Global Sustainability Performance and Regional Disparities: A Machine Learning Approach Based on the 2025 SDG Index
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Data and Methodology
3.1. Data Source
- SDG Index Score: Overall national score reflecting progress towards the 17 SDGs.
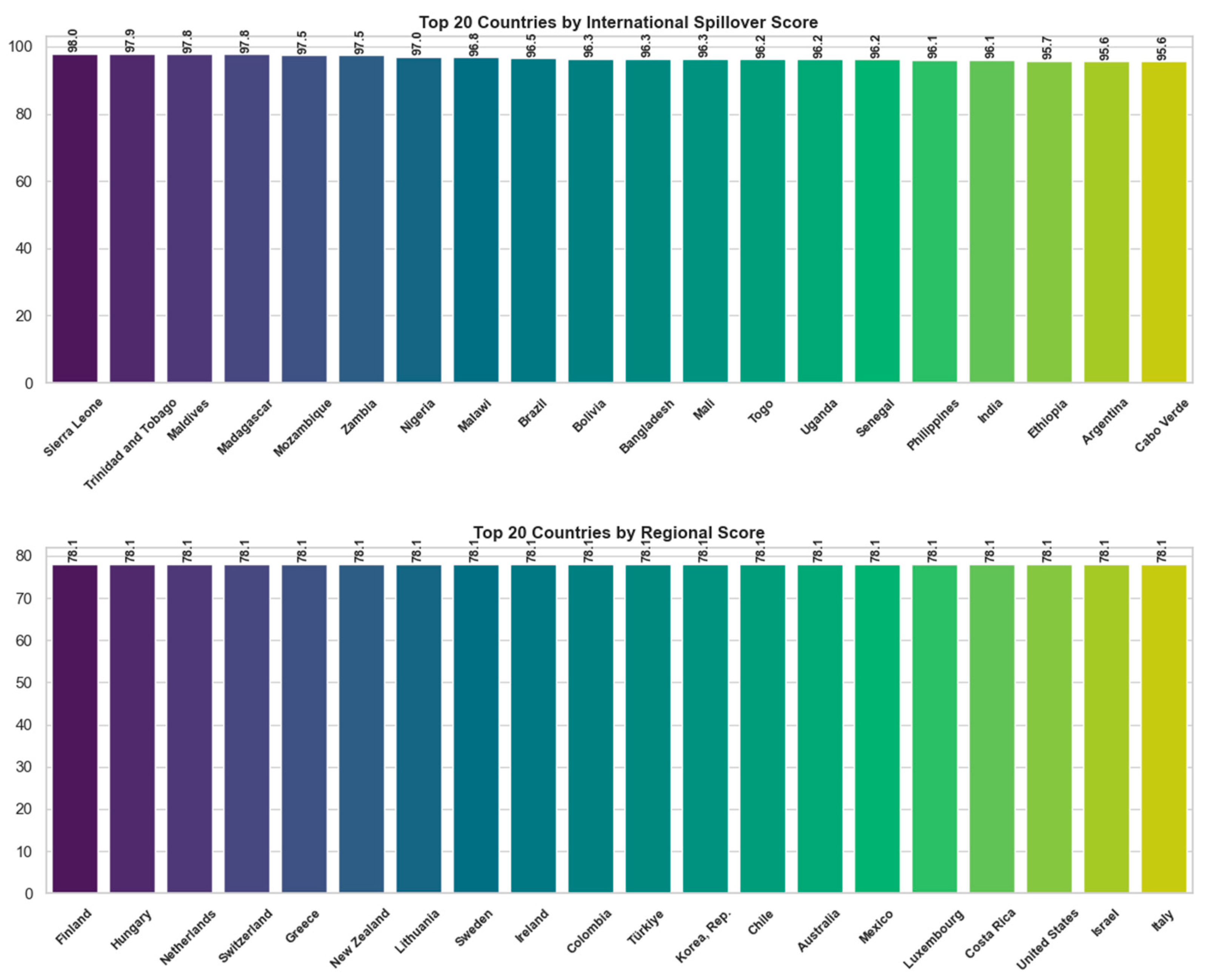
- International Spillovers Score (0–100): Degree to which a country’s actions influence sustainability in other countries.
- Regional Score (0–100): Average sustainability performance of a country’s assigned macro-region.
- Region: Geopolitical macro-region category.
