1. Introduction
In recent years, ecological security in major water source basins has garnered mounting global concern, particularly amid accelerating environmental change and intensifying human activities. China’s recent national strategies—notably the 14th Five-Year Plan for Environmental and Ecological Protection and the general framework for National Land Spatial Planning (2021–2035)—explicitly prioritize ecological civilization advancement, emphasizing how ecosystem services are essential for promoting sustainable regional development and maintaining ecological security at the national level [
1,
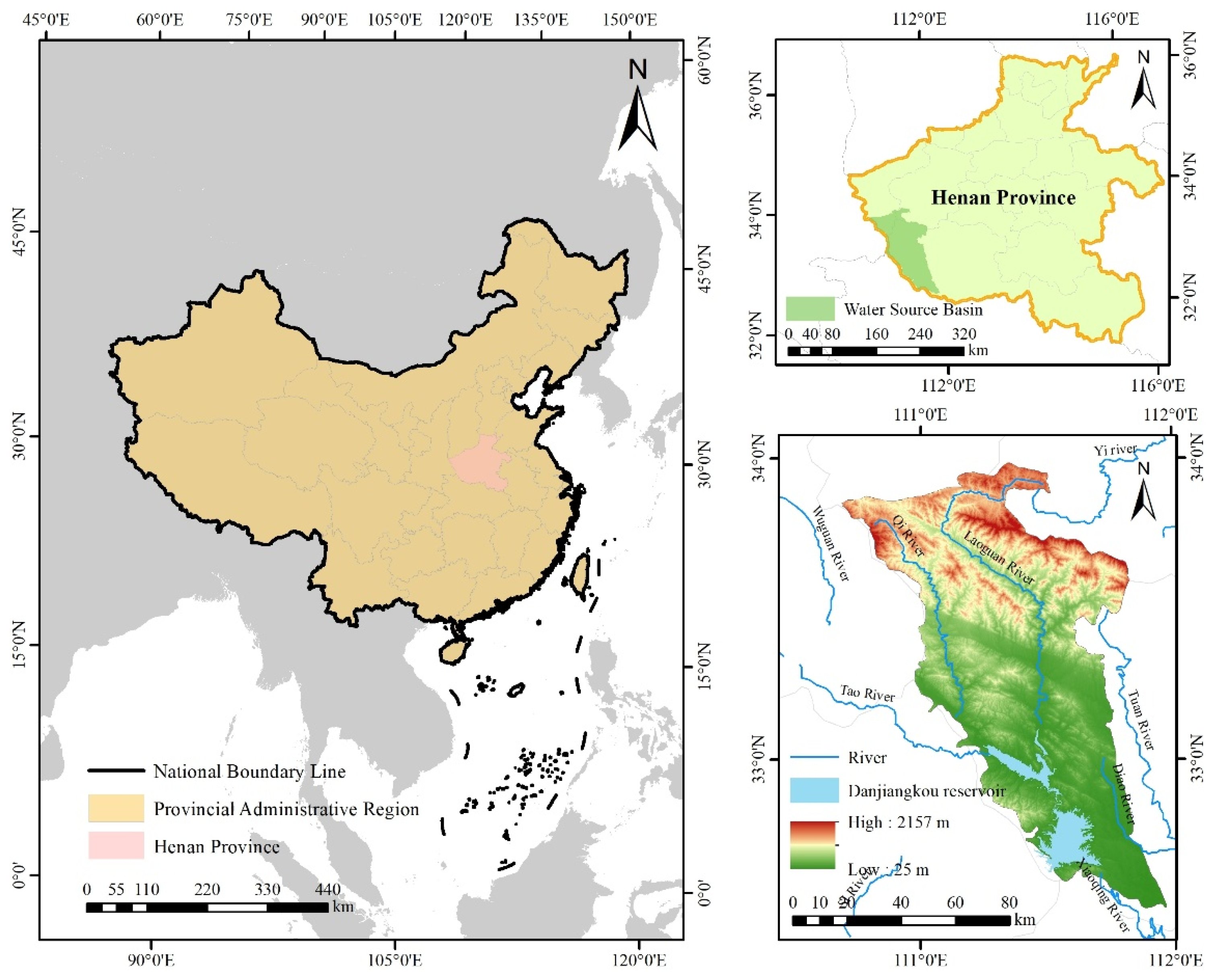
2]. The Danjiangkou Reservoir, an integral part of the Water Diversion Project from South to North, is the biggest artificial freshwater lake in Asia and a first-class water source protection region designated by the government [
3]. Its function in regulating and storing water resources has not only mitigated freshwater shortages in northern China but also played a vital role in maintaining regional ecological stability.
