A Multi-Layered, Progressive Model of Self-Driving Tourists’ Environmental Responsibility Behavior: Enriched Tourism Destination 6A Framework
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Self-Driving Tours
2.2. Environmental Responsibility Behavior
2.3. Tourism Destination 6A Framework
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Research Design
3.2. Research Site
3.3. Data Collection Administration
3.4. Data Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Open Coding
4.2. Axial Coding
4.3. Selective Coding
4.4. Theoretical Saturation Test
- (1)
- Adding five additional interviews during the later stage of coding (participants 21–25, including government officials, academics, industry practitioners, and local residents) to assess whether any new conceptual codes emerged.
- (2)
- Reanalyzing the frequencies and interrelationships of existing codes to confirm structural stability and coherence among the categories.
5. Discussion
5.1. Theoretical Contributions
- (1)
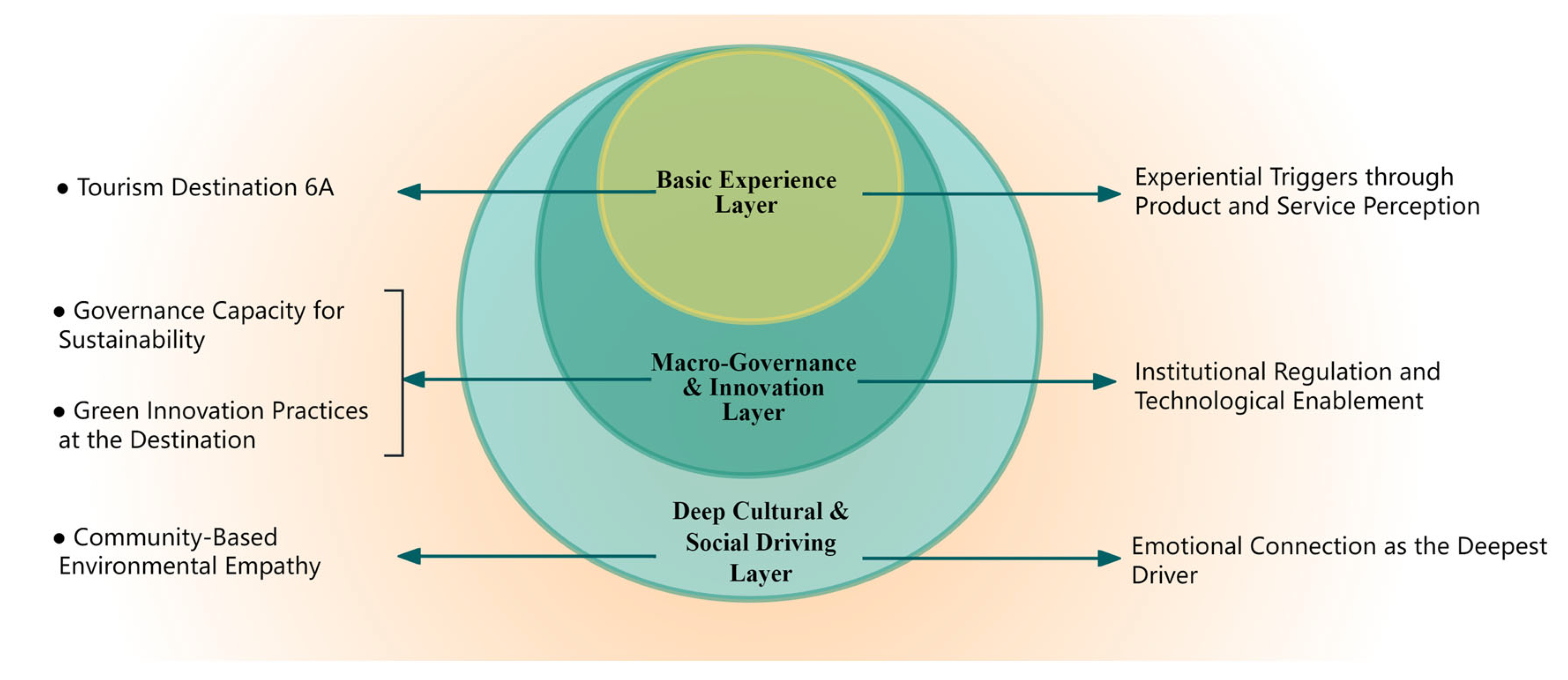
- Extending the 6A lens from triggers to a layered process. We position the classic 6A framework as the Basic Experience Layer that provides proximal experiential triggers but theorize that ERB becomes robust only when macro-governance structures and community-level culture/empathy are engaged. This reframes ERB formation from single-layer stimuli to a progressive, multi-layer process [69,74].