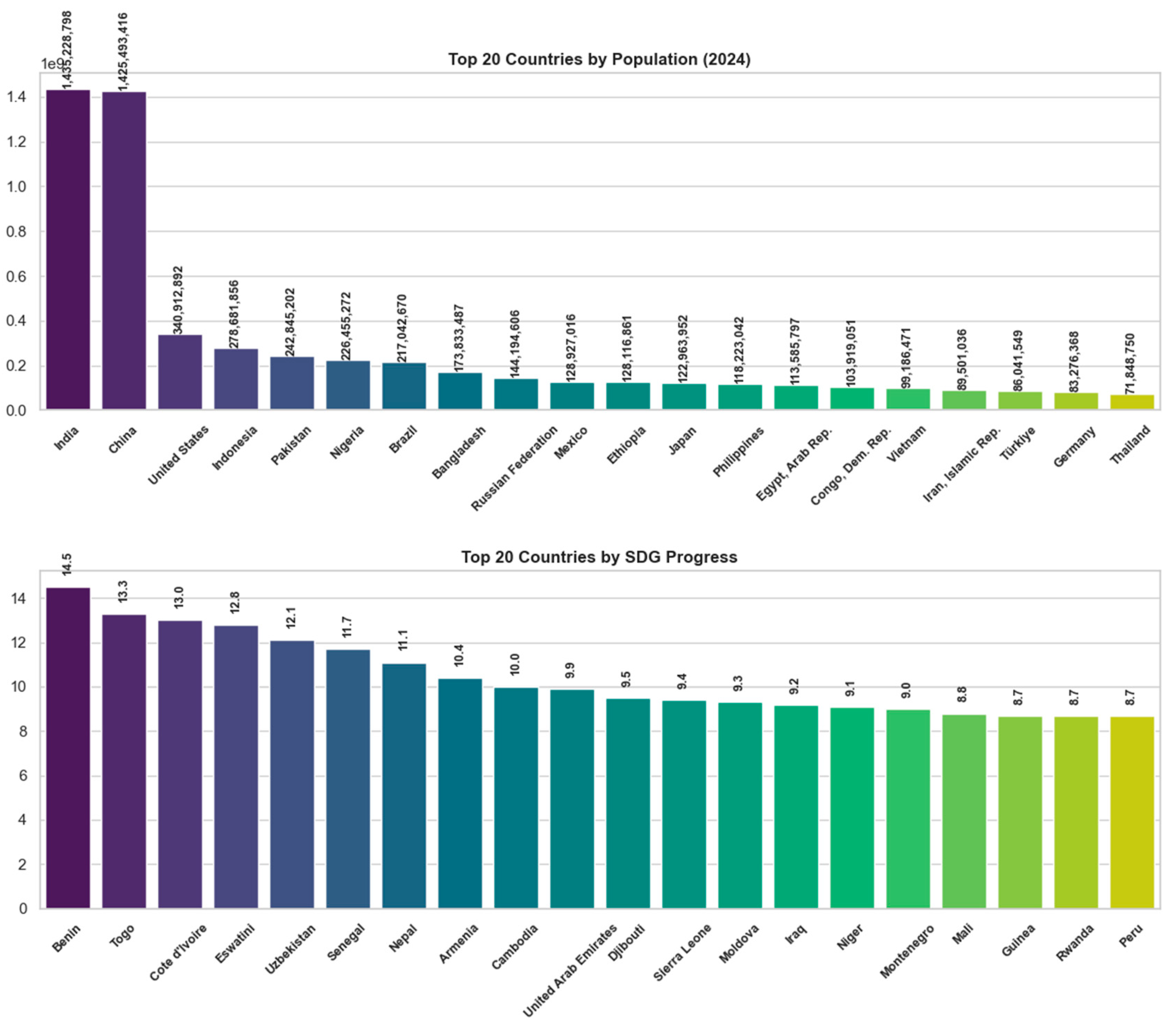
- Population (2024): Population size, included to account for the influence of population size.
- Progress on Headline SDG Indicators (% points): Recent rate of national SDG indicator score change.
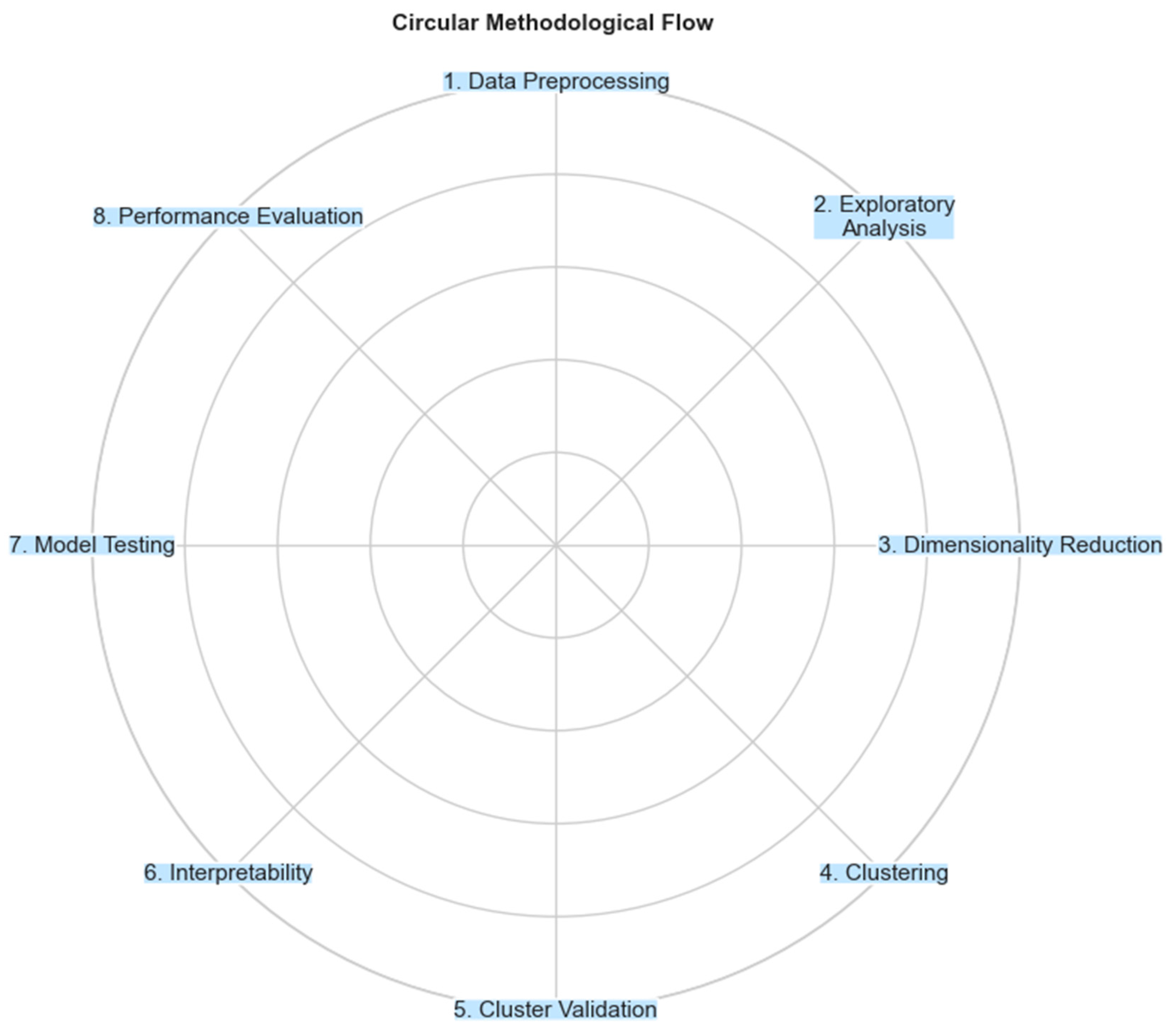
3.2. Methodological Framework
3.2.1. Preprocessing
3.2.2. Exploratory Analysis
3.2.3. Dimensionality Reduction
3.2.4. Clustering
3.2.5. Cluster Validation
3.2.6. Interpretability
3.2.7. Model Testing
3.2.8. Predictive Performance Evaluation
4. Empirical Results and Findings
4.1. Exploratory Analysis
4.2. Clustering Analysis
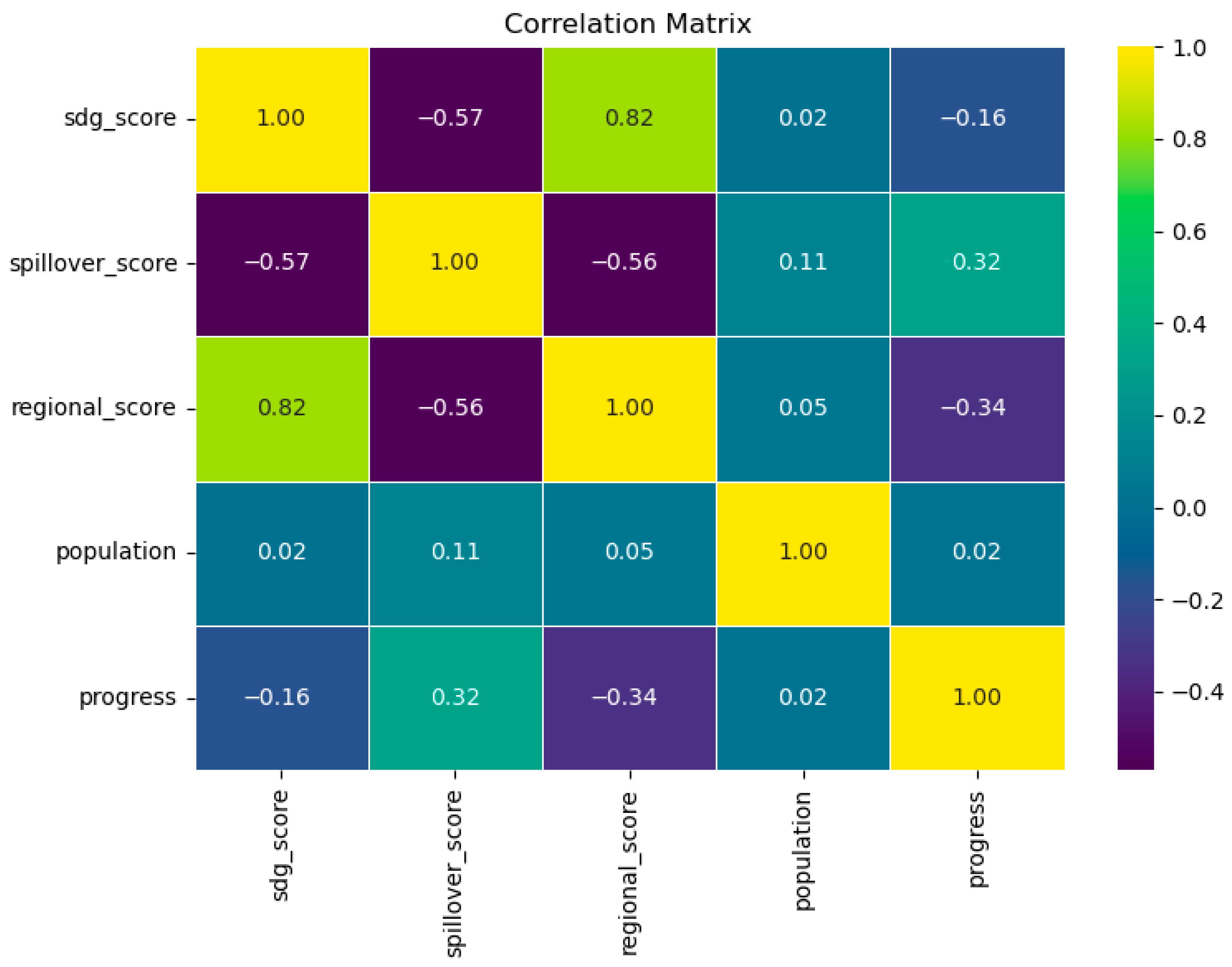
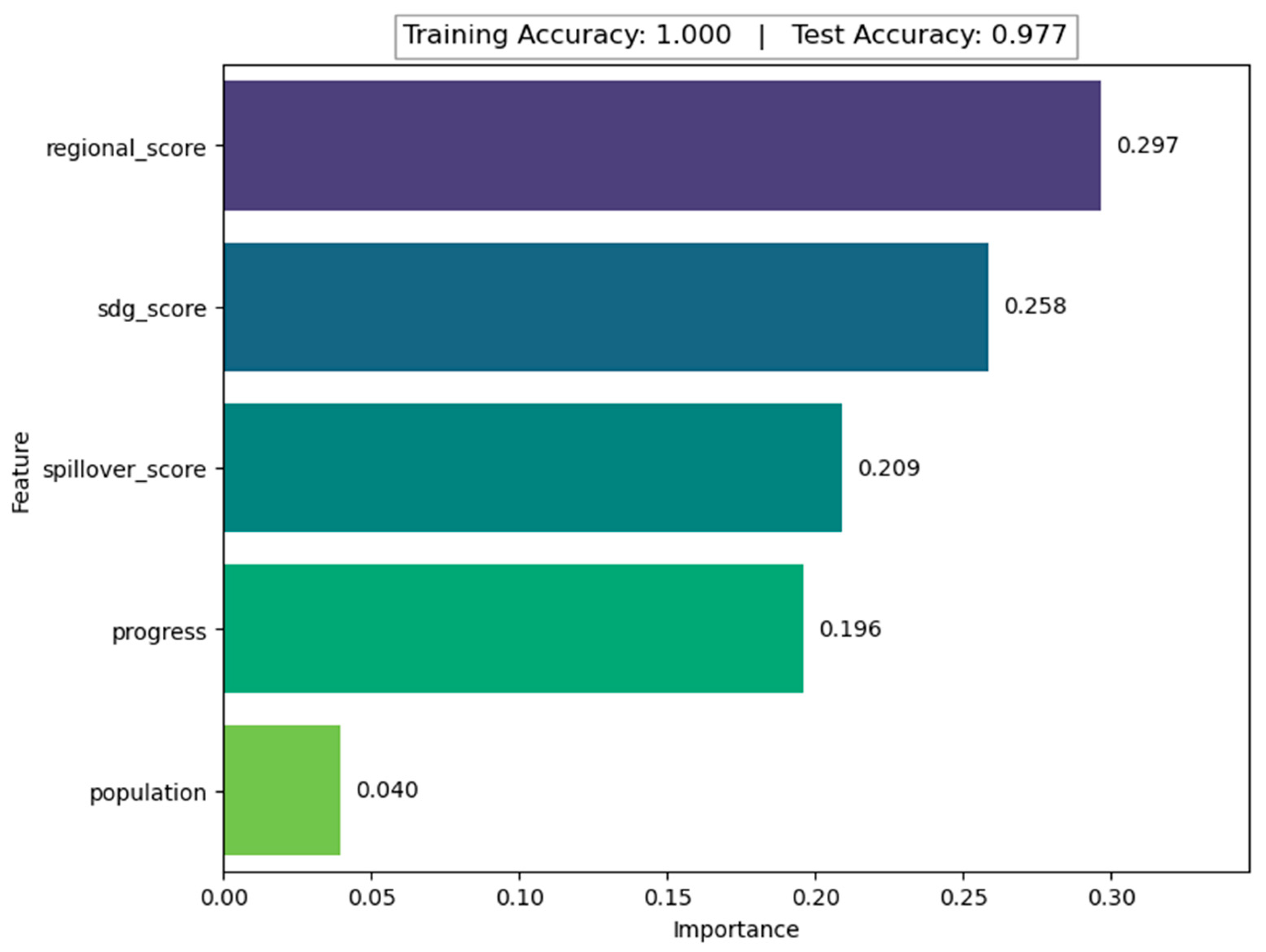
- PC1 is heavily influenced by sdg_score and regional_score, and negatively by spillover_score, indicating a general sustainability gradient.
- PC2 is almost entirely driven by the population variable, distinguishing countries by size.
- PC3 strongly reflects the progress metric, capturing recent sustainability dynamics.
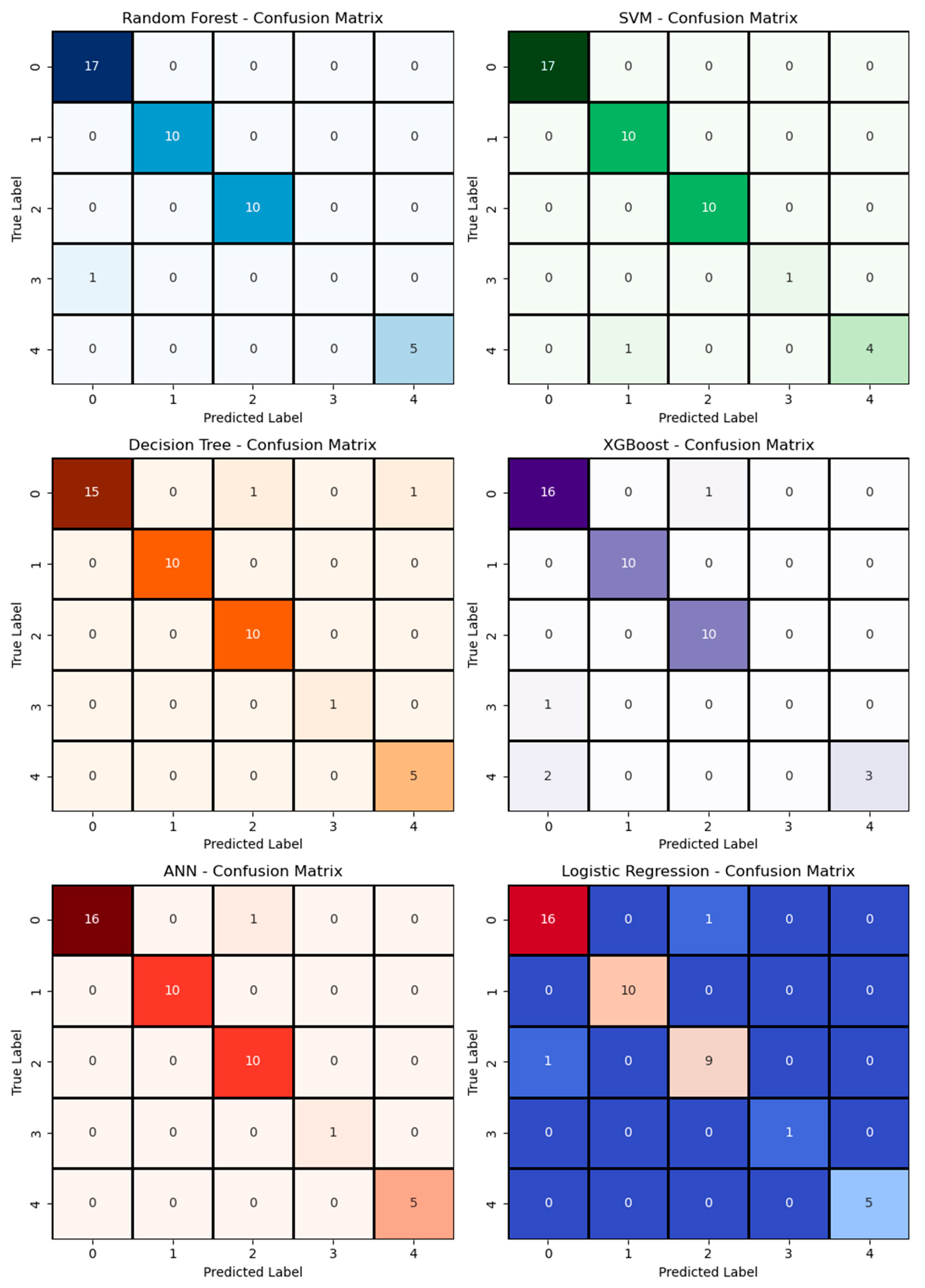
4.3. Validating the Accuracy of Clusters with Machine Learning Algorithms
4.4. Visualization and Model Performance Assessment with ROC Curves
5. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Assembly, G. Resolution Adopted by the General Assembly on 1 September 2015. Available online: https://docs.un.org/en/A/RES/70/1 (accessed on 3 July 2025).
- Sachs, J.D.; Kroll, C.; Lafortune, G.; Fuller, G.; Woelm, F. Sustainable Development Report 2022; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Sasmaz, M.U.; Sakar, E.; Yayla, Y.E.; Akkucuk, U. The Relationship between Renewable Energy and Human Development in OECD Countries: A Panel Data Analysis. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Vaio, A.; Palladino, R.; Hassan, R.; Escobar, O. Artificial Intelligence and Business Models in the Sustainable Development Goals Perspective: A Systematic Literature Review. J. Bus. Res. 2020, 121, 283–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audretsch, D.B.; Belitski, M.; Caiazza, R.; Desai, S. The Role of Institutions in Latent and Emergent Entrepreneurship. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2022, 174, 121263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, U.; Sroufe, R.; Bozan, K. Designing Value Chains for Industry 4.0 and a Circular Economy: A Review of the Literature. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wen, X. Sustainability Assessment of Cities Using Multicriteria Decision-Making Combined with Deep Learning Methods. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 111, 105571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Sarachaga, J.M.; Jato-Espino, D.; Castro-Fresno, D. Is the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) Index an Adequate Framework to Measure the Progress of the 2030 Agenda? Sustain. Dev. 2018, 26, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwitondi, K.S.; Munyakazi, I.; Gatsheni, B.N. A Robust Machine Learning Approach to SDG Data Segmentation. J. Big Data 2020, 7, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Neve, J.-E.; Sachs, J.D. The SDGs and Human Well-Being: A Global Analysis of Synergies, Trade-Offs, and Regional Differences. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellantuono, L.; Monaco, A.; Tangaro, S.; Amoroso, N.; Aquaro, V.; Bellotti, R. An Equity-Oriented Rethink of Global Rankings with Complex Networks Mapping Development. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciarra, C.; Chiarotti, G.; Ridolfi, L.; Laio, F. A Network Approach to Rank Countries Chasing Sustainable Development. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keys, P.W.; Barnes, E.A.; Carter, N.H. A Machine-Learning Approach to Human Footprint Index Estimation with Applications to Sustainable Development. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 044061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, G.; Santos, J.; SantClair, G.; Gomide, J.; Santos, L. A Comparative Analysis of Countries’ Performance According to SDG Indicators Based on Machine Learning. In Anais do XVIII Encontro Nacional de Inteligência Artificial e Computacional (ENIAC 2021); Sociedade Brasileira de Computação: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2021; pp. 141–152. [Google Scholar]
- García Villena, E.; Pascual Barrera, A.; Álvarez, R.M.; Dzul López, L.A.; Tutusaus Pifarré, K.; Vidal Mazón, J.L.; Miró Vera, Y.A.; Brie, S.; López Flores, M.A. Evaluation of the Sustainable Development Goals in the Diagnosis and Prediction of the Sustainability of Projects Aimed at Local Communities in Latin America and the Caribbean. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 11188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadikia, A.; Rajabifard, A.; Kalantari, M. Region-Income-Based Prioritisation of Sustainable Development Goals by Gradient Boosting Machine. Sustain. Sci. 2022, 17, 1939–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayanand, D. From Data to Impact: Machine Learning Models for Sustainable Development Region Classification- Accelerating the Achievement of Sustainable Development Goals through Predictive Analytics. Int. J. Multidiscip. Res. 2023, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, M.W.L.; Clark, J.N.; Small, E.A.; Mayoral, E.F.; Santos-Rodríguez, R. Monitoring Sustainable Global Development Along Shared Socioeconomic Pathways. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.04416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Abdelnour, Y.S.K.; Cardoso, I.M.C.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.T.; Oh, J.H. Assessing Regional Disparities in Human Development and Multidimensional Poverty: A Satellite Imagery and Machine Learning Approach. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (BigData), Sorrento, Italy, 15 December 2023; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 6113–6115. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, T.; Li, J. Environmental Sustainability Performance Assessment in Relation to Visibility in African Regions with Interpretable Machine Learning. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 428, 139414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, R.; Arora, K.; Bagga, N.; Aggarwal, M. A Review of Machine Learning for Sustainable Development Goals. In 2024 7th International Conference on Contemporary Computing and Informatics (IC3I); IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 50–54. [Google Scholar]
