Improvement of Construction Workers’ Drowsiness Detection and Classification via Text-to-Image Augmentation and Computer Vision
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background and Review of Prior Studies
2.1. Drowsiness Detection Using Computer Vision
2.2. Applications of Text-to-Image (T2I) for Image Augmentation
3. Methodology
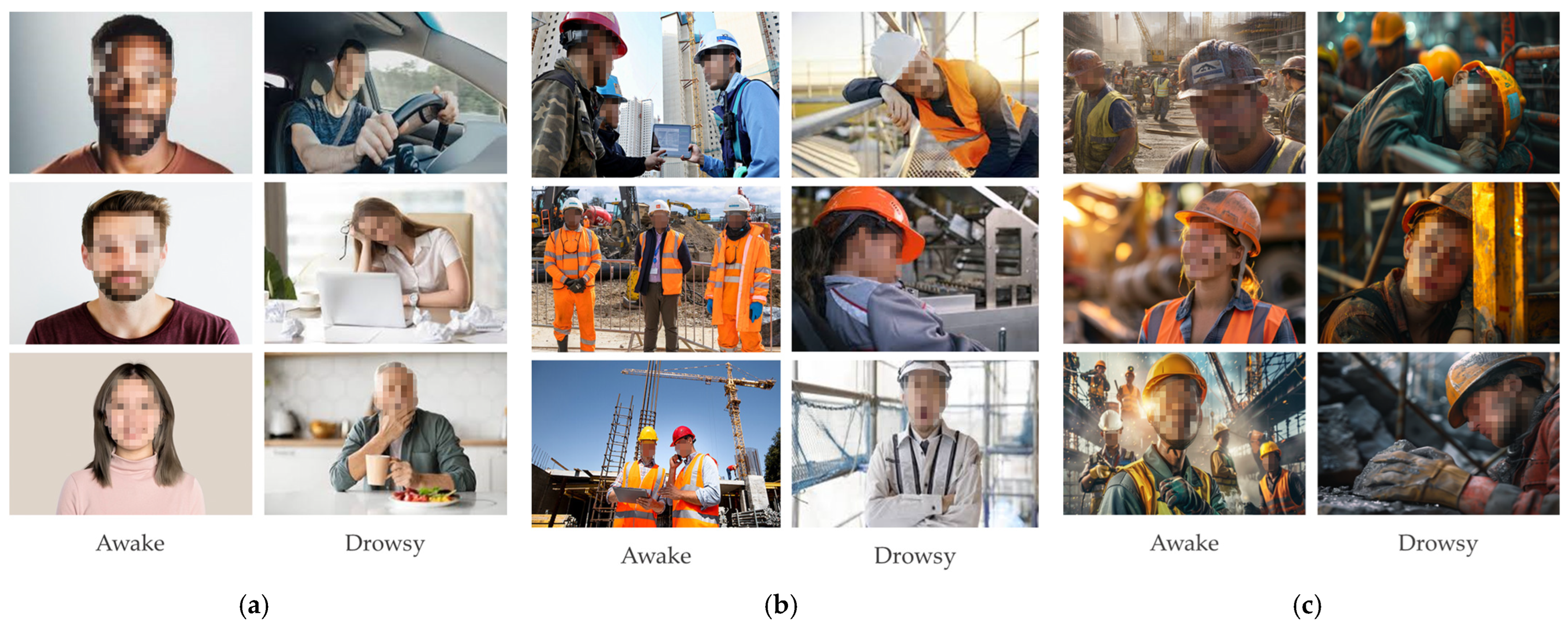
3.1. Imagery Dataset Construction
3.2. Data Labeling
3.3. Drowsiness Detection and Classification Model Development
3.4. Performance Comparison Using Evaluation Metrics
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Impacts of Domain-Specific Datasets on Performance
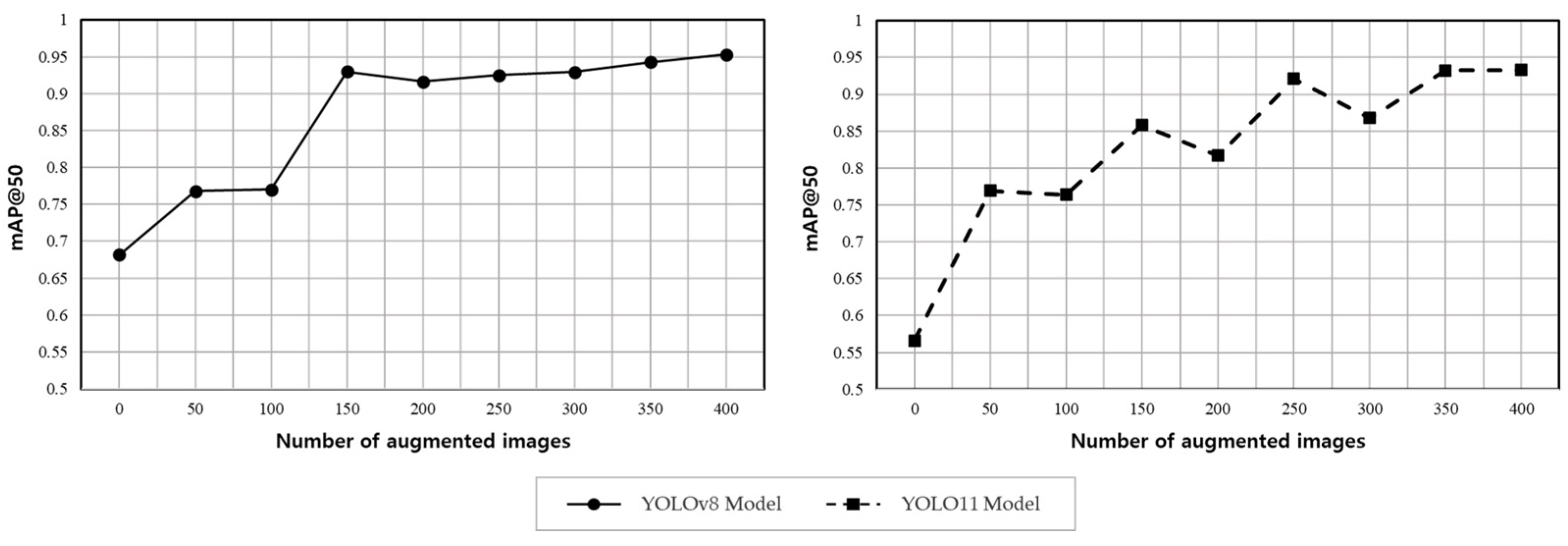
4.2. Impacts of Augmented Dataset Size on Performance
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumi, L.; Jeong, J.; Jeong, J.; Son, J.; Mun, H. Network-Based Safety Risk Analysis and Interactive Dashboard for Root Cause Identification in Construction Accident Management. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2025, 256, 110814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onososen, A.O.; Musonda, I.; Onatayo, D.; Saka, A.B.; Adekunle, S.A.; Onatayo, E. Drowsiness Detection of Construction Workers: Accident Prevention Leveraging Yolov8 Deep Learning and Computer Vision Techniques. Buildings 2025, 15, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namian, M.; Taherpour, F.; Ghiasvand, E.; Turkan, Y. Insidious Safety Threat of Fatigue: Investigating Construction Workers’ Risk of Accident Due to Fatigue. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2021, 147, 04021162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Safety Council. Fatigue in Safety Critical Industries—Impacts, Risks & Recommendations. 2018. Available online: https://www.nsc.org/getmedia/4b5503b3-5e0b-474d-af19-c419cedb4c17/fatigue-in-safety-critical-industries.pdf.aspx?srsltid=AfmBOoo87il8WHnx3GvbkWnefQ5uWmDO9QI5eeqpixxoOdENTjZgbPqm (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Zhou, H.; Chan, A.P.-C.; Yang, Y.; Yi, W. A Systematic Review of Mental States and Safety Performance of Construction Workers. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2025, 151, 03125007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, P.P.; Mohd Yusoff, H.; Hod, R. Individual Evaluation of Fatigue at Work to Enhance the Safety Performance in the Construction Industry: A Systematic Review. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0287892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharibi, V.; Mokarami, H.; Cousins, R.; Jahangiri, M.; Eskandari, D. Excessive Daytime Sleepiness and Safety Performance: Comparing Proactive and Reactive Approaches. Int. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2020, 11, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Murphy, L.A.; Fang, D.; Caban-Martinez, A.J. Influence of Fatigue on Construction Workers’ Physical and Cognitive Function. Occup. Med. 2015, 65, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.-L.; Sun, Y.-M.; Chuang, K.-H.; Hsu, D.