Upcycling Arundo donax Biomass: A Systematic Review of Applications, Materials, and Environmental Benefits for Greener Construction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Arundo donax Overview
2.1. Botanical and Residual Biomass
2.2. Issues of Alien Species Diffusion
2.3. Arundo donax: A Terrestrial Invasive Alien Species
2.4. Control Strategies and Management Challenges
3. Methodology
- A Keyword Co-occurrence Map, to identify dominant research themes;
- A Source Co-Citation Map, to analyze relationships between journals;
- A Country Co-Authorship Map, to visualize international collaboration patterns.
- “Based on this abstract, which material category best describes the study?”;
- “Summarize the main contribution using 3–5 technical keywords.”
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Scientific Production Trends and Thematic Distribution
4.2. Bibliometric Analysis
4.3. Literature Review
- Development of novel materials;
- Development and performance analysis of innovative technical elements.
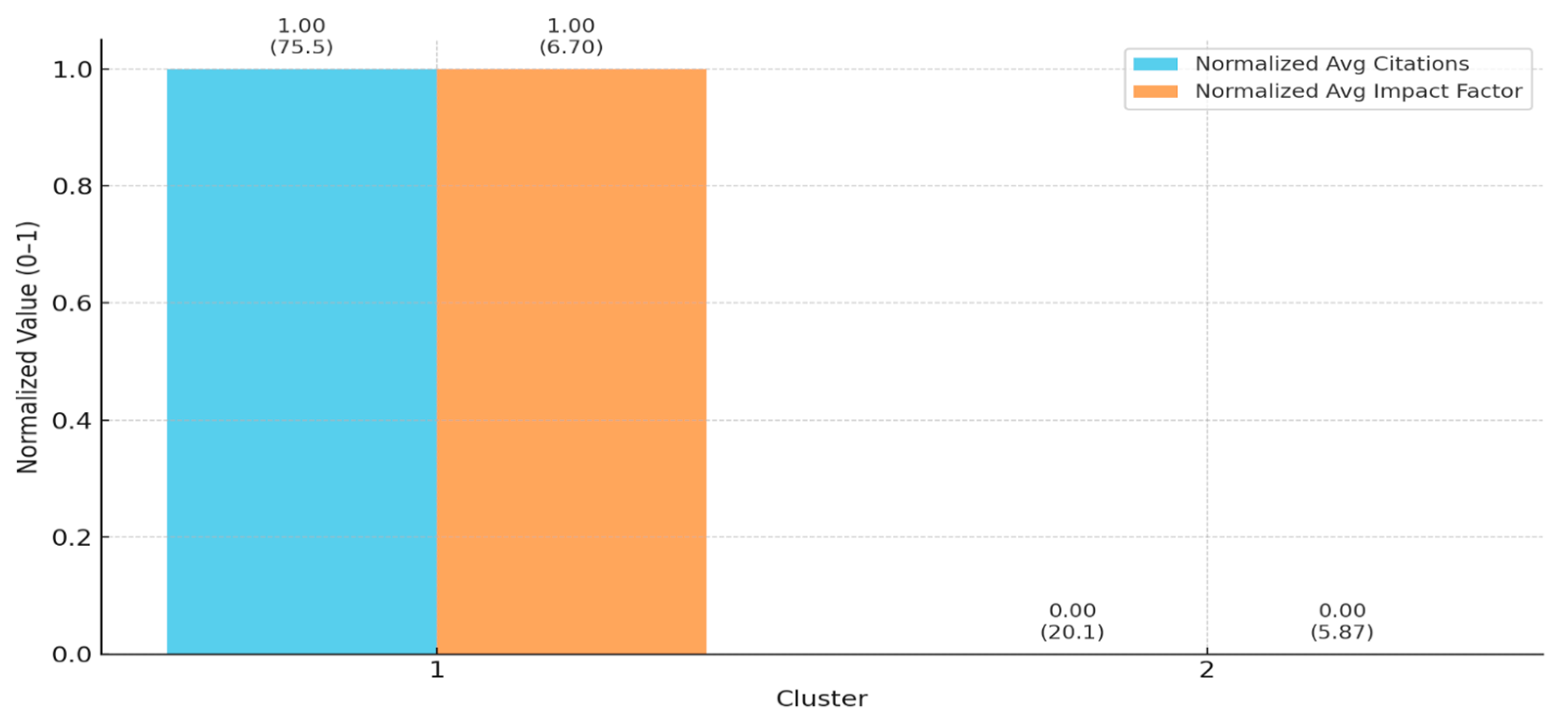
4.3.1. Cluster 1: Development of Novel Materials
4.3.2. Cluster 2: Development and Performance Analysis of Innovative Technical Elements
5. Conclusions
- Develop shared testing protocols for mechanical, thermal, and environmental properties of bio-materials incorporating AD;
- Investigate the effects of different pre-treatments on performance, especially for polymer–fiber composites;
- Quantify environmental impacts through LCA and carbon footprint analysis, supporting data-driven decisions;
- Expand experimental work on structural applications, upscaling from lab-scale to pilot or real-world demonstrators;
- Critically explore socio-environmental trade-offs, especially in relation to the dual status of AD as both a resource and a species with ecological risks.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Glossary
| Bio-aggregate | A granular material derived from biological sources, used as filler or structural component in construction composites. |
| Bio-based material | A material derived wholly or partly from biomass (plants, microorganisms, or other biological sources), used to reduce reliance on fossil resources. Bio-based refers to origin, not necessarily biodegradability. |
| Bio-composite | A composite material composed of at least one bio-based component (e.g., binder, aggregate, etc.) and/or reinforcement (e.g., natural fibers). It may include both fully bio-based and partially bio-based components. |
| Biomass | Organic matter from plants and animals that can be used as a renewable energy source or raw material, including wood, agricultural residues, and other biological materials. |
| Composite material | A material made by combining two or more different substances (e.g., matrix, fibers, aggregates, etc.) that work together to produce properties superior to those of the individual components alone. |
| Culm | The hollow, jointed stem of certain grasses and plants such as bamboo and reeds, which provides structural support and is often used in construction and crafts. |
| Fiber | A thread-like natural or synthetic material, often derived from plants, animals, or minerals, used in textiles, ropes, and other products for its strength and flexibility. |
| Invasive alien plant species (IAPS) | Plant species introduced outside their natural distribution range, which spread rapidly and cause environmental, economic, or health-related harm. |
| Invasive alien species (IAS) | Non-native plants or animals introduced to a new environment that spread rapidly, often causing harm to native ecosystems, economies, or human health. |
| Lignocellulosic material | Plant-based material composed primarily of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin. Commonly used as reinforcement or filler. |
