A Conceptual Framework for Enabling Structural Steel Reuse Utilizing Circular Economy in Modular Construction
Abstract
1. Introduction
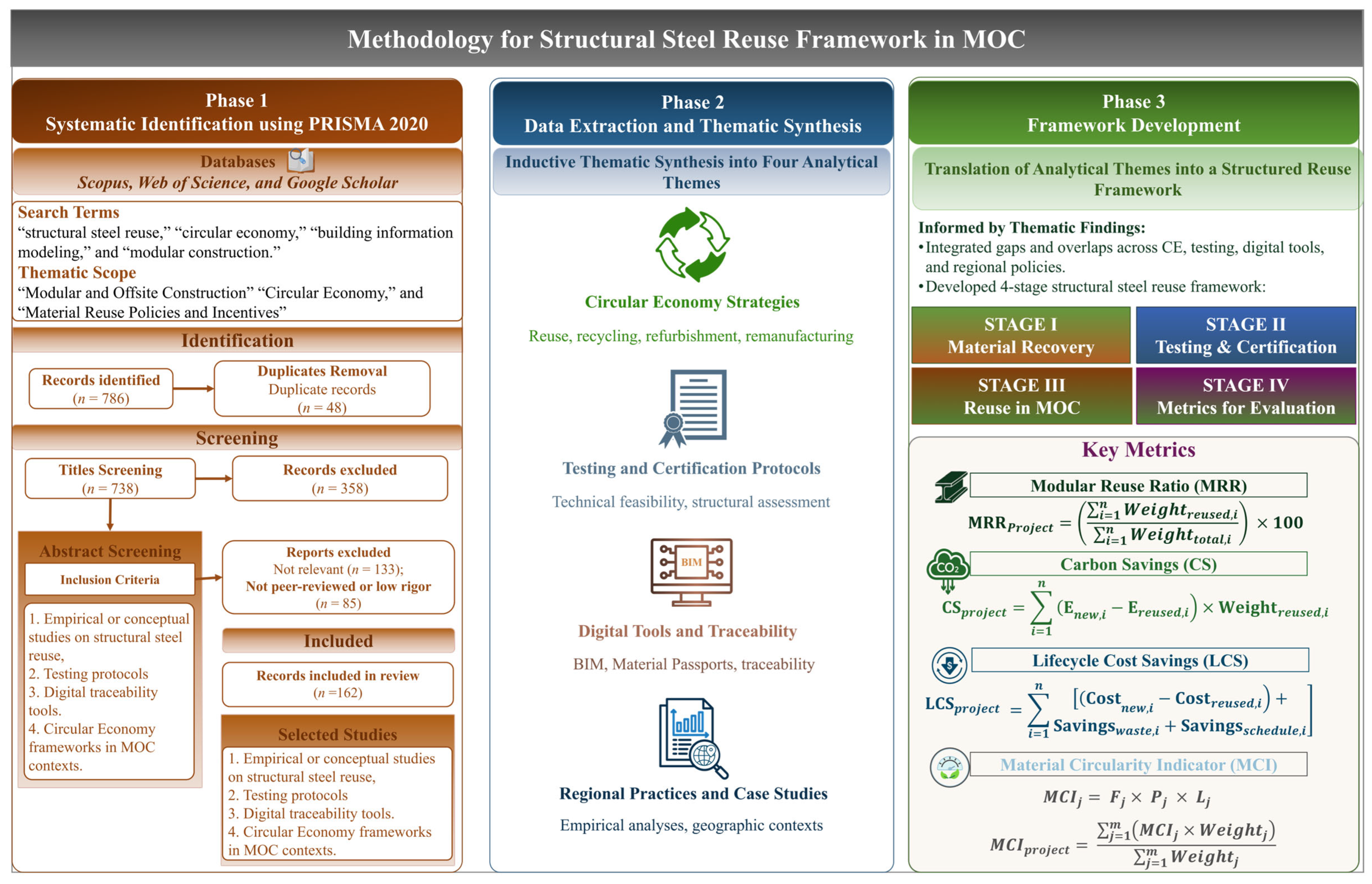
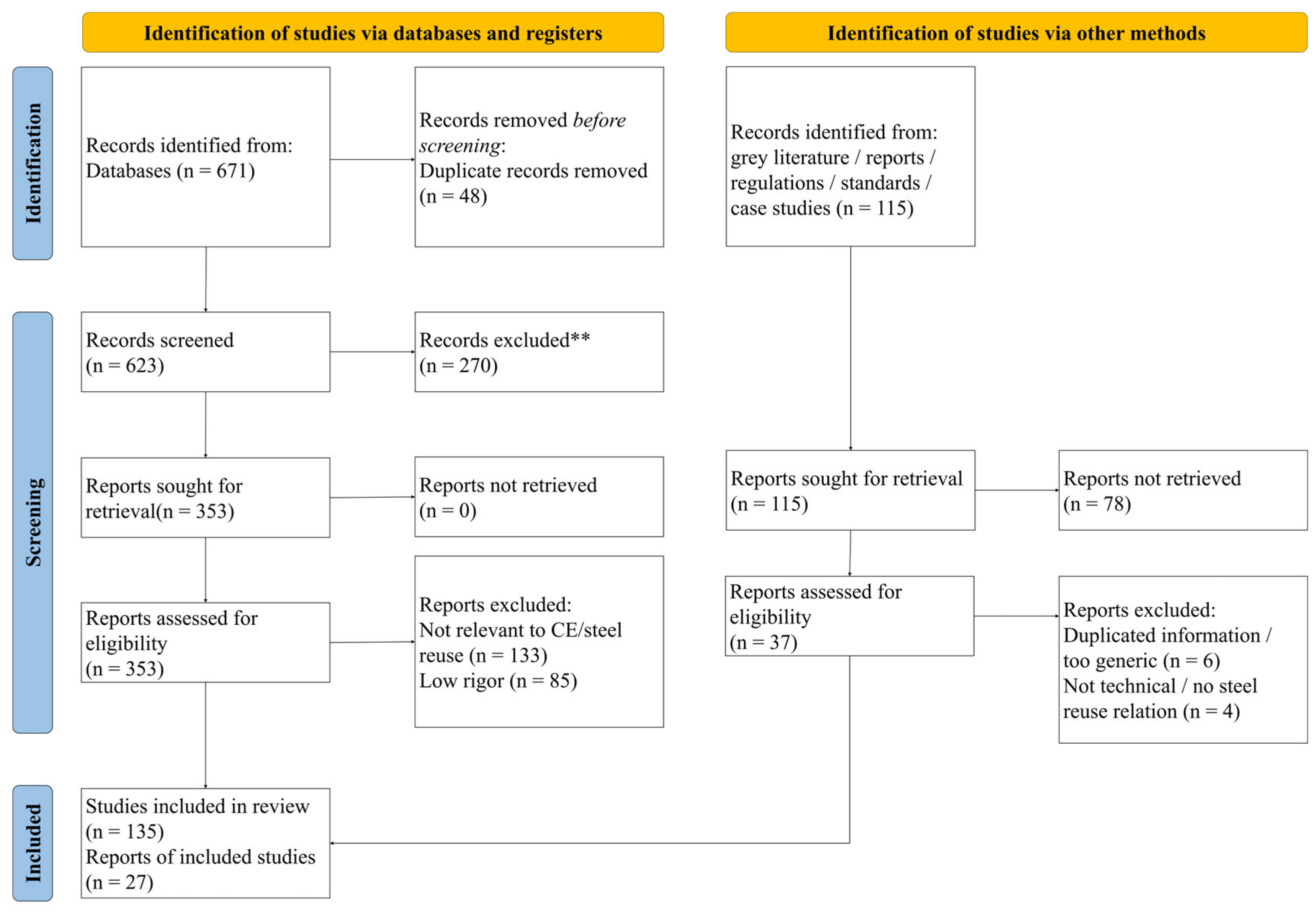
2. Materials and Methods
3. Literature Review
3.1. Theme 1: CE Strategies for Structural Steel Reuse
3.2. Theme 2: Testing and Certification Protocols for Structural Steel Reuse
3.3. Theme 3: Digital Tools and Traceability
3.4. Theme 4: Regional Practices and Case Studies
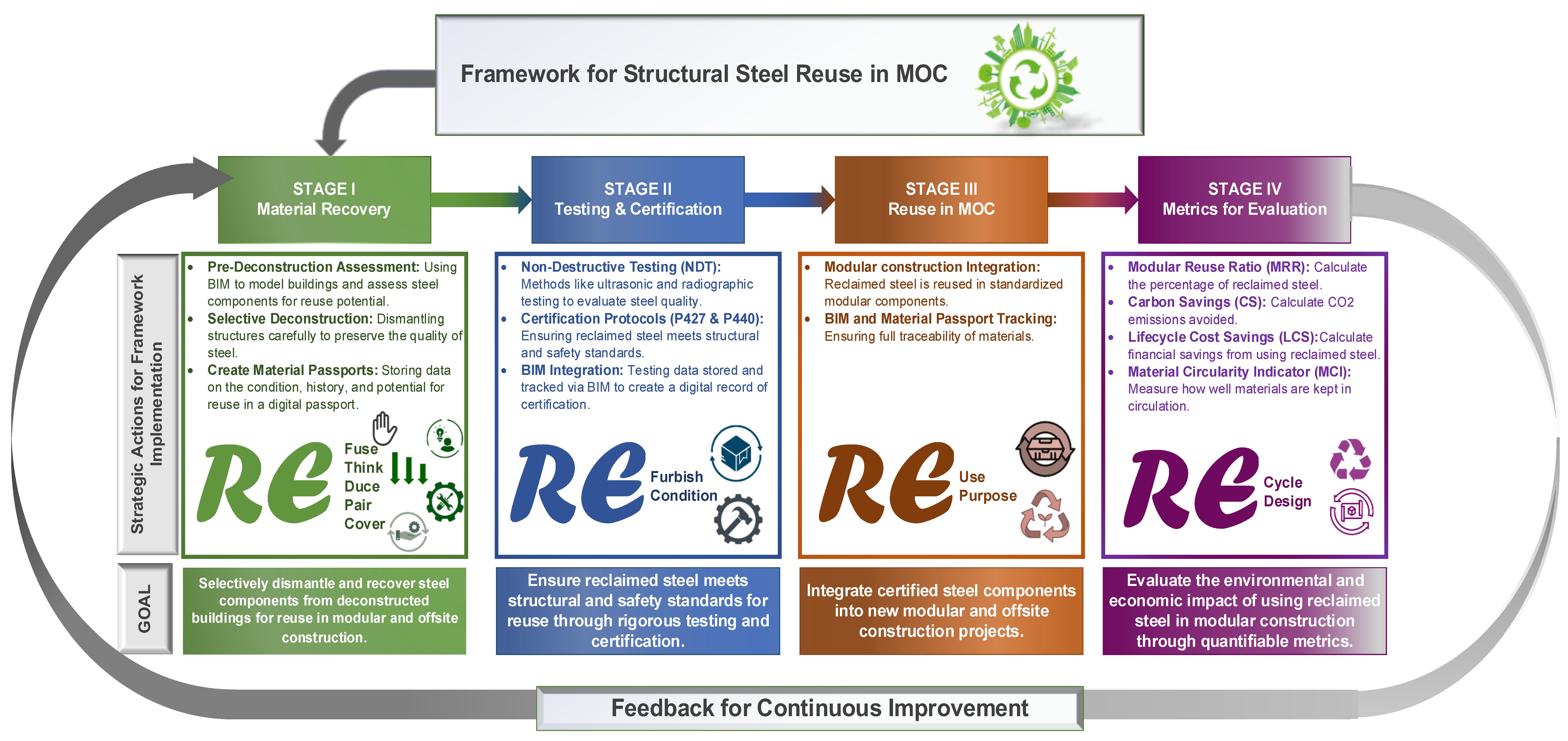
4. Framework Development
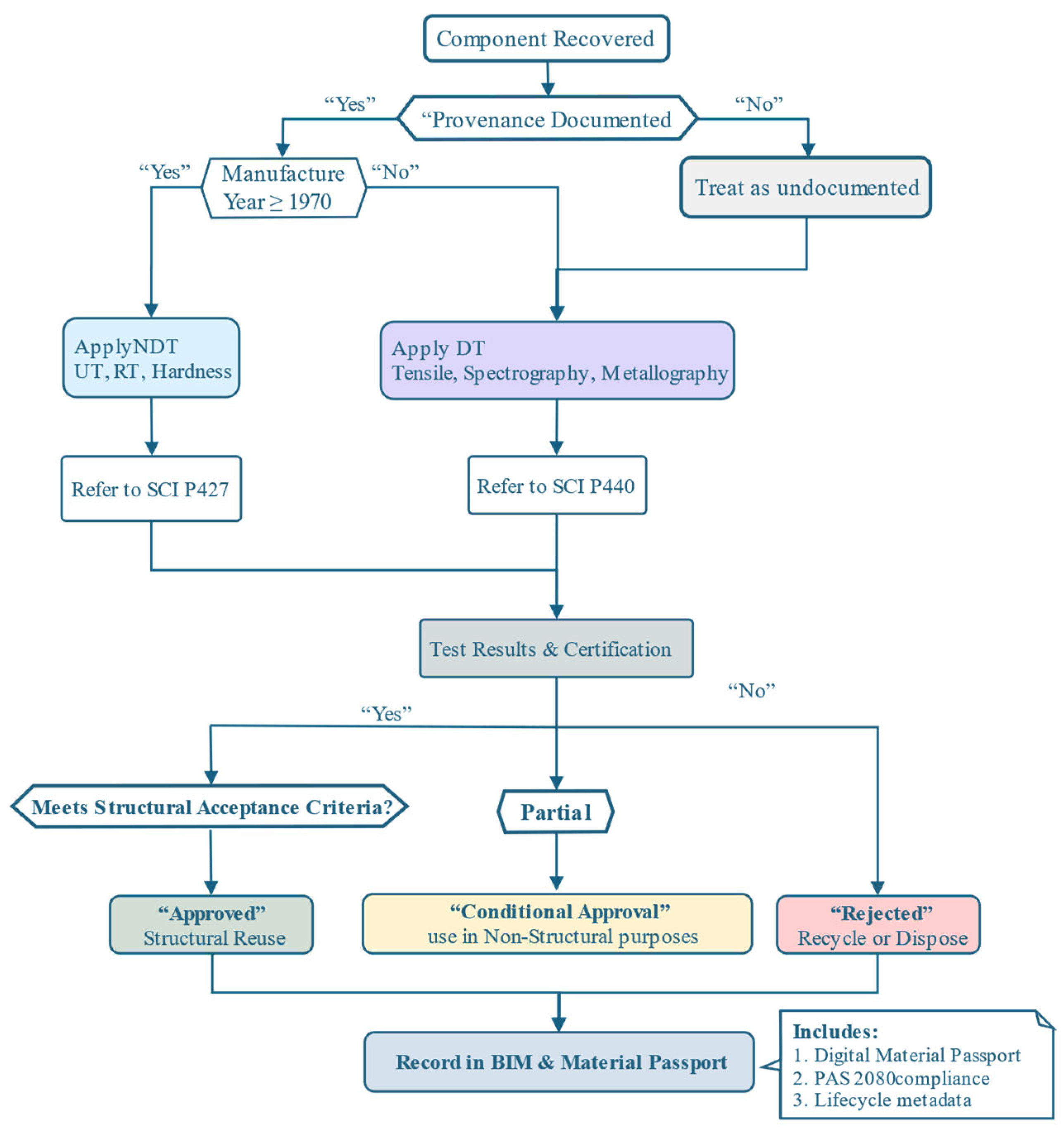
4.1. Stage I: Material Recovery
4.2. Stage II: Testing & Certification
4.3. Stage III: Reuse in MOC
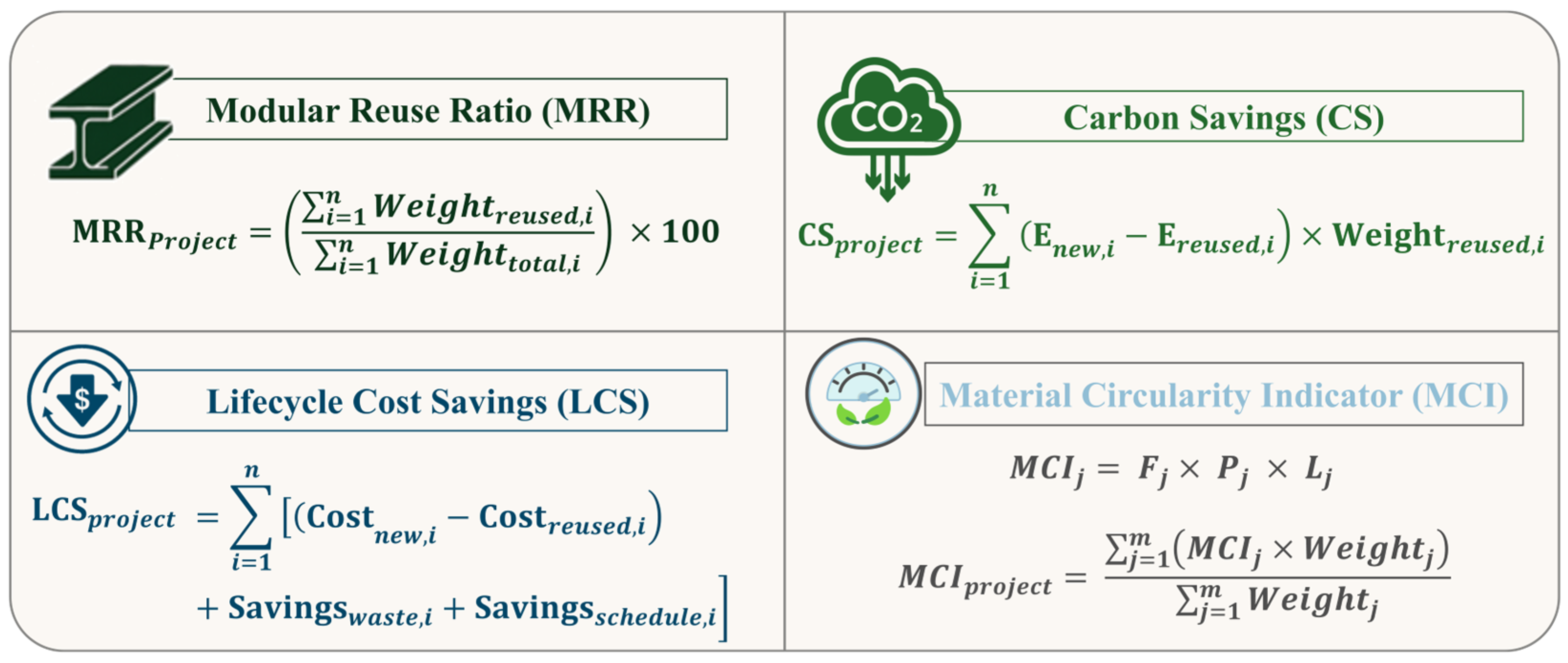
4.4. Stage IV: Performance Evaluation Through Sustainability Metrics
4.4.1. Modular Reuse Ratio (MRR)
4.4.2. Carbon Savings (CS)
4.4.3. Lifecycle Cost Savings (LCS)
4.4.4. Material Circularity Indicator (MCI)
5. Discussion
5.1. Implications for Structural Steel Reuse in MOC
5.2. Future Research
6. Concluding Remarks
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ASTM | American Society for Testing and Materials |
| BIM | Building Information Modeling |
| CE | Circular Economy |
| C&DW | Construction and Demolition Waste |
| CSA | Canadian Standards Association |
| DfD | Design for Disassembly |
