Digital-Technology-Enhanced Immersive Learning in Chinese Secondary School Geography Education: A Comprehensive Comparative Analysis of Sustainable Pedagogical Transformation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Theoretical Foundations for Sustainable Digital Geography Education
2.2. Comparative Sustainability Analysis of Digital Versus Traditional Geography Education
2.3. Challenges and Opportunities in Sustainable Digital Geography Education
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Comparative Research Design and Sustainability Framework
3.2. Site Selection and Comparative Sampling Strategy
3.3. Comparative Data Collection Instruments and Procedures
3.4. Comparative Data Analysis Strategy
3.5. Integration of Comparative Findings
4. Results
4.1. Comprehensive Sustainability Performance Analysis
4.2. Educational Effectiveness and Learning Outcome Comparisons
4.3. Economic Viability and Resource Efficiency Analysis
4.4. Social Equity and Implementation Scalability
5. Discussion
5.1. Reconceptualizing Sustainability in Educational Technology Integration
5.2. Pedagogical Innovation Through Sustainability Constraints
5.3. Confronting Equity Challenges in Sustainable Education Transformation
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tsivitanidou, O.E.; Georgiou, Y.; Ioannou, A. A Learning Experience in Inquiry-Based Physics with Immersive Virtual Reality: Student Perceptions and an Interaction Effect Between Conceptual Gains and Attitudinal Profiles. J. Sci. Educ. Technol. 2021, 30, 841–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stieler-Hunt, C.; Jones, C. A professional development model to facilitate teacher adoption of interactive, immersive digital games for classroom learning. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 2019, 50, 264–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Xu, S. A Study on Factors Influencing Digital Reading Behavior of Junior High School Students. Libri 2024, 74, 255–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, M.H.; Herbert, C.; Polly, P. A synthetic review of learning theories, elements and virtual environment simulation types to improve learning within higher education. Think Ski. Creat. 2025, 56, 101732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbaripour, A.N.; Talebian, N.; Miller, D.; Tumpa, R.J.; Zhang, W.; Golmoradi, M.; Skitmore, M. A Systematic Review of the Impact of Emerging Technologies on Student Learning, Engagement, and Employability in Built Environment Education. Buildings 2024, 14, 2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, W.; Samuel, J. Grassroots organisations and the sustainable development goals: No one left behind? BMJ 2019, 365, l2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodwin, J.; Zaman, U. Editorial: Mental health stigma and UN Sustainable Development Goals. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1190406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolaou, C.K. Editorial: Nutrition and sustainable development goal 17: Partnerships for the goals. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1480618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wu, T.; Zhang, H.; Yang, D. National innovation systems and the achievement of sustainable development goals: Effect of knowledge-based dynamic capability. J. Innov. Knowl. 