How Does Trade Openness Drive New-Type Urbanization in Regions of China? The Moderating Role of Industrial Upgrading
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Background and Research Hypothesis
2.1. Theoretical Background
2.1.1. Trade Openness and New Type Urbanization
2.1.2. Industrial Structure Upgrading and New Type Urbanization
2.1.3. Relationship Among Trade Openness, Industrial Structure Upgrading, and New Type Urbanization
2.2. Critical Review and Research Gap
2.2.1. Critical Review
2.2.2. Research Gap
2.3. Research Hypotheses
3. Research Methodology
3.1. Sample and Data Sources
3.2. Modeling Design
3.3. Variable Definition and Description
- (1)
- Explained variable
- (2)
- Explanatory variable
- (3)
- Control variables
- (4)
- Moderator variable
3.4. Endogenous Test Model
3.5. Robustness Tests Model
3.5.1. Variable Substitution
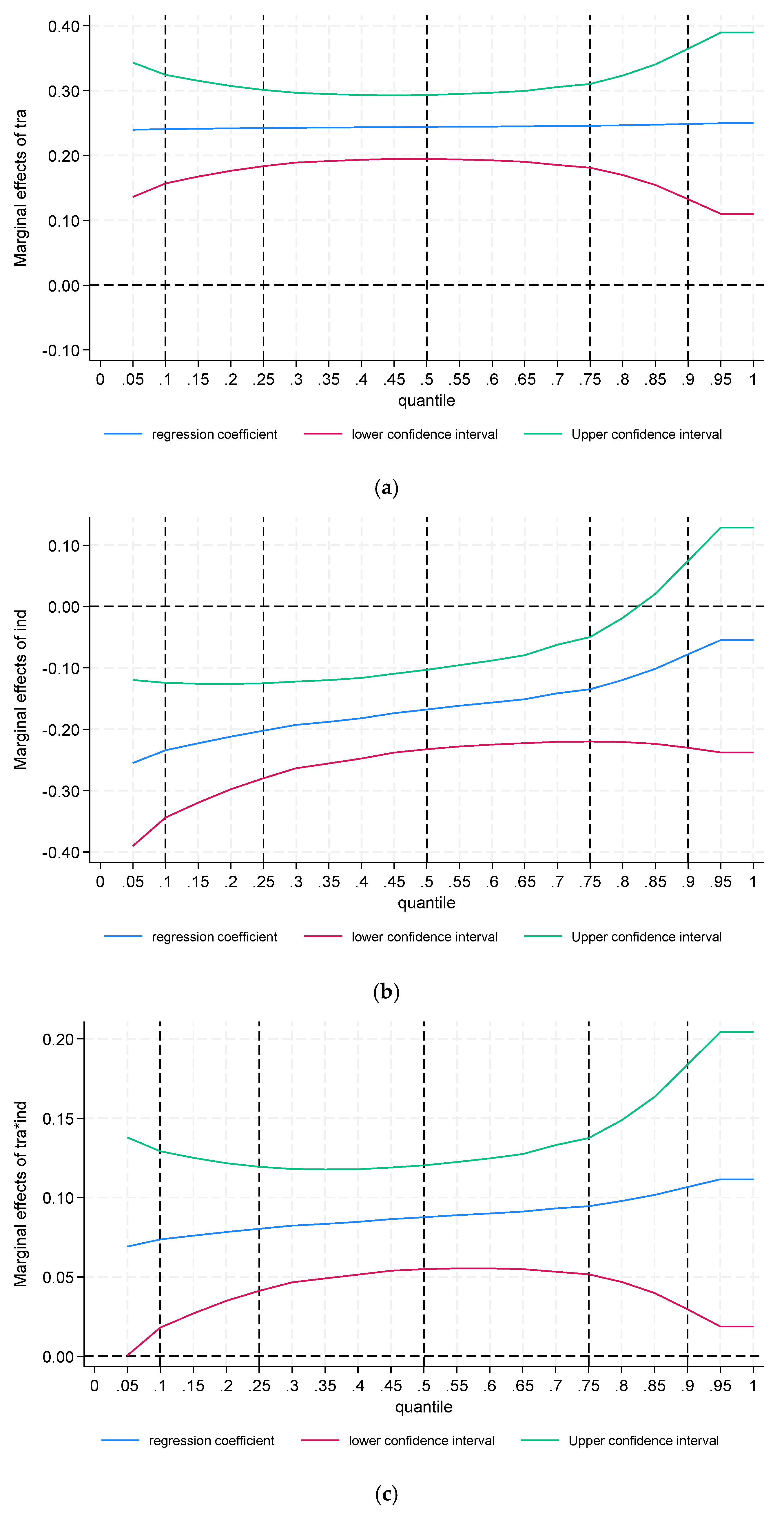
3.5.2. Quantile Regression
4. Results
4.1. Descriptive Statistics
4.2. Benchmark Regression and Mechanism Testing
4.3. Endogenous Test
4.4. Robustness Tests
- (1)
- Variable Substitution
- (2)
- Quantile Regression
- (3)
- Shorter Sample Intervals
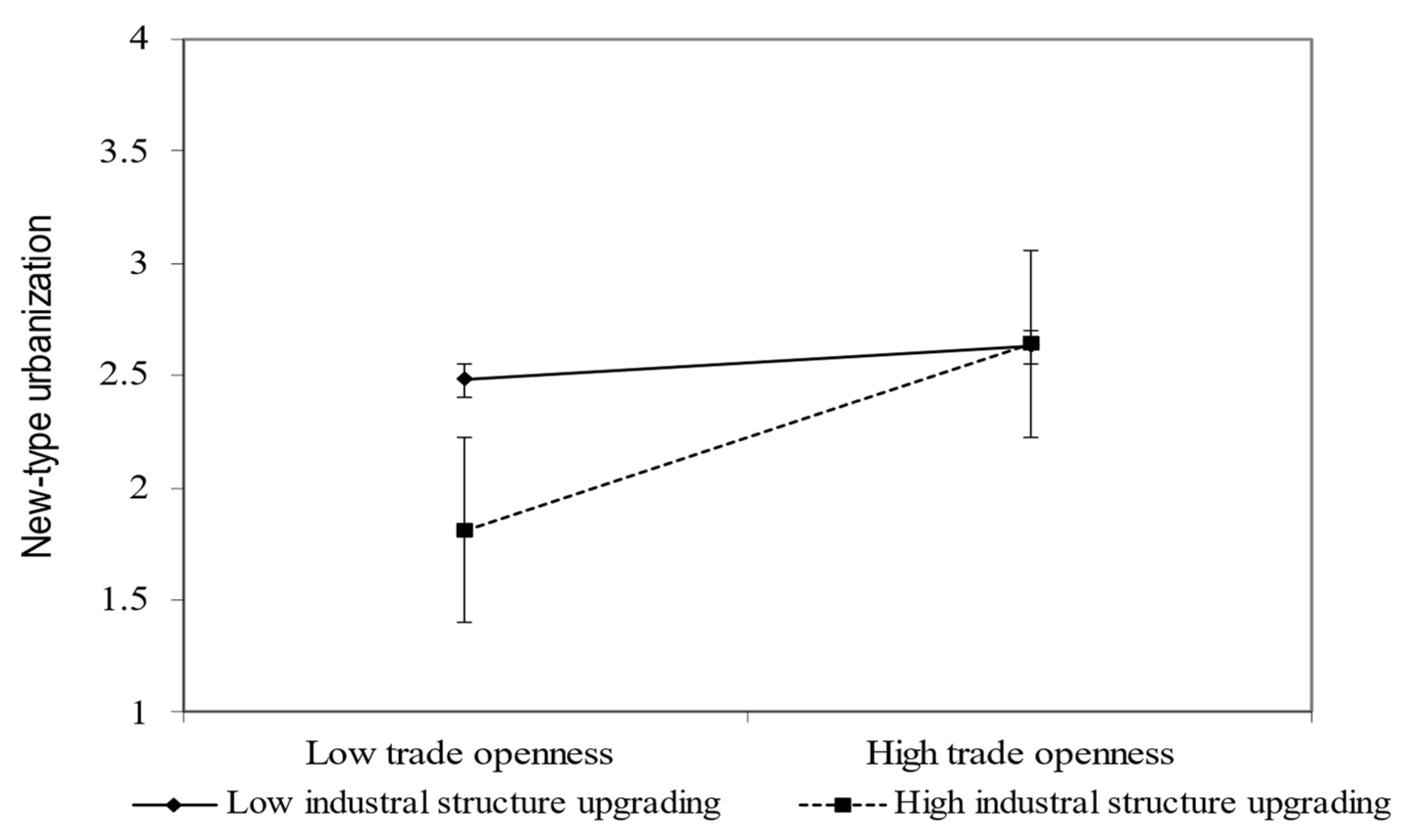
4.5. Analysis of Heterogeneity
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, X.; Genovese, P.V. Assessment on the Spatial Distribution Suitability of Ethnic Minority Villages in Fujian Province Based on Geo Detector and AHP Method. Land 2022, 11, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Tu, G.; Huang, X. The Impact of New Urbanization Policy on In Situ Urbanization—Policy Test Based on Difference-in-Differences Model. Land 2021, 10, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Wang, L. Revisiting China’s provincial energy efficiency and its influencing factors. Energy 2020, 208, 118361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tchitchoua, J.; Tsomb, E.I.B.T.; Madomo, J. Export diversification and income inequality in Central Africa: An analysis of the employment channel. J. Int. Trade Econ. Dev. 2023, 33, 618–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC). National New-Type Urbanization Plan (2014–2020); State Council of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Li, K.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, Y. Can Population Mobility Make Cities More Resilient? Evidence from the Analysis of Baidu Migration Big Data in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cai, Q. Impact Mechanism of New Urbanization on Environmental Pollution: Empirical Analysis Based on Spatial Panel Model. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 928100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Zhou, Y. The impact of high-tech product export trade on regional carbon performance in China: The mediating roles of industrial structure supererogation, low-carbon technological innovation, and human capital accumulation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 31148–31163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; He, C. Impact of Trade Openness on Urbanization: Evidence from China. Bachelor’s Thesis, Jönköping University, Jönköping, Sweden, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Petty, W. Political Arithmetick; Robert Clavel: London, UK, 1672. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, W.A. Economic development with unlimited supplies of labour. Manch. Sch. 1954, 28, 139–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todaro, M.P. Economic Development, 6th ed.; Longman: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Chenery, H.B.; Syrquin, M. Patterns of Development, 1950–1970; Oxford University Press: London, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Blyth, C.A.; Kuznets, S. Economic Growth of Nations: Total Output and Production Structure. Economica 1973, 40, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moir, H. Dynamic relationships between labor force structure, urbanization, and development. Econ. Dev. Cult. Chang. 1977, 26, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertinelli, L.; Strobl, E. Urbanisation, urban concentration and economic development. Urban Stud. 2007, 44, 2499–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.-L. Study on the Effect of Industrial Structure Advancement on Urban Productive Space. Diyu Yanjiu Yu Kaifa 2009, 28, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Chhabra, M.; Giri, A.K.; Kumar, A. The impact of trade openness on urbanization: Empirical evidence from BRICS economies. J. Public Aff. 2021, 22, e2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausmann, R.; Pritchett, L.; Rodrik, D. Growth Accelerations. J. Econ. Growth 2005, 10, 303–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Duan, Y. How Digitalization Shapes Export Product Quality: Evidence from China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krugman, P.R. Increasing returns, Monopolistic competition, and International Trade. J. Int. Econ. 1979, 9, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coe, D.T.; Helpman, E. International R&D spillovers. Eur. Econ. Rev. 1995, 39, 859–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wang, X.; Huang, Z.; Fan, B. Overcoming the middle-income trap: International experiences and China’s choice. China Econ. J. 2021, 14, 336–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, W. The driving factors behind coal demand in China from 1997 to 2012: An empirical study of input-output structural decomposition analysis. Energy Policy 2016, 95, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kugler, P. Growth, exports and cointegration: An empirical investigation. Rev. World Econ. 1991, 127, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenery, H.B.; Elkington, H. Structural Change and Development Policy; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Lei, H.; Zhao, S. The impact of FDI on industrial structure upgrading and carbon emission under the constraints of environmental regulation. Environ. Technol. 