Enhancing the Resilience of the Environment—Economy—Society Composite System in the Upper Yellow River from the Perspective of Configuration Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
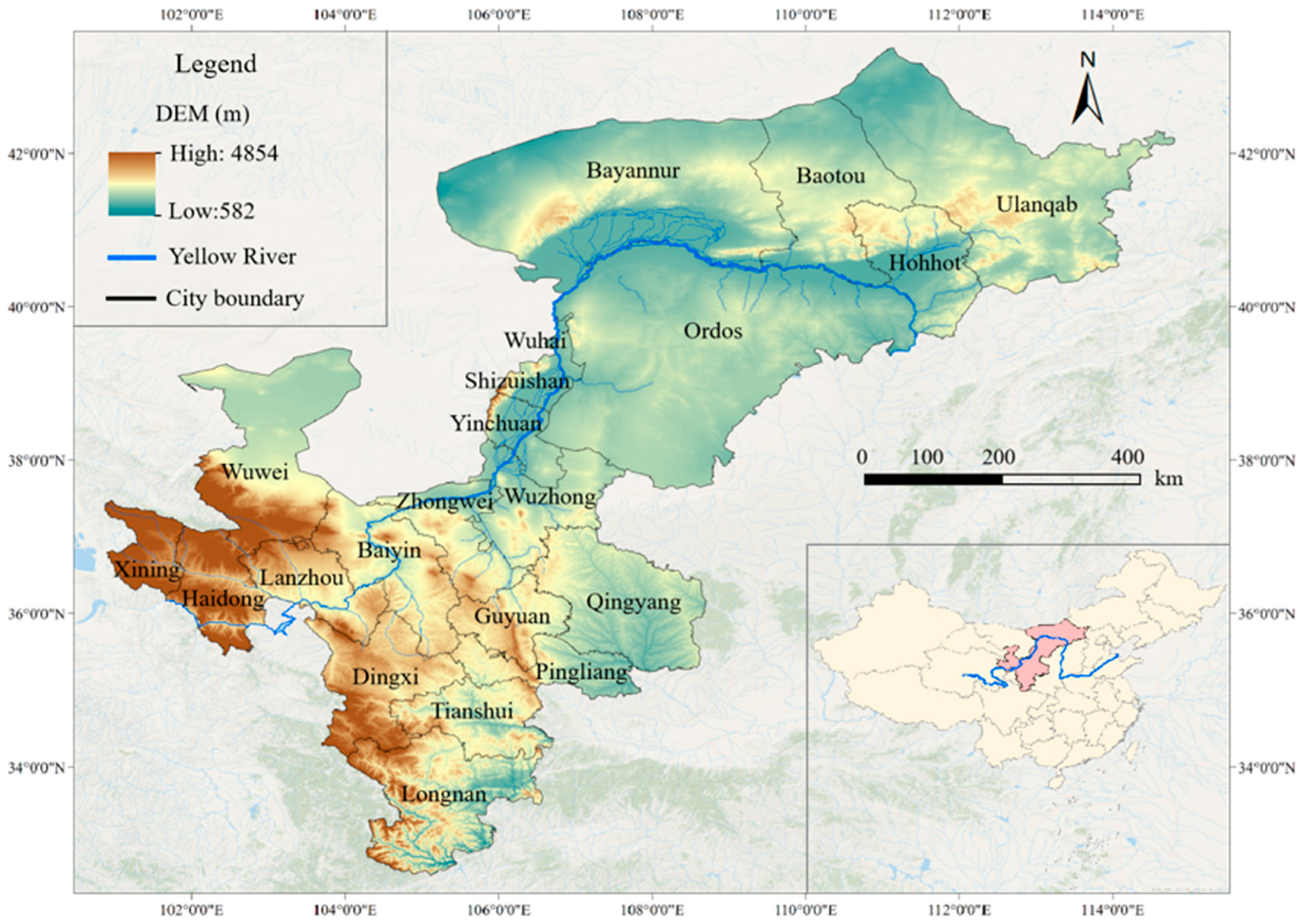
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Research Methods
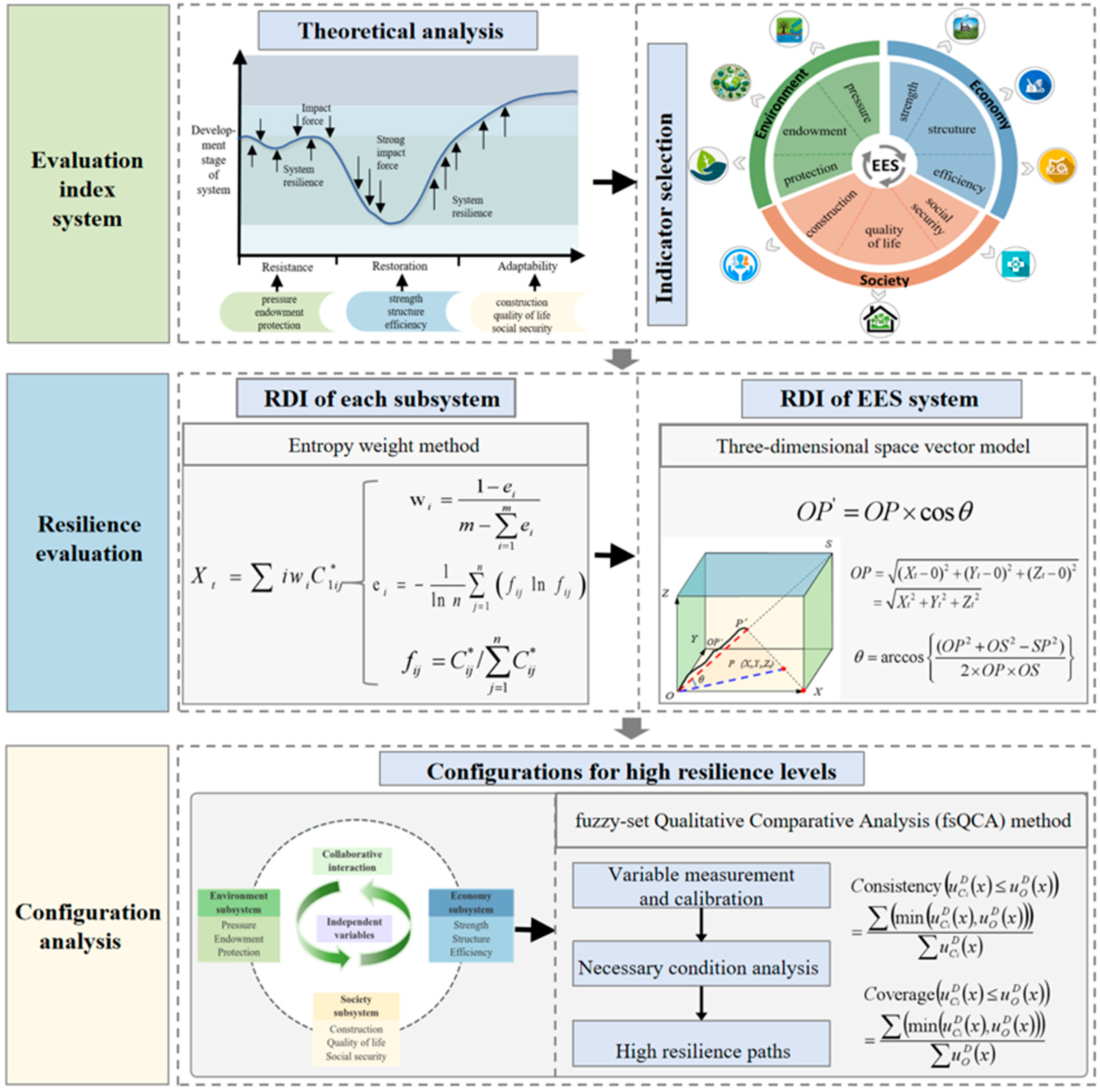
2.2.1. Evaluation Index System
2.2.2. Resilience Evaluation
2.2.3. Configuration Analysis
- (1)
- Variable measurement
- (2)
- Variable calibration
3. Results
3.1. Resilience Assessment of the EES Composite System
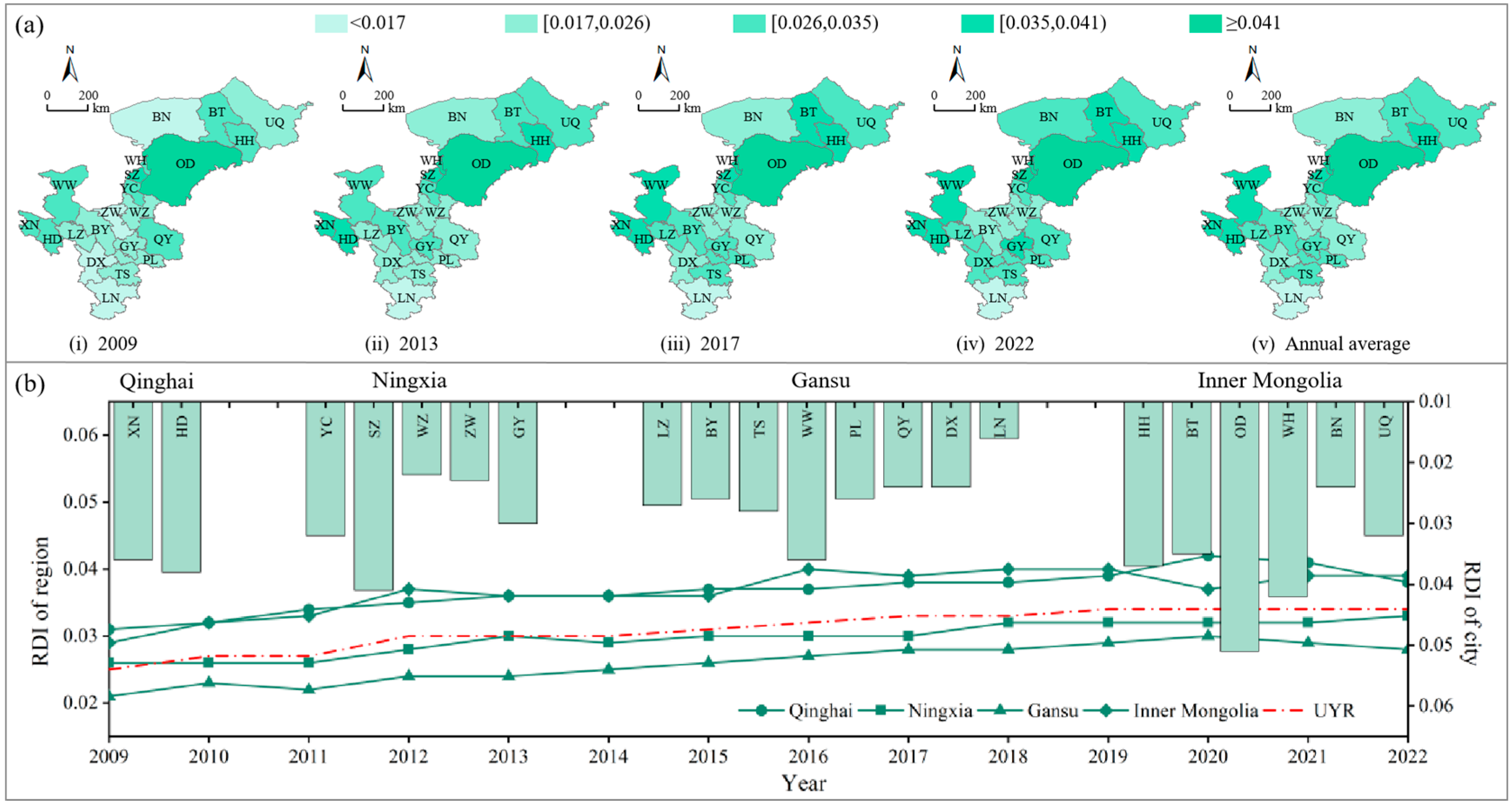
3.1.1. RDI of the Environment, Economy, and Society Subsystems
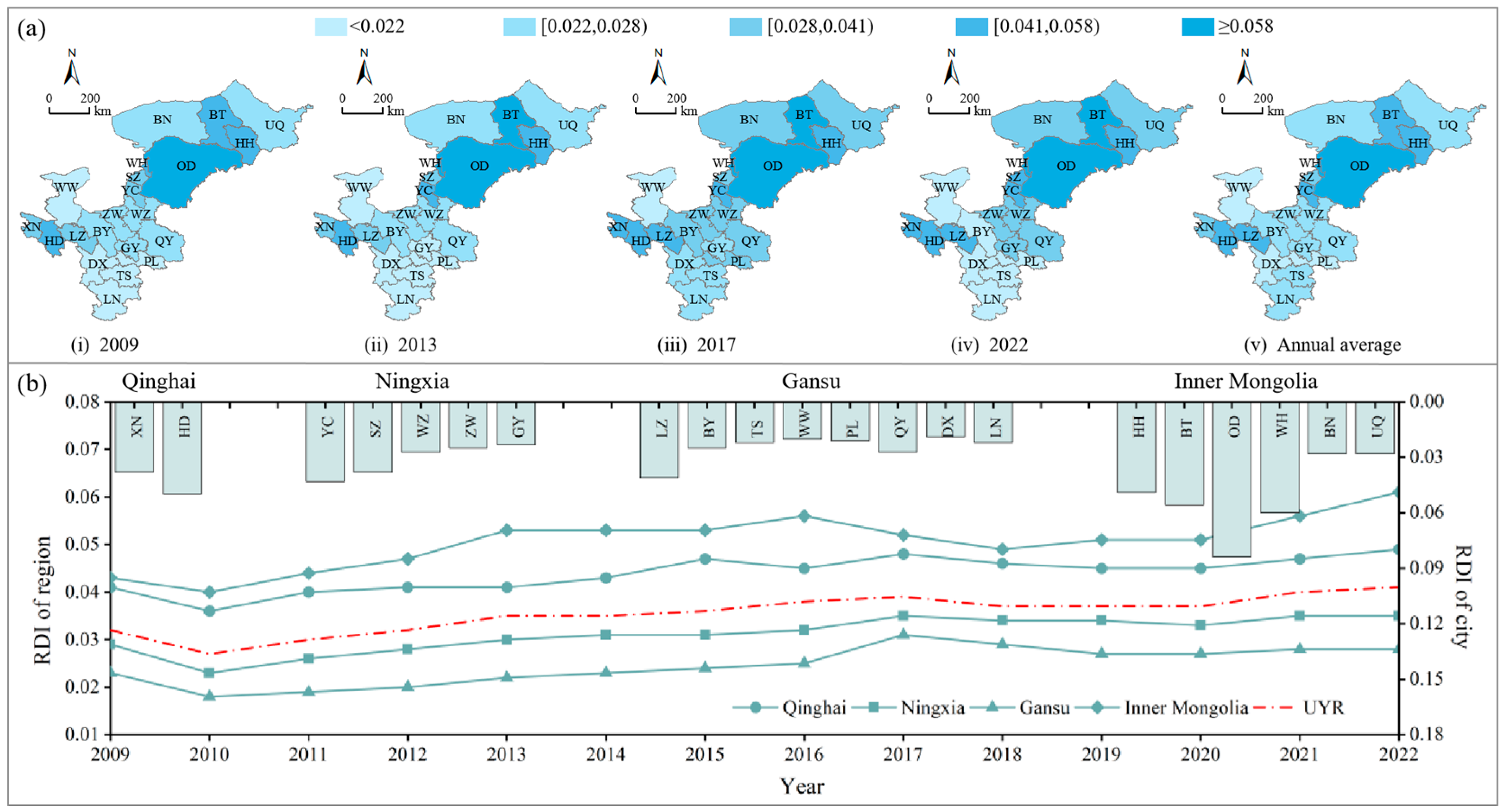
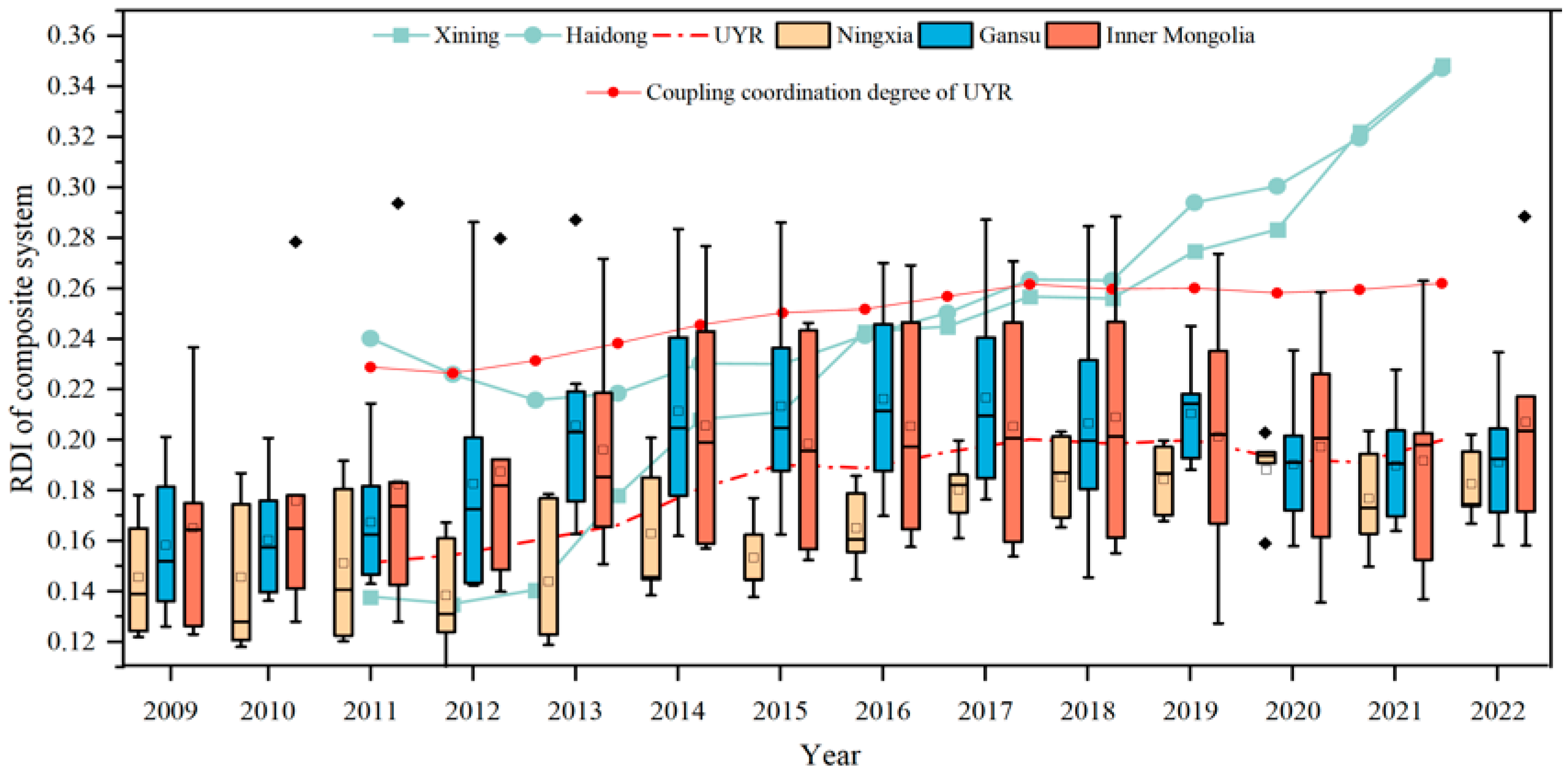
3.1.2. RDI of the EES Composite System
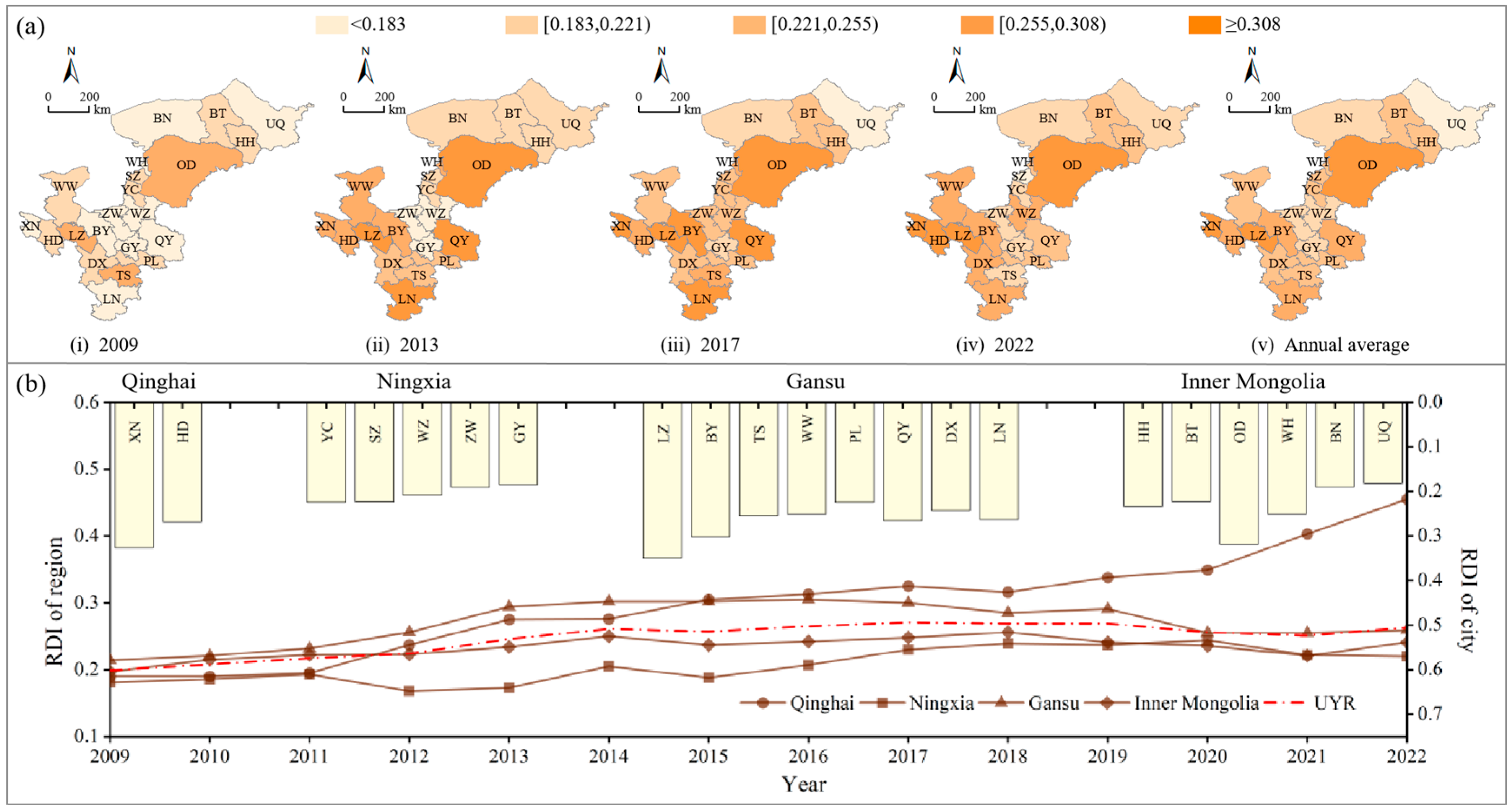
- (1)
- Temporal variation
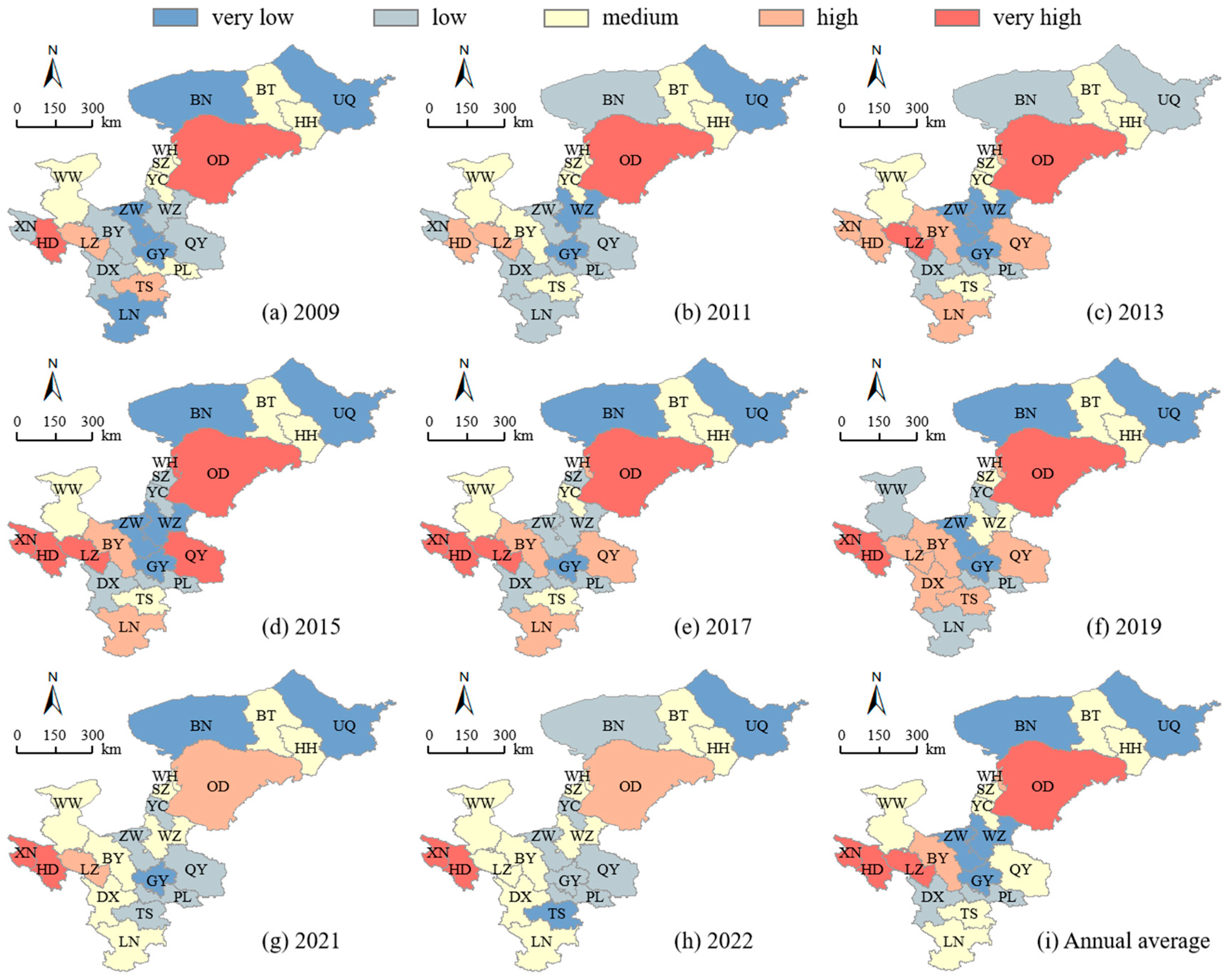
- (2)
- Spatial distribution
3.2. Configuration Analysis of the EES Composite System Resilience
3.2.1. Necessity Analysis of Single Condition for High Resilience
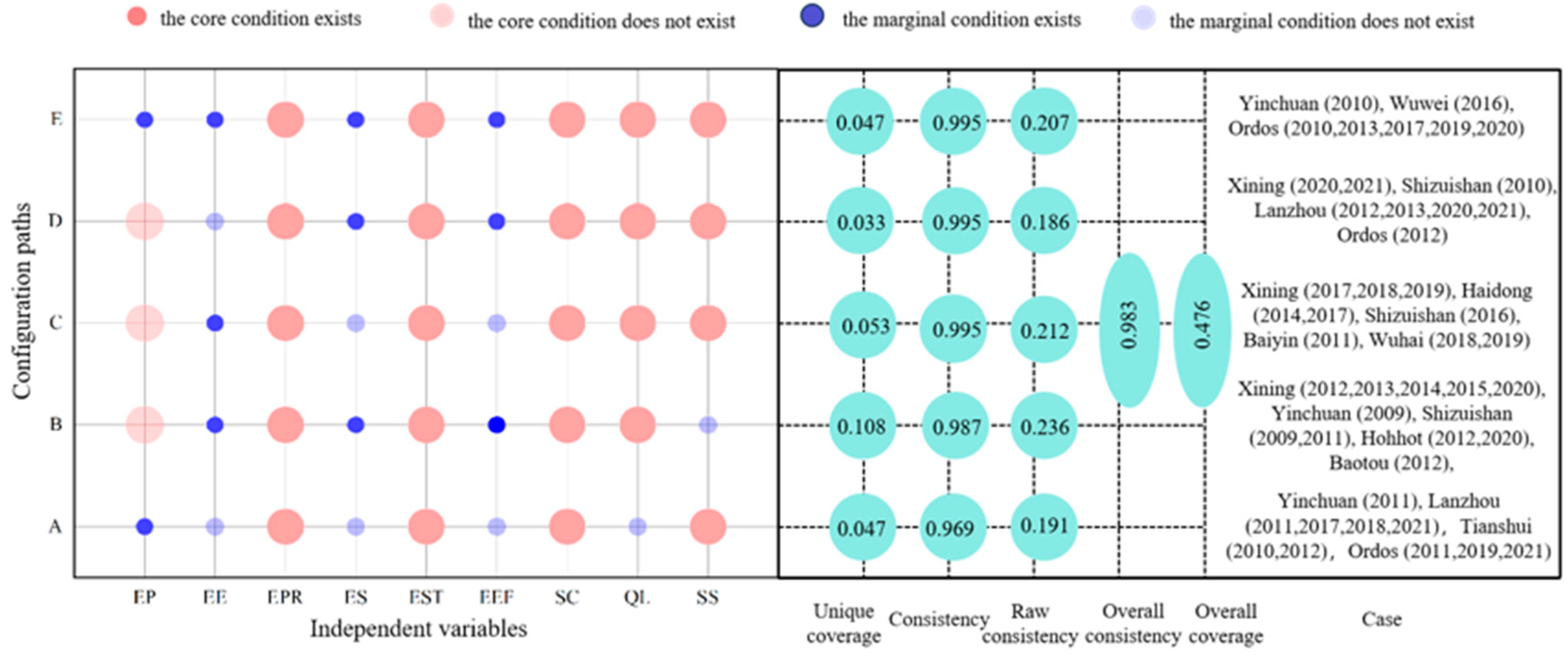
3.2.2. Configurations for High Resilience Levels
4. Discussion
4.1. Resilience Assessment of the EES Composite System
4.2. Configuration Analysis of the EES Composite System Resilience
4.3. Limitations and Prospects
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rather, M.A.; Bhuyan, S.; Chowdhury, R.; Sarma, R.; Roy, S.; Neog, P.R. Nanoremediation strategies to address environmental problems. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 886, 163998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastien-Olvera, B.A.; Conte, M.N.; Dong, X.; Briceno, T.; Batker, D.; Emmerling, J.; Tavoni, M.; Granella, F.; Moore, F.C. Unequal climate impacts on global values of natural capital. Nature 2024, 625, 722–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, F.C.; Lacasse, K.; Mach, K.J.; Shin, Y.A.; Gross, L.J.; Beckage, B. Determinants of emissions pathways in the coupled climate-social system. Nature 2022, 603, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Zheng, R.; Duan, S.; Wang, W.; Li, X. Exploring the path of rural ecological landscape construction from the perspective of a composite ecosystem. J. Agric. Resour. Environ. 2023, 40, 1180–1189. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, C.; Wen, Q.; Ding, J.; Wu, X.; Shi, L. Ecosystem services and their trade-offs and synergies in the upper reaches of the Yellow River Basin. Ecol. Sin. 2024, 44, 5003–5013. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, C.; Xu, P. Overall Safety and Emergency Response Framework Based on System Resilience: Conceptual Logic and Construction Path. Chin. Public Adm. 2023, 39, 137–144. [Google Scholar]