As a representative large reservoir-type water source, however, the Danjiangkou Reservoir faces intensifying ecological stressors driven by watershed land-use transitions. These land-use transitions—propelled by urban expansion, agricultural intensification, and ecological restoration initiatives like China’s Grain for Green Program—amplify ecosystem service vulnerability, generating complex trade-offs and synergies among key services: water yield, soil conservation, carbon sequestration, and habitat quality [
4]. Green and low-carbon development strategies, which emphasize both carbon reduction and ecological conservation, are key drivers of land use transformation, particularly through reforestation and restoration projects [
5]. These transitions directly influence land use structure and alter the functional capacities of ecosystems [
6]. As the primary substrate for socio-ecological systems, land manifests distinct carbon source and carbon sink dynamics across use types. Construction land expansion, for example, drives net carbon emissions through energy-intensive infrastructure and reduced carbon sequestration capacity [
7]. Thus, optimizing land use structure serves as a critical mechanism for advancing green, low-carbon development. This requires not only reducing carbon emissions but also maintaining the diversity, functionality, and sustainability of ecosystem services—particularly key regulating services such as water purification and soil retention [
8,
9]. Conversely, enhancing key ecosystem services, particularly forest-based carbon sequestration and water purification, directly advances low-carbon objectives by amplifying natural carbon sinks and reducing emission-intensive water treatment needs [
10]. As national green spatial planning advances, land’s ecological functions are poised to transform, triggering novel patterns of trade-offs and synergies among ecosystem services [
11].
Despite advances in ecosystem service interaction research, persistent theoretical gaps impede synthesis. First, while trade-offs and synergies are foundational concepts, inconsistent definitions and blurred conceptual boundaries generate fragmented, non-comparable findings [
12,
13]. Second, current methods are largely limited to static spatial snapshots or simple correlation analyses, which fail to capture the non-linear dynamics and spatiotemporal evolution of ecosystem services across scales [
14]. Third, while land use change is widely acknowledged as a key driver of ecosystem service dynamics, it is frequently treated as an external variable, lacking integration into the analytical framework [
15]. These limitations restrict our understanding of feedback mechanisms, threshold effects, and functional transformations in ecosystem services [
16]. Such theoretical gaps hinder a comprehensive understanding of ecosystem functioning and impede the formulation of effective policy and management strategies.
From a practical standpoint, watershed management must reconcile multiple, often conflicting, objectives. For instance, ecological restoration through afforestation may enhance carbon storage and soil conservation, but it can also reduce water yield, exacerbating downstream water supply pressures [
17]. Similarly, agricultural expansion in marginal areas may boost short-term food production but increase non-point source pollution and habitat fragmentation. In this context, understanding the trade-offs and synergies among ecosystem services under land use change is critical for improving watershed ecological governance and spatial planning [
18]. This is especially true for the Danjiangkou Reservoir, a key strategic water source. As ecological zoning, redline demarcation, and compensation mechanisms continue to evolve, there is an urgent need for a scientific, spatially explicit decision-making framework to support multi-objective coordination.
Accordingly, this study analyzes land use variations in the Xichuan segment of the Danjiangkou Reservoir Basin from 2012 to 2022. Utilizing the InVEST model, it assessed five ecosystem services—water purification, soil retention, carbon storage, habitat quality, and water yield—to investigate their spatiotemporal variations, assess trade-offs and synergies, and explore the relationships between land use variations and ecosystem services. This was carried out by integrating land use variation, ecosystem service functions, and their trade-off and synergy interactions into a cohesive analytical framework. The purpose of this study is to clarify the response mechanisms that connect ecosystem services and land use change. Ultimately, it contributes to a more systematic theoretical foundation for watershed ecological management and provides scientific support for spatial optimization, ecological redline planning, and sustainable resource allocation in key water source regions.