| DT | Destructive Testing |
| EN | Eurocode (European Standards) |
| GHG | Greenhouse Gas |
| LCA | Life Cycle Assessment |
| LCS | Lifecycle Cost Saving |
| MCI | Material Circularity Indicator |
| MOC | Modular and Offsite Construction |
| MP | Material Passport |
| MRR | Modular Reuse Ratio |
| NDT | Non-Destructive Testing |
| SCI | Steel Construction Institute |
References
- United Nations Environment Programme. Global Status Report for Buildings and Construction 2024/2025: Not Just Another Brick in the Wall—The Solutions Exist. Scaling Them Will Build on Progress and Cut Emissions Fast; United Nations Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Y.; Li, Y.; Hao, Y.; Yu, T.; Hu, H. Greenhouse Gas Control in Steel Manufacturing: Inventory, Assurance, and Strategic Reduction Review. Carbon Res. 2024, 3, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEA. Iron & Steel—IEA. Available online: https://www.iea.org/energy-system/industry/steel (accessed on 17 April 2025).
- de Villafranca Casas, M.J.; Smit, S.; Nilsson, A.; Kuramochi, T. Climate Targets by Major Steel Companies: An Assessment of Collective Ambition and Planned Emission Reduction Measures. Energy Clim. Change 2024, 5, 100120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- British Constructional Steelwork Association. The Model Specification for the Purchase of Reclaimed Steel Sections, Issue 1; British Constructional Steelwork Association: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, R. Reusing Structural Steel: Guidance for Designers, Contractors, and Clients. Struct. Eng. J. Inst. Struct. Eng. 2023, 101, 16–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunant, C.F.; Drewniok, M.P.; Sansom, M.; Corbey, S.; Cullen, J.M.; Allwood, J.M. Options to Make Steel Reuse Profitable: An Analysis of Cost and Risk Distribution across the UK Construction Value Chain. J. Clean Prod. 2018, 183, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Government of Canada 2023 Progress Report on the 2030 Emissions Reduction Plan: Part I. Available online: https://www.canada.ca/en/services/environment/weather/climatechange/climate-plan/climate-plan-overview/emissions-reduction-2030/2023-progress-report/part-1.html (accessed on 11 September 2025).
- Shukla, P.R.; Skea, J.; Slade, R.; Al Khourdajie, A.; van Diemen, R.; McCollum, D.; Pathak, M.; Some, S.; Vyas, P.; Fradera, R. Climate Change 2022: Mitigation of Climate Change. Contribution of Working Group III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC); Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2022; Volume 10, ISBN 9781009157926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEA CO2 Emissions in 2022; IEA: Paris, France, 2023.
