An Improved Method for Disassembly Depth Optimization of End-of-Life Smartphones Based on PSO-BP Neural Network Predictive Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
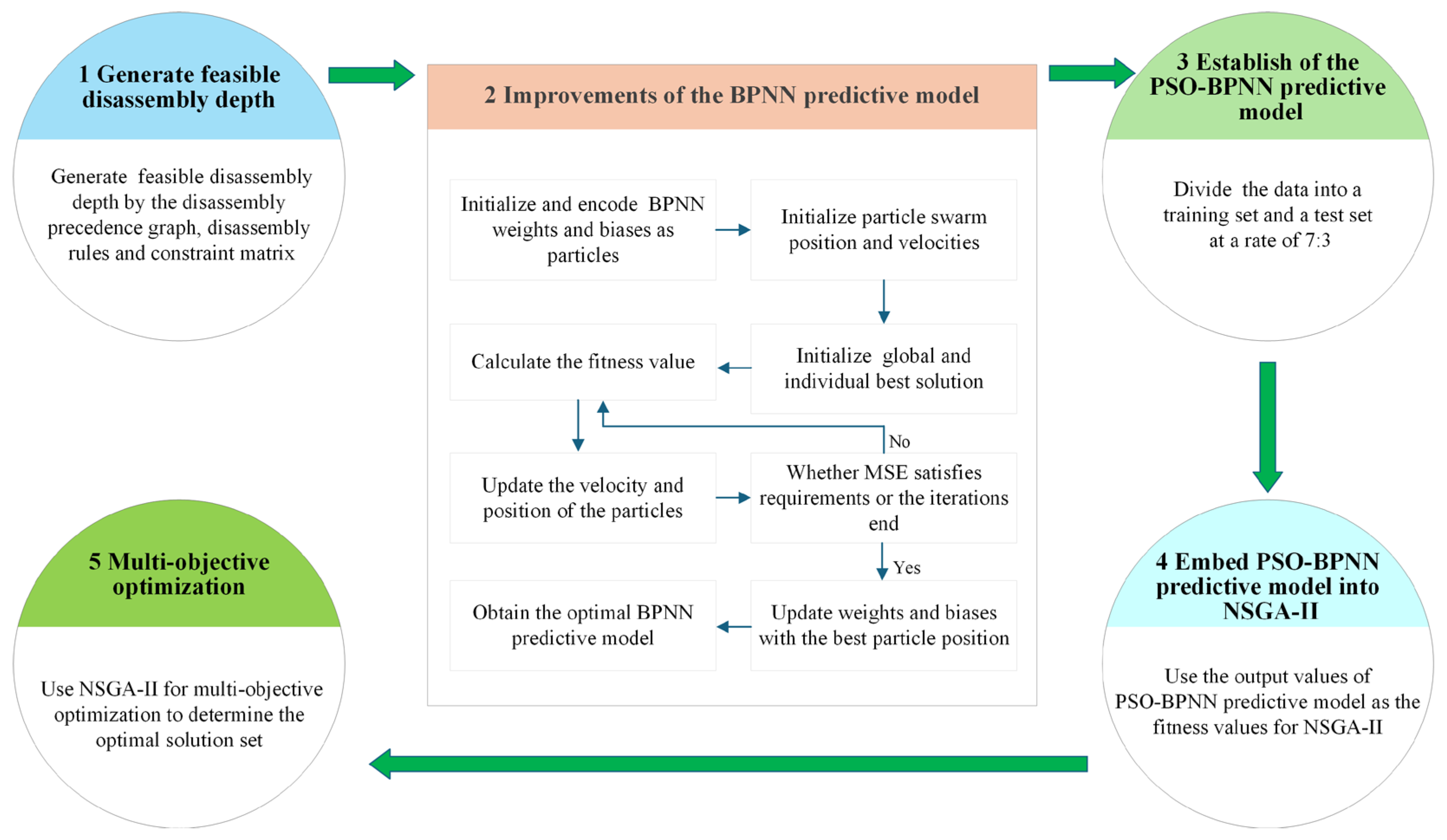
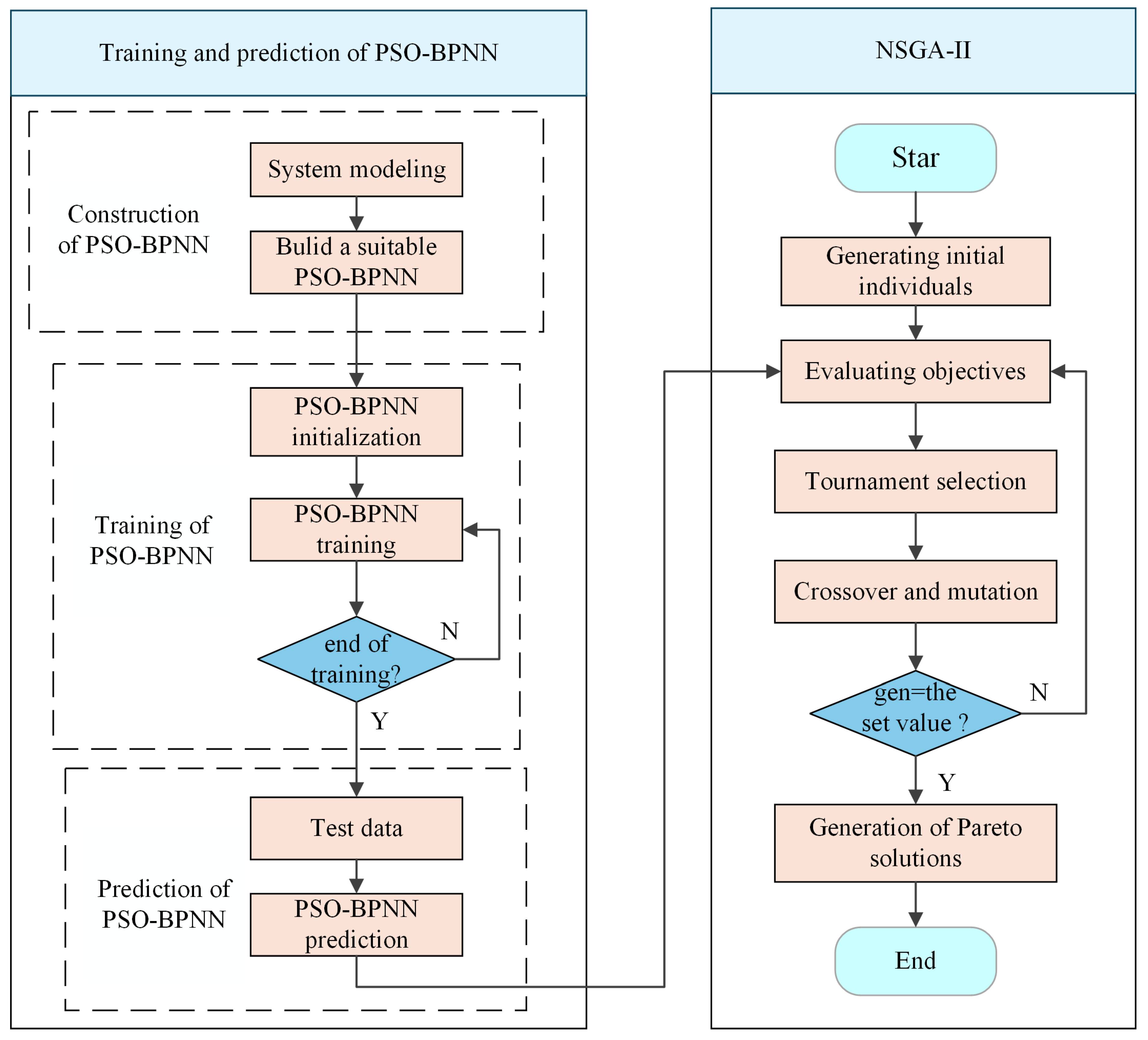
2. Disassembly Depth Optimization Method Based on PSO-BPNN Model
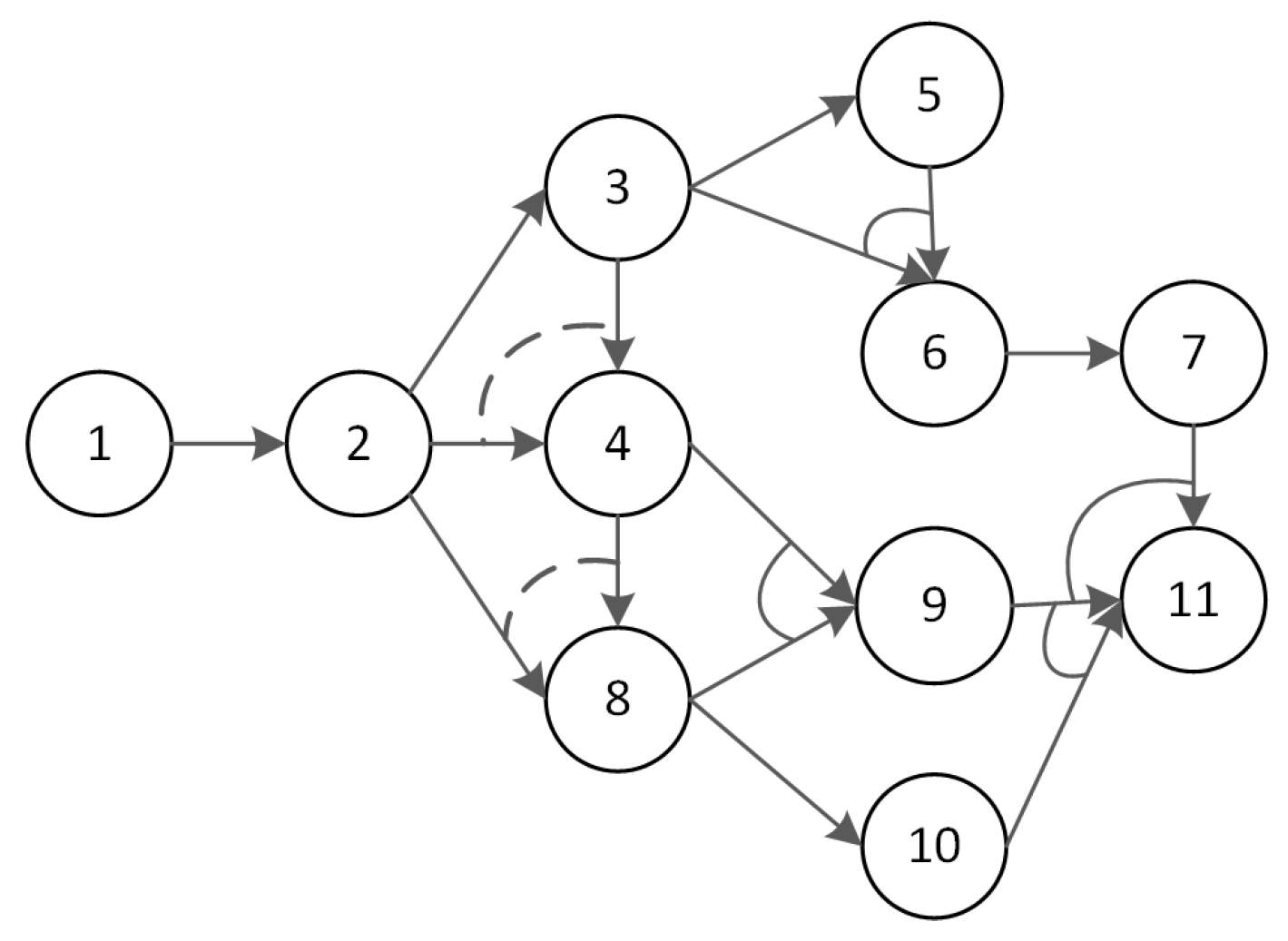
2.1. Generate Feasible Disassembly Depth
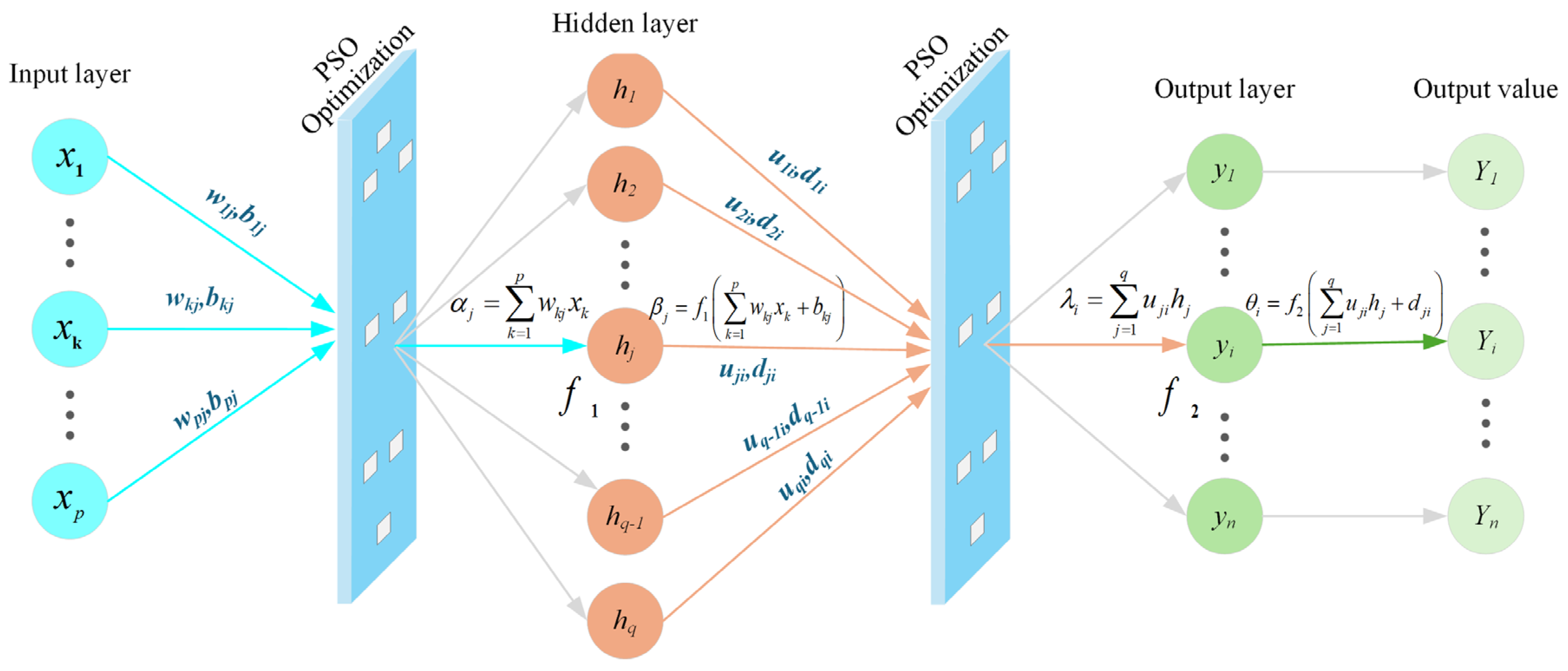
2.2. Improvements of the BPNN Predictive Model
2.3. Establishment of the PSO-BPNN Predictive Model
2.4. Embed the PSO-BPNN Predictive Model into NSGA-II
2.5. Multi-Objective Optimization
3. Case Study
3.1. Fundamental Data
3.2. Disassembly Schemes
4. Results and Discussion
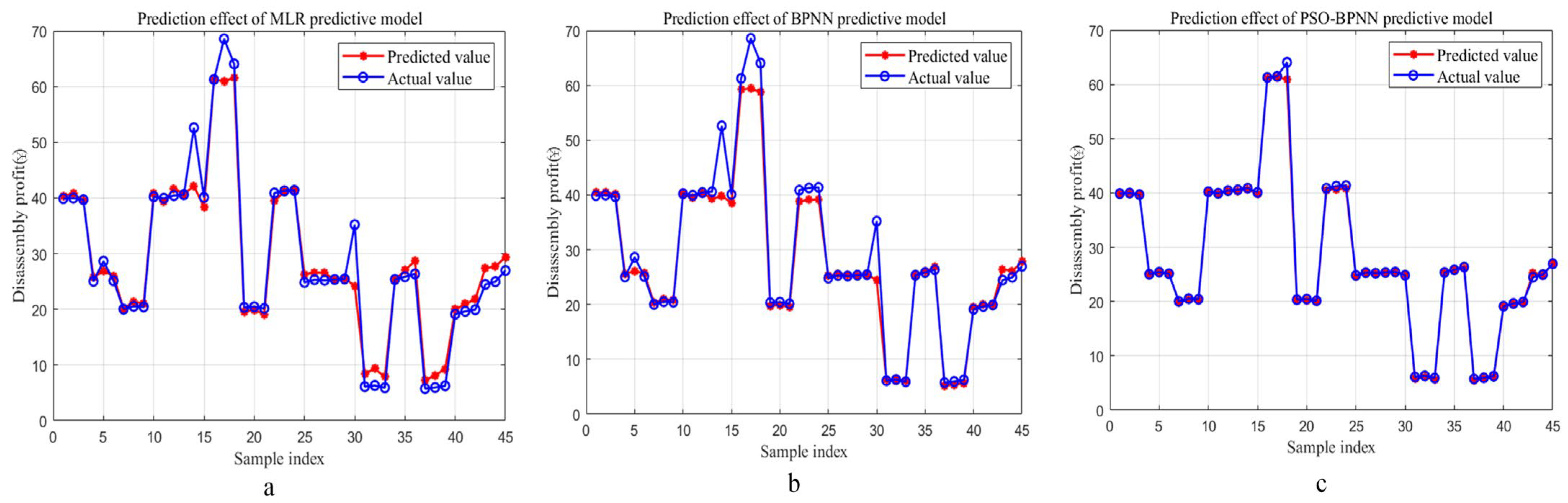
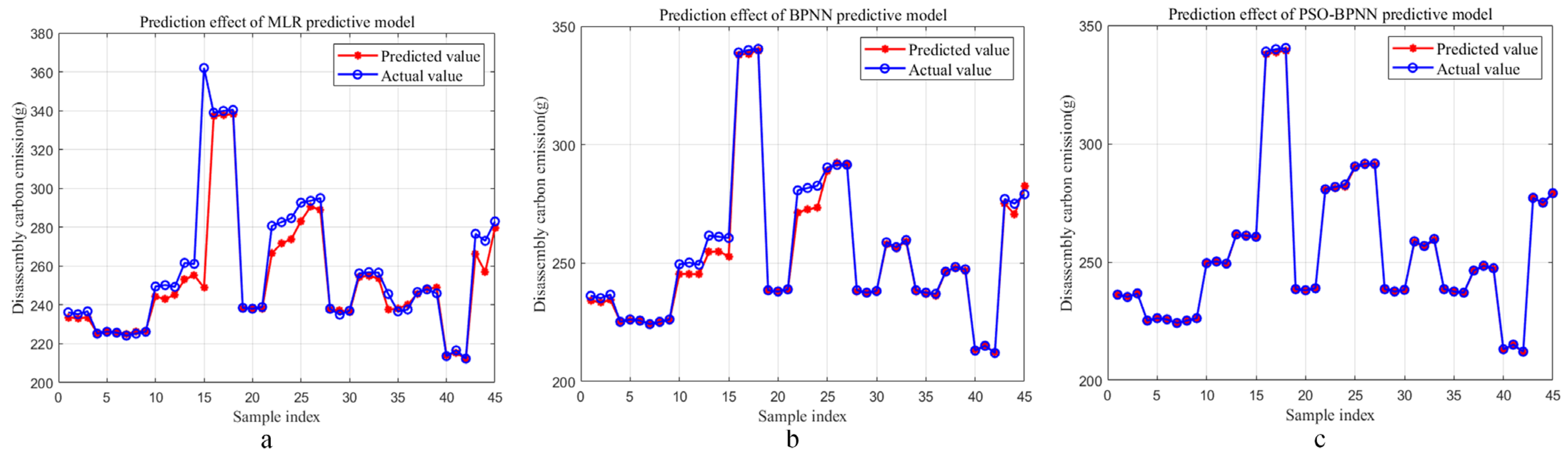
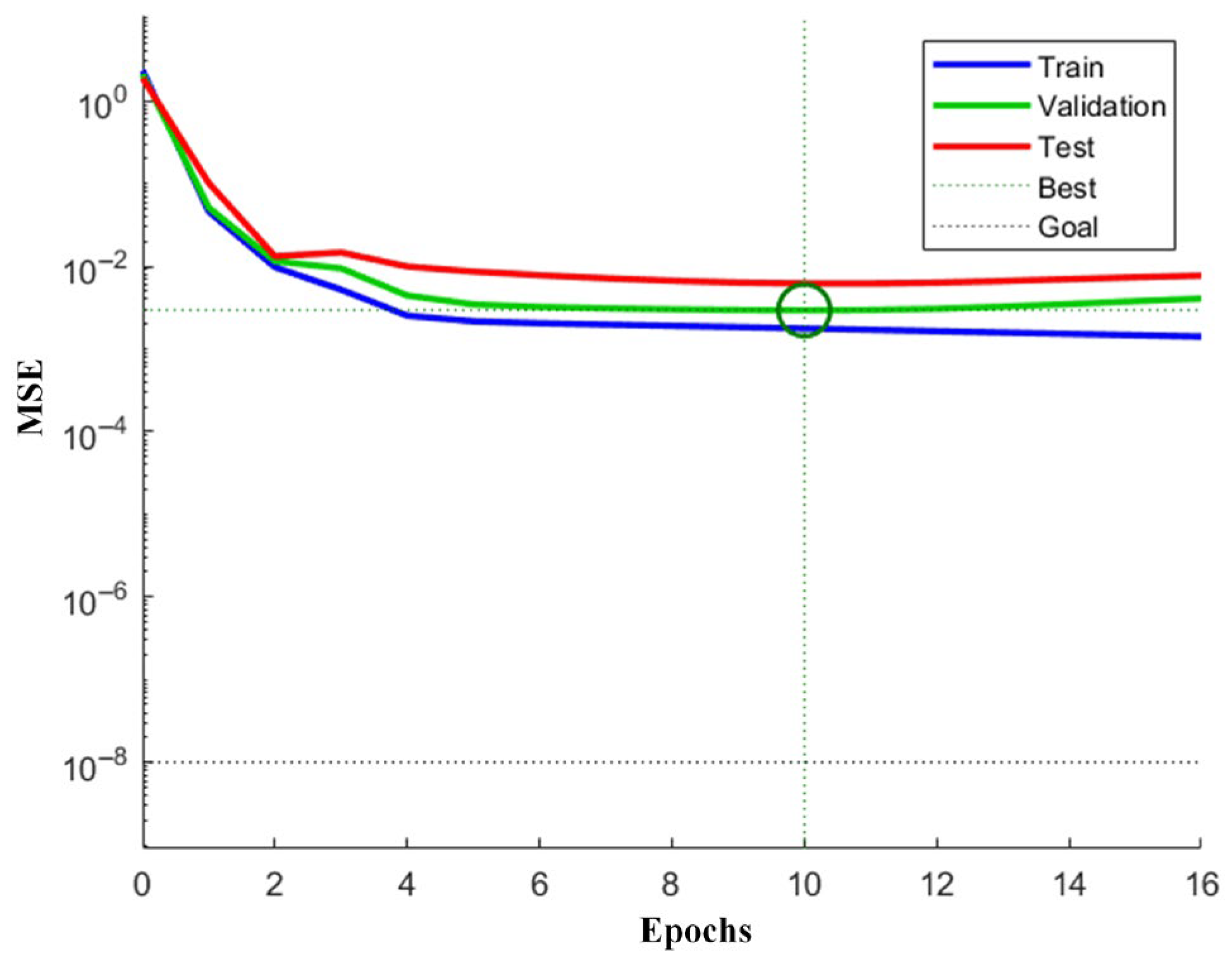
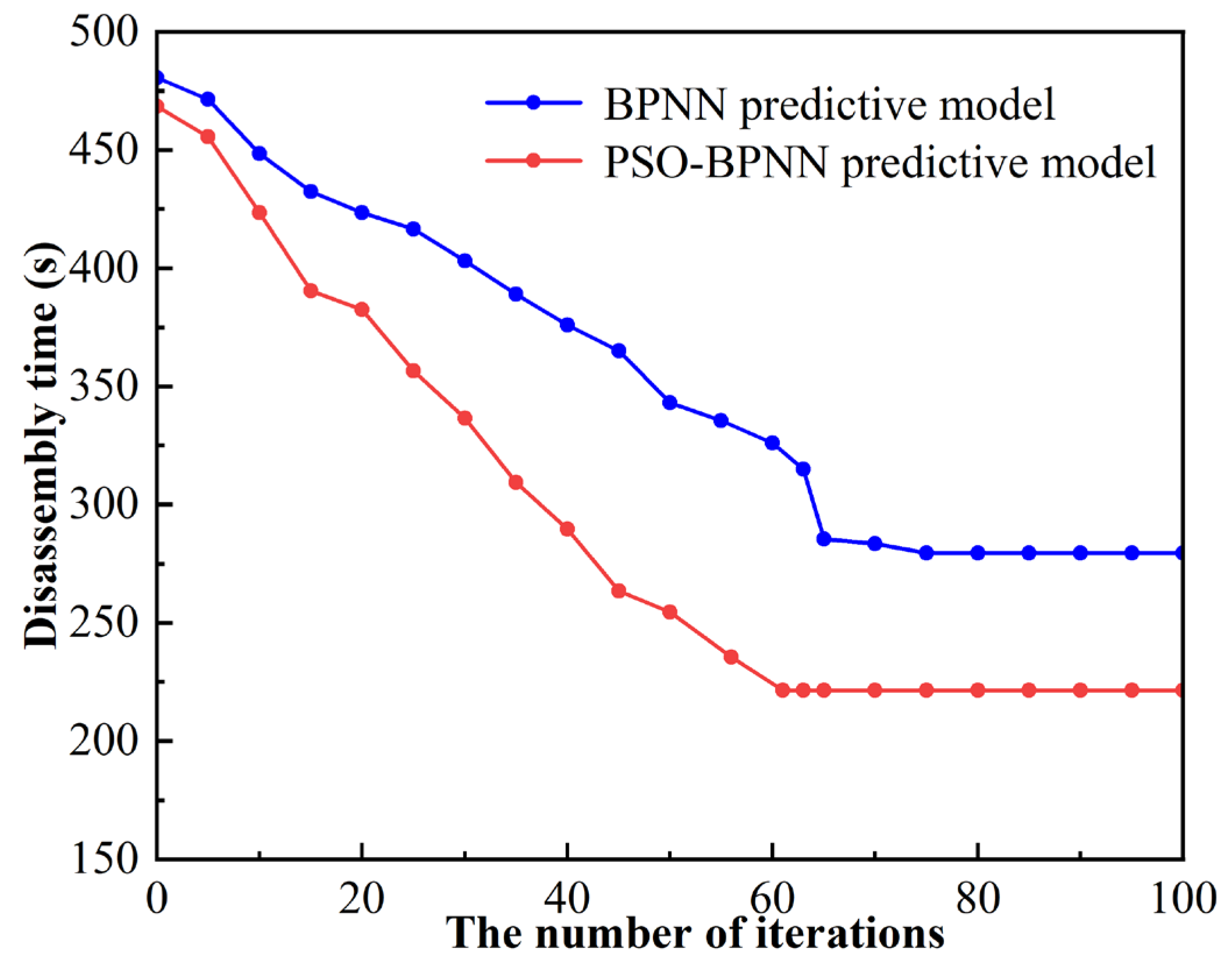
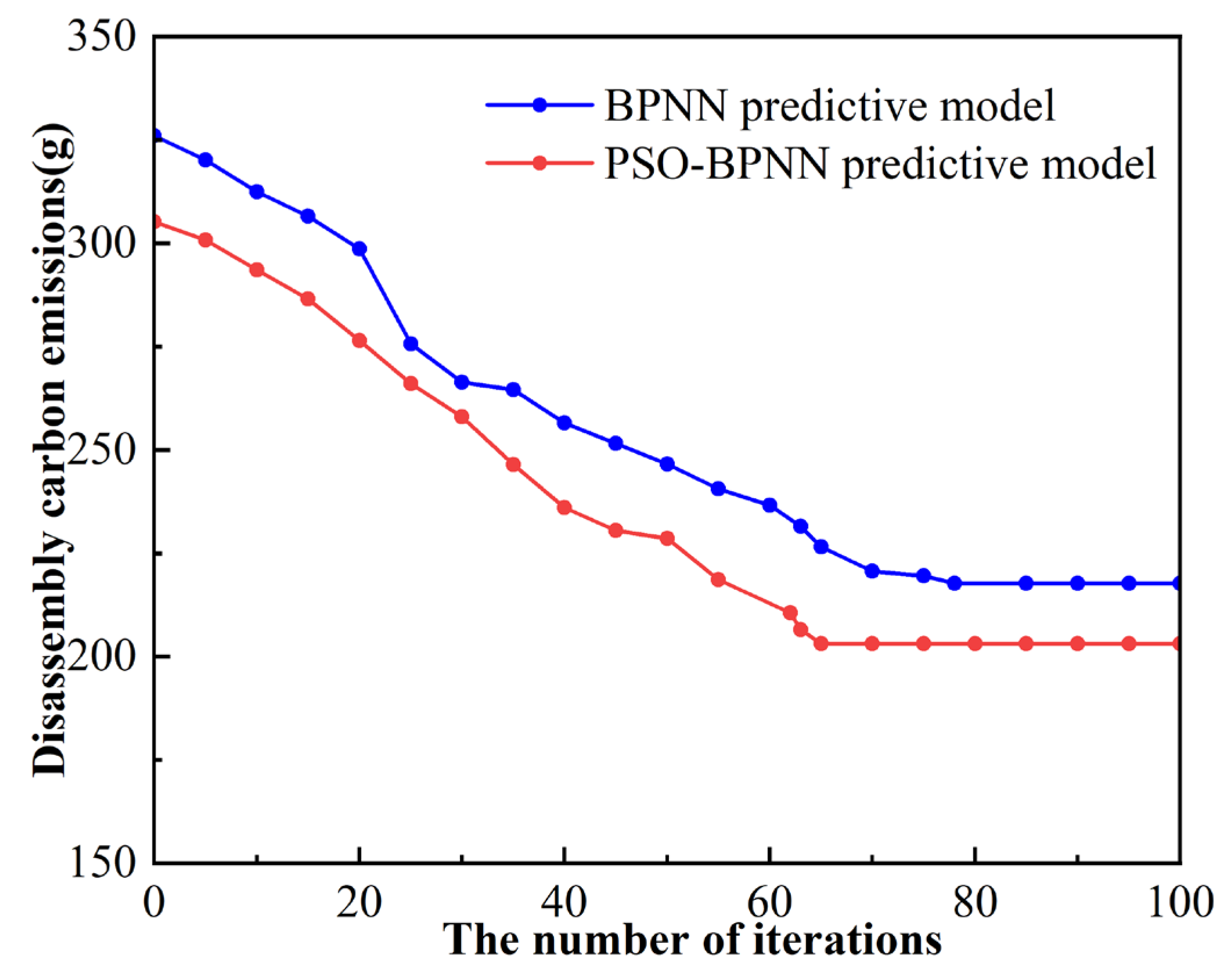
4.1. Discussion for Prediction Results of the PSO-BPNN Predictive Model
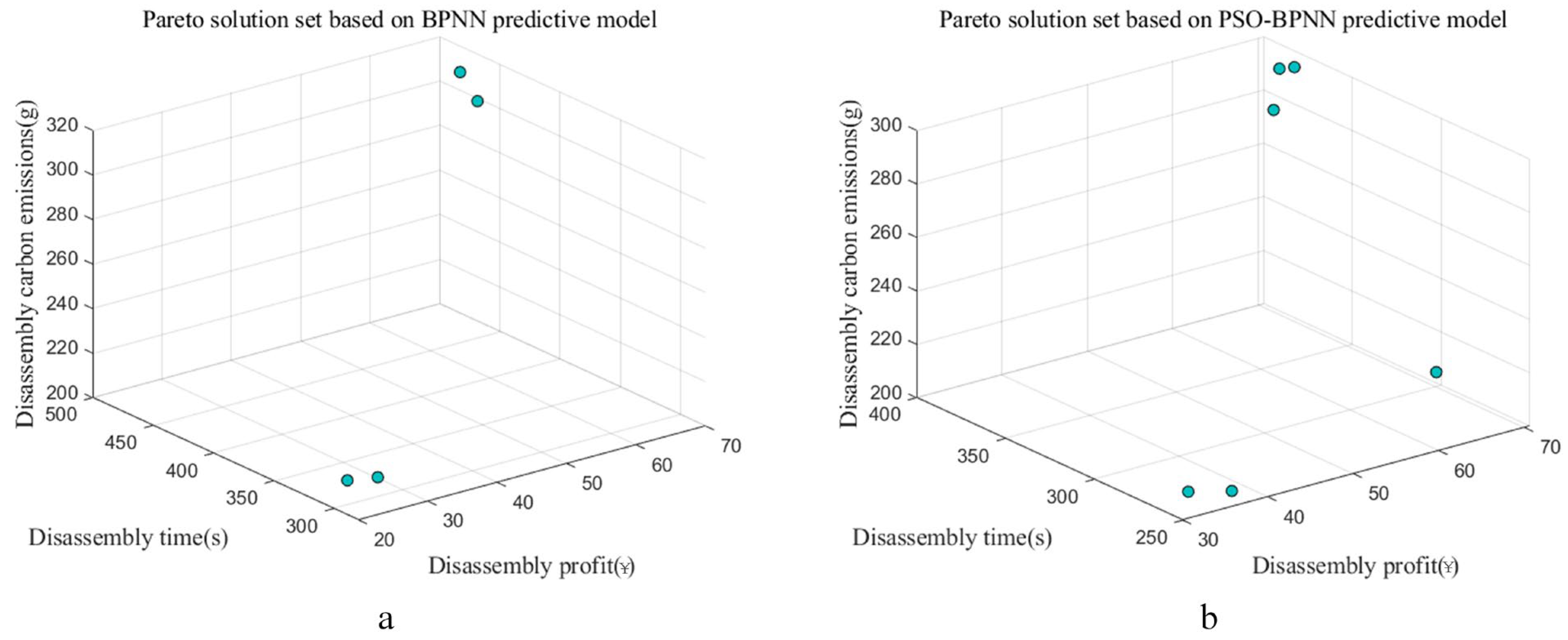
4.2. Discussion for the Pareto Optimal Solutions
4.3. The Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zeng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, T.; Zheng, H. Robotic disassembly line balancing and sequencing problem considering energy-saving and high-profit for waste household appliances. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 381, 135209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Li, B.; Ma, S.; Zhu, M.; Dong, C.; Xiang, M.; Cheng, H.; Yu, Y. The recycling potential of unregulated waste electrical and electronic equipment in China: Generation, economic value, and cost-benefit analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 402, 136702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Shi, Y.; Arthanari, T.; Gao, Y.; Li, X. Examining the Chinese mobile phone industry in the reverse supply chains. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2022, 82, 109407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulivindala, A.K.; Bahubalendruni, M.V.A.R.; P, M.B.; Eswaran, M. Mechanical disassembly sequence planning for end-of-life products to maximize recyclability. Sādhanā 2023, 48, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Wu, Q.; Wang, M.; He, D.; Fang, H. A novel recycling method using machine vision to assist in the processing of stacked waste fans. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2024, 26, 1649–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clegg, A.J.; Williams, D.J. The strategic and competitive implications of recycling and design for disassembly in the electronics industry. IEEE 1994, 33, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillon, P.S. Salvageability by design. IEEE Spectrum 1994, 31, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, D.A.P.; Ijomah, W.L.; Windmill, J.F.C. End-of-life decision tool with emphasis on remanufacturing. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 148, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, X.; Gao, L. Modeling and optimization of multi-objective partial disassembly line balancing problem considering hazard and profit. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 211, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentaha, M.L.; Dolgui, A.; Battaïa, O.; Hu, J. Profit-oriented partial disassembly line design: Dealing with hazardous parts and task processing times uncertainty. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2018, 56, 7220–7242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, T.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, J. A Pareto-discrete hummingbird algorithm for partial sequence-dependent disassembly line balancing problem considering tool requirements. J. Manuf. Syst. 2021, 60, 406–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, T.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, T.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J. Multimanned partial disassembly line balancing optimization considering end-of-life states of products and skill differences of workers. J. Manuf. Syst. 2023, 66, 107–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, L.; Chu, X.; Yin, F.; Li, H. Multi-Objective Disassembly Depth Optimization for End-of-Life Smartphones Considering the Overall Safety of the Disassembly Process. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Noronha, F.P.; Kwade, A.; Droder, K. Advancing Material Separation Efficiency Through Extended Disassembly Depth in Pretreatment Processes for Lithium-ion Batteries Recycling. Procedia CIRP 2024, 127, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wang, G.; Xiao, J.; Zheng, P.; Pei, E. Partially observable deep reinforcement learning for multi-agent strategy optimization of human-robot collaborative disassembly: A case of retired electric vehicle battery. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2024, 89, 102775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhang, M.; Lu, Y.; Jia, Y.; Xu, Y. An ontology and rule-based method for human–robot collaborative disassembly planning in smart remanufacturing. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2024, 89, 102766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yan, J.; Xing, Z. Energy requirements evaluation of milling machines based on thermal equilibrium and empirical modelling. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 52, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, K.; Xia, W.; Shen, R.; Luo, G.; Cheng, Y.; Su, W.; Su, A. Optimization of heterogeneous continuous flow hydrogenation using FTIR inline analysis: A comparative study of multi-objective Bayesian optimization and kinetic modeling. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2025, 302, 120901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashiro, H.; Nonaka, H. Estimation of processing time using machine learning and real factory data for optimization of parallel machine scheduling problem. Oper. Res. Perspect. 2021, 8, 100196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Xia, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, X. A Novel Multi-Efficiency Optimization Method for Disassembly Line Balancing Problem. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Tang, Q.; Liu, J.; Liu, Z.; Pham, D.C. Disassembly sequence planning using discrete Bees algorithm for human-robot collaboration in remanufacturing. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2020, 62, 101860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, M.; Chen, W. Human-robot collaboration disassembly planning for end-of-life power batteries. J. Manuf. Syst. 2023, 69, 271–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Wu, D.; Qu, L. Parallel disassembly sequence planning using improved ant colony algorithm. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 113, 2327–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yuan, G.; Zhuang, Q.; Tian, G. Multi-objective low-carbon disassembly line balancing for agricultural machinery using MDFOA and fuzzy AHP. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 233, 1465–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, L. Optimizing a disassembly sequence planning with success rates of disassembly operations via a variable neighborhood search algorithm. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 157540–157549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuo, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, T.