Photovoltaic Energy Modeling Using Machine Learning Applied to Meteorological Variables
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection and Preparation
2.3. Machine Learning Methods
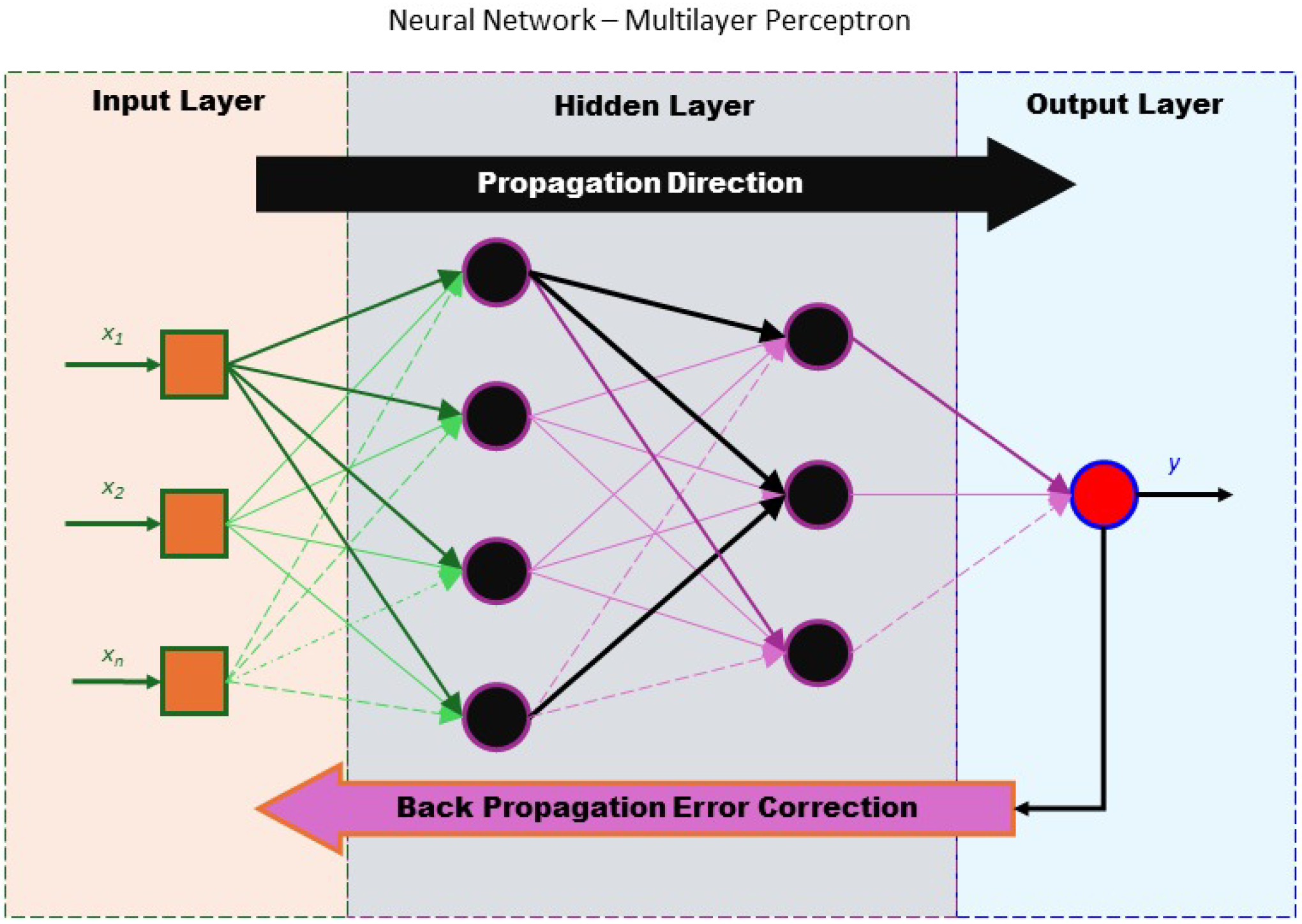
2.3.1. Long-Short-Term Memory (LSTM) Recurrent Neural Network
2.3.2. Sarimax
2.3.3. Support Vector Regressor (SVR)
2.3.4. Random Forest (RF)
2.4. Metrics
3. Results and Discussion
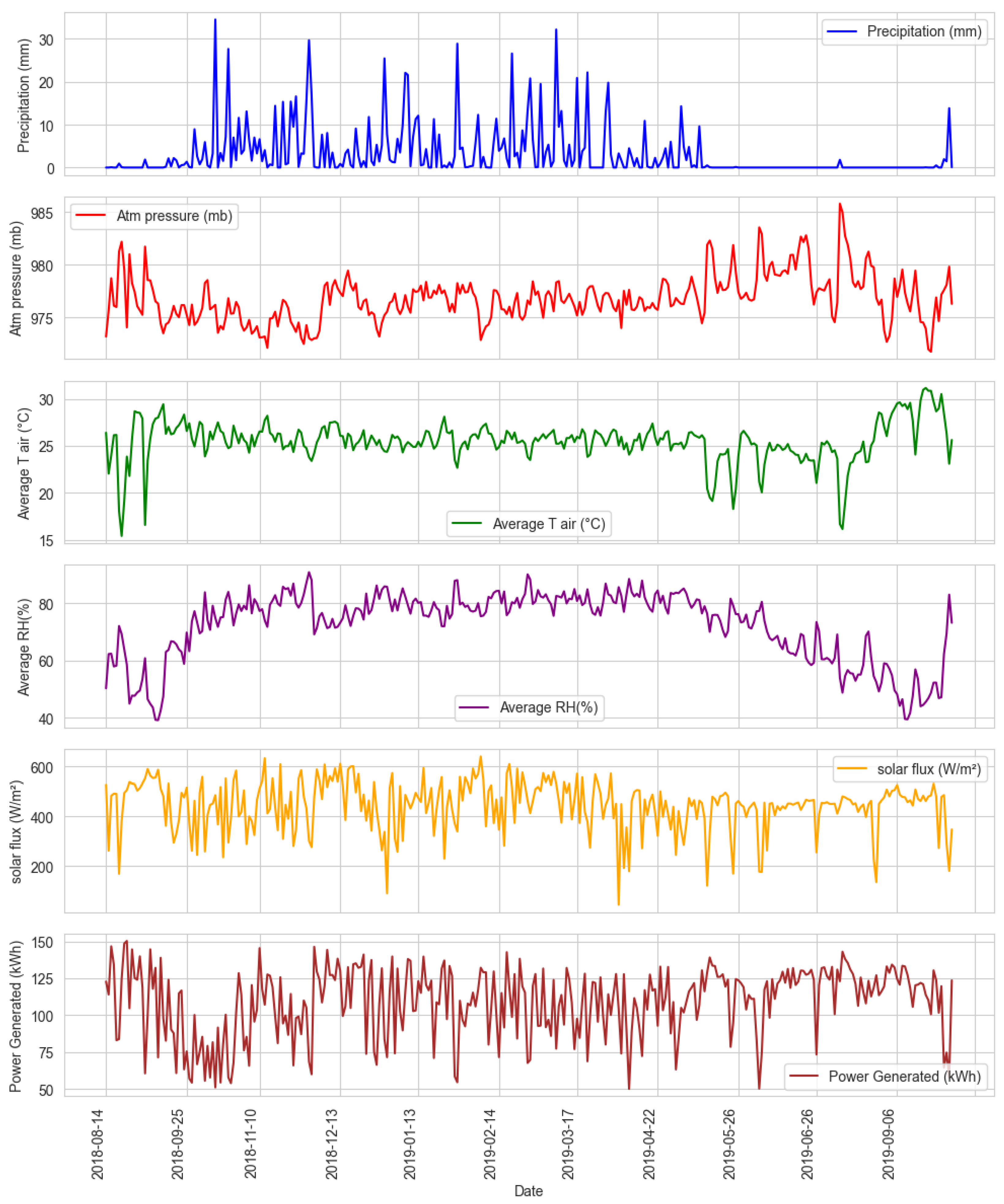
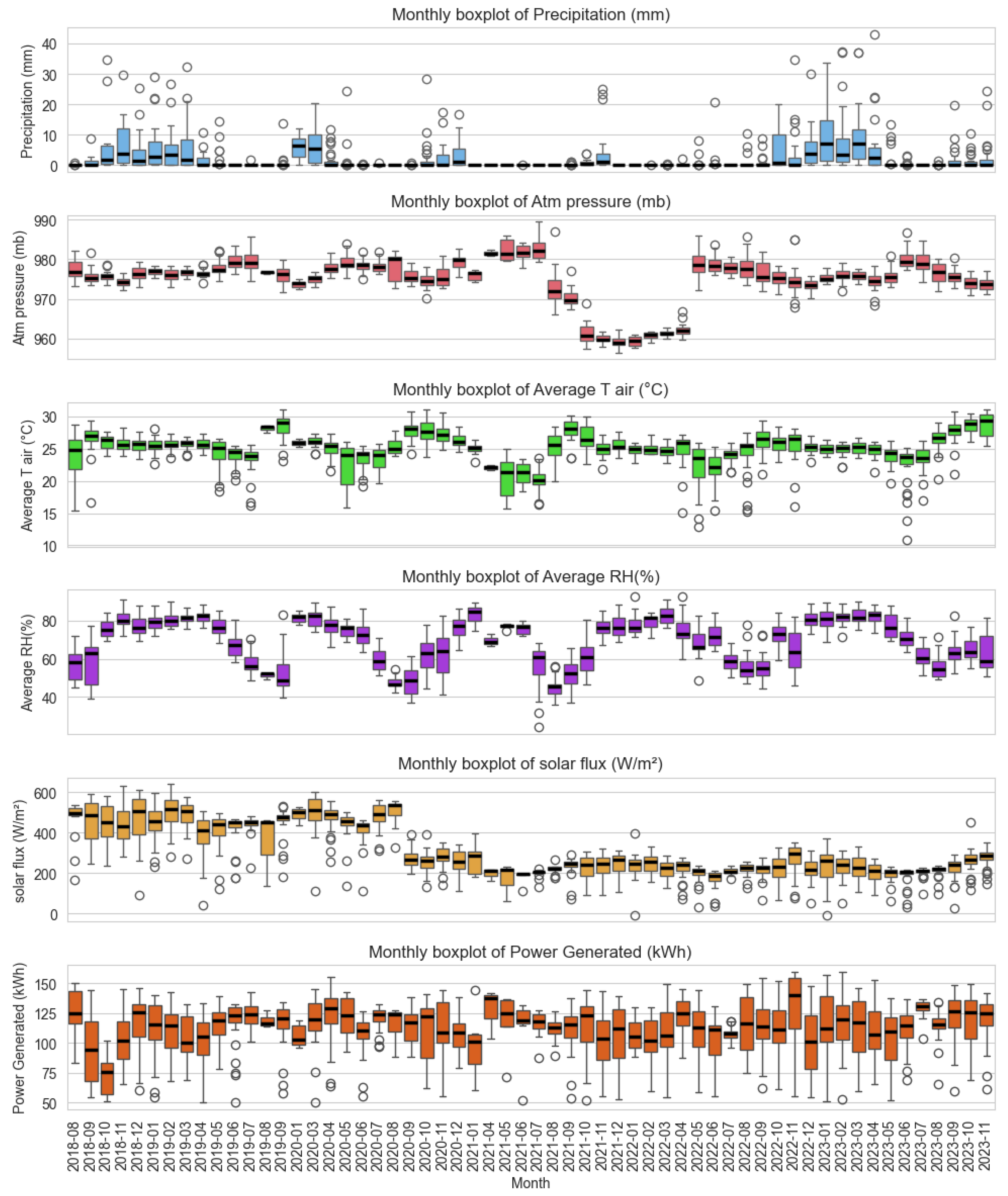
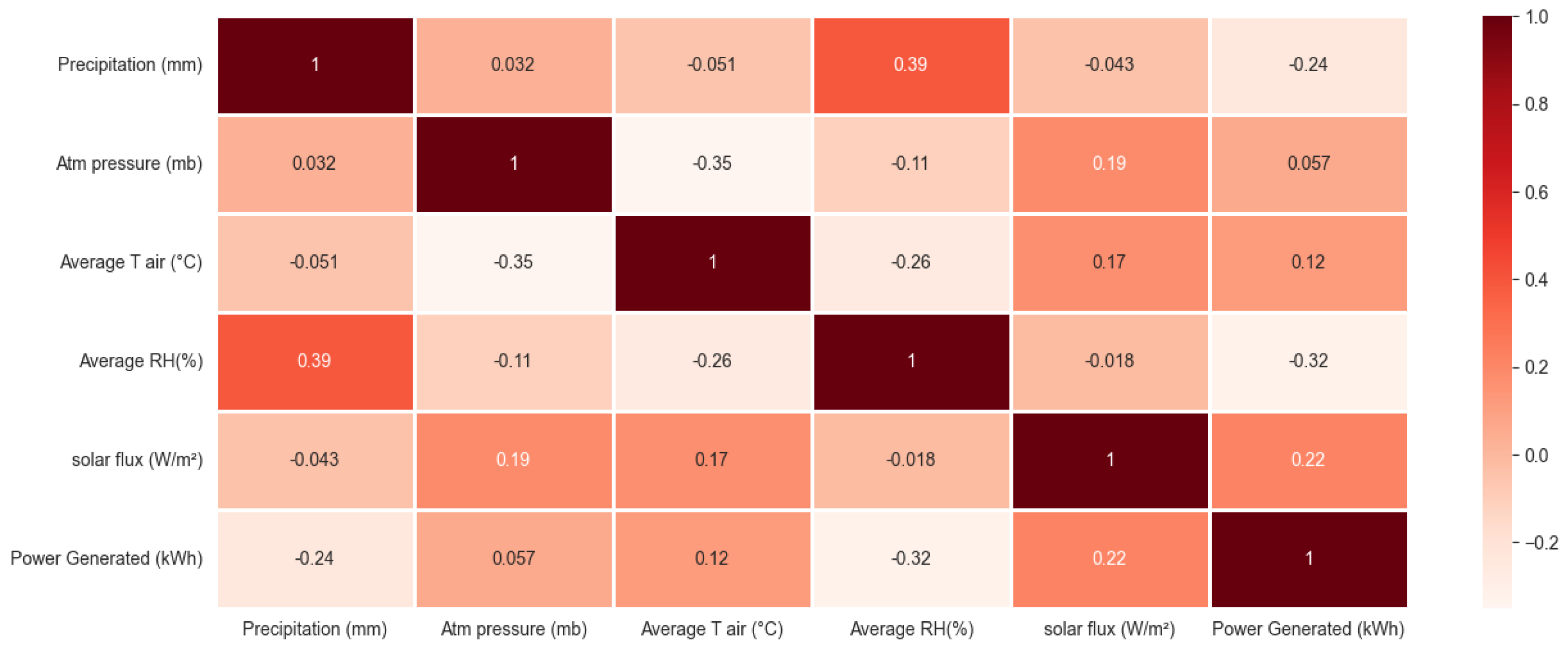
3.1. Variations in Meteorological Parameters
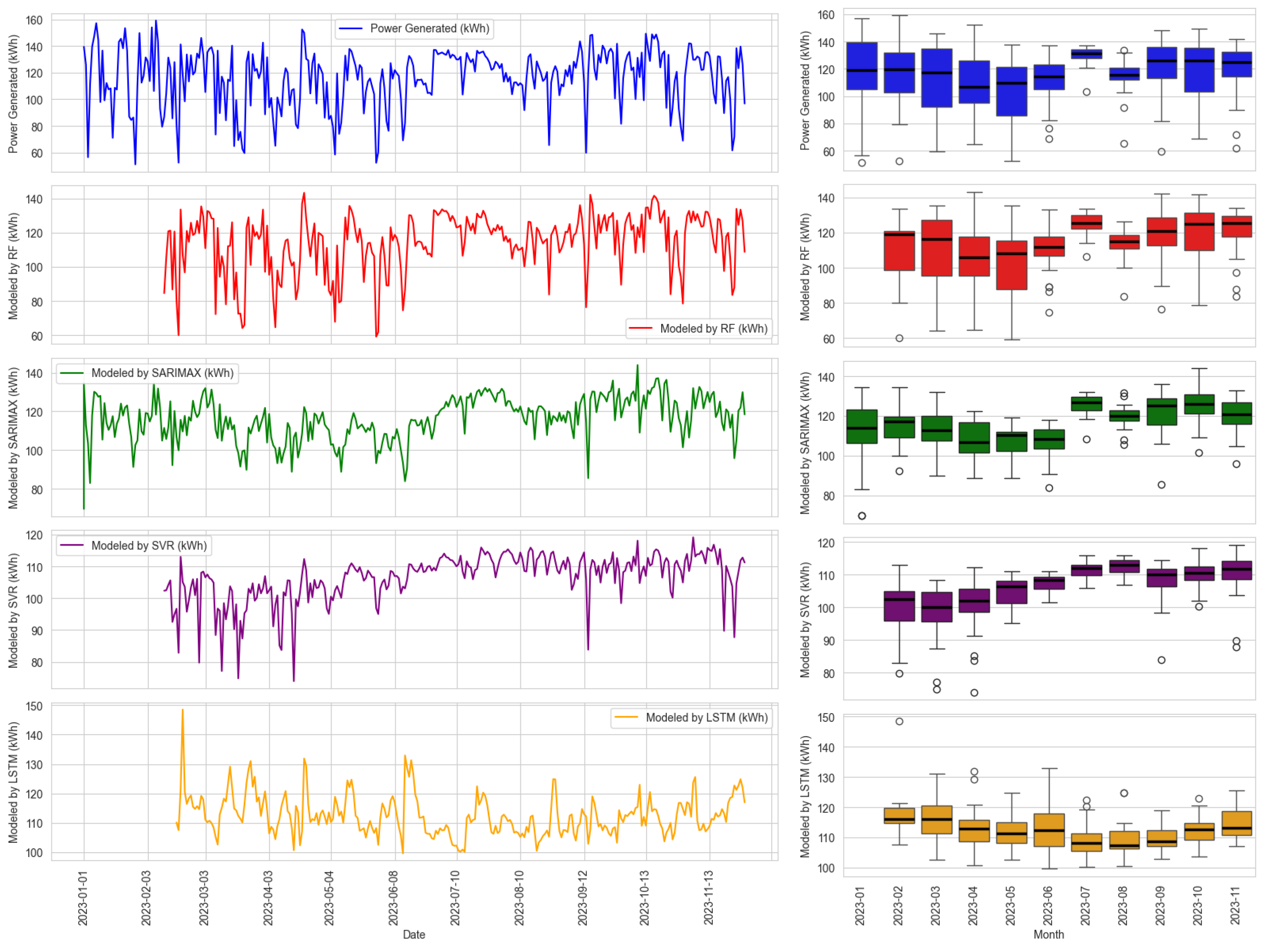
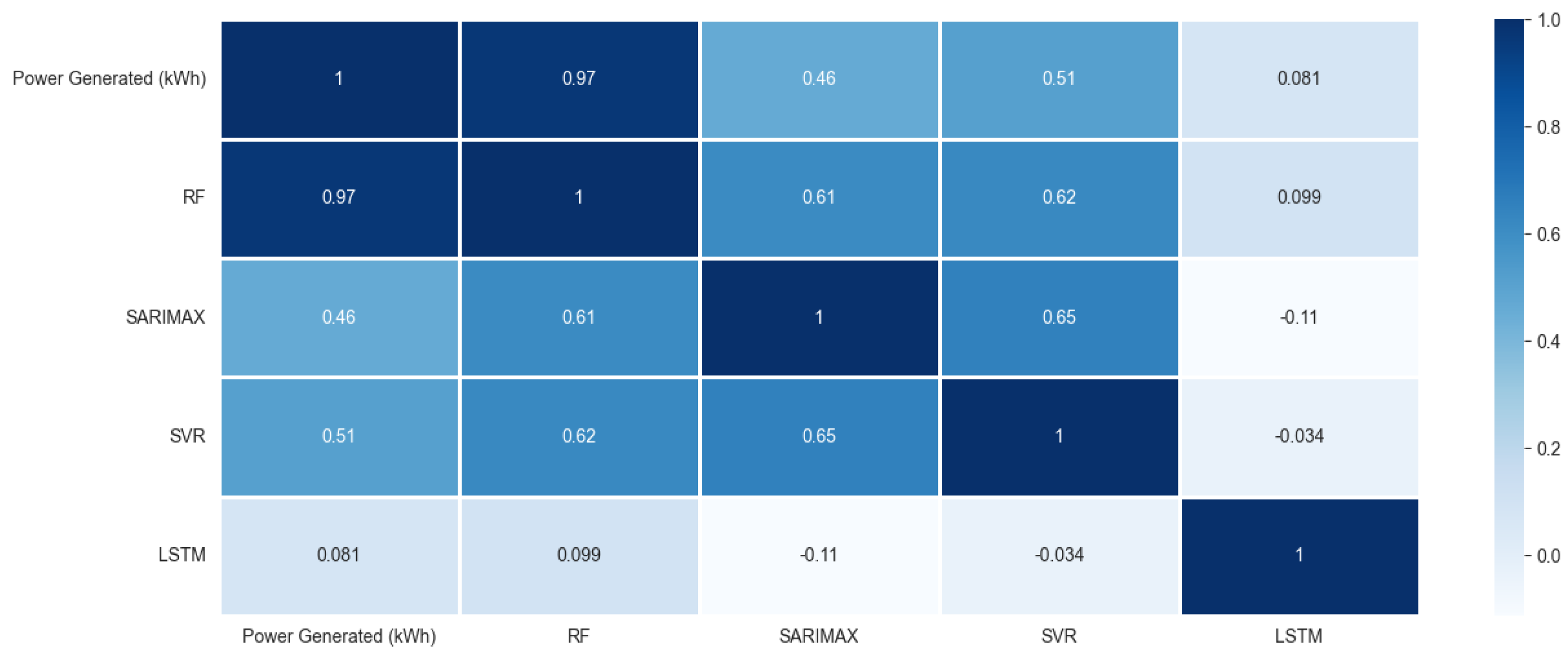
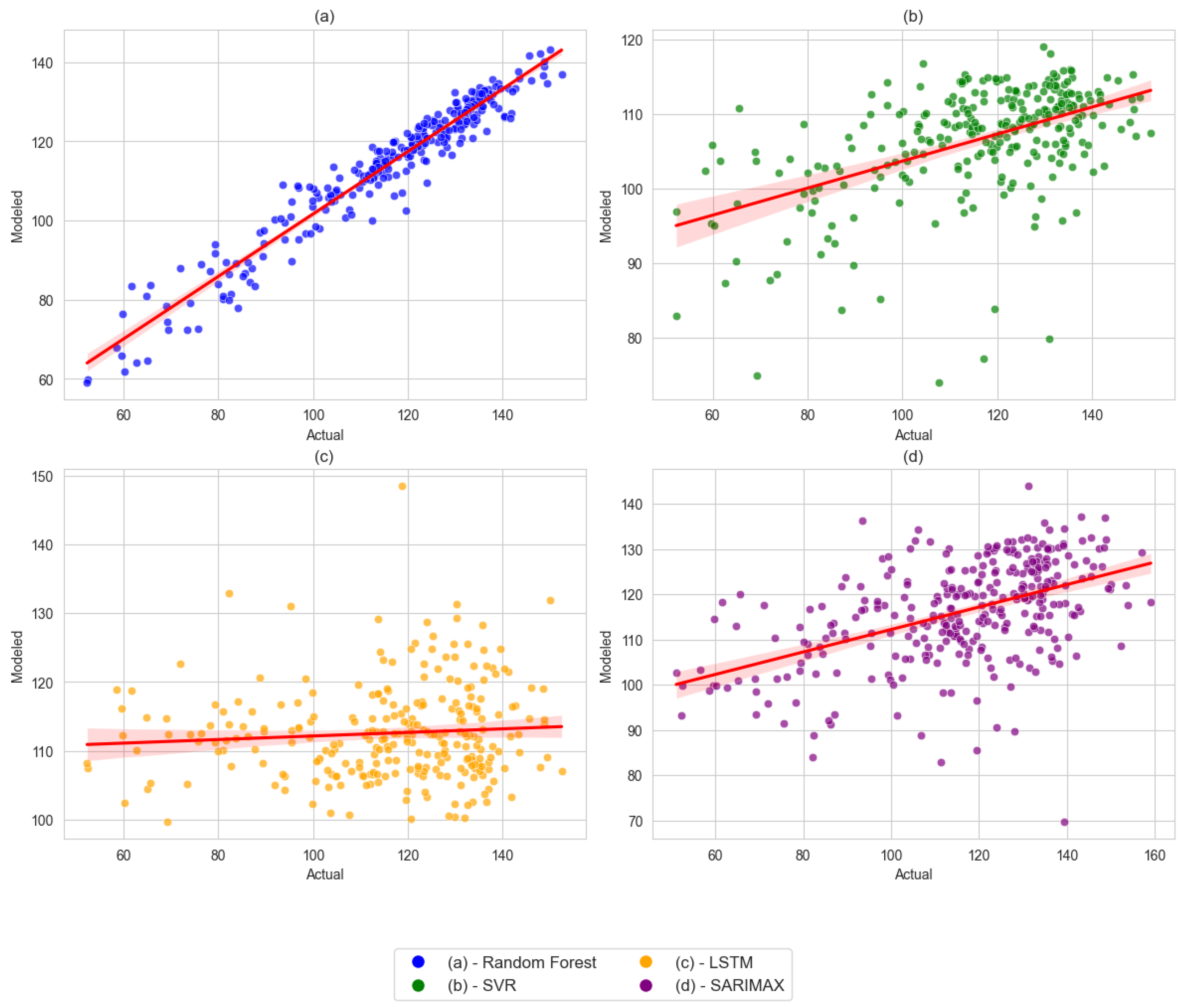
3.2. Evaluating the Performance of Machine Learning Models
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gernaat, D.; de Boer, H.D.; Daioglou, V.; Yalew, S.; Müller, C.; van Vuuren, D.V. Climate change impacts on renewable energy supply. Nat. Clim. Change 2021, 11, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solaun, K.; Cerdá, E. Climate change impacts on renewable energy generation. A review of quantitative projections. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 116, 109415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, A.; Chen, L.; Yang, M.; Msigwa, G.; Farghali, M.; Fawzy, S.; Rooney, D.W.; Yap, P. Cost, environmental impact, and resilience