Abstract
Educational tourism serves as a vital avenue for enhancing students’ practical skills and knowledge acquisition. As key components of educational tourism, the spatial distribution and accessibility of educational tourism bases significantly influence the effectiveness of study tour programs. Here, we employed stepwise regression analysis and geographically weighted regression (GWR) to analyze the spatial distribution characteristics, accessibility, and driving factors of educational tourism bases along the Yellow River region. The results indicate that museums accounted for the greatest proportion at 25.14% of the nine types of educational tourism bases. The educational tourism bases show a pattern of “dense in the southeast and sparse in the northwest.” Furthermore, they demonstrate clustered distributions centered around provincial capitals. The key factors influencing the distribution of educational tourism bases, ranked from highest to lowest based on the absolute value of the GWR coefficient, are as follows: 4A and above scenic spots > urbanization rate > internet broadband users > length of classified roads > education expenditure. The accessibility of educational tourism bases is basically consistent in terms of time and spatial distance, both showing better accessibility in the southeast than in the northwest. However, where Sichuan Province and Gansu Province meet, time accessibility is better, while distance accessibility is worse. These findings provide valuable insights for promoting the sustainable development of educational tourism in the Yellow River region.
1. Introduction
Educational tourism, as a comprehensive new form of combining tourism and education, both develops students’ practical skills and allows them to appreciate the relationship between humans and the land [1,2]. Educational tourism is a form of travel where learning serves as the primary or secondary objective [1,3]. Participants acquire knowledge, skills, or cultural experiences through immersive activities that often go beyond traditional classroom settings [4]. With rapid socio-economic development and growing recognition of the practical value of educational tourism, it has attracted widespread attention from the government and the community, especially scholars [1,2,5,6].
The concept of educational tourism remains fluid, making it difficult to arrive at a standardized definition. Scholars across different contexts have proposed varying interpretations [7,8,9]. For instance, Japan emphasizes “Study Tours” [10,11], while the USA and other countries frame it through seasonal camps [12,13]. Similarly, Korea’s “Membership Training” [14] and the UK’s historical “Grand Tour” [15] reflect culturally distinct approaches to blending education and travel. Despite terminological diversity, educational tourism broadly encompasses travel-based learning experiences that transcend traditional classroom settings, integrating cultural immersion, skill development, and knowledge acquisition. Existing research has explored multiple dimensions of educational tourism, including management frameworks [16], theoretical foundations [7,10], policy and institutional development [15], and socioeconomic and cultural impacts [12,17]. In China, educational tourism emerged as a distinct field in the 1990s [18]. Recent studies have examined conceptual models [18], characteristics and typologies [19], and cross-cultural comparative analyses [20,21]. Educational tourism bases are places where students learn and live during study travel programs, providing core products and services for travel activities [22,23]. However, few studies addressed the spatial distribution and accessibility of educational tourism bases—key factors influencing the feasibility and equity of learning opportunities. Therefore, we offer practical insights for policymakers and stakeholders by analyzing sustainable development of educational tourism bases.
Recent studies examined the spatial distribution of tourism resources [1,11], while few focused on educational tourism bases—a growing sector driven by increasing demand for experiential learning and study tours. The existing literature demonstrates a methodological imbalance, with predominant reliance on qualitative evaluations of educational tourism resources [7,24]. To better understand the spatial aggregation characteristics of such resources, kernel density analysis offers a robust analytical tool for identifying geographic concentration patterns [25]. Furthermore, integrating both time- and distance-based traffic accessibility measures provides a more comprehensive perspective on spatiotemporal convenience [26,27]. Therefore, this study employs kernel density analysis alongside temporal and distance accessibility evaluations to systematically investigate the spatial clustering of educational tourism resources and their transportation convenience along the Yellow River region. Furthermore, quantitative spatial analyses employing geospatial modeling techniques to explore the factors influencing educational tourism bases remain underutilized. The majority of studies overlooked the unique spatial patterns and accessibility challenges of these facilities. In the spatial model, current research predominantly utilizes Ordinary Least Squares (OLS) regression and stepwise regression analysis to construct a global linear model between independent and dependent variables for analyzing the determinants of tourism base spatial distribution [28,29]. However, the global parameter estimates generated by OLS and stepwise regression analysis may obscure localized spatial heterogeneity, thereby making it difficult to elucidate the underlying mechanisms driving the spatial differentiation of tourism base distributions. However, Geographically Weighted Regression (GWR) addresses these limitations by allowing regression coefficients to vary spatially, thereby revealing place-specific dynamics [29]. Therefore, we introduce the stepwise regression analysis and GWR to more accurately reveal the overall and local differences in the distribution drivers of educational tourism bases in different regions, providing planning references for policymakers.
As the birthplace of Chinese culture, the Yellow River is rich in natural and human resources. It is therefore of typical significance in educational tourism [30,31]. Current research on educational tourism along the Yellow River has focused on the cultural value of educational tourism [32] , the development of specific study resources [33], and the formulation of study-related policies [34]. The development of educational tourism bases in China is still in its early stages, with various regions actively promoting the construction of such bases. However, few studies have quantitatively examined the spatial distribution patterns, accessibility, and underlying driving factors of educational tourism bases along the Yellow River from a geospatial perspective. Therefore, this study both provides a theoretical basis for local governments to optimize the layout of educational tourism resources and offers innovative ideas for the sustainable development of educational tourism at cultural heritage sites both domestically and internationally.
