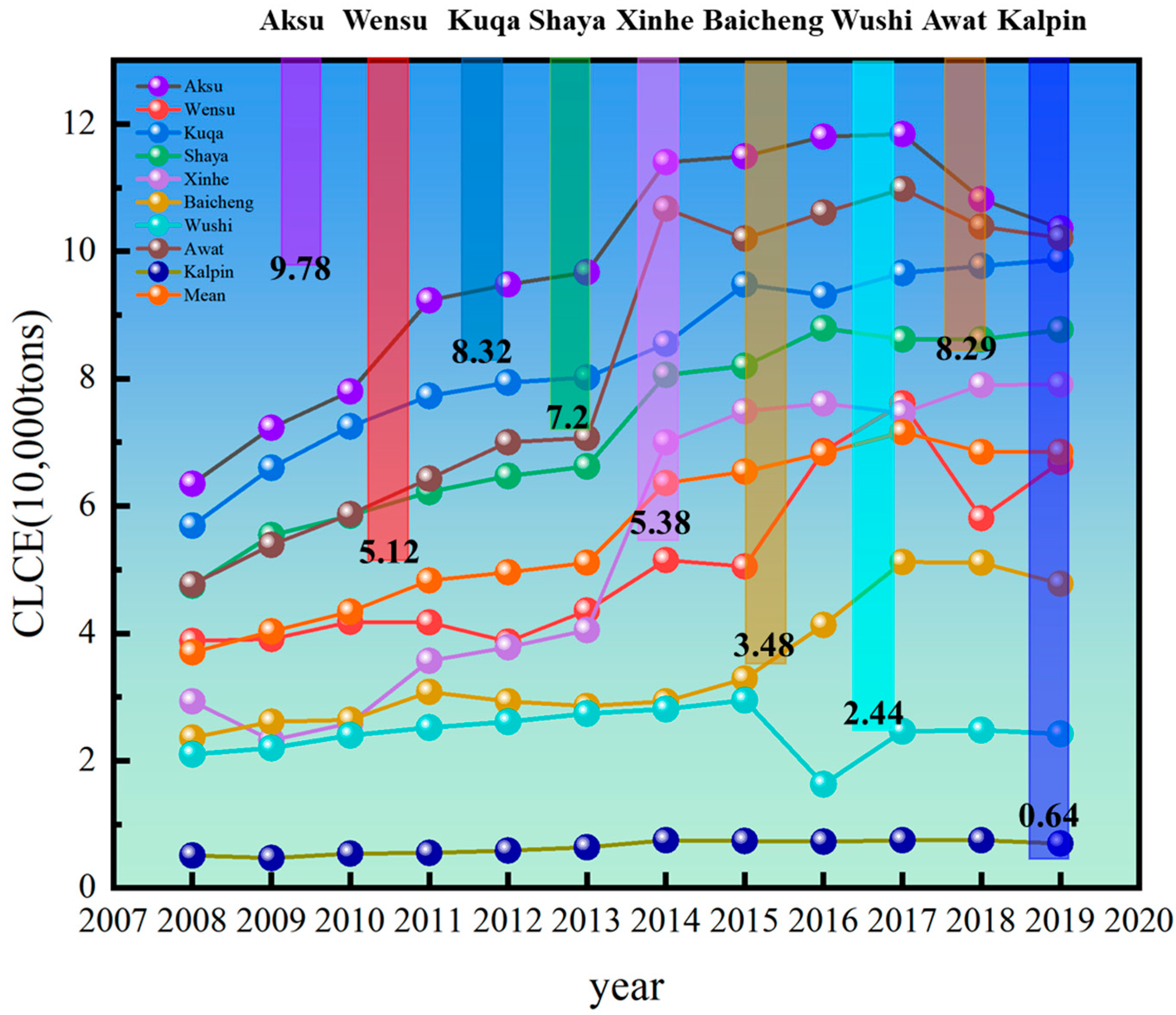
We utilized the empirical coefficient method to calculate the CLCE of Aksu. The following three results were obtained: (1) The results (Figure 4) indicate that the total CLCE in Aksu initially increased, followed by a decrease, but overall demonstrated growth, from 3.7 t in 2008 to an average of 5.63 t in 2019. (2) Among the counties and cities in the study region, Aksu ranks first in total CLCE despite having a smaller sown area of crops compared to Kuqa and Shaya. This is attributed as the main reason for its lower ECLU. (3) During the study period, Kalpin exhibited the smallest total CLCE among all counties and cities in Aksu, with an average of less than 1. Nevertheless, it ranked first in terms of ECLU. (4) The highest total CLCE (7.16 on average) was recorded in 2017 during the study period, but it did not align consistently with changes in the ECLU during the same period (the lowest being 0.769 in 2015).
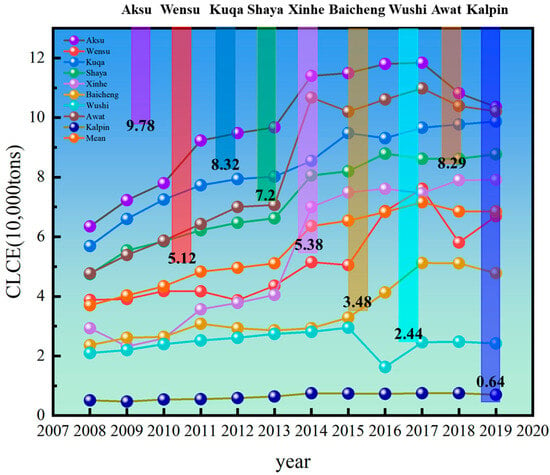
Figure 4.
CLCE by counties and cities in Aksu, 2008–2019 (unit: 10,000 tons).
4.3. ECLU and CLCE Based on Different Property Ownership
Based on the Super-SBM model, the 209 questionnaires were categorized into two groups: collective cultivated land and state-owned cultivated land. Two types of questionnaires were calculated and analyzed for the CLCE from the perspective of farmers in Aksu, as shown in Table 4. The results indicated that collective cultivated land had a lower CLCE than state-owned cultivated land, which corresponded to the low value of agricultural output. Furthermore, the investigation of food and non-food CLCE differences among farming households on both collective cultivated land and state-owned cultivated land revealed that the CLCE intensity of non-food crops was stronger than that of food crops in both types of land.

Table 4.
Average results of the survey of CLCE of farmers in Aksu.