2023, 31, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Li, W.; Cao, S. Driving factors for coordinating urbanization with conservation of the ecological environment in China. AMBIO J. Human. Environ. 2021, 50, 1269–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Chen, S.; Zhang, B. Smart city construction and new-type urbanization quality improvement. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 21074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.; Tian, L.; Jia, R. New energy demonstration city, spatial spillover, and carbon emission efficiency: Evidence from China’s quasi-natural experiment. Energy Policy 2023, 173, 113389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Zhao, H. Spatial relocation of pollution-intensive industry and the mechanism in Yangtze River Delta. Geogr. Res. 2015, 34, 504–512. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, M.; Zhang, W. Industrial structure upgrading, urbanization and urban-rural income disparity: Evidence from China. Appl. Econ. Lett. 2020, 28, 1321–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Paudel, K.P. Economic openness, government efficiency, and urbanization. Rev. Dev. Econ. 2021, 25, 1351–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Cai, Z.; Ding, X.; Di, R.; Xiao, Q. What Factors Affect the Level of Green Urbanization in the Yellow River Basin in the Context of New-Type Urbanization? Sustainability 2020, 12, 2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeets, R. Collecting the Pieces of the FDI Knowledge Spillovers Puzzle. World Bank. Res. Obs. 2008, 23, 107–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitsch, V. Trade Openness and Urban Concentration: New Evidence. J. Econ. Integr. 2006, 21, 340–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wan, G. Exploring the Trade-Urbanization Nexus in Developing Economies: Evidence and Implications; Working Paper Series No. 636; Asian Development Bank Institute: Tokyo, Japan, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hyun, H.-J.; Hur, J. Trade Openness and Vertical Structure: Evidence From Korean Firm-Level Data. Open Econ. Rev. 2013, 25, 701–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, D. Trade and urbanization: Evidence from Hungary. Am. Econ. J. Microecon. 2022, 14, 733–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Chou, R.-J. Rural revitalization of Xiamei: The development experiences of integrating tea tourism with ancient village preservation. J. Rural. Stud. 2022, 90, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, F.; Li, J. Does new-type urbanization help reduce haze pollution damage? Evidence from China’s county-level panel data. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 47123–47136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhong, C.; Li, C. Research on the Impact of the Digital Economy on China’s New-Type Urbanization: Based on Spatial and Mediation Models. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, R.; Quigley, J.M.; Wilhelmsson, M. Urbanization, productivity, and innovation: Evidence from investment in higher education. J. Urban. Econ. 2009, 66, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, D. The political economy of urbanization in advanced capitalist societies: The case of the United States. In The Social Economy of Cities; Urban Affairs Annual: Beverley Hills, CA, USA, 1975; pp. 119–163. [Google Scholar]