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Junqi, L. Multimanned disassembly line balancing optimization considering walking workers and task evaluation indicators. J. Manuf. Syst. 2024, 72, 263–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, L. Physics-Informed Neural Network-Based Nonlinear Model Predictive Control for Automated Guided Vehicle Trajectory Tracking. World Electr. Veh. J. 2024, 15, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, Y.J.; Villalonga, A.; Castaño, F. Automated machine learning methodology for optimizing production processes in small and medium-sized enterprises. Oper. Res. Perspect. 2024, 12, 100308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, L.; Jiao, S.; Zhao, F.; Southerland, J.W.; Yin, F. An improved identification method based on Bayesian regularization optimization for the imbalanced proportion plastics recycling using NIR spectroscopy. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2024, 26, 3838–3851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tian, Y.; Hu, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, K.; Liu, Y. Predictive modelling and Pareto optimization for energy efficient grinding based on aANN-embedded NSGA II algorithm. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 327, 129479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroon, M. An Eulerian constitutive model for rate-dependent inelasticity enhanced by neural networks. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2024, 430, 117241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, T.; Tanabe, K. Neural network ensembles for band gap prediction. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2025, 246, 113327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Zhou, H.; Li, M.; Yan, S. A neural network method for the escape rate in metastable system. Phys. A 2025, 674, 130759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Ren, J.; Yan, J.; Wu, X.; Dang, F. Research on a concrete compressive strength prediction method based on the random forest and LCSSA-improved BP neural network. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 76, 107150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Tang, B.; Zeng, X.; Zhou, P.; Kang, P.; Long, H. Short-term wind speed forecasting based on long short-term memory and improved BP neural network. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2022, 134, 107365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xie, C.; Liu, B.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Z.; Tai, H. Self-adaptive temperature and humidity compensation based on improved deep BP neural network for NO2 detection in complex environment. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 362, 131812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Yang, Y.; Maheshwari, M.; Li, N. Parameter optimization for FPSO design using an improved FOA and IFOA-BP neural network. Ocean Eng. 2019, 175, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhao, X.; Ke, Q.; Dong, W.; Zhong, Y. Disassembly line balancing optimization method for high efficiency and low carbon emission. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf.-Green Technol. 2019, 8, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.L.; Behdad, S.; Liang, X.; Zheng, M. Task allocation and planning for product disassembly with human–robot collaboration. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2022, 76, 102306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartono, N.; Ramírez, F.J.; Pham, D.T. A multiobjective decision-making approach for modelling and planning economically and environmentally sustainable robotic disassembly for remanufacturing. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2023, 184, 109535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Han, Y. Two sided disassembly line balancing problem with rest time of works: A constraint programming model and an improved NSGA II algorithm. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 239, 122323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, W.; Guo, J.; Wang, K.; Gao, L. Multi-objective collaborative optimization of green disassembly planning and recovery option decision considering the learning effect. J. Manuf. Syst. 2025, 80, 324–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Terzi, S. Large language model-guided graph convolution network reasoning system for complex human-robot collaboration disassembly operations. Procedia CIRP 2025, 134, 43–48. Available online: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0 (accessed on 1 September 2025). [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Wang, C.; Cong, L.; Du, Q. A sequential disassembly planning approach based on knowledge graph and graph isomorphism network for supporting power battery remanufacturing. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 507, 145558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Terzi, S.; Tao, F.; Anwer, N.; Eynard, B. Multi-scenario digital twin-driven human-robot collaboration multi-task disassembly process planning based on dynamic time petri-net and heterogeneous multi-agent double deep Q-learning network. J. Manuf. Syst. 2025, 83, 284–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reula, M.; Parreño-Torres, C.; Ramírez, F.J. A set of novel Mixed-Integer Linear Programming models for robotic disassembly sequence planning in sustainable remanufacturing. J. Manuf. Syst. 2025, 82, 1046–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Li, Z.; Zheng, C.; Li, T.