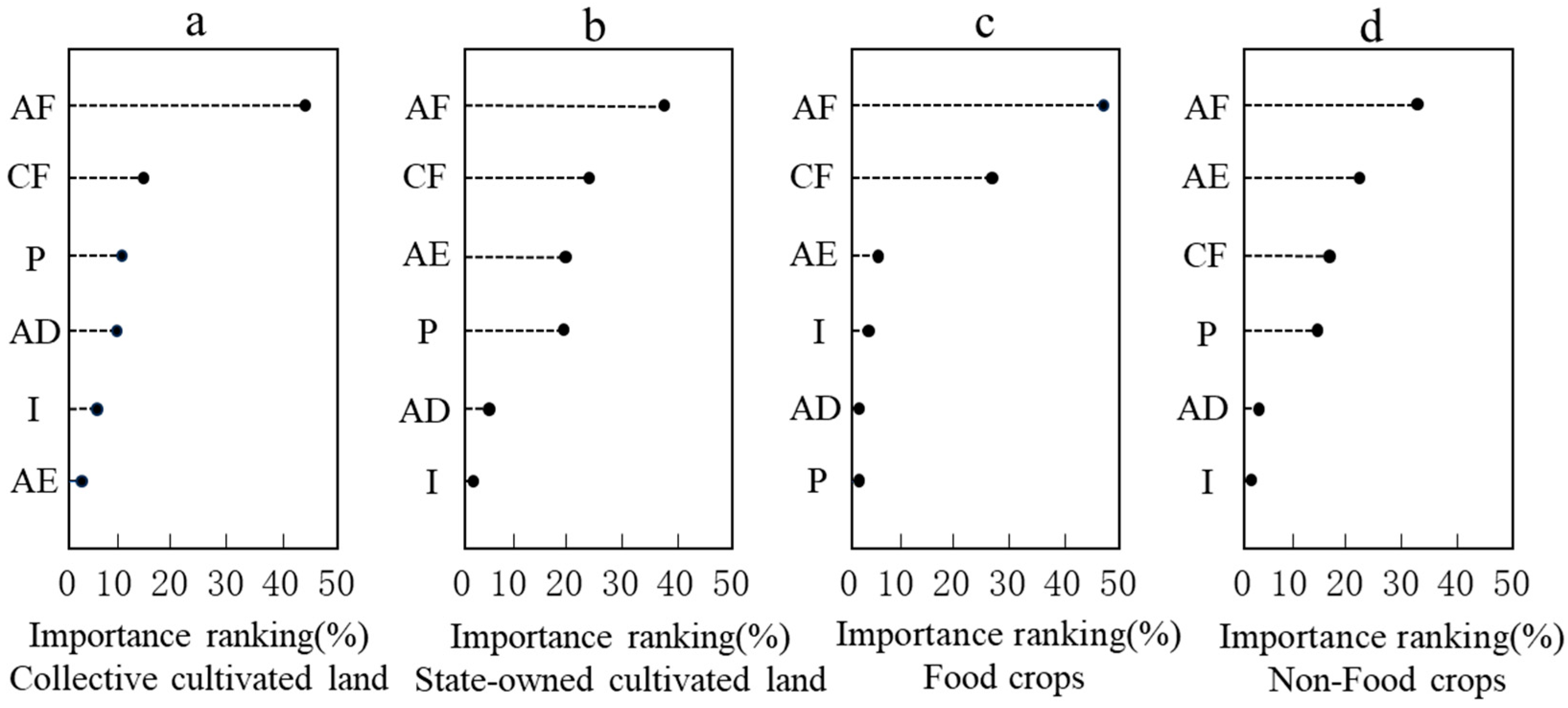
As illustrated in Figure 5, the RFR model was utilized to determine the IncMSE ranking of factors influencing CLCE in the study area based on data from the 209 surveys. It should be noted that variable importance derived from the random forest model reflects each factor’s contribution to predictive accuracy rather than direct causal influence. The results consistently indicate that AF is the most important predictor of CLCE for both collective cultivated land and state-owned cultivated land. The CF ranks second in importance for both cultivated land types, following AF (Figure 5a,b). Additionally, we assessed the relative importance of factors affecting CLCE in food crops versus non-food crops (Figure 5c,d). Notably, after AF, AE shows a stronger association with CLCE in agricultural production for non-food crops than for food crops. Overall, the factors examined contribute more substantially to predicting CLCE in state-owned cultivated land than in collective cultivated land and show greater importance for non-food crops compared to food crops. The remaining four factors (P, AD, I, and AE) exhibit varying levels of association with CLCE.

Figure 5.
Ranking of influencing factors of CLCE based on the questionnaire. (a) Collective cultivated land; (b) State-owned cultivated land; (c) Food crops; (d) Non-Food crops.
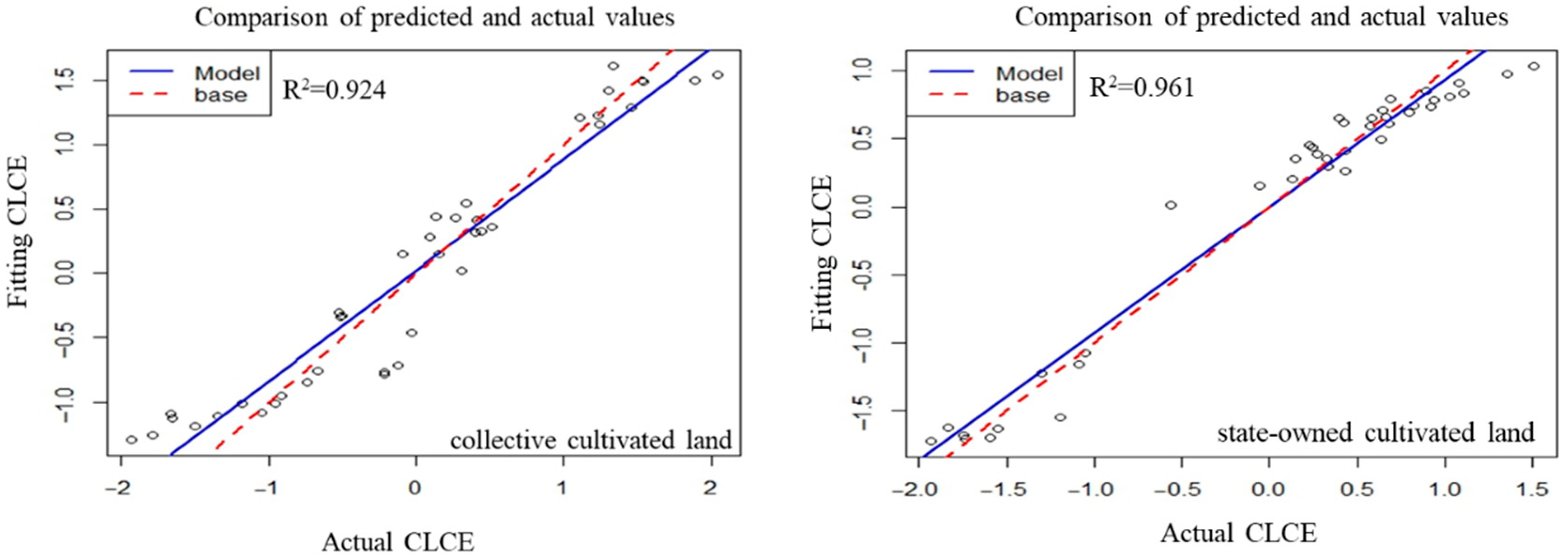
The CLCE is influenced by multiple factors and often leads to collinearity issues, which diminish the explanatory power of each factor for CLCE. However, the RFR model does not require consideration of this issue and can assess the importance of each influencing factor for different types of CLCE. All variables were z-score normalized from the data from the 209 surveys. The R2 and RMSE of the model were calculated, resulting in a scatter plot comparing the fitted values with the calculated values (Figure 6). The results indicate that the RF model has a good fitting effect for CLCE of Aksu; all model R2 values are greater than 0.92, demonstrating high precision with RMSE values less than 0.3.
