The Effect of Intelligent Development on Green Economy Efficiency: An Analysis Based on China’s Province-Level Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Hypothesis
2.1. Nonlinear Impact of Intelligent Development on Green Economy Efficiency
2.2. The Moderation Effect of Environmental Regulation, Green Finance, and Industrial Agglomeration
3. Model Construction and Variable Selection
3.1. Model Construction
3.2. Variable Selection
3.2.1. Dependent Variable
3.2.2. Explanatory Variable
3.2.3. Moderating Variables
3.2.4. Control Variables
3.3. Sample Selection and Data Source
4. Results
4.1. Baseline Regression Results
4.2. Robustness Test
4.3. Moderation Tests
4.4. Heterogeneity Tests
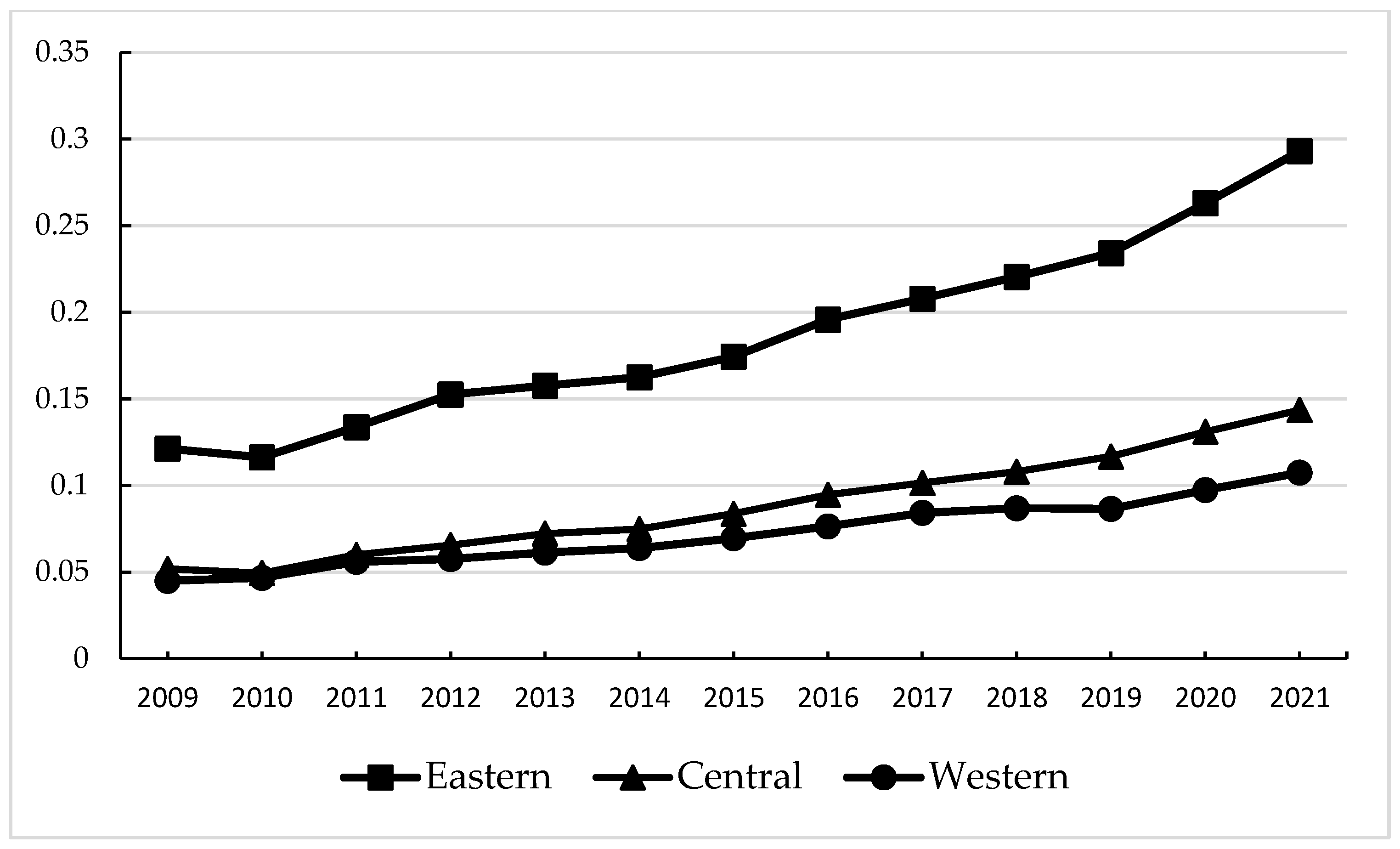
4.4.1. Regional Heterogeneity Tests
4.4.2. Temporal Heterogeneity Tests
5. Conclusions and Policy Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, L.D.; Xu, E.L.; Li, L. Industry 4.0: State of the Art and Future Trends. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2018, 56, 2941–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Mai, S. Big data development and enterprise green innovation: Text analysis of listed companies’ annual reports. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2024, 96, 103703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Liu, Q. Driving Green Innovation Through Digital Transformation: Empirical Insights on Regional Variations. Sustainability 2024, 16, 10716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, S.; Fan, Z. Modeling the role of environmental regulations in regional green economy efficiency of China: Empirical evidence from super efficiency DEA-Tobit model. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 261, 110227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Bo, N.; Wang, X. Can greater openness improve green economy efficiency of countries along the Belt and Road Initiative? Heliyon 2024, 10, e26684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Sun, Z. Influence mechanisms of financial and manufacturing co-agglomeration on green economy efficiency from multiple perspectives. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 471, 143371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yajie, L.; Feng, D. How technological innovation impacts urban green economy efficiency in emerging economies: A case study of 278 Chinese cities. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 169, 105534. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhu, H. The Impact of Industrial Intelligence on Carbon Emissions: Evidence from the Three Largest Economies. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Chen, Q.; Qin, X.; Zhang, X. Study on the influence of industrial intelligence on carbon emission efficiency–an empirical analysis of China’s Yangtze River Economic Belt. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 82248–82263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X. Quantifying the Impact of Intelligence on Energy Efficiency in China. E3S Web Conf. 2023, 369, 02004. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, C.; Zang, C.; Wu, A.; Long, H.; Yu, C.; Liu, Y. Assessing the impact of industrial intelligence on urban carbon emission performance: Evidence from China. Heliyon 2024, 10, e30144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatima, T.; Li, B.; Malik, S.A.; Zhang, D. The Spatial Effect of Industrial Intelligence on High-Quality Green Development of Industry under Environmental Regulations and Low Carbon Intensity. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Wang, G.; Han, X. Impacts of artificial intelligence on carbon emissions in China: In terms of artificial intelligence type and regional differences. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 113, 105682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Xu, J. Can urban digital intelligence transformation promote corporate green innovation? Evidence from China. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 371, 123245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, H. Green entrepreneurship success in the age of generative artificial intelligence: The interplay of technology adoption, knowledge management, and government support. Technol. Soc. 2024, 79, 102744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yang, C.; Ge, W.; Liu, G.; Yang, X.; Ran, Q. Can industrial intelligence promote green transformation? New insights from heavily polluting listed enterprises in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 421, 138550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yining, Z.; Zhong, W. Intelligence and Green Total Factor Productivity Based on China’s Province-Level Manufacturing Data. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ling, J. The Impact of Manufacturing Intelligence on Green Development Efficiency: A Study Based on Chinese Data. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Qingjiang, H.; Shui, Y. Sustainable manufacturing intelligence: Pathways for high-quality and energy-efficient economic growth. Econ. Change Restruct. 2024, 57, 100. [Google Scholar]
- Siying, Y.; Fengshuo, L. Impact of industrial intelligence on green total factor productivity: The indispensability of the environmental system. Ecol. Econ. 2024, 216, 108021. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.R.; Wang, L.K.; Miao, Z. The impact of digital technology innovation on green total-factor energy efficiency in China: Does economic development matter? Energy Policy 2024, 194, 114342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Kamal, F. The Impact of Information and Communication Technology Adoption on Multinational Firm Boundary Decisions. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2016, 47, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuntia, J.T.; Saldanha, S.; Mithas, V. Sambamurthy. Information Technology and Sustainability: Evidence from an Emerging Economy. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2018, 27, 756–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luyao, Z. Analysis of Computer-Based Blockchain Technology in Cross-Border E-commerce Platforms. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2022, 2022, 5083518. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, R.; Li, Q. The impact of IT change on corporate environmental violations: Toward information asymmetry and stakeholder theory. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 371, 123240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.N.; Moaniba, I.M. Does innovation respond to climate change? Empirical evidence from patents and greenhouse gas emissions. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2017, 122, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gollop, F.M.; Roberts, M.J. Environmental regulations and productivity growth: The case of fossil-fueled electric power generation. J. Political Econ. 1983, 91, 654–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, M.E.; Linde, C.V.D. Towards a New Conception of the Environment-Competitiveness Relationship. J. Econ. Perspect. 1995, 4, 97–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Huang, Z.; Fan, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, R.; Song, M. The impact of environmental regulation on regional economic growth: A case study of the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0290607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Teng, Y.-P.; Wu, S.; Chen, H. Does Green Finance Expand China’s Green Development Space? Evidence from the Ecological Environment Improvement Perspective. Systems 2023, 11, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z. Green Finance and Sustainability; Business Science Reference: Hershey, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz, J.L. Financial development, institutional investors, and economic growth. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2018, 54, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y. How does agglomeration promote the product in-novation of Chinese firms? China Econ. Rev. 2015, 35, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccone, A.; Hall, R.E. Productivity and the Density of Economic Activity. Am. Econ. Rev. 1996, 86, 54–70. [Google Scholar]
