Abstract
The scientific site selection for pallet pooling systems is pivotal to enhancing logistics efficiency and environmental performance. However, previous studies mainly adopt single-objective optimization approaches, which fail to simultaneously account for economic, environmental, and operational performance factors. The contribution of this paper lies in proposing an integrated decision-making method based on BWM-GIS-DEA to address the site selection problem for pallet pooling service centers. First, the Best-Worst Method (BWM) determines the weights of 13 criteria across 5 dimensions: economic, transportation, geographical location, technological, and service coverage. These criteria include factors such as the distribution density of pallet manufacturers and potential customers. Then, suitability maps are generated using Geographic Information System (GIS) spatial overlay technology to identify 6 alternative cities. Finally, a two-layer Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA) model is applied to measure the efficiency of the alternative sites. This method is applied in Inner Mongolia, China, and Ejin Horo Banner is identified as the optimal site with an efficiency score of 1.156, demonstrating superior resource allocation characterized by lower land costs and higher pallet turnover rates. The proposed framework not only fills a methodological gap in sustainable facility location research but also provides a replicable and policy-ready tool to guide practical decision-making.
1. Introduction
With the accelerated restructuring of global supply chains and the deepening implementation of the sustainable development strategy, resource intensification and green transformation of logistics systems have become focal points of international concern. As a type of important equipment for unitized operations in logistics, pallets are increasingly adopted across various industries due to their cost-effectiveness and environmental friendliness. At the same time, pallets create value for sustainable logistics networks and enhance operational efficiency [1]. Pallet pooling refers to the coordinated use and social application of pallets, serving as the cornerstone for the logistics sector to achieve mechanized operations, enhance supply capacity, and reduce handling costs. Studies show that the pallet pooling mode results in the lowest carbon equivalent emissions among all pallet management modes, achieving a reduction of up to 38% in carbon emissions [2]. In practice, pallet pooling is a logistics management model in which standardized pallets are owned and maintained by a pooling service provider, and are rented or shared among multiple enterprises in the supply chain. The provider is responsible for pallet circulation, recovery, repair, and redistribution, while users lease pallets according to demand. This approach not only improves pallet utilization and reduces costs, but also supports pallet standardization and sustainability. However, in China’s pallet industry, approximately 1.2 billion pallets are still used once. In contrast, the pallet pooling system consists of only around 24 million standardized pallets, with a penetration rate of just 1.8%. These data are reported by the China Federation of Logistics & Purchasing (CFLP) based on publicly available statistics. This highlights the urgent need for large-scale development of pallet pooling systems. The site selection of pallet pooling service centers is a critical approach to addressing the issues of resource decentralization and inefficient operations.
Although the environmental and economic value of pallet pooling has been widely recognized [3], the site selection of pallet pooling service centers still faces the dual challenges of theoretical approaches and application scenarios. From a theoretical perspective, previous studies on site selection focus on single-objective optimization such as minimizing cost [4] or shortening routes [5], while insufficient attention has been given to the multidimensional synergistic impacts of economic feasibility, geographic appropriateness, technological accessibility, and service coverage. For example, Wang [6] constructed a cost optimization model based on a two-stage hybrid algorithm, but the absence of spatial data analysis tools resulted in a limited match between the proposed site selection and the actual logistics network. From a practical perspective, sparsely populated regions, characterized by dispersed logistics nodes and weak infrastructure, often lead to an efficiency–coverage paradox in traditional site selection models. Site selection improves the service efficiency but sacrifices the accessibility of services, while decentralized layout expands the coverage but increases the service and management costs [7]. These regions are in urgent need of an integrated site selection methodology that combines multi-criteria decision-making, spatial analysis, and efficiency measurement to achieve a dynamic balance between resource inputs and service outputs.
Based on the literature review, this study addresses the following research question: How can we develop a scientific and effective method to select the optimal location for a pallet pooling service center? This problem is complex and involves multi-dimensional constraints. It requires a comprehensive assessment of transport accessibility, land price, labor wage, geographic conditions, technological readiness, and pallet service coverage. The GIS analysis accounts for spatial heterogeneity, scale effects, and layer reclassification, and the suitability maps reflect these factors. Criterion weights are derived from BWM and expressed as global weights across categories and sub-criteria; these weights are matched to the suitability maps. Candidate sites are treated as DMUs. GIS suitability is linked to input–output efficiency using DEA-RAM and super-efficiency, and the results are visualized on the map. When several locations are efficient, the approach yields a stable and discriminative ranking. The framework is applicable to different logistics scenarios through parameter calibration, while the model structure remains unchanged. To address the theoretical and practical gaps identified above, this study proposes a BWM-GIS-DEA integrated site selection framework for pallet pooling service centers, which incorporates multi-dimensional decision criteria, spatial analysis, and dynamic efficiency measurement to support optimal resource allocation in broad and complex regional scenarios. First, the BWM model is used to quantify the weights of 13 decision criteria, such as tertiary industry growth rate, railway network, and terrain factors, addressing the issues of high subjectivity and low consistency in traditional weight calculation methods. Then, suitability maps are generated based on GIS spatial overlay technology to select the alternative areas with both site advantages and resource endowments. Finally, the two-layer DEA model is applied to break through the traditional efficiency boundaries and realize the precise ranking of fully efficient units.
This study addresses the following possible hypotheses: BWM and GIS do not impose additional assumptions. Therefore, the DEA-RAM model in this paper is developed under the assumption of Variable Returns to Scale (VRS).
This paper makes several important contributions. First, the BWM-GIS-DEA method is introduced into the site selection for pallet pooling service centers for the first time, which fills the theoretical gap of multi-dimensional decision-making models. Second, we construct site selection factors covering pallet manufacturers distribution density, pallet potential customer distribution density, and other influencing factors, and establish site selection measurement indicators covering average land price, labor wage, and pallet ownership. This significantly improves the model’s multi-dimensional decision-making capabilities in terms of resource endowment suitability and operating cost controllability in pallet pooling scenarios. Third, at the practical level, the proposed framework is applied to the construction sequence planning of pallet pooling service centers in Inner Mongolia, China.
The remainder of this paper is structured as follows: Section 2 presents a review of the relevant literature; Section 3 describes the methodology of the BWM-GIS-DEA integrated decision-making framework; Section 4 presents case studies and results; Section 5 discusses the social insights derived from the study; and conclusions are given in Section 6.
2. Literature Review
This section provides a comprehensive literature review addressing the site selection problem of pallet pooling service centers. It systematically reviews the current development status of pallet pooling systems, the application of the BWM in multi-criteria decision-making (MCDM), the utilization of GIS for spatial analysis, and the deployment of DEA in site selection. The primary objective of this review is to establish a theoretical foundation for the development of an integrated BWM-GIS-DEA methodological framework, aimed at supporting scientifically grounded and rational decision-making in the site selection of pallet pooling service centers.
2.1. Pallet Pooling
Pallets serve as critical unitized load equipment that underpin the functioning of global supply chains and are widely utilized across diverse industries. In response to increasing pressures for resource conservation and the attainment of carbon neutrality targets, pallet pooling has emerged as a sustainable and cost-effective alternative to traditional pallet management practices, attracting growing interest from both academia and industry [8].
In the foundational research on pallet pooling systems, Chen [9] conducted a comprehensive review of its applications, providing a detailed analysis of the associated benefits, mode selection, and allocation algorithms. They highlighted the considerable potential of pallet pooling in modern logistics. Chen and Liu [10] found that pallet pooling modes can significantly improve logistics efficiency and reduce the waste of social resources. Wu et al. [11] proposed a pallet pooling system, which effectively solved the service reliability of traditional centralized management and enhanced resource recycling efficiency and supply chain transparency. Accorsi et al. [12] used GIS to quantitatively analyze the transport operations of a pallet pooling network operated by a major national retailer, and concluded that the development of the pallet pooling mode can reduce the distance traveled by 65% of the vehicle and reduce pollutant emissions by 60%. Zhang et al. [13] conducted an in-depth study on the circular economic performance of pallet pooling systems by developing a comprehensive evaluation framework. Their findings indicated that pallet pooling can significantly reduce the carbon footprint by up to 95%, underscoring its important role in promoting sustainable development.
Although previous studies confirm the multidimensional value of pallet pooling in enhancing logistics efficiency, optimizing resource allocation, and fostering sustainable supply chains, the site selection of pallet pooling service centers remains largely unexplored. This research gap offers a promising direction for innovation in the present study.