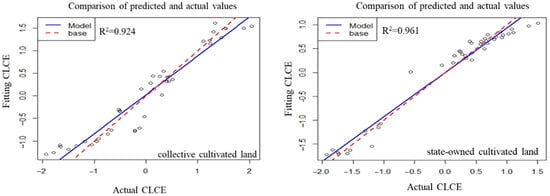
Figure 6.
Random forest model fitting results. The circles in the figure represent the correlation values between actual carbon emissions and simulated carbon emissions.
4.4. Kernel Density Analysis
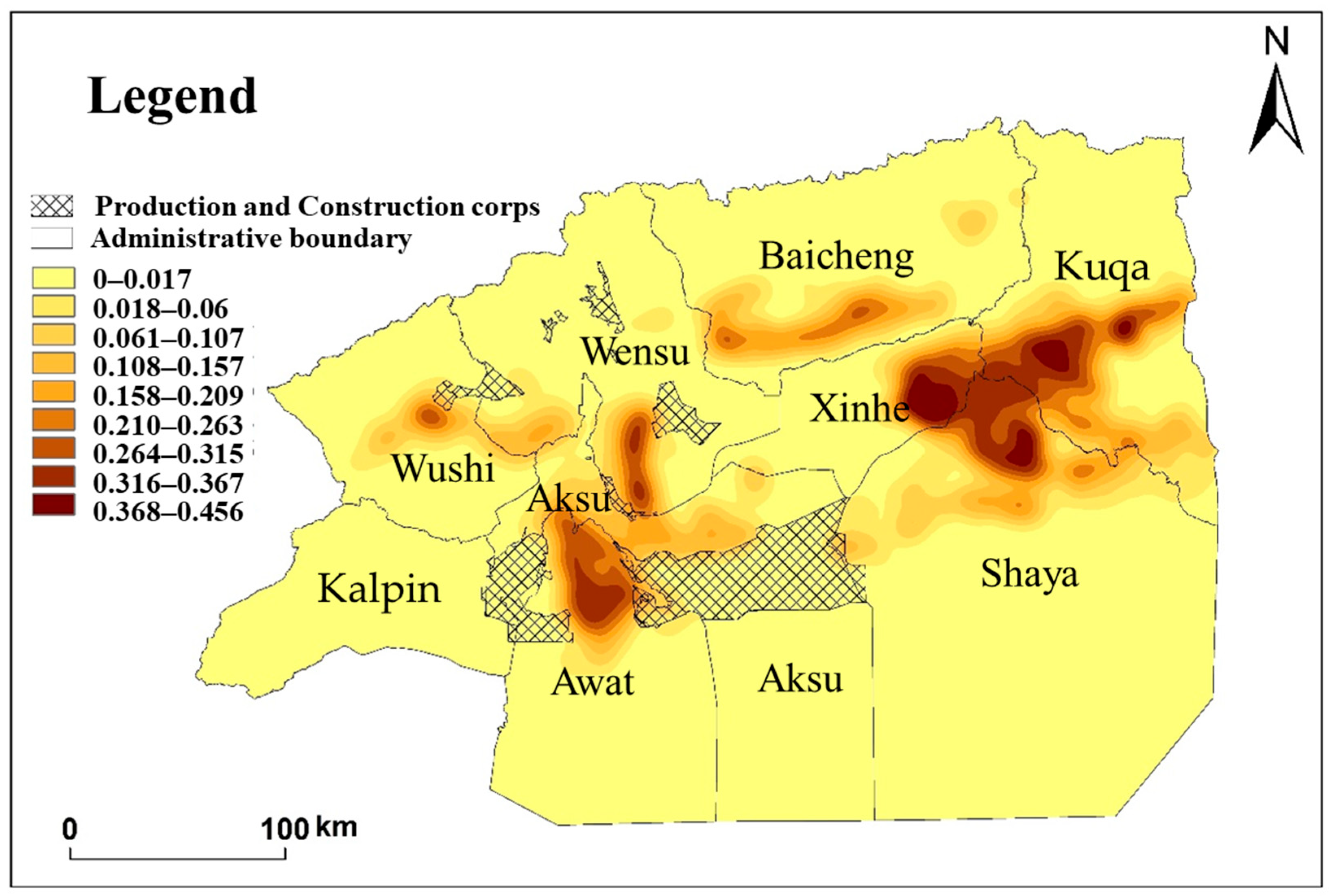
In this paper, the nuclear density of CLCE in the Aksu area was estimated by trend extrapolation using the empirical coefficients of six CLCE sources in Aksu and the data from 209 questionnaires of different cultivated land types and crops (Figure 7). The results revealed several key findings: (1) Kuqa, Xinhe, Shaya, and Awat exhibited higher total CLCE compared to other counties. (2) Carbon emissions from state-owned cultivated land were found to be greater than those from collective cultivated land in Aksu. (3) Specific areas such as Bishibagh in Kuqa, Gullebagh and Tuoyboldi in Shaya, and Yuqikate and Weigan in Xinhe demonstrated high levels of CLCE, with a kernel density value of approximately 0.4. Additionally, Tashaizhike in Xinhe; Yingmaili, Hailou, and Hongqi in Shaya; Allahag and Qiman in Kuqa; Ayibagh, Ulukele, and Tamutoglak in Awati; Yakorek in Wushi; and the Seed Farm in Wensu all showed high intensity of CLCE.
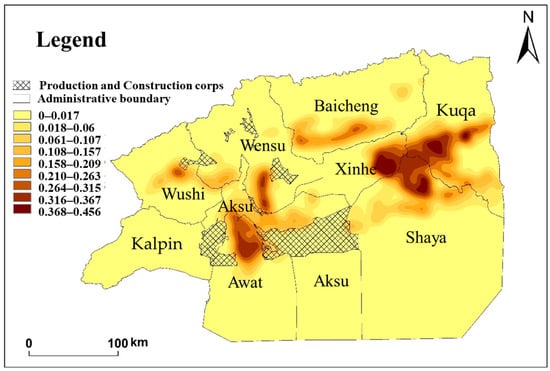
Figure 7.
Kernel density estimation map of CLCE in Aksu. Note: Based on the ownership of cultivated land in the Third National Land Survey, the empirical coefficient of cultivated land carbon emissions and 209 carbon emission items in the agricultural production process of farmers, the kernel density map of CLCE in Aksu was visualized by using the kernel density estimate method.