To better analyze the spatial distribution and accessibility of the educational tourism bases along the Yellow River, the main objectives of this study are as follows: (1) to assess the proportionate characteristics of different types of educational tourism bases; (2) to analyze the spatial distribution and accessibility of the educational tourism bases using ArcGIS; and (3) to explore the influencing factors of the educational tourism bases using stepwise regression analysis and the GWR model. Therefore, we employ geography-related theories and techniques to the research base to provide a new perspective for educational tourism.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of Study Area
The area along the Yellow River in this study refers to a buffer zone of 400 km that is centered on the mainstream of the Yellow River. Using the buffer analysis tool of ArcGIS 10.8, we created a 400 km zone around the Yellow River, which ensures full coverage of key provinces (e.g., Henan, Shandong) and partial inclusion of Sichuan/Gansu, while maintaining alignment with administrative boundaries to prevent data fragmentation. The study area mainly covers Qinghai, Henan, Shaanxi, Shanxi, Shandong, Gansu, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, and parts of Sichuan Province (Figure 1a,b). The region exhibits significant topographic diversity, spanning an elevation range from −117 to 7143 m (Figure 1c,d). The western headwater areas are characterized by high-altitude glacial landscapes and perennial snow cover, offering exceptional opportunities for research and education in geosciences and climate studies. The central Loess Plateau, distinguished by pronounced soil erosion and extensive gully systems, provides an ideal natural laboratory for investigating land degradation processes and sustainable land-use practices. In contrast, the eastern alluvial plains, renowned for their fertile soils and long-standing association with agricultural civilizations, highlight the pivotal role of fluvial processes in the development of China’s cultural heritage. As the cradle of Chinese civilization, the Yellow River basin harbors unparalleled historical, geological, and ecological resources. These distinctive features both shape the region’s cultural and environmental identity and establish a robust foundation for the advancement of educational tourism and interdisciplinary research.
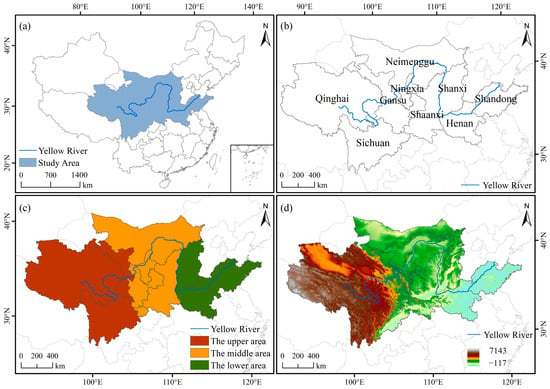
Figure 1.
Study area distribution map: (a) location of the study area in China, (b) provinces in the study area, (c) upper, middle, and lower areas of the Yellow River, and (d) elevation of the study area.
2.2. Date Sources
Educational tourism bases along the Yellow River are categorized into 146 national-level and 403 provincial-level, based on official lists issued by national and provincial cultural and tourism authorities (e.g., Notice from the Ministry of Education’s Office on the Publication of the List of National Research and Practice Education Bases and Camps for Primary and Secondary School Students in 2018). Building upon prior scholarly classifications [22,35] and accounting for the unique characteristics and educational objectives of tourism resources in the Yellow River Basin, this study categorizes educational tourism bases into nine types, each defined with conceptual clarity and illustrative examples (Table 1).

Table 1.
Nine types of educational tourism bases and their definitions.
The educational tourism bases are mainly sourced from government websites. The vector data of the study area is from the geospatial data cloud (http://www.gscloud.cn (accessed on 6 May 2023)). Road data is derived from the Resource and Environmental Science and Data Center (https://www.resdc.cn (accessed on 20 July 2025)). Population data and socio-economic data are obtained from the statistical yearbooks and statistical bulletins of the local municipalities involved in the study area.
We utilized the mileage data of classified highways from the statistical yearbooks of prefecture-level cities to explore the driving factors behind the spatial distribution characteristics of the educational tourism bases. However, we applied the national road vector data from the geospatial data cloud in the accessibility analysis https://www.gscloud.cn/sources/ (accessed on 6 May 2023). The length of the route and the time required were calculated according to the design speeds of different levels of roads as stipulated in the Technical Standards for Highway Engineering of the People’s Republic of China. The design speeds of motorways, national roads, provincial roads, county roads, township and village roads, and other roads are 100 km/h, 70 km/h, 50 km/h, 40 km/h, 30 km/h, and 25 km/h, respectively. The weighted average travel times among the educational tourism bases were calculated and normalized by the network analysis function of ArcGIS software.
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Kernel Density Analysis
The kernel density mainly calculates the density of an element in its surrounding neighborhood to reflect the spatial distribution characteristics of the element. The formula is as follows:
where is a kernel density function, n presents the number of educational tourism bases; denotes the search radius; means the kernel density at the center of the data grid, and xi indicates kernel density of educational tourism bases.
2.3.2. Accessibility Analysis
Accessibility is the ease with which any point within a geographical area can be reached by other points [36]. It is usually measured in terms of weighted average travel time and the coefficient of time accessibility.
The weighted average travel time refers to the level of regional accessibility in terms of spatial distance, time cost, and economic cost. The weighted average travel time within a region is inversely proportional to the level of accessibility. It can be calculated as follows:
where represents the weighted average travel time for each research base in the study area. indicates the shortest time from research base to research base . is the quality of research base , which can be replaced by economic indicators such as GDP per capita. In this study, we used tourism income per unit area instead.
The coefficient of time accessibility is the ratio of the weighted average travel time of each research base to the average accessibility of each research base within the road network. This is used to reflect the level of accessibility of the educational tourism bases. The calculation formula is as follows:
where is the coefficient of accessibility of research base , and is its weighted average travel time. The smaller the coefficient of accessibility, the higher the accessibility of the research base in the study area. A coefficient of accessibility greater than 1 indicates a low level of accessibility to the research base. A coefficient of accessibility less than 1 denotes a high level of accessibility to the research base.
2.3.3. Stepwise Regression Analysis
Stepwise regression analysis involves introducing variables into the model one by one to be sure that only significant variables are included in the regression equation. It is continually iterated to ensure that the final set of explanatory variables obtained is optimal. Its calculation formula is as follows:
where is the explanatory variable, = 1, 2, 3, …, ; presents the variable coefficient, = 1, 2, 3, … . denotes the residual item.