Zhou and Song [14] developed a pallet service center site selection model to minimize the total system cost by considering the supply and demand time matching and the stochastic demand of enterprises. However, their study focused primarily on cost factors and did not explore the broader impact of multidimensional factors in site selections. Similarly, Zhou et al. [15] combined the vehicle routing problem (VRP) and the Chinese postman problem (CPP) to develop an optimization model for solving the route optimization problem of pallet service centers under multiple constraints. Nonetheless, their analysis was limited to route optimization and did not consider the relationship between site selection and the efficiency of pallet service centers. Notably, these studies addressed only the site selection of pallet service centers, rather than pallet pooling service centers. This theoretical gap provides an innovative opportunity for this study to propose a BWM-GIS-DEA site selection decision framework.
Although the advantages and service modes of pallet pooling systems have been widely explored in logistics management, there is still a lack of research on the site of pallet pooling service centers, especially in the context of MCDM. Therefore, this study aims to fill this research gap by focusing on analyzing the site selection of pallet pooling service centers to optimize resource allocation and enhance service efficiency.
2.2. Application of BWM in Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis
MCDA is a systematic method for addressing complex decision-making problems. It assists decision makers in identifying optimal choices by evaluating and prioritizing multiple criteria, objectives, or attributes. MCDA requires the assignment of weights to each decision factor. This step is critical to ensure the accuracy of the decision, as the weights directly influence the evaluation of alternatives [16]. The decision maker considers the factors and their weights to compare the alternatives and then rank them based on defined criteria, leading to a rational decision [17].
The BWM, a novel MCDM approach, was first proposed by Rezaei [18] and has been widely applied to various MCDM problems. This method demonstrates strong performance in pairwise comparisons by significantly reducing the number of comparisons required, while also maintaining a high level of consistency in judgments [19]. As a result, BWM has been widely adopted to determine the weights of decision-making factors, addressing challenges in supply chain management, environmental protection, sustainable development, and security. For instance, Hsu et al. [20] applied BWM to estimate a job satisfaction index representing the social pillar of sustainable development. Rezaei et al. [21] employed BWM to assign weights to 6 core indicators in the Global Logistics Performance Index, offering strategic recommendations for transport and logistics policymakers. Badri Ahmadi et al. [22] involved 38 experts to apply the BWM for evaluating and prioritizing social sustainability criteria, and pointed out that social sustainability is often overlooked in developing countries.
Despite the high reliability of BWM as an MCDM method, certain limitations remain in its standalone application, particularly in complex and multi-dimensional decision problems where it may fail to capture all relevant factors. To address this issue, recent studies integrate BWM with other decision-making approaches to develop weighting models that are more reliable and less susceptible to subjective bias, allowing for more effective handling of real-world complexity. Li and Fei [23] combined BWM with the decision testing and evaluation laboratory (DEMATEL) method to systematically identify and analyze the key barriers to UAV emergency rescue. Guo and Chen [24] innovatively integrated BWM with the DEA-BCE model to propose 4 new goal-setting methods. To find the optimal goal-decision unit within the production possibility set, they also introduced a fifth new method for the global optimization of goal-setting and control. Wang et al. [6] innovatively combined BWM with system theoretical process analysis (STPA) to comprehensively assess the safety of hydrogen liquefaction systems from both qualitative and quantitative perspectives. This approach provided a new research direction for enhancing system safety and reliability. In the field of energy, Badi et al. [25] integrated BWM with hierarchical analysis to enhance the determination of criteria weights. They then ranked the alternatives using a compromise solution ranking method, ultimately selecting the optimal wind farm site in Libya.
2.3. GIS Analysis of Suitability Maps
With the rapid development of the social economy, spatial site selection problems have become increasingly complex, and the limitations of traditional site selection methods are gradually emerging. GIS, through the combination of multiple decision-making methods, has shown significant advantages in complex spatial planning problems. This integration provides strong technical support for spatial site selection and has become an essential tool in modern site research. Du studied the classification and evaluation of green space accessibility based on GIS [26]. Zhu et al. [27] proposed a two-level site selection method for electric-hydrogen hybrid refueling stations based on GIS and Fuzzy-TODIM, which comprehensively considered photovoltaic and wind energy resources as well as hydrogen energy policies. The study demonstrates that combining GIS with multi-criteria decision-making models can effectively integrate multi-dimensional information and offer accurate solutions for site selection problems.
In the study of site selection problems, researchers widely apply GIS and multi-decision analysis methods. Chen et al. [9] developed a GIS-based site selection framework for deep-sea offshore wind power hydrogen production projects (DS-OWHP), which provides new insights for the site selection of offshore energy infrastructure. Meanwhile, Yilmaz et al. [28] combined GIS with Fuzzy Hierarchical Analysis (FAHP) to evaluate 11 criteria for solar power plant site selection. Aghaloo et al. [29] further combined GIS with the BWM-fuzzy logic method to provide an innovative solution for the high-precision site selection of solar-wind hybrid renewable energy systems. They highlighted the technical advantages of GIS in multi-source data processing and accurate modeling. Rane et al. [30] proposed a landfill site selection model that considered 12 environmental, physical, and socio-economic factors, and used GIS analysis to identify appropriate landfill sites with cost-effectiveness, environmental sustainability, and public acceptability. Bi et al. [31] proposed an EVCS expansion plan for Haidian District, Beijing, which uses a new indicator system, FAHP, GIS, and MABAC to select A4 as the optimal site, verifying robustness and providing practical recommendations. Ghiyas et al. [32] developed an integrated CSP site selection framework in Bushehr Province, Iran, combining GIS-based fuzzy multi-criteria analysis, climate modeling, and machine learning to enhance spatial prediction accuracy and support sustainable energy planning under climate change conditions. Gökler [33] proposed a hybrid PF-AHP–GIS approach for solar power plant site selection in Eskişehir, Turkey, demonstrating that PF-AHP provides more accurate and differentiated suitability mapping than IF-AHP by better reflecting expert judgments and key spatial criteria.
From the above literature, it can be concluded that GIS significantly enhances the ability to solve spatial site selection problems through visual analysis, multi-source data processing and flexible combination with MCDM methods. In this study, GIS is primarily applied during the preliminary site selection stage. Suitability maps are generated to support the screening of alternative sites for the pallet pooling service centers. This approach effectively integrates economic, transportation, geographical location, technological, and service coverage factors. It provides a solid foundation for the DEA efficiency measurement and site selection.
2.4. Application of DEA in Site Selection
DEA was originally proposed by Charnes et al. [34]. It is a non-parametric efficiency evaluation method that establishes a production frontier and derives relative efficiency scores by solving a series of linear programming problems. It is often combined with MCDM weighting and spatial screening to evaluate the relative performance of alternatives in multi-input and multi-output contexts. DEA establishes the production frontier and derives the relative efficiency scores by solving a series of linear programming problems. With the advancement and application of DEA, several studies systematically summarized the developments in DEA research. Emrouznejad and Yang [35] provided a comprehensive overview of the theoretical development, application scenarios, and research trends of DEA from 1978 to 2016. They emphasized the flexibility and potential for theoretical expansion of DEA in different decision-making scenarios. Sueyoshi et al. [36] focused on reviewing the application of DEA in the field of energy and environment in the last 40 years, and analyzed its merits and drawbacks as a sustainability measurement tool.
To overcome the limitation of traditional radial DEA models that require separate handling of input and output orientations, Cooper et al. [37] proposed the Range Adjusted Measure (RAM), which simultaneously optimized input minimization and output maximization through an additive approach and provided a unified framework for comprehensive efficiency measurement. Ma et al. [38] improved the modified RAM model and demonstrated its significant enhancement in the efficiency of complex logistics resource allocation. Chen et al. [39] proposed an integrated RAM model that completes both efficiency measurement and super-efficiency ranking in a single process. They applied the model to assess the performance of China’s regional cold-chain logistics system and demonstrated its high efficiency and accuracy in multi-objective co-optimization.