of renewable energy under a changing climate: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 21, 741–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Tao, Z.; Agyekum, E.B.; Fahad, S.; Tahir, M.; Salman, M. Sustainable rural electrification: Energy-economic feasibility analysis of autonomous hydrogen-based hybrid energy system. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 141, 460–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalew, S.; van Vliet, M.V.; Gernaat, D.; Ludwig, F.; Miara, A.; Park, C.; Byers, E.; Cian, E.D.; Piontek, F.; Iyer, G.; et al. Impacts of climate change on energy systems in global and regional scenarios. Nat. Energy 2020, 5, 794–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronin, J.; Anandarajah, G.; Dessens, O. Climate change impacts on the energy system: A review of trends and gaps. Clim. Change 2018, 151, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Liu, J.; Yang, H. Air pollution and soiling implications for solar photovoltaic power generation: A comprehensive review. Appl. Energy 2021, 298, 117247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhake, H.; Kosmopoulos, P.; Mantakas, A.; Kashyap, Y.; El-Askary, H.; Elbadawy, O. Climatological Trends and Effects of Aerosols and Clouds on Large Solar Parks: Application Examples in Benban (Egypt) and Al Dhafrah (UAE). Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- REN21. Renewables 2020 Global Status Report: Chapter 01—Renewable Energy in 2019. In Renewable Energy Policy Network for the 21st Century; REN21: Paris, France, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Dutta, R.; Chanda, K.; Maity, R. Future of solar energy potential in a changing climate across the world: A CMIP6 multi-model ensemble analysis. Renew. Energy 2022, 188, 819–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazil Breaks Record for Solar Energy Expansion in 2023. 2023. Available online: https://canalsolar.com.br/en/Brazil-records-record-expansion-of-solar-energy-in-2023/ (accessed on 13 May 2025).
- Chen, Y.; Yue, X.; Tian, C.; Letu, H.; Wang, L.; Zhou, H.; Zhao, Y.; Fu, W.; Xu, Z.; Peng, D.; et al. Assessment of solar energy potential in China using an ensemble of photovoltaic power models. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 877, 162979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.G.; Hassan, H.; Ookawara, S.; Nada, S.A. Investigation of the performance enhancement of building-integrated photovoltaic system using evaporative porous clay applied in different building’s directions. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 82, 108292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazali Ali, M.; Hassan, H.; Ookawara, S.; Nada, S.A. Assessment of evaporative porous clay cooler for Building-Integrated photovoltaic systems via energy, exergy, economic and environmental approaches. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2024, 51, 102641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paletta, Q.; Terrén-Serrano, G.; Nie, Y.; Li, B.; Bieker, J.; Zhang, W.; Dubus, L.; Dev, S.; Feng, C. Advances in solar forecasting: Computer vision with deep learning. Adv. Appl. Energy 2023, 11, 100150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Yang, K.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Z. Photovoltaic power forecasting: A dual-attention gated recurrent unit framework incorporating weather clustering and transfer learning strategy. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 130, 107691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wen, Y.; Nanehkaran, Y.; Suzauddola, M.; Chen, W.; Zhang, D. Machine learning techniques for stock price prediction and graphic signal recognition. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 121, 106038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaviria, J.; Narváez, G.; Guillén, C.; Giraldo, L.F.; Bressan, M. Machine learning in photovoltaic systems: A review. Renew. Energy 2022, 196, 298–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, M.; Majumder, I.; Nayak, N. Solar photovoltaic power forecasting using optimized modified extreme learning machine technique. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2018, 21, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Li, Z.; Li, Z. Prediction of Daily Climate Using Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) Model. Int. J. Innov. Sci. Res. Technol. (IJISRT) 2024, 9, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwokolo, S.C.; Eyime, E.; Obiwulu, A.U.; Meyer, E.L.; Ahia, C.C.; Ogbulezie, J.; Proutsos, N. A multi-model approach based on CARIMA-SARIMA-GPM for assessing the impacts of climate change on concentrated photovoltaic (CPV) potential. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2024, 134, 103560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zia, S. Climate Change Forecasting Using Machine Learning SARIMA Model. iRASD J. Comput. Sci. Inf. Technol. 2021, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Gou, Y.; He, L.; Bai, H.; Hu, C. High-resolution temperature and salinity model analysis using support vector regression. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2024, 15, 1517–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delbari, M.; Sharifazari, S.; Mohammadi, E. Modeling daily soil temperature over diverse climate conditions in Iran—A comparison of multiple linear regression and support vector regression techniques. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2019, 135, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.H.P.; Oliveira, M.D.F.; Santos, R.F.; Almeida, G.R. Performance of potato cultivars under different irrigation managements in a semi-arid climate. Rev. Ciências Agrárias Ambient. 2018, 25, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palácios, R.; Sallo, F.; Santos, A.; Nogueira, J.; Santana, F. Estimation of Direct Radiative Forcing of Aerosols on the Surface in the Pantanal-Cerrado Transition Region in the State of Mato Grosso, Brazil. Rev. Bras. Climatol. 2015, 16, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Ramírez, D.; Andrade-Flores, M.; Eck, T.F.; Stein, A.F.; O’Neill, N.T.; Lyamani, H.; Gassó, S.; Whiteman, D.N.; Veselovskii, I.; Velarde, F.; et al. Multi year aerosol characterization in the tropical Andes and in adjacent Amazonia using AERONET measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 166, 412–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 9060:2018; Specification and Classification of Instruments for Measuring Hemispherical Solar and Direct Solar Radiation. ISO Copyright Office: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. Available online: https://www.iso.org (accessed on 13 May 2025).
- Vijh, M.; Chandola, D.; Tikkiwal, V.; Kumar, A. Stock Closing Price Prediction using Machine Learning Techniques. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2020, 167, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, F.; Zameer, A.; Muneeb, M. A novel genetic LSTM model for wind power forecast. Energy 2021, 223, 120069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshewey, A.M.; Shams, M.Y.; Elhady, A.M.; Shohieb, S.M.; Abdelhamid, A.A.; Ibrahim, A.; Tarek, Z. A Novel WD-SARIMAX Model for Temperature Forecasting Using Daily Delhi Climate Dataset. Sustainability 2023, 15, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jändel, M. A neural support vector machine. Neural Netw. 2010, 23, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahouar, A.; Ben Hadj Slama, J. Hour-ahead wind power forecast based on random forests. Renew. Energy 2017, 109, 529–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamińska, J.A. The use of random forests in modelling short-term air pollution effects based on traffic and meteorological conditions: A case study in Wrocław. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 217, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadhav, A.V.; Rahul, P.R.C.; Kumar, V.; Dumka, U.C.; Bhawar, R.L. Spatiotemporal Assessment of Surface Solar Dimming in India: Impacts of Multi-Level Clouds and Atmospheric Aerosols. Climate 2024, 12, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sustainable Development Goals. 2020. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/goals. (accessed on 13 May 2025).