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Spatiotemporal Patterns of Land Use Change
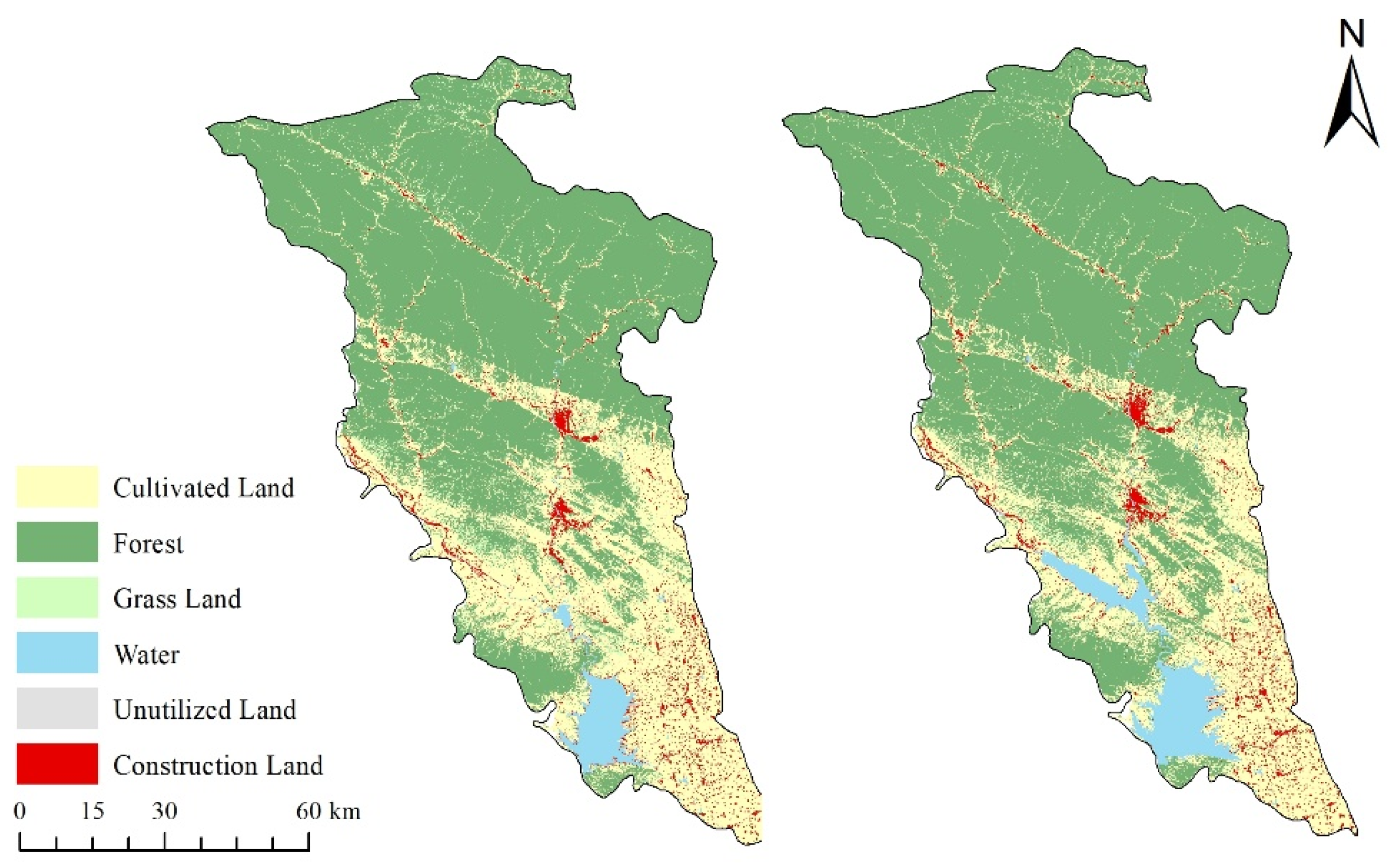
The remote sensing images from 2012 and 2022 were analyzed using the random forest method to classify six distinct land use types: cultivated land, forest land, grassland, water bodies, built-up land, and unused land. This resulted in the spatial distribution of the different land use types in the Danjiangkou Reservoir watershed, as shown in
Figure 3.
From
Figure 3, it is evident that, during the study period, the areas of water bodies and built-up land in the research area significantly increased, while the changes in other land types were relatively minor. The increase in built-up land primarily occurred in the urban areas of Xixia County and Xichuan County, as well as in some townships in Dengzhou City, in the southeastern part of the study area. Over the past decade, rapid economic growth has driven urban development, further contributing to the expansion of the built-up land in these regions. The elevation of the Danjiangkou Reservoir dam to 176.6 m has raised its water storage capacity, increased the flooded area upstream, and expanded the overall water area of the reservoir to 1050 km
2, resulting in the most noticeable change in the water body area.
A statistical analysis was performed on the remote sensing classification results for the years 2012 and 2022 to assess the changes in the areas of the land use types. The land use transfer matrix was subsequently employed to derive the transfer results across the six land use types, as illustrated in
Figure 4.
Figure 4 illustrates that, from 2012 to 2022, the study basin underwent a notable transformation in land use patterns, characterized by substantial conversions from cultivated land and grassland to forestland and water bodies. During this period, a total of 416.81 km
2 of cultivated land was converted: 240.91 km
2 (57.81%) to forestland, 144.65 km
2 (34.71%) to water bodies, and 38.43 km
2 (9.22%) to construction land. These transitions reflect the initial outcomes of policies promoting the return of farmland to forest and the restoration of wetlands.