The methodological advantages of the super-efficiency DEA model in the efficiency measurement of multidimensional complex systems were demonstrated in several fields. For example, Liu et al. [40] verified the applicability of super-efficiency DEA model under the multi-dimensional economic-social-environmental constraints by using the super-efficiency DEA model to dynamically measure the efficiency of medical resource allocation in Guangxi Province, China. Furthermore, Shu et al. [41] conducted a super-efficiency SBM-DEA model to measure energy efficiency across 168 economies worldwide. This study verified the adaptability of the model in multi-input, multi-output, and cross-regional collaborative optimization scenarios, providing valuable methodological support for the efficiency measurement of multi-objective complex systems. The above studies demonstrate that RAM offers valuable methodological support for the multi-objective optimization of complex systems. Additionally, the super-efficiency DEA efficiency model overcomes the limitations of traditional models in efficiency ranking, providing a crucial theoretical foundation for constructing the comprehensive decision-making framework of BWM-GIS-DEA in this paper.
For the specific application of the site selection problem, researchers develop a variety of hybrid methods based on DEA. Yazdani et al. [42] proposed a two-stage integrated decision-making model. The model first employs DEA to identify effective options for the site of a logistics center in the Autonomous Community of Spain, followed by a detailed measurement. Wang et al. [43] combined DEA with G-AHP and G-TOPSIS for multidimensional measurement of solar photovoltaic plant site selection in Vietnam. Raad and Rajendran [44] developed a hybrid model combining robust SBM-DEA, multivariate regression, and MCDM-GIS to address airport site selection in developing countries.
Based on the previous studies, it is evident that the DEA method exhibits scale-independence, multidimensional analytical capabilities, and a high degree of compatibility with other models in MCDM contexts. These attributes render the DEA method particularly suitable for measuring the efficiency of site selection for pallet pooling service centers, thereby offering a more robust and reliable foundation for decision support.
2.5. Research Gap and Contributions
In summary, the literature shows that each method solves part of the problem and has limits. BWM provides criterion weights with good internal consistency, but it depends on expert judgment. GIS captures spatial differences and produces suitability maps, but overlay results can change with scale and reclassification. DEA measures relative efficiency with multiple inputs and outputs, but it does not include spatial suitability or explicit weighting and is sensitive to variable choice.
The integrated BWM–GIS–DEA design combines these strengths. BWM supplies consistent weights. GIS turns the weighted criteria into suitability maps. DEA uses a RAM model with super efficiency DEA to rank the screened alternatives by performance. Some trade-offs remain, so we add safeguards: a BWM consistency check and a diverse expert panel; standardized GIS preprocessing and two-level normalization at the category and sub-level standard; and a simple, well-justified set of DEA inputs and outputs plus a super-efficiency DEA step to improve discrimination. This summary leads directly to the methodology in the next section.
3. Methodology
This section provides a systematic description of the comprehensive decision-making model constructed in this study and presents the method used to recommend decisions based on the model. First, the BWM model is used to determine site selection factors. Then, the factor weights generated by the BWM model are applied, combined with geographic information data, to derive alternative options using GIS. Finally, site selection measurement indicators are determined. The DEA-RAM model and the super-efficiency DEA model are then used to select the optimal site. The technical roadmap of the proposed integrated site selection decision-making model is illustrated in Figure 1.
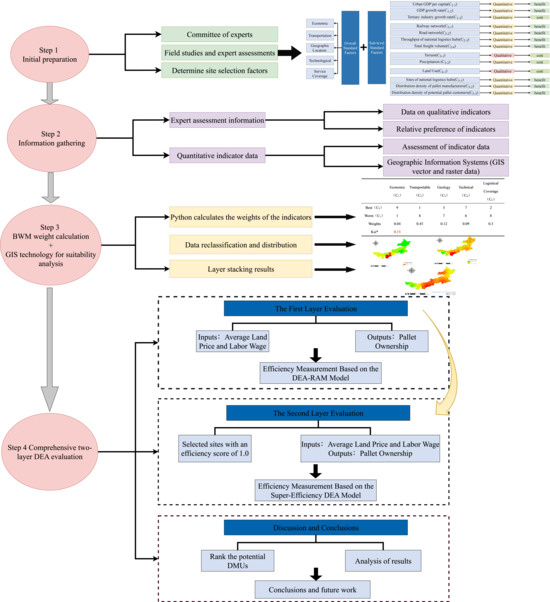
Figure 1.
Technology road map for integrated decision-making models. Ksi *: It is a consistency ratio to evaluate the consistency of the judgment matrix.
The integration of BWM, GIS, and DEA is motivated by their complementarity: BWM reduces subjectivity and improves consistency in weight assignment; GIS enables spatial overlay and visualization to assess suitability; and DEA measures efficiency by considering input–output relationships, thus providing a robust ranking of alternatives. The combination ensures that the site selection results are scientifically rigorous, spatially grounded, and efficiency oriented.
3.1. BWM
In MCDM, the determination of criteria weights is a critical process that significantly influences the effectiveness, scientific validity, and accuracy of the decision-making model. Among these, the BWM, introduced by Rezaei [21], has attracted increasing attention due to its notable advantages in consistency assessment and computational efficiency. BWM efficiently derives weight distribution by identifying the best and worst criteria and formulating a linear optimization model. Its straightforward implementation and high consistency of results make it particularly suitable for this study’s weight determination process. The indicators are determined based on geographical features and refined through expert consultation, which is a commonly adopted approach in multi-criteria site selection studies [27,29].
The BWM was selected for this study due to its ability to minimize the number of pairwise comparisons while ensuring consistency in judgment. Compared with other weighting methods, it is less prone to bias and is suitable for complex multi-criteria environments. It should be noted that BWM belongs to the category of subjective weighting methods. The weights are obtained from expert evaluations, and the BWM is applied to minimize inconsistency in subjective judgments and improve reliability. BWM has also been widely applied in many fields as a decision-making tool. This method is effective, as it requires fewer comparisons while still maintaining a high level of consistency. These features make BWM particularly appropriate for the 13 decision criteria across the 5 dimensions used in this study.
Step 1. A decision maker defines a set of criteria on which decisions are based.
Step 2. Through comparison and evaluation, the decision maker identifies the best (e.g., most desirable, most important) and worst (e.g., least desirable, least important) criteria.
Step 3. The decision maker conducts pairwise comparisons of all criteria on a scale from 1 to 9 and assigns priority levels that represent the relative importance of the best criterion over each of the others, as shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
BWM consistency index.
The resulting comparisons construct a vector called the Best-to-others vector: . where denotes the preference of the best criterion over criteria . Clearly, .
Step 4. The decision maker repeats the same process for the worst criterion. Each of the remaining criteria is compared to the worst criterion on a scale from 1 to 9 to determine their relative importance. The resulting comparison constructs a vector called the Other-to-worst vector: . where represents the preference of the best criterion over criteria . Clearly, .
The optimal weightings criteria are calculated as follows . For each pair of and , the optimal weight must satisfy the following conditions: and . To fulfill these conditions, researchers minimize the maximum absolute differences of and for all criteria. The BWM model is formulated by incorporating the non-negativity constraint and sum condition of the weights:
Model (1) can be transformed into:
where , and are the preferences of the best criterion over criteria , the preferences of criteria over the worst criterion, and the preferences of the best criterion over the worst criterion, respectively. When for all criteria , it indicates that all pairwise comparisons among criteria satisfy the strict consistency condition, meaning the comparisons are perfectly consistent.
However, in actual comparisons, these preferences may not be entirely consistent. Therefore, Rezaei [21] introduced a consistency ratio to assess the degree of consistency of comparison results. Start by calculating the minimum consistency of the comparison as follows:
According to the parameter range set by the decision maker, the value of the variable lies between 1 and . Among them, the default maximum value of is 9, but the decision maker can define it as an upper limit of other values based on actual needs. Consistency decreases when is lower or higher than or . The resulting highest degree of inconsistency occurs when and reach their maximum values (when is reached). It is also known that and when the parameter and are set to their maximum values within their allowable ranges, the formula will exhibit the highest level of inconsistency. Thus, it can be equivalently expressed as:
For minimum consistency , there is:
Finally, the BWM consistency ratio is calculated using ξ and the corresponding consistency index after obtaining the optimal value as follows:
3.2. GIS Analysis
GIS spatial analysis provides support for multidimensional spatial decision-making through the processing and visualization of geographic data, optimizes resource allocation, and enhances decision-making efficiency. In recent years, due to its unique advantages in handling complex geographic information and conducting comprehensive multi-factor analysis, GIS has found widespread application in site selection. Site selection involves multiple factors, such as railway networks, road networks, terrain and distribution density of pallet manufacturers. GIS can effectively integrate and analyze these spatial data, provide accurate suitability assessments, and help decision makers select the optimal site under multiple factors.