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, L. A Q-learning-oriented multi-objective teaching-learning-based optimization algorithm for balancing U-shaped disassembly lines. Appl. Soft Comput. 2025, 177, 113273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.; Kim, Z.; Yu, J.; Kim, G.; Hwang, S. Development of NOx reduction system utilizing artificial neural network (ANN) and genetic algorithm (GA). J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 232, 1418–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tharwat, A.; Schenck, W. A conceptual and practical comparison of PSO-style optimization algorithms. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2021, 167, 114430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Liu, Y.; Jiao, L.; Wang, L. Multi-objective optimization of reservoir group operation after Inter-basin water transfer jointing SWAT model and NSGA-II. J. Hydrol. 2025, 66, 133431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Jia, X. Multi-objective optimization of CFRP drilling parameters with a hybrid method integrating the ANN, NSGA-II and fuzzy C-means. Compos. Struct. 2020, 235, 111803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongxiang, X.; Wei, W.; Bin, S.; Iibo, L.; Yijun, C.; Jiushuai, D.; Xin, S. Research on carbon emission accounting and carbon emission reduction path of coal preparation plant. Miner. Eng. 2024, 217, 108955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chen, C.; Wang, L.; Zeng, W.; Li, Z. Uncertainty quantification of once-through steam generator for nuclear steam supply system using latin hypercube sampling method. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2023, 55, 2395–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Reference | Product Type | DM | OM | Objectives | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD | PD | MM | NNM | INNM | DS | DE | DT | DP | DC | SI | ||
| [38] | Automobile engine | + | + | + | + | |||||||
| [39] | Used hard disk drive | + | + | + | + | |||||||
| [40] | Gear pumps | + | + | + | + | |||||||
| [13] | EoL smartphone | + | + | + | + | + | + | |||||
| [41] | Refrigerator disassembly line | + | + | + | + | |||||||
| [42] | Refrigerator disassembly | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||
| [43] | EoL battery packs | + | + | + | + | |||||||
