Designing Sustainable Urban Green Spaces: Audio-Visual Interaction for Psychological Restoration
Abstract
1. Introduction
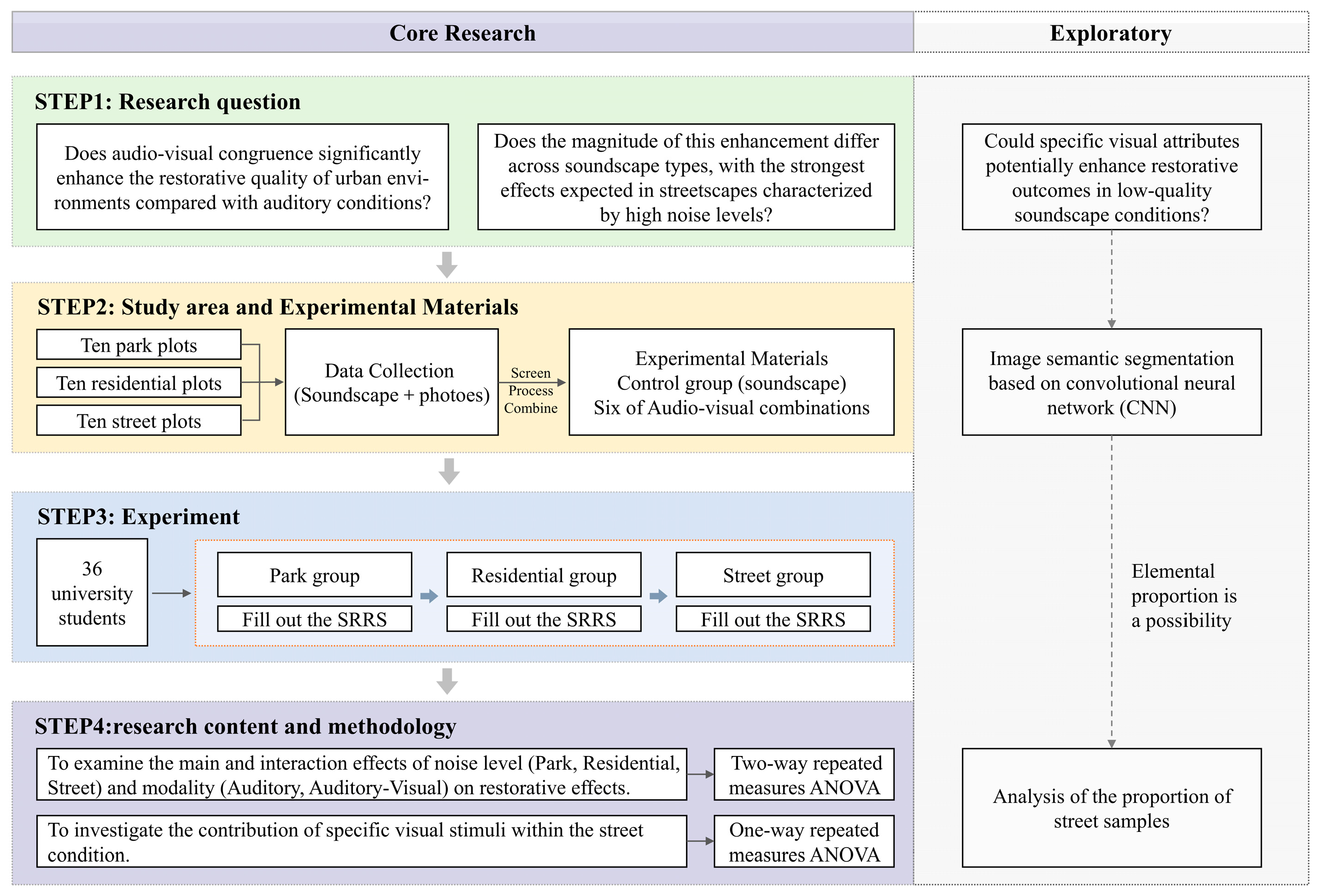
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
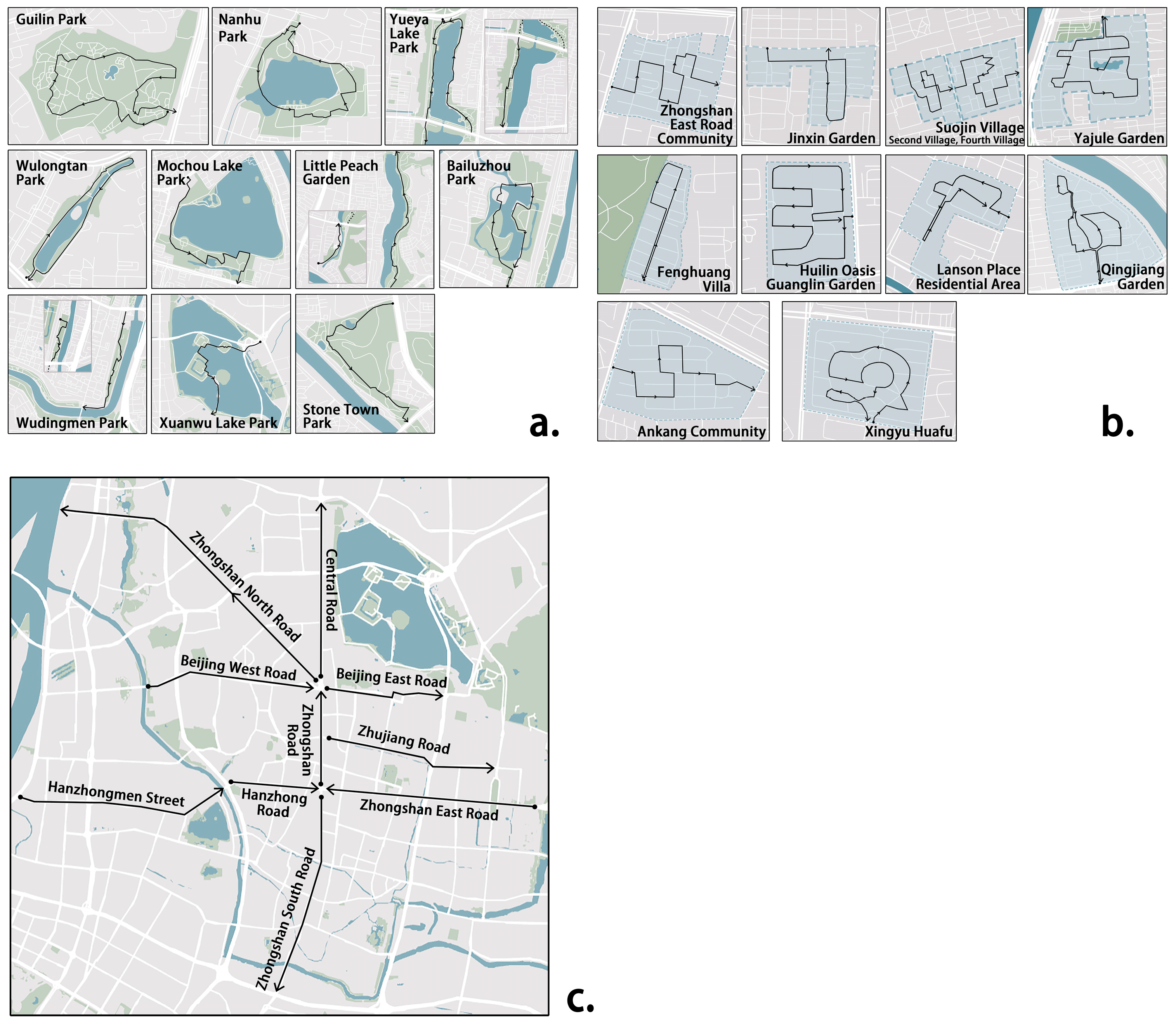
2.2. Site Selection and Survey Design
2.3. Experimental Materials
2.3.1. Soundscape Materials
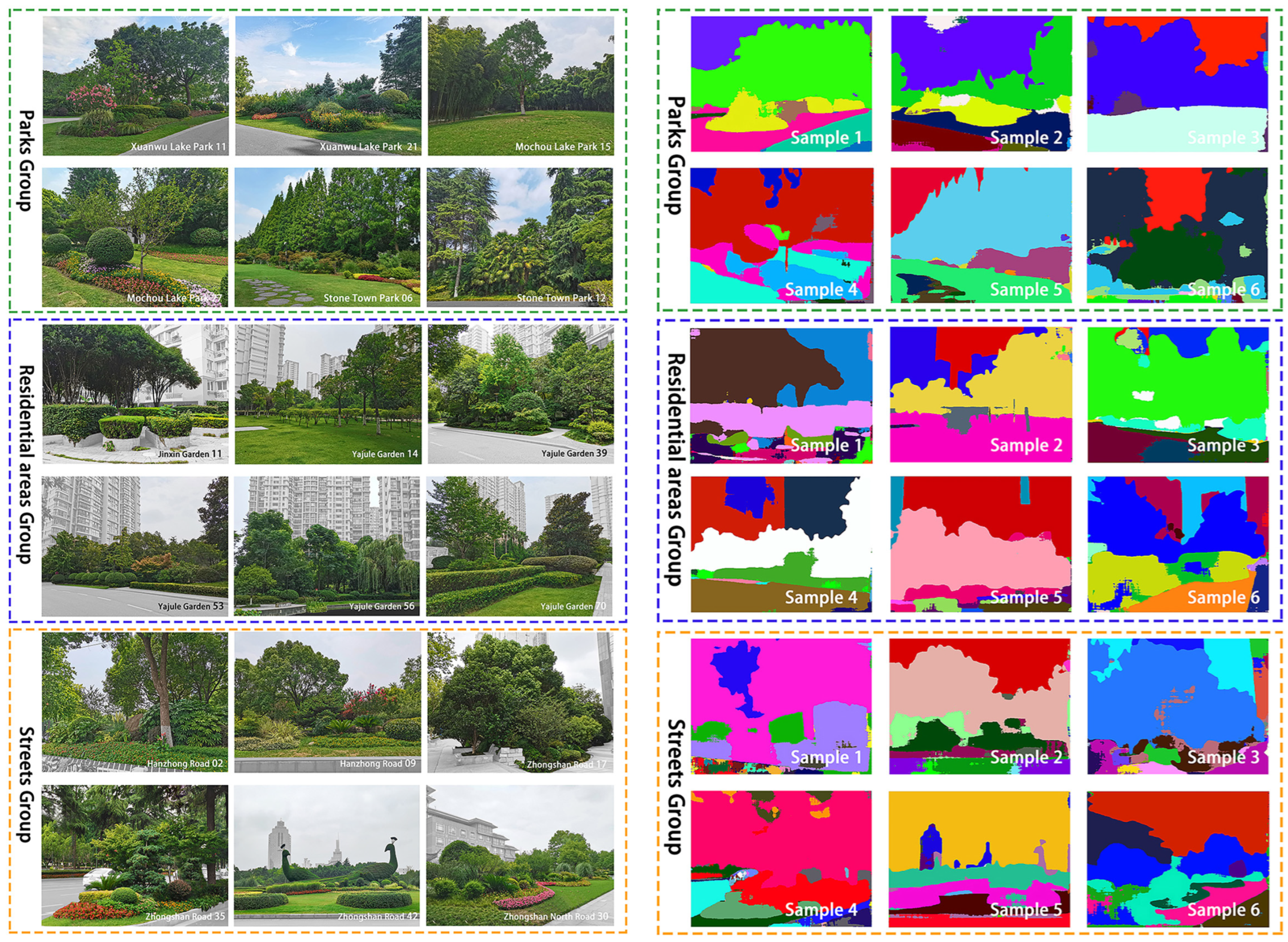
2.3.2. Visual and Audio-Visual Combination Materials
2.4. Evaluation Methodology and Instruments
2.4.1. Evaluation Method
2.4.2. Evaluation Scale
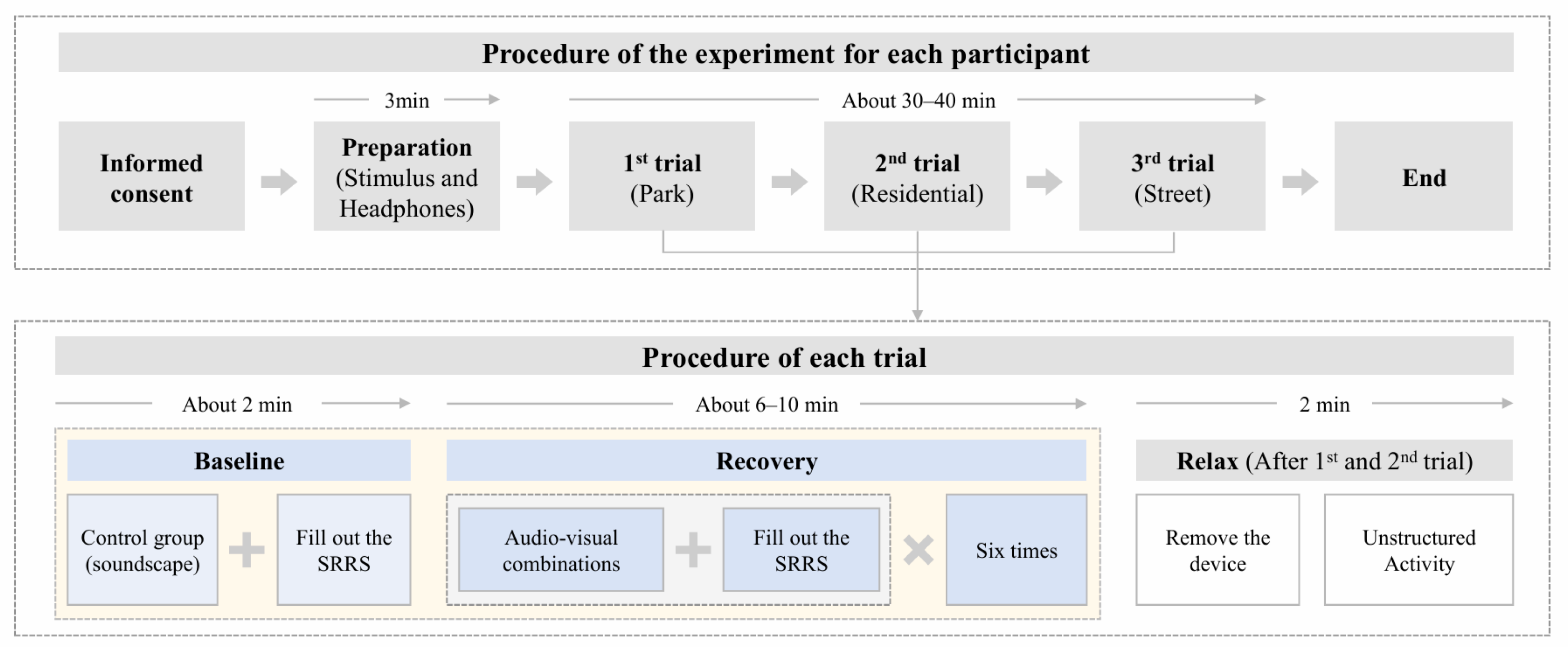
2.5. Experimental Procedure
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
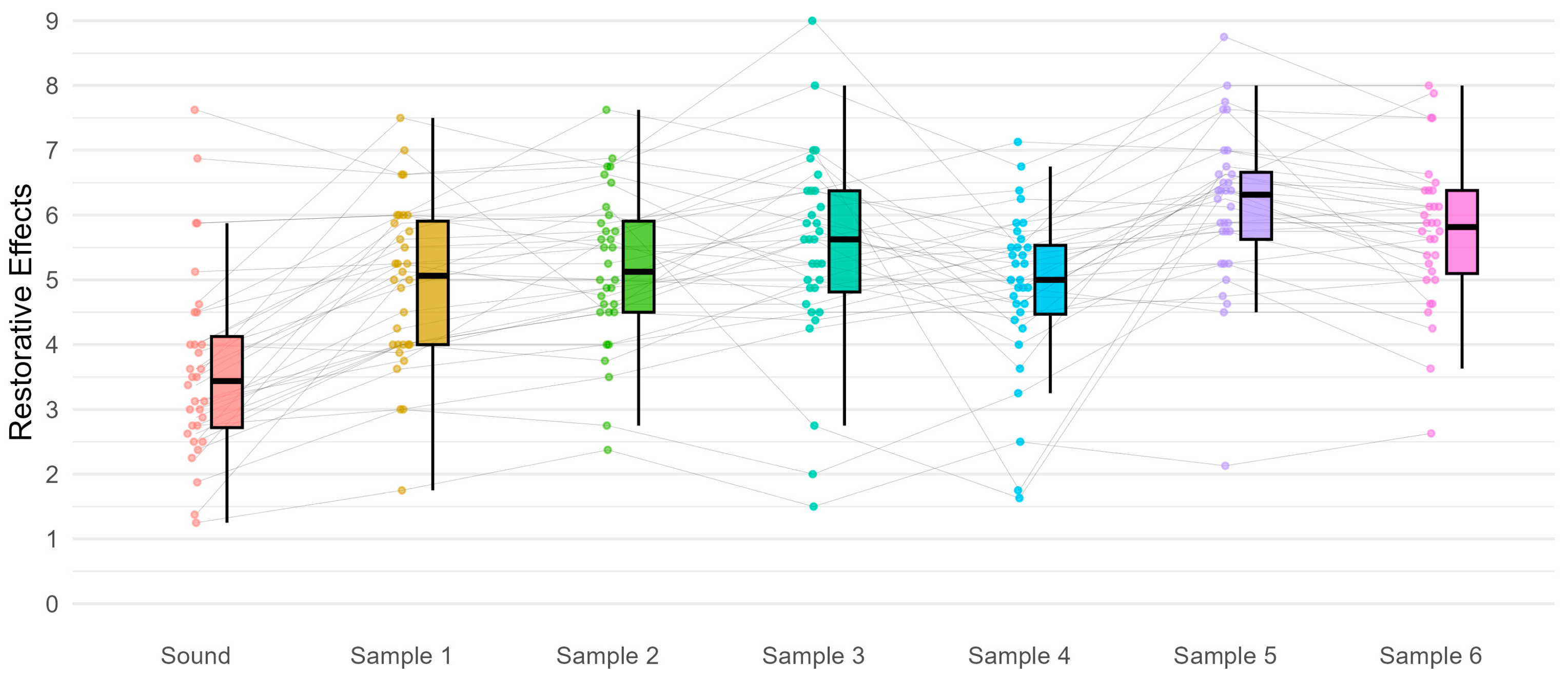
3.1. The Role of Noise Levels and Modality in Restorative Effects
3.2. Follow-Up Analysis: Effects of Visual Stimuli in the Street Condition
4. Discussion
4.1. Overall Effects of Audiovisual Interaction
4.2. Compensatory Role of Visual Elements Across Soundscapes
4.3. Limitations
4.4. Future Research
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1
| Type of Green Space | No. | Name of Sample Site | District |
|---|---|---|---|
| Park Green Space | 01 | Xuanwu Lake Park | Xuanwu District |
| 02 | Stone Town Park | Gulou District | |
| 03 | Little Peach Garden | Gulou District | |
| 04 | Gulin Park | Gulou District | |
| 05 | Wulongtan Park | Gulou District | |
| 06 | Bailuzhou Park | Qinhuai District | |
| 07 | Yueya Lake Park | Qinhuai District | |
| 08 | Wudingmen Park | Qinhuai District | |
| 09 | Mochou Lake Park | Jianye District | |
| 10 | Nanhu Park | Jianye District | |
| Residential Green Space | 01 | Suojin Village (Second Village, Fourth Village) | Xuanwu District |
| 02 | Fenghuang Villa | Xuanwu District | |
| 03 | Jinxin Garden | Gulou District | |
| 04 | Huilin Oasis Guanglin Garden | Gulou District | |
| 05 | Qingjiang Garden | Gulou District | |
| 06 | Yajule Garden | Qinhuai District | |
| 07 | Langshi Xiyuan | Qinhuai District | |
| 08 | Zhongshan East Road Community | Qinhuai District | |
| 09 | Xingyu Huafu | Jianye District | |
| 10 | Ankang Community | Jianye District | |
| Street Green Space | 01 | Zhongshan Road | Xuanwu District |
| 02 | Beijing East Road | Xuanwu District | |
| 03 | Zhujiang Road | Xuanwu District | |
| 04 | Zhongshan North Road | Gulou District | |
| 05 | Beijing West Road | Gulou District | |
| 06 | Hanzhong Road | Qinhuai District | |
| 07 | Zhongshan South Road | Qinhuai District | |
| 08 | Central Road | Between Xuanwu and Gulou Districts | |
| 09 | Zhongshan East Road | Between Xuanwu and Qinhuai Districts | |
| 10 | Hanzhongmen Street | Between Gulou and Jianye Districts |
Appendix A.2
