Exploring Heterogeneous and Non-Linear Effects of the Built Environment on Street Quality: A Computational Approach Towards Precise Regeneration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Measuring Street Quality: Towards a Multi-Dimensional Framework
2.2. The Complex Influence Mechanisms of the Built Environment
2.3. The Paradigm Shift Towards Precise Urban Regeneration
2.4. Research Gap and Our Study
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Research Framework
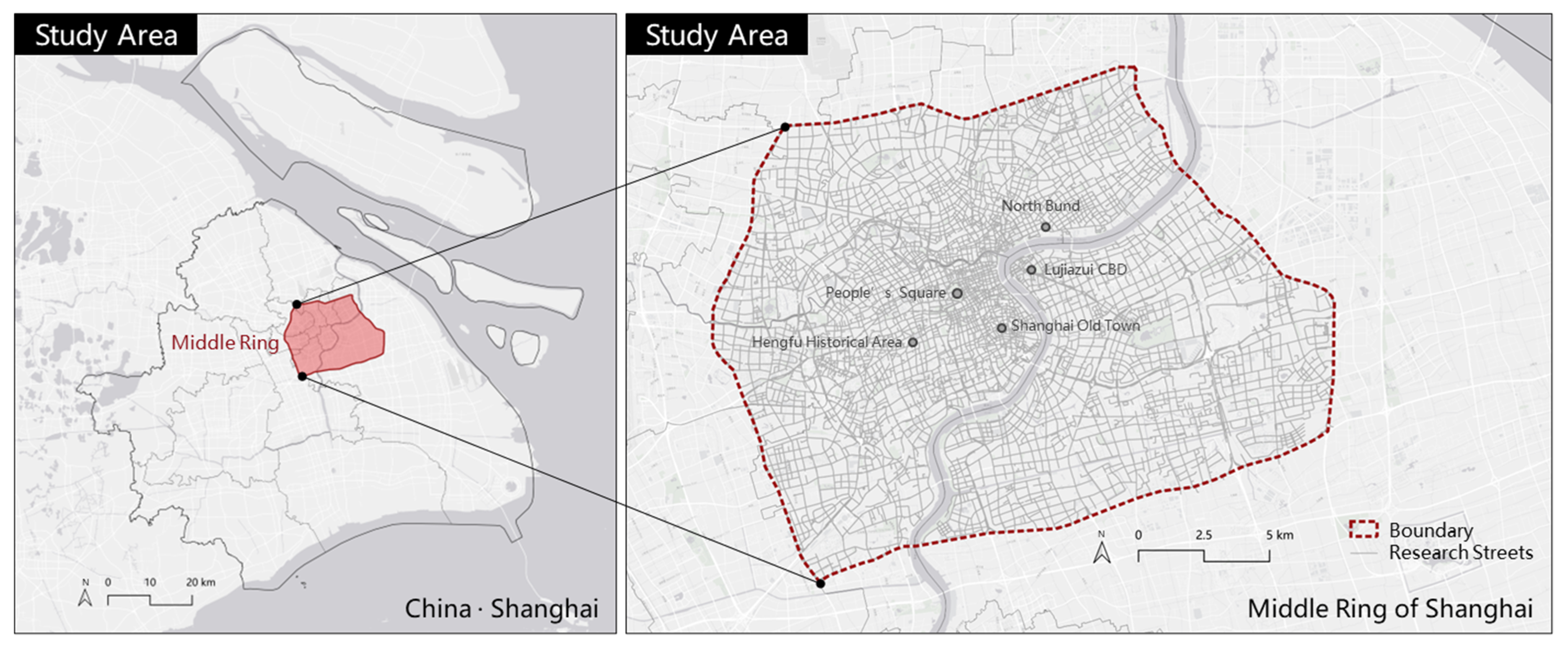
3.2. Study Area
3.3. Measuring Street Quality
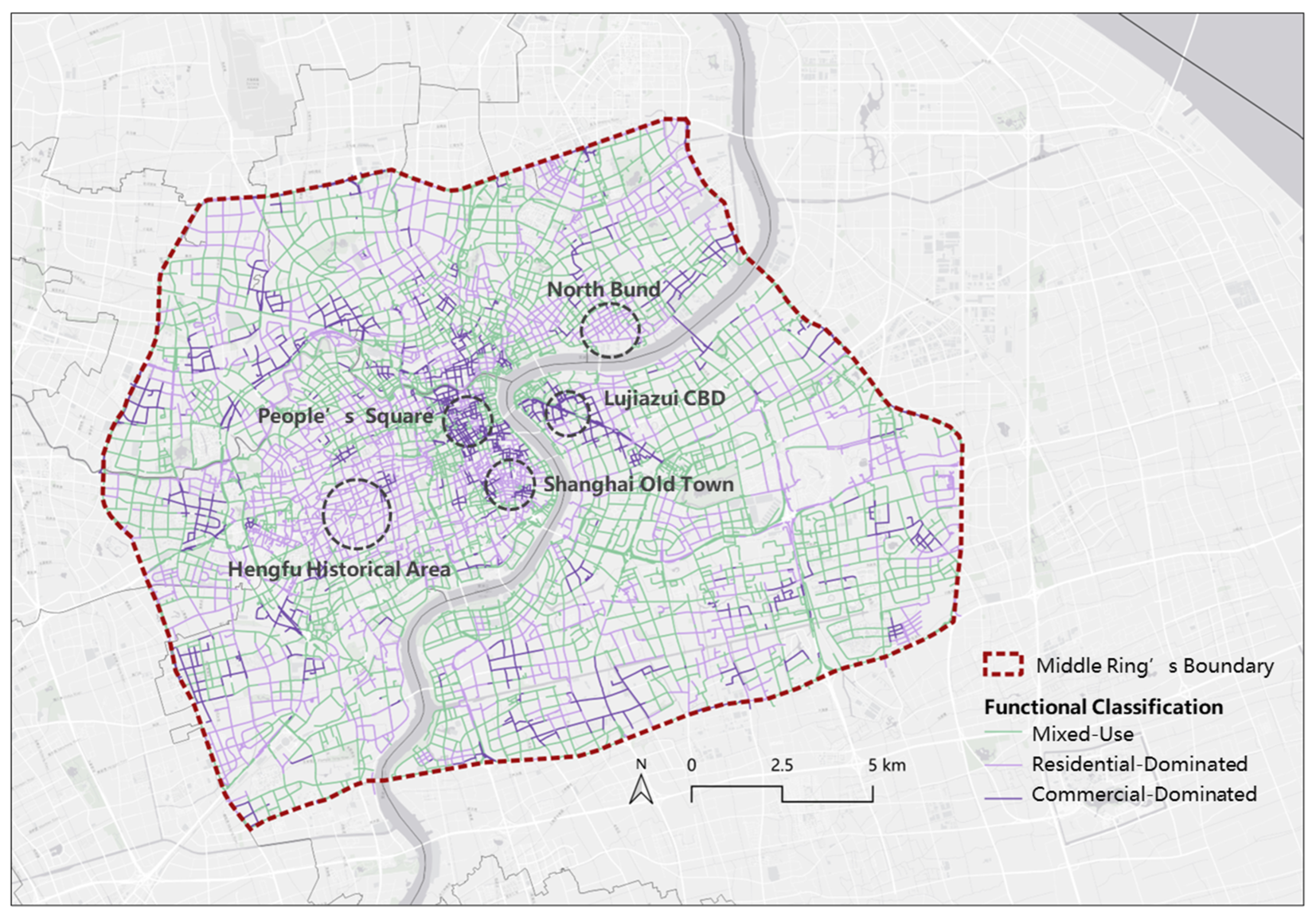
3.3.1. Street Classification Based on Dominant Functions
3.3.2. Measuring the Dimensions of Street Quality
3.3.3. AHP-Based Weighting for Comprehensive Quality
3.4. Measuring Built Environment Factors
3.5. Modeling and Interpreting the Non-Linear Effects
3.5.1. GBDT Modeling
3.5.2. SHAP Interpretation
4. Results
4.1. Measurement Results of Street Quality
4.1.1. A Core-Periphery Pattern of Comprehensive Street Quality
4.1.2. Distinct Spatial Patterns Across Quality Dimensions
4.1.3. Distinct Spatial Patterns Across Street Function Types
4.2. Heterogeneous Importance of Built Environment Factors
4.3. Non-Linear Effect of Built Environment Factors
5. Discussion
5.1. Measuring Comprehensive Street Quality Toward Better Public Space
5.2. Function-Sensitive Analysis Informing Precise Street Regeneration
5.3. Limitations and Future Research
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| sDNA | Spatial Design Network Analysis |