4.5. Analysis of Influencing Factors of CLCE
- (1)
- Factor detection
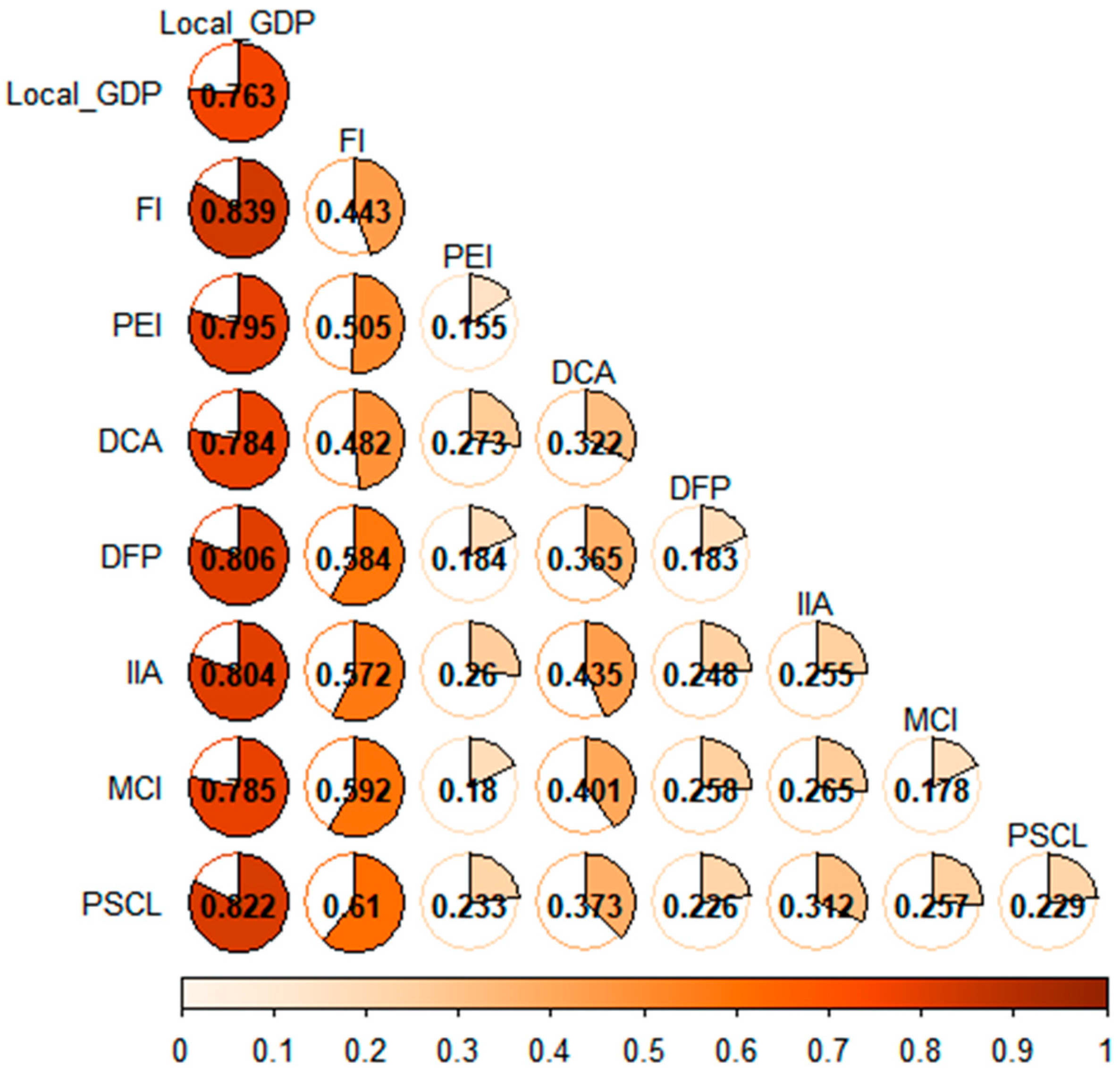
In this study, the effects of various factors on the spatial differentiation of CLCE were further explored using Geo-detector analysis. The results of factor detection for CLCE in Aksu indicated that all factors were statistically significant at a 5% level (Table 5). The explanatory power of each factor in explaining the change in CLCE in Aksu was ranked as follows: Local_GDP (q value 0.763) > FI (q value 0.443) > DCA (q value 0.321) > IIA (q value 0.254) > PSCL (q value 0.229) > DFP (q value 0.182) > MCI (q value 0.178) > PEI (q value 0.155). It was found that the proportion of effective irrigated area (PEI) had the weakest explanatory power for CLCE in Aksu, while Local_GDP had the strongest explanatory power, followed by farmer income (FI).

Table 5.
The q value of the CLCE influencing factor.
- (2)
- Interactive detection
Based on the identification of the driving factors of CLCE, further exploration was conducted to examine the interaction of each driving factor (Figure 8). The interaction type of each driving factor is a nonlinear enhancement, indicating that the double factor interaction positively strengthens the driving force of each single factor on CLCE in Aksu. The interaction between Local_GDP and FI (0.839) had a stronger effect on the CLCE in Aksu than that of a single factor (0.763 and 0.443). The interaction between these two factors has the strongest influence on CLCE in Aksu compared to any other pair of factors. Additionally, it was found that the interactions between Local_GDP and DFP, Local_GDP and IIA, and Local_GDP and PSCL exhibited stronger explanatory power for CLCE than did any single factor, with an interaction force reaching more than 0.8.
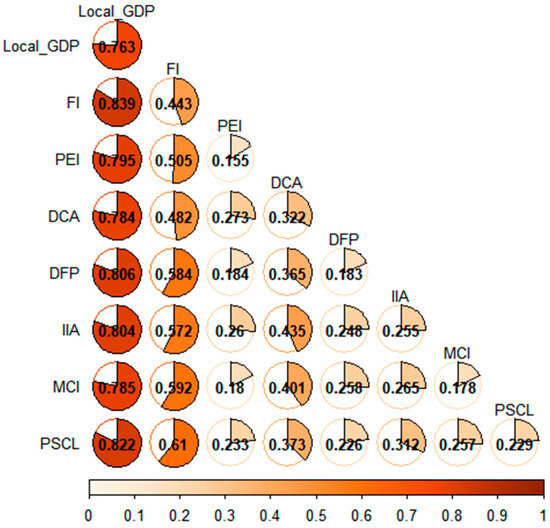
Figure 8.
Explanatory powers of the interaction of various factors on the CLCE in Aksu.
5. Discussions
Based on the Super-SBM model, this study quantitatively calculated the ECLU in Aksu, Xinjiang, from 2008 to 2019. The ECLU of various counties in Aksu exhibited a fluctuating trend and spatiotemporal differences. However, there was no obvious inverse change trend between CLCE and ECLU during the study period. Based on integrated analysis of household survey data and the Third National Land Survey, cultivated land under collective ownership exhibited lower carbon emissions (CE) than state-owned land, while food crop cultivation generated lower CE than non-food crops. Kernel density estimation of cultivated land carbon emissions (CLCE) revealed significantly higher concentrations in the eastern counties than in other regions (although it is an estimated result extrapolated from the 209 household surveys of the entire study area). The detection results from Geo-detector factor analysis indicated that Local_GDP was the main influencing factor for CLCE. Furthermore, interactive detection results revealed that the interaction between Local_GDP and FI had the strongest influence on cultivated land carbon emissions at 0.839.