- Tone, K. Dealing with Undesirable Outputs in DEA: A Slacks-Based Measure (SBM) Approach; North American Productivity Workshop: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2004; pp. 44–45. [Google Scholar]
- Barnhart, S.W.; Miller, E.M. Problems in the estimation of equations containing perpetual inventory measured capital. J. Macroecon. 1990, 12, 637–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Hou, Y. How does the industrial intelligence reshape the employment structure of the labor force. Ind. Econ. China 2019, 374, 61–79. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Li, L.S.; Liu, J.; Cheng, Z.H. Intelligent development and the transformation of economic development mode, Theoretical mechanism and empirical evidence. Econ. Rev. 2020, 2, 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Cao, J. Enhancing Green Total Factor Productivity through Corporate Social Responsibility: The Moderating Effect of Environmental Regulations. Financ. Res. Lett. 2024, 71, 106466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Yang, G.; Chen, T. The role of green finance and digital inclusive finance in promoting economic sustainable development: A perspective from new quality productivity. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lei, L. How does industrial agglomeration affect internal structures of green economy in China? An analysis based on a three-hierarchy meta-frontier DEA and systematic GMM approach. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2024, 206, 123560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haans, R.F.J.; Pieters, C.; He, Z.L. Thinking about U: Theorizing and testing U- and inverted U-shaped relationships in strategy research. Strateg. Manag. J. 2016, 37, 1177–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baihe, Z. Industrial Maintenance Service Quality Evaluation and Improvement Strategies: A Case Study of a Corporation. Ph.D. Thesis, ISCTE—Instituto Universitario de Lisboa, Lisboa, Portugal, 2021; p. 31195541. [Google Scholar]

| Primary Indicator | Secondary Indicator | Specific Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| Fundamental investment | Fund investment | R&D expenditure of high-tech industries/R&D expenditure of all enterprises |
| Talent investment | Number of high-tech industry employees/number of employees | |
| Number of scientific and technical employees/number of employees | ||
| Facility investment | Number of R&D institutions in high-tech industries | |
| Length of long-distance optical cable lines/regional area | ||
| Number of Internet Broadband Access Ports | ||
| Technology application | Knowledge innovation | Number of invention patent applications |
| Number of scientific papers published | ||
| Material innovation | Number of R&D projects in high-tech industries | |
| Number of new product development projects | ||
| Market efficiency | Enterprise income | Total profits of high-tech industry/number of high-tech enterprises |
| Primary business income of high-tech industry/number of high-tech industry employees | ||
| New product sales revenue of high-tech industry/number of high-tech industry employees | ||
| Capital operation | R&D investment intensity |
| Types of Variables | Variables | Obs | Mean | St. Dev | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent variable | Gee | 390 | 0.6549 | 0.1406 | 0.5005 | 1 |
| Explanatory variable | IT | 390 | 0.1187 | 0.0929 | 0.0154 | 0.7136 |
| Moderating variables | ENV | 390 | 0.1213 | 0.1260 | 0.0009 | 1.1034 |
| GFIN | 390 | 0.3496 | 0.1419 | 0.0745 | 0.7086 | |
| IAGG | 390 | 0.2575 | 0.3750 | 0.0039 | 2.1707 | |
| Control variables | FIN | 390 | 0.9824 | 0.4605 | 0.2584 | 3.0265 |