| GBDT | Gradient Boosting Decision Tree |
| LBS | Location-Based Services |
| RD | Residential-Dominated |
| CD | Commercial-Dominated |
| MU | Mixed-Use |
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Introduction and Instructions
| Judgment of Comparison | Assigned Value |
| Row is Extremely more important than Column | 9 |
| Row is Very strongly more important than Column | 7 |
| Row is Strongly more important than Column | 5 |
| Row is Moderately more important than Column | 3 |
| Row is Equally important as Column | 1 |
| Row is Moderately less important than Column | 1/3 |
| Row is Strongly less important than Column | 1/5 |
| Row is Very strongly less important than Column | 1/7 |
| Row is Extremely less important than Column | 1/9 |
Appendix A.2. Definitions of Key Concept
- (a)
- Quality Dimensions
- (b)
- Street Functional Types
Appendix A.3. Pairwise Comparison Matrices
- Matrix 1:
- Judgments for Residential-Dominant Streets
| Residential-Dominant | Visual Quality | Functional Quality | Vibrancy Quality |
| Visual Quality | 1 | [Your judgment here] | [Your judgment here] |
| Functional Quality | - | 1 | [Your judgment here] |
| Vibrancy Quality | - | - | 1 |
- Matrix 2:
- Judgments for Commercial-Dominant Streets
| Commercial-Dominant | Visual Quality | Functional Quality | Vibrancy Quality |
| Visual Quality | 1 | [Your judgment here] | [Your judgment here] |
| Functional Quality | - | 1 | [Your judgment here] |
| Vibrancy Quality | - | - | 1 |
- Matrix 3:
- Judgments for Mixed-Use Streets
| Mixed-Use | Visual Quality | Functional Quality | Vibrancy Quality |