Simultaneously, 223.50 km2 of forestland was transformed, with 130.19 km2 (58.25%) converted to water bodies and 89.91 km2 (40.23%) converted to cultivated land. Although afforestation remains a central policy objective, the increasing demand for agricultural land has resulted in a partial reversion of forestland to farmland. In particular, certain forested areas were converted to cultivated land to mitigate surface runoff and soil erosion, thereby contributing to the protection of water quality in the source region of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project’s Middle Route. Additionally, dam heightening and water impoundment activities inundated large tracts of forestland, resulting in significant conversions from forestland to water bodies.
A total of 77.60 km2 of grassland was converted during the study period, of which 44.80 km2 (57.73%) was transformed into cultivated land and 31.66 km2 (40.80%) into forestland. The predominant driver of grassland-to-farmland conversion lies in the higher direct economic returns of agricultural land—especially following the implementation of grazing restrictions. In areas with relatively flat terrain, low risk of soil erosion, and favorable cultivation conditions, local farmers have increasingly converted grassland into farmland to enhance household income. Moreover, to maintain a dynamic balance in the total area of cultivated land, local governments have prioritized the use of grassland with suitable topography and soil conditions as a key source of supplementary farmland, accounting for nearly 58% of grassland conversions.
Meanwhile, the conversion of grassland to forestland (40.80%) was largely driven by ecological restoration programs initiated by regional management authorities. These programs target degraded or sloped grasslands—typically exhibiting low ecological productivity and high erosion risk—and aim to improve ecological function by transforming them into forestland, which offers enhanced ecosystem services and improved soil and water conservation capacity.
3.2. Ecosystem Services Change Analysis
3.2.1. Analysis of Spatial Pattern Changes in Ecosystem Services
For the ten-year period of 2012–2022, the analysis shows varying degrees of change in the ecosystem services within the Danjiangkou Reservoir water source area (
Figure 5).
Overall, the water yield and total carbon storage show an upward trend, while the total nitrogen output, total phosphorus output, and soil erosion amount exhibit a downward trend. The overall changes in the total nitrogen output, total phosphorus output, and habitat quality are relatively small, whereas the changes in the water yield, soil erosion amount, and total carbon storage are more significant. The maximum values for the total nitrogen output and total phosphorus output, which reflect the water purification function, decreased from 2.625 kg·hm−2·a−1 and 0.283 kg·hm−2·a−1 in 2012 to 2.507 kg·hm−2·a−1 and 0.265 kg·hm−2·a−1 in 2022, respectively. In the densely populated urban areas in the central and southeastern regions of the research area, the spatial distribution of the total nitrogen and total phosphorus output reduction expanded. This indicates that the water source area has restricted or prohibited pollutant emissions, reduced the use of fertilizers and pesticides, and strengthened the vegetation management to mitigate soil erosion, leading to a decrease in the surface total nitrogen and phosphorus output. The water yield and soil erosion amount were the two ecosystem service parameters that exhibited the highest variability throughout the study period. The water yield increased from 579.45 m3 to 787.77 m3; spatially, in the northern region of the water source in Danjiangkou, the ranges with lower water yields expanded with increasing altitude by 2022, while the central region, influenced by reforestation and grassland restoration, has largely transitioned into a high-water-yield area. Soil erosion decreased from 318.71 t−1 to 241.59 t−1 as part of the farmland was converted into forests or grassland during the study period. The reduction in land use intensity, along with reforestation and other vegetation restoration measures, increased the surface cover, leading to a significant reduction in soil erosion. The total carbon storage increased from 20.59 10t9·km−2 to 23.68 10t9·km−2, with the changes primarily distributed in areas of increased construction land and those with expanded water bodies in the water source region. This indicates that, with economic development, urban built-up areas have been continuously expanded, occupying a significant amount of unused land, while the increase in the water body area contributed to a decrease in the total carbon storage during the study period. The habitat quality showed a relatively small degree of change and range throughout the study period.
3.2.2. Spatiotemporal Change Analysis of Ecosystem Services
The spatial distribution of the interannual trends covering the period from 2012 to 2022 in the six ecosystem services in the Danjiangkou Reservoir water source area is shown in
Figure 6.