| Filename | Unknown | Wall | Building | Sky | Floor | Tree | Road | Grass | Sidewalk | Person |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample1 | 7.64% | 0.43% | 0.96% | 8.02% | 0.01% | 56.27% | 0.00% | 0.22% | 0.00% | 0.00% |
| Sample2 | 6.50% | 5.45% | 0.00% | 21.96% | 0.00% | 40.80% | 0.01% | 4.86% | 0.00% | 0.00% |
| Sample3 | 5.39% | 3.33% | 2.61% | 11.90% | 0.64% | 55.16% | 0.00% | 0.36% | 6.64% | 0.11% |
| Sample4 | 3.04% | 2.33% | 0.00% | 1.57% | 0.00% | 56.15% | 4.52% | 5.86% | 1.84% | 0.00% |
| Sample5 | 3.54% | 0.08% | 3.17% | 50.48% | 0.00% | 13.32% | 8.06% | 8.27% | 0.00% | 0.00% |
| Sample6 | 4.47% | 0.00% | 10.06% | 32.93% | 0.00% | 21.38% | 0.02% | 9.38% | 5.89% | 0.00% |
| Filename | Ground | Table | Plant | Chair | Car | Couch | House | Mirror | Field | Fence |
| Sample1 | 0.67% | 0.17% | 20.69% | 0.83% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.81% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.78% |
| Sample2 | 0.00% | 0.00% | 11.91% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.82% |
| Sample3 | 1.54% | 0.00% | 6.05% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.23% | 0.00% | 0.00% |
| Sample4 | 0.00% | 0.00% | 14.94% | 0.00% | 0.14% | 0.18% | 0.06% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.04% |
| Sample5 | 0.00% | 0.00% | 11.81% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.01% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% |
| Sample6 | 0.00% | 0.00% | 11.92% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.01% | 0.00% |
| Filename | Rock | Railroad | Base | Column | Sand | Skyscraper | Path | Stairs | Flower | Palm |
| Sample1 | 0.00% | 0.43% | 0.17% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.02% | 0.10% | 0.88% | 0.10% |
| Sample2 | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.39% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 5.54% | 0.00% | 1.42% | 0.24% |
| Sample3 | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.04% | 0.03% | 0.00% | 1.99% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% |
| Sample4 | 0.34% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.05% | 0.00% | 5.85% | 2.62% |
| Sample5 | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.12% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.34% | 0.06% |
| Sample6 | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.03% | 0.00% | 2.82% | 1.02% |
| Filename | Towers | Awnings | Streetlights | Poles | Railings | Fountains | Awnings | Steps | Planters | Sculptures |
| Sample1 | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.02% | 0.08% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% |
| Sample2 | 0.01% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.07% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% |