| Visual Quality | 1 | [Your judgment here] | [Your judgment here] |
| Functional Quality | - | 1 | [Your judgment here] |
| Vibrancy Quality | - | - | 1 |
Appendix B
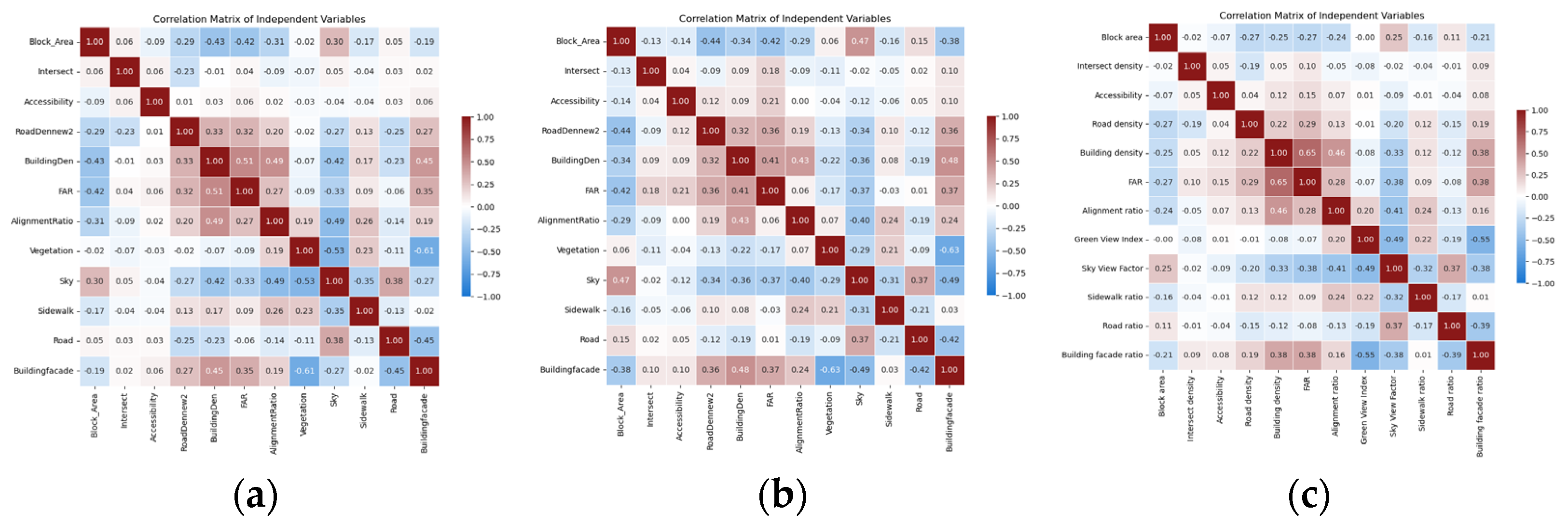
Appendix C
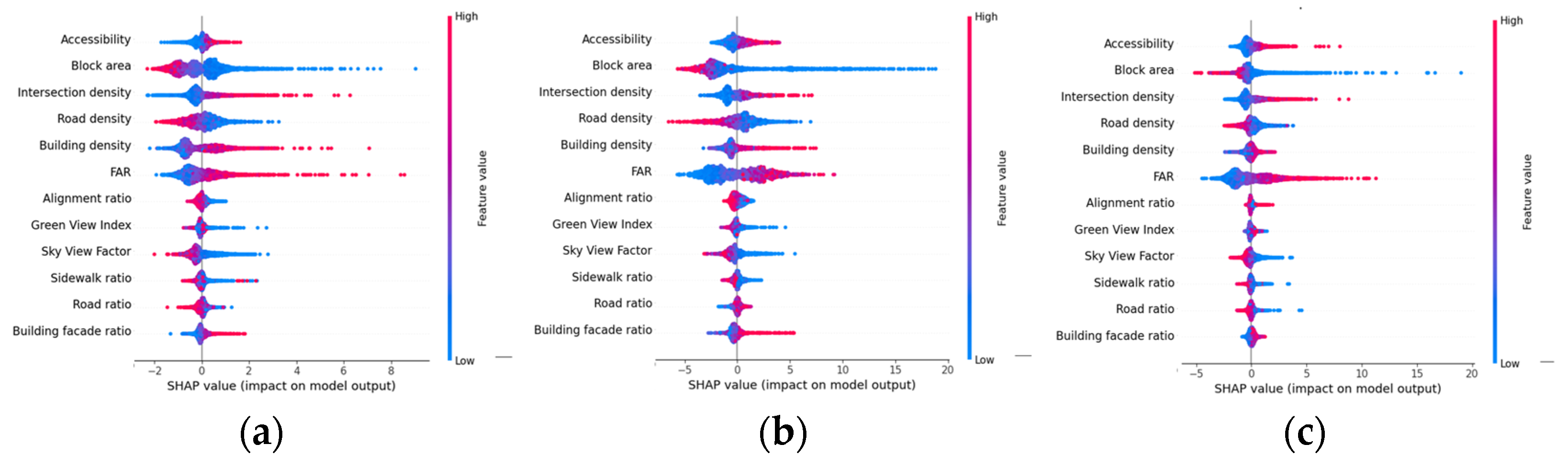
References
- UN-Habitat. Healthier Cities and Communities Through Public Spaces; UN-Habitat: Nairobi, Kenya, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Gehl, J. Cities for People; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-1-59726-984-1. [Google Scholar]
- Von Schönfeld, K.C.; Bertolini, L. Urban Streets: Epitomes of Planning Challenges and Opportunities at the Interface of Public Space and Mobility. Cities 2017, 68, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, J.D. Street Fairs: Social Space, Social Performance. Theatre J. 1996, 48, 301–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porta, S.; Latora, V.; Wang, F.; Rueda, S.; Strano, E.; Scellato, S.; Cardillo, A.; Belli, E.; Càrdenas, F.; Cormenzana, B.; et al. Street Centrality and the Location of Economic Activities in Barcelona. Urban Stud. 2011, 49, 1471–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Long, Y.; Sun, W.; Lu, Y.; Yang, X.; Tang, J. Evaluating Cities’ Vitality and Identifying Ghost Cities in China with Emerging Geographical Data. Cities 2017, 63, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanghai Planning and Land Resource Administration Bureau. Shanghai Street Design Guidelines; Shanghai Planning and Land Resource Administration Bureau: Shanghai, China, 2016.
