Abstract
Damage to human health caused by As-contaminated water can be prevented using proper As-removal techniques, such as employing excellent arsenic adsorbents. In this study, the combined addition of Mg- and Ca-based adsorbents was investigated for the efficient removal of As from contaminated water. Following a previous study on As(V), As-removal tests targeting As(III) and several additional tests, including X-ray diffraction analysis, were conducted to clarify the mechanism of the improved performance of the combined-addition As removal. Similarly as for As(V), the combined additions of both MgCO3 + CaO and MgCO3 + Ca(OH)2 improved As(III)-removal performance while inhibiting the leaching of base material components; however, they did not remove As(III) as effectively as As(V). The differences in the removal ratios of As(V) and As(III) in these combined additions were concluded to be primarily due to the different As-removal mechanisms. Mg(OH)2 and CaCO3 were generated, and As(III) was incorporated into the generated precipitate of Mg(OH)2 but not into that of CaCO3. Conversely, As(V) was incorporated into both Mg(OH)2 and CaCO3. Additionally, MgCO3 + Ca(OH)2 was evaluated as a more efficient combined-addition method because MgCO3 + Ca(OH)2 exhibited a higher As-removal ratio value than MgO + CaO. Proposals have been made to remove As(III) using activated carbon modified with heavy metals or transition elements, or concrete waste grafted with polymers, but these methods are complicated to prepare, costly, and involve the risk of leaching of harmful components. Adsorbents that use general Mg and Ca components as their base material do not contain such harmful components. The Mg- and Ca-based adsorbents are readily available and low-cost, and, best of all, there is no concern that they will leach harmful components. Therefore, widespread use of Mg- and Ca-based adsorbents as a measure against arsenic contamination could greatly contribute to a sustainable society.
1. Introduction
The contamination of As in groundwater and well water has become a global problem, and several researchers have reported on the state of its contamination. In 2020, Kobya et al. [1] presented a tabulated review of As concentrations in groundwater in Asia (Bangladesh, Pakistan, China, India, Nepal, Vietnam, Taiwan, and Thailand), America (USA, Canada, Mexico, Argentina, and Chile), Africa (South Africa and Ghana), Europe (Hungary, Serbia, Croatia, and Greece), and Oceania (Australia). Moreover, in 2019, Abiye and Bhattachaya [2] reported maximum As concentrations of 6150 μg/L west of Johannesburg, South Africa. These extremely high levels of As contamination are probably due to the release of As from minerals such as arsenopyrite, arsenic oxide, sulfharsenide, arsenopyritic reefs, leucopyrite, löllingite, and scorodite contained in aquifer rocks [2]. Numerous studies have reported on the adverse effects of exposure to As-contaminated water on human health [3]. For example, ingesting inorganic As causes various skin lesions, skin cancers, and other internal cancers, such as lung, bladder, liver, and kidney cancers [3]. To address these harmful effects, the World Health Organization (WHO) guidelines for drinking water quality have set a provisional As guideline value of 0.01 mg/L [4]. In Japan, the environmental and effluent standards for As are 0.01 and 0.1 mg/L, respectively [5,6].
Most health damage caused by As can be prevented by properly treating As-contaminated water, prompting several researchers to propose and review various As-removal techniques [7,8,9,10]. These methods can be divided into ion exchange, adsorption, filtration, oxidation, and electrocoagulation methods. Among them, adsorption method is generally easy and has low operating costs, making it the method most easily adopted in economically disadvantaged developing countries. Even quite recently, there have been many reports of research on As(III) removal using new adsorbents. Chuc et al. (2024) studied the As(III) removal using zirconia (ZrO2)-activated carbon (AC) composite synthesized from AC and ZrO2 nanoparticles by a hydrothermal process [11]. The adsorption of arsenite onto a ZrO2-AC surface was studied by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) spectra. It was reported that the results confirmed the simultaneous adsorption of both As(V) and As(III) on the surface of ZrO2-AC materials. They explained that this was because some of the As(III) was oxidized to As(V) during the experiment, and As(III) and As(V) were adsorbed simultaneously. They also reported that with increasing solution pH, the adsorption efficiency of arsenite onto ZrO2-AC was maximal at a pH of about 5 and then decreased at higher pH. They explained that at pH > 5, the negative charges of ZrO2-AC and the fraction of arsenite oxoanions increased, resulting in an enhanced electrostatic repulsion between arsenite and the ZrO2-AC. Furthermore, they reported that the adsorption data fit well to either the Langmuir or Freundlich isotherm, and the maximum monolayer adsorption capacity for arsenite on ZrO2-AC is 64 mg/g [11]. Yadegari et al. (2024) developed an adsorbent grafted with allyl alcohol and vinyl acetate polymers to concrete waste for As(III) removal [12]. They named their adsorbent CW@MPTMS@poly(AA-co-VyAc)@PABA. In their adsorption test with pH as a parameter, the removal efficiency of As(III) improved with an increase in the pH of the solution from 5 to 7. In their adsorption test with temperature as a parameter, the removal efficiency improved from 55 to 75% with a decrease in temperature from 45 to 25 °C. Therefore, they suggested that the As(III) sorption reaction was exothermic by CW@MPTMS@poly(AA-co-VyAc)@PABA. The Freundlich isotherm model with their data provided a better fit to experimental results than the Langmuir, Temkin, and Dubinin–Radushkevich. The maximum As(III) sorption capacity of CW@MPTMS@poly(AA-co-VyAc)@PABA was assessed from the non-linear Langmuir isotherm model by them, which comprised 6.818 mg/g. Furthermore, the evaluation with the Dubinin-Radushkevich model indicated that the As(III) sorption onto CW@MPTMS@poly(AA-co-VyAc)@PABA was physical adsorption. They inferred that hydrogen bonds were mainly generated between O–H functional groups on the As(III) ion and NH2 and O–H groups of CW@MPTMS@poly(AA-co-VyAc)@PABA, which contributed to the adsorption process and enabled the high removal efficiency [12]. Choudhury et al. (2025) studied As(III) removal using bagasse-manganese-aluminum (B-Mn-Al), a sugarcane bagasse-derived biochar impregnated with Mn and Al [13]. They revealed that 34.70 wt% of the B-Mn-Al was metal, of which 6.12% was Al and 28.58% was Mn by energy-dispersive X-ray (EDS) analysis. Additionally, analysis of the X-ray diffraction (XRD) spectrum indicated the presence of Mn and Al as aluminum manganese (Al6Mn). It also verified the successful adsorption of As as manganese arsenide (Mn2As) on the surface. They reported that by maintaining a contact time of 65 min, the adsorption percentage of As(III) jumped from 44.96% at an adsorbent dosage of 0.25 g/L to 91.43% at a dosage of 1.375 g/L adsorbent. As the solution pH increased from 2 to 9, the redox reaction between As(III) and manganese (Mn) oxides was suppressed, leading to a noticeable decrease in As(III) removal. They considered that the adsorption of As(III) on B-Mn-Al adsorbent surface occurred in two routes; one was electrostatic adsorption, and the other one was through ion or ligand exchange between the adsorbate arsenate ion and the active functional groups on the adsorbent surface. The data analysis showed that the correlation coefficient for the Langmuir isotherm was higher than that for the Freundlich isotherm. As(III) adsorption capacity of the adsorbent calculated by them was 55 mg/g [13].
Both Mg- and Ca-based adsorbents [14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21], which are safe for human health, are recommended as environmentally friendly and sustainable adsorbents [22]. A previous study examined the As(V)-removal performance of various combinations of Mg- and Ca-based adsorbents [22]. Both MgCO3 + CaO and MgCO3 + Ca(OH)2 combined additions were the most effective for removing As(V) among the combinations tested. Additionally, these combinations significantly inhibited the leaching of Mg and Ca from the adsorbent base material. However, whether the same improvements are achieved for As(III) has not yet been confirmed. In this study, As(III) removal tests were performed corresponding to the As(V) removal tests performed in a previous study [22]. The As(III)-removal performances of various combinations of Mg- and Ca-based adsorbents were investigated, and the mechanisms of As-removal improvement and Mg- and Ca-leaching inhibition by the MgCO3 + CaO and MgCO3 + Ca(OH)2 combined additions were experimentally investigated. Additionally, X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis was carried out to verify the generation of Mg(OH)2 and CaCO3 in the combined addition test of MgCO3-CaO or MgCO3-Ca(OH)2 that was inferred in a previous study [22]. The solid samples for XRD analysis were prepared in the absence of As, in the presence of As(V) or As(III). Furthermore, to verify the incorporation of As into the produced Mg(OH)2 or CaCO3, ‘Mg(NO3)-addition tests’ and ‘Ca(NO3)2- and Na2CO3-addition tests’ were performed using alkaline As(III) and As(V) solutions. Similarly to a previous study on As(V) removal [22], investigating how the combination of different types of adsorbents affects As(III) removal will also provide important guidance for designing new high-performance treatments.
2. Materials and Methods
The reagents used in this study were purchased from FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation (Osaka, Japan), unless specified otherwise.
2.1. Mg- and Ca-Based Adsorbents
Following a method presented in a previous study [22], MgO, Mg(OH)2, and MgCO3 were employed as the Mg-based adsorbents, while CaO, Ca(OH)2, and CaCO3 were used as the Ca-based adsorbents. The specific characteristics of each adsorbent (Mg and Ca contents, reagent purity, median particle diameter, and Brunauer–Emmett–Teller surface area) are described by Sugita et al. [22]. The median particle size Dp50 (μm), the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface area SBET (m2/g), the measured Mg content αMg (%), the measured Ca contents αCa (%), and the reagent purity (obtained from αMg and αCa) P (%) are shown in Table 1. The data in the table were obtained from a previous study [22].