| Sample3 | 2.78% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.04% | 0.00% | 0.78% | 0.08% | 0.16% | 0.04% | 0.01% |
| Sample4 | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.04% | 0.39% | 0.00% | 0.02% | 0.00% | 0.04% |
| Sample5 | 0.73% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% |
| Sample6 | 0.00% | 0.01% | 0.01% | 0.05% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% |
References
- Southworth, M. The Sonic Environment of Cities. Environ. Behav. 1969, 1, 49–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carles, J.L.; Barrio, I.L.; de Lucio, J.V. Sound Influence on Landscape Values. Landsc. Urban Plan. 1999, 43, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torresin, S.; Pernigotto, G.; Cappelletti, F.; Gasparella, A. Combined Effects of Environmental Factors on Human Perception and Objective Performance: A Review of Experimental Laboratory Works. Indoor Air 2018, 28, 525–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carles, J.; Bernáldez, F.; Lucio, J.D. Audio-visual Interactions and Soundscape Preferences. Landsc. Res. 1992, 17, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.Y.; Jeon, J.Y. Designing Sound and Visual Components for Enhancement of Urban Soundscapes. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2013, 134, 2026–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irvine, K.N.; Devine-Wright, P.; Payne, S.R.; Fuller, R.A.; Painter, B.; Gaston, K.J. Green Space, Soundscape and Urban Sustainability: An Interdisciplinary, Empirical Study. Local Environ. 2009, 14, 155–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, S.R. The Production of a Perceived Restorativeness Soundscape Scale. Appl. Acoust. 2013, 74, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barclay, L. Augmenting Urban Space with Environmental Soundscapes and Mobile Technologies. Acoust. Ecol. Rev. 2017, 16, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Renterghem, T.; Vanhecke, K.; Filipan, K.; Sun, K.; De Pessemier, T.; De Coensel, B.; Joseph, W.; Botteldooren, D. Interactive Soundscape Augmentation by Natural Sounds in a Noise Polluted Urban Park. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2020, 194, 103705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobianchi, M.; Drever, J.L.; Lavia, L. Adaptive Soundscape Design for Liveable Urban Spaces: A Hybrid Methodology across Environmental Acoustics and Sonic Art. Cities Health 2021, 5, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, R.; Kaplan, S. The Experience of Nature: A Psychological Perspective; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1989; pp. 7–340. ISBN 