2.3.4. Geographically Weighted Regression Analysis (GWR)
As the natural and social environments vary from region to region, the relationships between variables vary with geographic location, and the variables are “spatially non-stationary”. The GWR model incorporates the ideas of variable covariance regression and local regression [37,38,39]. It can be used to explore local features of the relationships between variables, enabling accurate geographical identification of “spatial non-stationarity”. The formula is as follows:
where Yi means the explained variable, which is educational tourism bases density. (ui, vi) represents the geospatial coordinates of the i-th observation. denotes the observed value of the explanatory variable xk at the location (ui, vi). indicates the random error term.
3. Results
3.1. Structural Characteristics of Educational Tourism Bases
3.1.1. Types and Structure of Educational Tourism Bases
As shown in Figure 2, along the Yellow River region, museums constitute the largest category among national-level educational tourism bases, accounting for 31.21%. This is followed by integrated practice bases, which represent 21.99%. Categories such as defense science and technology and patriotic education each exceed 10%. At the provincial level, natural resources form the most prominent category, comprising 24.02% of educational tourism bases, while museums represent 23.04%, making it the second largest category. Overall, across all educational tourism bases in the Yellow River region, museums represent the highest proportion at 25.14%, followed by natural resources at 20.4%.
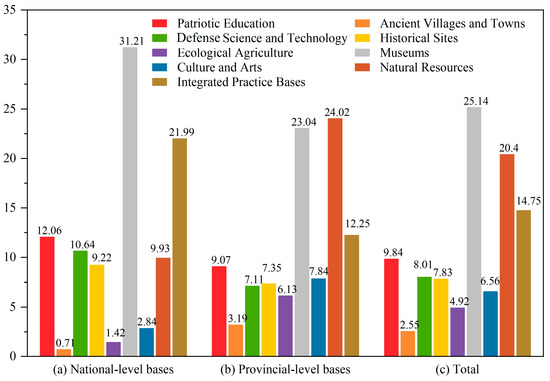
Figure 2.
Types and structure of educational tourism bases (%).
3.1.2. Spatial Structure of Various Types of Educational Tourism Bases
The composition of educational tourism bases in the Yellow River region, divided into upper, middle, and lower reaches, is presented in Table 2. Overall, spatial variability exists among the different types of educational tourism bases. Specifically, in the upper reaches, museums, comprehensive bases, and natural resources constitute the three main types, accounting for 34.78%, 26.09%, and 14.13% of the total educational tourism bases, respectively. In the middle reaches, natural resources, museums, and comprehensive bases are the predominant types, representing 21.46%, 20.09%, and 17.35% of the studied bases in this section, respectively. In the lower reaches, museums account for 26.05% of the total, followed by natural resources at 21.85% and patriotic education bases at 13.87%. In general, museums and natural resource-based educational tourism bases maintain a large and relatively stable proportion across all sections of the Yellow River region.

Table 2.
Spatial structure diagram of each type of educational tourism base (%).
3.2. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of the Educational Tourism Bases Along the Yellow River
3.2.1. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Educational Tourism Bases at Different Levels
Educational tourism bases in the study area can be categorized into national-level and provincial-level bases. The densities of national and provincial educational tourism bases are 0.56 × 10−4/km2 and 1.61 × 10−4/km2, respectively. As illustrated in Figure 3, both levels exhibit similar spatial distribution patterns, with a predominant concentration in the eastern region. Additionally, national-level educational tourism bases (Figure 3a) are distributed more uniformly across the area, whereas provincial-level bases (Figure 3b) demonstrate a distinct spatial clustering pattern.
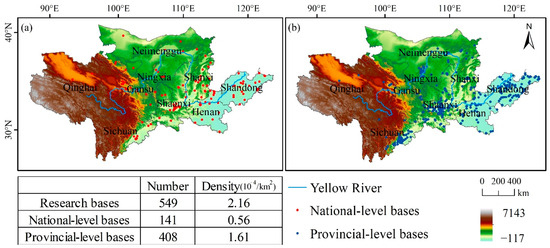
Figure 3.
National-level and provincial-level bases distribution map: (a) national-level bases and (b) Provincial-level bases.
3.2.2. Spatial Distribution Density of Educational Tourism Bases
We employed kernel density analysis to conduct an in-depth investigation of the spatial distribution characteristics of educational tourism bases in the Yellow River region. Overall, three high-density zones (relative density > 10) and four sub-high-density zones (relative density > 5) were identified within the study area. As depicted in Figure 4, the high-density zones are primarily concentrated in Shaanxi, Shandong, and Sichuan. The four sub-high-density zones are located in Henan, Shanxi, Ningxia, and Qinghai, respectively. The southeastern part of the study area exhibits a higher density of educational tourism bases, while the northwestern part shows a more dispersed pattern. High-density areas are mainly clustered in provincial capital cities and exhibit a block-like distribution pattern. At the provincial level, Ningxia has the highest density of educational bases (7.48 × 10−4/km2), followed by Shaanxi (7.25 × 10−4/km2). In terms of the upper, middle, and lower reaches of the Yellow River region, the downstream region has the highest density (4.92 × 10−4/km2), while the upstream region has the lowest (0.79 × 10−4/km2).
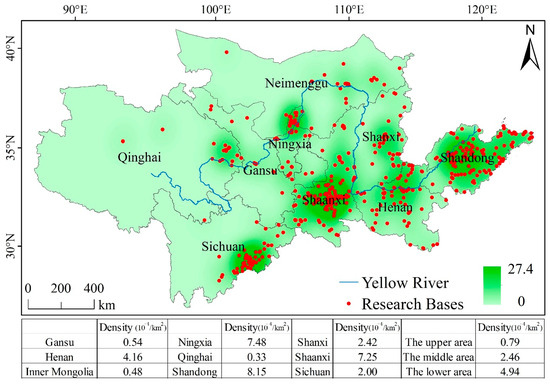
Figure 4.