Table 1.
Characteristics of Mg-based and Ca-based adsorbents used in this study.
2.2. As(III) Removal Tests Using Mg- and Ca-Based Adsorbents
2.2.1. Preparation of Synthetic As(III)-Contaminated Water
Powdered sodium arsenite (NaAsO2, 90%) was dissolved in deionized water, and stock solutions of As(III) (2000 mg As/L) were prepared. The synthetic As(III)-contaminated water was prepared by diluting the As(III) stock solution with deionized water. The initial As concentrations, CAS0, were 1 and 10 mg/L. The pH of the solution was adjusted to approximately 7 using aqueous HNO3 and NaOH. The pH immediately after pH adjustment is referred to as the initial pH, pH0. Incidentally, the reason why the value of pH0 was set to 7 in this study is because groundwater (well water), which usually has a pH close to neutral, is used for drinking and farming.
2.2.2. Experiment Procedure
The experimental procedure for the As(III)-removal test was the same as that used for the As(V)-removal test in a previous study [22], except that the synthetically contaminated water used was different. One or two types of adsorbents were weighed into a 50 mL polypropylene centrifuge tube. The amount of each adsorbent was set as the adsorbent concentration when 50 mL of the liquid was added. The centrifuge tube containing the adsorbent was immediately sealed after adding 50 mL of the fabricated synthetic As(III)-contaminated water and shaken in a constant-temperature shaker (approximately 180 rpm at 20–25 °C). Subsequently, the tubes were centrifuged for 24 h, and the supernatant was filtered through a syringe filter with a pore diameter of 0.45 μm and collected in a polypropylene vessel. The pH of the filtrate (treated water) was immediately measured and referred to as the final pH (pHf). As, Mg, and Ca in the treated water were quantified using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS; Agilent 7700X, Agilent Technologies, Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA) and inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES; SII SPS3500DD, Seiko Instruments Inc., Chiba, Japan), and were denoted as CAS, CMg, and CCa, respectively. In the single-addition tests, the two adsorbent concentrations (WAd/V) were set at 0.2 and 0.4 g/L. In the combined-addition tests with two types of adsorbents, the WAd/V of each adsorbent was 0.2 g/L, with a total adsorbent concentration (ΣWAd/V) of 0.4 g/L.
2.3. Experimental Reproducibility
To confirm the reproducibility of the experiments, As(III)-removal tests were conducted thrice under specific conditions for each adsorbent. The experimental conditions were CAS0 = 1.007 mg/L, pH0 = 7.27, and WAd/V = 0.2 g/L. The measured values and standard errors are listed in Table 2, which indicates that the experimental reproducibility of this study was reasonably good.

Table 2.
Mean values and standard errors obtained from three replicated experiments.
2.4. Preparation of Samples for X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
To clarify the mechanisms of As removal in the combined additions of MgCO3 + CaO and MgCO3 + Ca(OH)2, the following samples were prepared for XRD analysis.
- (a)
- Sample mixed with equal amounts of unused MgCO3 and CaO;
- (b)
- Sample mixed with equal amounts of unused MgCO3 and Ca(OH)2;
- (c)
- Solid sample collected after adding MgCO3 and CaO (each 0.4 g/L) to deionized water;
- (d)
- Solid sample collected after adding MgCO3 and Ca(OH)2 (each 0.4 g/L) to deionized water;
- (e)
- Solid sample collected after adding MgCO3 and CaO (each 0.4 g/L) to the As(III) solution (CAS0 = 10 mg/L and pH0 = 7);
- (f)
- Solid sample collected after adding MgCO3 and Ca(OH)2 (each 0.4 g/L) to the As(III) solution (CAS0 = 10 mg/L and pH0 = 7);
- (g)
- Solid sample collected after adding MgCO3 and CaO (each 0.4 g/L) to the As(V) solution (CAS0 = 10 mg/L and pH0 = 7);
- (h)
- Solid sample collected after adding MgCO3 and Ca(OH)2 (each 0.4 g/L) to the As(V) solution (CAS0 = 10 mg/L and pH0 = 7).
The As(III) solutions used for samples (e) and (f) were prepared as described in Section 2.2.1. The As(V) solution used for samples (g) and (h) was prepared by dissolving the Na2HAsO4·7H2O powder reagent in deionized water and adjusting the solution pH with aqueous HNO3 and NaOH. To prepare samples (c)–(h), 250 mL of the prepared solution (deionized water, As(III) solution, or As(V) solution) was placed into four different TPX beakers. Subsequently, 0.1 g of MgCO3 and 0.1 g of CaO or Ca(OH)2 were added to each beaker, followed by immediate stirring using a magnetic stirrer for 24 h. The samples were then subjected to solid–liquid separation via suction filtration (filter pore size: 0.45 μm). The collected solutions were combined into single containers, and the concentrations of As, Mg, and Ca in the collected solutions of (e)–(h) were determined using ICP-MS and ICP-AES. The collected solid samples were dried overnight at 40 °C, and the crystalline phases of the prepared samples were identified using powder XRD (RINT-2500, Rigaku Co., Akishima, Japan) at the GSJ-Lab (AIST).
2.5. Confirmation Tests for As Removal by Generated Mg(OH)2 and CaCO3
As described in Section 3.4, As(III) removal via the combined additions of MgCO3 and CaO or MgCO3 + Ca(OH)2 was presumed to be attributed to the generated Mg(OH)2 and/or CaCO3. Therefore, several tests were performed to confirm whether the primary mechanism of As(III) and/or As(V) removal was the generation of Mg(OH)2 or CaCO3.
2.5.1. Mg(NO3)2-Addition Tests with Alkaline As Solutions
An As(III) solution (2100 mL; CAS0 = 10 mg/L) with a pH0 = 12 (adjusted using an aqueous NaOH solution) was prepared. Subsequently, 250 mL of the As(III) solution was placed into five separate TPX beakers, and 1 g of Mg(NO3)2·6H2O powdered reagent (Wako 1st grade) was added to each beaker, followed by immediate stirring with a magnetic stirrer. Because Mg(NO3)2·6H2O is a readily soluble substance, it quickly dissolved; however, new precipitates formed during stirring. After stirring for 24 h, the samples were subjected to solid–liquid separation via suction filtration (filter pore size: 0.45 μm), and the collected solutions were combined in a single container. The As and Mg contents in the collected solutions were determined using ICP-MS and ICP-AES, respectively. The precipitate was removed via filtration, dried overnight at 40 °C in a dryer, and collected in a container. The dried samples were analyzed using a powder XRD apparatus. The WAd/V value of Mg(NO3)2·6H2O in the tests was 4 g/L, which corresponded to an Mg concentration of 0.38 g/L, assuming a reagent purity of 100%. However, the actual reagent purity was <100% because Mg(NO3)2·6H2O is a deliquescent substance. Therefore, the value of WAd/V was determined by considering the following factors: collecting the amount of precipitate required for XRD analysis, assuming that Mg(NO3)2·6H2O is converted to Mg(OH)2, and correctly determining whether As has been removed or not. For As(V) removal, the tests were performed under the same conditions using an As(V) solution (CAS0 = 10 mg/L and pH0 = 12) instead of the As(III) solution.
2.5.2. Ca(NO3)2- and Na2CO3-Addition Tests with Alkaline As Solutions
In this series of experiments, the As(III) and As(V) solutions were prepared as described in Section 2.5.1. Briefly, 250 mL of the prepared As(III) solution was placed into three separate TPX beakers, and 0.67 and 0.30 g of Ca(NO3)2·4H2O and Na2CO3 powder reagents (Wako 1st grade), respectively, were added to each beaker, followed by immediate stirring with a magnetic stirrer. Similarly to Mg(NO3)2·6H2O, both Ca(NO3)2·4H2O and Na2CO3 were readily soluble substances that quickly dissolved; however, new precipitates formed during stirring. After stirring for 24 h, the samples were subjected to solid–liquid separation via suction filtration (filter pore size: 0.45 μm). The collected solutions were combined in single containers. The As and Ca contents in the collected solutions were determined using ICP-MS and ICP-AES, respectively. The precipitate removed by the filter was dried overnight at 40 °C in a dryer and collected in a container. The dried samples were analyzed using a powder XRD apparatus. The WAd/V of Ca(NO3)2·4H2O was 2.7 g/L, which corresponded to a Ca concentration of 0.46 g/L, assuming a reagent purity of 100%. However, similarly to Mg(NO3)2·6H2O, the actual reagent purity was <100% because Ca(NO3)2·4H2O is a deliquescent substance. The WAd/V of Na2CO3 was 1.2 g/L, which was an appropriate amount in terms of molar ratio for producing CaCO3 relative to the amount of Ca added. The tests were performed under the same conditions using the As(V) solution instead of the As(III) solution.
The types of experiments performed in this study and the valences of As tested in them are outlined in Table 3.