-J. Work Fatigue and Physiological Symptoms in Different Occupations of High-Elevation Construction Workers. Appl. Ergon. 2009, 40, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, K.; Jeon, J. Systematic Literature Review of Wearable Devices and Data Analytics for Construction Safety and Health. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 257, 125038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Lee, B.-L.; Chung, W.-Y. Smartwatch-Based Wearable EEG System for Driver Drowsiness Detection. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 7169–7180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, C.R.; Lee, S.; Sun, C.; Jebelli, H.; Yang, K.; Choi, B. Wearable Sensing Technology Applications in Construction Safety and Health. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2019, 145, 03119007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.; Hwang, S.; Lee, S. What Drives Construction Workers’ Acceptance of Wearable Technologies in the Workplace?: Indoor Localization and Wearable Health Devices for Occupational Safety and Health. Autom. Constr. 2017, 84, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshawrab, M.; Adda, M.; Bouzouane, A.; Ibrahim, H.; Raad, A. Smart Wearables for the Detection of Occupational Physical Fatigue: A Literature Review. Sensors 2022, 22, 7472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudlal, H.; Serrhini, M.; Tahiri, A. Towards a Low-Cost and Privacy-Preserving Indoor Activity Recognition System Using Wifi Channel State Information. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2025, 84, 35761–35792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudlal, H.; Serrhini, M.; Tahiri, A. CSHA-CSI: Towards Contactless Sensing of Human Activities Utilizing WiFi Channel State Information. In Proceedings of the 2024 3rd International Conference on Embedded Systems and Artificial Intelligence (ESAI), Fez, Morocco, 19–20 December 2024; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.-H.; Kim, T.-J.; Park, Y.-H.; Yoon, S.-H.; Jeon, J.-H.; Kim, J.-W. Barriers to the Adoption of Computer Vision-Based Object Recognition in Construction Sites—Analyzing Barriers to Safety Technology Adoption Using the Technology Acceptance Model. Korean J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2025, 26, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Park, S.; Kim, J.; Kim, J. A Vision-Based Pipe Support Displacement Measurement Method Using Moire Patterns. Korean J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2022, 23, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Won, J.; Koo, C. A Strategic Approach to Enhancing the Practical Applicability of Vision-Based Detection and Classification Models for Construction Tools—Sensitivity Analysis of Model Performance Depending on Confidence Threshold. Korean J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2025, 26, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabash, M.S. Applications of Computer Vision to Improve Construction Site Safety and Monitoring; ProQuest Dissertations & Theses: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2023; ISBN 979-8-3744-0109-7. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, P.; Wergeles, N.; Shang, Y. A Survey and Performance Evaluation of Deep Learning Methods for Small Object Detection. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 172, 114602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Yoon, S.; Fuentes, A.; Park, D.S. A Comprehensive Survey of Image Augmentation Techniques for Deep Learning. Pattern Recognit. 2023, 137, 109347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, N.E.; Loey, M.; Mirjalili, S. A Comprehensive Survey of Recent Trends in Deep Learning for Digital Images Augmentation. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2022, 55, 2351–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.; Seo, S.; Koo, C. Synthetic Video Generation Process Model for Enhancing the Activity Recognition Performance of Heavy Construction Equipment—Utilizing 3D Simulations in Unreal Engine Environment. Korean J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2025, 26, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frolov, S.; Hinz, T.; Raue, F.; Hees, J.; Dengel, A. Adversarial Text-to-Image Synthesis: A Review. Neural Netw. 2021, 144, 187–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arakawa, T. Trends and Future Prospects of the Drowsiness Detection and Estimation Technology. Sensors 2021, 21, 7921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.; Yang, K. Analysis of AI Model Performance for EMG-Based Human-Robot Handover State Recognition. Korean J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2025, 26, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, S.; Monteiro, T.; Lobo, A.; Couto, A.; Cunha, L.; Ferreira, S. Analyzing Driver Drowsiness: From Causes to Effects. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathvik, S.; Alsharef, A.; Singh, A.K.; Shah, M.A.; ShivaKumar, G. Enhancing Construction Safety: Predicting Worker Sleep Deprivation Using Machine Learning Algorithms. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 15716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albadawi, Y.; Takruri, M.; Awad, M. A Review of Recent Developments in Driver Drowsiness Detection Systems. Sensors 2022, 22, 2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigari, M.-H.; Pourshahabi, M.-R.; Soryani, M.; Fathy, M. A Review on Driver Face Monitoring Systems for Fatigue and Distraction Detection. IJAST 2014, 64, 73–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, T. PERCLOS-Based Technologies for Detecting Drowsiness: Current Evidence and Future Directions. SLEEP Adv. 2023, 4, zpad006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhmudov, F.; Turimov, D.; Xamidov, M.; Nazarov, F.; Cho, Y.-I. Real-Time Fatigue Detection Algorithms Using Machine Learning for Yawning and Eye State. Sensors 2024, 24, 7810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francois, J.; Khalafalla, M.; Kobelo, D.; Williams, J. Preventing Drowsy Driving Accidents in the Construction Industry Using Computer Vision and Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the Construction Research Congress 2024, Des Moines, IA, USA, 20–23 March 2024; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2024; pp. 435–444. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, O.F.; Ibrahim, A.F.; Gomaa, A.; Makhlouf, M.A.; Hafiz, B. Real-Time Driver Drowsiness Detection Using Transformer Architectures: A Novel Deep Learning Approach. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 17493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essahraui, S.; Lamaakal, I.; El Hamly, I.; Maleh, Y.; Ouahbi, I.; El Makkaoui, K.; Filali Bouami, M.; Pławiak, P.; Alfarraj, O.; Abd El-Latif, A.A. Real-Time Driver Drowsiness Detection Using Facial Analysis and Machine Learning Techniques. Sensors 2025, 25, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Mark Liao, H.-Y.; Wu, Y.-H.; Chen, P.-Y.; Hsieh, J.-W.; Yeh, I.-H. CSPNet: A New Backbone That Can Enhance Learning Capability of CNN. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 1571–1580. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, S.; Han, D.; Chun, S.; Oh, S.J.; Yoo, Y.; Choe, J. CutMix: Regularization Strategy to Train Strong Classifiers with Localizable Features. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 6022–6031. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, M.; Chen, C.; Xiao, B.; Seo, J. Vision-Based Detection Method for Construction Site Monitoring by Integrating Data Augmentation and Semisupervised Learning. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2024, 150, 04024027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yin, X. A Semi-Supervised Learning Detection Method for Vision-Based Monitoring of Construction Sites by Integrating Teacher-Student Networks and Data Augmentation. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2021, 50, 101372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, J. Personal Protective Equipment Detection for Construction Workers: A Novel Dataset and Enhanced YOLOv5 Approach. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 47338–47358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, S.; Baek, F.; Park, S.; Kim, W.; Kim, H. Image Augmentation to Improve Construction Resource Detection Using Generative Adversarial Networks, Cut-and-Paste, and Image Transformation Techniques. Autom. Constr. 2020, 115, 103198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suto, J. Using Data Augmentation to Improve the Generalization Capability of an Object Detector on Remote-Sensed Insect Trap Images. Sensors 2024, 24, 4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangha, H.S.; Darr, M.J. Influence of Model Size and Image Augmentations on Object Detection in Low-Contrast Complex Background Scenes. AI 2025, 6, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, A.; Shen, B.; Tian, J.; Hu, Z. Differentiable RandAugment: Learning Selecting Weights and Magnitude Distributions of Image Transformations. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2023, 32, 2413–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Kang, G.; Kim, J.; Yoon, S.; Jeon, J. Generative AI-Driven Data Augmentation for Enhanced Construction Hazard Detection. Autom. Constr. 2025, 177, 106317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Kaddour, J.; Zhang, X.; Nie, Y.; Liu, Z.; Kong, L.; Liu, Q. TTIDA: Controllable Generative Data Augmentation via Text-to-Text and Text-to-Image Models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.08821. [Google Scholar]
- Aqeel, M.; Bellete, K.D.; Setti, F. RoadFusion: Latent Diffusion Model for Pavement Defect Detection. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2507.15346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Dong, X.; Chen, C.; Zhuang, W.; Lyu, L. A Simple Background Augmentation Method for Object Detection with Diffusion Model. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2024; Leonardis, A., Ricci, E., Roth, S., Russakovsky, O., Sattler, T., Varol, G., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; Volume 15124, pp. 462–479. ISBN 978-3-031-72847-1. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, W.-Y.; Lin, J.-W. High-Quality Text-to-Image Generation Using High-Detail Feature-Preserving Network. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thampanichwat, C.; Wongvorachan, T.; Sirisakdi, L.; Chunhajinda, P.; Bunyarittikit, S.; Wongmahasiri, R. Mindful Architecture from Text-to-Image AI Perspectives: A Case Study of DALL-E, Midjourney, and Stable Diffusion. Buildings 2025, 15, 972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borji, A. Generated Faces in the Wild: Quantitative Comparison of Stable Diffusion, Midjourney and DALL-E 2. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2210.00586. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, L.; Konz, N. Computer Vision Techniques in Manufacturing. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man. Cybern. Syst. 2023, 53, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Persello, C.; Stein, A. Building Outline Delineation: From Aerial Images to Polygons with an Improved End-to-End Learning Framework. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 175, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Ergu, D.; Liu, F.; Cai, Y.; Ma, B. A Review of Yolo Algorithm Developments. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2022, 199, 1066–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, H.; Duan, X.; Guo, J.; Liu, H.; Gu, J.; Bi, L.; Chen, H. DC-YOLOv8: Small-Size Object Detection Algorithm Based on Camera Sensor. Electronics 2023, 12, 2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhsh, Z.A.; Jansen, N.; Saeed, A. Damage Detection Using In-Domain and Cross-Domain Transfer Learning. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 16921–16936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
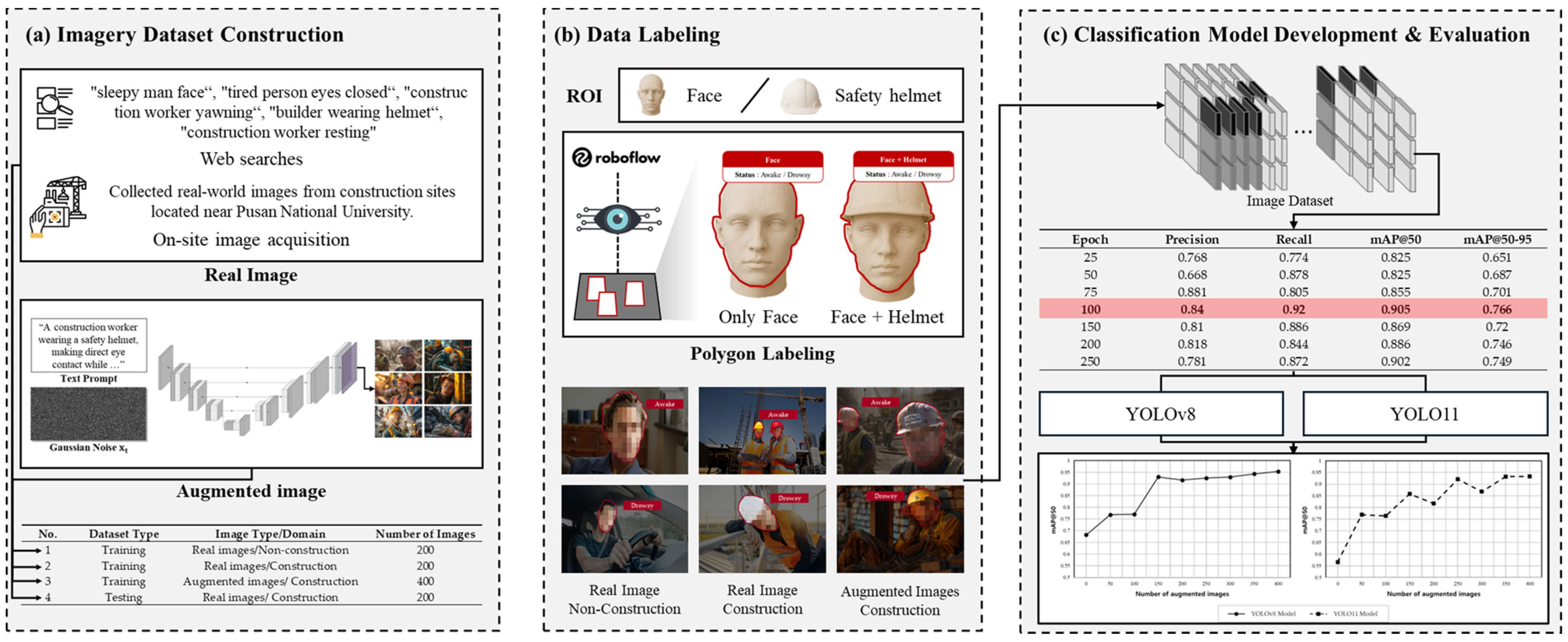


| No. | Dataset Type | Image Type/Domain | Number of Images |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Training | Real images/Non-construction | 200 |