Kernel density analysis.
3.3. Spatial Accessibility Characteristics of Educational Tourism Bases
3.3.1. Time Accessibility Analysis of Educational Tourism Bases
The weighted average travel time, which represents the mean of the shortest travel times between educational tourism bases, reflects the degree of proximity between the studied sites. A lower value of this indicator suggests better accessibility between educational tourism bases, while a higher value indicates weaker accessibility. As shown in Figure 5a, the weighted travel time in the northwestern part of the study area is generally higher than that in the eastern region, indicating that the time accessibility of educational tourism bases is better in the east compared to the west. At the provincial level, areas with relatively high weighted travel times are mainly concentrated in Henan, Shaanxi, and Shanxi provinces. The time accessibility of the studied sites in the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River is better than that in the upper reaches.
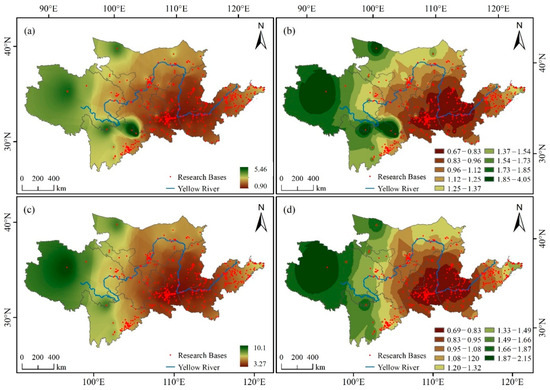
Figure 5.
Accessibility of traffic: (a) weighted travel time, (b) coefficient for weighted travel time, (c) distance accessibility, and (d) coefficient for distance accessibility.
Along the Yellow River region, the weighted travel time coefficient of educational tourism bases gradually increases from the central area toward the peripheral regions, demonstrating a distinct “core-periphery” pattern (Figure 5b). Areas with a weighted travel time coefficient below 0.83 are primarily located near the junction of Shanxi, Henan, and Shaanxi provinces, indicating that the studied sites in this region exhibit the best time accessibility. In contrast, regions with a coefficient exceeding 1.85 are mainly distributed in the northwestern part of the study area, suggesting relatively poor time accessibility of educational tourism bases in these locations.
3.3.2. Distance Accessibility Analysis of Educational Tourism Bases
The distance accessibility between educational tourism bases in the eastern part of the study area is superior to that in the western region (Figure 5c). It is basically consistent with the spatial distribution law of time accessibility. However, in the southwest, there are significant differences between distance accessibility and time accessibility. As shown in Figure 5d, the distance accessibility coefficient in the upper reaches of the Yellow River is higher than that in the middle and lower reaches, indicating that transportation between educational tourism bases is more convenient in the middle and lower sections of the Yellow River. Areas with a distance accessibility value of less than 0.83 are mainly concentrated in Henan, Shaanxi, and Shanxi provinces, suggesting a more concentrated distribution of educational tourism bases and better transport connectivity in these regions. In contrast, regions with a distance accessibility coefficient greater than 1.87 are primarily located in the Qinghai Province, northern Sichuan Province, and western Inner Mongolia, reflecting a relatively dispersed distribution of educational tourism bases and poor distance accessibility in these areas.
An inconsistency between time accessibility and distance accessibility is observed in the educational tourism bases located at the border between Sichuan and Gansu provinces. Specifically, time accessibility is relatively good, whereas distance accessibility is poor at this border. This discrepancy can be largely attributed to the complex topography and relatively underdeveloped economic conditions in the region. Transportation in this area mainly relies on roads, which are generally of low grade.
4. Analysis of the Driving Factors Influencing the Spatial Distribution of Educational Tourism Bases
4.1. Stepwise Regression Analysis of Educational Tourism Bases
The spatial heterogeneity of educational tourism bases was the result of a combination of factors. The 86 administrative municipalities along the Yellow River Basin were used as the research unit. According to the special characteristics of the Yellow River Basin and the research results of previous scholars, 8 factors were selected from five aspects, including accessibility, economic development level, education development level, tourism reception capacity, and study demand potential, to explore the driving factors of the spatial heterogeneity of educational tourism bases. These factors were chosen due to their direct or indirect influence on the establishment, operation, and attractiveness of educational tourism bases. It is worth noting that the quality grading of tourist attractions in China is categorized into five distinct levels in accordance with the national standard Classification and Grading of Tourist Attractions. These levels, listed in descending order, are AAAAA (commonly referred to as 5A), AAAA (4A), AAA (3A), AA (2A), and A (1A). In this article, “4A level and above scenic spots” include both 4A and higher-rated (5A) attractions, denoting a high-quality destination with well-developed facilities, services, and cultural or natural significance. The specific factors and their relevance to educational tourism are detailed in Table 3.

Table 3.
The Influencing Factors of the Spatial Distribution of Educational Tourism Resources and Their Justification for Educational Tourism Relevance.
The stepwise regression model in SPSS 26.0 software was used to conduct regression analysis on the eight variable factors. The results of the stepwise regression analysis were illustrated in Table 4. The stepwise regression analysis revealed four models with varying predictors (X1–X8). Key findings indicated that X4 (Beta = 0.787–1.016, p < 0.001) and X6 (Beta = 0.294–0.337, p ≤ 0.005) consistently exerted significant positive effects, while X5 showed a robust negative influence (Beta = −0.346–−0.377, p ≤ 0.036). X1 had a weaker but significant negative association (p ≤ 0.025). Non-significant predictors (X2, X3, and X8) were sequentially removed, with minimal impact on explanatory power (R2 = 0.601). Model 4 was selected as the optimal solution based on the principle of parsimony and a comprehensive evaluation of fit statistics. Although Model 3 exhibits a marginally lower Root Mean Square Error (RMSE = 4.527), the RMSE of Model 4 (4.557) remains highly competitive. This minimal degradation in predictive accuracy is a reasonable trade-off for achieving a more streamlined and theoretically defensible model. By exclusively retaining the five statistically significant variables (X1, X4, X5, X6, X7), Model 4 effectively eliminates noise from non-significant predictors, enhancing model clarity and reducing the risk of overfitting. The adjusted R2 value of 0.576 indicates that this parsimonious model still explains approximately 57.6% of the variance in the distribution of research and education tourism bases, suggesting a moderately good fit. Therefore, the regression equation for the optimal model (Model 4) is formulated as Y = −0.00019X1 + 0.00000903X4 + 0.25X6 + 0.082X7 − 0.008X5 − 3.205.