- (2)
- Articulating cross-level mechanisms and sequencing. We specify a three-step pathway—regulatory clarity → technological enablement → cultural internalization—that explains how destinations convert momentary pro-environmental intentions into enacted and persistent behaviors [29,70,71]. This sequencing operates through two complementary routes: an instrumental route that reduces price/friction via C1–C2, and a normative–affective route consolidated by C3. This sequencing aligns with recent findings on policy-supported PBC, low-friction digital nudges, and community contagion of ERB [69,70,71,73].
- (3)
- Boundary conditions for transferability. We propose that the effects are stronger under higher governance maturity, higher digital readiness, and stronger community cohesion. Recent studies corroborate that policy regimes and affect-laden experiences (e.g., awe) condition PEB formation [70,81]. These propositions invite future comparative tests across destination types and regulatory environments. Additionally, the influence of C3 is likely contingent on stakeholder alignment and perceived fairness within communities. Heterogeneous interests and power asymmetries can moderate empathy-driven pathways to ERB [77,80].
5.2. Practical Implications
- (1)
- Governance and capacity management. Destinations should pair clear rules with graduated enforcement (e.g., on-site guidance + soft penalties for first offenses) and implement capacity limits/time-phased reservations on sensitive sites. Such policy mixes are shown to narrow the intention–behavior gap and stabilize ERB [70].
- (2)
- Technological enablement (“design for low-effort green”). Deploy digital nudges in navigation and booking flows (default green routes/parking, refill prompts, waste-sorting cues), and use post-trip flashback nudges via chatbots to sustain spillover behaviors at home [71,72]. These tools specifically target friction and attentional limits that commonly block ERB enactment. Pair digital design with light economic instruments—deposit–refund, time-of-day/proximity parking fees, and micro-rewards in apps—to shift behavior with low burden [70,75,76].
- (3)
- Community-anchored empathy. Support programs where residents model visible PEB (e.g., attendant-led sorting, local volunteer crews) and micro-narratives that humanize ecosystem impacts; both mechanisms heighten empathy and pro-environmental atmosphere, which in turn lift tourists’ ERB [73,74]. Ethical guardrails (privacy, transparency, opt-out) should accompany all digital interventions. On the other hand, map stakeholders and salience; co-design programs with residents and SMEs; specify benefit-sharing and rotate volunteer workloads; and establish low-friction grievance and feedback channels. Such participatory and meta-governance measures help manage conflict and sustain community-anchored empathy [78,79].
5.3. Limitations and Future Research
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Code | Open Code Label | Frequency | Supporting Excerpt | Interviewer ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | Strict Environmental Regulations | 18 | “We have issued stricter vehicle restrictions and emission standards, equipped with smart monitoring and enforcement teams.” | 1 |
| A2 | Joint Law Enforcement Mechanism | 15 | “We have established a joint enforcement mechanism with public security, transport, and tourism departments to jointly penalize serious environmental violations.” | 2 |
| A3 | Tourist Credit Record | 12 | “Some serious violations are included in individuals’ tourism credit records, affecting their access to travel services in Lijiang.” | 1 |
| A4 | Ecological Red Line Designation | 10 | “We have designated ecological red lines across the entire Lijiang region, clearly defining no-development zones.” | 5 |
| A5 | Environmental Carrying Capacity Assessment | 9 | “We issue real-time alerts and divert visitor flow based on tourist volume to avoid excessive environmental pressure.” | 4 |
| A6 | Multi-Stakeholder Collaboration | 14 | “We regularly hold environmental protection forums involving tourism enterprises and community residents to jointly develop action plans.” | 1 |
| A7 | Ecological Compensation Mechanism | 8 | “For ecologically impacted areas due to tourism development, developers are required to conduct restoration or provide compensation.” | 5 |
| A8 | Smart Tourism App | 16 | “The official tourism app provides real-time traffic updates and air quality index, and recommends green travel routes.” | 1 |
| A9 | New Energy Charging Stations | 13 | “We piloted smart charging stations for new energy vehicles along popular self-driving routes and scenic entrances.” | 1 |