5.1. The Characteristics and Relationship of ECLU and CLCE Change in Aksu
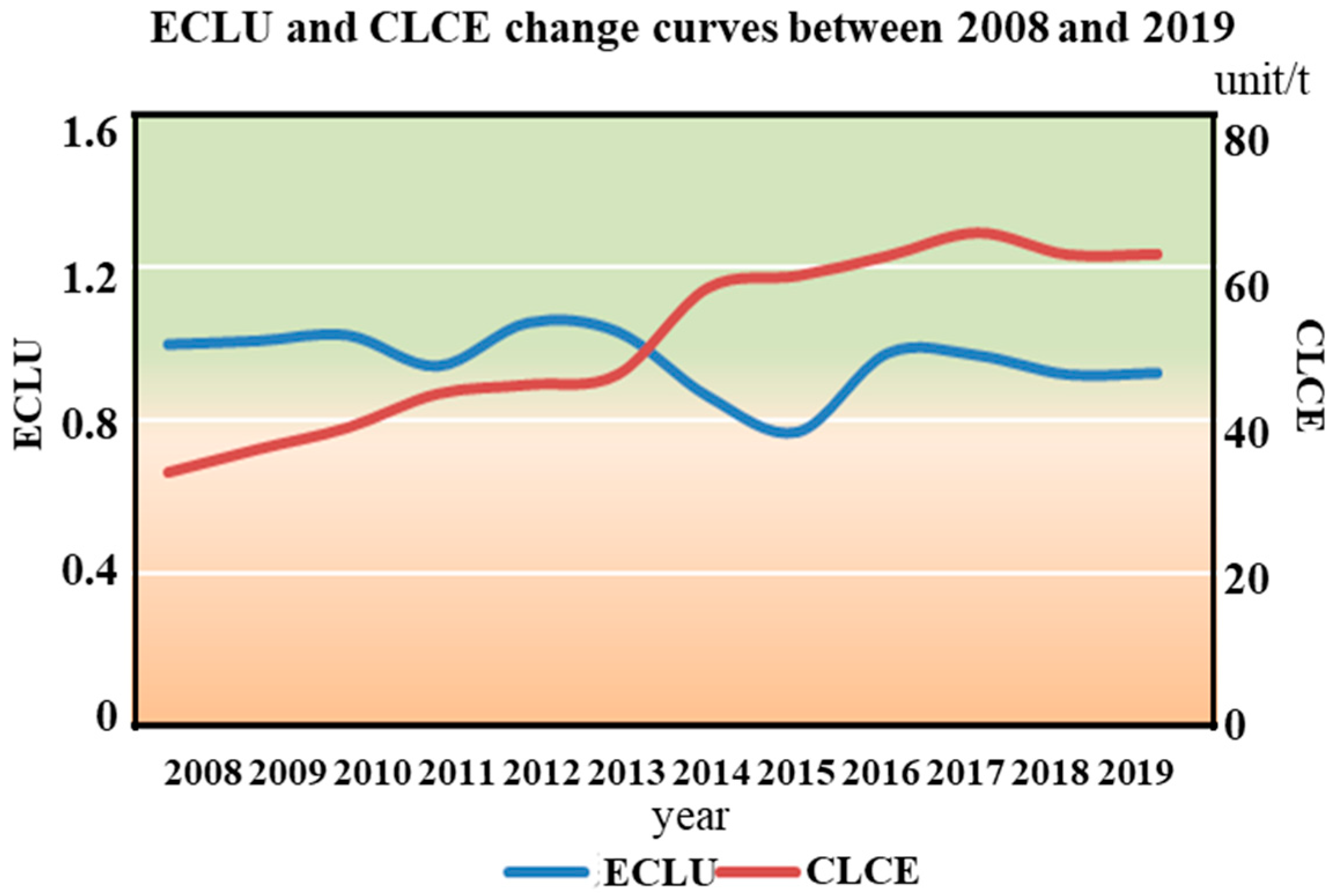
From 2008 to 2019, the ECLU in Aksu exhibited fluctuating changes, according to the findings. However, the CLCE showed a gradually increasing trend (Figure 9). Previous studies have indicated that the degree of sustainable intensification of cultivated land in Xinjiang is low compared with other regions in China [54], indirectly suggesting low ECLU in Xinjiang. Additionally, another study reported findings consistent with ours: it revealed that the average green utilization efficiency of cultivated land in Western China stood at 0.923 over the period 2000–2020 [4]. Notably, this study also employed the Super-SBM model, aligning with the methodological approach we adopted for calculating the ECLU. A key distinction, however, is that Yang et al. incorporated non-point source pollution as an undesirable output in their analysis, and the Pesticides are not regarded as a source of carbon emissions either.
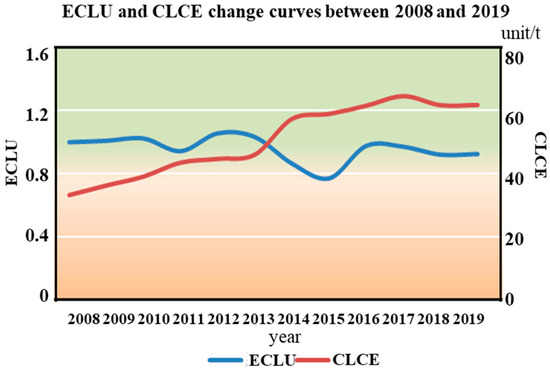
Figure 9.
Curve of ECLU and CLCE in Aksu between 2008 to 2019. Note: ECLU (left Y-axis): Eco-Efficiency of Cultivated Land Utilization calculated based on the super-efficiency SBM model (dimensionless); CLCE (right Y-axis): total carbon emissions from cultivated land in the current year (unit/t).
In principle, the improvement of the ECLU mainly depends on the increase in expected output or the decrease in unexpected output (referred to as CLCE in this paper). The ECLU and CLCE should exhibit an inverse proportional change. During the study period, the expected output of cultivated land in Aksu increased from CNY 97.83 million to CNY 2729.12 million. Concurrently, the CLCE also increased, leading to fluctuations and even a slight decrease in the ECLU. A certain degree of decline in the ECLU suggests a need for further improvement in the production link of cultivated land in the future.
5.2. Policy Implications
The results of the questionnaire survey indicate that the carbon emission of collective cultivated land in Aksu is lower than that of state-owned cultivated land. Additionally, it is evident that the economic output per unit area of state-owned cultivated land is slightly higher than that of collectively cultivated land in Aksu. Therefore, focusing solely on adjusting land ownership to improve the ECLU would be unreasonable if we disregard economic output. This conclusion aligns with previous research findings, which emphasize the significant impact of land-tenure structure on the ECLU [32,35,38].