978-0-521-34139-4. [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich, R.S. Aesthetic and Affective Response to Natural Environment. Hum. Behav. Environ. Adv. Theory Res. 1983, 6, 85–125. [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich, R.S. Human Responses to Vegetation and Landscapes. Landsc. Urban Plan. 1986, 13, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Renterghem, T. Towards Explaining the Positive Effect of Vegetation on the Perception of Environmental Noise. Urban For. Urban Green. 2019, 40, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, L. Audio-Visual Analysis of Visitors’ Landscape Preference for City Parks: A Case Study from Zhangzhou, China. Forests 2022, 13, 1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viollon, S.; Lavandier, C.; Drake, C. Influence of Visual Setting on Sound Ratings in an Urban Environment. Appl. Acoust. 2002, 63, 493–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, C.S.R. Designing Landscapes for Psychological Restoration: Adding Considerations of Sound. Master’s Thesis, University of Guelph, Guelph, ON, Canada, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, Y.; Meng, Q.; Li, M.; Yang, D.; Wu, Y. Using Soundscape Diversity to Interpret Soundscape Evaluation in Urban Green Spaces—Relationship, Integration, and Application. Urban For. Urban Green. 2024, 97, 128371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamps, A.E. Demographic Effects in Environmental Aesthetics: A Meta-Analysis. J. Plan. Lit. 1999, 14, 155–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhu, X.; Xu, Y.; Yang, H.; Wu, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y. Assessing the Visual Quality of Green Landscaping in Rural Residential Areas: The Case of Changzhou, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 951–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. The Study of Urban Space SensationBased on the SD Method. Master’s Thesis, Tongji University, Shanghai, China, 2008. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.-G.; Buchner, A. G*power 3: A Flexible Statistical Power Analysis Program for the Social, Behavioral, and Biomedical Sciences. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 12913-1:2014; Acoustics—Soundscape—Part 1: Definition and Conceptual Framework. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014.
- ISO/TS 12913-2:2018; Acoustics—Soundscape—Part 2: Data Collection and Reporting Requirements. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018.