- Castelli, T.; Mocenni, C.; Dimitri, G.M. A Machine Learning Approach to Assess Sustainable Development Goals Food Performances: The Italian Case. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0296465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenary, K.; Pirian Kalat, O.; Sharifi, A. Forecasting Sustainable Development Goals Scores by 2030 Using Machine Learning Models. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 32, 6520–6538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Du, J.; Wang, Y.; Cui, X.; Dong, J.; Gu, P.; Hao, Y.; Xue, K.; Duan, H.; Xia, A.; et al. Overlooked Uneven Progress across Sustainable Development Goals at the Global Scale: Challenges and Opportunities. Innovation 2024, 5, 100573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Skene, K.R.; Wang, S.; Ji, Q.; Zheng, H.; Zhou, C.; Tian, K.; Pradhan, P.; Meadows, M.E.; Fu, B. Beyond Borders: Assessing Global Sustainability through Interconnected Systems. Sustain. Dev. 2025, 33, 1909–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Rodríguez, A.; Núñez, M.; Pérez, M.R.; Govezensky, T.; Barrio, R.A.; Gershenson, C.; Kaski, K.K.; Tagüeña, J. Sustainable Visions: Unsupervised Machine Learning Insights on Global Development Goals. PloS ONE 2025, 20, e0317412. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, F.; Wang, H.; Tzachor, A.; Hidalgo, C.A.; Schandl, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, W.-Q.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, Y.-G.; et al. The Disparities and Development Trajectories of Nations in Achieving the Sustainable Development Goals. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, S.; Basel, S. Classifying Global Economies Based on Sustainable Development Goals: A Data-Driven Clustering Approach. Sustain. Dev. 2025, 33, 4543–4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; He, B.; Fujita, T. Does Environmental Regulation Affect Inward Foreign Direct Investment? Evidence from China. Appl. Econ. Lett. 2024, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, N.; Hussein, S. Data Dimensional Reduction and Principal Components Analysis. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2019, 163, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gewers, F.L.; Ferreira, G.R.; De Arruda, H.F.; Silva, F.N.; Comin, C.H.; Amancio, D.R.; Costa, L.D.F. Principal Component Analysis. ACM Comput. Surv. 2022, 54, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih Hasan, B.M.; Abdulazeez, A.M. A Review of Principal Component Analysis Algorithm for Dimensionality Reduction. J. Soft Comput. Data Min. 2021, 2, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishwaran, H. Multivariate Statistics; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2025; ISBN 9781003493679. [Google Scholar]
- France, S.L.; Akkucuk, U. A Review, Framework, and R Toolkit for Exploring, Evaluating, and Comparing Visualization Methods. Vis. Comput. 2021, 37, 457–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacQueen, J. Some Methods for Classification and Analysis of Multivariate Observations. In Berkeley Symposium on Mathematical Statistics and Probability, Proceedings of the 5th Berkeley Symposium on Mathematical Statistics and Probability, Berkely, CA, USA, 21 June–18 July 1965; Project Eucid: Durham, CA, USA, 1967; Volume 1, pp. 281–297. [Google Scholar]