| [44] | Retired power battery | + | + | + | + | |||||||
| [45] | NEV-P50 battery | + | + | + | + | |||||||
| [46] | Gear pumps | + | + | + | + | |||||||
| [24] | Corn harvester cutting table | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||
| [47] | U-shaped disassembly lines | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||
| This study | EoL smartphone | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||
| Predictive Model | Parameters/Hyperparameters | Applicable Scenarios |
|---|---|---|
| RF | Tree structure and integrated parameters | Classification/regression tasks |
| SVM | Kernel function and regularization parameters | Small sample classification and high-dimensional space problems |
| LSTM | Loop structure and training parameters | Time series data prediction |
| GBM | Integrate and iterate parameters | Structured data regression/classification |
| MLP | Network structure and optimization parameters | Nonlinear regression/classification |
| LR | Regularization and optimization parameters | Binary classification task |
| DT | Tree structure parameters | Simple classification/regression |
| BPNN | Network structure and training parameters | Nonlinear fitting, pattern recognition |
| Tool Name | Tool Operational Parameters | The Tool Damage Cost for Each Use |
|---|---|---|
| Electric screw bit | Power: 50 w; Rotational speed: 500 r/min | 0.01 |
| Hot air gun | Power: 600 w; Heating temperature: 100 °C | 0.01 |
| SIM-ejector tool | Moving speed: 0.5 m/s | 0.005 |
| ESD-safe tweezer | Moving speed: 0.5 m/s | 0.005 |
| Black stick | Moving speed: 0.5 m/s | 0.005 |
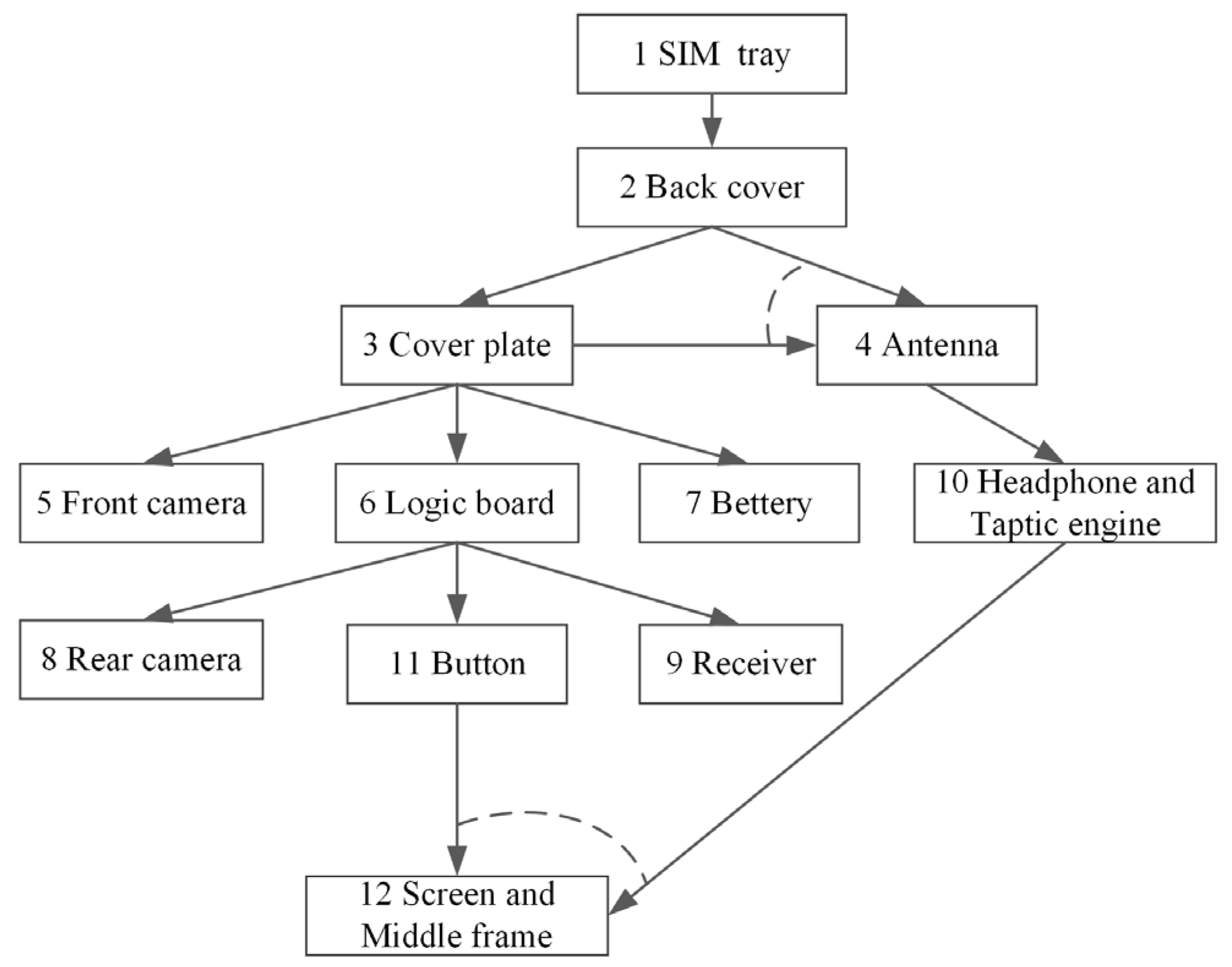
| Part No. | Part Name | Connection Method of Parts | Disassembly Tools and Usage Sequence | Disassembly Direction | Market Recovery Rate | Market Recovery Price (CNY) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SIM tray | Insert | SIM-ejector tool | −Y | 95% | 0.5 |
| 2 | Back cover | Adhesive | Hot air gun → Black stick | +Z | 95% | 0.5 |
| 3 | Cover plate | Screws + Buckle | Electric screw bit | +Z | 95% | 5 |
| 4 | Antenna | Snap-fit | Black stick | +Z | 95% | 1 |
| 5 | Front camera | Clip-on Connector | Black stick | +Z | 98% | 15 |
| 6 | Logic board | Screws + Snap-fit | Electric screw bit → Black stick | +Z | 99% | 45 |
| 7 | Battery | Adhesive | Hot air gun → Black stick | +Z | 99% | 20 |
| 8 | Rear camera | Clip-on Connector | Black stick | +Z | 98% | 20 |
| 9 | Receiver | Adhesive | ESD-safe tweezer | +Z | 95% | 0.5 |
| 10 | Headphone and Taptic engine | Adhesive + Snap-fit | Black stick | +Z | 95% | 0.5 |