| Natural fiber composite (NFC) | A type of biocomposite in which the reinforcement phase consists of natural fibers (e.g., flax, hemp, Arundo donax). The matrix may be either synthetic or bio-based. |
| Non-conventional material | A material not commonly used in standard industrial or construction practices, often characterized by alternative origins, innovative compositions, or unstandardized properties. This category may include natural, bio-based, recycled, or waste-derived materials, and is typically explored for its sustainability potential or local availability. |
| Plant species | A group of plants that share common characteristics and are capable of interbreeding to produce fertile offspring, classified under the same scientific name in taxonomy. |
| Plant sub-species | A taxonomic category below species, representing a distinct population within a species that has unique genetic, morphological, or geographical characteristics but can still interbreed with other members of the species. |
| Plant-based resources | Natural materials derived from plants, including fibers, stems, leaves, seeds, and other parts, used for manufacturing, construction, textiles, food, and various industrial applications. |
| Reed | A tall, slender grass-like plant typically found in wetlands, with hollow stems used traditionally in thatching, weaving, and as raw material in various crafts. |
| Renewable raw material/(re)source | A natural resource that can regenerate within a human timescale, including agricultural or forestry residues and dedicated bio-crops. |
| Waste-based (or waste-derived) composite | A composite material in which one or more components (e.g., matrix, reinforcement, filler, etc.) are derived from post-consumer, agricultural, industrial, or organic waste. These composites aim to valorize waste streams by integrating them into functional materials, thereby promoting circular economy and resource efficiency. |
References
- United Nations, UN Academic Impact (UNAI). 2025. Available online: https://www.un.org/en/academic-impact/sustainability# (accessed on 28 June 2025).
- Li, K.; Zou, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Shuai, C. Assessing the spatial-temporal environmental efficiency of global construction sector. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sing, C.P.; Huang, M.; Shen, Z.L. Exploring the decoupling evolution of carbon emission from economic efficiency in the construction sector: A comparative perspective. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2025, 128, 106464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations, UN Environment Programme (UNEP), Building Materials and the Climate: Constructing a New Future. 2023. Available online: https://www.unep.org/resources/report/building-materials-and-climate-constructing-new-future (accessed on 28 June 2025).
- United Nations, UN Environment Programme (UNEP) UNEP, Global Status Report for Building and Construction. 2024. Available online: https://www.unep.org/resources/report/global-status-report-buildings-and-construction (accessed on 28 June 2025).
- Barreca, F.; Martinez Gabarron, A.; Flores Yepes, J.A.; Pastor Pérez, J.J. Innovative use of giant reed and cork residues for panels of buildings in Mediterranean area. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 140, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrandez-García, A.A.; Ortuño, T.G.; Ferrandez-Villena, M.; Ferrandez-Garcia, A.; Ferrandez-García, M.T. Evaluation of particleboards made from Giant Reed (Arundo donax L.) bonded with cement and potato starch. Polymers 2022, 14, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IUCN—International Union for Conservation of Nature, Italian Committee, Lista Rossa degli Ecosistemi d’Italia. 2023. Available online: https://www.iucn.it/pdf/Lista-Rossa-Ecosistemi-Italia_2023.pdf (accessed on 28 June 2025).