3.3. The DEA Model
DEA is a non-parametric method for efficiency measurement, which does not require the specification of a production function. It produces relatively objective results, and most importantly, can measure the efficiency of decision-making units with multiple inputs and multiple outputs.
The DEA-RAM model applied in this study has several advantages. It accommodates multiple types of input and output indicators. Its objective function takes into account the influence of both the number of indicators and the data range on the results, which ensures that the calculated efficiency scores do not show bias due to changes in the number of indicators. Moreover, the number of input and output indicators of decision-making units does not affect the selection of the optimal solution, and there is eliminating the need for preprocessing of the original data.
Step 1: The GIS analysis results are used to divide the study area into administrative units. This division provides a spatial basis for the following efficiency assessment. Each administrative division unit represents a potential alternative site, fully ensuring the rationality and operability of the spatial distribution.
Step 2: On this basis, scientific site selection measurement indicators are established. Key indicators involved in the site selection process are identified, and corresponding input and output variables are defined according to these indicators.
Step 3: Adopt the DEA-RAM model to calculate the comprehensive efficiency of each administrative unit, compare the efficiency scores of different sites, and identify the optimal site for construction.
The previous DEA-RAM model was proposed by Cooper et al. [37], as shown below:
To avoid the issues caused by the non-linearity of the objective function, additional mathematical transformations are required to measure the inefficiency ratio. However, the goal of this study is to obtain the maximum efficiency score. The final mathematical transformation model is as follows:
where , are the th input and th output of , respectively. , denote the slack variables for the th input and th output, respectively; is the range of the th input; is the range of the th output; Constraint denotes the model’s assumption of variable returns to scale.
Step 4: After the application of the DEA-RAM model, multiple decision-making units (DMUs) may simultaneously reach the production frontier, leading to relative efficiency among several units and making it difficult to determine superiority. To address this issue, the super-efficiency DEA model has been introduced. This approach eliminates the limitation of the DEA-RAM model, which restricts further assessment and comparison among efficient units, and allows for a clear differentiation and ranking of DMUs. As the exclusion of the efficient unit causes the frontier to retract, the originally efficient unit achieves a super-efficiency score greater than 1.0. This method addresses the traditional DEA model’s limitation in distinguishing among fully efficient units by relaxing the convexity constraints of the production possibility set. Its theoretical validity was established by Andersen and Petersen within the axiomatic framework of super-efficiency models. Due to the limitations of the input-oriented radial model, further mathematical transformations are required to construct a non-oriented super-efficiency DEA model. The resulting transformed model is as follows:
where and indicate ’s inputs savings, outputs surpluses, respectively.
4. Case Studies
The proposed integrated BWM-GIS-DEA comprehensive decision-making model is applied to the site selection of pallet pooling service centers in Inner Mongolia, China. As shown in Figure 2, Inner Mongolia spans across three major regions: Northeast, North, and Northwest China. Currently, Inner Mongolia has not yet established a pallet pooling system. As a result, the region has a pallet standardization rate of less than 10%, a unit logistics cost 5% higher than the national average. Establishing pallet pooling service centers can effectively improve pallet standardization rates and significantly reduce logistics costs. Therefore, it is imperative to establish pallet pooling service centers to enhance regional logistics efficiency and reduce overall logistics expenditures.
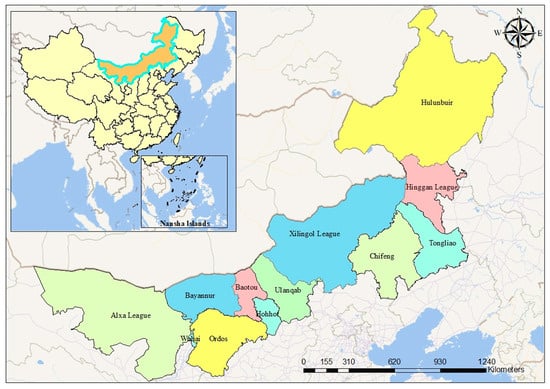
Figure 2.
Location map of Inner Mongolia.
In this section, key factors for the site selection for pallet pooling service centers are determined based on the geographical characteristics of the region and expert consultation.
In this task, the weights of 13 criteria are determined across five dimensions: economic factors (C1), transportation factors (C2), geographic location factors (C3), technological factors (C4), and service coverage factors (C5). In this study, the reclassification process was applied to transform the original raster layer values into new indicator categories. Reclassification refers to reorganizing or reinterpreting the values of raster data, with the critical step being to establish a clear correspondence between the original data and the newly defined classes. The criteria for reclassification were determined according to the characteristics of the original datasets and the practical conditions of the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, and further refined through expert consultation to ensure that the indicator settings are reasonable and locally applicable. The correspondence between the original values and the reclassified results is presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
The outline of the input layers for the GIS.
The site selection factors identified in this study are explained in full below.
Urban GDP per capita (C1-1): GDP per capita serves as a crucial socio-economic factor for the site selection of a pallet pooling operations center, as it indirectly reflects the economic strength and market demand of a region. A higher GDP per capita typically indicates stronger consumer demand, higher levels of industrialization, and more complex logistics requirements, all of which significantly influence the operation and demand for the pallet pooling system. Therefore, selecting cities with higher GDP per capita for the establishment of pallet pooling service centers can contribute to the efficient flow of pallet resources and enhance overall service efficiency.
GDP growth rate (C1-2): The GDP growth rate reflects the growth potential and vitality of a region’s economy. Selecting a region with a higher GDP growth rate indicates that the region’s economy is expanding, with increased market demand and a corresponding rise in demand for logistics services. This offers greater service opportunities and potential for growth for the pallet pooling system.
Tertiary industry growth rate (C1-3): The tertiary industry growth rate reflects the development of a region’s service sector, particularly industries closely associated with pallet pooling, such as logistics, transportation, and retail. The rapid expansion of the service industry directly drives the demand for logistics infrastructure and the efficient utilization of resources. Consequently, selecting regions with higher tertiary industry growth rates can better address market demand, enhance the return on investment in pallet pooling service centers, and promote the coordinated development of regional economies.
Railway network (C2-1): The factor aims to assign priority to the railway network to access pallet pooling service centers based on the distance between sites. Pallets, as equipment of cargo, often require rail transport for long-distance transportation of bulk goods. Railway transport offers high capacity and low unit transport costs, so the coverage of the railway network directly impacts the logistics costs and transportation efficiency of pallet pooling service centers. In this study, the railway network was divided into five levels.
Road network (C2-2): The development level of the road network also significantly influences the service efficiency and logistics costs of a pallet pooling service center. A well-developed road network can enhance pallet circulation efficiency, shorten transportation time, and reduce transportation costs, particularly for short-distance and fast inter-city distribution. In this study, the road network was categorized into five levels.
Throughput of national logistics hubs (C2-3): A logistics hub with high throughput means that logistics demand is concentrated in the region and goods circulate frequently, while pallets, as an important part of logistics infrastructure, will have higher demand for use and stronger market mobility. The construction of pallet pooling service centers in these regions can not only improve the efficiency of the use of pallet resources, but also effectively reduce the problem of returning empty pallets in the transport process.
Total freight volume (C2-4): Firstly, the core function of pallet pooling service centers is to optimize the pooling and circulation of pallet resources. A higher total freight volume indicates a greater demand for logistics and transportation services in the region, particularly for mobile assets such as pallets, which will also increase accordingly. Secondly, regions with a higher total freight volume typically feature well-developed transport infrastructure and a more established logistics chain, which further facilitates the efficient flow and pooling of pallets. Therefore, selecting regions with higher total freight volume for the site of pallet pooling service centers can optimize pallet utilization and sustain the service center’s profitability.
Terrain (C3-1): Terrain conditions significantly affect land development feasibility and service ease. Flatter areas are generally more suitable for large logistics centers as they lower construction costs and improve accessibility. In contrast, regions with complex or sloping terrain may require additional infrastructure, such as reinforced roads or protective facilities. These regions are also more prone to flooding and geological hazards, which occur 3–5 times more frequently than in flat areas, posing risks to the safety of palletized assets and service continuity. This increases investment costs and may reduce service efficiency.
Precipitation (C3-2): Warehousing and transportation facilities in pallet pooling service centers must be kept dry to prevent moisture, corrosion, or deformation of pallets, which can negatively impact their lifespan and transport efficiency. In regions with high rainfall, the need for increased waterproofing requirements for these facilities leads to higher construction and maintenance costs.