Table 3.
Correspondence table between experiment types and As valences.
3. Results
3.1. As-Removal Ratio
3.1.1. As-Removal Ratio for Single Addition of One Type of Adsorbent
The values of CAS0 and CAS for the single-addition tests are listed in Table 4. The values for CAS0 = 1 mg/L and WAd/V = 0.2 g/L were obtained from Table 2.

Table 4.
Values of CAS0 and CAS for the single-addition tests.
The values of CAS (mg/L) were converted to the As-removal ratio RAS (%) using Equation (1) to facilitate a comparison because the As(III)-removal tests were performed with two different initial As concentrations.
RAS = (CAS0 − CAS)/CAS0 × 100.
Figure 1 shows RAS calculated using data on Table 4 for the single-addition As(III)-removal tests. Figure 1a and Figure 1b show the RAS values for CAS0 = 1 and 10 mg/L with WAd/V = 0.2 g/L, respectively. Figure 1c and Figure 1d show the RAS values for CAS0 = 1 and 10 mg/L with WAd/V = 0.4 g/L, respectively.
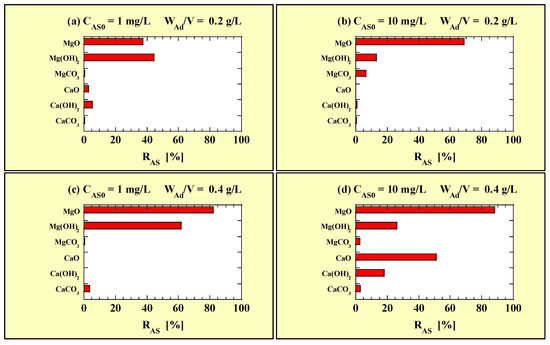
Figure 1.
RAS for the single-addition tests at (a) CAS0 = 1 mg/L with WAd/V = 0.2 g/L; (b) CAS0 = 10 mg/L with WAd/V = 0.2 g/L; (c) CAS0 = 1 mg/L with WAd/V = 0.4 g/L; (d) CAS0 = 10 mg/L with WAd/V = 0.4 g/L.
As shown in Figure 1, MgO and Mg(OH)2 exhibited As(III)-removal abilities, and their RAS values were higher when WAd/V was higher; however, MgCO3 minimally removed As(III) under the test conditions. The Ca-based adsorbents could not remove As(III) under most conditions, as shown in Figure 1a–c. However, when CAS0 = 10 mg/L and WAd/V = 0.4 g/L (Figure 1d), they exhibited a significant increase in RAS values, particularly when the RAS of CaO was >50%. The RAS of each adsorbent varied depending on the combination of CAS0 and WAd/V; however, MgO exhibited the highest As(III)-removal performance.
3.1.2. As-Removal Ratio for Combined Addition of Two Types of Adsorbents
The CAS values for the combined-addition tests at CAS0 = 1 and 10 mg/L are listed in Table 3 and Table 4, respectively. The measured values of CAS0 for the combined-addition tests at CAS0 = 1 and 10 mg/L were 1.07–1.11 and 10.7–10.8 mg/L, respectively. Figure 2 shows the RAS values calculated using the data in Table 5 and Table 6. In particular, Figure 2a and Figure 2b show the RAS values for CAS0 = 1 and 10 mg/L with ΣWAd/V = 0.4 g/L, respectively.
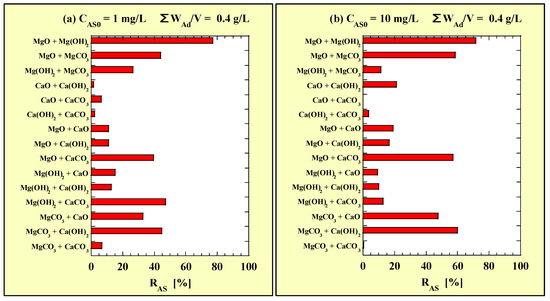
Figure 2.
RAS for the combined-addition tests at (a) CAS0 = 1 mg/L; (b) CAS0 = 10 mg/L.

Table 5.
Values of CAS for the combined-addition tests at CAS0 = 1 mg/L.

Table 6.
Values of CAS for the combined-addition tests at CAS0 = 10 mg/L.
The RAS value was the highest for MgO + Mg(OH)2 among the combined additions; however, it was higher for the single addition of MgO with WAd/V = 0.4 g/L, as shown in Figure 1c,d. For the combinations containing Mg(OH)2 and for MgCO3 + CaCO3, the RAS values were lower at CAS0 = 10 mg/L than at CAS0 = 1 mg/L. For the other combinations, the RAS was higher at CAS0 = 10 mg/L than at CAS0 = 1 mg/L.
A previous study on As(V) removal [22] reported that MgCO3 + CaO and MgCO3 + Ca(OH)2 could remove almost 100% of As(V) at CAS0 = 1 mg/L and >60% at CAS0 =10 mg/L. However, for these two combinations, the RAS values of As(III) attained <45% and <60% at CAS0 = 1 and 10 mg/L, respectively, in this study. Although the single addition of 0.2 g/L of MgCO3, CaO, or Ca(OH)2 minimally removed As(III), as shown in Figure 1a,b, the combined addition of 0.2 g/L of MgCO3 and 0.2 g/L of CaO or Ca(OH)2 exhibited reasonable As(III)-removal performance.
3.2. Mg- and Ca-Residual Ratios
3.2.1. Mg- and Ca-Residual Ratios for Single Addition of One Type of Adsorbent
The values of CMg and CCa for the single-addition tests are listed in Table 7. The CMg and CCa values for CAS0 = 1 mg/L and WAd/V = 0.2 g/L were obtained from Table 2.