Table 4.
Stepwise regression models of research and education tourism bases and their driving factors.
4.2. GWR of Educational Tourism Bases
The five variables of 4A and above scenic spots, urbanization rate, length of classified highway, internet broadband users, and education expenditure passed the significance test in Model 4. The stepwise regression was used to select the optimal set of explanatory variables for constructing the model of educational tourism base development. In contrast, the GWR allows regression coefficients to vary spatially, thereby capturing localized characteristics. Therefore, we applied the GWR to the variables from Model 4 to examine the spatial dynamics of the regression coefficients associated with educational tourism.
The GWR was applied to the variables of Model 4 to explore spatially varying relationships. As shown in Table 5, the GWR model yielded an improved adjusted R2 of 0.643, demonstrating a better fit than the global regression model. It accounts for nearly 64.3% of the variance, highlighting the importance of spatial heterogeneity in explaining the distribution of educational tourism bases. However, it should be noted that a substantial portion of the variance remains unexplained by the predictors included in Model 4 (about 35.7%). This limitation underscores that factors not captured in the analysis also may significantly influence the establishment and distribution of educational tourism bases, such as policy interventions, cultural characteristics, or other unmeasured variables.

Table 5.
GWR analysis of the factors influencing educational tourism bases.
The results of the GWR model, which estimates the coefficients of factors influencing the research base, are summarized in Table 6. The coefficients for the five explanatory variables exhibit notable spatial heterogeneity, as indicated by their respective ranges and distributions. The number of 4A-level and above scenic spots demonstrates a strong positive influence, with coefficients ranging from 0.024 to 0.362 and a high mean value of 0.240. The urbanization rate also shows a positive association on average (mean = 0.053), albeit with greater variability, spanning from −0.035 to 0.116. In contrast, the length of classified highways and the number of internet broadband users consistently exhibit negative effects, with mean coefficients of −0.00025 and −0.00910, respectively. Finally, education expenditure shows a positive but minimal impact, with a very low mean coefficient of 0.00001 and negligible variability.

Table 6.
The maximum, minimum, mean, and standard deviation of the coefficients of the five variables in the GWR model.
4.2.1. Impact of 4A and Above Scenic Spots and Urbanization Rate on Educational Tourism Bases
The regression coefficients for 4A-level and above scenic spots were consistently positive, indicating a significant positive correlation between the spatial distribution of educational tourism bases and the number of such scenic spots (Figure 6a). In other words, regions with a higher number of 4A and above scenic spots tend to host a greater number of educational tourism bases. The highest regression coefficient was observed in eastern Shandong Province, exceeding 3.02 × 10−1, while the lowest values were found in Qinghai and Sichuan Provinces, ranging from 0.24 × 10−1 to 1.29 × 10−1. Overall, the regression coefficients exhibited notable spatial variability, with higher values in eastern regions and lower values in western regions. Additionally, the influence of urbanization rate on the distribution of educational tourism bases also displayed spatial heterogeneity (Figure 6b). Negative regression coefficients for urbanization rate were primarily concentrated in the northeastern Qinghai Province, northern Gansu Province, western Inner Mongolia, and the Shandong Peninsula. In contrast, most other regions exhibited positive coefficients. The highest coefficient was recorded in Henan Province, with a value of 11.63 × 10−2.
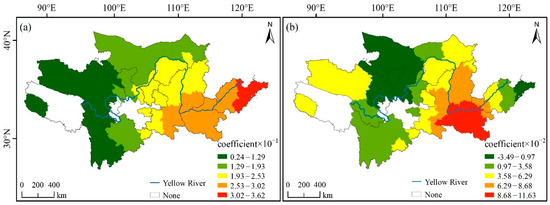
Figure 6.
GWR model: (a) coefficient of 4A-level and above scenic spots and (b) coefficient of urbanization rate.
4.2.2. Impact of Length of Classified Highway on Educational Tourism Bases
The regression coefficients of classified highway length exhibited notable spatial heterogeneity in their influence on the distribution of educational tourism bases (Figure 7a). Lower coefficients were concentrated primarily in the central region, suggesting that variations in highway length had a relatively limited effect on the establishment of educational tourism bases in this area. In contrast, higher regression coefficients were observed in both the eastern and western regions, indicating a stronger association between classified highway length and educational tourism bases in these parts.
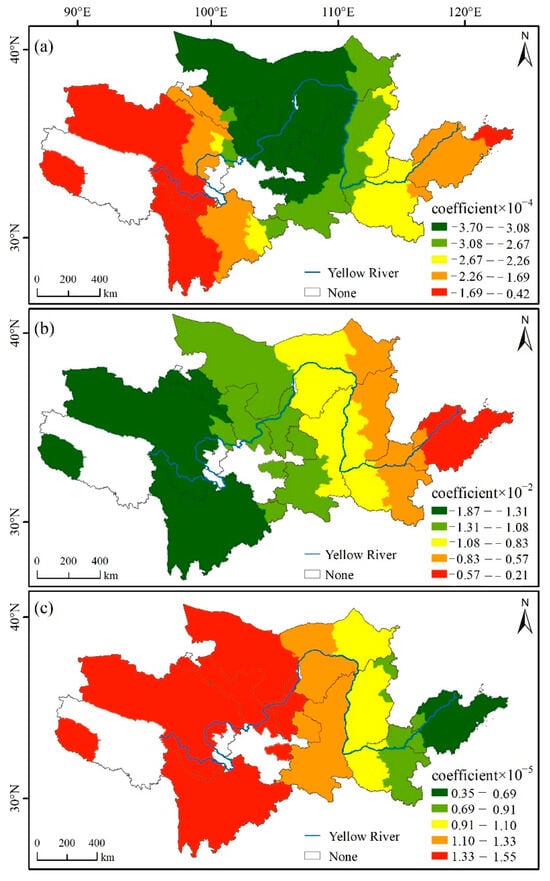
Figure 7.