- Büyüközkan, G.; Ilicak, Ö.; Feyzioglu, O. A review of urban resilience literature. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 77, 103579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datola, G. Implementing urban resilience in urban planning: A comprehensive framework for urban resilience evaluation. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 98, 104821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Guo, J.; Ou, M.; Qian, H. The “Rigidity-Elasticity-Resilience” of systematic farmland protection: Theoretical framework and implementation path. Planners 2023, 39, 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.J.; Wu, Y. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Influencing Factors of Urban Ecological Resilience: Evidence from the Yellow River Basin, China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 7114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Wang, D.; Chen, Y. An evaluation method for resilience of airport pavement based on topology and toughness triangle theory. J. Air Force Eng. Univ. 2024, 25, 29–36+127. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, J.; Lin, S.; Zhu, P. Coupling and coordinated development of urban resilience and urban land use efficiency and the influencing factors: A Case study of Yangtze River Economic Belt. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2024, 33, 2315–2328. [Google Scholar]
- Song, H.; Zou, Z.; Yang, Z.; Qin, Y. Spatial-temporal evolution, regional differences and obstacle factors identification of urban resilience in Shaanxi Province. J. Catastrophology 2025, 40, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, W.; Kuang, C.E.; Li, W.; Di, Y. Spatial correlation network and impacts of urban renewal and ecological resilience in urban agglomerations in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River. Scientia Geogr. Sin. 2024, 44, 1936–1945. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, H.J.; Jia, X.C. Application analysis of green building materials in urban three-dimensional landscape design. Int. J. Nanotechnol. 2022, 19, 1117–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, A.H.; Wu, Y.M.; Gao, X. A 3D Two-Phase Landslide Dynamical Model on GIS Platform. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Miao, C. Spatio-temporal characteristics and influencing factors of regional economic resilience in China. Econ. Geogr. 2023, 43, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, F.; Liu, Q.; Wang, P.C. Spatiotemporal characteristics of ecological resilience and its influencing factors in the Yellow River Basin of China. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 16988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W. Spatio-temporal evolution characteristics and influencing factors of economic resilience in the Yellow River Basin. Stat. Decis. 2024, 40, 132–137. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Yao, L.; Li, Y.; Lei, Y. Spatial-temporal evolution characteristics of social-ecological system resilience in Hexi region. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2023, 37, 38–47. [Google Scholar]