| A10 | Smart Waste Sorting Systems | 11 | “Smart sorting equipment automatically recognizes garbage types and issues alerts based on waste volume.” | 1 |
| A11 | Environmental Sensors | 9 | “We piloted the installation of smart sensors to monitor waste, water quality, and noise levels in real time.” | 2 |
| A12 | AR-Based Environmental Tasks | 8 | “We designed AR-based environmental tasks where tourists can scan signs to learn about ecology and complete challenges.” | 4 |
| A13 | Carbon Credit System | 7 | “We piloted a blockchain-based carbon credit system to encourage low-carbon travel and green activities.” | 5 |
| A14 | Smart Parking System | 10 | “We piloted a smart parking management system allowing for advance reservations to reduce unnecessary idling and emissions.” | 3 |
| A15 | Eco Navigation Alerts | 9 | “In collaboration with navigation companies, we marked ecologically sensitive areas and no-parking zones on maps.” | 2 |
| A16 | Naxi Ecological Wisdom | 17 | “Naxi cultural values embody harmony between humans and nature, as reflected in everyday life.” | 3 |
| A17 | Household Waste Sorting | 15 | “Residents in the old town sort waste meticulously, with some families composting food scraps themselves.” | 1 |
| A18 | Community Environmental Role Models | 14 | “Tourists feel embarrassed to litter after witnessing residents’ strong environmental habits.” | 1 |
| A19 | Eco-Friendly Homestays | 12 | “Eco-friendly homestay demonstration sites run by locals proactively share environmental stories with guests.” | 4 |
| A20 | Cultural Experience Activities | 11 | “Visitors are invited to participate in traditional farming activities to learn about ecological agriculture.” | 1 |
| A21 | Emotional Resonance | 13 | “When tourists see how much locals cherish their homeland, it evokes strong emotional resonance.” | 2 |
| A22 | Ecological Interpreters | 10 | “Local residents act as ecological interpreters, sharing stories about land protection with visitors.” | 5 |
| A23 | Environmental Storytelling | 9 | “Guesthouse owners tell stories about protecting the snow mountain, which inspires tourists’ sense of responsibility.” | 1 |
| A24 | Volunteer Guidance | 8 | “Volunteers guide tourists in waste sorting and urban managers stop littering behaviors.” | 1 |
| A25 | Green Cultural Products | 7 | “We promote handicrafts made from recycled materials that convey environmental values.” | 4 |
| A26 | Environmental Point Incentives | 8 | “Tourists can earn points for eco-friendly behaviors and exchange them for souvenirs.” | 11 |
| A27 | Leave-No-Trace Camping | 7 | “We emphasize the leave-no-trace concept to reduce environmental footprints during camping.” | 11 |
| A28 | Eco-Driving Challenge Events | 6 | “We organize eco-driving challenges that record fuel-saving and waste-sorting performance.” | 13 |
| A29 | Environmental Training | 8 | “The government conducts environmental training to communicate policy and technical requirements to practitioners.” | 11 |
| A30 | Blacklist System | 7 | “Tourists who damage the environment are blacklisted and restricted from re-entering parks.” | 15 |
| Axial Code | Included Open Codes | Logical Relationship Explanation | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| B1: Policy, Regulation, and Collaborative Governance | A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A24, A29, A30 | Through strict regulations, joint law enforcement, and multi-stakeholder collaboration, an institutional constraint and social supervision system is formed to regulate tourist behavior. | 101 |
| B2: Smart Technology and Green Innovation | A8, A9, A10, A11, A12, A13, A14, A15, A26, A27, A28 | By leveraging smart technologies and incentive mechanisms, the cost of engaging in ERB is reduced, thereby enhancing tourist participation. | 94 |
| B3: Community Culture and Emotional Resonance | A16, A17, A18, A19, A20, A21, A22, A23, A25 | Through cultural transmission, local resident role modeling, and emotional interaction, tourists are inspired to resonate with and internalize environmental values. | 103 |
| Selective Code | Included Axial Codes | Included Open Codes | Relationship Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| C1: Destination Governance Capacity for Sustainability | B1 | A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A24, A29, A30 | Through regulatory constraints, multi-stakeholder collaboration, and social oversight, a systematic governance structure is established to regulate tourist behavior. |
| C2: Green Innovation Practices at the Destination | B2 | A8, A9, A10, A11, A12, A13, A14, A15, A26, A27, A28 | By leveraging smart technologies and incentive mechanisms, the cost of ERB is reduced, enhancing tourists’ willingness to participate. |