| 11 | Button | Adhesive + Snap-fit | ESD-safe tweezer | +Z | 95% | 0.5 |
| 12 | Screen and Middle frame | Adhesive | Hot air gun → Black stick → ESD-safe tweezer | −Z | 98% | 1.5 |
| Energy Type | Utilization (M) | Carbon Emission Factors (C) |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical energy | Power consumption of equipment (M1) | C1 = 0.5 kg/kw h |
| Diesel fuel | Power consumption of material transportation (M2) | C2 = 2.31 kg/L |
| Gasoline | Power consumption of material transportation (M3) | C3 = 3.68 kg/L |
| Group Number | No. | The Disassembly Depth | Disassembly Time (s) | Disassembly Profit (¥) | Disassembly Carbon Emissions (g) | The Non-Inferior Solution | The Optimized Solution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 1 | 1-2-3-5-6-7-8 | 279.5 | 22.72 | 218.6 | × | × |
| 2 | 1-2-3-6-8-5 | 290.5 | 20.39 | 217.7 | × | × | |
| 3 | 1-2-3-6-10-5-8-7-11-12 | 471.5 | 70.58 | 315.6 | × | × | |
| 4 | 1-2-3-5-6-8-11-12 | 416.5 | 60.98 | 319.4 | √ | × | |
| B | 1 | 1-2-3-5-6-7-8 | 221.5 | 63.19 | 207.8 | √ | √ |
| 2 | 1-2-3-6-8-5 | 254.5 | 36.94 | 204.9 | √ | × | |
| 3 | 1-2-3-6-10-5-8-7-11-12 | 390.5 | 70.58 | 290.7 | √ | √ | |
| 4 | 1-2-3-6-7-5-8-9-11-12 | 382.5 | 70.31 | 293.8 | √ | √ | |
| 5 | 1-2-3-6-5-7-8-11-9-12 | 368.5 | 64.90 | 287.3 | √ | × | |
| 6 | 1-2-3-6-7-8 | 264.3 | 33.62 | 203.1 | √ | × |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiao, S.; Li, L.; Yin, F.; Yu, Y. An Improved Method for Disassembly Depth Optimization of End-of-Life Smartphones Based on PSO-BP Neural Network Predictive Model. Sustainability 2025, 17, 9032. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17209032
Jiao S, Li L, Yin F, Yu Y. An Improved Method for Disassembly Depth Optimization of End-of-Life Smartphones Based on PSO-BP Neural Network Predictive Model. Sustainability. 2025; 17(20):9032. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17209032
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiao, Shengqiang, Lin Li, Fengfu Yin, and Yang Yu. 2025. "An Improved Method for Disassembly Depth Optimization of End-of-Life Smartphones Based on PSO-BP Neural Network Predictive Model" Sustainability 17, no. 20: 9032. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17209032
APA StyleJiao, S., Li, L., Yin, F., & Yu, Y. (2025). An Improved Method for Disassembly Depth Optimization of End-of-Life Smartphones Based on PSO-BP Neural Network Predictive Model. Sustainability, 17(20), 9032. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17209032