- Shibata, S.; Tokuhiro, K.; Ikeuchi, A.; Ito, M.; Kaji, H.; Muramatsu, M. Visual Properties and Perceived Restorativeness in Green Offices: A Photographic Evaluation of Office Environments with Various Degrees of Greening. Front. Psychol. 2024, 15, 1443540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Kim, E.J. Differences of Restorative Effects While Viewing Urban Landscapes and Green Landscapes. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Liang, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, P.; Bie, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, R.; Wang, J.; Guan, Q. A Human-Machine Adversarial Scoring Framework for Urban Perception Assessment Using Street-View Images. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2019, 33, 2363–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, D.J.; France, J. France Landscape Evaluation: A Comparative Study. J. Environ. Manag. 1980, 10, 263–275. [Google Scholar]
- Shuttleworth, S.; Shuttleworth, S. The Use of Photographs as an Environment Presentation Medium in Landscape Studies. J. Environ. Manage 1980, 11, 61–76. [Google Scholar]
- Arriaza, M.; Cañas-Ortega, J.F.; Cañas-Madueño, J.A.; Ruiz-Aviles, P. Assessing the Visual Quality of Rural Landscapes. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2004, 69, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañas, I.; Ayuga, E.; Ayuga, F. A Contribution to the Assessment of Scenic Quality of Landscapes Based on Preferences Expressed by the Public. Land Use Policy 2009, 26, 1173–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartig, T.; Böök, A.; Garvill, J.; Olsson, T.; Gärling, T. Environmental Influences on Psychological Restoration. Scand. J. Psychol. 1996, 37, 378–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pflüger, Y.; Rackham, A.; Larned, S. The Aesthetic Value of River Flows: An Assessment of Flow Preferences for Large and Small Rivers. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2010, 95, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Luo, P.; Wang, R.; Cai, Y. Correlations between Aesthetic Preferences of River and Landscape Characters. J. Environ. Eng. Landsc. Manag. 2013, 21, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seamon, D. A Geography of the Lifeworld (Routledge Revivals): Movement, Rest and Encounter; Routledge: London, UK, 2015; ISBN 978-1-315-71569-8. [Google Scholar]
- Han, K.-T. A Reliable and Valid Self-Rating Measure of the Restorative Quality of Natural Environments. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2003, 64, 209–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Li, Z.; Xuan, X.; Li, Q.; Shi, L.; Sun, X.; Zhu, K.; Shi, Y. Influence of Hospital Outdoor Rest Space on the Eye Movement Measures and Self-Rating Restoration of Staff. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 855857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, X.