GWR model: (a) coefficient of length of classified highway, (b) coefficient of internet broadband users, and (c) coefficient of education expenditure.
4.2.3. Impact of Internet Broadband Users on Educational Tourism Bases
The impact of internet broadband users on educational tourism bases showed a certain gradient distribution (Figure 7b). The provinces with a greater impact on educational tourism bases were Shandong and Henan, while the provinces with a smaller impact on educational tourism bases were Qinghai, Sichuan, and Gansu. The regression coefficient for internet broadband users was negative and consistent with reality, suggesting that the number of internet broadband users affected the distribution of educational tourism bases.
4.2.4. Impact of Education Expenditure on Educational Tourism Bases
As illustrated in Figure 7c, the regression coefficient for education expenditure tended to increase from east to west. This indicated that there was a higher coefficient for education expenditure in the west and a lower coefficient for education expenditure in the east of the study area. The education expenditure profile has a positive effect on the number of educational tourism bases. The education expenditure is lower in the western part of the study area than in the eastern part, but its regression coefficient is higher than in the eastern part. This indicates that the number of studies based in the west is more sensitive to the impact of education expenditure.
5. Discussion
5.1. Comparison with Related Research Conclusions
From a spatial distribution perspective, education tourism bases along the Yellow River region display a clear multi-nucleated agglomeration pattern. This is similar to other bases such as rural tourism villages [40,41] and high-level scenic spots [36,42], with formations of belt-shaped or cluster-shaped concentrations centered on provincial capitals. The study finding is consistent with domestic research that generally shows a denser distribution in the eastern regions and a sparser presence in the west [22,35]. A strong spatial coupling is observed between the distribution of education tourism bases and that of 4A-level and above tourist scenic spots. This correlation is significantly stronger than any other driving factors considered in this study, a view supported by most existing literature [36,40]. The well-established tourist markets and mature infrastructure of 4A-level and above tourist scenic spots are widely recognized as key factors driving the development of nearby education tourism bases. However, it should be noted that unlike other types of tourism bases, the visitor source for education tourism bases consists largely of primary and secondary school students. Therefore, local investment in education also exerts considerable influence on the spatial distribution of these bases.
At the provincial level, the distribution of educational tourism bases showed spatial differences, with high-density areas of educational tourism bases located in Shaanxi Province, Shandong Province, and Sichuan Province. A possible explanation for this might be the importance that local governments attach to educational tourism bases. Shaanxi Province announced three batches of educational tourism bases. Sichuan and Shandong Province announced two batches of educational tourism bases. The density of regional bases may also be related to the history of local development [22]. For example, the city of Xi’an in Shaanxi Province was once the capital of 13 dynasties, leaving behind a series of cultural relics and monuments such as the Terracotta Warriors and Horses of Qin and the ancient city walls. This provided rich historical resources for the educational tourism bases [43]. In addition, Shaanxi Province’s comprehensive strength in science and education ranked among the top in China and was an important base for scientific research and production in the fields of aviation, aerospace, machinery, electronics, and agriculture [44,45]. Chengdu, the capital of Sichuan Province, is located on the western edge of the Sichuan Basin and has significant vertical climatic differences. Therefore, the abundance and relatively concentrated distribution of biological resources provide an excellent foundation for the development of educational tourism bases [46]. Shandong Province is the birthplace of Confucian culture [47]. Its natural and humanistic study resources are abundant, such as a series of educational tourism bases in Qufu, Three Confucius, Mount Tai, and so on [47]. In addition, Shandong’s red revolutionary sites provide a wealth of resources for educational tourism [48]. Meanwhile, Shandong Province has a series of policies that are conducive to the development of research and study. This has also facilitated the development of educational tourism bases to a certain extent [22].
An interesting finding was the inconsistency between the time accessibility and distance accessibility of the educational tourism bases where Sichuan Province and Gansu Province meet. Specifically, time accessibility is better, while distance accessibility is worse. This is mainly due to the complex topography of the area and the relatively poor economic development. Transport is mainly by road, and the road grades are low. For example, about 90% of the roads in Aba are of class III or below, and less than 1% are highways [49]. The above mentioned contributes to the poor time accessibility and better distance accessibility of educational tourism bases in the region.
5.2. Policy Recommendations for Educational Tourism Bases Development
To ensure the sustainable and balanced growth of educational tourism, the following policy recommendations are proposed:
- (1)
- Implement differentiated regional development strategies. Resource-rich provinces (e.g., Shaanxi, Sichuan) should prioritize sustainable visitor management and ecological conservation to mitigate the risks of overcrowding and environmental degradation. Policy-advanced regions (e.g., Shandong) are encouraged to share best practices in using strategic interventions to foster tourism development. Less accessible areas, particularly in western China, require targeted infrastructure investment and enhanced promotional efforts to improve both physical and perceptual accessibility.
- (2)
- Promote regional integration and thematic route development. Rather than supporting isolated attractions, policymakers should facilitate the formation of collaborative regional networks. This involves strategically designing and promoting integrated itineraries that connect multiple bases based on thematic linkages, such as revolutionary heritage or ecological science, and strengthening transportation connectivity to improve educational value and visitor experience.