- Beijing Municipal Institute of City Planning & Design; Beijing Municipal Commission of Planning and Natural Resources. Urban Design Guidelines for Beijing Street Regeneration and Governance; Beijing Municipal Commission of Planning and Natural Resources: Beijing, China, 2022.
- Chen, Z.; Fan, J. Influence of Grouping and Driving Mechanisms on Urban Renewal Performance Using a Six-Dimensional Benefit Framework. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2024, 150, 04024033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Liu, W.; Lu, J.; Song, C.; Meng, Y.; Wang, J.; Xing, H. Urban Function as a New Perspective for Adaptive Street Quality Assessment. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caigang, Z.; Shaoying, L.; Zhangzhi, T.; Feng, G.; Zhifeng, W. Nonlinear and Threshold Effects of Traffic Condition and Built Environment on Dockless Bike Sharing at Street Level. J. Transp. Geogr. 2022, 102, 103375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhao, L.; Xiao, Y.; Lu, Y. Investigating the Spatiotemporal Pattern between the Built Environment and Urban Vibrancy Using Big Data in Shenzhen, China. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2022, 95, 101827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, Y.; Jia, T.; Zhou, L.; Hijazi, I.H. The Six Dimensions of Built Environment on Urban Vitality: Fusion Evidence from Multi-Source Data. Cities 2022, 121, 103482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Huang, C.; Ye, Y. Measuring Street Quality: A Human-Centered Exploration Based on Multi-Sourced Data and Classical Urban Design Theories. Buildings 2024, 14, 3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ye, Y.; Zeng, W.; Chiaradia, A. A Systematic Measurement of Street Quality through Multi-Sourced Urban Data: A Human-Oriented Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Guo, Y.; Mou, Y. Assessing the Walkability of High-Density Neighborhoods: Development and Reliability of the High-Density Environment Assessment Tool (HEAT). J. Transp. Health 2024, 38, 101847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; De Vos, J.; Zhao, P.; Yang, M.; Witlox, F. Examining Non-Linear Built Environment Effects on Elderly’s Walking: A Random Forest Approach. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2020, 88, 102552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Wang, B.; Liu, W.; Zhou, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, S. Assessment of Street Space Quality and Subjective Well-Being Mismatch and Its Impact, Using Multi-Source Big Data. Cities 2024, 147, 104797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Qin, C.; Xiao, L.; Ye, Y. The Nonlinear Relationships between Built Environment Features and Urban Street Vitality: A Data-Driven Exploration. Environ. Plan. B Urban Anal. City Sci. 2024, 51, 195–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Chen, D.; Xu, W. Modular Design Strategies for Community Public Spaces in the Context of Rapid Urban Transformation: Balancing Spatial Efficiency and Cultural Continuity. Sustainability 2025, 17, 7480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massengale, J.; Dover, V. Street Design: The Secret to Great Cities and Towns; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-1-118-06670-6. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs, A.B. Great Streets; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1993; ISBN 978-0-262-10048-9. [Google Scholar]