- Miu, H.; Zhong, Z.; Hou, B.; Han, J.; Du, X. Dynamic seismic resilience assessment method for water distribution networks based on system dynamics. Eng. Mech. 2023, 40, 99–112. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, L.; Wu, F. Assessment of socioeconomic-ecological composite system resilience and its influencing factors analysis in Nepal. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 625–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Sun, Z.; Jing, X.; Yang, Y. Research on strategies for enhancing the resilience of the”Water Energy Grain Carbon”system in the Yellow River Basin under the Background of High Quality Development. China Rural. Water Hydropower 2024, 11, 1–11+20. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, R.; Kong, L.; Guo, L.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tang, H. Resilience evaluation of water resources system in Xinyang City based on multiple methods. J. Water Resour. Water Eng. 2024, 35, 12–19. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, W.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, W.; Ouyang, Q.; Luo, H. Basis vectors-guided support vector machines for seismic resilience assessment of RC frames. J. Build. Struct. 2024, 45, 81–91. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, H.; Qian, L.; Li, Z.; Huang, J. Study on resilience assessment of flood and landslide disasters in mountainous urban areas. J. Disaster Prev. Mitig. Eng. 2024, 44, 751–761. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, M.; Du, Y.; Wang, W. Configurational perspective and qualitative comparative analysis: The new way of empirical research in Library and Information Science. J. China Soc. Sci. Tech. Inf. 2021, 40, 424–434. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Ma, C.; Wei, L.; Cheng, J.; Wei, J.; Zeng, D. Poverty reduction turn and high-quality development in the upper reaches of the Yellow River. Resour. Sci. 2020, 42, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.Z.; Li, W.; Liu, X.G.; Li, P.F.; Yan, L.; Liang, C. Synergistic Systems of Digitalization and Urbanization in Driving Urban Green Development: A Configurational Analysis of China’s Yellow River Basin. Systems 2025, 13, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Chen, H.; Wen, Q. Coupling coordination degree between Digital Economy and Green Development and its promotion path in the upper reaches of the Yellow River at the prefecture level. Econ. Geogr. 2024, 44, 22–32. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.P.; Ji, W.; Hou, M.C.; Ma, T.Y.; Mao, J.H. Evaluation of efficiency and resilience of agricultural water resources system in the Yellow River Basin, China. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 266, 107605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Chao, X. Coupling coordinated development of digital infrastructure, economic resilience and enbironmental protection in the Yellow River Basin. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2023, 37, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, D.; Liang, S.; Lin, X. Spatial and temporal evolution characteristics and influencing factors of National Aquatic Germplasm Reserves in the Yangtze River Basin. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2024, 33, 1663–1678. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, B.; Jiang, E.H.; Li, J.Q.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C. Coupling coordination relationship of water resources, eco-environment and socio-economy in the water-receiving area of the Lower Yellow River. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 160, 111766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragin, C.C. The Comparative Method; University of California Press: Oakland, CA, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, S.; Chen, K. Configuration Theory and QCA Method from a Complex Dynamic Perspective: Research Progress and Future Directions. J. Manag. World 2021, 37, 180–197. [Google Scholar]
- Ragin, C.C. Fuzzy-Set Social Science; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ragin, C.C. Redesigning Social Inquiry: Fuzzy Sets and Beyond; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Fiss, P.C. Building Better Causal Theories: A Fuzzy Set Approach to Typologies in Organization Research. Acad. Manag. J. 2011, 54, 393–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.Q.; Wagemann, C. Set-Theoretic Methods for the Social Sciences: A Guide to Qualitative Comparative Analysis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Sahoo, S.; Lim, W.M.; Kraus, S.; Bamel, U. Fuzzy-set qualitative comparative analysis (fsQCA) in business and management research: A contemporary overview. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2022, 178, 121599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, S. Spatio-temporal evolution and obstacles identification of complex ecosystem resilience in Qilian Mountain area. Arid Land Geogr. 2024, 47, 237–247. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Niu, J. Spatio-temporal evolution and influencing factors of urban ecological resilience in the Yellow River Basin. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 8309–8320. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, K.; Kong, D.; An, C. Spatial-temporal evolution pattern and coordinated development of human-environment system resilience in the Yellow River Basin. J. Desert Res. 2023, 43, 246–257. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Sun, M.; Termer, G.; Alatan, A. Study on urban resilience assessment and optimization path in the Yellow River Basin. J. Inn. Mong. Minzu Univ. (Philos. Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2023, 49, 74–84. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Ru, S.; Xue, F. Spatio⁃temporal pattern and dynamic evolution of ecological resilience in the Yellow River Basin: Based on the analysis of emergy ecological footprint model. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2024, 34, 136–147. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Hou, J.; Ma, C.; Yang, C.; Wang, Y. Spatio-temporal differentiation of the composite ecosystem resilience in the ecologically fragile area in the upper reaches of the Yellow River: A case study in Ningxia. Arid Zone Res. 2023, 40, 303–312. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Zhong, P.S.; Zhang, J.Z.; Zhang, L. Spatial-temporal differentiation and driving factors of ecological resilience in the Yellow River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Miao, C.; Chen, Z. Urban ecological resilience, social networks and its influencing factors in the Yellow River Basin. Arid. Land Geogr. 2024, 16, 3410. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Cui, X.; Dong, Y.; Guan, J.; Wang, J.; Xi, Z.; Li, C. Spatio-temporal heterogeneity and influencing factors in the synergistic enhancement of urban ecological resilience: Evidence from the Yellow River Basin of China. Appl. Geogr. 2024, 173, 103459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ren, Y.; Zhou, L. Spatio-temporal evolution characteristics and influencing factors of urban ecological resilience in the Yellow River Basin. Arid Land Geogr. 2024, 47, 445–454. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.Q.; He, W.J.; Jiang, E.H.; Qu, B.; Yuan, L.; Degefu, D.M.; Ramsey, T.S. Spatio-Temporal Evaluation of Water Resources System Resilience and Identification of Its Driving Factors in the Yellow River Basin. Water 2024, 16, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.L.; Liu, R.; Huang, T. Analyzing Spatial-Temporal Patterns and Driving Mechanisms of Ecological Resilience Using the Driving Force-Pressure-State-Influence-Response and Environment-Economy-Society Model: A Case Study of 280 Cities in China. Systems 2024, 12, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K. A complexity configurations of risk mitigants for supply chain country risk. Ann. Oper. Res. 2024, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowell, M.; Cousins, T. Equity and the Chief Resilience Officer in the era of 100 Resilient Cities: A qualitative comparative analysis of US resilience strategies. Cities 2022, 131, 103946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Cai, R.; Du, J.; Hu, W. Climate change and marine ecosystems: Impacts, adaptation, and vulnerability. Trans. Atmos. Sci. 2022, 45, 489–501. [Google Scholar]