- (3)
- Enhance flagship scenic spots and integrated supporting capacity. Select a number of outstanding tourist attractions with high resource value and significant market potential for focused cultivation and investment. The high-quality development of these core scenic areas will radiatively drive the overall upgrade of the educational tourism destination.
5.3. Limitations and Future Research Directions
We only considered the data on classified highways in the yearbook as a driving factor when analyzing the factors affecting the educational tourism bases. However, long-distance travel in the Yellow River basin for cross-provincial rail/high-speed rail may be decisive for the influencing factors of educational tourism bases. In future research, we will add rail/high-speed rail to further explore the influencing factors of educational tourism bases.
The stepwise regression analysis and GWR model explained only two-thirds of the variance, and a third of it was not explained by the predictors. The number of educational tourism bases can be explained in two-thirds by 4A-level and above specific spots, urbanization rate, etc. The remaining one-third of the variance remains unexplained, suggesting the influence of other factors not captured in the current models. Therefore, it is essential to incorporate a more comprehensive set of driving factors to enhance explanatory power in future research, such as policy support, economic incentives, cultural elements, and other currently unmeasured variables.
While this study employed GWR to analyze the influencing factors of educational tourism bases, it is important to note that some factors may exhibit global rather than spatially varying effects. GWR assumes that all relationships are locally determined, which may not fully capture the underlying mechanisms. Future research could adopt a Mixed Geographically Weighted Regression (MGWR) model, which distinguishes between global (fixed) and local (spatially varying) effects, thereby improving the accuracy and interpretability of the results.
6. Conclusions
The spatial distribution of educational tourism bases along the Yellow River is highly heterogeneous, exhibiting a distinct “dense in the southeast and sparse in the northwest” pattern. Kernel density analysis further indicates that these bases form clustered distributions centered around provincial capitals.
In descending order of absolute values of the coefficient according to GWR, the key factors affecting the distribution of educational tourism bases are 4A and above scenic spots > urbanization rate > internet broadband users > length of classified highway > education expenditure. Among these, 4A and above scenic spots have a significant positive contribution to the development level of educational tourism bases in the eastern part of the study area. Therefore, policymakers should actively promote the construction of high-level scenic areas to drive the growth of educational tourism.
Accessibility is generally higher in the southeast compared to the northwest along the Yellow River region. An exception occurs at the intersection of northwest Sichuan Province and Gansu Province, where a noticeable discrepancy arises between temporal and spatial accessibility: spatial accessibility remains relatively high, while temporal accessibility is significantly constrained. This anomaly can be attributed to the relatively low technical standards of local roads and an underdeveloped multimodal transportation system. Therefore, efforts should be made to enhance the construction of high-class roads in similar areas to improve time accessibility.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Q.W. and C.-H.Y.; methodology and validation, C.-H.Y.; software, D.-C.Z.; formal analysis and investigation, D.-C.Z. and C.-H.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, Q.W. and Q.-P.Z.; writing—review and editing, Q.W., C.-H.Y. and C.-H.Y.; funding acquisition, Q.-P.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by The Natural Science Foundation of China (32060279); the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2022MD063, ZR202103050228, ZR2023QC232); the Shandong Province Key Research and Development Program (Soft Science) Project (2022RKY07005); the Startup Fund of Liaocheng University (318052036, 318052116); and the Development Program for Youth Innovation Team in Higher Education Institutions of Shandong Province (2022KJ110).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no competing interests.
References
- Tomasi, S.; Paviotti, G.; Cavicchi, A. Educational Tourism and Local Development: The Role of Universities. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selby, M. Mobile student experience: The place of tourism. Ann. Tour. Res. 2021, 90, 103253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Lv, X. Red heart at dark sites: The production of embodied patriotic ritual in tourism. Tour. Manag. 2025, 106, 104975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, X.; Fan, A.; Cai, L.A. Affective learning in short-term educational travel abroad: An exploratory mixed-method study. Tour. Manag. 2023, 94, 104649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Pei, T.; Jeronen, E.; Wang, Z.; Xu, L. Teaching and Learning Methods for Promoting Sustainability in Tourism Education. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.-P.; Lee, K.-Y.; Kabre, P.M.; Hsieh, C.-M. Impacts of Educational Agritourism on Students’ Future Career Intentions: Evidence from Agricultural Exchange Programs. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kırlar-Can, B.; Ertaş, M.; Kozak, M. Understanding the philosophy of tourism education: A perspective study in Turkey. Int. J. Tour. Res. 2021, 23, 1112–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airey, D. Education for tourism: A perspective article. Tour. Rev. 2019, 75, 260–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, J.; Gray, T.; Truong, S. Does growth in the outdoors stay in the outdoors? The impact of an extended residential and outdoor learning experience on student motivation, engagement and 21st century capabilities. Front. Psychol. 2023, 14, 1102610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, K.; Sakamoto, K.; Funck, C. Dark tourism as educational tourism: The case of ‘hope tourism’ in Fukushima, Japan. J. Herit. Tour. 2021, 16, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xu, M.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhuang, W.; Li, C. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Japan’s Forest Therapy Bases and Their Influencing Factors. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, A.; Frogel, M.; Foltin, G. The Pediatric Disaster Mental Health Intervention: Meeting the Primary Care Special Needs of Children in the Aftermath of Disasters. Prehospital Disaster Med. 2019, 34, s60–s61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, S.A. Boys left behind: The effects of summer camp and follow-up strategies on academic, personal, and social competencies. Econ. Educ. Rev. 2023, 93, 102370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, N.; Lee, J.; Park, D.H.; Lee, S.K.; Nam, S.Y.; Lee, S.; Kim, M.; Kang, H.; Kim, E.; Kim, M.; et al. Blood Glucose Control and Related Factors at a Camp for Korean Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes. Compr. Child Adolesc. Nurs. 2018, 41, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansén, E. Den statskloka resan: Adelns peregrinationer 1610–1680 (‘Travel in Search of Political Prudence: The Grand Tour of the Nobility 1610–1680′). J. Tour. Hist. 2020, 12, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohe, Y. Assessing Managerial Efficiency of Educational Tourism in Agriculture: Case of Dairy Farms in Japan. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.M.; Liddell, J.L.; Ferreira, R.J. An Evaluation of the Positive Action Program for Youth Violence Prevention: From Schools to Summer Camps. Child Adolesc. Soc. Work J. 2018, 35, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Xu, T. The Study Tour in China: An Emerging Mode for Practical Education. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L. Current Situation and Countermeasure Analysis of Study Tour—Taking Guangzhou as an Example. IOP Conf. Series. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 612, 032115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Jing, C. Effects of Study-Abroad Experiences on Chinese Students’ L2 Learning Activities and Study-Abroad Motivations. Chin. J. Appl. Linguist. 2021, 44, 21–34+126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, B.B.; Lu, F.J.H.; Gill, D.L.; Liu, S.H.; Chyi, T.; Chen, B. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Effects of Outdoor Education Programs on Adolescents’ Self-Efficacy. Percept. Mot. Ski. 2021, 128, 1932–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, R.; Li, H.; Tian, F. The Spatial Distribution and Its Influencing Factors of China’s National Study Travel Base. J. Geogr. Sci. 2021, 41, 1139–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Shao, H.; Xu, C. Research hotspots analysis of study travel based on Cite Space. Geogr. Teach. 2019, 18, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, M.A.M.; Shelley, B.; Ooi, C.-S. Uses of tourism resources for educational and community development: A systematic literature review and lessons. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2024, 53, 101278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranyai, D.; Sipos, T. Black-Spot Analysis in Hungary Based on Kernel Density Estimation. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Cai, Z.; Li, H. Accessibility of Medical Facilities in Multiple Traffic Modes: A Study in Guangzhou, China. Complexity 2020, 2020, 8819836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Guo, Q.; Lv, Q.; Zhao, X. From accessibility of traffic to accessibility of service: The spatial analysis of N-minute service circle of urban park system. J. Asian Archit. Build. Eng. 2023, 22, 3680–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Bai, H. The impact and regional heterogeneity analysis of tourism development on urban-rural income gap. Econ. Anal. Policy 2023, 80, 1539–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Zhong, Y.; Fan, J. Estimating the Spatial Heterogeneity and Seasonal Differences of the Contribution of Tourism Industry Activities to Night Light Index by POI. Sustainability 2022, 14, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, G.; Ju, H. The spatial pattern and influencing factors of tourism development in the Yellow River Basin of China. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Li, X. Eco-tourism benefit evaluation of Yellow River based on principal component analysis. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2020, 39, 8907–8915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Gu, X.; Yuan, Q.; Chen, N.; Jin, Q. Evaluation and Spatiotemporal Differentiation of Cultural Tourism Development Potential: The Case of the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yellow River. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2023, 12, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-L.; Yang, l. The design of geography study tour in the style of “teaching and research”—Taking the Yellow River Xiaolangdi Water Conservancy Hub Scenic Area as an example. J. Green Sci. Technol. 2021, 23, 219–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Yuan, L.; Lin, Z.-T.; Lu, X.-X. Design strategies for study tours based on geography core literacy—An example of study tour design in Dongying City, Shandong Province. Geogr. Teach. 2019, 12, 28–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lao, Y.; Lin, X.; Wu, S. Spatial Pattern of National Study Base and Its Influencing Factors. J. Fujian Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2021, 37, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Chen, C. Spatial Distribution and Accessibility of High Level Scenic Spots in Inner Mongolia. Sustainability 2022, 14, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, J.M.; Bulchand-Gidumal, J.; Suárez-Vega, R. Using accommodation price determinants to segment tourist areas. J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2021, 21, 100622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lu, C.; Mao, J.; Sun, D.; Li, H.; Lu, C. Spatial–Temporal Heterogeneity and the Related Influencing Factors of Tourism Efficiency in China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, A.; Xu, T.; Gao, J.; Liu, C.; Han, L. Multi-scale spatiotemporal wetland loss and its critical influencing factors in China determined using innovative grid-based GWR. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 149, 110144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Zhao, B.; Feng, Y. Spatial distribution and influencing factors of rural tourism: A case study of Henan Province. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, J.; Lu, Y.; Han, F.; Ma, X.; Yang, Z. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of the Rural Tourism Villages in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau and Its Influencing Factors. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 9330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.-Y. Research on Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Mechanism of 4A Level and Above Tourism Scenic Spots in Henan Province. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 186, 012043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Yin, C. Research on the Communication Strategy of History and Culture in Shaanxi Based on BP Neural Network Model. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 8965622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Wang, J.-E.; Huang, Y.-J.; Gu, H.-Y. Spatial heterogeneity and scale effects of factors influencing the distribution of high-tech enterprises in China. Geogr. Res. 2022, 41, 1338–1351. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.-Y. Study on Foreign Direct Investment on High Quality Development of Yellow River Basin Economic Zone—An empirical analysis based on prefecture-level cities in the Yellow River Basin. Sci. Decis.-Mak. 2021, 291, 89–102. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.; Hu, A.; Gan, X.; Zhao, X.; Huang, Y. Spatial and Temporal Characteristics of Ecosystem Service Trade-Off and Synergy Relationships in the Western Sichuan Plateau, China. Forests 2022, 13, 1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, A.; Cai, J.; Chen, F.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Z.; Xie, Q.; Yu, S. Sustainability Assessment of Cultural Heritage in Shandong Province. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-F.; Liang, X.-L.; Li, Y.-W. Study on the integration of tourism industry and red culture in Shandong Province under the background of cultural tourism integration. China J. Commer. 2022, 856, 35–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Li, H. Study on the Interactive Development of Transportation and Regional Economy in Ethnic Areas—Take Aba Tibetan and Qiang Autonomous Prefecture in Sichuan as an example. Reform Econ. Syst. 2015, 194, 78–84. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).