Table 7.
Values of CMg and CCa for the single-addition tests.
Because the Mg and Ca components were leached out from the Mg- and Ca-based adsorbents, the amounts of Mg and Ca remaining as solids in the liquid were calculated as the Mg-residual ratio RMg [%] and Ca-residual ratio RCa [%], respectively, using the following equations:
where αMg and αCa are the Mg and Ca contents in the adsorbent, respectively. These values were described in a previous study [22].
RMg = 100 − (CMg × 1000)/[WAd/V × (αMg/100)] × 100
RCa = 100 − (CCa × 1000)/[WAd/V × (αCa/100)] × 100
Figure 3 shows the RMg and RCa values calculated using the data in Table 7 for single-addition As(III)-removal tests. Figure 3a and Figure 3b show the RMg and RCa values for CAS0 = 1 and 10 mg/L with WAd/V = 0.2 g/L, respectively. Figure 3c and Figure 3d show the RMg and RCa values for CAS0 = 1 and 10 mg/L with WAd/V = 0.4 g/L, respectively. No clear difference was observed in the RMg and RCa values owing to CAS0; however, they were slightly higher when WAd/V was higher. The RMg values of MgO and Mg(OH)2 were similar, but that of MgCO3 was lower. The RCa value of CaCO3 was >90% under all conditions in this study, which was significantly higher than those of the other Ca-based adsorbents. Notably, the RCa value of Ca(OH)2 was the lowest.
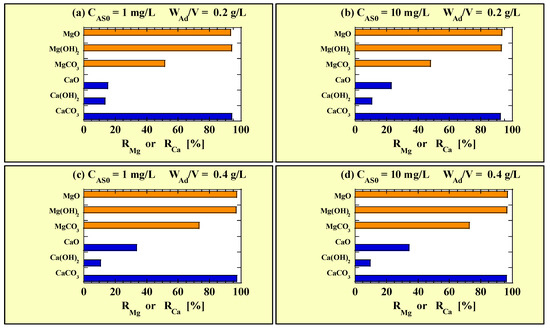
Figure 3.
RMg and RCa for the combined-addition tests at (a) CAS0 = 1 mg/L with WAd/V = 0.2 g/L; (b) CAS0 = 10 mg/L with WAd/V = 0.2 g/L; (c) CAS0 = 1 mg/L with WAd/V = 0.4 g/L; (d) CAS0 = 10 mg/L with WAd/V = 0.4 g/L. ■ RMg; ■ RCa.
3.2.2. Mg- and Ca-Residual Ratios for Combined Addition of Two Types of Adsorbents
The values of CMg and CCa for the combined-addition tests are presented in Table 8 and Table 9, respectively. Figure 4 shows the RMg values calculated using data in Table 8 for the combined-addition tests. Figure 4a and Figure 4b show the RMg values for CAS0 = 1 and 10 mg/L with ΣWAd/V = 0.4 g/L, respectively.

Table 8.
Values of CMg for the combined-addition tests.

Table 9.
Values of CCa for the combined-addition tests.
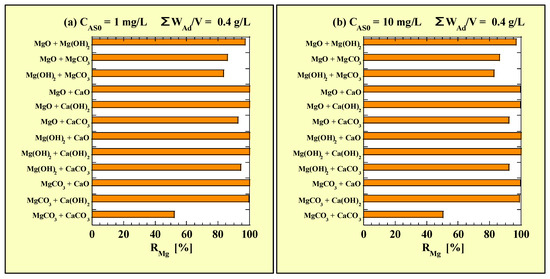
Figure 4.
RMg for the combined-addition tests at (a) CAS0 = 1 mg/L; (b) CAS0 = 10 mg/L.
As shown in Figure 4, no clear difference was observed in the RMg values between the combined- and single-addition tests owing to CAS0. For all the Mg-based adsorbents, RMg was close to 100% when they were combined with CaO or Ca(OH)2. The values of RMg when Mg-based adsorbents were combined with CaCO3 were similar to the values for the single-addition tests with WAd/V = 0.2 g/L, and MgCO3 + CaCO3 exhibited the lowest value (approximately 50%). Regarding only the Mg-based adsorbents, the RMg value was the highest for MgO + Mg(OH)2 (approximately 97%) and lowest for Mg(OH)2 + MgCO3 (approximately 83%).
Figure 5 shows the RCa values calculated using the data in Table 9 for the combined-addition As(III)-removal tests. Figure 5a and Figure 5b show the RCa values for CAS0 = 1 and 10 mg/L with ΣWAd/V = 0.4 g/L, respectively.
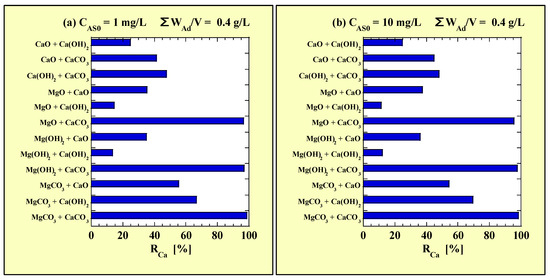
Figure 5.
RCa for the combined-addition tests at (a) CAS0 = 1 mg/L; (b) CAS0 = 10 mg/L.
As shown in Figure 5, no clear difference was observed in the RCa values between the combined- and single-addition tests due to CAS0. For all the Ca-based adsorbents, RCa tended to increase when combined with any Mg-based adsorbent. Particularly, for CaO and Ca(OH)2, the RCa value was significantly increased when they were combined with MgCO3 compared to their single additions (11–23% to 54–70%). Moreover, the RCa value of CaCO3 when combined with any Mg-based adsorbent was 95% (92–94% for the single addition of 0.2 g/L). Regarding only the Ca-based adsorbents, the RCa value was the highest for Ca(OH)2 + CaCO3 (approximately 48%) and lowest for CaO + Ca(OH)2 (approximately 25%).
3.3. pH of Treated Water
3.3.1. pH of Treated Water for Single Addition of One Type of Adsorbent
Figure 6 shows the pHf values for the single-addition As(III)-removal tests. Figure 6a and Figure 6b show the pHf values for CAS0 = 1 and 10 mg/L with WAd/V = 0.2 g/L, respectively. Figure 6c and Figure 6d show the pHf values for CAS0 = 1 and 10 mg/L with WAd/V = 0.4 g/L, respectively. The measured pH0 values for the single-addition tests at CAS0 = 1 and 10 mg/L were 7.27–7.41 and 6.80–7.38, respectively. Regardless of the adsorbent added, the pH shifted towards alkalinity. The pHf values under the test conditions were in the following order: CaCO3 < Mg(OH)2 < MgO, MgCO3 < CaO, Ca(OH)2. No clear effect of CAS0 on pHf was observed for any of the adsorbents. Additionally, for the Mg-based adsorbents and CaCO3, no clear effect on pHf was observed when WAd/V increased from 0.2 to 0.4 g/L. However, for CaO and Ca(OH)2, the pHf increased with increasing WAd/V.
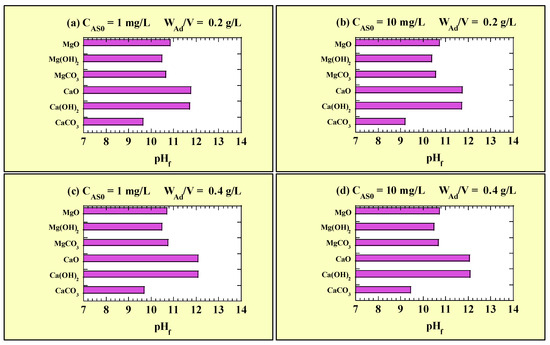
Figure 6.
pHf for the single-addition tests at (a) CAS0 = 1 mg/L with WAd/V = 0.2 g/L; (b) CAS0 = 10 mg/L with WAd/V = 0.2 g/L; (c) CAS0 = 1 mg/L with WAd/V = 0.4 g/L; (d) CAS0 = 10 mg/L with WAd/V = 0.4 g/L.
3.3.2. pH of Treated Water for Combined Addition of Two Types of Adsorbents
Figure 7 shows the pHf values for the combined-addition As(III)-removal tests. Figure 7a and Figure 7b show the pHf values for CAS0 = 1 and 10 mg/L with ΣWAd/V = 0.4 g/L, respectively. The measured values of pH0 for the combined-addition tests at CAS0 = 1 and 10 mg/L were 7.01–7.27 and 6.80–7.05, respectively. Similarly as with the single addition, the pH shifted to alkaline in the combined addition, and no clear difference in pHf was observed owing to CAS0. Among the combined additions, the pHf value was the highest in CaO + Ca(OH)2 and lowest in Mg(OH)2 + MgCO3. In the combined addition of Mg-based adsorbents with CaO or Ca(OH)2, the pHf was slightly lower than that in the single addition of CaO or Ca(OH)2. With the combined addition of CaCO3 with CaO or Ca(OH)2, the pHf value was similar to that with the single addition of CaO or Ca(OH)2. With the combined addition of Mg-based adsorbents and CaCO3, the pHf value was lower than the value for each addition of the Mg-based adsorbent.
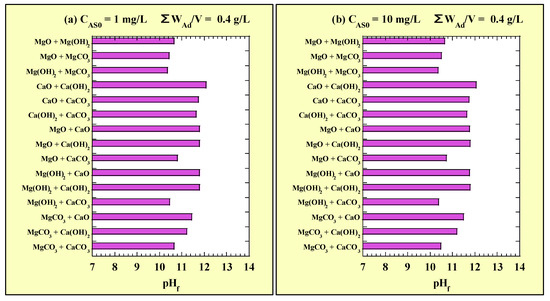
Figure 7.
pHf for the combined-addition tests at (a) CAS0 = 1 mg/L; (b) CAS0 = 10 mg/L.
3.4. XRD Patterns for MgCO3 + CaO, and MgCO3 + Ca(OH)2
The XRD patterns of the MgCO3 + CaO and MgCO3 + Ca(OH)2 mixtures are shown in Figure 8a and Figure 8b, respectively. The XRD patterns of the ‘solids collected after stirring MgCO3 + CaO in deionized water’ and ‘solids collected after stirring MgCO3 + Ca(OH)2 in deionized water’ are shown in Figure 8c and Figure 8d, respectively. The XRD patterns of the ‘solids collected after stirring MgCO3 + CaO in an As(III) solution’ and ‘solids collected after stirring MgCO3 + Ca(OH)2 in an As(III) solution’ are shown in Figure 8e and Figure 8f, respectively. The XRD patterns of the ‘solids collected after stirring MgCO3 + CaO in an As(V) solution’ and ‘solids collected after stirring MgCO3 + Ca(OH)2 in an As(V) solution’ are shown in Figure 8g and Figure 8h, respectively.
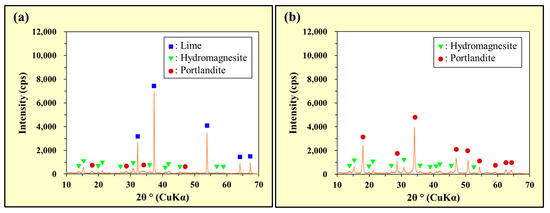
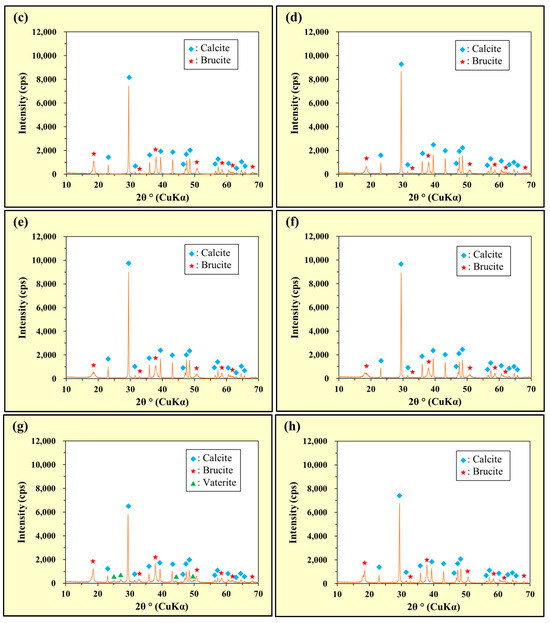
Figure 8.
Powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns: (a) MgCO3 + CaO, (b) MgCO3 + Ca(OH)2, (c) solids collected after stirring MgCO3 + CaO in deionized water, (d) solids collected after stirring MgCO3 + Ca(OH)2 in deionized water, (e) solids collected after stirring MgCO3 + CaO in the As(III) solution, (f) solids collected after stirring MgCO3 + Ca(OH)2 in the As(III) solution, (g) solids collected after stirring MgCO3 + CaO in the As(V) solution, and (h) solids collected after stirring MgCO3 + Ca(OH)2 in the As(V) solution.
As shown in Figure 8a, weak peaks of Ca(OH)2 (portlandite) were observed in addition to the peaks assigned to Mg5(CO3)4(OH)2·4H2O (hydromagnesite) and CaO (lime), corresponding to the composition of the reagents. Although no peak was attributable to Ca(OH)2 in the CaO reagent, XRD analysis of the CaO and MgCO3 mixture was performed approximately one day after preparation. We assumed that some of the CaO reacted with the moisture contained in the MgCO3 reagent to generate Ca(OH)2. Figure 8b shows only the peaks of Mg5(CO3)4(OH)2·4H2O (hydromagnesite) and Ca(OH)2 (portlandite), and Figure 8c–h show the peaks of Mg(OH)2 (brucite) and CaCO3 (primarily calcite, but traces of vaterite are also present in Figure 8g). Therefore, in deionized water and the As(III) solution, MgCO3 was transformed into Mg(OH)2, and CaO and Ca(OH)2 were transformed into CaCO3. Moreover, no peaks indicated the generation of arsenite and/or arsenate precipitates (Figure 8e–h). These results suggested that As(III) and As(V) in the solutions were not solidified and removed from the liquid phase as precipitates of arsenite and/or arsenate species, but were instead incorporated into the generated precipitates of Mg(OH)2 and/or CaCO3.
Table 10 shows the test conditions for preparing samples (e)–(h) for the XRD analysis and the pH and composition of the filtrate following solid–liquid separation and RAS. WMgCO3/V, WCaO/V, and WCa(OH)2/V in Table 10 were the additive concentrations of MgCO3, CaO, and Ca(OH)2, respectively.