- Suárez, L.; Castellano, J.; Romero, F.; Marrero, M.D.; Benítez, A.N.; Ortega, Z. Environmental hazards of giant reed (Arundo donax L.) in the macaronesia region and its characterisation as a potential source for the production of natural fibre composites. Polymers 2021, 13, 2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malheiro, R.; Morillas, A.; Ansolin, A.; Fernandes, J.; Camões, A.; Amorim, M.T.; Monteiro Silva, S.; Mateus, R. Thermal Performance and Durability Evaluation of Arundo donax towards an Improvement in the Knowledge of Sustainable Building Materials. Energies 2023, 16, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, S.; Rigual, V.; Raspolli Galletti, A.M.; Parajó, J.C. Integral fractionation of Arundo donax using biphasic mixtures of solvents derived from biomass: An environmentally friendly approach. Biomass Bioenergy 2024, 190, 107398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarone, N.; Iovane, G.; Marranzini, D.; Sessa, R.; Correia Guedes, M.; Faggiano, B. Arundo donax L. as sustainable building material. Sustain. Build. 2023, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philokyprou, M.; Michael, A.; Malaktou, E. A typological, environmental and socio-cultural study of semi-open spaces in the Eastern Mediterranean vernacular architecture: The case of Cyprus. Front. Archit. Res. 2021, 10, 483–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabaieh, M.; Sakr, M. BUILDING WITH REEDS. Revitalizing a Building Tradition for Low Carbon Building Practice. In Proceedings of the CIAV-ICTC 2015: ICOMOS Thailand International Conference, Bangkok, Thailand, 6–9 November 2015; Available online: https://www.icomosictc.org/p/past-conferences.html (accessed on 28 June 2025).
- Acta Plantarum, Indice dei Nomi delle Specie Botaniche Presenti in Italia, Arundo donax L. 2025. Available online: https://www.actaplantarum.org/flora/flora_info.php?id=507646 (accessed on 28 June 2025).
- Sanz Elorza, M.; Dana Sánchez, E.D.; Sobrino Vesperinas, E. Atlas de las Plantas Alóctonas Invasoras de España; Dirección General para la Biodiversidad: Madrid, Spain, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Barreca, F. Use of giant reed Arundo donax L. in rural constructions. Agric. Eng. Int. CIGR J. 2012, 14, 46–52. [Google Scholar]
- García-Ortuño, T.; Ferrández García, M.T.; Andreu, J.; Ferrández-Villena, M.; Ferrández Garcia, C.E. Study of the mechanical properties of giant reed as a green building material. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Advances in Civil, Structural and Environmental Engineering—ACSEE, Zurich, Switzerland, 25–28 October 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, S.C.; Gomes, A.P.; Nunes, P.; Fernandes, M.; Maia, A.; Bacelar, E.; Rocha, J.; Cruz, R.; Boatto, A.; Ravishankar, A.P.; et al. Leaf surfaces and neolithization- the case of Arundo donax L. Front. Plants Sci. 2022, 13, 999252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato-Noguchi, H.; Kato, M. The Invasive Mechanism and Impact of Arundo donax, One of the World’s 100 Worst Invasive Alien Species. Plants 2025, 14, 2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Ruiz, J.; Hardion, L.; Del Monte, J.P.; Vila, B.; Santín-Montanyá, M.I. Monographs on invasive plants in Europe N° 4: Arundo donax L. Bot. Lett. 2021, 168, 131–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LIFE MedCLIFF Project, Acting for NatureManaging Invasive Plants to Conserve Habitats. Available online: https://lifemedcliffs.org/en/context/invasive-flora/giant-reed-arundo-donax/?utm_source=chatgpt.com (accessed on 28 June 2025).
- European Commission, OPTIMA Project, Optimization of Perennial Grasses for Biomass Production. Available online: http://www.optimafp7.eu/ (accessed on 28 June 2025).
- Longo, S. Lotta Biologica Alla Canna Gigante Arundo donax Negli USA, Georgofili Info. 2018. Available online: https://www.georgofili.info/contenuti/lotta-biologica-alla-canna-gigante-arundo-donax-negli-usa/5600 (accessed on 28 June 2025).
- Cortés, E.; Kirk, A.A.; Goolsby, J.A.; Moran, P.J.; Racelis, A.E.; Marcos-García, M.A. Impact of the Arundo scale Rhizaspidiotus donacis (Hemiptera: Diaspididae) on the weight of Arundo donax (Poaceae: Arundinoideae) rhizomes in Languedoc southern France and Mediterranean Spain. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2011, 21, 1369–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, S.E.; Fath, B.D. Encyclopedia of Ecology, C3 Photosynthesis; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; ISBN 978-0-08-045405-4. [Google Scholar]
- Ceotto, E.; Di Candilo, M. Shoot cuttings propagation of giant reed (Arundo donax L.) in water and moist soil: The path forward? Biomass Bioenergy 2010, 23, 1614–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lino, G.; Espigul, P.; Nogués, S.; Serrat, X. Arundo donax L. growth potential under different abiotic stress. Heliyon 2023, 9, e15521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewandowski, I.; Scurlock, J.M.O.; Lindvall, E.; Christou, M. The development and current status of perennial rhizomatous grasses as energy crops in the US and Europe. Biomass Bioenergy 2003, 25, 335–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, A.; Teixeira, G.; Frazão Moreira, J.R. Relationships between leaf anatomical features of Arundo donax and glyphosate efficacy. Rev. Ciências Agrárias 2015, 38, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISSG—Invasive Species Specialist Group, Global Invasive Species Database. 2025. Available online: https://www.iucngisd.org/gisd/speciesname/Arundo+donax (accessed on 28 June 2025).