Figure 6 illustrates that, among the six ecosystem service indicators, only the total nitrogen output showed significant changes throughout the study period, while the other five ecosystem service indicators changed relatively little. The area with a slight improvement in its total nitrogen output was largely concentrated in the northern region, where forest land is abundant. Overall, the total phosphorus output exhibited a clear improvement, with only a few areas showing significant degradation. The results regarding these two water quality purification indicators suggest that the reservoir management authorities have achieved some progress in addressing agricultural non-point source pollution, soil erosion control, and the construction of ecologically clean, small watersheds in the upper reaches of the Danjiang River. The water yield in certain regions of the upper Danjiang River and at the eastern edge of the reservoir has shown significant decline. According to a comparative study of the changes in land use, this area has become a submerged zone due to the reservoir’s expansion. The regional evaporation, root limiting layer depth, and plant available water content have all been severely affected, resulting in a noticeable decline in the water yield in this area. Soil erosion has also experienced localized, significant degradation in the reservoir area and upstream basin. There are still many areas of sloped cultivated land in this region, and the reduction in soil thickness will further decrease the effectiveness of soil and water conservation. When land is overexploited, it can lead to new forms of human-induced erosion. The trend in total carbon storage mostly shows a significant improvement, while areas of notable degradation are concentrated at the edges of the reservoir inundation zone. The expansion of the reservoir has altered the land use structure at the edges of this inundation zone. The reduction in the forest and grassland area within the region is the main reason for the apparent degradation in total carbon storage. Conversely, the habitat quality at the edges of the reservoir inundation zone shows a clear trend of improvement. As the reservoir expands, other land use types have been converted into water bodies, and the management authorities have strengthened the ecological protection in the surrounding areas, enhancing the habitat quality in this region.
3.3. Analysis of Synergies and Trade-Offs in Ecosystem Services
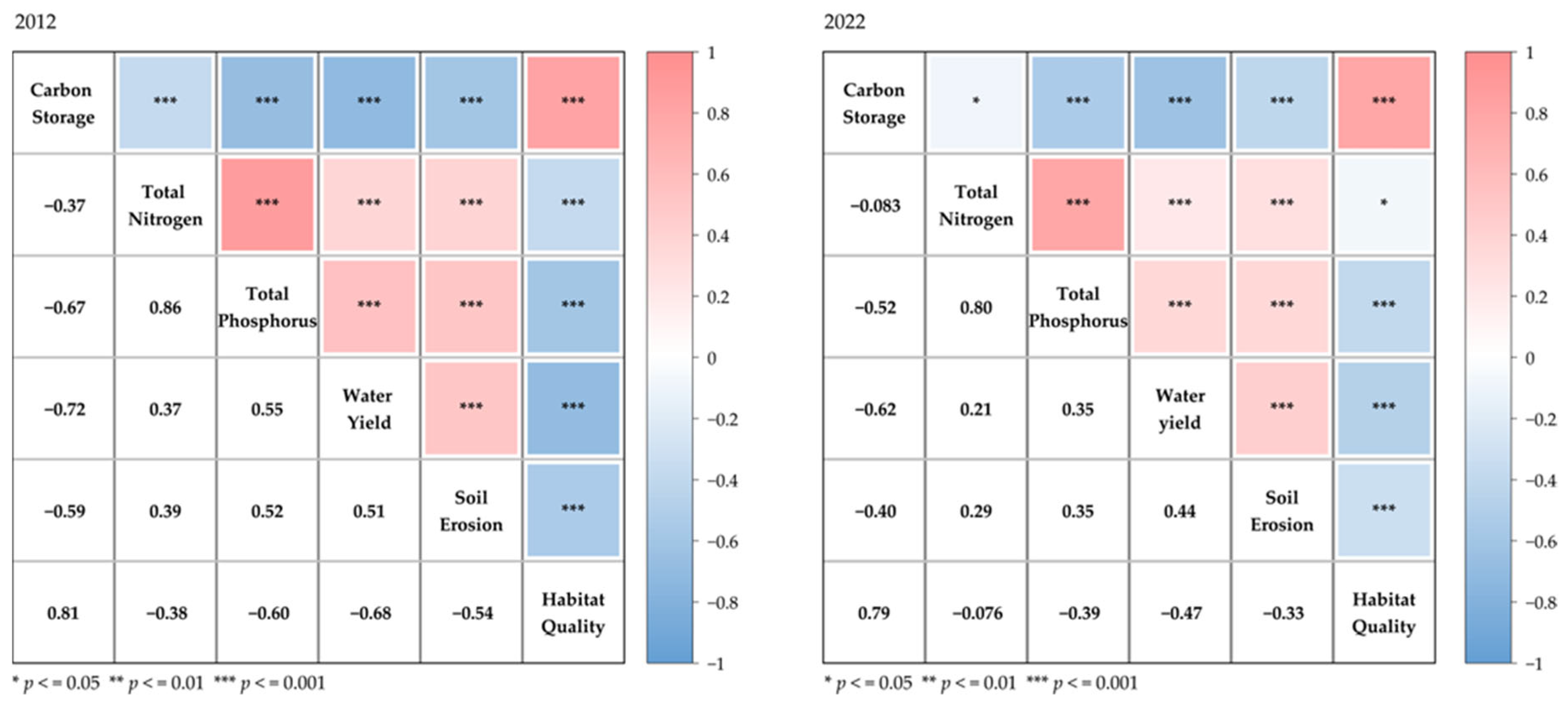
The results of the correlation analysis of the six ecosystem service indicators are presented in
Figure 7. In 2012, the correlation coefficients among all pairs of ecosystem services were statistically significant at the 0.001 level, indicating robust interrelationships. By contrast, in 2022, the correlations remained statistically significant, though at varying levels, with most passing the 0.05 and 0.001 significance thresholds. This shift suggests potential changes in the interaction strength among ecosystem services over time, possibly driven by evolving land use patterns and ecological management practices.