The empirical analysis reveals significantly higher carbon emissions from state-owned cultivated land relative to collective land (p < 0.01), attributable to fundamental institutional divergences in management objectives, technological investment, and policy frameworks. For management objectives, collective land operations prioritize livelihood security through diversified subsistence farming, whereas state-owned cultivated land pursues economies of scale via specialized monocropping systems. In terms of technological investment, collective farmland remains constrained by fragmented smallholder techniques with limited precision agriculture adoption. Conversely, state-owned domains demonstrate advanced technological integration, particularly in intelligent irrigation systems, which ensure efficient water utilization. Direct cash transfers characterize collective land subsidies, enhancing household income but failing to incentivize sustainable practices. State farm subsidies, however, are strategically channeled into maintaining large-scale agricultural production—exemplified by agricultural machinery procurement policies prioritizing grain output targets. This institutional arrangement inadvertently sustains high chemical fertilizer application levels.
The core of the ECLU lies in synergistic enhancement, which means “maximizing the expected output while minimizing resource input and environmental damage (carbon emissions) as much as possible.” The advantage of state-owned cultivated land lies in its high expected output, while its disadvantage is its high unexpected output (carbon emissions). The advantage of collective cultivated land lies in its low unexpected output (carbon emissions), while its disadvantage is the low expected output. Therefore, the policy suggestion of “two-way differentiation” is put forward. For state-owned cultivated land, the policy focus should be placed on “reducing emissions and increasing efficiency”. Through the application of green technologies and precision agricultural management, high output can be maintained while significantly reducing the carbon emission intensity per unit of output. The goal is “green intensification”. For collective cultivated land, the policy focus should be placed on “increasing production and carbon sequestration”. Through means such as technology promotion, moderate-scale operation, and infrastructure improvement, production potential should be tapped while maintaining and optimizing its original low-carbon model. The goal is “high efficiency and low carbonization”. Finally, promote the agricultural carbon emission trading market, allowing state-owned land with high costs of low-carbon technologies to purchase quotas from collective land with good emission reduction effects, thereby minimizing the overall regional emission reduction costs.
Regardless, whether it is state-owned cultivated land or collectively owned cultivated land, the improvement of the ECLU is inseparable from farmers. The enhancement of the ECLU is centered on economic output, conservation of cultivated land resources, and protection of the ecological environment with the goal of achieving coordinated development of the economy, society, and environment. The green utilization behavior of cultivated land by farmers is closely related to the ECLU [55]. This paper investigates the carbon emissions of collective cultivated land and state-owned cultivated land from the perspective of farming households and aims to propose policy suggestions for sustainable and intensive utilization of cultivated land. Currently, many scholars focus on the influencing factors of the ECLU. However, most research is based on statistical data, with studies from the perspective of farming households in oasis areas being even rarer. From the farmer’s perspective, it is crucial to enhance their awareness of environmental protection and reduce the excessive use of agricultural film, chemical fertilizers, and pesticides in order to avoid negative marginal benefits [56]. Additionally, the ECLU can be enhanced through the implementation of agricultural subsidies, agricultural insurance, and other measures by the government. In terms of the land scale, state-owned cultivated land generally has a larger area compared to collective cultivated land in Aksu. As a result, carbon emissions from state-owned cultivated land in oases are higher than those from collective cultivated land. Furthermore, a larger agricultural area can facilitate the operation of agricultural machinery and enable environmentally friendly investments such as plow-less cultivation systems and precision fertilization [57], which aligns with previous research findings [58,59]. Moreover, cultivated land in Aksu is increasingly transitioning from smallholder collective management to large-scale operations. This shift has critical implications for individual land managers’ practices regarding ecological land-use efficiency.
5.3. Limitations and Prospects
The findings indicate that for the ECLU in Aksu, Keplin ranks highest and Shaya the lowest. This finding is based on a consistent level of agricultural production technology throughout the entire region, as well as uniform natural environmental conditions (including terrain slope, soil properties, sunlight, wind, rain, and other factors) and under identical conditions of land, labor, fertilizer, machinery, and other inputs. However, it should be noted that these factors are not consistent across the study area; significant differences exist among different farming households. Therefore, comparing the ECLU among different regions becomes difficult when ignoring the variations in natural and technical inputs [1]. The “intangible” inputs from nature and “tangible” technical and material inputs deserve attention in future studies.
The sampling survey method was employed to investigate farming households on state-owned and collective cultivated land in Aksu. The carbon emission items data from farmers participating in agricultural production were used to calculate the CLCE. Therefore, this study has the limitation of spatial data extrapolation. The kernel density estimation of CLCE in the study area was visualized using data from the Third National Land Survey and the empirical coefficient of carbon emission items. This study’s spatial analysis of carbon emissions relies on extrapolating the average input values from a small-scale household survey (n = 209) to the entire region. This method assumes a homogeneity of input intensity that contradicts the study’s own findings of spatial heterogeneity, and the representativeness of the small sample has not been rigorously verified. Therefore, the resulting spatial distribution maps (e.g., Figure 7) carry a degree of uncertainty, and any conclusions drawn from them must be treated with extreme caution.
In this study, six factors were selected for the analysis of CLCE’s driving mechanism. Based on statistical data and empirical coefficient methods, this study calculated the CLCE and utilized Geo-detector to identify that the primary factor influencing CLCE in Aksu was Local_GDP. The questionnaire also aligns with the survey indicators designed by popular empirical coefficient methods. This not only verifies the consistency of CE accounting and influencing factors of CL in the study area with statistical results but also aims to deeply analyze potential differences in CLCE based on land ownership properties and crop types. While the RF model effectively simulates CLCE in the study area, future research should focus on incorporating other variables for multivariate CLCE estimation in order to control excessive carbon emission behavior during cropland production. The calculation of CLCE in this study provides a scientific basis for formulating policies related to farmland tenure adjustment for Aksu. Additionally, it is important to consider factors such as agricultural mechanization level, planting structure, and farmers’ education levels as potential influencers of CLCE. Consequently, future studies should take into account these factors. Furthermore, future research should focus on the development of the ECLU to provide food security and a low-carbon orientation. While this study elucidates the mechanisms of action among the ECLU–CLCE ownership structures in Xinjiang’s arid oases, its generalizability is contextually bounded by three key dimensions: (1) Geographical applicability. The framework demonstrates the strongest validity in agriculturally pressured drylands characterized by fragile oasis ecosystems dependent on snowmelt irrigation, high crop-specific concentration (e.g., cotton), and the presence of dual land-tenure systems. (2) The constraints of land ownership. Collective lands maintained household responsibility systems with fragmented plots (<4 ha avg.) accounting for 42%, while state farms retained Soviet-style large-scale operations. (3) Methodological limitations. Unmeasured confounders: soil organic carbon variations were not incorporated due to data scarcity.