- Schlör, H.; Venghaus, S.; Märker, C.; Hake, J.F. Managing the resilience space of the German energy system—A vector analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 218, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Chen, J.; Yang, X. Assessment and prediction of social-ecological system’s vulnerability based on optimized SVM model: A case study of the Qinling-Daba Mountains in southern Shaanxi. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 476, 143682. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, W.; Song, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S. Analysis of spatial and temporal changes and driving factors of ecological vulnerability in Sanjiangyuan Region. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2024, 33, 1648–1660. [Google Scholar]
- Xi, L.; Feng, Y.; Qi, Z.; Cao, X.; Ding, J.; Cui, M. Risk assessment of desertification in Tarim Basim based on comprehensive evaluation index. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2025, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Zhou, D.; Fan, J.; Zhang, H.; Yue, X. Consistency analysis of the spatial distribution patterns and their drivers of the ecological vulnerability on the Loess Plateau. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, Q.K.; Tong, H.T.; Nguyen, L.D.; Nguyen, T.N.T.; Ngo, T.D.; Hong Quang, N.; Dinh, A.T.; Pham, M.P. Landscape Dynamics and Environmental Fragility Zoning in Hinh River Basin: Insights for protecting natural ecosystems. One Ecosyst. 2024, 9, e134088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Nandy, S.; Nath, A.J.; Mehta, D.; Pandey, R. Spatially Explicit climate change vulnerability assessment of ecological systems along altitudinal gradients in the Indian Himalayan region. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 2024, 22, 100377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, A.; Sharma, L.K. Spatial E-PSR modelling for ecological sensitivity assessment for arid rangeland resilience and management. Ecol. Model. 2023, 478, 110283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Target Layer | Criteria layer | Indicator Layer | Indicator Acquisition Method | Unit | Attribute |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Environment subsystem [A] | Pressure [A1] | Industrial wastewater discharge per unit of GDP [A11] | Total industrial wastewater discharge/total GDP | t/10,000 yuan | − |
| Industrial SO2 emissions per unit of GDP [A12] | Total industrial SO2 emissions/total GDP | t/10,000 yuan | − | ||
| Industrial smoke (dust) emissions per unit of GDP [A13] | Total industrial smoke (dust) emissions/total GDP | t/10,000 yuan | − | ||
| Water resources development and utilization [A14] | Statistic data | % | − | ||