- Demirgüç Kunt, A.; Levine, R. Bank Based and Market Based Financial Systems: Cross Country Comparisons; World Bank Policy Research Working Paper; No. WPS 2143; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 1999; pp. 1–41. [Google Scholar]
- Grossman, J. The evolution of Inhaler Technology. J. Asthma 1994, 31, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, B.; Zou, H.; Chen, S.; Huang, J. The effect of industrial structure adjustment on China’s energy intensity: Evidence from linear and nonlinear analysis. Energy 2021, 218, 119517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Wang, G.; Han, X. Artificial intelligence, industrial structure optimization, and CO2 emissions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 108757–108773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Jiang, Q.; Dong, X.; Dong, K.; Jiang, H. How does industrial structure adjustment reduce CO2 emissions? Spatial and mediation effects analysis for China. Energy Econ. 2022, 105, 105704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T. The Mechanism Analysis of Openness on Economic Fluctuations. Mod. Econ. Sci. 2020, 42, 13–24. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y. Trade Liberalization, Industry Scale and Regional Wage Gap. World Econ. Study 2012, 8, 28–36. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.; Wang, X.; Zhang, T. Does trade openness affect migrants’ marriage? Evidence from China. J. Int. Trade Econ. Dev. 2024, 34, 640–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busse, M.; Dary, S.K.; Wüstenfeld, J. Trade liberalization and manufacturing employment in developing countries. Struct. Chang. Econ. Dyn. 2024, 70, 410–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Sun, L.; Zou, L. State ownership and corporate performance: A quantile regression analysis of Chinese listed companies. China Econ. Rev. 2009, 20, 703–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Target Level | Normative Layer | Indicator Layer | Property |
|---|---|---|---|
| New Urbanization Level | Population Urbanization | Proportion of urban population (%) | Positive |
| Urban population density (persons/km2) | Positive | ||
| Share of secondary and tertiary employment (%) | Positive | ||
| Economic Urbanization | Per capita gross regional product | Positive | |
| Wages of employed persons in urban units (CNY) | Positive | ||
| Gross regional product growth rate (%) | Positive | ||
| Social Urbanization | Health technicians per 1000 population | Positive | |
| Per capita expenditure on education (CNY) | Positive | ||
| Roads per capita (square meters) | Positive | ||
| Ecological Urbanization | Per capita green space in parks (square meters) | Positive | |
| Rate of non-hazardous treatment of domestic waste (%) | Positive | ||