- Rusdiana, L.; Hardita, V.C. Algoritma K-Means Dalam Pengelompokan Surat Keluar Pada Program Studi Teknik Informatika STMIK Palangkaraya. J. Saintekom 2023, 13, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paratama, M.A.Y.; Hidayah, A.R.; Avini, T. Clusterıng K-Means Untuk Analısıs Pola Persebaran Bencana Alam Dı Indonesıa. J. Inform. Dan Tekonologi Komput. (JITEK) 2023, 3, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, S. Least Squares Quantization in PCM. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1982, 28, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.S.; Kumar, N.; Aswathy, J.; Vaddadi, S.K.; Akbar, S.A.; Panchariya, P.C. K-Means Algorithm: An Unsupervised Clustering Approach Using Various Similarity/Dissimilarity Measures. In Intelligent Sustainable Systems: Proceedings of ICISS 2021; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 805–813. [Google Scholar]
- Çelik, S.; Cömertler, N. Investigation of Happiness of Countries with K-Means Clustering and Discriminant Analysis. J. Curr. Res. Bus. Econ. 2021, 11, 15–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tan, H. K-Means Algorithm Based on Initial Cluster Center Optimization. In The International Conference on Cyber Security Intelligence and Analytics; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 310–316. [Google Scholar]
- Gruzdeva, T.V.; Ushakov, A.V. K-Means Clustering via a Nonconvex Optimization Approach. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Mathematical Optimization Theory and Operations Research, Irkutsk, Russia, 5–10 July 2021; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 462–476. [Google Scholar]
- Sagala, N.T.M.; Gunawan, A.A.S. Discovering the Optimal Number of Crime Cluster Using Elbow, Silhouette, Gap Statistics, and NbClust Methods. ComTech Comput. Math. Eng. Appl. 2022, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wala, J.; Herman, H.; Umar, R.; Suwanti, S. Heart Disease Clustering Modeling Using a Combination of the K-Means Clustering Algorithm and the Elbow Method. Sci. J. Inform. 2024, 11, 903–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseeuw, P.J. Silhouettes: A Graphical Aid to the Interpretation and Validation of Cluster Analysis. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 1987, 20, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelik, S.; Doğanlı, B.; Şaşmaz, M.Ü.; Akkucuk, U. Accuracy Comparison of Machine Learning Algorithms on World Happiness Index Data. Mathematics 2025, 13, 1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somarribas, J.; Loteanu, A. Using Micro-Processor Vector Instructions to Optimize Unsupervised Machine Learning K-Means Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 11th Latin American Symposium on Circuits & Systems (LASCAS), San Jose, Costa Rica, 25–28 February 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Maori, N.A.; Evanita, E. Metode Elbow Dalam Optimasi Jumlah Cluster Pada K-Means Clustering. Simetris J. Tek. Mesin Elektro Ilmu Komput. 