| Water consumption per 10,000 GDP [A15] | Total water use/total GDP | m3/10,000 yuan | − | ||
| Endowment [A2] | Greening coverage in built-up areas [A21] | Statistic data | % | + | |
| Green space per capita in parks [A22] | Statistic data | m2 | + | ||
| Per capita water resources [A23] | Total water resources/year-end resident population | m3/person | + | ||
| Protection [A3] | Urban sewage treatment rate [A31] | Statistic data | % | + | |
| Harmless treatment rate of municipal household garbage [A32] | Statistic data | % | + | ||
| Comprehensive utilization rate of general industrial solid waste [A33] | Statistic data | % | + | ||
| Economy subsystem [B] | Strength [B1] | Per capita GDP [B11] | Total GDP/year-end resident population | Yuan/person | + |
| Fixed asset investment per person [B12] | Fixed asset investment/year-end resident population | Yuan/person | + | ||
| General budget per capita local fiscal budget revenue [B13] | General budget local fiscal budget revenue/year-end resident population | Yuan/person | + | ||
| Structure [B2] | Proportion of primary industry [B21] | Statistic data | % | − | |
| Proportion of secondary industry [B22] | Statistic data | % | + | ||
| Proportion of tertiary Industry [B23] | Statistic data | % | + | ||
| Index of advanced industrial structure [B24] | Value added of tertiary industry/value added of secondary industry | - | + | ||
| Efficiency [B3] | Input–output ratio [B31] | General budget local fiscal budget revenue/fixed asset investment | % | + | |
| GDP rate of rise [B32] | GDP growth/total GDP for the year | % | + | ||
| Society subsystem [C] | Construction [C1] | Drainage density in built-up areas [C11] | Statistic data | km/km2 | + |
| Urban road space per capita [C12] | Statistic data | m2/person | + | ||
| Density of population [C13] | Statistic data | person/km2 | + | ||
| Internet penetration rate [C14] | Statistic data | % | + | ||
| Urbanization rate [C15] | Statistic data | % | + | ||
| Quality [C2] | Engel’s coefficient for urban households [C21] | Statistic data | % | − | |
| Per capita living consumption expenditure of urban residents [C22] | Statistic data | Yuan/person | + | ||
| Per capita disposable income of urban residents [C23] | Statistic data | Yuan/person | + | ||
| Security [C3] | Share of health care expenditure in fiscal expenditures [C31] | Expenditure on healthcare/total fiscal expenditure | % | + | |
| Share of social security and employment expenditures in fiscal expenditures [C32] | Social security and employment expenditure/total fiscal expenditure | % | + | ||
| Social insurance coverage [C33] | (Health insurance for urban workers + pension insurance)/year-end resident population | % | + | ||
| Urban registered unemployment rate [C34] | Statistic data | % | − |