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, D.; Huang, Q.; Wang, M.; Dong, J. Quantitative Model Study of the Psychological Recovery Benefit of Landscape Environment Based on Eye Movement Tracking Technology. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neale, C.; Lopez, S.; Roe, J. Psychological Restoration and the Effect of People in Nature and Urban Scenes: A Laboratory Experiment. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaede, R. Validity in Image-Based Research: A Delphi Study. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Stellenbosch, Stellenbosch, South Africa, 1 December 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Mostajeran, F.; Krzikawski, J.; Steinicke, F.; Kühn, S. Effects of Exposure to Immersive Videos and Photo Slideshows of Forest and Urban Environments. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, J.F.; Hoffman, R.E. Rating Reliability and Representation Validity in Scenic Landscape Assessments. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2001, 54, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, N.G.; Lee, P.-J.; Imran, M.; Jeong, J.-H. Role of Sounds in Perception of Enclosure in Urban Street Canyons. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 90, 104394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Wei, P.; Wang, Q.; Sun, W.; Yuan, M.; Shao, S.; Zhu, D.; Xue, Y. The Effects of Audio-Visual Perceptual Characteristics on Environmental Health of Pedestrian Streets with Traffic Noise: A Case Study in Dalian, China. Front. Psychol. 2023, 14, 1122639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, L.E. On Cross-Modal Similarity: Auditory-Visual Interactions in Speeded Discrimination. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 1987, 13, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGurk, H.; MacDonald, J. Hearing Lips and Seeing Voices. Nature 1976, 264, 746–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radeau, M.; Bertelson, P. Adaptation to Auditory-Visual Discordance and Ventriloquism in Semirealistic Situations. Percept. Psychophys. 1977, 22, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, D.H.; McCarthy, T.J.; Welch, R.B. Discrepancy and Nondiscrepancy Methods of Assessing Visual-Auditory Interaction. Percept. Psychophys. 1983, 33, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, S.; Verheij, R.A.; Groenewegen, P.P.; Spreeuwenberg, P. Natural Environments—Healthy Environments? An Exploratory Analysis of the Relationship between Greenspace and Health. Environ. Plan. Econ. Space 2003, 35, 1717–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andringa, T.; van den Bosch, K. Core Affect and Soundscape Assessment: Fore- and Background Design for Quality of Life. In Proceedings of the Internoise 2013, Innsbruck, Austria, 15–18 September 2013. [Google Scholar]