In 2012, the correlation coefficients between the total carbon storage and the total nitrogen output, total phosphorus output, water yield, and soil erosion were −0.37, −0.67, −0.72, and −0.59, respectively. All correlation coefficients were less than 0; this indicates a trade-off relationship between the total carbon storage and these four ecosystem services. Conversely, the correlation coefficient between the total carbon storage and the habitat quality was 0.81, indicating strong synergy between these two ecosystem services. The correlation coefficients for the total nitrogen output and the total phosphorus output, water yield, soil erosion, and habitat quality were 0.86, 0.37, 0.39, and −0.38, respectively. This indicates a significant synergy between total nitrogen and total phosphorus outputs, a weak synergy with soil erosion and habitat quality, and a weak trade-off relationship with habitat quality. Regarding the total phosphorus output, its correlation coefficients with the water yield, soil erosion, and habitat quality were 0.55, 0.52, and −0.60, respectively, indicating moderate synergy with the water yield and soil erosion and a moderate trade-off relationship with habitat quality. The correlation coefficient between the water yield and soil erosion was 0.51, indicating moderate synergy, while the correlation coefficient between the water yield and habitat quality was −0.68, indicating a strong trade-off relationship. The correlation coefficient between soil erosion and habitat quality was −0.54, indicating a moderate trade-off relationship.
In 2022, the correlation coefficients between the total carbon storage and the total nitrogen output, total phosphorus output, water yield, and soil erosion were −0.083, −0.52, −0.62, and −0.40, respectively. Compared to 2012, these coefficients remained below 0, indicating a trade-off relationship. However, the correlation coefficient between the total carbon storage and habitat quality was 0.79, still reflecting the strong synergy between these two ecosystem services. The correlation coefficients for the total nitrogen output and the total phosphorus output, water yield, soil erosion, and habitat quality were 0.80, 0.21, 0.29, and −0.076, respectively. This indicates that the total nitrogen output continued to exhibit strong synergy with the total phosphorus output, weak synergy with the water yield and soil erosion, and a very weak trade-off relationship with the habitat quality. The correlation coefficients between the total phosphorus output and the water yield, soil erosion, and habitat quality were 0.35, 0.35, and −0.39, respectively. This indicates that the total phosphorus output has weak synergy with both the water yield and soil erosion and a weak trade-off relationship with the habitat quality. The correlation coefficient between the water yield and soil erosion was 0.44, indicating moderate synergy, while the correlation coefficient with habitat quality was −0.47, indicating a moderate trade-off relationship. The correlation coefficient between soil erosion and habitat quality was −0.33, representing a weak trade-off relationship.
Through the above synergy and trade-off analysis, it is evident that the synergy and trade-off relationships among all six ecosystem services in the Danjiangkou Reservoir were weakened during the study period.
3.4. Analysis of the Correlation Between Land Use Change and Ecosystem Services
A partial correlation analysis was conducted on the land use classification results from 2012 and 2022, along with the six ecosystem services, to understand the relationship between land use change and ecosystem services during the study period in the Danjiangkou Reservoir (
Figure 8).