- World Steel Association. Sustainability Indicators 2024 Report; World Steel Association: Brussels, Belgium, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Ubolsook, P.; Podong, C.; Sedpho, S.; Jansanthea, P. Assessing the Environmental Impact of Construction Waste Management in Northern Thailand: An Approach to Estimate Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Cumulative Energy Demand. J. Clean Prod. 2024, 467, 142961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, J.F.T.; Pacca, S.A. Carbon Reduction Potential and Costs through Circular Bioeconomy in the Brazilian Steel Industry. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 169, 105517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihai, F.-C. Construction and Demolition Waste in Romania: The Route from Illegal Dumping to Building Materials. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, H.; Chebrolu, D.; Chadee, A.; Brooks, T. Too Good to Waste: Examining Circular Economy Opportunities, Barriers, and Indicators for Sustainable Construction and Demolition Waste Management. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2024, 48, 460–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goddin, J.; Marshall, K.; Pereira, A.; Design, G.; Herrmann, S.; Ds, S.; Sam, J.; Dupont, T.; Krieger, C.; Lenges, E.; et al. Circularity Indicators: An Approach to Measuring Circularity—Methodology; Ellen MacArthur Foundation: Cowes, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Geissdoerfer, M.; Savaget, P.; Bocken, N.M.P.; Hultink, E.J. The Circular Economy—A New Sustainability Paradigm? J. Clean Prod. 2017, 143, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchherr, J.; Reike, D.; Hekkert, M. Conceptualizing the Circular Economy: An Analysis of 114 Definitions. Resour Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 127, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Communication From The Commission To The European Parliament, The Council, The European Economic And Social Committee And The Committee Of The Regions A New Circular Economy Action Plan For a Cleaner and More Competitive Europe; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Potting, J.; Hekkert, M.P.; Worrell, E.; Hanemaaijer, A. Aldert Hanemaaijer Circular Economy: Measuring Innovation in the Product Chain; PBL Netherlands Environmental Assessment Agency: The Haag, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Nuñez-Cacho, P.; Górecki, J.; Molina-Moreno, V.; Corpas-Iglesias, F.A. What Gets Measured, Gets Done: Development of a Circular Economy Measurement Scale for Building Industry. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EMR. Environmental Product Declaration Reusable Steel; The International EPD System—EPD International AB: Stockholm, Sweden, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Brütting, J.; Vandervaeren, C.; Senatore, G.; De Temmerman, N.; Fivet, C. Environmental Impact Minimization of Reticular Structures Made of Reused and New Elements through Life Cycle Assessment and Mixed-Integer Linear Programming. Energy Build. 2020, 215, 109827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minunno, R.; O’Grady, T.; Morrison, G.M.; Gruner, R.L. Exploring Environmental Benefits of Reuse and Recycle Practices: A Circular Economy Case Study of a Modular Building. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 160, 104855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomponi, F.; Moncaster, A. Circular Economy for the Built Environment: A Research Framework. J. Clean Prod. 2017, 143, 710–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çimen, Ö. Construction and Built Environment in Circular Economy: A Comprehensive Literature Review. J. Clean Prod. 2021, 305, 127180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.A.; Nazzal, M.A.; Darras, B.M.; Deiab, I.M. A Comprehensive Multi-Level Circular Economy Assessment Framework. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2022, 32, 700–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.E. Off-Site and Modular Construction Explained; National Institute of Building Sciences, Off-Site Construction Council: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Nadeem, G.; Safiee, N.A.; Bakar, N.A.; Karim, I.A.; Nasir, N.A.M. Connection Design in Modular Steel Construction: A Review. Structures 2021, 33, 3239–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuni, I.Y.; Shen, G.Q. Developing Critical Success Factors for Integrating Circular Economy into Modular Construction Projects in Hong Kong. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2022, 29, 574–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, G.L.; Shih, S.G.; Wagiri, F. Circular Economy and Sustainable Development Goals: Exploring the Potentials of Reusable Modular Components in Circular Economy Business Model. J. Clean Prod. 2023, 414, 137503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, V.W.Y.; Hao, J.J.L. Prefabrication as a Mean of Minimizing Construction Waste on Site. Int. J. Constr. Manag. 2014, 14, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shooshtarian, S.; Wong, P.S.; Maqsood, T. Circular Economy in Modular Construction: An Australian Case Study. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 103, 112182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ly, D.H.; Le, Q.H.; Hoang Nhat Nguyen, T.D.; Ahn, Y.; Kim, K.; Kwon, N. Advancing Modular Construction through Circular Economy: Insights from Semi-Automated PRISMA Analysis and Topic Modeling. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 98, 111232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamali, M.; Hewage, K.; Sadiq, R. Conventional versus Modular Construction Methods: A Comparative Cradle-to-Gate LCA for Residential Buildings. Energy Build. 2019, 204, 109479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, R.; Brown, D.; Sansom, M. Structural Steel Reuse: Assessment, Testing and Design Principles. SCI Publication P427; The Steel Construction Institute (SCI): Ascot, UK, 2019; ISBN 978-1-85942-243-4. [Google Scholar]
- Jaskowska-Lemańska, J.; Sagan, J. Non-Destructive Testing Methods as a Main Tool Supporting Effective Waste Management in Construction Processes. Arch. Civ. Eng. 2019, 65, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chow, C.L.; Lau, D. Artificial Intelligence-Enhanced Non-Destructive Defect Detection for Civil Infrastructure. Autom. Constr. 2025, 171, 105996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutamanis, A. From Building Information Modelling to Digital Twins: Digital Representation for a Circular Economy. In A Circular Built Environment in the Digital Age; De Wolf, C., Çetin, S., Bocken, N.M.P., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 3–20. ISBN 978-3-031-39675-5. [Google Scholar]
- Bjerke, A.J.F.; Amoudi, O. Towards Net-Zero Construction Projects by Applying BIM-Enabled Circular Economy. In 1st International Conference on Net-Zero Built Environment; Kioumarsi, M., Shafei, B., Eds.; Springer Nature Switzerland: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; pp. 1597–1609. [Google Scholar]
- Kaewunruen, S.; Baniotopoulos, C.; Guo, Y.; Sengsri, P.; Teuffel, P.; Bajare, D. 6D-BIM Applications to Enrich Circular Value Chains and Stakeholder Engagement Within Built Environments. In 4th International Conference “Coordinating Engineering for Sustainability and Resilience” & Midterm Conference of CircularB “Implementation of Circular Economy in the Built Environment”; Ungureanu, V., Bragança, L., Baniotopoulos, C., Abdalla, K.M., Eds.; Springer Nature Swizerland: Cham, Swizterland, 2024; pp. 346–356. [Google Scholar]
- Munaro, M.R.; Tavares, S.F. Materials Passport’s Review: Challenges and Opportunities toward a Circular Economy Building Sector. Built Environ. Proj. Asset Manag. 2021, 11, 767–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoosain, M.S.; Paul, B.S.; Raza, S.M.; Ramakrishna, S. Material Passports and Circular Economy. In An Introduction to Circular Economy; Liu, L., Ramakrishna, S., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 131–158. ISBN 978-981-15-8510-4. [Google Scholar]
- Byers, B.S.; De Wolf, C. QR Code-Based Material Passports for Component Reuse Across Life Cycle Stages in Small-Scale Construction. Circ. Econ. 2023, 1, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elghaish, F.; Hosseini, M.R.; Kocaturk, T.; Arashpour, M.; Bararzadeh Ledari, M. Digitalised Circular Construction Supply Chain: An Integrated BIM-Blockchain Solution. Autom. Constr. 2023, 148, 104746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksson, P.J.; Cucurachi, S.; Guinée, J.B.; Heijungs, R.; Troell, M.; Ziegler, F. A Rapid Review of Meta-Analyses and Systematic Reviews of Environmental Footprints of Food Commodities and Diets. Glob. Food Sec. 2021, 28, 100508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasiades, K.; Blom, J.; Buyle, M.; Audenaert, A. Translating the Circular Economy to Bridge Construction: Lessons Learnt from a Critical Literature Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 117, 109522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuni, I.Y. Mapping the Barriers to Circular Economy Adoption in the Construction Industry: A Systematic Review, Pareto Analysis, and Mitigation Strategy Map. Build Environ 2022, 223, 109453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartsch, H.; Eyben, F.; Voelkel, J.; Feldmann, M. On the Development of Regulations for the Increased Reuse of Steel Structures. In Life-Cycle of Structures and Infrastructure Systems, Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium on Life-Cycle Civil Engineering, IALCCE 2023, Milan, Italy, 2–6 July 2023; CRC Press: London, UK, 2023; pp. 1287–1294. [Google Scholar]
- Coelho, A.M.G.; Pimentel, R.; Ungureanu, V.; Hradil, P.; Kesti, J. European Recommendations for Reuse of Steel Products in Single-Storey Buildings. PROGRESS-Provisions for Greater Reuse of Steel Structures, 1st ed.; ECCS-European Convention for Constructional Steelwork: Brussels, Belgium, 2020; ISBN 9789291471706. [Google Scholar]
- Miatto, A.; Emami, N.; Goodwin, K.; West, J.; Taskhiri, M.S.; Wiedmann, T.; Schandl, H. Australia’s Circular Economy Metrics and Indicators. J. Ind. Ecol. 2024, 28, 216–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, J.; Walbridge, S.; Haas, C.; Saari, R. Understanding the Total Life Cycle Cost Implications of Reusing Structural Steel. Env. Syst. Decis. 2017, 37, 101–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönfelder, L.; Byers, B.S.; Honic, M.; De Wolf, C. A Steel Element Reuse Ontology for Building Audits in Circular Construction. Dev. Built Environ. 2025, 21, 100638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, B.; Honic, M.; Leite, F.; Herthogs, P.; Stouffs, R. Augmenting Materials Passports to Support Disassembly Planning Based on Building Information Modelling Standards. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 90, 109083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Grady, T.; Minunno, R.; Chong, H.Y.; Morrison, G.M. Design for Disassembly, Deconstruction and Resilience: A Circular Economy Index for the Built Environment. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 175, 105847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ness, D.; Swift, J.; Ranasinghe, D.C.; Xing, K.; Soebarto, V. Smart Steel: New Paradigms for the Reuse of Steel Enabled by Digital Tracking and Modelling. J. Clean Prod. 2015, 98, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assefa, G.; Ambler, C. To Demolish or Not to Demolish: Life Cycle Consideration of Repurposing Buildings. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 28, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConnell, J.; Wennick, T.; Schumacher, T.; Keller, P.; Thostenson, E.T. Evaluating Structural Steel for Reuse through Field Monitoring. In IABSE Symposium: Engineering for Progress, Nature and People, Madrid, Spain, 3–5 September 2014; International Association for Bridge and Structural Engineering (IABSE): Zurich, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 3174–3181. [Google Scholar]
- BS EN 1090-2:2018+A1:2024; Execution of Steel Structures and Aluminium Structures—Technical requirements for Steel Structures. BSI (British Standards Institute): London, UK, 2024; ISBN 978-0-539-21835-0.