Land use (C4-1): The grasslands in Inner Mongolia are part of the plains, characterized by flat terrain, easy accessibility, and low development costs, which make them ideal for construction. In contrast, arable land and forests are restricted by protection policies and are unsuitable for development, while the use of barren land resources is limited. Therefore, prioritizing grassland areas can effectively reduce construction costs and provide suitable space to meet the needs of constructing a pallet pooling service center.
Sites of national logistics hubs (C5-1): National logistics hubs serve as the core nodes of the logistics network, with efficient logistics distribution capacities and extensive transport network connections. These hubs can offer convenient logistics channels and a stable flow of cargo for pallet pooling service centers. Inner Mongolia has 8 national logistics hubs, which makes it crucial to prioritize locations near these hubs. This approach enables full integration of the existing intermodal transport network and infrastructure resources, through the intensive use of railways, highways, and warehousing facilities to significantly reduce pallet transfer costs. Additionally, the mature logistics service cluster and policy support system in these hubs can enhance regional supply chain coordination and service responsiveness, and provide a strategic foundation for the construction of a large-scale, highly flexible pallet pooling service centers.
Distribution density of pallet manufacturers (C5-2): Priority should be given to regions with a high distribution density of pallet manufacturers, as this can shorten the supply chain response radius, significantly reduce purchasing and transport costs, and ensure an adequate and timely supply of pallets. In addition, a high distribution density of pallet manufacturers reduces inventory pressure, improves turnover speed, enables dynamic inventory optimization, and strengthens emergency response capabilities, thereby enhancing the overall service efficiency of the pallet pooling system and providing stable resources for large-scale operations.
Distribution density of potential pallet customers (C5-3): The distribution density of potential customers not only directly influences the frequency of pallet use and turnover speed but also affects the service coverage and distribution efficiency of the service center. Selecting a region with a high distribution density of potential customers for the construction of pallet pooling service centers helps reduce the distance for empty pallet transport and improves asset turnover efficiency. At the same time, leveraging the scale demand network to form the multi-path elasticity of service capacity and enhance the operational resilience under unexpected scenarios.
4.1. BWM and GIS Results
After identifying the standard factors for the site of pallet pooling service centers, we conduct a weighting exercise involving experts from logistics, transport management, and related fields, as detailed in Table 3.

Table 3.
Profile of experts.
To ensure the scientific rigor and consistency of site selection, the experts engage in thorough discussions through an online platform and ultimately reach a consensus on site selection factors, as shown in Figure 3, and the relative importance of each site selection factors, as presented in Table 4.
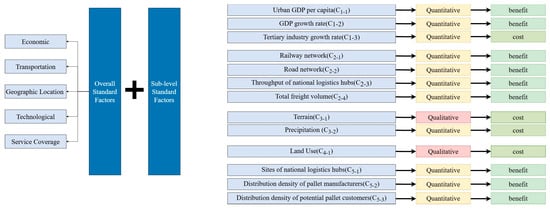
Figure 3.
Factors of site selection.

Table 4.
BWM results for categories and their weights.
Next, we apply the BWM model to accurately calculate the weights of each site selection factor, with the results provided in Table 5, offering a quantitative foundation for subsequent GIS site selection. The second-to-last column in the paper, “Weights,” lists the BWM weights for each sub-level standard.

Table 5.
Weights of BWM results and global weights of sub-level standard.
Transport factors were identified as the most important (best) category, while economic factors were considered the least important (worst) category. The corresponding weights and inconsistency ratios for each category are presented in Table 4, where C2 > C5 > C3 > C4 > C1. In the next step, we first apply the BWM model to each overall standard individually to compute the weights of overall standard factors. Then, we apply the BWM model to each sub-level standard individually to calculate the weights of sub-level standard factors and determine the specific weights for the sub-level standard within each overall standard.
After completing the weight determination process, we use ArcGIS to generate a suitability map for each sub-level standard factor, as shown in Figure 4. The raster data used in this study have a pixel size of 30 m × 30 m.
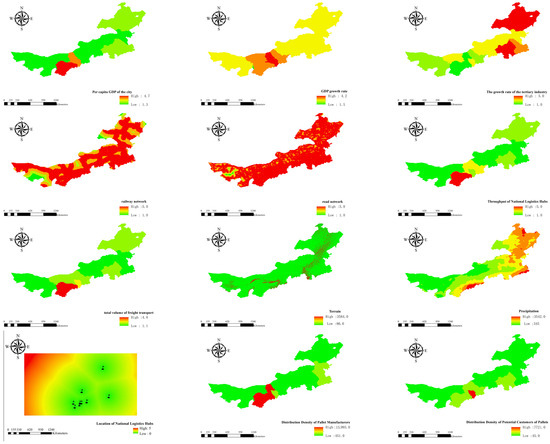
Figure 4.
Suitability maps of sub-level standard factors.
Building on this, we further overlay the suitability map of each sub-level standard factor to generate the overall standard factors suitability map, as shown in Figure 5.
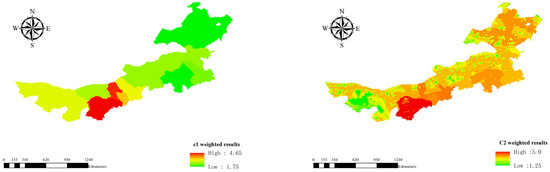
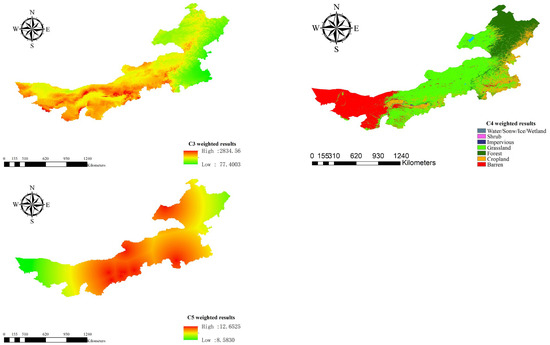
Figure 5.
Suitability maps of overall standard factors.
Ultimately, by combining the suitability maps of overall standard factors, a global suitability map is calculated as an alternative for the site of pallet pooling service centers, as shown in Figure 6.
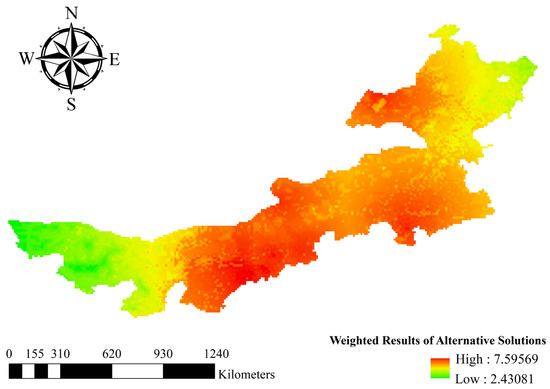
Figure 6.
Global suitability map.
Based on the results of this analysis, 6 alternative cities are identified as alternative sites for pallet pooling service centers. All these site options effectively meet the actual needs of pallet pooling service centers in Inner Mongolia.
From the economic, transportation, geographic location, technological, and service coverage factors, these 6 alternative cities are all suitable, with satisfactory characteristics for pallet pooling service centers. However, due to factors such as average land price and labor wage, we should select the optimal site from among them. Therefore, in the second stage, the 6 alternative cities identified from the GIS map will be measured by DEA, based on the new decision standard provided by the experts.
4.2. DEA Measurement of Alternative Sites
There are two issues with the alternatives for pallet pooling service centers identified based on the BWM and GIS methodologies: first, multiple alternatives exist within a region; second, pallet pooling service centers impossible not be constructed simultaneously across regions. Therefore, it is essential to determine the construction timing by conducting a DEA measurement of the site selection.
4.2.1. The First Layer Efficiency Measurement—Based on the DEA-RAM Model
Based on the GIS-generated alternatives, 6 alternative cities are divided into 18 DMUs, labeled A1 to A18 (as shown in Figure 7), according to administrative regions.