Table 10.
Test conditions and pH and composition of the filtrate for XRD analysis.
For both As(III) and As(V) (Figure 8), the RAS value of the combined addition of MgCO3 with Ca(OH)2 was higher than that with CaO. In both the combined additions of MgCO3 with CaO and Ca(OH)2, the RAS value was higher for As(V) than for As(III).
3.5. Results of Mg(NO3)2-Addition Tests with Alkaline As Solutions
The XRD patterns of the precipitates collected during the tests are shown in Figure 9. In particular, Figure 9a and Figure 9b show the precipitates in the As(III) and As(V) solutions, respectively.
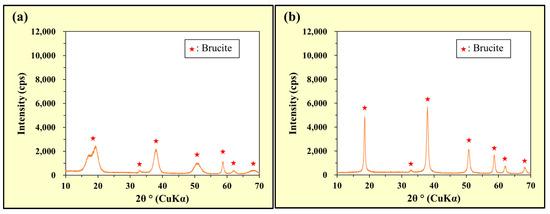
Figure 9.
Powder XRD patterns of the precipitates collected after stirring Mg(NO3)2 in the (a) As(III) and (b) As(V) solutions.
Although differences were attributed to fairly broad peaks (Figure 9a) and sharper peaks (Figure 9b), peaks indicating the generation of Mg(OH)2 (brucite) were observed in both Figure 9a,b. Therefore, Mg2+ was released by the dissolution of Mg(NO3)2 and combined with OH− to generate Mg(OH)2 in alkaline solutions.
The test conditions and results are listed in Table 11. WMg(NO3)2/V in the table is the additive concentration of Mg(NO3)2·6H2O in solution.

Table 11.
Values for Mg(NO3)2-addition tests with alkaline As solutions.
Although the RAS value for As(III) was lower than that for As(V), both RAS values exceeded 95%, indicating that As was effectively removed from the liquid phase. Combined with the XRD results, As(III) and As(V) were effectively incorporated into the generated precipitate of Mg(OH)2.
3.6. Results of Ca(NO3)2- and Na2CO3-Addition Tests with Alkaline As Solutions
The XRD patterns of the precipitates collected during the tests are shown in Figure 10. In particular, Figure 10a and Figure 10b show the precipitates in the As(III) and As(V) solutions, respectively.
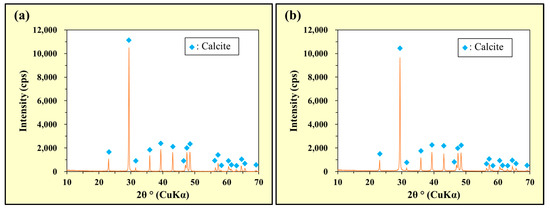
Figure 10.
Powder XRD patterns of the precipitates collected after stirring Ca(NO3)2 and Na2CO3 in the (a) As(III) and (b) As(V) solutions.
In both Figure 10a,b, strong peaks indicating the generation of CaCO3 (calcite) were observed. These results confirmed that the Ca2+ released by the dissolution of Ca(NO3)2 combined with CO32− released by the dissolution of Na2CO3 to generate CaCO3 in the alkaline solutions.
The test conditions and results are listed in Table 12. WCa(NO3)2/V and WNa2CO3/V in Table 12 are the additive concentrations of Ca(NO3)2·4H2O and Na2CO3, respectively.