2023, 8, 100310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustakim, K.R.; Eo, M.Y.; Mustakim, I.G.; Kim, S.M. Sustainable Development Goals for Cleft Care. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2025, 36, e258–e264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criollo-C, S.; Uzcategui, J.E.C.; Guerrero-Arias, A.; Samala, A.D.; Rawas, S.; Lujan-Mora, S. Analysis of the Mental Workload Associated with the Use of Virtual Reality Technology as Support in the Higher Educational Model. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 114370–114381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buragohain, D.; Chaudhary, S.; Punpeng, G.; Sharma, A.; Am-in, N.; Wuttisittikulkij, L. Analyzing the Impact and Prospects of Metaverse in Learning Environments Through Systematic and Case Study Research. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 141261–141276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zammit, J. Could virtual reality be the next approach for international students learning Maltese? Educ. Technol. Res. Dev. 2024, 72, 3471–3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Kang, J.; Xu, M.; Wu, F.; Zhang, H.; Huang, H.; Niyato, D.; Mao, S. Efficient Twin Migration in Vehicular Metaverses: Multi-Agent Split Deep Reinforcement Learning with Spatio-Temporal Trajectory Generation. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2025, 24, 8214–8227. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Sensibaugh, T.; Bodenheimer, B.; McNamara, T.P.; Nazareth, A.; Newcombe, N.; Minear, M.; Klippel, A. Desktop versus immersive virtual environments: Effects on spatial learning. Spat. Cogn. Comput. 2020, 20, 328–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, S.; Agrawal, A.; Alyuz, N.; Chierichetti, R.; Durham, L.M.; Manuvinakurike, R.; Okur, E.; Sahay, S.; Sharma, S.; Sherry, J.; et al. Exploring Kid Space in the wild: A preliminary study of multimodal and immersive collaborative play-based learning experiences. Educ. Technol. Res. Dev. 2022, 70, 205–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassenfeldt, C.; Jacques, J.; Baggili, I. Exploring the Learning Efficacy of Digital Forensics Concepts and Bagging & Tagging of Digital Devices in Immersive Virtual Reality. Forensic Sci. Int. Digit. 2020, 33, 301011. [Google Scholar]
- Kee, T.; Zhang, H. Digital Experiential Learning for Sustainable Horticulture and Landscape Management Education. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, S.; Gao, J.; Hu, H.; Liu, J.; Wu, W.; Wang, J.; Huang, X.; Lai, H.; et al. Mitochondrial genome assembly and comparative analysis of decaploid Camellia hainanica. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 16, 1556379. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Z.; Yang, H. From Game Elements to Active Learning Intentions: Exploring the Driving Factors in Digital Learning Platforms. SAGE Open 2023, 13, 21582440231208932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udeozor, C.; Chan, P.; Abegao, F.R.; Glassey, J. Game-based assessment framework for virtual reality, augmented reality and digital game-based learning. Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. 2023, 20, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plecher, D.A.; Herber, F.; Eichhorn, C.; Pongratz, A.; Tanson, G.; Klinker, G. HieroQuest—A SeriousGame for Learning Egyptian Hieroglyphs. ACM J. Comput. Cult. Herit. 