- Ortega, Z.; Romero, F.; Paz, R.; Suárez, L.; Benítez, A.N.; Marrero, M.D. Valorization of invasive plants from macaronesia as filler materials in the production of natural fiber composites by rotational molding. Polymers 2021, 13, 2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiore, V.; Scalici, T.; Vitale, G.; Valenza, A. Static and dynamic mechanical properties of Arundo donax fillers-epoxy composites. Mater. Des. 2014, 57, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z. Invasive Alien Species (IAS) spread, impact and management. Theor. Nat. Sci. 2023, 7, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentili, R.; Schaffner, U.; Martinoli, A.; Citterio, S. Invasive alien species and biodiversity: Impacts and management. Biodiversity 2021, 22, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzaro, L.; Bolpagni, R.; Buffa, G.; Gentili, R.; Lonati, M.; Stinca, A.T.R.; Acosta, A. Impact of invasive alien plants on native plant communities and Natura 2000 habitats: State of the art, gap analysis and perspectives in Italy. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 274, 111140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGeoch, M.A.; Butchart, S.H.; Spear, D.; Marais, E.; Kleynhans, E.J.; Symes, A.; Chanson, J.; Hoffmann, M. Global indicators of biological invasion: Species numbers, biodiversity impact and policy responses. Divers. Distrib. 2010, 16, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paini, D.R.; Sheppard, A.W.; Cook, D.C.; De Barro, P.J.; Worner, S.P.; Thomas, M.B. Global threat to agriculture from invasive species. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 7575–7579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pejchar, L.; Mooney, H.A. Invasive species, ecosystem services and human well-being. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2009, 24, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turbelin, A.J.; Malamud, B.D.; Francis, R.A. Mapping the global state of invasive alien species: Patterns of invasion and policy responses. Global Ecol. Biogeogr. 2017, 26, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta Solís, M. Los Bambúes y Pseudobambúes Económicos del Ecuador; Editorial Universitaria: Quito, Ecuador, 1960; 39p, Available online: https://www.dspace.uce.edu.ec/entities/publication/8426773a-4dc2-4b32-8a4f-cb2ccb0c8f0d (accessed on 28 June 2025).
- Fernández Nieto, M.A. Arquitectura Vegetal: Estrategias Materiales = Plant Architecture: Material Strategies; Colección i+u (Investigación y Universidad); Ediciones Asimétricas: Madrid, Spain, 2018; ISBN 978-8494917813. [Google Scholar]
- Mota, B.; Sorolla, A. Caña a la Caña es. 2014. Available online: www.naturalea.eu (accessed on 28 June 2025).
- Del Toro, I.; Ribbons, R.R.; Pelini, S.L. The little things that run the world revisited: A review of ant-mediated ecosystem services and disservices (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Myrmecol. News 2012, 17, 133–146. [Google Scholar]
- Ortega, Z.; Bolaji, I.; Suárez, L.; Cunningham, E. A review of the use of giant reed (Arundo donax L.) in the biorefineries context. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2024, 40, 305–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couvreur, L.; Buzo, A. Construir con Caña. Ministerio de Cultura y Deporte de España. Instituto del Patrimonio Cultural de España, 2019. Available online: https://www.calameo.com/books/0000753353002d71f89fe (accessed on 28 June 2025).
- Herrera, I.; Vargas, A.; Rizzo, K.; Panchana, K.; Freire, E.; Espinoza, B. Plantas Exóticas Invasoras del Ecuador Continental; Fuentes, E., Ed.; Federal Universidad Espíritu Santo: Espírito Santo, Brazil, 2022; Available online: www.uees.edu.ec (accessed on 28 June 2025).
- Garófano, L. La “Arundo donax”, la Caña Invasora Que Agravó la Riada de Valencia y lo Arrasó todo: Quitar un Kilómetro Cuesta un Millón. El Español, 11 November 2024. Available online: https://www.elespanol.com/valencia/reconstruir-valencia/20241111/arundo-donax-canainvasora-agravo-riada-valencia-arraso-quitar-kilometro-cuesta-millon/899660164_0.html (accessed on 28 June 2025).