| Greening coverage in built-up areas (%) | Positive |
| Variable | Targets | Abbreviation | Clarification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Explained Variable | Degree of new urbanization | urb | See Table 1 |
| Explanatory Variable | Trade dependence | tra | Ratio of total import and export volume to gross regional product |
| Moderator Variable | Upgrading of industrial structure | ind | Consists of the advanced industrial structure and the rationalization of the industrial structure |
| Control Variables | Level of financialization | fin | Value added of the financial sector as a percentage of gross regional product |
| Human capital | hum | Number of university students per 10,000 urban residents | |
| Science and technology innovation | tech | Financial investment in science and technology as a share of gross regional product | |
| Fixed asset investment level | fal | Ratio of urban fixed asset investment to gross regional product |
| Variable | N | Mean | Sd | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tra | 465 | 4229 | 4639 | 110.6 | 22,999 |
| urb | 465 | 0.445 | 0.0946 | 0.246 | 0.745 |
| ind | 465 | 0.268 | 0.129 | 0.133 | 0.988 |
| fin | 465 | 0.0677 | 0.0314 | 0.0188 | 0.196 |
| tech | 465 | 59,698 | 105,683 | 93 | 872,209 |
| hum | 465 | 87.08 | 56.58 | 2.940 | 282.3 |
| fal | 465 | 12.20 | 11.56 | −56.60 | 41.30 |
| Baseline Model | Controlled Model | Moderation Model | Interaction Model | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| urb | urb | urb | urb | |
| tra | 0.426 *** | 0.238 *** | 0.236 *** | 0.244 *** |
| (25.33) | (8.35) | (8.29) | (8.96) | |
| ind | −0.046 | −0.164 *** | ||
| (−1.91) | (−5.57) | |||
| tra × ind | 0.170 *** | |||
| (6.49) | ||||
| hum | 0.028 | 0.027 | −0.022 | |
| (1.18) | (1.13) | (−0.91) | ||
| fin | 0.238 *** | 0.277 *** | 0.216 *** | |
| (7.58) | (7.42) | (5.85) | ||
| tech | 0.082 *** | 0.078 *** | 0.103 *** | |
| (3.64) | (3.49) | (4.70) | ||
| fal | 0.037 | 0.040 | 0.037 | |
| (1.64) | (1.78) | (1.71) | ||
| β0 | −1.473 *** | −1.237 *** | −1.230 *** | −1.320 *** |
| (−22.86) | (−17.16) | (−17.09) | (−18.80) | |
| N | 465.000 | 465.000 | 465.000 | 465.000 |
| R-squared |
| First Model | Second Model | |
|---|---|---|
| Variables | (urb) | (urb) |
| iv | 0.2839 *** | |
| (11.9139) | ||
| tra | 0.2230 *** | |
| (3.9284) | ||
| hum | 0.3570 *** | 0.0326 |
| (11.1799) | (1.1758) | |
| fal | −0.1380 *** | 0.0353 |
| (−4.2564) | (1.5376) | |
| fin | 0.7597 *** | 0.2508 *** |
| (25.3992) | (4.8336) | |
| tech | 0.1342 *** | 0.0846 *** |
| (4.2127) | (3.5714) | |
| β0 | 1.1153 *** | −1.2188 *** |
| (12.0553) | (−13.3476) | |
| Observations | 465 | 465 |
| R-squared | 0.780 | 0.895 |
| Moderation Model | Interaction Model | |
|---|---|---|
| urb | urb | |
| open | 0.298 *** | 0.252 *** |
| (9.34) | (7.68) | |
| ind | −0.137 *** | −0.231 *** |
| (−5.40) | (−7.16) | |
| open × ind | 0.137 *** | |
| (4.55) | ||
| hum | −0.003 | −0.024 |
| (−0.13) | (−1.02) | |
| fal | 0.045 * | 0.040 |
| (2.04) | (1.82) | |