Table 12.
Values for Ca(NO3)2- and Na2CO3-addition tests with alkaline As solutions.
The RAS value for As(V) was high (approximately 89%), while that for As(III) was only 0.3%, indicating that As(III) was minimally removed. Combined with the XRD results, the amount of As incorporated into the generated precipitate of CaCO3 depended on the As valence, with As(V) being more readily incorporated than As(III).
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Combined Addition
4.1.1. Effects of Combined Addition on As-Removal Performance
When multiple adsorbents are combined, the RAS value is typically unequal to the sum of the individual adsorbent RAS values. This apparent combined-adsorbent synergistic effect was evaluated using a method similar to that used in a previous study [17]. The highest of the two single-addition RAS values for each adsorbent in the combined-addition test was subtracted from the RAS value in the combined-addition test. The obtained difference was denoted as ΔRAS.
Each ΔRAS value of the combined additions is shown in Figure 11. Figure 11a and Figure 11b correspond to CAS0 = 1 and 10 mg/L, respectively, and the results from the single-addition tests with WAd/V = 0.4 g/L are included.
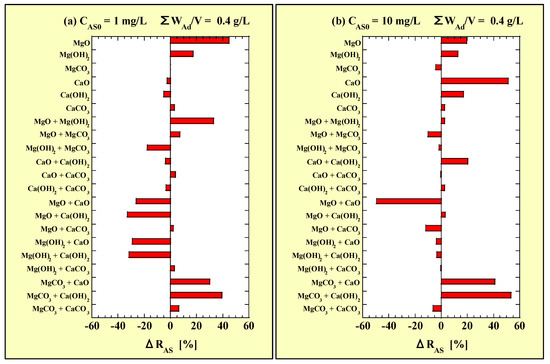
Figure 11.
ΔRAS for the combined-addition tests at (a) CAS0 = 1 mg/L and (b) CAS0 = 10 mg/L.
Figure 11 shows that the ΔRAS value significantly varied with adsorbent combination and CAS0. At CAS0 = 1 mg/L, the ΔRAS values for the MgO single addition and MgO + Mg(OH)2, MgCO3 + CaO, and MgCO3 + Ca(OH)2 combined additions were positive. However, the ΔRAS value for the combined addition of MgO or Mg(OH)2 with CaO or Ca(OH)2 was negative. At CAS0 = 10 mg/L, the ΔRAS values for the CaO single addition and MgCO3 + CaO, and MgCO3 + Ca(OH)2 combined additions were positive. Moreover, the ΔRAS value for the combined addition of MgO with CaO was negative. Therefore, from the viewpoint of ΔRAS, when ΣWAd/V increased from 0.2 to 0.4 g/L, the MgO single addition at CAS0 = 1 mg/L and CaO single addition at CAS0 = 10 mg/L exhibited the most improved As(III)-removal performances. However, both MgCO3 + CaO and MgCO3 + Ca(OH)2 had extremely high ΔRAS values at both CAS0 = 1 and 10 g/L, indicating that combined addition had an extremely high synergistic effect on the removal performance of As(III). This result was similar to that for As(V) reported in a previous study [22].
4.1.2. Effects of Combined Addition on Mg- and Ca-Leaching Behaviors
Even if the Mg or Ca residual ratio was the same, the leached amount of Mg or Ca differed depending on the type of Mg- or Ca-based adsorbent used. Therefore, to evaluate the effects of combined addition on Mg- or Ca-leaching behavior, we compared the amount of change in CMg or CCa. Thus, the higher CMg or CCa value in the single-addition test (WAd/V = 0.2 g/L) of the two types of adsorbents used in the combined-addition test (ΣWAd/V = 0.4 g/L) was subtracted from the CMg or CCa value in the combined-addition test. The obtained difference was denoted as ΔCMg or ΔCCa. The lower the value of ΔCMg or ΔCCa, the higher the effects of inhibiting Mg- or Ca-leaching.
Each ΔCMg value of the combined additions is shown in Figure 12. Figure 12a and Figure 12b correspond to CAS0 = 1 and 10 mg/L, respectively. Similarly to the ΔCMg value, each ΔCCa value of the combined additions is shown in Figure 13. Figure 13a and Figure 13b correspond to CAS0 = 1 and 10 mg/L, respectively.
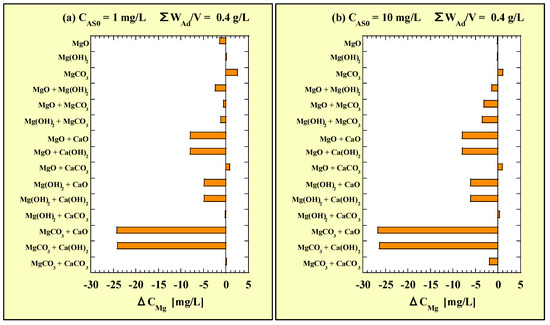
Figure 12.
ΔCMg for the combined-addition tests at (a) CAS0 = 1 mg/L and (b) CAS0 = 10 mg/L.
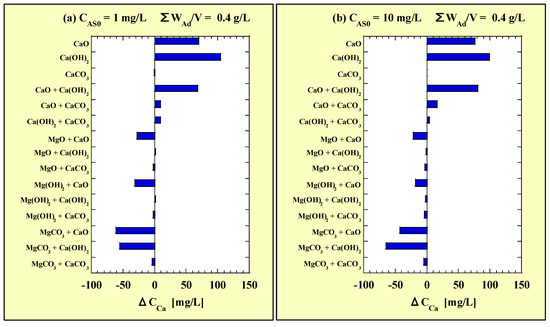
Figure 13.
ΔCCa for the combined-addition tests at (a) CAS0 = 1 mg/L and (b) CAS0 = 10 mg/L.
Unlike ΔRAS, no clear influence of CAS0 was observed for ΔCMg or ΔCCa. In both the combined addition among the Mg-based adsorbents and with CaCO3, the ΔCMg value was within ±5 mg/L. In the combined addition of any one of the Mg-based adsorbents with CaO or Ca(OH)2, the ΔCMg value was a large negative. Therefore, the combined addition of CaO or Ca(OH)2 inhibited the leaching of Mg from Mg-based adsorbents. Although no clear difference was observed between CaO and Ca(OH)2 in the Mg-leaching inhibition effects, the order was as follows: MgCO3 > MgO > Mg(OH)2.
In the combined addition among Ca-based adsorbents, except CaCO3, the ΔCCa values were large positive values. The amount of Ca leaching from CaCO3 was originally low, and the ΔCCa value was −5 to 16 mg/L even in the combined addition of CaCO3 with other Ca-based adsorbents. Minimal effects on the Ca-leaching behavior from other Ca-based adsorbents were observed. Conversely, in the combined addition of CaO with any one of the Mg-based adsorbents, the ΔCCa value was significantly negative. Additionally, for Ca(OH)2, the ΔCCa value was significantly negative only in the combined addition with MgCO3. Thus, MgCO3 exerted Ca-leaching inhibitory effects on both CaO and Ca(OH)2.
4.2. As-Removal Mechanisms in the Combined Additions of MgCO3 + CaO and MgCO3 + Ca(OH)2
4.2.1. Incorporation of As into the Generated Precipitates of Mg(OH)2 + CaCO3
Table 13 shows the various estimated values relating to the solid samples collected from the As solutions with added MgCO3 + CaO and MgCO3 + Ca(OH)2, which were obtained using the data in Table 10.