| Category | No. | Name | Audio Total Duration | Natural Sound | Human Sound | Mechanical Sound | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duration | Proportion | Duration | Proportion | Duration | Proportion | ||||
| Park | 01 | Xuanwu Lake Park | 0:19:43 | 0:19:43 | 100% | 0:15:14 | 77% | 0:00:18 | 2% |
| 02 | Stone City Park | 0:17:09 | 0:17:09 | 100% | 0:05:13 | 30% | 0:02:27 | 14% | |
| 03 | Little Peach Garden | 0:27:04 | 0:27:04 | 100% | 0:13:20 | 49% | 0:02:32 | 9% | |
| 04 | Gulin Park | 0:26:45 | 0:26:45 | 100% | 0:13:15 | 50% | 0:03:10 | 12% | |
| 05 | Wulongtan Park | 0:39:04 | 0:39:04 | 100% | 0:27:26 | 70% | 0:04:41 | 12% | |
| 06 | Bailuzhou Park | 0:19:46 | 0:19:46 | 100% | 0:10:56 | 55% | 0:09:06 | 46% | |
| 07 | Yueya Lake Park | 0:37:19 | 0:37:19 | 100% | 0:33:01 | 88% | 0:08:33 | 23% | |
| 08 | Wudingmen Park | 0:17:58 | 0:17:58 | 100% | 0:09:41 | 54% | 0:02:02 | 11% | |
| 09 | Mochou Lake Park | 0:35:15 | 0:35:15 | 100% | 0:22:51 | 65% | 0:02:20 | 7% | |
| 10 | Nanhu Park | 0:23:43 | 0:23:43 | 100% | 0:22:38 | 95% | 0:04:27 | 19% | |
| Residential | 01 | Jinxin Garden | 0:19:43 | 0:19:43 | 100% | 0:03:02 | 15% | 0:01:38 | 8% |
| 02 | Suojin Second Village | 0:15:22 | 0:15:22 | 100% | 0:04:20 | 28% | 0:01:10 | 8% | |
| Suojin Fourth Village | 0:17:48 | 0:17:48 | 100% | 0:09:26 | 53% | 0:03:39 | 21% | ||
| 03 | Yajule Garden | 0:37:05 | 0:37:05 | 100% | 0:07:52 | 21% | 0:03:19 | 9% | |
| 04 | Fenghuang Villa | 0:14:54 | 0:14:54 | 100% | 0:03:11 | 21% | 0:02:33 | 17% | |
| 05 | Huilin Oasis Guanglin Garden | 0:13:32 | 0:13:32 | 100% | 0:04:53 | 36% | 0:02:41 | 20% | |
| 06 | Qingjiang Garden | 0:18:40 | 0:18:40 | 100% | 0:06:00 | 32% | 0:05:41 | 30% | |
| 07 | Langshi Xiyuan | 0:15:42 | 0:15:42 | 100% | 0:06:47 | 43% | 0:07:50 | 50% | |
| 08 | Zhongshan East Road Community | 0:08:30 | 0:08:30 | 100% | 0:01:07 | 13% | 0:00:54 | 11% | |
| 09 | Xingyu Huafu | 0:18:54 | 0:18:54 | 100% | 0:01:50 | 10% | 0:07:12 | 38% | |
| 10 | Ankang Community | 0:08:25 | 0:08:25 | 100% | 0:02:25 | 29% | 0:01:47 | 21% | |
| Street | 01 | Hanzhong Road | 0:22:09 | —— | —— | 0:04:26 | 20% | 0:22:09 | 100% |
| 02 | Zhongshan North Road | 0:45:10 | —— | —— | 0:05:58 | 13% | 0:45:10 | 100% | |
| 03 | Zhongshan Road | 0:23:49 | —— | —— | 0:04:50 | 20% | 0:23:49 | 100% | |
| 04 | Central Road | 0:26:55 | —— | —— | 0:08:42 | 32% | 0:26:55 | 100% | |
| 05 | Beijing East Road | 0:24:45 | —— | —— | 0:03:59 | 16% | 0:24:45 | 100% | |
| 06 | Beijing West Road | 0:19:41 | —— | —— | 0:01:33 | 8% | 0:19:41 | 100% | |