From
Figure 8, it can be seen that cropland and built-up land have a positive correlation with the total carbon storage, while forest, grassland, water, and unused land show a negative correlation. This indicates that areas with extensive forest coverage and good ecological protection tend to have lower total carbon storage, whereas regions with concentrated cropland and high levels of urbanization, which are more influenced by human activities, have relatively higher total carbon storage. The total nitrogen output is similar to the total phosphorus output, with forest land and grassland showing a positive correlation with both the total nitrogen and total phosphorus outputs, while cropland, built-up land, water bodies, and unused land exhibit a negative correlation. As the area of cropland increases, the outputs of total nitrogen and total phosphorus also increase, indicating that cropland is the primary land use type that reduces the water quality purification function. In contrast, forest land and grassland have stronger water quality purification functions, while water bodies, built-up land, and unused land have a weaker impact on water quality purification. The water yield shows a positive correlation with all six land use types, with built-up land having the strongest correlation, while the other land use types exhibit weaker correlations. An increase in the built-up land area reduces precipitation infiltration, leading to an increase in surface runoff, which leads to an increase in the water yield. However, this does not indicate that built-up land enhances the water yield ecological service in the region, as built-up land lacks the capacity for water source conservation. The three land use types—cropland, forest land, and grassland—intercept or absorb precipitation and surface water. Although the water yield decreases, they can enhance the watershed’s water conservation capacity. Water bodies and unused land have a relatively weak impact on the water yield. Soil erosion shows a negative correlation with cropland, unused land, built-up land, and water bodies, while it has a positive correlation with forest land and grassland. Built-up land and cropland are more affected by human activities, and their low vegetation coverage weakens the soil conservation capacity. Unused land has a relatively weak capacity for water and soil conservation, making it highly susceptible to water and soil loss due to heavy rainfall. Forests and grassland intercept precipitation and can help to consolidate the soil, thereby reducing the erosive effects of rainfall on the ground. Habitat quality is positively correlated with forest land, grassland, water bodies, and unused land, while it is negatively correlated with cropland and built-up land. Cropland and built-up land are more significantly impacted by human activities, leading to a decrease in habitat quality, whereas forest land, grassland, water bodies, and unused land are less affected by human activities, effectively enhancing the habitat quality in this region.
4. Discussion
The relationships of trade-offs and synergies among ecosystem services arise from the intricate interactions between environmental conditions and land use patterns [
29]. As a major water source region in China, the Danjiangkou Reservoir Basin is subject to stringent water and ecological protection policies, which have driven significant changes in land use types and intensities within the basin. Land use changes have consequently modified ecological processes and impacted the provision of ecosystem services. Land use changes and their effects on ecosystem services in the Danjiangkou Reservoir Basin from 2012 to 2022 were analyzed, with the objective of clarifying how land use changes influence the trade-offs and synergies among ecosystem services in significant water source regions.
Between 2012 and 2022, cultivated land was the primary land use type that was mostly transformed into construction, forest, and water body land. This change was consistent with the trend of changes in the evaluation results of ecosystem services. Driven by the expansion of forest land and water bodies, water yield, total carbon storage, and habitat quality increased, while agricultural activities decreased and vegetation coverage increased, leading to a reduction in total nitrogen output, total phosphorus output, and soil erosion. This verified that land use is a key driver of changes in ecosystem services [
30]. At the same time, the area of construction land increased, but the areas of forest land and water bodies also increased, while the area of cultivated land decreased. This led to a trade-off relationship between habitat quality and soil erosion and carbon sequestration, but a synergy relationship with water purification and water yield. Soil erosion is mainly related to vegetation such as forest land and grassland. During the study period, the area of forest land increased, while the area of grassland decreased, so grassland was the main land use type contributing to the increase in soil erosion in the study area. The proportion of different land use types in the region is the main factor affecting changes in water yield. Construction land has the strongest water yield capacity, followed by forest land and water bodies. The increase in construction land was relatively small, while the areas of forest land and water bodies increased significantly. Therefore, the increase in forest land and water bodies led to these being the main two land use types to contribute to the increase in regional water yield. In summary, forest land has the greatest impact on the ecosystem service functions of water source areas. Water source areas should ensure water supply while avoiding excessive development of construction land in the surrounding areas, and actively restore and protect forest land, grassland, and other ecological land to avoid disrupting the balance of regional ecosystem services and further enhance the region’s water purification, carbon sequestration, water yield, and habitat quality.
