Dynamic Changes in Dew Amount in Southern Slope of Boluohuoluo Mountain, Middle Tianshan Mountains
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
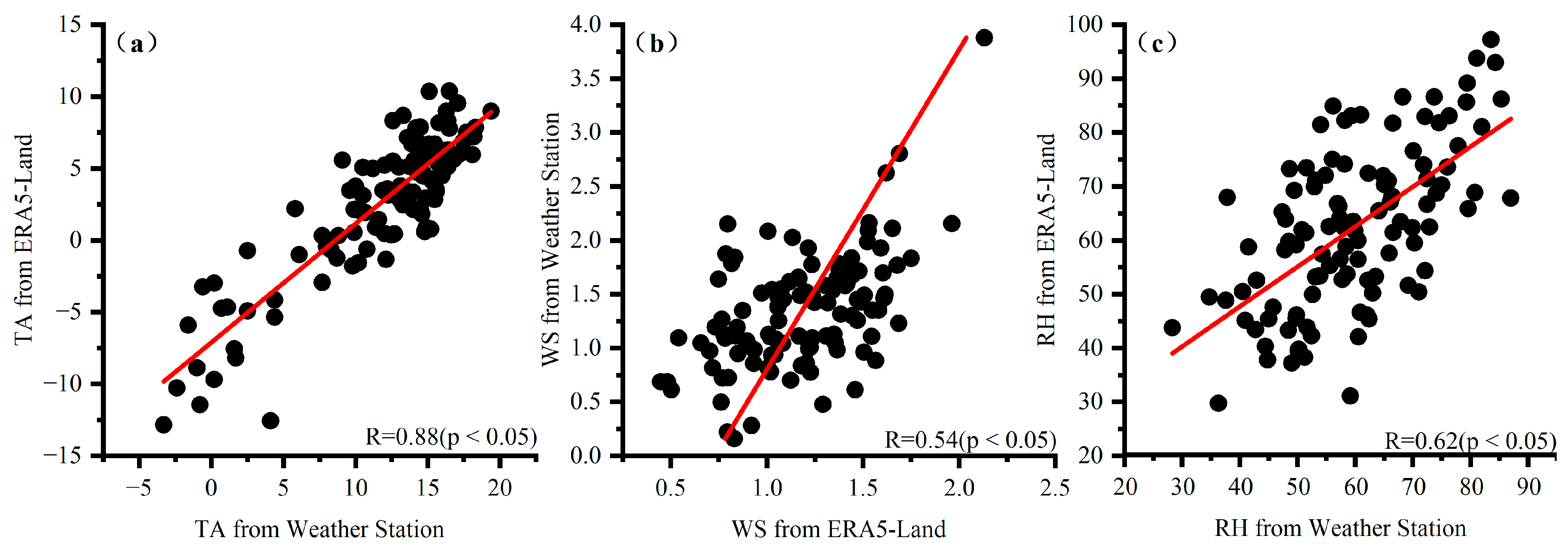
2.2. Data
2.3. Random Forest Model
2.4. Analysis of the Trend of Estimated Dew Amount
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Monthly Dew Amount Statistics
3.2. Long Term Changes in Dew Amount from June to October
4. Discussion
4.1. Historical Dew Amount
4.2. Trend of Model Input Variables
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gerlein-Safdi, C.; Koohafkan, M.C.; Chung, M.; Rockwell, F.E.; Thompson, S.; Caylor, K.K. Dew deposition suppresses transpiration & carbon uptake in leaves. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 259, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuure, J.; Korpela, A.; Hautala, M.; Hakojärvi, M.; Mikkola, H.; Räsänen, M.; Duplissy, J.; Pellikka, P.; Petäjä, T.; Kulmala, M. Comparison of surface foil materials & dew collectors location in an arid area: A one-year field experiment in Kenya. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 276–277, 107613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groh, J.; Slawitsch, V.; Herndl, M.; Graf, A.; Vereecken, H.; Pütz, T. Determining dew and hoar frost formation for a low mountain range and alpine grassland site by weighable lysimeter. J. Hydrol. 2018, 563, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, A.J.; Lincoln, N.K.; Rachmilevitch, S.; Shelef, O. Modified Hiltner Dew Balance to Re-Estimate Dewfall Accumulation as a Reliable Water Source in the Negev Desert. Water 2020, 12, 2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.J.; Zhang, L.X.; Chen, Q.; Ma, Z.Y.; Wang, H.; Shangguan, Z.J.; Wang, L.X.; He, J.S. Dew formation reduction in global warming experiments and the potential consequences. J. Hydrol. 2021, 593, 125819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Hao, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y. Populus euphratica counteracts drought stress through the dew coupling and root hydraulic redistribution processes. Ann. Bot. 2023, 131, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, Z.; Li, L.; Qin, S.; Zhang, Y. Foliar water uptake of four shrub species in a semi-arid desert. J. Arid Environ. 2021, 195, 104629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, G.; Yasutake, D.; Minami, K.; Kimura, K.; Marui, A.; Yueru, W.; Feng, J.; Wang, W.; Mori, M.; Kitano, M. Evaluation of the physiological significance of leaf wetting by dew as a supplemental water resource in semi-arid crop production. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 255, 106964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.J.; Li, S.; Li, Y. Leaf water uptake strategy of desert plants in the Junggar Basin, China. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2011, 35, 893. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Ratcliffe, S. Relationship between dew presence & Bassia dasyphylla plant growth. J. Arid Land 2012, 4, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, X.; Li, C.; Guo, B.; Ma, J.; Ayup, M.; Chen, Z. Dew formation & its long-term trend in a desert riparian forest ecosystem on the eastern edge of the Taklimakan Desert in China. J. Hydrol. 2012, 472–473, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Zhao, W. Dew formation and its variation in Haloxylon ammodendron plantations at the edge of a desert oasis, Northwestern China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 247, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, G.; Zhang, H.; Gao, D.; Fei, H.; Guo, C.; Ren, M.; Liu, Y. Controlled condensation by liquid contact-induced adaptations of molecular conformations in self-assembled monolayers. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Elumalai, S.P.; Chand, S.; Rout, P.R. Assessment of dew harvesting as a sustainable water source and air quality indicator: A case study of Dhanbad, Jharkhand, India. Environ. Technol. 2024, 46, 2123–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Wu, L.; Ai, S.; Guo, Z.; Liu, W. Bionic collection system for fog-dew harvesting inspired from desert beetle. Nano Today 2023, 52, 101979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, M.; Sun, J.; Liu, M.; Du, B.; Liu, Y.; Jin, Y.; Wen, R.; Lan, Z.; Zhou, X.; et al. Rapid and Persistent Suction Condensation on Hydrophilic Surfaces for High-Efficiency Water Collection. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 7411–7418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagar, A.; Kumar, R.; Srikrishnarka, P.; Thomas, T.; Pradeep, T. Scalable Drop-to-Film Condensation on a Nanostructured Hierarchical Surface for Enhanced Humidity Harvesting. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 1540–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, S.; Yang, F.-L.; Yue, P.; Yao, T.; Wang, W.-Y. Characteristics of Dew Formation and Distribution, and Its Contribution to the Surface Water Budget in a Semi-arid Region in China. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2015, 154, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beysens, D. Estimating dew yield worldwide from a few meteo data. Atmos. Res. 2016, 167, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atashi, N.; Tuure, J.; Alakukku, L.; Rahimi, D.; Pellikka, P.; Zaidan, M.A.; Vuollekoski, H.; Räsänen, M.; Kulmala, M.; Vesala, T.; et al. An Attempt to Utilize a Regional Dew Formation Model in Kenya. Water 2021, 13, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwagata, T.; Maruyama, A.; Kondo, J.; Watanabe, T. Theoretical Study on Dew Formation in Plant Canopies Based on a One-Layer Energy-Balance Model. Agric. Forest Meteorol. 2024, 354, 109911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uclés, O.; Villagarcía, L.; Moro, M.J.; Canton, Y.; Domingo, F. Role of dewfall in the water balance of a semiarid coastal steppe ecosystem. Hydrol. Process. 2013, 28, 2271–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekouch, I.; Lekouch, K.; Muselli, M.; Mongruel, A.; Kabbachi, B.; Beysens, D. Rooftop dew, fog & rain collection in southwest Morocco & predictive dew modeling using neural networks. J. Hydrol. 2012, 448–449, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Luo, G.; Hellwich, O.; Chen, C.; Zhang, W.; Xie, M.; He, H.; Shi, H.; Wang, Y. A framework for estimating actual evapotranspiration at weather stations without flux observations by combining data from MODIS & flux towers through a machine learning approach. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 127047. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, T.; Li, X.; Jia, R.; Feng, L. A novel integrated method based on a machine learning model for estimating evapotranspiration in dryland. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 126881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Guo, Z.; Liu, S.; He, X.; Meng, Y.; Xu, Z.; Xia, Y.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Y.; et al. Evaluating different machine learning methods for upscaling evapotranspiration from flux towers to the regional scale. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 8674–8690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, F.; Du, Y.; Cao, G.; Wang, B.; Guo, X. Seasonal variations and sources of the dew from stable isotopes in alpine meadows. Hydrol. Process. 2023, 37, e14977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Jiao, W.; Beysens, D.; Kaseke, K.F.; Medici, M.-G.; Li, F.; Wang, L. Investigating the role of evaporation in dew formation under different climates using O-17-excess. J. Hydrol. 2021, 592, 125847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, Q. Atmospheric physical characteristics of dew formation in semi-arid loess plateau. Acta Phys. Sin. 2011, 60, 059203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Huang, F.; Zhu, S.; Bu, L.; Qi, Z.; Li, L. Dew amount and its long-term variation in the Kunes River Valley, Northwest China. J. Arid Land 2022, 14, 753–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-R.; Jia, R.-L.; Zhang, Z.-S.; Zhang, P.; Hui, R. Hydrological response of biological soil crusts to global warming: A ten-year simulative study. Glob. Change Biol. 2018, 24, 4960–4971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Zhao, W. Dew variability in three habitats of a sand dune transect in a desert oasis ecotone, Northwestern China. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 1399–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.W.; Zhang, S.Y.; Luo, Z.N.; Fan, T.W. Relationship between production performance and rainfall in desert steppe of Nileke County, Xinjiang. Grass Fed Livest. 2021, 4, 26–32. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.J. How to leverage the positive climate conditions of Nileke County to promote agricultural production. China Agric. Inf. 2013, 1, 102. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bian, Y.W.; Mu, C.H.; Wang, Z.M. Analysis of the development status of modern agriculture in Nileke County. Xinjiang Agric. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 6–8. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Li, J.W.; Luo, Z.N. Study on the changes of grassland productivity in desert steppe of Nileke County. Xinjiang Anim. Husb. 2016, 11, 26, 60–61. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Li, J.W.; Luo, Z.N. Study on the changes of grassland productivity in grazing prohibition areas of Nileke County: A case of temperate meadow steppe. Xinjiang Anim. Husb. 2020, 35, 41–46. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration—Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements; FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, F.; Feng, T.; Guo, Z.; Li, L. Impact of Winter Snowfall on Vegetation Greenness in Central Asia. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biau, G.; Scornet, E. A random forest guided tour. Test 2016, 25, 197–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gocic, M.; Trajkovic, S. Analysis of changes in meteorological variables using Mann-Kendall and Sen’s slope estimator statistical tests in Serbia. Glob. Planet. Change 2013, 100, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Tang, D.; Wang, T.; Wang, M.; Wagan, B. Precipitation trends over time using Mann-Kendall and spearman’s rho tests in swat river basin, Pakistan. Adv. Meteorol. 2015, 2015, 431860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Month | Temporal Stage | |Z| | β | Trend |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| June–October | 1970–2022 | 2.67 | 0 | No significant trend |
| 1970–1986 | 1.06 | −0.01 | Decrease | |
| 1986–2004 | 1.43 | 0 | No significant trend | |
| 2004–2022 | 3.67 | −0.01 | Significantly decrease | |
| June | 1970–2022 | 1.89 | −0.01 | Decrease |
| 1979–1986 | 0.37 | −0.05 | Decrease | |
| 1986–2004 | 0.42 | 0.01 | Increase | |
| 2004–2022 | 1.54 | −0.02 | Decrease | |
| July | 1970–2022 | 1.43 | −0.01 | Decrease |
| 1979–1986 | 0 | 0 | No significant trend | |
| 1986–2004 | 1.12 | 0.01 | Increase | |
| 2004–2022 | 1.19 | −0.01 | Decrease | |
| August | 1970–2022 | 0.3 | 0 | No significant trend |
| 1979–1986 | 0.37 | −0.02 | Decrease | |
| 1986–2004 | 1.68 | 0.03 | Increase | |
| 2004–2022 | 0.7 | −0.01 | Decrease | |
| September | 1970–2022 | 2.48 | −0.01 | Significantly decrease |
| 1979–1986 | 1.11 | −0.04 | Decrease | |
| 1986–2004 | 0.14 | 0 | No significant trend | |
| 2004–2022 | 2.24 | −0.05 | Significantly decrease | |
| October | 1970–2022 | 0.04 | 0 | No significant trend |
| 1979–1986 | 0.87 | −0.08 | Decrease | |
| 1986–2004 | 0.35 | 0 | No significant trend | |
| 2004–2022 | 3.15 | −0.08 | Significantly decrease |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tu, C.; Wang, W.; Wang, F.; Gong, P. Dynamic Changes in Dew Amount in Southern Slope of Boluohuoluo Mountain, Middle Tianshan Mountains. Sustainability 2025, 17, 8931. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17198931
Tu C, Wang W, Wang F, Gong P. Dynamic Changes in Dew Amount in Southern Slope of Boluohuoluo Mountain, Middle Tianshan Mountains. Sustainability. 2025; 17(19):8931. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17198931
Chicago/Turabian StyleTu, Chenwei, Wanrui Wang, Feng Wang, and Peiyao Gong. 2025. "Dynamic Changes in Dew Amount in Southern Slope of Boluohuoluo Mountain, Middle Tianshan Mountains" Sustainability 17, no. 19: 8931. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17198931
APA StyleTu, C., Wang, W., Wang, F., & Gong, P. (2025). Dynamic Changes in Dew Amount in Southern Slope of Boluohuoluo Mountain, Middle Tianshan Mountains. Sustainability, 17(19), 8931. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17198931