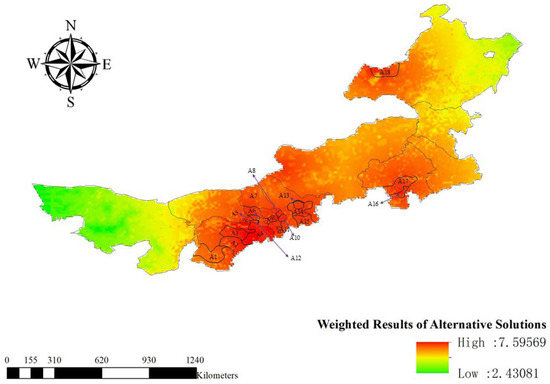
Figure 7.
Map of the division of alternative sites.
The average land price and labor wage are selected as input indicators, while the number of pallets owned is used as the output indicator. Table 6 shows the input and output indicators.

Table 6.
The input and output indicators.
Average land price reflects the scarcity of land resources from a spatial economic perspective, especially in regional economies. It indirectly constrains production efficiency by influencing firms’ site choices and long-term investment strategies. Average land price is part of fixed costs and reveals potential constraints on resource allocation due to regional differences, even though its direct correlation with output is weak. Labor wage is the core indicator of dynamic inputs in the production system. An increase in labor wage leads to an increase in efficiency by upgrading the system or adding more pallets. As a key indicator of logistics efficiency, pallet ownership directly reflects the level of asset allocation in the transport chain. An increase in pallet ownership generally signifies an enhancement in logistics efficiency, thereby carrying a clear and measurable impact on output performance.
The Pearson correlation coefficients among the DEA input and output variables are shown in Figure 8. The correlation between Labor Wage and Pallet Ownership is 0.69, which indicates a moderate positive relationship. In contrast, the correlations of Average Land Price with Labor Wage (−0.13) and with Pallet Ownership (0.03) are both weak and reflect almost no linear relationship. These results suggest that no significant multicollinearity exists among the variables, and the variables are suitable for inclusion in the DEA model.
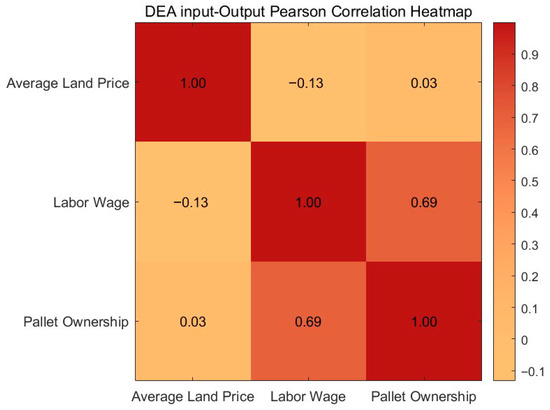
Figure 8.
Heat map of Pearson’s correlation coefficient.
The DEA-RAM model is then applied to calculate the efficiency score of each DMU. As shown in Figure 9, the results of the DEA-RAM model calculations indicate that transport factors play a crucial role in the site selection of pallet pooling service centers. Sites with an efficiency score of 1.0, such as A2, A5, A6, A9, A12, A14, and A18, demonstrate high resource utilization efficiency. These areas are capable of achieving a high level of pallet usage while maintaining relatively low inputs in terms of average land price and labor wage. This indicates that the convenience of transport and the control of logistics costs are optimized in these sites and the service efficiency of the pallet pooling system is fully reflected.
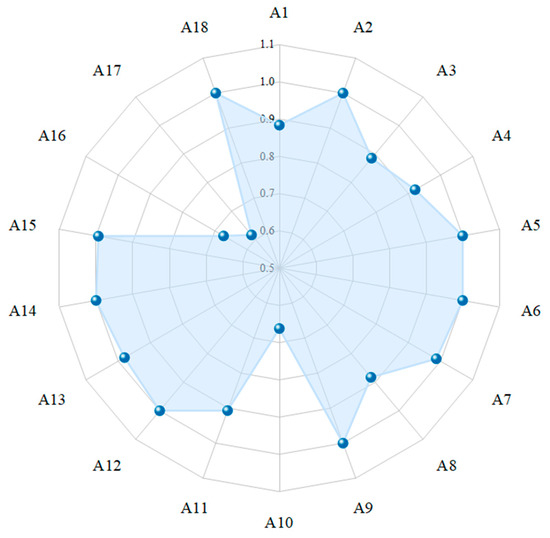
Figure 9.
Efficiency scores of DMUs.
On the other hand, sites with lower efficiency scores, such as A4 and A3, fail to optimize resource allocation due to higher average land price and labor wage, despite owning a larger number of pallets. High input costs limit the efficient utilization of pallet resources in these areas, highlighting the need to thoroughly consider the input-output relationship between average land price and labor wage in the site selection of pallet pooling operations.
The site selection of a pallet pooling service center relies not only on pallet demand but also on factors such as land price and labor wage. A scientific choice of location should reduce costs and ensure efficient pallet flows, thereby improving service efficiency.
4.2.2. The Second Layer Efficiency Measurement—Based on the Super-Efficiency DEA Model
In this study, the preliminary efficiency measurement of the 18 DMUs is conducted using the DEA-RAM model, and the results are presented in Figure 9. 7 DMUs (A2, A5, A6, A9, A12, A14, and A18) lie on the production frontier, with each achieving a technical efficiency score of 1.0. This result reflects a phenomenon of efficiency homogenization. Given the limitations of the traditional DEA model in distinguishing among fully efficient DMUs, which hinders the prioritization of sites for constructing pallet pooling service centers, this study proposes a super-efficiency DEA model for secondary measurement. This approach allows fully efficient DMUs to surpass the frontier boundary, establishes a differentiated efficiency scale, and quantifies the relative advantages among efficient units, thereby providing a refined basis for hub site prioritization.
The DEA-RAM model exhibits inherent limitations in efficiency measurement, as it classifies DMUs in a binary manner into efficient units (efficiency score of 1.0) and inefficient units (efficiency score less than 1.0) by constructing a production frontier. Specifically, in the site selection of a pallet pooling service center, the decision maker’s primary objective is to rank the potential DMUs rather than merely identify their relative efficiency. However, the findings of this study highlight the need to move beyond this traditional classification framework.
The calculations yielded the final efficiency scores presented in Figure 10. It is evident that A2 achieves the highest efficiency score of 1.1560. Based on both the first and second layer DEA efficiency measurement, it was chosen to construct a pallet pooling service center in Ejin Horo Banner.
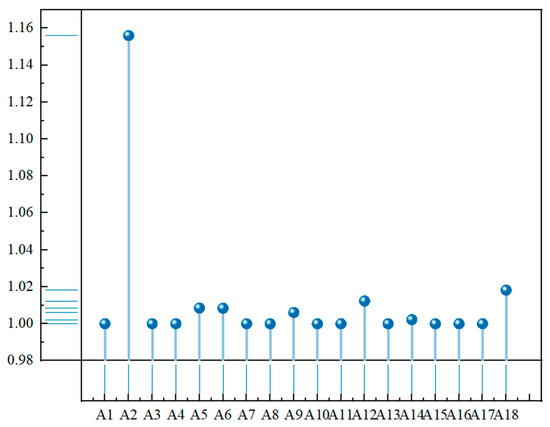
Figure 10.
Super-efficiency DEA results.
4.3. Comparative Analysis
Based on the two-layer DEA efficiency measurement framework, this study first identifies the effective DMUs (efficiency score= 1.0) located on the production frontier through the first-layer DEA-RAM model. In the second stage, the super-efficiency DEA model is applied to rank the frontier units more precisely. The data in Table 7 indicates that, as measured by the two-layer measurement, A2 demonstrates significant resource allocation effectiveness in the resource input dimension of pallet operations, with a super-efficiency score of 1.1560. This is notably higher than the second-ranking site, A4 (efficiency score = 1.0182). This result suggests that, while maintaining the current output level, A2 can still accommodate up to 15.6% input redundancy, which establishes it as the optimal site for the pallet pooling operations center. Through the two-layer DEA efficiency measurement, Ejin Horo Banner, Ordos, is finally selected as the priority construction site.

Table 7.
Results of two-layer DEA efficiency measurement.
It avoids the limitations of traditional single-objective optimization or isolated tools by combining BWM GIS and DEA. BWM determines weights for 13 criteria across 5 dimensions with consistency checks to reduce subjectivity. GIS generates a global suitability map to screen 6 alternative cities and resolve the efficiency coverage paradox in sparse regions like Inner Mongolia. The two-layer DEA which includes DEA-RAM and super efficiency DEA identifies fully efficient DMUs and ranks them clearly solving the efficiency homogenization issue that traditional DEA cannot address. This integrated approach meets the complex demands of pallet pooling service center site selection that traditional methods fail to satisfy.