- ASTM A6/A6M-21; Standard Specification for General Requirements for Rolled Structural Steel Bars, Plates, Shapes, and Sheet Piling. ASTM (Advancing Standards Transforming Markets) International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Brütting, J.; Senatore, G.; Schevenels, M.; Fivet, C. Optimum Design of Frame Structures From a Stock of Reclaimed Elements. Front. Built Environ. 2020, 6, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wastling, T.; Charnley, F.; Moreno, M. Design for Circular Behaviour: Considering Users in a Circular Economy. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dams, B.; Maskell, D.; Shea, A.; Allen, S.; Driesser, M.; Kretschmann, T.; Walker, P.; Emmitt, S. A Circular Construction Evaluation Framework to Promote Designing for Disassembly and Adaptability. J. Clean Prod. 2021, 316, 128122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhardt, L.C.M.; Birgisdóttir, H.; Birkved, M. Life Cycle Assessment of a Danish Office Building Designed for Disassembly. Build. Res. Inf. 2019, 47, 666–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostapska, K.; Rüther, P.; Loli, A.; Gradeci, K. Design for Disassembly: A Systematic Scoping Review and Analysis of Built Structures Designed for Disassembly. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2024, 48, 377–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brütting, J.; Desruelle, J.; Senatore, G.; Fivet, C. Design of Truss Structures Through Reuse. Structures 2019, 18, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, S.; Zoghi, M.; Blázquez, T.; Dall’O, G. New Level(s) Framework: Assessing the Affinity between the Main International Green Building Rating Systems and the European Scheme. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 155, 111924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoth, K.; Fufa, S.M.; Seilskjær, E. Barriers, Success Factors, and Perspectives for the Reuse of Construction Products in Norway. J. Clean Prod. 2022, 337, 130494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, S.; Coleman, N.; Hodgson, P.; Collins, N.; Brimacombe, L. Evaluating the Environmental Dimension of Material Efficiency Strategies Relating to the Circular Economy. Sustainability 2018, 10, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braakman, L.; Bhochhibhoya, S.; de Graaf, R. Exploring the Relationship between the Level of Circularity and the Life Cycle Costs of a One-Family House. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 164, 105149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Densley Tingley, D.; Cooper, S.; Cullen, J. Understanding and Overcoming the Barriers to Structural Steel Reuse, a UK Perspective. J. Clean Prod. 2017, 148, 642–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whalen, K.A.; Milios, L.; Nussholz, J. Bridging the Gap: Barriers and Potential for Scaling Reuse Practices in the Swedish ICT Sector. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 135, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nußholz, J.L.K.; Rasmussen, F.N.; Whalen, K.; Plepys, A. Material Reuse in Buildings: Implications of a Circular Business Model for Sustainable Value Creation. J. Clean Prod. 2020, 245, 118546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zheng, B.; Luk, C.; Yuen, K.-f.; Chan, A. Towards a Sustainable Circular Economy: Understanding the Environmental Credits and Loads of Reusing Modular Building Components from a Multi-Use Cycle Perspective. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2024, 46, 543–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinante, C.; Sacco, P.; Orzes, G.; Borgianni, Y. Circular Economy Metrics: Literature Review and Company-Level Classification Framework. J. Clean Prod. 2021, 288, 125090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.d.P.S.L.; de Oliveira, E.A.; Fonseca, A.M. Strategies to Promote Circular Economy in the Management of Construction and Demolition Waste at the Regional Level: A Case Study in Manaus, Brazil. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2021, 23, 2713–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudarsan, J.S.; Gavali, H. Application of BIM in Conjunction with Circular Economy Principles for Sustainable Construction. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 26, 7455–7468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askar, R.; Karaca, F.; Bragança, L.; Gervásio, H. The Role of BIM in Supporting Circularity: A Conceptual Framework for Developing BIM-Based Circularity Assessment Models in Buildings. In 4th International Conference “Coordinating Engineering for Sustainability and Resilience” & Midterm Conference of CircularB “Implementation of Circular Economy in the Built Environment”; Ungureanu, V., Bragança, L., Baniotopoulos, C., Abdalla, K.M., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; Volume 489, pp. 649–658. ISBN 978-3-031-57799-4 978-3-031-57800-7. [Google Scholar]
- Durdyev, S.; Koc, K.; Tleuken, A.; Budayan, C.; Ekmekcioğlu, Ö.; Karaca, F. Barriers to Circular Economy Implementation in the Construction Industry: Causal Assessment Model. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 27, 4045–4081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, D.R.; Ryan, N.A.; Syndergaard, K.; Zhu, Y. The Potential for Material Circularity and Independence in the U.S. Steel Sector. J. Ind. Ecol. 2020, 24, 748–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, N.A.; Miller, S.A.; Skerlos, S.J.; Cooper, D.R. Reducing CO2Emissions from U.S. Steel Consumption by 70% by 2050. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 14598–14608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavropoulos, P.; Panagiotopoulou, V.C.; Papacharalampopoulos, A.; Aivaliotis, P.; Georgopoulos, D.; Smyrniotakis, K. A Framework for CO2 Emission Reduction in Manufacturing Industries: A Steel Industry Case. Designs 2022, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gervasio, H.; da Silva, L.S.; D’Antimo, M. The Contribution of Low Carbon Steel to the Decarbonization of the Building Sector. In Life-Cycle of Structures and Infrastructure Systems, Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium on Life-Cycle Civil Engineering, IALCCE 2023, Milan, Italy, 2–6 July 2023; CRC Press/Balkema: London, UK, 2023; pp. 2429–2436. [Google Scholar]
- Hradil, P.; Fülöp, L.; Wahlström, M.; Del Castillo, C. The New Construction Products Regulation: Opportunity or Barrier for Reused Constructional Steel? In Life-Cycle of Structures and Infrastructure Systems, Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium on Life-Cycle Civil Engineering, IALCCE 2023, Milan, Italy, 2–6 July 2023; CRC Press: London, UK, 2023; pp. 743–750. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, D.; Dougherty, L.A. Reuse Of Pre-1970 Steelwork: Supplement to P427; The Steel Construction Institute (SCI): Ascot, Berkshire, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kanyilmaz, A.; Birhane, M.; Fishwick, R.; del Castillo, C. Reuse of Steel in the Construction Industry: Challenges and Opportunities. Int. J. Steel Struct. 2023, 23, 1399–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Mitchell, D.; Blanche, J.; Harper, S.; Tang, W.; Pancholi, K.; Baines, L.; Bucknall, D.G.; Flynn, D. A Review of Sensing Technologies for Non-Destructive Evaluation of Structural Composite Materials. J. Compos. Sci. 2021, 5, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, S.; Dackermann, U. A Systematic Review of Advanced Sensor Technologies for Non-Destructive Testing and Structural Health Monitoring. Sensors 2023, 23, 2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, M.; Scheer, C.; Böhm, V.; Reimche, W.; Bach, F.