| C3: Community-Based Environmental Empathy | B3 | A16, A17, A18, A19, A20, A21, A22, A23, A25 | Through cultural transmission, resident role modeling, and emotional interaction, tourists are inspired to resonate with and internalize environmental values. |
References
- Spenceley, A.; Rylance, A. The contribution of tourism to achieving the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals. In A Research Agenda for Sustainable Tourism; Edward Elgar Publishing: Northampton, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 107–125. [Google Scholar]
- Boluk, K.A.; Cavaliere, C.T.; Higgins-Desbiolles, F. A critical framework for interrogating the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals 2030 Agenda in tourism. J. Sustain. Tour. 2019, 27, 847–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Han, J. Development and SWOT Analysis of Self-Drive Tourism in Shandong Province. Res. Land Nat. Resour. 2016, 72–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prideaux, B. Drive and car tourism: A perspective article. Tour. Rev. 2019, 75, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Shi, J. Aberrant driving behaviors by tourists: A study of drivers in China. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2020, 146, 105738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Rhim, A.H.R.; Chiu, D.K.; Ho, K.K. Information search behavior among Chinese self-drive tourists in the smartphone era. Inf. Discov. Deliv. 2021, 50, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Xu, H.; Hannam, K. A touristic habitation: Automobilities of Chinese driving tourists. Tour. Geogr. 2022, 25, 1047–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.-M.; Wu, H.C. How do environmental knowledge, environmental sensitivity, and place attachment affect environmentally responsible behavior? An integrated approach for sustainable island tourism. J. Sustain. Tour. 2014, 23, 557–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLeod, N. Self-guided trails—A route to more responsible tourism? Tour. Recreat. Res. 2016, 41, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sun, Y.-Y.; Faturay, F.; Lenzen, M.; Gössling, S.; Higham, J. Drivers of global tourism carbon emissions. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 10384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zientara, P.; Jażdżewska-Gutta, M.; Bąk, M.; Zamojska, A. What drives tourists’ sustainable mobility at city destinations? Insights from ten European capital cities. J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2024, 33, 100931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Chi, X.; Norman, R.; Zhang, Y.; Song, C. Tourists’ urban travel modes: Choices for enhanced transport and environmental sustainability. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2024, 129, 104144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creany, N.; Monz, C.A.; Esser, S.M. Understanding visitor attitudes towards the timed-entry reservation system in Rocky Mountain National Park: Contemporary managed access as a social-ecological system. J. Outdoor Recreat. Tour. 2024, 45, 100736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogowski, M.; Zawilińska, B.; Hibner, J. Managing tourism pressure: Exploring tourist traffic patterns and seasonality in mountain national parks to alleviate overtourism effects. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 373, 123430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Luo, L.; Lai, Q.; Dong, C.; Feng, C. A network perspective on tourism waste management: An evolutionary game analysis of stakeholders’ participation in the Third Pole region. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 445, 141378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Culture and Tourism of the People’s Republic of China. Guidelines for Civilized Guidance in Tourist Attractions. 2022. Available online: https://zwgk.mct.gov.cn/zfxxgkml/qt/202210/t20221017_936555.html (accessed on 17 October 2022).
- Lijiang Culture and Tourism Bureau of China. Policy Interpretation of the Implementation Rules for the Lijiang Tourism Regulations. 2025. Available online: https://lijiang.gov.cn/ljsrmzf/c102144/202501/6979fe7e808746d3a34c9cd106413fb8.shtml (accessed on 9 January 2025).
- Yunnan Provincial Forestry and Grassland Bureau; Yunnan Provincial Department of Ecology and Environment; Yunnan Provincial Department of Culture and Tourism. Notice on Regulating Tourism Activities in Nature Reserves. 2025. Available online: https://lcj.yn.gov.cn/html/2025/ynswj_0702/244.html (accessed on 2 July 2025).