2020, 13, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wang, D.; Lo, T.; Huang, X. Historical architecture pedagogy meets virtual technologies: A comparative case study. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2024, 29, 14835–14874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scuotto, C.; Triberti, S.; Iavarone, M.L.; Limone, P. Digital interventions to support morality: A scoping review. Br. J. Educ. Psychol. 2024, 94, 1072–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieger, M.B.; Risch, B. How to Maximise Spatial Presence: Design Guidelines for a Virtual Learning Environment for School Use. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2023, 29, 2517–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Kliestik, T.; Rowland, Z.; Bugaj, M. Immersive collaborative business process and extended reality-driven industrial metaverse technologies for economic value co-creation in 3D digital twin factories. Oecon. Copernic. 2025, 16, 125–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Yang, C.; Xing, Y.; Jiang, Z. Immersive human-computer—Computer interaction and digital entertainment new media application in English e-learning mode. Entertain. Comput. 2025, 52, 100878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, K.A.; Brown, A. Immersive virtual reality (VR) for digital media making: Transmediation is key. Learn. Media Technol. 2022, 47, 179–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laine, J.; Rastas, E.; Seitamaa, A.; Hakkarainen, K.; Korhonen, T. Immersive virtual reality for complex skills training: Content analysis of experienced challenges. Virtual Real. 2024, 28, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Cao, P. Digital media entertainment technology based on artificial intelligence robot in art teaching simulation. Entertain. Comput. 2025, 52, 100792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, N.; Murphy, D.; Condon, E.; Lonergan, D.; Lordan, N.; Ni Theachain, D.; O Buachalla, C.; Ui Ghealbhain, C.; McHugh, M.; O’Hehir, C.; et al. Immersive virtual reality in second-level education: A partnered narrative on the challenges and opportunities for STEM engagement. Access Microbiol. 2025, 7, 001028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, P.; Ynnerman, A. Immersive visual interfaces-assessing usability by the effects of learning/results from an empirical study. J. Comput. Inf. Sci. Eng. 2004, 4, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisani, S.; Miller, A.; Hall, M. Digital modes of interpretation of Pictish sculpture. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2024, 29, 10009–10042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, J.; Glize, B.; Laganaro, M. Impact of immersive virtual reality compared to a digital static approach in word (re)learning in post-stroke aphasia and neurotypical adults: Lexical-semantic effects? Neuropsychologia 2025, 208, 109069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmagid, A.S.; Jabli, N.M.; Al-Mohaya, A.Y.; Teleb, A.A. Integrating Interactive Metaverse Environments and Generative Artificial Intelligence to Promote the Green Digital Economy and e-Entrepreneurship in Higher Education. Sustainability 2025, 17, 5594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colecchia, F.; Giunchi, D.; Qin, R.; Ceccaldi, E.; Wang, F. Editorial: Machine learning and immersive technologies for user-centered digital healthcare innovation. Front. Big Data 2025, 8, 1567941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Thompson, C.E.; Choi, J.; Waddill, C.B.; Choi, S. Effectiveness of Immersive Virtual Reality in Nursing Education Systematic Review. Nurs. Educ. 2022, 47, E57–E61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilashi, M.; Abumalloh, R.A. i-TAM: A model for immersive technology acceptance. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2025, 30, 7689–7717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, A.; Brandtner, C. Green in their own way: Pragmatic and progressive means for cities to overcome institutional barriers to sustainability. Urban Stud. 2024, 61, 2513–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimmo, J. Planning and design strategies for sustainability and profit: Pragmatic sustainable design on building and urban scales. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2005, 73, 75–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Adamo, I.; Gastaldi, M.; Nallapaneni, M.K. Europe Moves toward Pragmatic Sustainability: A More Human and Fraternal Approach. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickman, L.A. Pragmatic paths to environmental sustainability. J. Agric. Environ. Ethic 2007, 20, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolan, D.A. Pragmatic Sustainability: Theoretical and Practical Tools. J. Plan. Educ. Res. 2011, 31, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- York, J.G. Pragmatic Sustainability: Translating Environmental Ethics into Competitive Advantage. J. Bus. Ethics 2009, 85, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Chou, F.; Lee, Y. Awareness of Residents Regarding the Construction of a Sustainable Urban Community: A Case Study of Action Research in Taiwan. Syst. Pract. Action Res. 2010, 23, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Lee, T.; Wang, C. Influence Analysis of Sustainability Perceptions on Sense of Community and Support for Sustainable Community Development in Relocated Communities. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Dong, X.; Zhou, Q.; Du, S. Spatiotemporal Big Data Empower Community Modeling, Monitoring, Evaluation, and Optimization for Sustainable Community Development: A review of challenges and opportunities. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2025, 13, 8–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockyer, P.; Le Fevre, D.; Vickers, M. Implementation and sustainability of student peer-led physical activity programs in a school community. J. Prof. Cap. Community 2024, 9, 154–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Cates, C.; Gueroult, A.M.; Narantsolmon, G. Sustainable equipment donation in otolaryngology in low-resource settings. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. 2024, 32, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, J.M.E.; Gallego-Schmid, A.; Azapagic, A. Building a business case for implementation of a circular economy in higher education institutions. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 220, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renfors, S. Education for the circular economy in higher education: An overview of the current state. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2024, 25, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakariya, M.Z.; Teh, J. A Systematic Review on Cascading Failures Models in Renewable Power Systems with Dynamics Perspective and Protections Modeling. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2023, 214, 108928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golam, M.; Tuli, E.A.; Alief, R.N.; Kim, D.; Lee, J. Meta-Learning: A Digital Learning Management Framework Using Blockchain for Metaverses. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 92774–92786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buragohain, D.; Meng, Y.; Chaudhary, S. Metaverse Impact and Trends in Sustainable Integration of Immersive Technologies in Education. Comput. Appl. Eng. Educ. 2025, 33, e70024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karuppiah, K.; Sankaranarayanan, B. An integrated multi-criteria decision-making approach for evaluating e-waste mitigation strategies. Appl. Soft Comput. 2023, 144, 110420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owusu-Twum, M.Y.; Kumi-Amoah, G.; Heve, W.K.; Lente, I.; Owusu, S.A.; Larbi, L.; Amfo-Otu, R. Electronic waste control and management in Ghana: A critical assessment of the law, perceptions and practices. Waste Manag. Res. 2022, 40, 1794–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, K.; Teo, H.; Chan, H.C.; Tan, B.C.Y. Conceptualizing and Testing a Social Cognitive Model of the Digital Divide. Inf. Syst. Res. 2011, 22, 170–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Li, P.; Li, Q.; Zhang, H. To be, or not to be, happy? That’s the question: A study on three levels of the digital divide and individual happiness in China. Inf. Technol. People 2024, 37, 1802–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grazzini, G.; Milazzo, A. Energy fluxes and their relations within energy plants. Energy Convers. Manag. 2007, 48, 1720–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z. Metaverse-based online English teaching scheme in multi-source and cross-domain environment. Fractals 2023, 31, 2340153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, G.; Ioannou, I.; Zhou, Y.; Bailey, J.; O’Leary, S. Mining interactions in immersive learning environments for real-time student feedback. Australas. J. Educ. Technol. 2013, 29, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, A.C.; Davis, L.L.; Kraemer, H.C. The role and interpretation of pilot studies in clinical research. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2011, 45, 626–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, J.; El Ebrashi, R. The interplay among green absorptive capacity, green entrepreneurial, and learning orientations and their effect on triple bottom line performance. Bus. Strateg. Environ. 2024, 33, 1962–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiley, M.; Halliday, D.P. Candidate and supervisor experiences of doctoral study in a structured, interdisciplinary training environment. Innov. Educ. Teach. Int. 2019, 56, 663–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinal, O.; Arguelles, A. Mixed reality and digital twins for astronaut training. Acta Astronaut. 2024, 219, 376–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; He, Z.; Du, J.; Chen, L.; Lin, P.; Fang, S. Assessing the effects of ecological engineering on carbon storage by linking the CA-Markov and InVEST models. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 98, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeabai, N.; Sakaraphantip, N.; Kunbuala, N.; Roongrueng, K.; Nukunudompanich, M. Integrated Assessment of Rooftop Photovoltaic Systems and Carbon Footprint for Organization: A Case Study of an Educational Facility in Thailand. Energies 2025, 18, 2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Yang, J.; Diao, Y.; Jin, R.; Guo, B.; Adamu, Z. Process and outcome-based evaluation between virtual really-driven and traditional construction safety training. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2022, 52, 101634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onkham, W.; Karwowski, W.; Ahram, T.Z. Economics of human performance and systems total ownership cost. Work 2012, 41, 2781–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Clerck, Q.; van Lier, T.; Messagie, M.; Macharis, C.; Van Mierlo, J.; Vanhaverbeke, L. Total Cost for Society: A persona-based analysis of electric and conventional vehicles. Transport Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2018, 64, 90–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, K.; Tate, J.E.; Wadud, Z.; Nellthorp, J. Total cost of ownership and market share for hybrid and electric vehicles in the UK, US and Japan. Appl. Energy 2018, 209, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Chen, J.; Chen, L.; Liu, Z.; Yi, C.; Xu, S.; Wang, J.; Kang, J. QoE-Aware Joint Visual and Haptic Signal Transmission with Adaptive Data Compression for Immersive Interactions in Human Digital Twin. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2025, 22, 2780–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Hak-soon, Y. Research on the E-learning platform for art teaching and immersive digital entertainment experience based on improved neural networks. Entertain. Comput. 2025, 52, 100768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

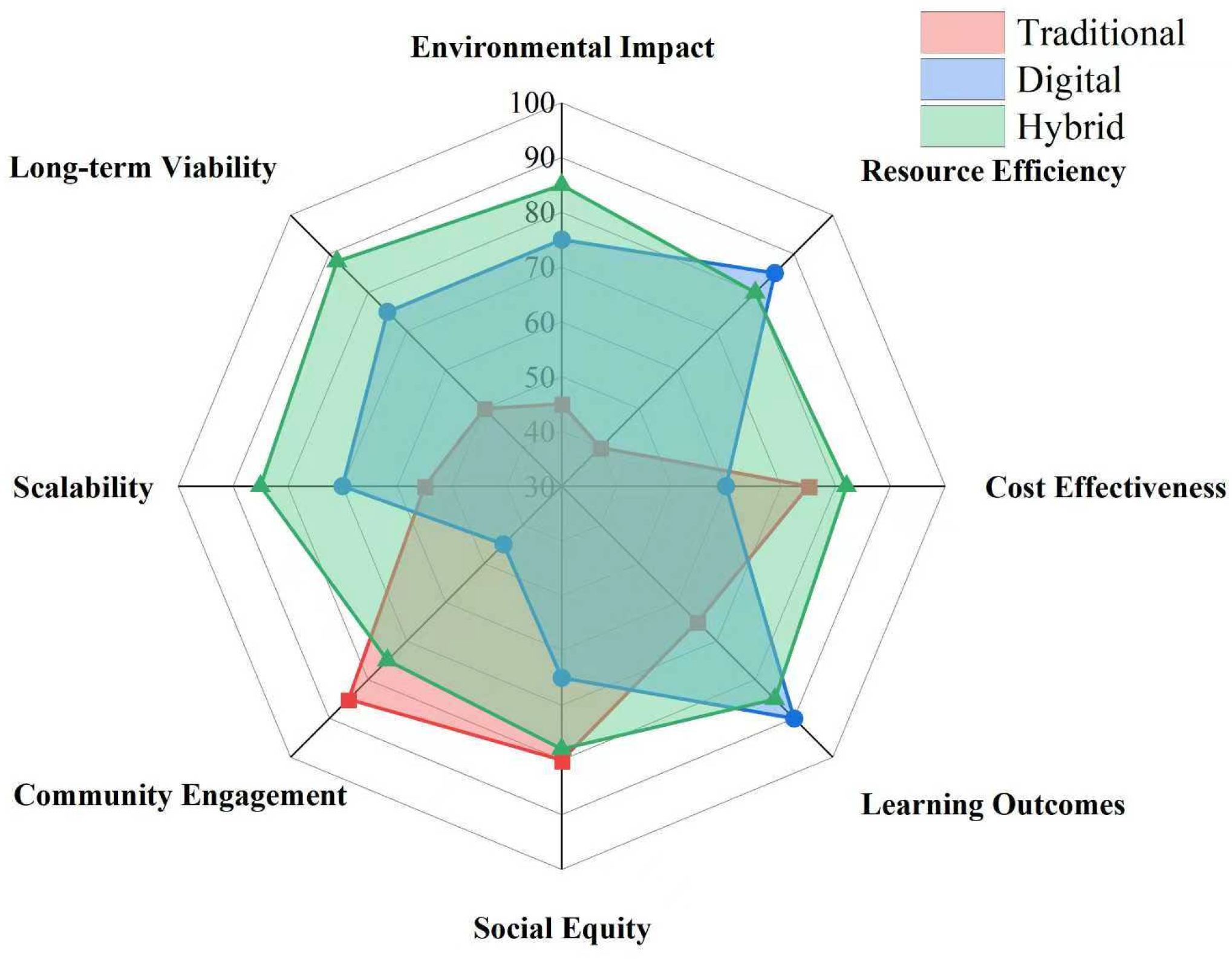


| Sustainability Indicator | Traditional | Digital | Hybrid | Best Performer |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Energy Use (kWh) | 234 | 847 | 521 | Traditional |
| Total Energy (kWh-equiv) | 1432 | 847 | 743 | Hybrid |
| Carbon Emissions (kg CO2) | 1876 | 623 | 512 | Hybrid |
| Paper Consumption (kg) | 487 | 12 | 89 | Digital |
| E-Waste Generation (kg) | 0 | 67 | 28 | Traditional |
| Water Usage (liters) | 8234 | 1245 | 2156 | Digital |
| Recyclable Waste (%) | 76% | 23% | 64% | Traditional |
| Biodegradable Waste (%) | 89% | 5% | 47% | Traditional |
| Learning Domain | Traditional | Digital | Hybrid | Statistical Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spatial Visualization | d = 0.34 | d = 0.92 | d = 0.83 | F (2, 807) = 47.3, p < 0.001 |
| Geographic Analysis | d = 0.45 | d = 0.87 | d = 0.79 | F (2, 807) = 39.6, p < 0.001 |
| Local Knowledge | d = 0.78 | d = 0.52 | d = 0.71 | F (2, 807) = 18.2, p < 0.001 |
| Systems Thinking | d = 0.38 | d = 0.81 | d = 0.76 | F (2, 807) = 41.7, p < 0.001 |
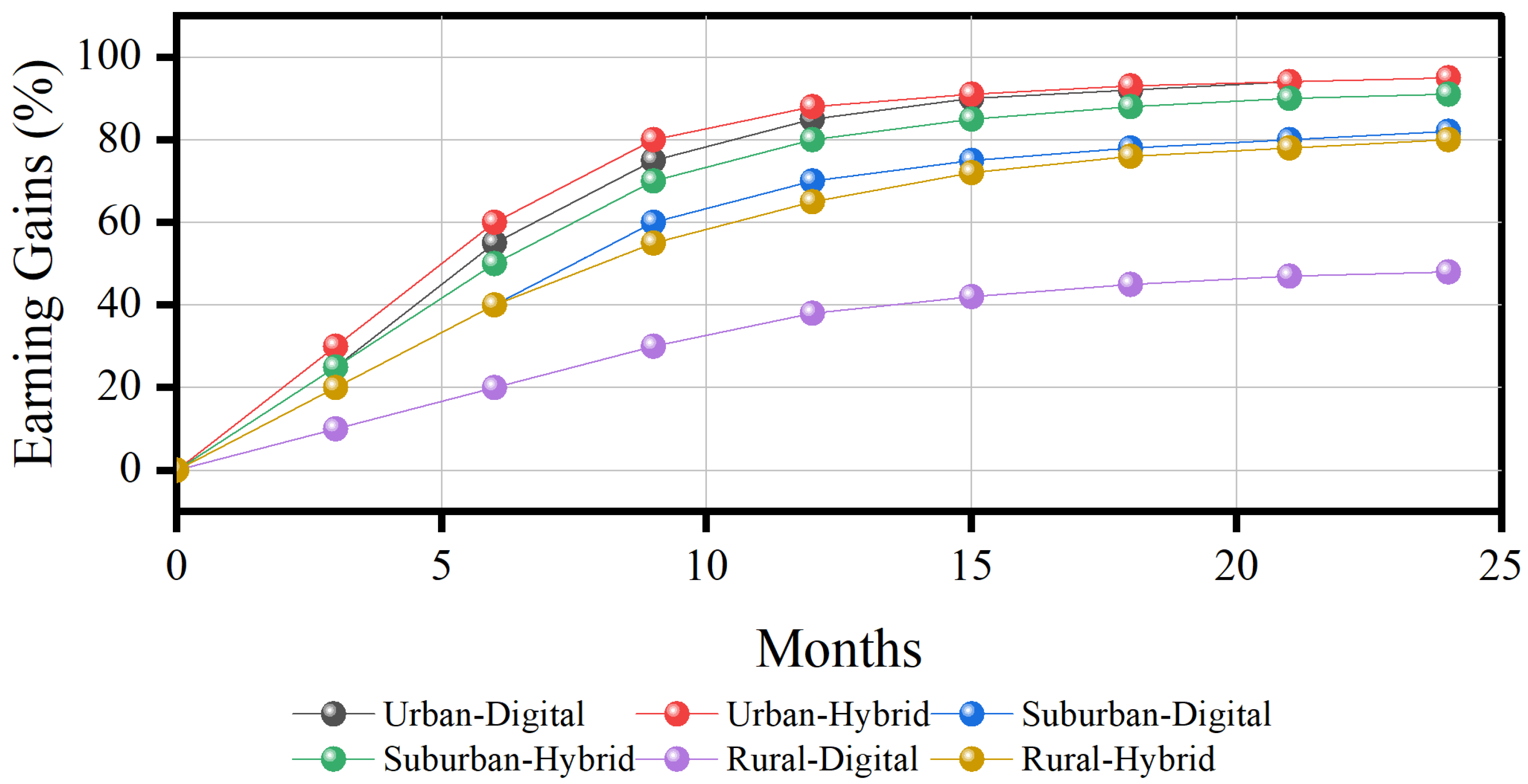
| Long-Term Retention (6 months) | 41% | 64% | 73% | χ2 (2) = 89.4, p < 0.001 |
| Engagement Sustainability | 48% | 67% | 71% | χ2 (2) = 56.3, p < 0.001 |
