Abstract
Tourism network attention, defined as the quantifiable measure of public interest toward tourism destinations through online search activities, has become a crucial indicator for understanding tourist behavior in the digital era. This study analyzes the spatiotemporal evolution of tourism network attention for Zhangjiajie National Forest Park using Baidu index data from 2013 to 2023. Results show three temporal phases: rapid rise (2013–2017), fluctuation adjustment (2018–2020), and recovery growth (2021–2023), with a “double-peak” seasonal pattern in July–August and April–May. Spatial distribution exhibits a “high East, low West” pattern with gradually increasing balance (coefficient of variation: 0.6849→0.5382). GDP, internet users, and transportation accessibility are dominant factors influencing spatial patterns.
1. Introduction
Tourism network attention represents the manifestation of users’ potential demand and realistic concern for tourism destinations, as reflected through online search behaviors and digital engagement patterns. This concept has been validated as a reliable indicator of tourism attractiveness and potential tourist demand [1]. In 2024,The number of eco-tourism tourists reached 2.76 billion, increasing by 9.1% year-on-year [2]. This statistic underscores the need for a clear operational definition of sustainability, defined as the ability to maintain tourism activities without compromising ecological integrity. It is significant for national forest parks, which face new challenges for managing sustainable tourism under growing digitalization. Most current study focuses on urban agglomeration and there is limited study about attention dynamics of eco-tourism places. Prior study lacks comprehensive investigation on how regional features determine spatial attention divergence, especially an interaction of economic, social, and geographical elements. This study explores attention trends for Zhangjiajie National Forest Park’s tourism network under geodetector modeling for 11 years’ data (2013–2023). In exploring how origin elements (economic power, digital infrastructure) and destination elements (accessibility, ecological quality) interact and generate attention trends, we embrace push–pull theory and spatial interaction theory. Study objectives are to: (1) delineate spatiotemporal evolution of tourist network attention; (2) quantify variables driving spatial attention differentiation; and (3) suggest recommendations for accurate marketing and sustainability.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Digital Tourism Attention Analysis
Big data has fundamentally changed how researchers study tourist behavior and destination attractiveness. Over the past decade, tourism network attention—the digital manifestation of tourist interest—has become a critical research focus. Researchers began using search engine data to predict tourism demand, recognizing digital footprints as reliable proxies for tourist interest [3]. This approach proved effective when applied to major attractions like the Forbidden City, where Baidu index data successfully predicted visitor flows and demonstrated strong correlations between online search patterns and actual arrivals [4]. Subsequent studies expanded these methods to analyze the spatial and temporal dimensions of tourism demand, establishing network attention as a quantifiable measure of public interest in destinations [5]. Recent research on Chinese national parks has used this approach to examine attention patterns over time, showing how seasonal variations reveal underlying tourist behavior dynamics [6]. Recent research demonstrates how big data transforms tourism marketing by tracking behavioral trends and research directions, emphasizing the critical role of user-generated content in shaping attention and destination selection [7]. These applications extend to complex system optimization in tourism contexts, where algorithmic approaches show considerable promise for addressing multi-objective challenges [8].
2.2. Forest Park Digital Management
Digital management has emerged as a cornerstone of modern forest park operations. Recent studies demonstrate how digital technologies are reshaping both park administration and visitor experiences, with researchers analyzing visitor behavior patterns to inform management strategies [9]. The integration of crowdsourced geospatial data has opened new avenues for understanding recreational visits to national forest parks, highlighting the critical role of visitor motivation insights in our increasingly digital landscape [10]. Comparative research reveals distinct patterns in digital forecasting tools: while Baidu index proves most effective for predicting domestic Chinese tourism demand, Google Trends excels in international tourism forecasting [11]. Building on these foundations, Baidu index has gained particular prominence as a tourism attention indicator in recent years. Studies show it effectively captures tourism demand fluctuations and maps tourism flow networks across Chinese provinces [12]. The platform’s appeal lies in its practical advantages—real-time data access, extensive sample coverage, and cost-effectiveness compared to conventional statistical methods.
2.3. Spatiotemporal Analysis
Spatial analysis techniques have undergone significant evolution in tourism research. The geodetector principle has proven particularly valuable for identifying the driving mechanisms behind spatial tourism patterns, effectively handling both linear and nonlinear relationships within complex tourism systems [13]. This methodological advancement has found practical application in border region studies, where researchers have applied spatial statistical methods to examine tourism efficiency patterns and identify the key determinants shaping regional tourism development [14]. Understanding temporal variations in tourist demand has become equally crucial for destination management. Seasonal strength indices now serve as powerful tools for analyzing tourist behavior patterns, offering both recognition capabilities and predictive insights that inform strategic planning [15]. The development of statistical modeling approaches for spatially stratified heterogeneous data has further enhanced researchers’ ability to uncover the complex geographic factors influencing tourism distribution patterns [16].
2.4. Influencing Factors
Tourism network attention patterns are influenced by multiple interconnected factors. Economic development, measured through GDP and per-capita disposable income, fundamentally drives tourism demand and online search behavior [17]. Urbanization rate and internet user numbers jointly determine the digital capacity for generating tourism attention, with urbanized and connected regions showing higher search volumes [18]. Geographic accessibility, including both physical distance and transportation time distance, creates distance decay effects where closer and more accessible destinations receive greater network attention [19]. Environmental quality factors, particularly forest coverage and air quality, influence destination attractiveness and subsequent online attention patterns [20]. These economic, social, geographic, and environmental factors operate synergistically rather than independently, creating integrated mechanisms that shape the spatial differentiation of tourism network attention [21].