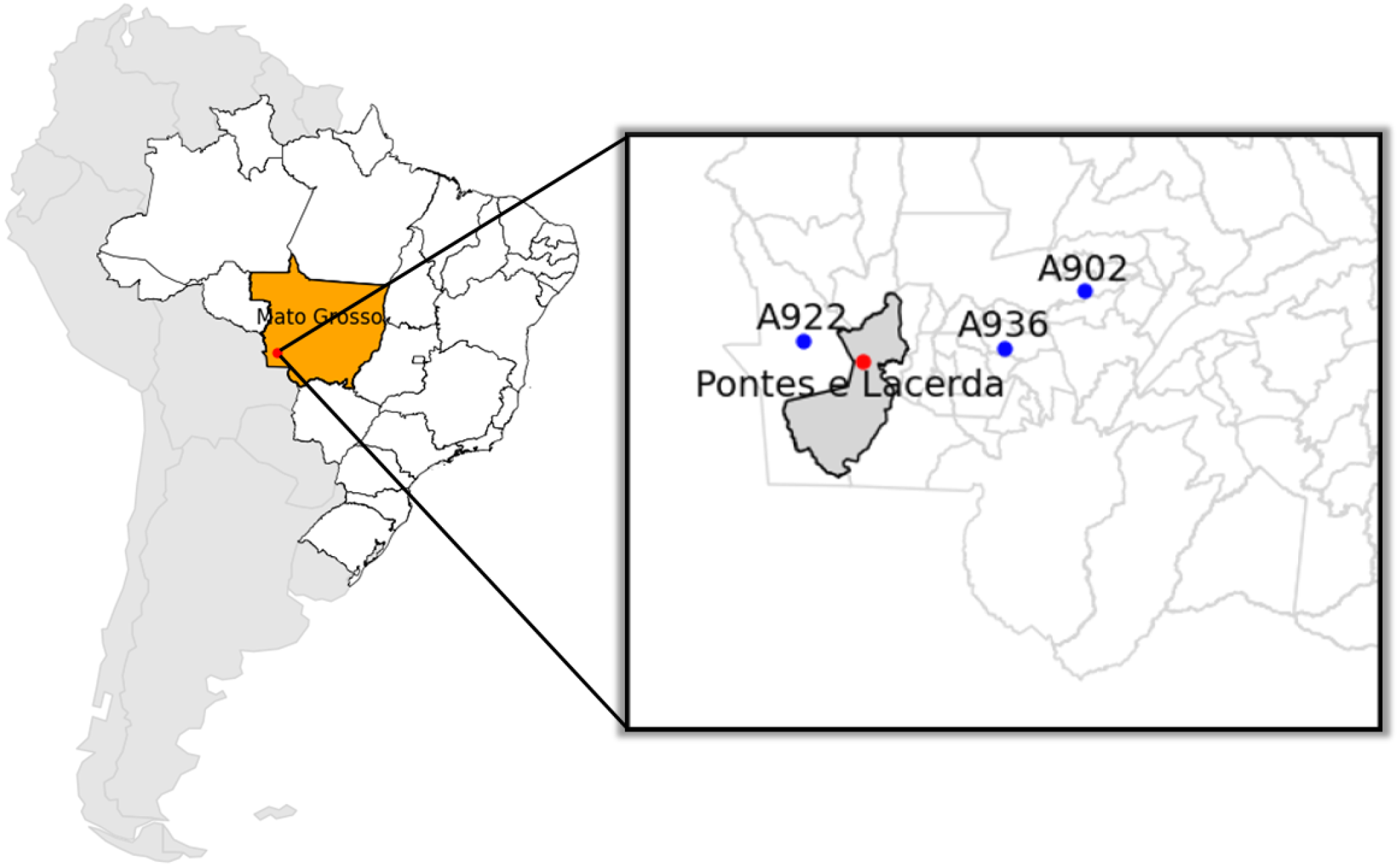
| Station Name | Code | Latitude | Longitude | Altitude (m) | Availability | Periodicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pontes e Lacerda | A937 | −15.1344 | −59.3461 | 272.53 | 1 January 2018–1 January 2024 | Daily |
| Salto do Céu | A936 | −15.1247 | −58.1272 | 300.83 | 1 January 2018–Present day | Daily |
| VBST | A922 | −15.0628 | −59.8731 | 213.00 | 1 January 2018–Present day | Daily |
| Tangará da Serra | A902 | −14.6500 | −57.4317 | 440.01 | 1 January 2018–Present day | Daily |
| Model | MAE | RMSE | d | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LSTM | 17.6327 | 21.9831 | 0.0782 | 0.0028 |
| SVR | 17.0499 | 20.6762 | 0.0436 | 0.5584 |
| SARIMAX | 14.7407 | 19.2534 | 0.2377 | 0.6155 |
| Random Forest | 4.9122 | 6.3778 | 0.9090 | 0.9720 |
| Model | 1st Run Time (s) | Average Time (s) | Current Memory (MB) | Peak Memory (MB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LSTM | 37.93 | 35.51 | 8.02 | 11.20 |
| SVR | 0.10 | 0.06 | 29.39 | 31.24 |
| SARIMAX | 3.87 | 3.42 | 1.40 | 167.51 |
| Random Forest | 7.27 | 3.72 | 0.02 | 0.86 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Campos, B.N.; Maionchi, D.d.O.; da Silva, J.G.; Biudes, M.S.; Oliveira, N.N.d.; Palácios, R.d.S. Photovoltaic Energy Modeling Using Machine Learning Applied to Meteorological Variables. Sustainability 2025, 17, 7506. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167506
de Campos BN, Maionchi DdO, da Silva JG, Biudes MS, Oliveira NNd, Palácios RdS. Photovoltaic Energy Modeling Using Machine Learning Applied to Meteorological Variables. Sustainability. 2025; 17(16):7506. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167506
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Campos, Bruno Neves, Daniela de Oliveira Maionchi, Junior Gonçalves da Silva, Marcelo Sacardi Biudes, Nicolas Neves de Oliveira, and Rafael da Silva Palácios. 2025. "Photovoltaic Energy Modeling Using Machine Learning Applied to Meteorological Variables" Sustainability 17, no. 16: 7506. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167506
APA Stylede Campos, B. N., Maionchi, D. d. O., da Silva, J. G., Biudes, M. S., Oliveira, N. N. d., & Palácios, R. d. S. (2025). Photovoltaic Energy Modeling Using Machine Learning Applied to Meteorological Variables. Sustainability, 17(16), 7506. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167506