- Dwyer, L. Sustainable Development of Tourism: Research and Policy Challenges. Highlights Sustain. 2023, 2, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GSTC. Global Sustainable Tourism Council Destination Criteria Version 2.0; Global Sustainable Tourism Council: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; Available online: https://www.gstcouncil.org/wp-content/uploads/GSTC-Destination-Criteria-v2.0.pdf (accessed on 28 December 2024).
- Karakas, E.; Atay, L. The impact of smart destination implementations in Malaga. J. Hosp. Tour. Technol. 2023, 14, 815–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, Y.M.; Nugroho, S.M.S.; Hariadi, M. Selection of tourism destinations priority using 6AsTD framework and TOPSIS. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Seminar on Research of Information Technology and Intelligent Systems (ISRITI), Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 5–6 December 2019; pp. 346–351. [Google Scholar]
- Buhalis, D. Marketing the competitive destination of the future. Tour. Manag. 2000, 21, 97–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatmawati, I.; Olga, F. Investigating The Determining Factors of Tourist Revisit Intention in a Natural-based Tourism Destination. E3S Web Conf. 2023, 444, 01014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusof, N.M.; Choy, E.A.; Halim, U.; Halimin, N.M.H.; Othman, M.Z.; Tambi, N.; Nawi, N.F.M. Heritage Tourism and Its Impact on The Local Communities: A Case Study in Ranau, Sabah. Int. J. Acad. Res. Bus. Soc. Sci. 2021, 11, 1805–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Liao, C.; Law, R.; Zhang, M. An Integrated Model of Destination Attractiveness and Tourists’ Environmentally Responsible Behavior: The Mediating Effect of Place Attachment. Behav. Sci. 2023, 13, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agustan; Rianse, U.; Sukotjo, E.; Faslih, A. Exploration and implementation of a smart tourism destination with the 6As framework & TOPSIS (case study: Wakatobi, Indonesia). Sci. Rev. Eng. Environ. Sci. (SREES) 2024, 33, 419–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, Y.M.; Putra, D.D.; Khan, N. Selecting Tourism Site Using 6 As Tourism Destinations Framework Based Multi-Criteria Recommender System. Appl. Inf. Syst. Manag. (AISM) 2023, 6, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makri, C.; Neely, A. Grounded theory: A guide for exploratory studies in management research. Int. J. Qual. Methods 2021, 20, 16094069211013654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tie, Y.C.; Birks, M.; Francis, K. Grounded theory research: A design framework for novice researchers. SAGE Open Med. 2019, 7, 2050312118822927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Cheng, J.; Xu, J.; Huang, Z. Self-driving tourism induced carbon emission flows and its determinants in well-developed regions: A case study of Jiangsu Province, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 186, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoor, M.; Wijaksana, T.I. Predictors of pro-environmental behavior: Moderating role of knowledge sharing and mediatory role of perceived environmental responsibility. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2022, 66, 1089–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Wang, X.; Wu, M.-Y.; Wei, W.; Morrison, A.M.; Kelly, C. The effect of destination source credibility on tourist environmentally responsible behavior: An application of stimulus-organism-response theory. J. Sustain. Tour. 2023, 31, 1797–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Berbekova, A.; Uysal, M.; Wang, J. Emotional solidarity and co-creation of experience as determinants of environmentally responsible behavior: A stimulus-organism-response theory perspective. J. Travel Res. 2024, 63, 115–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ji, C.; He, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, L. Tourists’ waste reduction behavioral intentions at tourist destinations: An integrative research framework. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 25, 540–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.; Kim, K.P.; Nguyen, T.H.D. The Green Accommodation Management Practices: The Role of Environmentally Responsible Tourist Markets in Understanding Tourists’ Pro-Environmental Behaviour. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Hsu, M.K.; Boostrom, R.E. From recreation to responsibility: Increasing environmentally responsible behavior in tourism. J. Bus. Res. 2020, 109, 557–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Wong, C.W.; Miao, X. Analysis of the trend in the knowledge of environmental responsibility research. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, L.J.; Wu, W.; Chen, Y.; Tian, R. Tourists’ environmentally responsible behavior: A new path of sustainable development of grassland tourism. Bus. Strat. Environ. 