5. Discussion
5.1. Findings and Implications
The integrated BWM-GIS-DEA method proposed in this paper addresses the limitations of conventional site selection models by combining multi-criteria weight assignment, spatial suitability analysis and efficiency measurement. This method provides a scientific and comprehensive framework for the site selection of complex logistics facilities.
Contrary to conventional models that typically depend on static weight assumptions or subjective scoring systems, the proposed method integrates the BWM to derive decision weights, thereby minimizing inconsistency. Additionally, GIS are employed to spatially analyze the distribution of supply and demand attributes, offering a localized perspective. The inclusion of DEA further refines the measurement process by implementing a performance-based ranking system that addresses input-output imbalances among the DMUs.
The effectiveness of this method is demonstrated through its application to a real-world case in Inner Mongolia. The method identifies Ejin Horo Banner as the most efficient site. This result is closely aligned with the region’s logistics demands and infrastructure readiness. Ejin Horo Banner features Ordos International Airport, multiple railway logistics parks, and national highways. This location provides it with significant logistics radiation advantages. Relying on abundant coal resources and a well-developed industrial chain, the region has generated an urgent demand for pallet pooling systems. Therefore, the construction of a pallet pooling service center has become imperative. It can not only efficiently support pallet circulation in the local area and surrounding cities (such as Baotou and Hohhot), improve logistics efficiency and resource utilization, but also provide strong support for reducing logistics costs and promoting green development in the region. This result indicates that the proposed method is not only theoretically robust but also practically reliable in guiding facility location decisions under conditions of spatial and economic complexity.
This paper has both practical value and theoretical significance. From a practical perspective, the integrated BWM–GIS–DEA framework provides logistics enterprises and local governments with a replicable tool. It helps reduce costs, improve pallet turnover, and expand service coverage in a phased manner. From a theoretical perspective, the study contributes an integrated methodological framework that can be applied beyond the Inner Mongolia case. It provides a replicable approach for logistics facility location research. Potential extensions include incorporating undesirable outputs in the DEA-RAM model. Another extension is developing dynamic multi-period GIS–DEA applications. These can capture evolving infrastructure and demand patterns.
The results of this study demonstrate that the integrated BWM–GIS–DEA framework can effectively identify optimal pallet pooling center locations by balancing economic, transportation, geographic, technological, and service coverage factors. This multidimensional approach goes beyond the traditional cost-centered perspective emphasized in earlier studies, such as Zhou and Song [14], which primarily focused on minimizing transportation expenses. In contrast, our model incorporates service coverage and geographic location. Therefore, it provides a more comprehensive evaluation consistent with the growing emphasis on sustainability in logistics research, as highlighted by Accorsi et al. [12]. Moreover, previous studies often relied on single-objective optimization or isolated methodological tools, leading to partial or biased results. Our research demonstrates that an integrated approach is capable of simultaneously handling spatial suitability, weight assignment, and efficiency evaluation. This directly addresses the shortcomings identified in the literature review, namely the lack of holistic frameworks that consider multiple objectives and the limited application of pallet pooling in sparsely populated regions. By overcoming these gaps, our findings not only validate the feasibility of pallet pooling center selection in the Inner Mongolia case but also offer generalizable insights for extending the methodology to areas with different population densities and economic structures.
5.2. Generalizability and Adaptation
The Integrated BWM-GIS DEA framework is portable. It needs to be calibrated and adjusted according to different situations. We consider two scenarios: densely populated urban areas and areas with different economic structures.
Because it is phased and data-driven, BWM supplies normalized criterion weights, GIS generates suitability-map raster, and DEA-RAM with super-efficiency DEA yields a performance-based ranking. This compatibility ensures that the same methodology can be employed without altering its fundamental structure. In practice, only variables are tuned categories and sub-level standard weights, the content and resolution of GIS layers, and DEA inputs and outputs. Undesired outputs can be added when appropriate. DMUs can be defined at city or regional scales. In dense cities or economies with different structures, decision makers add, remove, or rescale context-specific variables such as traffic congestion rates, land-lease prices, hub capacity, distribution density of pallet users, and freight throughput. The model itself requires no modification. Variable adjustments tailor the framework to each region.
6. Conclusions
6.1. Findings and Conclusions
This study innovatively proposes a BWM-GIS-DEA integrated decision-making method, which systematically constructs a multi-stage decision-making framework for the site selection of pallet pooling service centers. First, the weights for economic, transportation, geographic location, technological, and service coverage factors are quantified based on the BWM. Then, a global suitability map was generated by combining GIS spatial overlay analysis, from which 6 alternative cities were selected as the locations of pallet sharing service centers. These alternative sites not only meet high standards for transportation accessibility and terrain conditions but also offer comprehensive advantages in resource optimization and environmental impact control. Next, 6 alternative cities are subdivided into 18 DMUs, and their comprehensive technical efficiency is measured using a non-radial DEA-RAM model, identifying 7 fully efficient units (OTE = 1.0). To address the priority ranking problem among the fully efficient units, the super-efficiency DEA model is applied to overcome the limitations of traditional efficiency boundaries. Ultimately, Ejin Horo Banner, Ordos, is identified as the optimal construction site.
The results indicate that transportation factors hold the highest weight. Specifically, factors such as railway and road networks, the throughput of national logistics hubs, and total freight volume significantly influence the site selection decision. These factors not only affect the convenience and timeliness of transportation but also play a major role in determining transportation costs, which directly impact the service efficiency of pallet pooling service centers. In particular, shorter distances to railway and road networks lead to lower transportation costs and higher service efficiency. National logistics hubs with higher throughput and larger freight volumes show stronger regional pallet demand. This increase further promotes the growth of pallet pooling. Therefore, transportation factors are critical in optimizing the site selection of pallet pooling service centers.
This study contributes both theoretically and practically to the field of pallet pooling site selection by providing an integrated evaluation model and a replicable analytical framework. Previous studies mainly adopted single-objective optimization approaches, which fail to simultaneously account for economic, environmental, and operational performance factors. To address this gap, our study aims to answer the following research question: how can an integrated approach balance these multidimensional factors to achieve scientific site selection for pallet pooling? By implementing a combined BWM–GIS–DEA framework for selecting pallet pooling service centers, this study effectively incorporates multidimensional considerations into the site selection process. Thus, it offers a robust decision-making tool for both researchers and practitioners.
Despite these contributions, several limitations of the study should be acknowledged. First, the analysis is based on regional data and expert evaluations that are specific to the Inner Mongolia context. As a result, the weights derived through BWM and GIS reflect localized conditions, which may not be directly applicable to other geographical areas or industry sectors. Second, the model is constructed under a static framework and does not account for temporal variations such as changes in demand patterns or the development of infrastructure over time. Third, the DEA model employed in this study incorporates a relatively limited range of input and desired output indicators and does not include undesired outputs.
Future research can be deepened in the following directions: First, it is meaningful to introduce fuzzy sets or gray theory in weight calculation to deal with demand fluctuation and policy uncertainty. Second, it is also valuable to explore the synergistic relationship between facility expansion and network evolution by combining multi-period dynamic optimization models. And third, extending the framework to new logistics scenarios, such as cold-chain warehousing and shared distribution centers, to test its general applicability. Furthermore, the research results can serve as practical references for regional green logistics network planning and support the synergistic development of supply chain resilience and sustainability.
In summary, this study addresses the specific challenge of site selection for pallet pooling service centers through the application of the BWM-GIS-DEA integrated decision-making method. It also provides a theoretical foundation and practical guidance for the development of sustainable logistics networks.
6.2. Policy and Social Implications
Based on the core findings of the study and the identified improvement paths, the following recommendations for social impact and policy adjustments are put forward:
- (1)
- Given the advantages of the site selection of pallet pooling service center, relevant departments should provide long-term industrial land leasing services at such locations and similar nodes, and offer preferential rates.
- (2)
- Since constructing a pallet pooling service center near a transportation hub can enhance pallet sharing efficiency, relevant departments should prioritize the planning of logistics land around the hub and provide financial support for the last-mile road-to-rail connection facilities to reduce empty trips.
- (3)
- To promote pallet standardization, the government should provide subsidies to pallet pooling service center and establish unified contract standards for green logistics.