| Learning Domain | Traditional | Digital | Hybrid |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spatial Visualization | M = 52.3 (SD = 15.7), n = 270 | M = 71.8 (SD = 12.3), n = 270 | M = 68.9 (SD = 13.1), n = 270 |
| Geographic Analysis | M = 48.6 (SD = 14.2), n = 270 | M = 69.4 (SD = 11.8), n = 270 | M = 66.7 (SD = 12.5), n = 270 |
| Local Knowledge | M = 64.2 (SD = 13.9), n = 270 | M = 55.8 (SD = 16.2), n = 270 | M = 61.3 (SD = 14.4), n = 270 |
| Systems Thinking | M = 45.3 (SD = 16.8), n = 270 | M = 67.9 (SD = 13.2), n = 270 | M = 65.1 (SD = 13.8), n = 270 |
| Long-Term Retention (6 months) | M = 41.2% (SD = 18.3%), n = 270 | M = 63.8% (SD = 15.7%), n = 270 | M = 72.6% (SD = 12.4%), n = 270 |
| Cost Category | Traditional | Digital | Hybrid | Cost Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment | 3400 | 47,300 | 19,800 | Infrastructure and Devices |
| Annual Operations | 8700 | 4200 | 5100 | Materials and Energy |
| Maintenance/Repairs | 200/year | 3100/year | 1400/year | Technical Support |
| Professional Development | 1200/year | 3800/year | 2500/year | Training Requirements |
| End-of-Life Disposal | 50 | 1800 | 750 | E-Waste Management |
| Hidden Costs | 2100/year | 1500/year | 1700/year | Time and Externalities |
| 5-Year Total | 47,850 | 78,500 | 49,250 | |
| Per Student Per Year | 319 | 523 | 328 | Based on 30 Students |
| Cost Per Learning Gain Unit | 742 | 298 | 267 | Efficiency Metric |
| Equity Metric | Urban | Suburban | Rural | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trad. | Digital | Hybrid | Trad. | Digital | Hybrid | Trad. | Digital | Hybrid | |
| Achievement Gap Index | 0.43 | 0.28 | 0.31 | 0.47 | 0.39 | 0.35 | 0.51 | 0.63 | 0.44 |
| Access Equality (%) | 98% | 87% | 94% | 96% | 72% | 89% | 94% | 43% | 78% |
| Participation Rate (%) | 91% | 96% | 95% | 89% | 91% | 92% | 87% | 76% | 88% |
| Parent Satisfaction (%) | 72% | 84% | 81% | 69% | 74% | 78% | 74% | 51% | 71% |
| Teacher Confidence (%) | 89% | 67% | 83% | 86% | 62% | 79% | 91% | 48% | 77% |
| Community Engagement | High | Low | Medium | High | Medium | High | High | Low | High |
| Infrastructure Adequacy | 94% | 78% | 86% | 87% | 65% | 79% | 76% | 31% | 68% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Q.; Li, Y. Digital-Technology-Enhanced Immersive Learning in Chinese Secondary School Geography Education: A Comprehensive Comparative Analysis of Sustainable Pedagogical Transformation. Sustainability 2025, 17, 8478. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17188478
Liu Q, Li Y. Digital-Technology-Enhanced Immersive Learning in Chinese Secondary School Geography Education: A Comprehensive Comparative Analysis of Sustainable Pedagogical Transformation. Sustainability. 2025; 17(18):8478. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17188478
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Qiang, and Yifei Li. 2025. "Digital-Technology-Enhanced Immersive Learning in Chinese Secondary School Geography Education: A Comprehensive Comparative Analysis of Sustainable Pedagogical Transformation" Sustainability 17, no. 18: 8478. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17188478
APA StyleLiu, Q., & Li, Y. (2025). Digital-Technology-Enhanced Immersive Learning in Chinese Secondary School Geography Education: A Comprehensive Comparative Analysis of Sustainable Pedagogical Transformation. Sustainability, 17(18), 8478. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17188478