These constraints illuminate fertile ground for comparative studies across 7.06 million hectares of drylands in China, particularly through integrating satellite-based carbon emission verification (Sentinel-5P) with institutional analysis. By establishing Xinjiang as an arid-land sustainability laboratory, this work provides adaptable design principles—not universal prescriptions—for navigating the trilemma of food security, ecological resilience, and carbon neutrality in global drylands.
6. Conclusions
In this study, the Super-SBM model was utilized to quantify the ECLU considering unexpected output (CLCE) in Aksu. Then the empirical coefficient method was adopted to calculate the CLCE. Meanwhile, we estimated the CLCE by kernel density analysis, which showed spatial differences based on data from the Third National Land Survey and questionnaire surveys. Subsequently, the importance ranking of CLCE of collective cultivated land, state-owned cultivated land, food crops, and non-food crops was analyzed by using the RFR model. Finally, Geo-detector models were used to investigate the driving factors of CLCE and reveal spatial differentiation.
According to the results, (1) the overall ECLU values in Aksu first increased and then subsequently decreased with time. The Kalpin showed the highest ECLU during the study period, followed by Wensu and Wushi. (2) Aksu, Kuqa, and Awat ranked the top three in terms of CLCE, and the CLCE on collective land is less than that of state-owned land. Furthermore, the CLCE showed spatial heterogeneity. (3) The Local_GDP (q = 0.763) was the main driver of CLCE in Aksu. The interactive detection results showed that the Local_GDP and farmer income (FI) had the strongest effect (0.839) on the CLCE in Aksu, more than any other two-factor combination. All the interaction effects of two factors on the CLCE showed bi-factor nonlinear enhancement. Finally, by analyzing the ECLU and CLCE in Aksu, this study provides a comprehensive understanding of the eco-efficiency of cultivated land utilization in Aksu. This provides a basis for creating green and efficient cultivated land-use policies. The results of this study indicate that there are significant differences in carbon emission performance among different ownerships of cultivated land, but they reveal the limitations of merely pursuing maximum output or minimum emissions to enhance the ecological efficiency of farmlands. Therefore, future policies for enhancing the ecological efficiency of cultivated land should abandon the “one-size-fits-all” model and instead adopt a differentiated path based on ownership characteristics: For state-owned land, strengthen environmental constraints and promote its transformation towards “green and intensive”. For collective land, it is necessary to promote its “efficient and low-carbon” development through property rights system reform and green incentive measures. At the same time, efforts should be made to actively explore the establishment of cross-ownership ecological compensation and market transaction mechanisms, ultimately forming a new pattern of sustainable utilization of cultivated land featuring complementary advantages and coordinated efficiency.
Author Contributions
J.Z. conceived the data processing and visualization and wrote the paper; W.L. designed the software, acquired funding, and collected the data; H.W. audited the data and made revision suggestions; L.X. was responsible for methodology, supervision, and revision suggestions; S.L. provided review and supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42293272); the Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi (2021JJA150154); the Social Science Foundation of Guangxi (24SHB002); and the Emergency Management Joint Innovative Science and Technology project of Guangxi (2024GXYJ043).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study, since the survey did not collect any personally identifiable or sensitive information, according to https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2023-02/28/content_5743658.htm, accessed on 3 September 2025.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The survey data in this research can be accessed from https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.11648690; additional statistics data can be obtained from the website of the data source of Manuscript Table 1.
Acknowledgments
We thank the anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments and suggestions, which greatly improved this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Wang, J.Y.; Su, D.; Wu, Q.; Li, G.; Cao, Y. Study on eco-efficiency of cultivated land utilization based on the improvement of ecosystem services and emergy analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 882, 163489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.Q.; Hou, X.H.; Liu, J.M. Detection and attribution of changes in cultivated land use ecological efficiency: A case study on Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 137, 108753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO; IFAD; WW UNICEF. The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Mo, L. Empirical investigation of cultivated land Green Use Efficiency and influencing factors in China, 2000–2020. Land 2023, 12, 1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, B.; Lu, X.; Zhou, M.; Chen, D. Provincial cultivated land use efficiency in China: Empirical analysis based on the SBM-DEA model with carbon emissions considered. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2020, 151, 119874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.S. Introduction to land use and rural sustainability in China. Land Use Policy 2018, 74, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plieninger, T.; Hartel, T.; Martin-Lopez, B.; Beaufoy, G.; Bergmeier, E.; Kirby, K.; Montero, M.J.; Moreno, G.; Oteros-Rozas, E.; Van Uytvanck, J. Wood-pastures of Europe: Geographic coverage, social-ecological values, conservation management, and policy implications. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 190, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO 2021. The State of the World’s Land and Water Resources for Food and Agriculture—Systems at Breaking Point; Synthesis Report; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bommarco, R.; Kleijn, D.; Potts, S.G. Ecological intensification: Harnessing ecosystem services for food security. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2013, 28, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.T.; Hu, Z.H.; Hu, C. A highly agricultural river network in Jurong Reservoir watershed as significant CO2 and CH4 sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 769, 144558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.L.; Huang, Y.Q.; Choi, Y.; Shi, J. Evaluating the sustainable intensification of cultivated land use based on emergy analysis. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2021, 165, 120449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.Y.; Peng, W.L.; Niu, S.D.; Qu, Y.; Xin, Z. Evaluation of sustainable intensification of cultivated land use according to farming households’ livelihood types. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 138, 108848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.G.; Liu, Y.S.; Li, Y.R.; Chen, Y. Dynamic trends and driving forces of land use intensification of cultivated land in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2015, 25, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.Y.; Jin, X.B.; Xu, X.X.; Zhou, Y. A stage of cultivated land use towards sustainable intensification in China: Description and identification on anti-intensification. Habitat Int. 2022, 125, 102594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.D.; Lyu, X.; Gu, G.Z.; Zhou, X.; Peng, W. Sustainable Intensification of Cultivated Land Use and Its Influencing Factors at the Farming Household Scale: A Case Study of Shandong Province, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2021, 31, 109–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Chen, L.G.; Yang, B.; Shi, Z. Exploring provincial sustainable intensification of cultivated land use in China: An empirical study based on emergy analysis. Phys. Chem. Earth 2022, 128, 103287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Jin, X.B.; Xu, W.Y.; Gu, Z.; Yang, X.; Ren, J.; Fan, Y.; Zhou, Y. A New Framework of Land Use Efficiency for The Coordination Among Food, Economy and Ecology in Regional Development. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 135670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.G.; Deng, C.; Fan, Y.Q.; Zhang, P.; Lu, H. Spatial-Temporal Pattern and Evolution Trend of The Cultivated Land Use Eco-Efficiency in The National Pilot Zone for Ecological Conservation in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Yu, J.; Li, J.F.; Li, S.; Zhang, D.; Wu, D.; Pan, S.; Chen, W. Spatial correlation among cultivated land intensive use and carbon emission efficiency: A case study in the Yellow River Basin, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 43341–43360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Ao, X.H.; Zhang, Z.; Wan, Q.; Liu, X. Spatiotemporal variations of cultivated land use efficiency in the Yangtze River Economic Belt based on carbon emission constraints. J. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 30, 535–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.H.; Zhou, L.H.; Wang, Y.B. Prediction of the Spatial Pattern of Carbon Emissions Based on Simulation of Land Use Change under Different Scenarios. Land 2022, 11, 1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K.; Wang, H.W.; Ma, C.; Wu, C.; Zheng, X.; Xie, L. Carbon sinks and carbon emissions balance of land use transition in Xinjiang, China: Differences and compensation. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 22456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.D.; Zhu, X.Y.; Wang, Y.F. China’s agricultural green total factor productivity based on carbon emission: An analysis of evolution trend and influencing factors. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Gibson, J. Sustainable land use management for improving land eco-efficiency: A case study of Hebei, China. Ann. Oper. Res. 2020, 290, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Li, Y.; Tao, X.; Peng, X.; Li, N.; Zhu, Z. China greenhouse gas emissions from agricultural activities and its mitigation strategy. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2008, 24, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.L.; Chen, Q.R.; Wang, W.; He, Y. Analyzing the green efficiency of arable land use in China. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2018, 133, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Zhou, W.; Wu, T.; Wang, X.; Xu, J. Spatial-temporal characteristics of cultivated land use eco-efficiency under carbon constraints and its relationship with landscape pattern dynamics. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 114, 109140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Wang, Z.Q.; Zou, L.; Zhang, H.W. Exploring the eco-efficiency of cultivated land utilization and its influencing factors in China’s Yangtze River Economic Belt, 2001–2018. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 294, 112939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, H. Detection and attribution of changes in agricultural eco-efficiency within rapid urbanized areas: A case study in the urban agglomeration in the middle reaches of Yangtze River, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 144, 109533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.N.; Tan, L.; Yang, X. The Impact of Environmental Regulation on Cultivated Land Use Eco-Efficiency: Evidence from China. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.F.; Hu, S.G.; Du, G.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.S. Cultivated Land Use Benefits Under State and Collective Agrarian Property Regimes in China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koirala, K.H.; Mishra, A.; Mohanty, S. Impact of land ownership on productivity and efficiency of rice farmers: The case of the Philippines. Land Use Policy 2016, 50, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, B.; Mahesh, M. Does the Landowner’s Gender Affect Self-Cultivation and Farm Productivity? An Analysis for India. J. Dev. Stud. 2023, 59, 758–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadka, S.; Gyawali, B.R.; Shrestha, T.B. Exploring relationships among landownership, landscape diversity, and ecological productivity in Kentucky. Land Use Policy 2021, 111, 105723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, B.; Yu, L.L.; Yang, H.; Yin, S. Social capital, land tenure and the adoption of green control techniques by family farms: Evidence from Shandong and Henan Provinces of China. Land Use Policy 2019, 89, 104250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jombo, S.; Adam, E.; Odindi, J. Quantification of landscape transformation due to the Fast Track Land Reform Programme (FTLRP) in Zimbabwe using remotely sensed data. Land Use Policy 2017, 68, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kansanga, M.; Andersen, P.; Atuoye, K.; Mason-Renton, S. Contested commons: Agricultural modernization, tenure ambiguities and intra-familial land grabbing in Ghana. Land Use Policy 2018, 75, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migheli, M. Land ownership and use of pesticides. Evidence from the Mekong Delta. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 145, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, T.Y.; Zhang, X.H.; Xia, F.Q.; Lu, D. Function Evolution of Oasis Cultivated Land and Its Trade-Off and Synergy Relationship in Xinjiang, China. Land Use Policy 2022, 11, 1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhang, J.B.; He, Y.Y. Research on spatial-temporal characteristics and driving factor of agricultural carbon emissions in China. J. Integr. Agric. 2014, 13, 1393–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, W. A research of agricultural eco-efficiency measure in China and space-time differences. Chin. J. Popul. Resour. Environ. 2016, 26, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, K. A slacks-based measure of efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2001, 130, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charnes, A.; Cooper, W.W.; Rhodes, E. Measuring the efficiency of decision-making units. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1978, 2, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, T.O.; Marland, G. A synthesis of carbon sequestration, carbon emissions, and net carbon flux in agriculture: Comparing tillage practices in the United States. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2002, 91, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Guo, L.Y.; Liu, Y.S. Land consolidation boosting poverty alleviation in China: Theory and practice. Land Use Policy 2019, 82, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishwaran, H.; Kogalur, U.B.; Blackstone, E.H.; Lauer, M.S. Random survival forests. Ann. Appl. Stat. 2008, 2, 841–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Kan, A.; Zeng, Y.; Li, G.; Wang, M.; Ci, R. Population distribution pattern and influencing factors in Tibet based on Radom Forest model. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2019, 74, 664–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblatt, M. Remarks on some nonparametric estimates of a density function. Ann. Inst. Stat. Math. 1956, 27, 832–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Li, X.H.; Christakos, G.; Liao, Y.-L.; Zhang, T.; Gu, X.; Zheng, X.-Y. Geographical Detectors-Based Health Risk Assessment and its Application in the Neural Tube Defects Study of the Heshun Region, China. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 107–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.H.; Peng, F.L.; Bao, Z.H.; Qiao, Y.-K. Identification of the spatial distribution pattern and driving forces of underground parking space based on multi-source data: A case study of Fuzhou city in China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 72, 103084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.F.; Kuang, T.T.; Tao, S. Quantifying influences of natural factors on vegetation NDVI changes based on geographical detector in Sichuan, western China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 233, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.Y.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Z.Y.; Yu, J.; Liu, W.; Yu, R.; Wang, P. Attribution analysis of land degradation in Hainan Island based on geographical detector. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 141, 109119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Wang, H.W.; Liu, S.H. The ecosystem service values simulation and driving force analysis based on land use/land cover: A case study in inland rivers in arid areas of the Aksu River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 138, 108828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.H.; Yin, Y.Q.; Zhou, X. Does economic agglomeration affect the sustainable intensification of cultivated land use? Evidence from China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Lyu, X.; Peng, W.L.; Xin, Z. How to Evaluate the Green Utilization Efficiency of Cultivated Land in a Farming Household? A Case Study of Shandong Province, China. Land 2021, 10, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.H.; Lin, J.K.; Zhou, P.X.; Zheng, S.; Li, Z. Cultivated Land Input Behavior of Different Types of Rural Households and Its Impact on Cultivated Land-Use Efficiency: A Case Study of the Yimeng Mountain Area, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjunatha, A.V.; Anik, A.R.; Speelman, S.; Nuppenau, E.A. Impact of land fragmentation, farm size, land ownership and crop diversity on profit and efficiency of irrigated farms in India. Land Use Policy 2013, 31, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.R.; Xie, H.L. Temporal-Spatial Differentiation and Optimization Analysis of Cultivated Land Green Utilization Efficiency in China. Land 2019, 8, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, T.C.; Chen, W.X.; Liang, J.L.; Pan, S.; Ye, X. Identifying the driving forces of cultivated land fragmentation in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 105275–105292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).