2023, 33, 2143–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Fu, H.; Jiang, S. What is sustainable tourism in social media? Evidence from tweets. Probl. Perspect. Manag. 2023, 21, 204–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhurylo, V. Studying the European consumer behavior and motivations towards tourism service in the condition of globalization. Technol. Audit. Prod. Reserv. 2017, 2, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkoulgkoutsika, A.; Papaioannou, I.; Paraskevopoulou, C.; Tsekeridis, V. Innovation in the tourism industry through personalization for the case of Thessaloniki: Tourist types and their role in development strategies. Open Access Res. J. Sci. Technol. 2022, 5, 039–052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenton, M.; Pearce, P. Multidimensional scaling and tourism research. Ann. Tour. Res. 1988, 15, 236–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žabkar, V.; Brenčič, M.M.; Dmitrović, T. Modelling perceived quality, visitor satisfaction and behavioural intentions at the destination level. Tour. Manag. 2010, 31, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonincontri, P.; Micera, R. The experience co-creation in smart tourism destinations: A multiple case analysis of European destinations. Inf. Technol. Tour. 2016, 16, 285–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Descarten, R. Tourism 5A, Tourism Satisfaction, and Electronic Word of Mouth in a Small Island Destination. Int. JBHOST (J. Bus. Hosp. Tour.) 2023, 9, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Um, T.; Chung, N. Does smart tourism technology matter? Lessons from three smart tourism cities in South Korea. Asia Pac. J. Tour. Res. 2021, 26, 396–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambarwati, D.; Munawaroh, N.A. Do attraction, accesibility, amenities and ancillary for interest visiting of visitor? The role of customers satisfaction. Enrich. J. Manag. 2023, 13, 3268–3280. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, W.C.; Patitad, P.; Suto, H. Tourists” satisfaction: Benefits of inconvenience aspect. In Proceedings of The Fourth International Conference on Electronics and Software Science (ICESS2018), Takamatsu, Japan, 5–7 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pattiyagedara, S.; Fernando, P. Rural Tourism Niche-Market as a Development Strategy on Rural Community: Reference to Hiriwadunna Village Track, Meemure and Heeloya Knuckles Valley Tourism Village, Sri Lanka. Sri Lanka J. Manag. Stud. 2020, 2, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errichiello, L.; Micera, R. A process-based perspective of smart tourism destination governance. Eur. J. Tour. Res. 2021, 29, 2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inmor, S.; Na-Nan, K.; Phanniphong, K.; Jaturat, N.; Kůstka, M. The role of smart green tourism technologies in shaping tourist intentions: Balancing authenticity and sustainability in natural tourism. Environ. Chall. 2025, 19, 101171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Corte, V.; Del Gaudio, G.; Sepe, F.; Luongo, S. Destination Resilience and Innovation for Advanced Sustainable Tourism Management: A Bibliometric Analysis. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angella, F.; Maccioni, S.; De Carlo, M. Exploring destination sustainable development strategies: Triggers and levels of maturity. Sustain. Futures 2025, 9, 100515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drisko, J.W. Transferability and Generalization in Qualitative Research; Sage Publications: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2025; pp. 102–110. [Google Scholar]
- Stalmeijer, R.E.; Brown, M.E.L.; O’BRien, B.C. How to discuss transferability of qualitative research in health professions education. Clin. Teach. 2024, 21, e13762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallio, H.; Pietilä, A.; Johnson, M.; Kangasniemi, M. Systematic methodological review: Developing a framework for a qualitative semi-structured interview guide. J. Adv. Nurs. 2016, 72, 2954–2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creswell, J.W.; Poth, C.N. Qualitative Inquiry and Research Design: Choosing Among Five Approaches; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cascio, M.A.; Lee, E.; Vaudrin, N.; Freedman, D.A. A Team-based Approach to Open Coding: Considerations for Creating Intercoder Consensus. Field Methods 2019, 31, 116–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, F.; Adel, S.M.R.; Zareian, G.; Davoudi, M. Iranian EFL teachers’ and learners’ perceptions of the principles of critical thinking: A constructivist grounded theory study. Iran. J. Lang. Teach. Res. 2020, 8, 63–81. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Eisawi, D. A Design Framework for Novice Using Grounded Theory Methodology and Coding in Qualitative Research: Organisational Absorptive Capacity and Knowledge Management. Int. J. Qual. Methods 2022, 21, 16094069221113551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagger, M.S.; Cheung, M.W.-L.; Ajzen, I.; Hamilton, K. Perceived behavioral control moderating effects in the theory of planned behavior: A meta-analysis. Health Psychol. 2022, 41, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damberg, C.L.; Silverman, M.; Burgette, L.; Vaiana, M.E.; Ridgely, M.S. Are value-based incentives driving behavior change to improve value? Am. J. Manag. Care 2019, 25, e26. [Google Scholar]