-W. Materials Technology New Developments in Non-Destructive Testing for Quality Assurance in Component Manufacturing. Steel Res. Int. 2009, 80, 916–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wu, L.; Liu, Z.; Mo, Y. Quality Control Method of Steel Structure Construction Based on Digital Twin Technology. Digit. Twin 2023, 3, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doktor, M.S.; Fox, C.; Kurz, W.; Stockis, J.P. Characterization of Steel Buildings by Means of Non-Destructive Testing Methods. J. Math. Ind. 2018, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzas, Ó.; Cabaleiro, M.; Conde, B.; Cruz, Y.; Riveiro, B. Structural Health Control of Historical Steel Structures Using HBIM. Autom. Constr. 2022, 140, 104308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, M.; Shafiee, M. Structural Health Monitoring (SHM) and Determination of Surface Defects in Large Metallic Structures Using Ultrasonic Guided Waves. Sensors 2018, 18, 3958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olumo, A.; Haas, C. Building Material Reuse: An Optimization Framework for Sourcing New and Reclaimed Building Materials. J. Clean Prod. 2024, 479, 143892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Sánchez, I.M.; Somohano-Rodríguez, F.M.; Amor-Esteban, V.; Frías-Aceituno, J.V. Which Region and Which Sector Leads the Circular Economy? CEBIX, a Multivariant Index Based on Business Actions. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 297, 113299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çetin, S.; Raghu, D.; Honic, M.; Straub, A.; Gruis, V. Data Requirements and Availabilities for Material Passports: A Digitally Enabled Framework for Improving the Circularity of Existing Buildings. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2023, 40, 422–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariyani, D.; Hariyani, P.; Mishra, S.; Kumar Sharma, M. Leveraging Digital Technologies for Advancing Circular Economy Practices and Enhancing Life Cycle Analysis: A Systematic Literature Review. Waste Manag. Bull. 2024, 2, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmenegger, P. Design, Implementation, and Analysis of Decentralized Product Passport Systems for Circular Construction. Master’s Thesis, University of Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Kiesel, A.; Brandi, G.; Schlatter, J.; Gerber, A.; Langenberg, S. Structural Reuse of Decommissioned Ski Lift Steel Trusses for Load-Bearing Applications. Architecture 2024, 4, 835–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CSA S166:24; Design and Construction of Steel Structures. CSA (Canadian Standards Association) Group: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2024.
- Pedroso, M.F.; Tavares, V. Circular Economy Supporting Policies and Regulations: The Portuguese Case. In Springer Tracts in Civil Engineering; Springer Science and Business Media Deutschland GmbH: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; Volume Part F1844, pp. 277–290. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, C.; Oyekan, J.; Stergioulas, L.K. Distributed Manufacturing: A New Digital Framework for Sustainable Modular Construction. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntefua Saah, A.E.; Choi, J. Blockchain Technology in the AEC Industry: Scientometric Analysis of Research Activities. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 72, 106609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byers, B.; Emmenegger, P.; Hunhevicz, J.; Schumm, D.; Heisel, F.; Hall, D.; De Wolf, C. Decentralized Phygital Identifiers for Circular Construction. Preprint 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Tian, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhong, R.Y. Blockchain-Enabled Product Lifecycle Management. In Design and Operation of Production Networks for Mass Personalization in the Era of Cloud Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 349–379. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Gil, M.; Espinosa-Fernández, A.; López-Mesa, B. A New Functionality for the Digital Building Logbook: Assessing the Progress of Decarbonisation of National Building Sectors. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2024, 105, 107393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, M.; Batallé, A.; De Wolf, C.; Sollazzo, A.; Dubor, A.; Wang, T. Automating Building Element Detection for Deconstruction Planning and Material Reuse: A Case Study. Autom. Constr. 2023, 146, 104697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacovidou, E.; Purnell, P.; Tsavdaridis, K.D.; Poologanathan, K. Digitally Enabled Modular Construction for Promoting Modular Components Reuse: A UK View. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 42, 102820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzeddine, A.; García de Soto, B. Connecting Teams in Modular Construction Projects Using Game Engine Technology. Autom. Constr. 2021, 132, 103887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charef, R.; Alaka, H.; Ganjian, E. A BIM-Based Theoretical Framework for the Integration of the Asset End-of-Life Phase. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 225, 012067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasiades, K.; Goffin, J.; Rinke, M.; Buyle, M.; Audenaert, A.; Blom, J. Standardisation: An Essential Enabler for the Circular Reuse of Construction Components? A Trajectory for a Cleaner European Construction Industry. J. Clean Prod. 2021, 298, 126864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.H.; Zhang, C.; Di Maio, F.; Hu, M. Potential of BREEAM-C to Support Building Circularity Assessment: Insights from Case Study and Expert Interview. J. Clean Prod. 2024, 442, 140836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markou, I.; Sinnott, D.; Thomas, K. Current Methodologies of Creating Material Passports: A Systematic Literature Review. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2025, 22, e04267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honic, M.; Kovacic, I.; Aschenbrenner, P.; Ragossnig, A. Material Passports for the End-of-Life Stage of Buildings: Challenges and Potentials. J. Clean Prod. 2021, 319, 128702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arukala, S.R.; Pancharathi, R.K.; Pulukuri, A.R. Evaluation of Sustainable Performance Indicators for the Built Environment Using AHP Approach. J. Inst. Eng. Ser. A 2019, 100, 619–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadim, N.; Agliata, R.; Thaheem, M.J.; Mollo, L. Whole Building Circularity Indicator: A Circular Economy Assessment Framework for Promoting Circularity and Sustainability in Buildings and Construction. Build. Environ. 2023, 241, 110498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer-Raniga, U. Using the ReSOLVE Framework for Circularity in the Building and Construction Industry in Emerging Markets. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 294, 012002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, I.; Silva, D.A. Promoting Sustainability In The Construction Sector: Assessment Of The Reuse Of Construction Materials. Master’s Thesis, NOVA University of Lisbon, Lisbon, Portugal, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- González, A.; Sendra, C.; Herena, A.; Rosquillas, M.; Vaz, D. Methodology to Assess the Circularity in Building Construction and Refurbishment Activities. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. Adv. 2021, 12, 200051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- City of Amsterdam. Policy: Circular Economy; City of Amsterdam: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; Available online: https://www.amsterdam.nl/en/policy/sustainability/circular-economy/ (accessed on 11 August 2025).