| fin | 0.255 *** | 0.257 *** |
| (6.99) | (7.17) | |
| tech | 0.123 *** | 0.140 *** |
| (5.73) | (6.53) | |
| β0 | −1.273 *** | −1.295 *** |
| (−17.83) | (−18.49) | |
| N | 465.000 | 465.000 |
| R-squared |
| Q10 | Q25 | Q50 | Q75 | Q90 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tra | 0.269 *** | 0.254 *** | 0.268 *** | 0.384 *** | 0.395 *** |
| (5.98) | (9.15) | (8.67) | (8.19) | (6.53) | |
| ind | −0.519 *** | −0.425 *** | −0.212 *** | −0.172 *** | −0.195 ** |
| (−10.68) | (−14.15) | (−6.35) | (−3.40) | (−2.99) | |
| tra × ind | 0.259 *** | 0.279 *** | 0.198 *** | 0.248 *** | 0.383 *** |
| (6.01) | (10.47) | (6.68) | (5.51) | (6.60) | |
| hum | 0.038 | −0.015 | −0.050 | −0.070 | −0.083 |
| (0.98) | (−0.61) | (−1.87) | (−1.72) | (−1.59) | |
| fin | 0.334 *** | 0.261 *** | 0.192 *** | 0.092 | 0.032 |
| (5.50) | (6.96) | (4.58) | (1.45) | (0.40) | |
| tech | 0.051 | 0.080 *** | 0.122 *** | 0.111 ** | 0.099 * |
| (1.42) | (3.58) | (4.94) | (2.95) | (2.04) | |
| fal | 0.080 * | 0.051 * | 0.026 | 0.000 | −0.051 |
| (2.25) | (2.30) | (1.07) | (0.01) | (−1.06) | |
| β0 | −1.706 *** | −1.582 *** | −1.397 *** | −1.314 *** | −0.921 *** |
| (−14.75) | (−22.13) | (−17.53) | (−10.88) | (−5.92) | |
| N | 465.000 | 465.000 | 465.000 | 465.000 | 465.000 |
| R-squared |
| Eastern | Central | Western | |
|---|---|---|---|
| urb | urb | urb | |
| tra | 0.104 ** | 0.009 | 0.067 |
| (3.21) | (0.08) | (0.64) | |
| ind | 0.014 | −0.630 *** | −0.944 *** |
| (0.79) | (−9.14) | (−9.92) | |
| tra × ind | 0.011 ** | 0.001 | 0.013 |
| (3.11) | (0.19) | (1.20) | |
| hum | 0.133 *** | −0.130 *** | −0.083 |
| (4.91) | (−3.81) | (−1.30) | |
| fal | 0.068 * | 0.053 * | −0.074 * |
| (2.26) | (2.18) | (−2.56) | |
| fin | 0.403 *** | −0.090 | 0.038 |
| (11.17) | (−1.06) | (0.63) | |
| tech | 0.020 | 0.471 *** | 0.013 |
| (0.92) | (5.18) | (0.06) | |
| β0 | −1.016 *** | −1.883 *** | −2.059 *** |
| (−9.89) | (−18.86) | (−17.65) | |
| N | 121.000 | 120.000 | 166.000 |
| R-squared |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Hu, C.; Wu, Y. How Does Trade Openness Drive New-Type Urbanization in Regions of China? The Moderating Role of Industrial Upgrading. Sustainability 2025, 17, 7454. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167454
Liu J, Hu C, Wu Y. How Does Trade Openness Drive New-Type Urbanization in Regions of China? The Moderating Role of Industrial Upgrading. Sustainability. 2025; 17(16):7454. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167454
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jiatong, Cong Hu, and Yan Wu. 2025. "How Does Trade Openness Drive New-Type Urbanization in Regions of China? The Moderating Role of Industrial Upgrading" Sustainability 17, no. 16: 7454. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167454
APA StyleLiu, J., Hu, C., & Wu, Y. (2025). How Does Trade Openness Drive New-Type Urbanization in Regions of China? The Moderating Role of Industrial Upgrading. Sustainability, 17(16), 7454. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167454