- Pizarro, J.J.; Zumeta, L.N.; Bouchat, P.; Włodarczyk, A.; Rimé, B.; Basabe, N.; Amutio, A.; Paez, D. Emotional processes, collective behavior, and social movements: A meta-analytic review of collective effervescence outcomes during collective gatherings and demonstrations. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 974683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgenroth, T.; Ryan, M.K.; Peters, K. The Motivational Theory of Role Modeling: How Role Models Influence Role Aspirants’ Goals. Rev. Gen. Psychol. 2015, 19, 465–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhandilla, B.; Shokhan, R.; Mamrayeva, D. Conceptual foundations of the category of tourist destination. Bull. Karaganda Univ. Econ. Ser. 2022, 108, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, Y.M.; Nurhayati, H.; Harini, S.; Nugroho, S.M.S.; Hariadi, M. Decentralized tourism destinations rating system using 6AsTD framework and blockchain. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Smart Technology and Applications (ICoSTA), Surabaya, Indonesia, 20–20 February 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Rahimi, S.; Khatooni, M. Saturation in qualitative research: An evolutionary concept analysis. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. Adv. 2024, 6, 100174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Q.; Hsu, C.H. Urban travelers’ pro-environmental behaviors: Composition and role of pro-environmental contextual force. Tour. Manag. 2022, 92, 104561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, X.; Zou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, R. Driving factors of pro-environmental behavior among rural tourism destination residents-considering the moderating effect of environmental policies. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 7663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, X.; Wang, D.; Chang, J.; Li, H. Digital nudging for sustainable tourist behavior in new media. Tour. Manag. 2024, 107, 105087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majid, G.M.; Tussyadiah, I.; Kim, Y.R.; Chen, J.L. From Destination to Daily Life: A Longitudinal Study on the Effects of Flashback Nudging on Pro-environmental Behavior Spillover. J. Travel Res. 2025, 00472875251337777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Cao, X.; Font, X. Nudge pro-environmental contagion: Residents to tourists. Ann. Tour. Res. 2024, 105, 103738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Cheng, Z.-F.; Yang, H.-J. Empowering pro-environmental behavior in tourists through digital media: The influence of eco-guilt and empathy with nature. Front. Psychol. 2024, 15, 1387817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissel, M.; Gossen, M.; Reisch, L.A.; Sunstein, C.R. Driving sustainable change: A systematic map of behaviorally informed interventions to promote sustainable mobility behavior. PNAS Nexus 2025, 4, pgaf162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravind, A.; Mishra, S.; Meservy, M. Nudging towards sustainable urban mobility: Exploring behavioral interventions for promoting public transit. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2024, 129, 104130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Feng, X.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, Z. Perceived tourism implicit conflict among community residents and its spatial variation. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2024, 11, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, J.M.; Newig, J.; Loos, J. Participation in protected area governance: A systematic case survey of the evidence on ecological and social outcomes. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 336, 117593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Alam, N.; Stoffelen, A.; Bolderman, L.; Groote, P. Tourism metagovernance and the role of the state: Insights from post-blast Beirut. Ann. Tour. Res. 2024, 109, 103848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastegar, R.; Ruhanen, L. The injustices of rapid tourism growth: From recognition to restoration. Ann. Tour. Res. 2022, 97, 103504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Li, M.; Wen, J.; He, X. How do tourism activities and induced awe affect tourists’ pro-environmental behavior? Tour. Manag. 2024, 106, 105002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goertz, G.; Haggard, S. Large-N qualitative analysis (LNQA): Causal generalization in case study and multimethod research. Perspect. Politics 2023, 21, 1221–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Sort | Count | Centrality | Keywords |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 38 | 0.17 | Sustainable development |