2023, 14, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maulana, I.; Roestam, R. Optimizing KNN Algorithm Using Elbow Method for Predicting Voter Participation Using Fixed Voter List Data (DPT). J. Sos. Teknol. 2024, 4, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicaksono, A.P.; Widjaja, S.; Nugroho, M.F.; Putri, C.P. Elbow and Silhouette Methods for K Value Analysis of Ticket Sales Grouping on K-Means. Sistemasi 2024, 13, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Düntsch, I.; Gediga, G. Confusion Matrices and Rough Set Data Analysis. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1229, 012055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighi, S.; Jasemi, M.; Hessabi, S.; Zolanvari, A. PyCM: Multiclass Confusion Matrix Library in Python. J. Open Source Softw. 2018, 3, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Михайличенкo, А.А. Analytical Review of Methods for Assessing the Quality of Classification Algorithms. Вестник Адыгейскoгo Гoсударственнoгo Университета Серия «Естественнo-Математические и Технические Науки» 2023, 4, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbani, J.; Portier, P.-É.; Egyed-Zsigmond, E.; Nurbakova, D. Confusion Matrices: A Unified Theory. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 181372–181419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimvall, G. Accuracy of models. Sci Model Simul 2008, 15, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airbus Can Synthetic Data Really Improve Algorithm Accuracy? Available online: https://www.intelligence-airbusds.com/newsroom/news/can-synthetic-data-really-improve-algorithm-accuracy/ (accessed on 12 April 2022).
- Maindola, M.; Al-Fatlawy, R.R.; Kumar, R.; Boob, N.S.; Sreeja, S.P.; Sirisha, N.; Srivastava, A. Utilizing Random Forests for High-Accuracy Classification in Medical Diagnostics. In 2024 7th International Conference on Contemporary Computing and Informatics (IC3I); IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 1679–1685. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, W. Large-Scale Remote Sensing Image Target Recognition and Automatic Annotation. In Proceedings of the 2025 6th International Conference on Geology, Mapping and Remote Sensing (ICGMRS), Wuhan, Hubei, 25–27 April 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Bosch, N.; Paquette, L. Metrics for Discrete Student Models: Chance Levels, Comparisons, and Use Cases. J. Learn. Anal. 2018, 5, 86–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.; Lee, K. The Internet of Things (IoT): Applications, Investments, and Challenges for Enterprises. Bus. Horiz. 2015, 58, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, E.; Júnior, M.V.B.; Lobo Ferreira, W.L. A Importância De Utilizar Métricas Adequadas De Avaliação De Performance Em Modelos Preditivos De Machine Learning. Projectus 2023, 7, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, G.S.; Dass, S.; Prakash, F. The Synergy of Advanced Language Models, Sequential Skeleton Features, and GAN-Enhanced Data Augmentation for Unprecedented Precision. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on System, Computation, Automation and Networking (ICSCAN), Puducherry, India, 17–18 November 2023; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, L.; Mansour, Y.; Moran, S.; Shao, H. Probably Approximately Precision and Recall Learning. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2411.13029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J. Analysis of Precision and Accuracy in a Simple Model of Machine Learning. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2017, 71, 866–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yacouby, R.; Axman, D. Probabilistic Extension of Precision, Recall, and F1 Score for More Thorough Evaluation of Classification Models. In Proceedings of the First Workshop on Evaluation and Comparison of NLP Systems, Online; Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 16 March 2020; pp. 79–91. [Google Scholar]
- Midha, M.; Jain, A.K.; Sharma, V.; Shubham; Kaur, G.; Banerjee, D. Enhanced Car Damage Classification: A Fusion of Deep Learning and Random Forest Methods. In Proceedings of the 2024 Asia Pacific Conference on Innovation in Technology (APCIT), Mysuru, India, 26–27 July 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Manuel Molina Un Intruso de Otro Mundo: F1-Score. Rev. Electrónica AnestesiaR 2024, 16, 1–16. [CrossRef]
- Çelik, S.; Gökdemir, T.; Çondur, F. Statistical Analysis of the World Happiness Index by Regions. Qual. Quant. 2025, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Authors | Insights | Methods | Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diaz-Sarachaga et al. (2018) [8] | Focus on adequacy of SDG Index for 2030 Agenda | Suitability analysis, regional SDG Index creation |
|
| Mwitondi et al. (2020) [9] | Machine learning for SDG disparities in Africa | DSF, PCA, K-Means clustering |
|
| De Neve & Sachs (2020) [10] | Links between SDGs and subjective well-being | Correlations, OLS regressions, dominance analysis |
|
| Bellantuono et al. (2020) [11] | Complex network approach for global rankings | Network construction, community detection |
|
| Sciarra et al. (2021) [12] | Network approach to rank countries on SDGs | Bipartite networks, centrality metrics |
|
| Keys et al. (2021) [13] | Machine learning-based human footprint index | ml-HFI using satellite imagery |
|
| Souza et al. (2021) [14] | Clustering countries by SDG indicators over time | PCA, K-Means clustering |
|
| García Villena et al. (2022) [15] | Sustainability evaluation in Latin America projects | Supervised classifiers (SVM + SMOTE) |
|
| Asadikia et al. (2022) [16] | Geography, income influence on SDG achievement | Gradient Boosting Machine (GBM) |
|
| Vijayanand (2023) [17] | ML classification to predict regional sustainability differences | Data prep, ML models (RF, KNN, SVM, etc.) |
|
| Wan et al. (2023) [18] | Monitoring sustainable development via SSPs | Scoring algorithms, ML methods |
|
| Chang et al. (2023) [19] | Regional inequalities using satellite and ML | CNN on satellite imagery |
|
| Yao & Li (2023) [20] | Environmental sustainability in African countries | Explainable ML, panel data models |
|
| Raj et al. (2024) [21] | ML contributions to SDGs, ethical challenges | Review of ML applications and ethics |
|
| Castelli et al. (2024) [22] | Italy’s SDG progress using clustering | Unsupervised clustering |