- Gehl, J. Life Between Buildings: Using Public Space; The Danish Architectural Press: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2006; ISBN 978-87-7407-360-4. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Hang, T.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cao, L. Integrating Restorative Perception into Urban Street Planning: A Framework Using Street View Images, Deep Learning, and Space Syntax. Cities 2024, 147, 104791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handy, S.L.; Boarnet, M.G.; Ewing, R.; Killingsworth, R.E. How the Built Environment Affects Physical Activity: Views from Urban Planning. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2002, 23, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, J. The Death and Life of Great American Cities; Knopf Doubleday Publishing Group: New York, NY, USA, 1989; ISBN 978-0-679-74195-4. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, F.-Y.; Zeng, Z.-C.; Zhang, F.; Li, X.; Ng, E.; Norford, L.K. Mapping Sky, Tree, and Building View Factors of Street Canyons in a High-Density Urban Environment. Build. Environ. 2018, 134, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, W.; Ricard, R.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, W. Assessing Street-Level Urban Greenery Using Google Street View and a Modified Green View Index. Urban For. Urban Green. 2015, 14, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Chu, S.; Zong, W.; Li, S.; Wu, J.; Li, M. Use of Tencent Street View Imagery for Visual Perception of Streets. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2017, 6, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, T.; Ye, C.; Wang, Z.; Tang, G.; Zhang, W.; Ye, Y. City-Scale Mapping of Urban Façade Color Using Street-View Imagery. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Ye, D.; Ye, Y. Measuring the Transparency of Street Interface Based on Street View Images and Deep Learning: Taking Shanghai as an Example. Urban Plan. Int. 2023, 38, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Long, Y. Measuring Visual Quality of Street Space and Its Temporal Variation: Methodology and Its Application in the Hutong Area in Beijing. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2019, 191, 103436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Ma, S.; Tong, D.; Jia, Z.; Li, P.; Long, Y. Associations between the Quality of Street Space and the Attributes of the Built Environment Using Large Volumes of Street View Pictures. Environ. Plan. B Urban Anal. City Sci. 2022, 49, 1197–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, A.; Naik, N.; Parikh, D.; Raskar, R.; Hidalgo, C.A. Deep Learning the City: Quantifying Urban Perception at a Global Scale. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2016, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 196–212. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, N.; Saxe, S.; Roorda, M.; Hess, P.; Miller, E.J. Measuring the Completeness of Complete Streets. Transp. Rev. 2018, 38, 73–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, V. The Street: A Quintessential Social Public Space; Routledge: London, UK, 2013; ISBN 978-0-203-06763-5. [Google Scholar]
- Galaktionova, A.; Istrate, A.-L. Assessing Street Vitality Using Functional Density as a Proxy. Environ. Plan. B Urban Anal. City Sci. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Hu, X.; Wang, J.; Lu, A. How Diversity and Accessibility Affect Street Vitality in Historic Districts? Land 2023, 12, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Ta, N. How the Built Environment Affects the Spatiotemporal Pattern of Urban Vitality: A Comparison among Different Urban Functional Areas. Comput. Urban Sci. 2022, 2, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouratidis, K.; Poortinga, W. Built Environment, Urban Vitality and Social Cohesion: Do Vibrant Neighborhoods Foster Strong Communities? Landsc. Urban Plan. 2020, 204, 103951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, L. Identification of 71 Factors Influencing Urban Vitality and Examination of Their Spatial Dependence: A Comprehensive Validation Applying Multiple Machine-Learning Models. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 108, 105491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whyte, W.H., Jr. The Social Life of Small Urban Spaces; Conservation Foundation: Naperville, IL, USA, 1980; ISBN 978-0-89164-057-8. [Google Scholar]