| 2 | Training | Real images/Construction | 200 |
| 3 | Training | Augmented images/Construction | 400 |
| 4 | Testing | Real images/Construction | 200 |
| Epoch | Precision | Recall | mAP@50 | mAP@50-95 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | 0.768 | 0.774 | 0.825 | 0.651 |
| 50 | 0.668 | 0.878 | 0.825 | 0.687 |
| 75 | 0.881 | 0.805 | 0.855 | 0.701 |
| 100 | 0.84 | 0.92 | 0.905 | 0.766 |
| 150 | 0.81 | 0.886 | 0.869 | 0.72 |
| 200 | 0.818 | 0.844 | 0.886 | 0.746 |
| 250 | 0.781 | 0.872 | 0.902 | 0.749 |
| Model | Training Dataset (Domain/Number) | Testing Dataset (Domain/Number) | mAP@50 | mAP@50-95 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv8 | Non-construction/200 | Construction/200 | 0.534 | 0.236 |
| Construction/200 | 0.682 | 0.581 | ||
| YOLO11 | Non-construction/200 | 0.535 | 0.241 | |
| Construction/200 | 0.566 | 0.493 |
| No. | Number of Augmented Images | Total Number of Training Data | mAP@50 | mAP@50-95 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 0 | 200 | 0.682 | 0.581 |
| 1 | 50 | 250 | 0.768 | 0.693 |
| 2 | 100 | 300 | 0.77 | 0.668 |
| 3 | 150 | 350 | 0.93 | 0.836 |
| 4 | 200 | 400 | 0.916 | 0.825 |
| 5 | 250 | 450 | 0.925 | 0.821 |
| 6 | 300 | 500 | 0.929 | 0.85 |
| 7 | 350 | 550 | 0.943 | 0.87 |
| 8 | 400 | 600 | 0.953 | 0.871 |
| No. | Number of Augmented Images | Total Number of Training Data | mAP@50 | mAP@50-95 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 0 | 200 | 0.566 | 0.493 |
| 1 | 50 | 250 | 0.769 | 0.682 |
| 2 | 100 | 300 | 0.764 | 0.664 |
| 3 | 150 | 350 | 0.858 | 0.773 |
| 4 | 200 | 400 | 0.817 | 0.739 |
| 5 | 250 | 450 | 0.921 | 0.827 |
| 6 | 300 | 500 | 0.868 | 0.792 |
| 7 | 350 | 550 | 0.932 | 0.837 |
| 8 | 400 | 600 | 0.933 | 0.845 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jung, D.; Lee, Y.; Jeong, K.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.; Park, H.; Jeon, J. Improvement of Construction Workers’ Drowsiness Detection and Classification via Text-to-Image Augmentation and Computer Vision. Sustainability 2025, 17, 9158. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17209158
Jung D, Lee Y, Jeong K, Lee J, Kim J, Park H, Jeon J. Improvement of Construction Workers’ Drowsiness Detection and Classification via Text-to-Image Augmentation and Computer Vision. Sustainability. 2025; 17(20):9158. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17209158
Chicago/Turabian StyleJung, Daegyo, Yejun Lee, Kihyun Jeong, Jeehee Lee, Jinwoo Kim, Hyunjung Park, and Jungho Jeon. 2025. "Improvement of Construction Workers’ Drowsiness Detection and Classification via Text-to-Image Augmentation and Computer Vision" Sustainability 17, no. 20: 9158. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17209158
APA StyleJung, D., Lee, Y., Jeong, K., Lee, J., Kim, J., Park, H., & Jeon, J. (2025). Improvement of Construction Workers’ Drowsiness Detection and Classification via Text-to-Image Augmentation and Computer Vision. Sustainability, 17(20), 9158. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17209158