|
| Chenary et al. (2024) [23] | Forecasting SDG scores through 2030 | ARIMAX, Holt–Winters smoothing |
|
| Liu et al. (2024) [24] | SDG disparities, health risks, need for partnerships | Progress evenness index, quantitative analysis |
|
| Zhang et al. (2025) [25] | Sustainability index with spatial spillover analysis | New index construction, spatial framework |
|
| García-Rodríguez et al. (2025) [26] | Unsupervised ML for SDG correlations across countries | Unsupervised ML, data-driven methodology |
|
| Ma et al. (2025) [27] | SDG achievement paths via product space methodology | Economic complexity, product space |
|
| Jena & Basel (2025) [28] | Classification of countries by SDG performance | Gray Relational Analysis, K-Means clustering |
|
| k | WCSS (Inertia) | Silhouette Score |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 470.22 | 0.3309 |
| 3 | 345.38 | 0.3773 |
| 4 | 220.94 | 0.4031 |
| 5 | 169.69 | 0.4055 |
| 6 | 150.81 | 0.3385 |
| 7 | 133.12 | 0.3407 |
| 8 | 123.32 | 0.2737 |
| 9 | 113.67 | 0.2620 |
| 10 | 105.19 | 0.2523 |
| Feature | F-Value | p-Value | Significant (p < 0.05) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCA1 | 45.632 | 1.23 × 10−10 | Yes |
| PCA2 | 39.871 | 3.45 × 10−9 | Yes |
| Test Statistic | Value | F-Value | p-Value | Significant (p < 0.05) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wilks’ Lambda | 0.243 | 67.32 | 0.000 | Yes |
| Pillai’s Trace | 0.573 | 70.89 | 0.000 | Yes |
| Hotelling–Lawley Trace | 1.047 | 72.10 | 0.000 | Yes |
| Roy’s Largest Root | 0.823 | 69.55 | 0.000 | Yes |
| Model | Accuracy | Precision (Macro Avg) | Recall (Macro Avg) | F1 Score (Macro Avg) | ROC AUC (Macro) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Random Forest | 0.977 | 0.789 | 0.800 | 0.794 | 1.000 |
| SVM | 0.977 | 0.982 | 0.960 | 0.968 | 1.000 |
| Decision Tree | 0.953 | 0.948 | 0.976 | 0.960 | 0.974 |
| XGBoost | 0.907 | 0.750 | 0.708 | 0.718 | 0.835 |
| ANN | 0.977 | 0.982 | 0.988 | 0.984 | 1.000 |
| Logistic Regression | 0.953 | 0.968 | 0.968 | 0.968 | 0.994 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Çelik, S.; Öztürk, Ö.F.; Akkucuk, U.; Şaşmaz, M.Ü. Global Sustainability Performance and Regional Disparities: A Machine Learning Approach Based on the 2025 SDG Index. Sustainability 2025, 17, 7411. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167411
Çelik S, Öztürk ÖF, Akkucuk U, Şaşmaz MÜ. Global Sustainability Performance and Regional Disparities: A Machine Learning Approach Based on the 2025 SDG Index. Sustainability. 2025; 17(16):7411. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167411
Chicago/Turabian StyleÇelik, Sadullah, Ömer Faruk Öztürk, Ulas Akkucuk, and Mahmut Ünsal Şaşmaz. 2025. "Global Sustainability Performance and Regional Disparities: A Machine Learning Approach Based on the 2025 SDG Index" Sustainability 17, no. 16: 7411. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167411
APA StyleÇelik, S., Öztürk, Ö. F., Akkucuk, U., & Şaşmaz, M. Ü. (2025). Global Sustainability Performance and Regional Disparities: A Machine Learning Approach Based on the 2025 SDG Index. Sustainability, 17(16), 7411. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167411