| IND | 390 | 1.2757 | 0.7202 | 0.5271 | 5.2440 | |
| GOV | 390 | 0.2541 | 0.1119 | 0.1050 | 0.7583 | |
| INFOR | 390 | 0.0632 | 0.0517 | 0.0143 | 0.2896 | |
| GREEN | 390 | 0.0121 | 0.0323 | 0.0001 | 0.2213 | |
| FIND | 390 | 0.0196 | 0.0156 | 0.0001 | 0.0819 |
| Variable | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IT | −0.925 *** | −0.853 *** | −0.682 *** | −0.704 *** |
| (−4.18) | (−3.81) | (−3.12) | (−3.26) | |
| IT2 | 1.289 *** | 1.155 *** | 1.208 *** | 1.265 *** |
| (4.92) | (4.67) | (4.74) | (5.00) | |
| FIN | 0.034 *** | 0.037 *** | 0.029 *** | |
| (3.28) | (3.60) | (2.66) | ||
| IND | 0.003 | 0.017 | 0.028 * | |
| (0.19) | (1.09) | (1.76) | ||
| GOV | −0.210 *** | −0.203 *** | ||
| (−3.77) | (−3.66) | |||
| INFOR | 0.414 *** | 0.358 *** | ||
| (3.06) | (2.76) | |||
| GREEN | 0.309 * | |||
| (1.67) | ||||
| FIND | 0.744 *** | |||
| (2.76) | ||||
| Constant | 0.693 *** | 0.585 *** | 0.489 *** | 0.422 *** |
| (17.24) | (6.54) | (5.23) | (4.46) | |
| Observations | 390 | 390 | 390 | 390 |
| Variables | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| One-Year Lagged Explanatory Variables | Change Model | Recalculate Explanatory Variables | Winsorization of Samples | Substitute Control Variables | |
| IT | −0.654 *** | −0.139 * | −0.599 ** | −0.863 *** | |
| (−3.08) | (−1.90) | (−2.25) | (−3.95) | ||
| IT2 | 1.164 *** | 0.415 ** | 1.108 ** | 1.430 *** | |
| (4.82) | (2.15) | (2.52) | (5.64) | ||
| L.IT | −0.826 *** | ||||
| (−3.18) | |||||
| L.IT2 | 1.663 *** | ||||
| (4.89) | |||||
| Constant | 0.452 *** | 0.647 *** | 0.244 *** | 0.339 *** | 0.706 *** |
| (4.39) | (16.67) | (2.83) | (3.47) | (20.70) | |
| Controls | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| Observations | 360 | 390 | 390 | 390 | 390 |
| R-squared | 0.4521 |
| Variables | (1) Environmental Regulation | (2) Green Finance | (3) Industrial Agglomeration |
|---|---|---|---|
| IT | −0.597 *** | −0.442 ** | −0.451 * |
| (−2.70) | (−2.45) | (−1.84) | |
| IT2 | 1.316 *** | 1.096 ** | 0.870 ** |
| (5.06) | (2.09) | (2.30) | |
| D | 0.608 | 0.041 | 0.053 |
| (0.12) | (0.37) | (0.62) | |
| IT × D | −1.918 * | −2.644 ** | −2.273 ** |
| (−1.90) | (−2.30) | (−2.49) | |
| IT2 × D | 9.74 ** | 3.675 * | 3.987 * |
| (2.41) | (1.82) | (1.81) | |
| Constant | 0.392 *** | 0.323 *** | 0.219 *** |
| (4.17) | (2.69) | (2.91) | |
| Controls | yes | yes | yes |
| Observations | 390 | 390 | 390 |
| Variables | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| East | Central | West | 2009–2015 | 2016–2021 | |
| IT | −0.705 *** | −4.148 | 2.011 *** | 0.509 | −0.934 ** |
| (−4.27) | (−1.35) | (3.04) | (1.58) | (−2.16) | |
| IT2 | 1.327 *** | 13.119 | −6.083 *** | −1.289 * | 1.601 *** |
| (7.57) | (1.02) | (−2.66) | (−1.70) | (3.78) | |
| Constant | 0.604 *** | 0.536 *** | 0.487 *** | 0.411 *** | 0.539 ** |
| (8.39) | (5.61) | (10.72) | (3.53) | (2.35) | |
| Controls | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| Observations | 143 | 104 | 143 | 210 | 180 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, Y.; Pan, H. The Effect of Intelligent Development on Green Economy Efficiency: An Analysis Based on China’s Province-Level Data. Sustainability 2025, 17, 678. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17020678
Yao Y, Pan H. The Effect of Intelligent Development on Green Economy Efficiency: An Analysis Based on China’s Province-Level Data. Sustainability. 2025; 17(2):678. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17020678
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Yingyu, and Haiying Pan. 2025. "The Effect of Intelligent Development on Green Economy Efficiency: An Analysis Based on China’s Province-Level Data" Sustainability 17, no. 2: 678. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17020678
APA StyleYao, Y., & Pan, H. (2025). The Effect of Intelligent Development on Green Economy Efficiency: An Analysis Based on China’s Province-Level Data. Sustainability, 17(2), 678. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17020678