- Jalaladdini, S.; Oktay, D. Urban Public Spaces and Vitality: A Socio-Spatial Analysis in the Streets of Cypriot Towns. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 35, 664–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, M.; Zhu, Y.; Ferreira, J.; Ratti, C. Inferring Individual Daily Activities from Mobile Phone Traces: A Boston Example. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 2016, 43, 920–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Pei, T.; Shaw, S.-L.; Lu, F.; Li, M.; Cheng, S.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H. Fine-Grained Prediction of Urban Population Using Mobile Phone Location Data. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2018, 32, 1770–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Cui, C.; Liu, F.; Wu, Q.; Run, Y.; Han, Z. Multidimensional Urban Vitality on Streets: Spatial Patterns and Influence Factor Identification Using Multisource Urban Data. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2022, 11, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Han, Y.; Liu, M.; Ye, Y. Street Vitality and Built Environment Features: A Data-Informed Approach from Fourteen Chinese Cities. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 79, 103724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewing, R.; Handy, S. Measuring the Unmeasurable: Urban Design Qualities Related to Walkability. J. Urban Des. 2009, 14, 65–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Zhou, H.; Xue, L.; Yuan, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, C. Evaluating and Comparing Human Perceptions of Streets in Two Megacities by Integrating Street-View Images, Deep Learning, and Space Syntax. Buildings 2024, 14, 1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, R.; Wu, Z.; Tong, Z.; Qin, S.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, Y. How the Built Environment Promotes Public Transportation in Wuhan: A Multiscale Geographically Weighted Regression Analysis. Travel Behav. Soc. 2022, 29, 186–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Gruyer, D.; Zargayouna, M.; Tu, M. Exploring the Spatial Relationship between Urban Built Environment and Green Travel: An Improved Semi-Parametric GWR Approach. Int. J. Transp. Sci. Technol. 2024; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J. A Study on the Impact of Built Environment Elements on Satisfaction with Residency Whilst Considering Spatial Heterogeneity. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Cao, X.; Næss, P. Applying Gradient Boosting Decision Trees to Examine Non-Linear Effects of the Built Environment on Driving Distance in Oslo. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2018, 110, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwald, M.J.; Boarnet, M.G. The Built Environment as a Determinant of Walking Behavior: Analyzing Non-Work Pedestrian Travel in Portland, Oregon. Transp. Res. Rec. 2001, 1780, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Li, D.; Liu, X. How Block Density and Typology Affect Urban Vitality: An Exploratory Analysis in Shenzhen, China. Urban Geogr. 2018, 39, 631–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Z.; Zheng, X.; Chen, Y.; Qian, Q.; Zheng, Z.; Meng, X.; Kuang, J.; Chen, J.; Yang, N.; Shi, X. The Nonlinear Relationship and Synergistic Effects between Built Environment and Urban Vitality at the Neighborhood Scale: A Case Study of Guangzhou’s Central Urban Area. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Hu, Y.; Liang, C.; Wan, Q.; Dai, Q.; Yang, H. Understanding Nonlinear and Synergistic Effects of the Built Environment on Urban Vibrancy in Metro Station Areas. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2023, 70, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batty, M. Urban Analytics Defined. Sage J. 2019, 46, 403–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, N.; Chen, J.; Guo, S. The Relationship Between Urban Renewal and the Built Environment: A Systematic Review and Bibliometric Analysis. J. Plan. Lit. 2022, 37, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Gong, R.; Huo, J.; Fan, B. Building Façade Color Distribution, Color Harmony and Diversity in Relation to Street Functions: Using Street View Images and Deep Learning. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2023, 12, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Pang, C. A Spatial Visual Quality Evaluation Method for an Urban Commercial Pedestrian Street Based on Streetscape Images—Taking Tianjin Binjiang Road as an Example. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; He, Y.; Meng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, B.; Mango, J.; Li, X. Assessing Street Space Quality Using Street View Imagery and Function-Driven Method: The Case of Xiamen, China. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2022, 11, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calafiore, A.; Palmer, G.; Comber, S.; Arribas-Bel, D.; Singleton, A. A Geographic Data Science Framework for the Functional and Contextual Analysis of Human Dynamics within Global Cities. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2021, 85, 101539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, C.H.V.; Chiaradia, A.J.F. sDNA: 3-d Spatial Network Analysis for GIS, CAD, Command Line & Python. SoftwareX 2020, 12, 100525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevtsuk, A.; Kalvo, R. Modeling Pedestrian Activity in Cities with Urban Network Analysis. Environ. Plan. B Urban Anal. City Sci. 2024, 52, 377–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashihara, Y. The Aesthetic Townscape; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1984; ISBN 978-0-262-51031-8. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, I.E.; Venkatasubramanian, S.; Scheidegger, C.; Friedler, S.A. Problems with Shapley-Value-Based Explanations as Feature Importance Measures. In Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning, Vienna, Austria, 12–18 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Erion, G.; Chen, H.; DeGrave, A.; Prutkin, J.M.; Nair, B.; Katz, R.; Himmelfarb, J.; Bansal, N.; Lee, S.-I. From Local Explanations to Global Understanding with Explainable AI for Trees. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2020, 2, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couch, C.; Dennemann, A. Urban Regeneration and Sustainable Development in Britain: The Example of the Liverpool Ropewalks Partnership. Cities 2000, 17, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, Y.-H.; Lee, M.-S.; Wang, J.-W. Culture-Led Urban Regeneration Strategy: An Evaluation of the Management Strategies and Performance of Urban Regeneration Stations in Taipei City. Habitat Int. 2019, 86, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


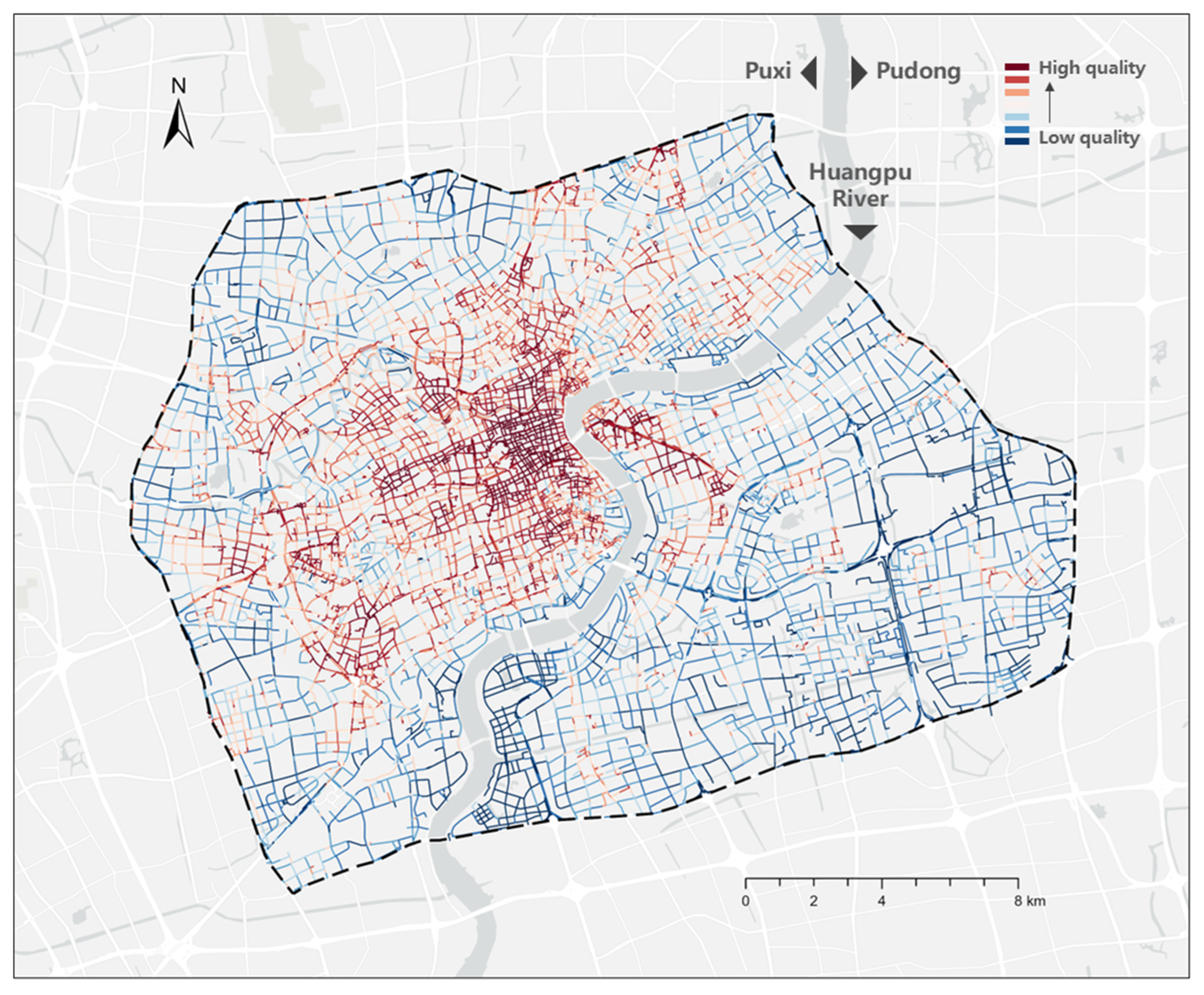
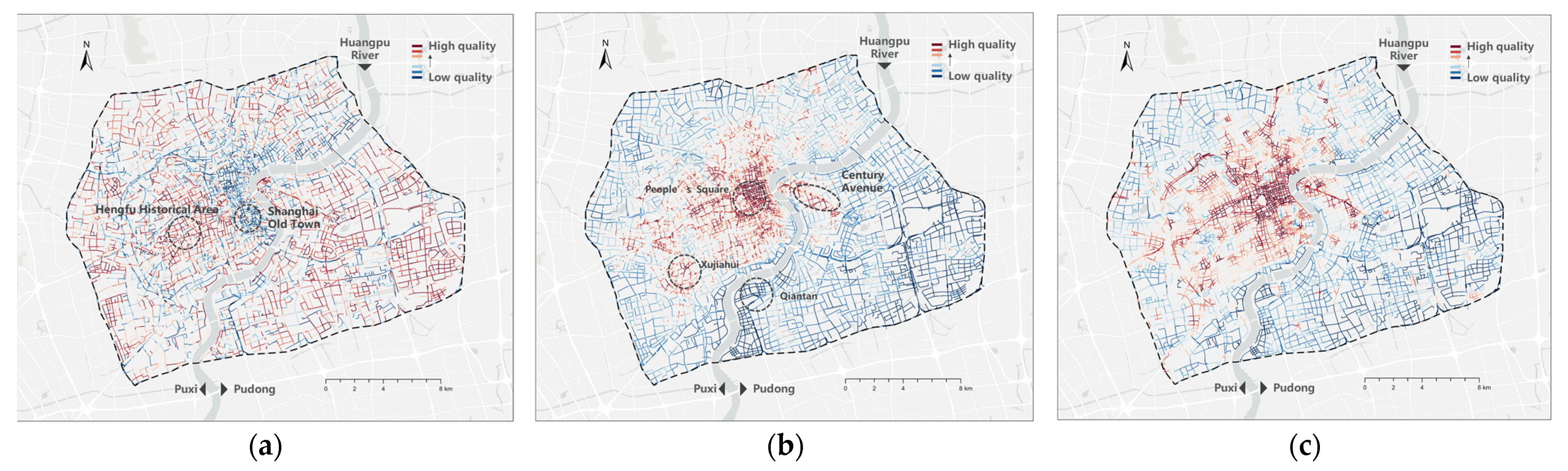

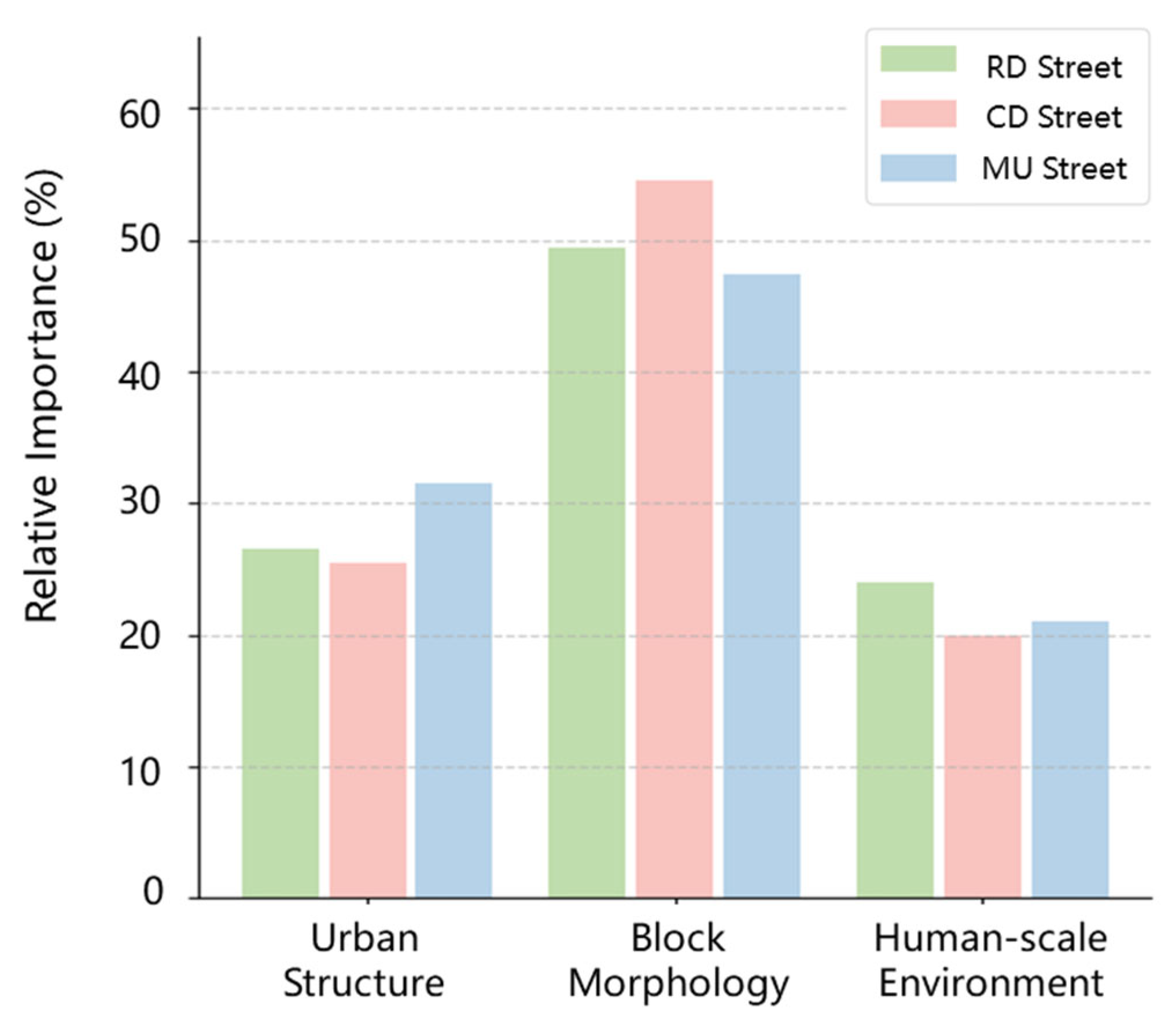


| Street Type | Visual Quality | Functionality | Vibrancy |
|---|---|---|---|
| RD | 0.1663 | 0.5262 | 0.3075 |
| CD | 0.1398 | 0.3562 | 0.5041 |
| MU | 0.1861 | 0.3835 | 0.4303 |
| Dimension | Factor | Description | Calculation Method/ Formulation | Symbolic Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urban Structure | Accessibility | The potential for through-movement determined by the spatial topology of the street network | sDNA plug-in for ArcMap 10.8, used to calculate Betweenness Centrality with an 800 m network radius (Cardiff University, https://sdna.cardiff.ac.uk, accessed on 20 June 2025). | is the total number of shortest paths between nodes s and t, is the number of such paths that passes through node v. |
| Road density | Concentration of road network | is the length of street in the buffer zone | ||
| Intersection density | Concentration of intersections | is the number of intersections in the buffer zone | ||
| Block Morphology | Block area | Average block area | is the area of block in the buffer zone | |
| Building density | Mean building density of urban blocks | is the area of buildings in the buffer zone, is the area of block in the buffer zone | ||