- Leone, R.; La Scalia, G.; Saeli, M. A critical review on reuse potentials of wood waste for innovative products and applications: Trends and future challenges. Sustain. Futures 2025, 10, 100869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Visualizing bibliometric networks. In Measuring Scholarly Impact; Ding, Y., Rousseau, R., Wolfram, D., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orechoff, A.; Norkina, S. Über die Alkaloide von Arundo donax L. Berichte Dtsch. Chem. Ges. (A B Ser.) 1935, 68, 436–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzi, S.; Molari, L.; Bignozzi, M.C.; Masi, G.; Saccani, A. Geopolymeric Composites Containing Industrial Waste Reinforced with Arundo donax Fibers. Buildings 2024, 14, 1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabkit, S.; Krache, R.; Amroune, S.; Jawaid, M.; Hachaichi, A.; Ismail, A.S.; Meraj, A. Effect of chemical treatments of Arundo donax L. fibre on mechanical and thermal properties of the PLA/PP blend composite filament for FDM 3D printing. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2024, 152, 106438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badagliacco, D.; Megna, B.; Valenza, A. Induced Modification of Flexural Toughness of Natural Hydraulic Lime Based Mortars by Addition of Giant Reed Fibers. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2020, 13, e00425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargin Karahancer, S.; Eriskin, E.; Sarioglu, O.; Capali, B.; Saltan, M.; Terzi, S. Utilization of Arundo donax in Hot Mix Asphalt as a fiber. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 125, 981–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalici, T.; Fiore, V.; Valenza, A. Effect of plasma treatment on the properties of Arundo donax L. leaf fibres and its bio-based epoxy composites: A preliminary study. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 94, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiore, V.; Scalici, T.; Valenza, A. Characterization of a new natural fiber from Arundo donax L. as potential reinforcement of polymer composites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 106, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiore, V.; Botta, L.; Scaffaro, R.; Valenza, A.; Pirrotta, A. PLA based biocomposites reinforced with Arundo donax fillers. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2014, 105, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cintura, E.; Faria, P.; Molari, L.; Mazzocchetti, L.; Dalle Donne, M.; Giorgini, L.; Nunes, L. Bio-based boards made of hazelnut shell and A. donax for indoor applications—A solution with good performance in case of fire. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 95, 110274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora-Ruiz, V.; Mejía-Parada, C.; Nuñez, B.; Pineda, S.M.; Prado, N.I.; Vallejo-Borda, J.A.; Arrieta-Baldovino, J. Experimental analysis of the cyclic behavior of rammed earth walls reinforced with Arundo donax natural fiber. Heliyon 2024, 10, e37084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitrone, F.; Ramos, D.; Vitagliano, V.; Ferrando, F.; Salvadó, J. All-lignocellulosic fiberboards from giant reed (Arundo donax L.): Effect of steam explosion pre-treatment on physical and mechanical properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 319, 126064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malheiro, R.; Ansolin, A.; Guarnier, C.; Fernandes, J.; Amorim, M.T.; Silva, S.M.; Mateus, R. The potential of the Reed as a Regenerative Building Material—Characterisation of Its Durability, Physical, and Thermal Performances. Energies 2021, 14, 4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molari, L.; Coppolino, F.S.; García, J.J. Arundo donax: A widespread plant with great potential as sustainable structural material. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 268, 121143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrandez-García, M.T.; Ferrandez-Garcia, A.; Garcia-Ortuño, T.; Ferrandez-Garcia, C.E.; Ferrandez-Villena, M. Assessment of the Physical, Mechanical and Acoustic Properties of Arundo donax L. Biomass in Low Pressure and Temperature Particleboards. Polymers 2020, 12, 1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrandez-Villena, M.; Ferrandez-Garcia, C.E.; Garcia-Ortuño, T.; Ferrandez-Garcia, A.; Ferrandez-Garcia, M.T. The influence of processing and particle size on binderless particleboards made from Arundo donax L. Rhizome. Polymers 2020, 12, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabarrón, A.M.; Yepes, J.F.; Pérez, J.P.; Serna, J.B.; Arnold, L.C.; Medrano, F.S. Increase of the flexural strength of construction elements made with plaster (calcium sulfate dihydrate) and common reed (Arundo donax L.). Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 66, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanzione, M.; Russo, V.; Verdolotti, L.; Sorrentino, A.; Di Serio, M.; Tesser, R.; Iannace SLavorgna, M. Synthesis and characterization of sustainable polyurethane foams based on polyhydroxyls with different terminal groups. Polymer 2018, 149, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



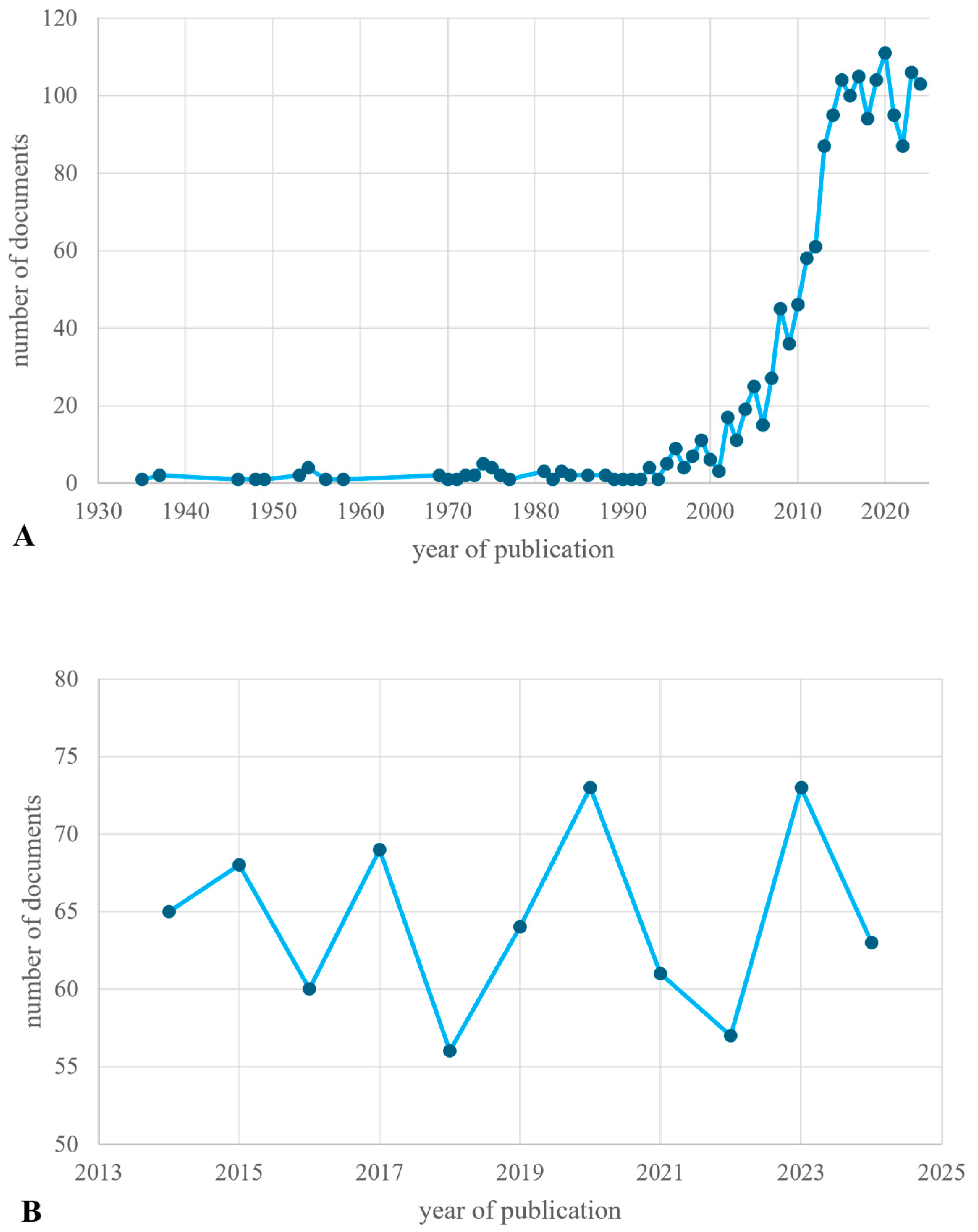
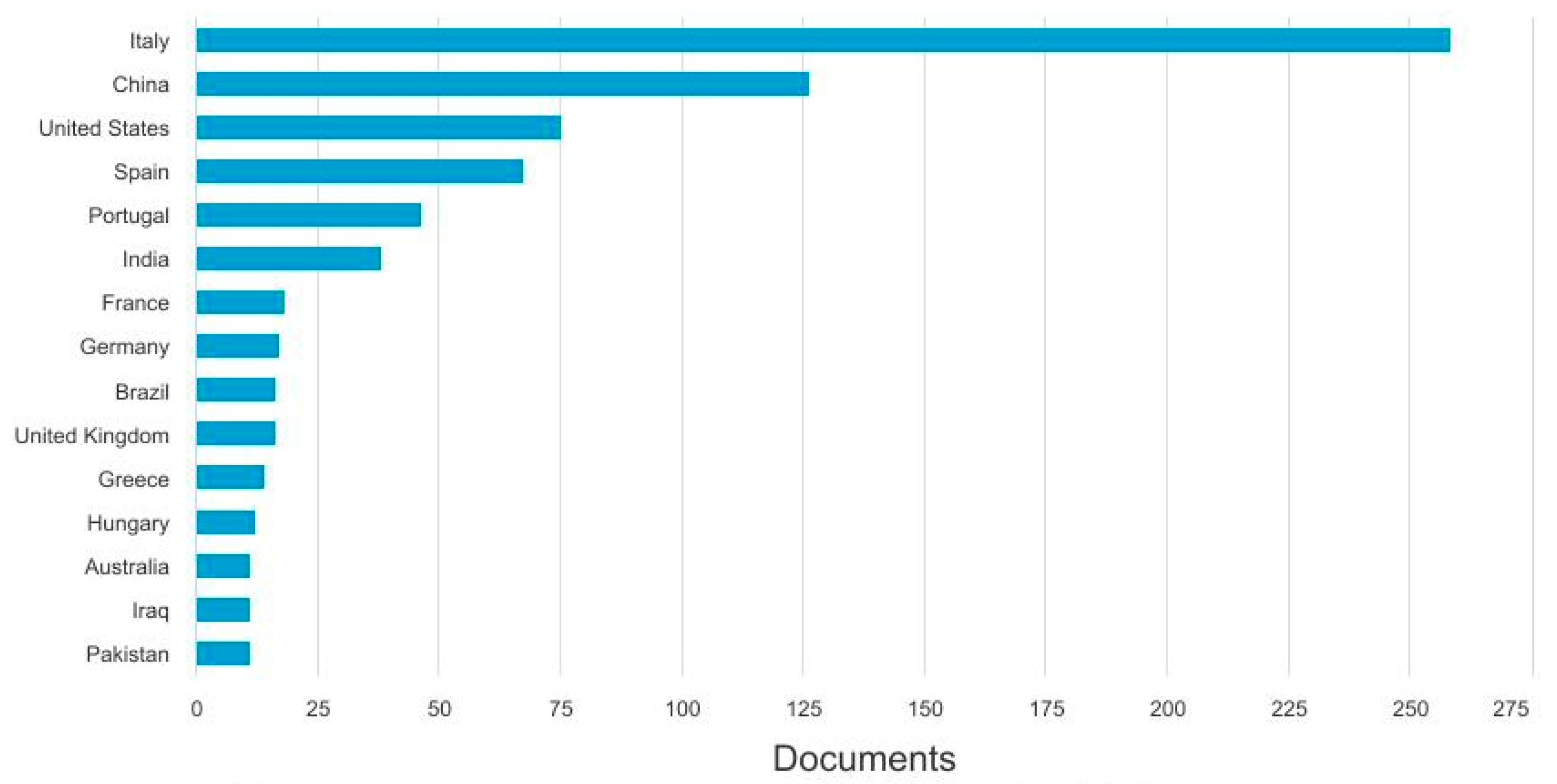

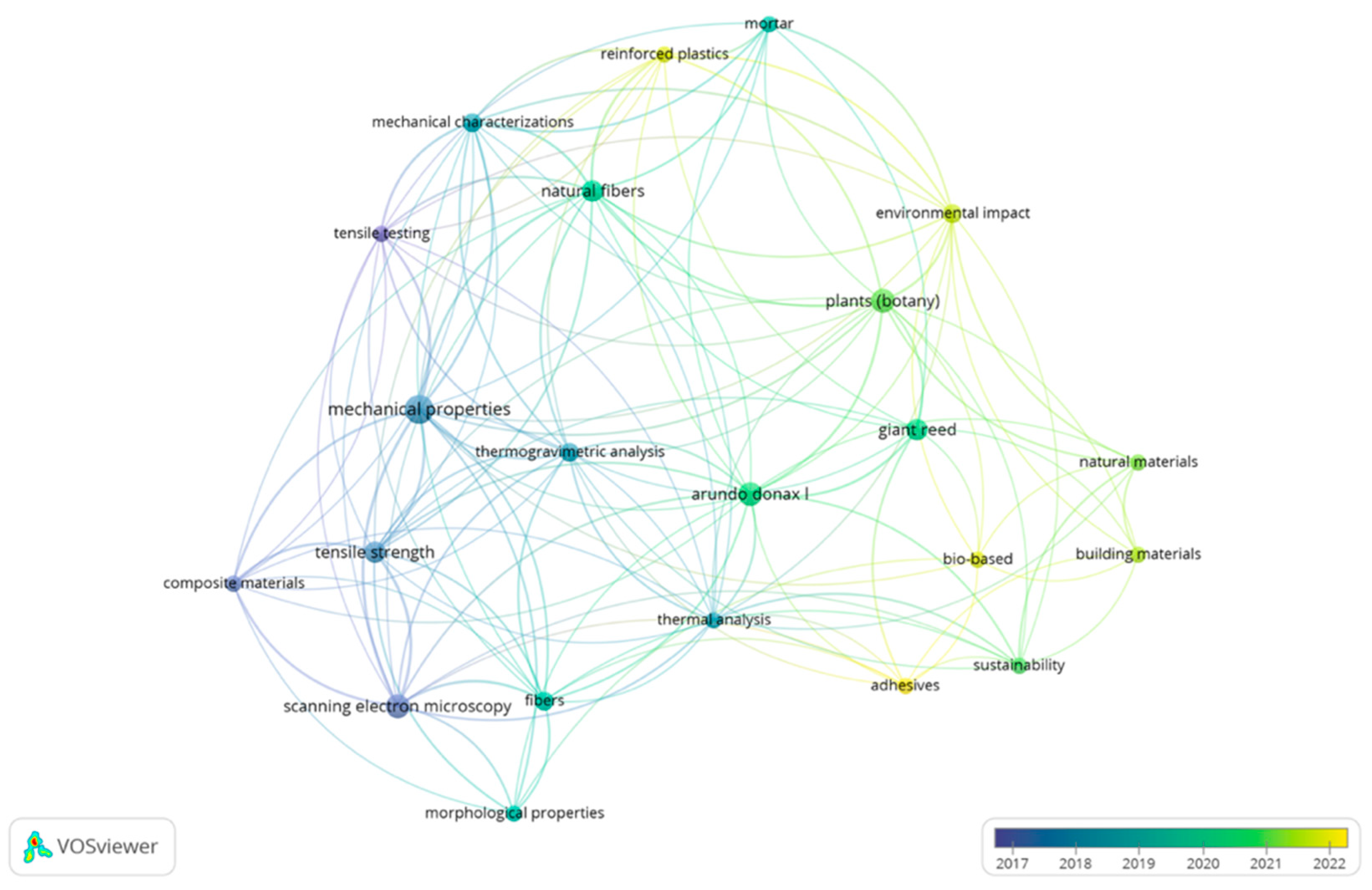

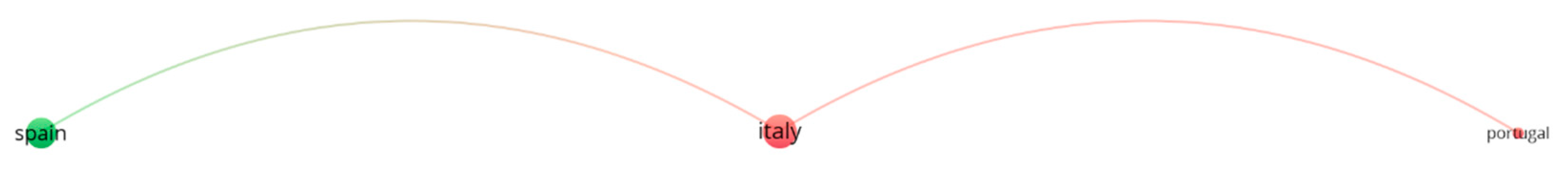
| Biomass Fraction | Description | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Culms (stalks) | Tall, hollow cylindrical stems (up to 8 m) | Lightweight, rigid, segmented; high structural integrity |
| Leaves | Long, narrow leaf blades (30 ÷ 50 cm) | Fibrous, flexible; high surface area |
| Rhizomes | Deep, woody underground roots | Dense lignocellulosic material; difficult to extract |
| Mixed biomass | Whole-plant residues from cutting/removal | Heterogeneous composition; variable fiber and moisture content |