- Torres-Guevara, L.E.; Prieto-Sandoval, V.; Mejia-Villa, A. Success Drivers for Implementing Circular Economy: A Case Study from the Building Sector in Colombia. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, M.D.; Dumontier, M.; Jan Aalbersberg, I.; Appleton, G.; Axton, M.; Baak, A.; Blomberg, N.; Boiten, J.W.; da Silva Santos, L.B.; Bourne, P.E.; et al. Erratum: Addendum: The FAIR Guiding Principles for Scientific Data Management and Stewardship (Scientific Data (2016) 3 (160018)). Sci. Data 2019, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuyts, W.; Sedlitzky, R.; Morita, M.; Tanikawa, H. Understanding and Managing Vacant Houses in Support of a Material Stock-Type Society—The Case of Kitakyushu, Japan. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavoura, F.; Veljkovic, M. Design Strategies and Technical Practices for Reusable Steel–Concrete Composite Structural Systems. In Creating a Roadmap Towards Circularity in the Built Environment; Bragança, L., Cvetkovska, M., Askar, R., Ungureanu, V., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 39–46. ISBN 978-3-031-45980-1. [Google Scholar]
- Eckelman, M.J.; Brown, C.; Troup, L.N.; Wang, L.; Webster, M.D.; Hajjar, J.F. Life Cycle Energy and Environmental Benefits of Novel Design-for-Deconstruction Structural Systems in Steel Buildings. Build. Environ. 2018, 143, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitayama, S.; Iuorio, O. Disassembly and Reuse of Structural Members in Steel-Framed Buildings: State-of-the-Art Review of Connection Systems and Future Research Trends. J. Arch. Eng. 2023, 29, 03123006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellen MacArthur Foundation. Artificial Intelligence and the Circular Economy: AI as a Tool to Accelerate the Transition; Ellen MacArthur Foundation: Cowes, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mollaei, A.; Byers, B.; Christovan, C.; Olumo, A.; De Wolf, C.; Bachmann, C.; Haas, C. A Global Perspective on Building Material Recovery Incorporating the Impact of Regional Factors. J. Clean Prod. 2023, 429, 139525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.V.; de Brito, J.; Dhir, R.K. Availability and Processing of Recycled Aggregates within the Construction and Demolition Supply Chain: A Review. J. Clean Prod. 2017, 143, 598–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victar, H.C.; Waidyasekara, K.G.A.S. Circular Economy Strategies for Waste Management in Sri Lanka: A Focus on Demolitions and Repurpose and Material Recovery and Production Stages. Waste Manag. Res. 2024, 42, 953–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 17640:2018; Non-Destructive Testing of Welds—Ultrasonic Testing—Techniques, Testing Levels, and Assessment. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018.
- ISO 10893-12:2011; Non-Destructive Testing of Steel Tubes—Part 12: Automated Full Peripheral Ultrasonic Thickness Testing of Seamless and Welded (Except Submerged Arc-Welded) Steel Tubes. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011.
- O’grady, T.M.; Brajkovich, N.; Minunno, R.; Chong, H.Y.; Morrison, G.M. Circular Economy and Virtual Reality in Advanced BIM-based Prefabricated Construction. Energies 2021, 14, 4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akanbi, L.A.; Oyedele, L.O.; Akinade, O.O.; Ajayi, A.O.; Davila Delgado, M.; Bilal, M.; Bello, S.A. Salvaging Building Materials in a Circular Economy: A BIM-Based Whole-Life Performance Estimator. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 129, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condotta, M.; Zatta, E. Reuse of Building Elements in the Architectural Practice and the European Regulatory Context: Inconsistencies and Possible Improvements. J. Clean Prod. 2021, 318, 128413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, J.T.M.; Diemer, A. Supply Chain Integration Strategies and Circularity in the European Steel Industry. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 153, 104517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wolf, C.; Byers, B.S.; Raghu, D.; Gordon, M.; Schwarzkopf, V.; Triantafyllidis, E. D5 Digital Circular Workflow: Five Digital Steps towards Matchmaking for Material Reuse in Construction. npj Mater. Sustain. 2024, 2, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PAS 2080:2023; Carbon Management in Buildings and Infrastructure. BSI: London, UK, 2023; ISBN 978-0-539-18034-3.
- Guidance Document for PAS 2080: Practical Actions and Examples to Accelerate the Decarbonisation of Buildings and Infrastructure; Institution of Civil Engineers (ICE); British Standards Institution (BSI): London, UK, 2023.
- Liew, J.Y.R.; Chua, Y.S.; Dai, Z. Steel Concrete Composite Systems for Modular Construction of High-Rise Buildings. Structures 2019, 21, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta, I.; Bakhoum, E.S.; Marzouk, M.M. Digitizing Material Passport for Sustainable Construction Projects Using BIM. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 43, 103233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, M.; von Zimmerman, L.; Haradhun, O.; Campanella, D.; Bräutigam, M.; De Wolf, C. Digitising Building Materials for Reuse with Reality Capture and Scan-to-BIM Technologies. In A Circular Built Environment in the Digital Age; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 41–55. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez, B.; Rausch, C.; Haas, C.; Hartmann, T. A Framework for BIM-Based Disassembly Models to Support Reuse of Building Components. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 175, 105825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trubina, N.; Leindecker, G.; Askar, R.; Karanafti, A.; Gómez-Gil, M.; Blázquez, T.; Güngör, B.; Bragança, L. Digital Technologies and Material Passports for Circularity in Buildings: An In-Depth Analysis of Current Practices and Emerging Trends. In Proceedings of the Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering; Springer Science and Business Media Deutschland GmbH: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; Volume 489 LNCE, pp. 690–699. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Gil, M.; Askar, R.; Karanafti, A.; Trubina, N.; Blázquez, T.; Güngör, B.; Bragança, L.; Leindecker, G. Unlocking the Potential of Material and Building Passports in the Transition to a Circular Economy in Buildings: A Critical Review. In 4th International Conference “Coordinating Engineering for Sustainability and Resilience” & Midterm Conference of CircularB “Implementation of Circular Economy in the Built Environment”; Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering; Springer Science and Business Media Deutschland GmbH: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; Volume 489 LNCE, pp. 404–413. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, S.F.; Kristensen, J.H.; Adamsen, S.; Christensen, A.; Waehrens, B.V. Digital Product Passports for a Circular Economy: Data Needs for Product Life Cycle Decision-Making. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2023, 37, 242–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarasinghe, I.; Hong, Y.; Stewart, R.A. Development of a Material Circularity Evaluation Framework for Building Construction Projects. J. Clean Prod. 2024, 436, 140562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Yang, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Pan, W. Artificial Intelligence and Robotics for Prefabricated and Modular Construction: A Systematic Literature Review. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2022, 148, 03122004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervez, H.; Ali, Y.; Petrillo, A. A Quantitative Assessment of Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Emissions from Conventional and Modular Construction: A Case of Developing Country. J. Clean Prod. 2021, 294, 126210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, M.; Zayed, T. Critical Factors for Successful Implementation of Just-in-Time Concept in Modular Integrated Construction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clean Prod. 2021, 284, 124716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basta, A.; Serror, M.H.; Marzouk, M. A BIM-Based Framework for Quantitative Assessment of Steel Structure Deconstructability. Autom. Constr. 2020, 111, 103064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, S.M.; Hegazy, H.; Zhang, J.; Mahdi, I.M.; Dessouki, A.K.; Rashid, I.A. Integrated BIM Framework for the Implementation of Steel Structure Projects. J. Archit. Eng. 2025, 31, 04025006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eleftheriadis, S.; Mumovic, D.; Greening, P. Life Cycle Energy Efficiency in Building Structures: A Review of Current Developments and Future Outlooks Based on BIM Capabilities. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 67, 811–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byers, B.S.; Gordon, M.; De Wolf, C.; Iuorio, O. Calculating Embodied Carbon for Reused Structural Components with Laser Scanning. In Life-Cycle of Structures and Infrastructure Systems, Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium on Life-Cycle Civil Engineering, IALCCE 2023, Milan, Italy, 2–6 July 2023; CRC Press: London, UK, 2023; pp. 149–156. [Google Scholar]