| Floor area ratio (FAR) | Mean FAR of urban blocks | is the Gross Floor Area (total floor area of all stories) of a single building, is the area of block in the buffer zone | ||
| Human-scale Environment | Alignment ratio | Ratio of the parallel building facade length to the street length | is the length of building facade parallel to the street, is the length of the street | |
| Green View Index (GVI) | Proportion of vegetation in street view | i represents a specific visual element (e.g., vegetation, sky, sidewalk)., is the number of pixel points of element i, N is the number of pixel points in the entire street view image | ||
| Sky View Factor (SVF) | Proportion of sky in street view | |||
| Sidewalk Ratio | Proportion of sidewalk in street view | |||
| Road ratio | Proportion of road surface in street view | |||
| Building façade ratio | Proportion of building facades in street view |
| Category | Parameter/ Metric | Model Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RD Model | CD Model | MU Model | ||
| Hyperparameter | learning rate | 0.033 | 0.031 | 0.042 |
| n estimators | 393 | 371 | 307 | |
| max depth | 7 | 9 | 9 | |
| Subsample | 0.6364 | 0.5989 | 0.8531 | |
| min samples leaf | 3 | 4 | 6 | |
| min samples split | 5 | 4 | 4 | |
| Performance | R-squared | 0.7229 | 0.7789 | 0.6649 |
| Factor | Residential-Dominant (RD) | Commercial-Dominant (CD) | Mixed-Use (MU) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Activation Point | Saturation Point | Trend | Activation Point | Saturation Point | Trend | Activation Point | Saturation Point | Trend | ||
| Urban structure | Accessibility | 1147.03 | 1506.63 | positive | 2651.51 | - | positive | 2162.86 | - | positive |
| Road density | 6.87 | 10.63 | negative | 8.01 | - | negative | 6.02 | 8.33 | negative | |
| Intersection density | 0.015 | - | positive | 0.014 | 0.01 | positive | 0.014 | - | positive | |
| Block morphology | Block area | 0.08 | 0.13 | negative | 0.03 | - | negative | 0.06 | 0.19 | negative |
| Building density | 0.23 | 0.25 | positive | 0.30 | 0.26 | positive | 0.24 | 0.28 | negative | |
| Floor area ratio (FAR) | 2.02 | - | positive | 2.50 | 4.0 | positive | 2.11 | - | positive | |
| Human-scale environment | Alignment ratio | 0.66 | 0.86 | U-shaped | 0.60 | - | negative | 0.18 | 0.87 | U-shaped |
| Green View Index (GVI) | 0.28 | 0.24 | U-shaped | 0.42 | 0.23 | U-shaped | 0.24 | 0.34 | U-shaped | |
| Sky View Factor (SVF) | 0.06 | 0.09 | negative | 0.05 | 0.16 | negative | 0.09 | 0.20 | negative | |
| Sidewalk Ratio | 0.015 | 0.031 | U-shaped | 0.020 | 0.033 | U-shaped | 0.075 | 0.029 | U-shaped | |
| Road ratio | 0.30 | - | negative | 0.28 | 0.31 | U-shaped | 0.30 | - | negative | |
| Building façade ratio | 0.26 | - | positive | 0.37 | 0.42 | positive | 0.20 | - | positive | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, X.; Ye, Y. Exploring Heterogeneous and Non-Linear Effects of the Built Environment on Street Quality: A Computational Approach Towards Precise Regeneration. Sustainability 2025, 17, 8714. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17198714
Xu J, Liu Y, Wu J, Wang X, Ye Y. Exploring Heterogeneous and Non-Linear Effects of the Built Environment on Street Quality: A Computational Approach Towards Precise Regeneration. Sustainability. 2025; 17(19):8714. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17198714
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Jiayu, Yuxuan Liu, Jingfen Wu, Xuan Wang, and Yu Ye. 2025. "Exploring Heterogeneous and Non-Linear Effects of the Built Environment on Street Quality: A Computational Approach Towards Precise Regeneration" Sustainability 17, no. 19: 8714. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17198714
APA StyleXu, J., Liu, Y., Wu, J., Wang, X., & Ye, Y. (2025). Exploring Heterogeneous and Non-Linear Effects of the Built Environment on Street Quality: A Computational Approach Towards Precise Regeneration. Sustainability, 17(19), 8714. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17198714