| Conditions and Results | Fuzzy Set Calibration | Descriptive Statistics | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Completely Not Affiliated | Intersection | Fully Affiliated | Mean Value | Standard Deviation | Maximum Value | Minimum Value | |
| Resilience of EES composite system | 0.005 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.005 | 0.001 | 0.006 | 0.004 |
| EP | 0.008 | 0.014 | 0.028 | 0.016 | 0.008 | 0.035 | 0.005 |
| EE | 0.008 | 0.010 | 0.010 | 0.009 | 0.001 | 0.010 | 0.006 |
| EPR | 0.003 | 0.009 | 0.033 | 0.014 | 0.012 | 0.056 | 0.003 |
| ES | 0.011 | 0.014 | 0.021 | 0.021 | 0.026 | 0.135 | 0.010 |
| EST | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.009 | 0.005 | 0.003 | 0.015 | 0.002 |
| EEF | 0.015 | 0.027 | 0.045 | 0.027 | 0.013 | 0.060 | 0.013 |
| SC | 0.008 | 0.010 | 0.020 | 0.012 | 0.004 | 0.021 | 0.008 |
| QL | 0.156 | 0.189 | 0.273 | 0.207 | 0.044 | 0.292 | 0.156 |
| SS | 0.138 | 0.177 | 0.260 | 0.183 | 0.038 | 0.261 | 0.137 |
| Variable | Consistency | Coverage | Variable | Consistency | Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP | 0.622 | 0.548 | ~EP | 0.582 | 0.590 |
| EE | 0.725 | 0.711 | ~EE | 0.515 | 0.466 |
| EPR | 0.759 | 0.662 | ~EPR | 0.521 | 0.533 |
| ES | 0.690 | 0.676 | ~ESS | 0.579 | 0.525 |
| EST | 0.582 | 0.733 | ~EST | 0.411 | 0.467 |
| EEF | 0.697 | 0.707 | ~EEF | 0.610 | 0.536 |
| SC | 0.702 | 0.741 | ~SC | 0.508 | 0.431 |
| QL | 0.769 | 0.717 | ~QL | 0.535 | 0.509 |
| SSS | 0.797 | 0.742 | ~SS | 0.468 | 0.446 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Jiang, E.; Qu, B.; Hao, L.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y. Enhancing the Resilience of the Environment—Economy—Society Composite System in the Upper Yellow River from the Perspective of Configuration Analysis. Sustainability 2025, 17, 8719. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17198719
Li J, Jiang E, Qu B, Hao L, Liu C, Liu Y. Enhancing the Resilience of the Environment—Economy—Society Composite System in the Upper Yellow River from the Perspective of Configuration Analysis. Sustainability. 2025; 17(19):8719. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17198719
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jiaqi, Enhui Jiang, Bo Qu, Lingang Hao, Chang Liu, and Ying Liu. 2025. "Enhancing the Resilience of the Environment—Economy—Society Composite System in the Upper Yellow River from the Perspective of Configuration Analysis" Sustainability 17, no. 19: 8719. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17198719
APA StyleLi, J., Jiang, E., Qu, B., Hao, L., Liu, C., & Liu, Y. (2025). Enhancing the Resilience of the Environment—Economy—Society Composite System in the Upper Yellow River from the Perspective of Configuration Analysis. Sustainability, 17(19), 8719. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17198719