All six ecosystem services exhibited distinct temporal and spatial change patterns, with both trade-offs and synergies weakening over time, supporting the hypothesis that ecosystem service interactions are governed by non-linear dynamics. This suggests that land use changes influence these interactions by altering key ecological processes such as vegetation cover and the hydrological cycle. The findings align with several previous studies, while also highlighting the unique characteristics of the Danjiangkou Reservoir basin as a major water source region. The result of those reductions in cultivated land alongside increases in forestland and water bodies positively affected water supply and carbon storage, underscoring the significant role of land use changes in shaping ecosystem service provision, consistent with Costanza and Bennett’s research [
31,
32]. Overall, trade-offs and synergies are prevalent among ecosystem services and are strongly modulated by shifts in land use types. The negative correlation between construction land and habitat quality highlighted the destructive effect of urbanization on biodiversity [
33]. The finding that an increase in forest coverage enhances the synergy between carbon storage and water purification, while potentially weakening the trade-off with water supply, was similar to key findings in the Nansi Lake Basin ecosystem services research [
34], although previous studies have mentioned that land use changes may affect trade-offs and synergies [
35]. This study found that improvements in trade-offs exceeded declines in synergies. This difference may be attributed to the stricter ecological protection policies enforced in the Danjiangkou Reservoir area, given its importance as a major water source in China. A decrease in synergy after restoration in the Danjiangkou Reservoir area was contrary to a previous study that pointed out enhanced synergy following the ecological restoration [
36]. This outcome may reflect the dual nature of ecological restoration measures in the region, where conflicting objectives of protection and development result in the superposition of positive restoration effects and negative disturbances, thereby weakening the synergy among ecosystem services. Although the increase in forest area would be expected to strengthen the synergy between carbon storage and habitat quality, the expansion of the reservoir’s water area and the inundation of forestland diminished this synergistic effect. The expansion of water bodies in the Danjiangkou Reservoir area partially reduced carbon storage; however, this was inconsistent with previous findings that an increase in water area generally enhances carbon storage [
37]. This reflects the unique characteristics of the region, where reservoir expansion improves water resource regulation but offsets some of the carbon sequestration benefits achieved through afforestation.
This study analyzed the influence of land use changes in the Danjiangkou Reservoir area on the trade-offs and synergies of regional ecosystem services, relying on static land classification data from 2012 and 2022. Consequently, it may have overlooked interannual fluctuations, particularly the immediate effects of severe climatic occurrences such as droughts on ecosystem services. Furthermore, the analysis was conducted solely at the watershed scale of the water source area, without considering scale effects at the sub-watershed level, thereby masking spatial heterogeneity within sub-watersheds. Future research should undertake a systematic investigation of land use dynamics and ecosystem service trade-offs and synergies across multiple spatial scales to improve the effectiveness of ecological protection policies tailored to regional conditions.
5. Conclusions
This study employed the InVEST model to assess the spatiotemporal evolution of trade-offs and synergies among ecosystem services in the Danjiangkou Reservoir Basin over the period from 2012 to 2022. Five key ecosystem services were evaluated across six indicators: water yield, water quality purification, soil erosion, carbon storage, and habitat quality. The main conclusions are as follows:
Between 2012 and 2022, among the selected ecosystem services, water yield, total carbon storage, and habitat quality exhibited upward trends. This suggests that vegetation restoration enhanced the river’s interception and water storage functions, increased carbon storage, improved the carbon sequestration capacity of forestland, and stabilized species habitats. Conversely, total nitrogen output, total phosphorus output, and soil erosion showed downward trends. Despite these improvements, excessive use of chemical fertilizers remains a concern, necessitating further control through the promotion of precision fertilization technologies and the establishment of ecological buffer zones. Additionally, ecological protection efforts should address the potential hidden erosion risks associated with the excessive expansion of economic forests.
Throughout the study period, all ecosystem service synergy and trade-off relationships weakened, with improvements in trade-offs outweighing declines in synergies. Policies such as farmland-to-forest conversion, soil and water conservation, and non-point source pollution control have reduced conflicts between water yield and other ecological services—including soil erosion control and carbon storage—thereby enhancing ecosystem stability. These shifts indicate that future environmental management in water source areas should prioritize optimizing intrinsic ecosystem connections rather than relying on single-objective governance, to achieve more effective synergies and overall improvements.
Cultivated land was the primary land use type converted during the study, predominantly transitioning into forestland, water bodies, and construction land. Cultivated land, forestland, water bodies, and construction land constitute the four core land use types exerting the greatest influence on the trade-off and synergy dynamics of ecosystem services within the basin. Changes in their landscape patterns have significantly driven the intensity of ecosystem service interactions. Forestland and water bodies enhance positive correlations and synergies among ecosystem services through processes such as vegetation transpiration, soil infiltration, and water purification. Conversely, cultivated and construction lands are subject to disturbances such as agricultural non-point source pollution and impervious surface expansion, which relate to trade-off relationships among ecosystem services. Forestland exerts the strongest influence on ecosystem service functions in the water source area. Therefore, expanding the extent of water conservation forests in the region is recommended to increase water yield and carbon storage via vegetation restoration while continuing to suppress soil erosion.