| 2 | 38 | 0.09 | Management |
| 3 | 37 | 0.13 | Sustainable tourism |
| 4 | 25 | 0.14 | Tourism |
| 5 | 24 | 0.46 | Conservation |
| 6 | 15 | 0.04 | Model |
| 7 | 15 | 0.27 | Protected areas |
| 8 | 15 | 0.26 | Attitudes |
| 9 | 15 | 0.03 | Satisfaction |
| 10 | 14 | 0.05 | Impact |
| Rank | Province | Region | Rank | Province | Region |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Yunnan | outhwest | 11 | Guangxi | South China |
| 2 | Guangdong | South China | 12 | Gansu | Northwest |
| 3 | Sichuan | Southwest | 13 | Jiangsu | East China |
| 4 | Beijing | North China | 14 | Hunan | Central China |
| 5 | Zhejiang | East China | 15 | Fujian | East China |
| 6 | Shandong | East China | 16 | Hubei | Central China |
| 7 | Inner Mongolia | North China | 17 | Hainan | South China |
| 8 | Shaanxi | Northwest | 18 | Jiangxi | East China |
| 9 | Xinjiang | Northwest | 19 | Shanxi | North China |
| 10 | Guizhou | Southwest | 20 | Chongqing | Southwest |
| Rank | Location | Visitors |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Lijiang | 38,461 |
| 2 | Kunming | 33,627 |
| 3 | Dali | 28,781 |
| 4 | Shangri-La | 17,408 |
| 5 | Shuhe | 15,596 |
| 6 | Xishuangbanna | 8543 |
| 7 | Shuanglang | 7313 |
| 8 | Diqing | 6738 |
| 8 | Tengchong | 4846 |
| 9 | Deqen County | 4714 |
| 10 | Chuxiong | 4531 |
| Interviewee Type | Number | ID | Professional Role | Average Years of Experience | Key Contributions to Research |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Government Officials/Tourism Management | 5 | 1–5 | Director/Bureau Chief Community-Level Personnel | 15 years (10–25) | Macro-level policies, regulations, inter-departmental coordination, and governance capacity. |
| Academic Scholars/Researchers | 5 | 6–10 | Professor/Research Fellow | 12 years (8–20) | Theoretical insights, environmental psychology, sustainable tourism trends, and behavioral economics. |
| Tourism Industry Practitioners | 5 | 11–15 | Operator/Manager/Supervisor | 10 years (7–18) | Industry practices, technological adoption, business strategies, market feedback, and operational challenges. |
| Local Community Representatives | 5 | 16–20 | Committee Head/Village Elder/NGO Leader/Local residents | 20 years (15–30) | Local culture, resident behavior, community initiatives, traditional ecological wisdom, and social dynamics. |
| Total | 20 | ||||
| Testing Stage | Data Source | New Codes Identified | Frequency Change | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Coding (Participants 1–20) | 20 interviews | A1–A30 | Total frequency: 600 | Formed 30 open codes, 3 axial codes, and 3 core categories |
| Supplementary Coding (Participants 21–25) | 5 interviews | None | Approx. 15% increase (e.g., A1 + 2, A8 + 3, etc.) | No new codes emerged; existing category relationships remained stable |
| Category Relationship Review | Reanalysis of the entire dataset | None | No change in logical relationships | Complementarity among core categories was further reinforced |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tong, X.; Phakdeephirot, N.; Jiang, S. A Multi-Layered, Progressive Model of Self-Driving Tourists’ Environmental Responsibility Behavior: Enriched Tourism Destination 6A Framework. Sustainability 2025, 17, 8786. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17198786
Tong X, Phakdeephirot N, Jiang S. A Multi-Layered, Progressive Model of Self-Driving Tourists’ Environmental Responsibility Behavior: Enriched Tourism Destination 6A Framework. Sustainability. 2025; 17(19):8786. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17198786
Chicago/Turabian StyleTong, Xinyang, Nutteera Phakdeephirot, and Songyu Jiang. 2025. "A Multi-Layered, Progressive Model of Self-Driving Tourists’ Environmental Responsibility Behavior: Enriched Tourism Destination 6A Framework" Sustainability 17, no. 19: 8786. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17198786
APA StyleTong, X., Phakdeephirot, N., & Jiang, S. (2025). A Multi-Layered, Progressive Model of Self-Driving Tourists’ Environmental Responsibility Behavior: Enriched Tourism Destination 6A Framework. Sustainability, 17(19), 8786. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17198786