Table 13.
Estimated values related to the solid samples collected from the As solutions with added MgCO3 + CaO and MgCO3 + Ca(OH)2.
WR-Mg(OH)2/V or WR-CaCO3/V in Table 13 is the concentration of solid Mg(OH)2 or CaCO3, respectively, in solution, assuming that all the Mg and Ca remaining in the solid state in the solution was in the form of Mg(OH)2 or CaCO3. In addition, when calculating WR-Mg(OH)2 and WR-CaCO3 from RMg and RCa, the molecular weights of Mg(OH)2 and CaCO3 were 58.3 and 100.1, respectively.
Furthermore, the QAS value in Table 13 was calculated using the following equation:
QAS = (CAS0 − CAS)/(WR-Mg(OH)2/V + WR-CaCO3/V).
As shown in Table 11, the QAS value was higher in MgCO3 + Ca(OH)2 than in MgCO3 + CaO and higher in As(V) than in As(III). Therefore, the condition for obtaining the highest As-removal efficiency was applying the combined addition of MgCO3 + Ca(OH)2 to As(V).
4.2.2. Incorporation of As into the Generated Precipitate of Mg(OH)2
Table 14 shows several estimated values relating to the precipitates collected from the alkaline As solutions with added Mg(NO3)2·6H2O, which were obtained using the data in Table 11.

Table 14.
Values of RMg, WR-Mg(OH)2/V, and QAS for Mg(NO3)2-addition tests with alkaline As solutions.
The RMg and WR-Mg(OH)2/V values were calculated assuming that the molecular weight of Mg(NO3)2·6H2O was 256.4 and the reagent purity was 100%. However, as described in Section 2.5.1, the actual reagent purity was <100% because Mg(NO3)2·6H2O is a deliquescent substance.
The As-removal mechanism in the tests with Mg(NO3)2 was coprecipitation accompanied by the generation of Mg(OH)2. The QAS values for both As(III) and As(V) were high, as shown in Table 14. The As-removal efficiency was essentially similar because the difference in QAS between As(III) and As(V) was not significantly large. Therefore, As incorporation occurred with the generation of Mg(OH)2 and was independent of the As valence.
4.2.3. Incorporation of As into the Generated Precipitate of CaCO3
Table 15 shows several estimated values relating to the precipitates collected from the alkaline As solutions with added Ca(NO3)2·4H2O, which were obtained using the data in Table 12.