| 07 | Zhongshan East Road | 0:29:03 | —— | —— | 0:04:53 | 17% | 0:29:03 | 100% | |
| 08 | Zhongshan South Road | 0:12:22 | —— | —— | 0:03:09 | 25% | 0:12:22 | 100% | |
| 09 | Hanzhongmen Street | 0:28:38 | —— | —— | 0:04:39 | 16% | 0:28:38 | 100% | |
| 10 | Zhujiang Road | 0:27:14 | —— | —— | 0:05:13 | 19% | 0:27:14 | 100% | |
| Mean Difference | SE | t | Cohen’s d | Pholm | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sound | Sample 1 | −1.316 | 0.203 | −6.495 | −1.005 | <0.001 |
| Sample 2 | −1.559 | 0.229 | −6.816 | −1.189 | <0.001 | |
| Sample 3 | −1.820 | 0.225 | −8.098 | −1.389 | <0.001 | |
| Sample 4 | −1.252 | 0.232 | −5.394 | −0.956 | <0.001 | |
| Sample 5 | −2.514 | 0.247 | −10.179 | −1.918 | <0.001 | |
| Sample 6 | −2.109 | 0.231 | −9.139 | −1.609 | <0.001 | |
| Sample 1 | Sample 2 | −0.242 | 0.134 | −1.814 | −0.185 | 0.397 |
| Sample 3 | −0.504 | 0.167 | −3.010 | −0.385 | 0.041 | |
| Sample 4 | 0.064 | 0.272 | 0.235 | 0.049 | 0.815 | |
| Sample 5 | −1.198 | 0.145 | −8.272 | −0.914 | <0.001 | |
| Sample 6 | −0.792 | 0.164 | −4.833 | −0.605 | <0.001 | |
| Sample 2 | Sample 3 | −0.262 | 0.202 | −1.298 | −0.200 | 0.611 |
| Sample 4 | 0.306 | 0.272 | 1.127 | 0.234 | 0.611 | |
| Sample 5 | −0.955 | 0.163 | −5.870 | −0.729 | <0.001 | |
| Sample 6 | −0.550 | 0.120 | −4.572 | −0.420 | <0.001 | |
| Sample 3 | Sample 4 | 0.568 | 0.261 | 2.174 | 0.433 | 0.225 |
| Sample 5 | −0.694 | 0.172 | −4.030 | −0.529 | 0.003 | |
| Sample 6 | −0.288 | 0.194 | −1.486 | −0.220 | 0.590 | |
| Sample 4 | Sample 5 | −1.262 | 0.246 | −5.131 | −0.963 | <0.001 |
| Sample 6 | −0.856 | 0.225 | −3.800 | −0.653 | 0.006 | |
| Sample 5 | Sample 6 | 0.405 | 0.135 | 3.010 | 0.309 | 0.041 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, D.-W. Designing Sustainable Urban Green Spaces: Audio-Visual Interaction for Psychological Restoration. Sustainability 2025, 17, 8906. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17198906
Zhang H, Zhu Z, Zhang D-W. Designing Sustainable Urban Green Spaces: Audio-Visual Interaction for Psychological Restoration. Sustainability. 2025; 17(19):8906. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17198906
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Haoning, Zunling Zhu, and Da-Wei Zhang. 2025. "Designing Sustainable Urban Green Spaces: Audio-Visual Interaction for Psychological Restoration" Sustainability 17, no. 19: 8906. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17198906
APA StyleZhang, H., Zhu, Z., & Zhang, D.-W. (2025). Designing Sustainable Urban Green Spaces: Audio-Visual Interaction for Psychological Restoration. Sustainability, 17(19), 8906. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17198906