- Mills, R. Holbein Gardens: Delivering a Low-Carbon Structure with Reclaimed Steel. Struct. Eng. 2023, 101, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guggemos, A.; Plaut, J.; Bergstrom, E.; Gotthelf, H.; Haney, J.; Ozbek, M.E. Greening Structural Steel Design, Fabrication and Erection: A Case Study of the National Renewable Energy Laboratory. In Structures Congress 2010; American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE): Orlando, FL, USA, 2010; pp. 1393–1404. [Google Scholar]
- Seats, D.C.; Schultz, J.A.; Carstensen, J.V. Automatic Design Generation of Trusses from a Reused Steel Stock Library Using Graphic Statics. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 98, 111166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglund-Brown, J.; Ochsendorf, J. Reusing Heavy-Section Steel in Buildings: Carbon Reduction Potential and Material Availability. J. Archit. Eng. 2025, 31, 04025020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nußholz, J.L.K.; Nygaard Rasmussen, F.; Milios, L. Circular Building Materials: Carbon Saving Potential and the Role of Business Model Innovation and Public Policy. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 141, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Najjar, A.; Malmqvist, T. Embodied Carbon Saving of Reusing Concrete Elements in New Buildings: A Swedish Pilot Study. Resour Conserv Recycl 2025, 212, 107930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglund-Brown, J. Structural Steel Reuse as a Cost-Effective Carbon Mitigation Strategy. Master’s Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, X.; Teng, Y.; Shen, G.Q.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Q. Comparative Analysis of Embodied Carbon Emissions in Steel and Concrete Modular Buildings. In Proceedings of the ICCREM 2024: ESG Development in the Construction Industry, Proceedings of the International Conference on Construction and Real Estate Management 2024, Guangzhou, China, 23–24 November 2024; pp. 1665–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vares, S.; Hradil, P.; Sansom, M.; Ungureanu, V. Economic Potential and Environmental Impacts of Reused Steel Structures. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2020, 16, 750–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, J.; Walbridge, S.; Haas, C. Life Cycle Analysis Of Structural Steel Reuse Using The Economic Input-Output Method. In Proceedings of the 5th International/11th Construction Specialty Conference, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 7–10 June 2015; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, C.; Hammond, G. Embodied Carbon-the ICE Database; Circular Ecology and University of Bath: Bath, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, H.; Chen, Q.; García De Soto, B.; Arashpour, M. Using BIM and LCA to Evaluate Material Circularity: Contributions to Building Design Improvements. In Proceedings of the 39th International Symposium on Automation and Robotics in Construction, Bogotá, Colombia, 13–15 July 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Jalaei, F.; Zoghi, M.; Khoshand, A. Life Cycle Environmental Impact Assessment to Manage and Optimize Construction Waste Using Building Information Modeling (BIM). Int. J. Constr. Manag. 2021, 21, 784–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, D.; Markopoulou, A.; Marengo, M.; Neri, I.; Chronis, A.; De Wolf, C. Enabling Component Reuse from Existing Buildings through Machine Learning, Using Google Street View to Enhance Building Databases. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Computer-Aided Architectural Design Research in Asia (CAADRIA 2022), Sydney, Australia, 9–15 April 2022; Volume 2, pp. 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonca, P.; Vieira, C. Embodied Carbon and Economic Cost Analysis of a Contemporary House Design Using Local and Reused Materials. Sustain. Futures 2022, 4, 100100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertin, I.; Lebrun, F.; Braham, N.; Le Roy, R. Construction, Deconstruction, Reuse of the Structural Elements: The Circular Economy to Reach Zero Carbon. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 323, 012020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, J. Development of Analysis Tools for the Facilitation of Increased Structural Steel Reuse. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, ON, Canada, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- WRAP. Designing out Waste: A Design Team Guide for Buildings; WRAP: Banbury, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Moraga, G.; Huysveld, S.; Mathieux, F.; Blengini, G.A.; Alaerts, L.; Van Acker, K.; de Meester, S.; Dewulf, J. Circular Economy Indicators: What Do They Measure? Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 146, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, D.R.; Skelton, A.C.H.; Moynihan, M.C.; Allwood, J.M. Component Level Strategies for Exploiting the Lifespan of Steel in Products. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2014, 84, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.; Elmasoudi, I.; Ghannam, M. Life Cycle Environmental Impact Assessment of Steel Structures Using Building Information Modeling. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 2025, 10, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küpfer, C.; Bertola, N.; Brütting, J.; Fivet, C. Decision Framework to Balance Environmental, Technical, Logistical, and Economic Criteria When Designing Structures With Reused Components. Front. Sustain. 2021, 2, 689877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, D.R.; Allwood, J.M. Reusing Steel and Aluminum Components at End of Product Life. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 10334–10340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 8501-1:2007; Preparation of Steel Substrates Before Application of Paints and Related Products—Visual Assessment of Surface Cleanliness—Part 1: Rust Grades and Preparation Grades of Uncoated Steel Substrates and of Steel Substrates After Overall Removal of Previous Coatings. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007.
- EN 1993-1-1:2005 + A1:2014; Eurocode 3: Design of Steel Structures—Part 1-1: General Rules and Rules for Buildings. European Committee for Standardization (CEN): Brussels, Belgium, 2014.
- ASTM E8/E8M-22; Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022. [CrossRef]
- BS EN 1993-1-6; Eurocode 3. Design of Steel Structures—Strength and Stability of Shell Structures. British Standards Institution: London, UK, 2025; ISBN 978 0 539 19303 9.
- Kirchherr, J.; Yang, N.H.N.; Schulze-Spüntrup, F.; Heerink, M.J.; Hartley, K. Conceptualizing the Circular Economy (Revisited): An Analysis of 221 Definitions. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 194, 107001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchherr, J.; van Santa, R. Research on the Circular Economy: A Critique of the Field. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 151, 104480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odenbreit, C.; Yang, J.; Kozma, A.; Romero, A.; Popa, N.; Hanus, F.; Obiala, R. Design for Disassembling, Reuse, and the Circular Economy: A Demonstration Building, “Petite Maison. ” ce/papers 2023, 6, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertin, I.; Saadé, M.; Le Roy, R.; Jaeger, J.M.; Feraille, A. Environmental Impacts of Design for Reuse Practices in the Building Sector. J. Clean Prod. 2022, 349, 131228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.M.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, K.; Lam, D.; Guo, W.; Li, L.; Ajayebi, A.; Hopkinson, P. Reclaiming Structural Steels from the End of Service Life Composite Structures for Reuse—An Assessment of the Viability of Different Methods. Dev. Built Environ. 2022, 10, 100077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, B.C.; Leite, F.; Faust, K.M. 4D-BIM to Enhance Construction Waste Reuse and Recycle Planning: Case Studies on Concrete and Drywall Waste Streams. Waste Manag. 2020, 116, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj, S.; Chan, T.M. Recommendations for Implementing Circular Economy in Construction: Direct Reuse of Steel Structures. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2024, 214, 108439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gharib, S.; Moselhi, O. A Conceptual Framework for Enabling Structural Steel Reuse Utilizing Circular Economy in Modular Construction. Sustainability 2025, 17, 8945. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17198945
Gharib S, Moselhi O. A Conceptual Framework for Enabling Structural Steel Reuse Utilizing Circular Economy in Modular Construction. Sustainability. 2025; 17(19):8945. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17198945
Chicago/Turabian StyleGharib, Shrouk, and Osama Moselhi. 2025. "A Conceptual Framework for Enabling Structural Steel Reuse Utilizing Circular Economy in Modular Construction" Sustainability 17, no. 19: 8945. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17198945
APA StyleGharib, S., & Moselhi, O. (2025). A Conceptual Framework for Enabling Structural Steel Reuse Utilizing Circular Economy in Modular Construction. Sustainability, 17(19), 8945. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17198945