Table 15.
Values of RCa, WR-CaCO3/V, and QAS for Ca(NO3)2 and Na2CO3-addition tests with alkaline As solutions.
The RCa and WR-CaCO3 values were calculated assuming the molecular weight of Ca(NO3)2·4H2O was 236.2 and the reagent purity was 100%. However, as described in Section 2.5.2, the actual reagent purity was <100% because Ca(NO3)2·4H2O is a deliquescent substance.
The As-removal mechanism in the combined-addition tests with Ca(NO3)2 and Na2CO3 was coprecipitation accompanied by the generation of CaCO3. The QAS value for As(III) was 0.04 mg/g, indicating that almost no As(III) was removed. The QAS of As(V) was approximately 7.8 mg/g, demonstrating that As(V) was removed by the generation of CaCO3. Therefore, the incorporation of As by the generated CaCO3 depended on the valence state of As.
Scanning electron microscope (SEM) image observation and elemental mapping by an EDS system for As adsorption on Mg- and Ca-based adsorbents have been carried out by other researchers [23,24]. Lin et al. (2023) studied As(V) removal using a monodispersed porous pinecone-like Mg(OH)2, and reported that As was abundantly and uniformly distributed in the adsorption products by an elemental As mapping diagram [23]. Meanwhile, Lee et al. (2024) studied As(V) removal using a wood bottom ash containing CaCO3 and Ca(OH)2 as main components [24]. Their elemental As mapping diagram also showed that As is uniformly adsorbed on the surface of the Ca-based adsorbent. From these results, it is considered that As is essentially uniformly adsorbed on the surface of the Mg- and Ca-based adsorbents used in this study, while, in the combined additions of MgCO3-CaO or MgCO3-Ca(OH)2, As may be concentrated in the generated Mg(OH)2 and CaCO3. Therefore, future tasks for this research include additional research such as SEM observation and elemental mapping with EDS.
4.3. Comprehensive Evaluation
The maximum As(III)-adsorption capacities of the three new adsorbents introduced in the Introduction section were 64 mg/g on ZrO2-AC, 6.8 mg/g on CW@MPTMS@poly(AA-co-VyAc)@PABA, and 55 mg/g on B-Mn-Al [11,12,13]. The adsorption mechanism of As(III) was mainly physical adsorption for CW@MPTMS@poly(AA-co-VyAc)@PABA, and essentially chemical adsorption for ZrO2-AC and B-Mn-Al [11,12,13]. A comparison of their maximum adsorption capacities would suggest that chemisorption is more advantageous for As(III) removal than physical adsorption. In this study, the maximum adsorption capacity for each combination of the Mg- and Ca-based adsorbents is unknown because there are not enough data to calculate the maximum adsorption amount from the Langmuir model. However, the Mg- and Ca-based adsorbents are also considered to have high adsorption capacities because their adsorption mechanism for As(III) is also chemical adsorption. Additionally, the Mg(NO3)2-addition tests showed that the combined addition of MgCO3-(OH)2 or MgCO3-CaO could generate Mg(OH)2 with high As(III) adsorption capacity (<30 mg/g). From the above, the combined addition of MgCO3-Ca(OH)2 or MgCO3-CaO is expected to be a valuable As(III)-removal method.
From the perspective of RAS, the most effective strategy for As(III) removal was the single addition of MgO or the combined addition of MgO with Mg(OH)2. Notably, the addition of MgCO3 or Ca-based adsorbents alone did not remove As(III); however, the combined addition of MgCO3 with CaO or Ca(OH)2 improved As(III)-removal performance. The single addition of 0.2 g/L CaO minimally removed As(III); however, that of 0.4 g/L CaO increased the RAS value. Thus, MgCO3, CaO, or Ca(OH)2 may be selected as less expensive adsorbents when the cost of MgO is higher than that of other adsorbents. Moreover, the combined addition of MgCO3 with CaO or Ca(OH)2 significantly inhibited the leaching of Mg and Ca, which are components of the base material.
The combined addition of MgCO3 with either CaO or Ca(OH)2 did not remove As(III) to the same extent as As(V). As described in Section 4.2.2 and Section 4.2.3, the Mg(OH)2 generated in these combined additions incorporated both As(V) and As(III). Conversely, CaCO3 incorporated As(V) but minimally incorporated As(III). Therefore, introducing a step for oxidizing As(III) to As(V) before applying the combined additions might be an effective strategy. A previous study [25] reported that adsorbed As(III) was more likely to re-leach than As(V). Therefore, As oxidation treatment is recommended to prevent secondary contamination due to the re-leaching of As from spent adsorbents.
When treating As in industrial wastewater, which has a more diverse composition of dissolved components than groundwater, it is extremely useful to have numerous options to propose appropriate adsorbent types and application methods that consider the characteristics of the wastewater.
5. Conclusions
In a previous study [22], the combined addition of Mg- and Ca-based adsorbents was investigated to improve As(V)-removal performance and inhibit the leaching of the base material components from the adsorbents (i.e., improving the environmental stability of the adsorbents). In this study, systematic tests for As(III) removal via the combined addition of Mg- and Ca-based adsorbents were conducted based on the above As(V) study. Additionally, X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis was carried out to verify the generation of Mg(OH)2 and CaCO3 in the combined addition test of MgCO3-CaO or MgCO3-Ca(OH)2 that was inferred in a previous study [22]. The solid samples for XRD analysis were prepared in the absence of As, in the presence of As(V) or As(III). Furthermore, to verify the incorporation of As into the produced Mg(OH)2 or CaCO3, Mg(NO3)-addition tests and Ca(NO3)2- and Na2CO3-addition tests were performed using alkaline As(III) and As(V) solutions.
As a result of the single- and combined-addition tests for As(III) removal, the RAS value was the highest for the single addition of MgO and the combined addition of MgO with Mg(OH)2. From the viewpoint of improving the RAS value and inhibiting the leaching of the base material components, the most significant synergistic effect was observed for MgCO3 + CaO and MgCO3 + Ca(OH)2. Notably, these two combined-addition methods achieved the highest RAS values in a previous study for As(V) removal [22]. Following As adsorption, the XRD analysis of the solid samples obtained from these two combined-addition tests confirmed that Mg(OH)2 and CaCO3 were produced. Subsequently, the results of the As-removal tests in which Mg(NO3)2·6H2O was added to an alkaline solution containing As(III) or As(V) demonstrated that As was removed from the liquid phase via incorporation by the generated Mg(OH)2, regardless of the As valence state. Moreover, the addition of both Ca(NO3)2·4H2O and Na2CO3 demonstrated that As(V) was incorporated during the generation of CaCO3; however, As(III) was not incorporated and remained in the solution.
These investigations elucidated the As-removal mechanism expressed by the combined addition of MgCO3 + CaO and MgCO3 + Ca(OH)2. As(V) was removed via incorporation into both Mg(OH)2 and CaCO3, whereas As(III) was removed from the liquid phase via incorporation into only Mg(OH)2. Moreover, MgCO3 + Ca(OH)2 was evaluated as a more efficient combined-addition method because MgCO3 + Ca(OH)2 exhibited a higher QAS value than MgO + CaO. The RAS value of As(III) was inferior to that of As(V) owing to the differences in the As-removal mechanisms. Therefore, it is recommended to convert As(III) to As(V) via oxidation before applying the combined-addition method.
Processing techniques such as doping and synthesis of various components on activated carbons and concrete wastes are complex and relatively expensive [11,12]. Fe-based adsorbents are also relatively expensive [18]. Additionally, adsorbents doped with heavy metal or transition elements such as Mn or cobalt have problems with their leaching [13,26], which may lead to health risks. Meanwhile, the only components that may leach from Mg- and Ca-based adsorbents are Mg and Ca components, which are harmless to humans and animals. Both Mg-based and Ca-based adsorbents are common and easily available, and they have the major advantages of having high As adsorption efficiency and almost no risk of components leaching from the base material causing adverse effects on human health or the ecosystem. As one measure against As contamination, widespread use of adsorbents based on Mg and Ca components, which are abundant on Earth and do not pose environmental pollution problems, could make a great contribution to a sustainable society.
This study reconfirmed the effectiveness of the combined addition of MgCO3-Ca(OH)2 or MgCO3-CaO for As removal. To increase the As-removal efficiency by this combined addition, it is considered necessary to investigate the optimal combined addition ratio. Additionally, it may be possible to promote the As-incorporation reaction by adjusting the pH appropriately. In the future, it is expected that this research will be further developed by focusing on these issues.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.S.; methodology, H.S., T.S. and J.H.; formal analysis, H.S. and K.M.; investigation, H.S. and K.M.; resources, H.S., K.M. and J.H.; data curation, H.S. and K.M.; writing—original draft preparation, H.S. and K.M.; writing—review and editing, H.S., K.M., T.S. and J.H.; supervision, J.H.; project administration, H.S.; funding acquisition, J.H., T.S. and H.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data supporting the findings of this study are available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We are deeply grateful to Terumi Oguma for her assistance with the experiments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Kobya, M.; Soltani, R.D.C.; Omwene, P.I.; Khataee, A. A review on decontamination of arsenic-contained water by electrocoagulation: Reactor configurations and operating cost along with removal mechanisms. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 17, 100519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abiye, T.A.; Bhattavharya, P. Arsenic concentration in groundwater Archetypal study from South Africa. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 9, 100246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Ng, J.C.; Naidu, R. Chronic exposure of arsenic via drinking water and its adverse health impacts on humans. Environ. Geochem. Health 2009, 31, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The World Health Organization (WHO). Arsenic. In Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th ed.; The World Health Organization: Tarxien, Malta, 2011; pp. 315–318. ISBN 9789241548151. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/44584/9789241548151_eng.pdf (accessed on 3 December 2024).
- Ministry of the Environment, Government of Japan. Environmental Quality Standards for Human Health. Available online: https://www.env.go.jp/en/water/wq/wp.pdf (accessed on 7 January 2025).
- Ministry of the Environment, Government of Japan. National Effluent Standards. Available online: https://www.env.go.jp/en/water/wq/nes.html (accessed on 7 January 2025).
- Jadhav, S.V.; Bringas, E.; Yadav, G.D.; Rathod, V.K.; Ortiz, I.; Marathe, K.V. Arsenic and fluoride contaminated groundwaters: A review of current technologies for contaminants removal. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 162, 306–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Paul, B. The global menace of arsenic and its conventional remediation-A critical review. Chemosphere 2016, 158, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Debsarkar, A.; Dutta, A. Technology alter-natives for decontamination of arsenic-rich groundwater—A critical review. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2019, 13, 277–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Patel, M.; Singh, P.; Bundschuh, J.; Pittman, C.U., Jr.; Trakal, L.; Mohan, D. Emerging technologies for arsenic removal from drinking water in rural and peri-urban areas: Methods, experience from, and options for Latin America. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 694, 133427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuc, P.N.; Bac, N.Q.; Thao, D.T.P.; Kien, N.T.; Chi, N.T.H.; Noi, N.V.; Nguyen, V.T.; Bich, N.T.H.; Nhiem, D.N.; Khieu, D.Q. Highly efficient adsorption of arsenite from aqueous by zirconia modified activated carbon. Environ. Eng. Res. 2024, 29, 230076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadegari, M.; Panahi, H.A.; Rahmati, S.H.; Mohammadi, A.; Imani, F. Poly(allyl alcohol-co-vinyl acetate)-grafted concrete waste for adsorptive removal of As(III). Mater. Chem. Phys. 2024, 326, 129826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, T.R.; Sajib, M.S.H.; Sowrav, S.F.F.; Khan, S.R.; Alam, M.N.E.; Amin, M.N. Nanostructured bi-metallic biochar: An innovative approach for arsenic (III) removal from contaminated water. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2025, 7, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.Y.; Tran, T.; Lee, Y.H.; Nam, Y.I., II; Senanayake, G.; Kim, M.J. Selective removal of arsenic(V) from a molybdate plant liquor by precipitation of magnesium arsenate. Hydrometallurgy 2010, 104, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tresintsi, S.; Simeonidis, K.; Katsikini, M.; Paloura, E.C.; Bantsis, G.; Mitrakas, M. A novel approach for arsenic adsorbents regeneration using MgO. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 265, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.Y.; Luo, T.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, Y.X.; Liu, J.H.; Huang, X.J. Porous hierarchically micro-/nanostructured MgO: Morphology control and their excellent performance in As(III) and As(V) removal. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 22242–22250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opiso, E.M.; Sato, T.; Morimoto, K.; Asai, A.; Anraku, S.; Numako, C.; Yoneda, T. Incorporation of arsenic during the formation of Mg-bearing minerals at alkaline condition. Miner. Eng. 2010, 23, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, J.; Wee, H.Y.; Kramer, T.A.; Autenrieth, R. Arsenic stabilization on water treatment residuals by calcium addition. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 165, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes-Hernandez, G.; Concha-Lozano, N.; Renard, F.; Quirico, E. Removal of oxyanions from synthetic wastewater via carbonation process of calcium hydroxide: Applied and fundamental aspects. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 788–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olyaie, E.; Banejad, H.; Afkhami, A.; Rahmani, A.; Khodaveisi, J. Development of a cost-effective technique to remove the arsenic contamination from aqueous solutions by calcium peroxide nanoparticles. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 95, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.-Y.; Lo, S.-L.; Kuan, W.-H. High concentration of arsenate removal by electrocoagulation with calcium. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 126, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugita, H.; Oguma, T.; Hara, J.; Zhang, M.; Kawabe, Y. Removal of arsenate from contaminated water via combined addition of magnesium-based and calcium-based adsorbent. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Chen, W.; Lin, F.; Zhu, H.; Wang, X. Exaggerated arsenic removal efficiency and pH adaptability by adsorption using monodispersed porous pinecone-like magnesium hydroxide. AQUA 2023, 72, 969–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-U.; Jeong, Y.; Lee, Y.-J.; Lee, C.-G.; Park, S.-J. Harnessing wood bottom ash for efficient arsenic removal from wastewater: Adsorption mechanisms and process optimization. Chemosphere 2024, 364, 143204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugita, H.; Morimoto, K.; Saito, T.; Hara, J. Effects of soils on environmental stability of spent Mg-based and Ca-based adsorbents containing arsenite. Sustainability 2024, 15, 4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, H.; Wu, Z.; Post, J.E.; Lanson, B.; Liu, Y.; Hu, B.; Wang, M.; Zhang, L.; Hong, M.; et al. Effects of cobalt doping on the reactivity of hausmannite for As(III) oxidation and As(V) adsorption. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 122, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).