Author Contributions
Y.D.: Conception and design, Methodology, Analysis and Interpretation of the data, Writing—original draft, Visualization. J.R.: Supervision, Validation, Revising content and editing. X.X.: Investigation, Validation, Revising content and editing. C.F.: Research, Validation. R.Z.: Software, Editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant [72262024], the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant [71862026], and the Graduate Research and Innovation Project of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region under Grant [KC2024014S].
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, J.W. Ren, upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
References
- Gürol, P.; Yurdabak, S.; Gul, A.Y.; Cakmak, E. Pallet pooling service provider selection with an intuitionistic fuzzy-based AROMAN model. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 498, 145189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrano, A.L.; Pazour, J.A.; Roy, D.; Thorn, B.K. Selection of pallet management strategies based on carbon emissions impact. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2015, 164, 258–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.; Carrano, A.L.; Pazour, J.A.; Gupta, A. Cost-effective pallet management strategies. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2016, 93, 358–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhakuni, M.S.; Bhakuni, P.; Das, A. Stability analysis of multi-criteria decision making techniques for relief centre location selection: A safety-centric relocation model with cost considerations. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2025, 144, 109932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, D. An improved multi-objective method for the selection of driverless taxi site locations. Int. J. Transp. Sci. Technol. 2024, 18, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ran, H.; Zhang, S. Location-routing optimization problem of country-township-village three-level green logistics network considering fuel-electric mixed fleets under carbon emission regulation. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2024, 194, 110343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, C.; Wang, Y.; Estefen, S.F.; Wang, Y. Layout optimization of the “Pipe+Ship” transmission network for the decentralized offshore wind power-hydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 59, 991–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Liu, B.; Wang, Z. An optimization model for multi-type pallet allocation over a pallet pool. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2017, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Jiang, X.; Huang, N.; Huang, Y.; Yong, X.; Xu, C. A two-stage framework for site selection of deep-sea offshore wind-to-hydrogen projects based on GIS—MULTIMOORA method under Pythagorean triangular fuzzy environment. Ocean Eng. 2024, 313, 119416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Liu, Y. Analysis of a Commercial Mode for the Pallet Pooling System. ICTE 2015, 2015, 2095–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.H.; Tsang, Y.P.; Lee, C.K.M.; Ching, W.K. A blockchain-iot platform for the smart pallet pooling management. Sensors 2021, 21, 6310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accorsi, R.; Baruffaldi, G.; Manzini, R.; Pini, C. Environmental impacts of reusable transport items: A case study of pallet pooling in a retailer supply chain. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wen, Z.; Tan, Y.; Ekins, P. Circular economy strategies for the booming industrial pallet use in China. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2024, 46, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; He, S.; Song, R. Optimization for Service Routes of Pallet Service Center Based on the Pallet Pool Mode. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2016, 2016, 5691735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Song, R. Location Model of Pallet Service Centers Based on the Pallet Pool Mode. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 3rd Information Technology, Networking, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (ITNEC), Piscataway, NJ, USA, 15–17 March 2019; pp. 1185–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosouli, S.; Hassani, R.A. Application of multi-criteria decision making (MCDM) model for solar plant location selection. Results Eng. 2024, 24, 103162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Işık, Ö.; Shabir, M.; Moslem, S. A hybrid MCDM framework for assessing urban competitiveness: A case study of European cities. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2024, 96, 102109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, J. Best-worst multi-criteria decision-making method. Omega 2015, 53, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, X.; Tang, M.; Liao, H.; Shen, W.; Lev, B. The state-of-the-art survey on integrations and applications of the best worst method in decision making: Why, what, what for and what’s next? Omega 2019, 87, 205–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, W.K.; Huang, S.H.; Le, T.N.N.; Huynh, N.T.; Wang, D.J. Assessing container terminals’ efficiency from the sustainable development perspective: The BWM-GRA-SBM model. Transp. Policy 2025, 162, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, J.; van Roekel, W.S.; Tavasszy, L. Measuring the relative importance of the logistics performance index indicators using Best Worst Method. Transp. Policy 2018, 68, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badri Ahmadi, H.; Kusi-Sarpong, S.; Rezaei, J. Assessing the social sustainability of supply chains using Best Worst Method. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 126, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Fei, L. Exploring obstacles to the use of unmanned aerial vehicles in emergency rescue: A BWM-DEMATEL approach. Technol. Soc. 2025, 81, 102863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Chen, L. DEA-BWM cross efficiency target setting with preferences. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2023, 183, 109525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badi, I.; Pamučar, D.; Stević, Ž.; Muhammad, L.J. Wind farm site selection using BWM-AHP-MARCOS method: A case study of Libya. Sci. Afr. 2023, 19, e01511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H. Urban landscape accessibility evaluation model based on GIS and spatial analysis. Results Eng. 2025, 25, 103723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Xiong, K.; Lei, G.; Luo, Y.; Liu, W. A study on the macro-micro two-stage site selection of electric-hydrogen hybrid refueling stations based on GIS and Fuzzy-TODIM. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 141, 444–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, İ.; Kocer, A.; Aksoy, E. Site selection for solar power plants using GIS and fuzzy analytic hierarchy process: Case study of the western mediterranean region of Turkiye. Renew. Energy 2024, 237, 121799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghaloo, K.; Ali, T.; Chiu, Y.R.; Sharifi, A. Optimal site selection for the solar-wind hybrid renewable energy systems in Bangladesh using an integrated GIS-based BWM-fuzzy logic method. Energy Convers. Manag. 2023, 283, 116899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rane, N.L.; Mallick, S.K.; Saha, A.; Pande, C.B.; Rane, J.; Roy, R.; Alshehri, F.; Radwan, N. Appraisal on suitable landfill site selection for municipal solid waste disposal using GIS and MIF methods. Phys. Chem. Earth 2024, 134, 103591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, H.; Gu, Y.; Lu, F.; Mahreen, S. Site selection of electric vehicle charging station expansion based on GIS-FAHP-MABAC. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 507, 145557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiyas, S.; Sikarudi, D.; Jafari, M. A novel integrated GIS-AI framework for optimal CSP plant site selec-tion: A multi-criteria approach under climate change scenarios in Bushehr, Iran. Adv. Space Res. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökler, S.H. Enhanced site selection for solar power plants utilizing the geographic information system and pythagorean fuzzy analytical hierarchy process method. Sustainable Energy. Grids Netw. 2025, 44, 101929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charnes, A.; Cooper, W.W.; Rhodes, E. Measuring the Efficiency of Decision Making Units. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1978, 2, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emrouznejad, A.; Yang, G.-L. A survey and analysis of the first 40 years of scholarly literature in DEA: 1978–2016. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2018, 61, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueyoshi, T.; Yuan, Y.; Goto, M. A literature study for DEA applied to energy and environment. Energy Econ. 2017, 62, 104–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, W.W.; Park, K.S.; Pastor, J.T. RAM: A Range Adjusted Measure of Inefficiency for Use with Additive Models, and Relations to Other Models and Measures in DEA. J. Product. Anal. 1999, 11, 5–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Ren, J.; Chen, C. Assessing the logistics industry efficiency with a modified range adjusted measure. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 17653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Ren, J.; Song, W.; Li, L. An integrated range-adjusted measure model with undesirable outputs. J. Ind. Manag. Optim. 2025, 21, 2925–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Mai, L.; Huang, F.; Zeng, Z. Regional healthcare resource allocation and decision-making: Evaluating the effectiveness of the three-stage super-efficiency DEA model. Heliyon 2024, 10, e40312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, T.; Liao, X.; Yang, S.; Yu, T. Towards sustainability: Evaluating energy efficiency with a super-efficiency SBM-DEA model across 168 economies. Appl. Energy 2024, 376, 124254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, M.; Chatterjee, P.; Pamucar, D.; Chakraborty, S. Development of an integrated decision making model for location selection of logistics centers in the Spanish autonomous communities. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 148, 113208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.N.; Dang, T.T.; Nguyen, N.A.T.; Wang, J.W. A combined Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA) and Grey Based Multiple Criteria Decision Making (G-MCDM) for solar PV power plants site selection: A case study in Vietnam. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 1124–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raad, N.G.; Rajendran, S. A hybrid robust SBM-DEA, multiple regression, and MCDM-GIS model for airport site selection: Case study of Sistan and Baluchestan Province, Iran. Transp. Eng. 2024, 16, 100235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).