| Cluster | Cluster Description | n° Documents | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cluster 1 | Development of novel materials | 11 | Manzi et al., 2024 [53] Tabkit et al., 2024 [54] Ortega et al., 2021 [32] Suárez et al., 2021 [9] Badagliacco et al., 2020 [55] Stanzione et al., 2018 [54] Sargin Karahancer et al., 2016 [56] Scalici et al., 2016 [57] Fiore et al., 2014 (a) [33] Fiore et al., 2014 (b) [58] Fiore et al., 2014 (c) [59] |
| Cluster 2 | Development and performance analysis of innovative technical elements | 11 | Cintura et al., 2024 [60] Mora-Ruiz et al., 2024 [61] Malheiro et al., 2023 [10] Ferrandez-García et al., 2022 [7] Vitrone et al., 2022 [62] Malheiro et al., 2021 [63] Molari et al., 2021 [64] Ferrandez-García et al., 2020 [65] Ferrandez-Villena et al., 2020 [66] Barreca et al., 2019 [6] Martínez Gabarrón et al., 2014 [67] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leone, R.; Lombardo, L.; Marchese Ragona, F.; Campisi, T.; Saeli, M. Upcycling Arundo donax Biomass: A Systematic Review of Applications, Materials, and Environmental Benefits for Greener Construction. Sustainability 2025, 17, 7402. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167402
Leone R, Lombardo L, Marchese Ragona F, Campisi T, Saeli M. Upcycling Arundo donax Biomass: A Systematic Review of Applications, Materials, and Environmental Benefits for Greener Construction. Sustainability. 2025; 17(16):7402. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167402
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeone, Rosanna, Luisa Lombardo, Federica Marchese Ragona, Tiziana Campisi, and Manfredi Saeli. 2025. "Upcycling Arundo donax Biomass: A Systematic Review of Applications, Materials, and Environmental Benefits for Greener Construction" Sustainability 17, no. 16: 7402. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167402
APA StyleLeone, R., Lombardo, L., Marchese Ragona, F., Campisi, T., & Saeli, M. (2025). Upcycling Arundo donax Biomass: A Systematic Review of Applications, Materials, and Environmental Benefits for Greener Construction. Sustainability, 17(16), 7402. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167402