2.5. The Theoretical Framework
This research integrates four core theories. Push–pull theory explains how origin market characteristics (economic development, population size) and destination attributes (environmental quality, accessibility) interact to generate tourism network attention [22,23]. Digital tourism behavior theory supports using Baidu index data as reliable indicators of tourism interest and travel intentions [24]. Spatial interaction theory, particularly gravity models, accounts for distance decay effects in tourism attention patterns [25]. For forest park destinations, sustainable tourism development theory provides the framework for balancing market development with environmental protection, ensuring attention patterns align with ecological carrying capacity [26]. These theories collectively explain how economic, social, geographic, and environmental factors shape spatial patterns of digital tourism interest.
3. Methodology
3.1. Study Area
Zhangjiajie National Forest Park occupies a prominent position in northwestern Hunan Province China, since its establishment in 1982. UNESCO inscribed it on the World Natural Heritage List in 1992, and it achieved the distinction of becoming China’s first World Geopark in 2007. Tourism growth at Zhangjiajie has been remarkable over the past two decades. Zhangjiajie National Forest Park received a record high of over 7.6973 million visitors in 2024 [27]. This influx of visitors has positively impacted the local economy, contributing to infrastructure development and job creation. The park’s recent embrace of smart tourism initiatives has created new opportunities for visitor engagement and operational efficiency. Digital transformation efforts now encompass online information services and modernized management systems, enhancing the overall tourist experience while generating valuable digital footprints.
3.2. Data Sources and Processing
Baidu index represents 70% of China’s search market and reflects keyword search frequency through weighted analysis of user search behavior [28]. It serves as a leading indicator for tourism interest and consideration, with established validity in academic literature [29]. While search behavior may not directly translate to actual visits, it effectively captures tourism attention patterns and market interest trends. In this study, the data of Zhangjiajie National Forest Park’s tourism online attention were obtained from the Baidu index platform (https://index.baidu.com). We selected keyword combinations such as “Zhangjiajie National Forest Park,” “Zhangjiajie Travels,” and “Zhangjiajie” to comprehensively capture public interest in Zhangjiajie tourism. However, the ambiguity surrounding the keyword “Zhangjiajie,” which could refer to both the city and the scenic area, is acknowledged as a limitation of this study. Despite this, the global recognition of the destination and the city’s tourism-oriented development suggest that tourism-related searches constitute a significant portion of the total search results. Additionally, sensitivity analysis confirmed consistent spatial patterns across all keyword combinations. Additional date sources include China Statistical Yearbook, China Tourism Statistical Yearbook, Provincial Statistical Yearbooks (2013–2023), and Zhangjiajie National Forest Park official website for economic, tourism, and visitor data [30]. It is important to note that while these data sources are reliable, the inherent limitations of each should be considered when interpreting the results, particularly regarding the potential discrepancies between online attention and actual visitor numbers.
3.3. Analytical Methodology
This section outlines the analytical methods employed in this study, focusing on the application of various theories to rigorously analyze tourism network attention patterns. Based on push–pull theory, digital tourism behavior theory, spatial interaction theory and sustainable tourism development theory, this study employs both temporal and spatial analytical methods to provide a comprehensive understanding of the driving forces behind tourism network attention. Three temporal indices and four spatial indices were selected to ensure a robust analysis of attention patterns. The geodetector method was utilized for its effectiveness in identifying driving factors while accommodating both linear and nonlinear relationships.
3.3.1. Temporal Analysis Methods
- (1)
- Inter-Annual Change Index
Inter-annual change index is a kind of index used to show the change in the relative amount of inter-annual difference of network attention, according to the trend of the annual index of network attention, calculate the inter-annual change in network attention in the year interval. This index quantifies the fluctuation in tourism interest over different years, effectively captures the long-term development trajectory of tourist destinations, helping identify different development stages [31]. The formula is as follows:
where Y is the inter-annual variation index; Ni is the annual index of network attention in year i; n represents the number of years. The closer the value of Y is to 100%, it indicates that the network attention is more stable and the inter-annual variation is smaller in the interval of the study year.
- (2)
- Seasonal Intensity Index
The seasonal intensity index as it effectively captures the temporal distribution patterns of tourist demand, tourism destinations typically exhibit distinct seasonal visitation patterns. This index assesses the variation in attention throughout the year, helping to identify peak tourism periods, which significantly impact their operations and management [32]. The formula is as follows:
where represents the seasonal intensity index, and Xm represents the proportion (%) of network attention in month m to the total attention in the whole year. The larger the value of S, the more significant the seasonal difference of network attention. On the contrary, S tends to 0, indicating that the network attention is more consistent across months.
- (3)
- Intra-Week Distribution Skewness Index
The intra-week distribution skewness index is established on the basis of the day-by-day network attention accumulation curve, which is used to investigate the centralized distribution characteristics of network attention in weekly time period. The intra-week distribution skewness index is ability to reveal tourists’ temporal behavior patterns within shorter time periods. Weekly search patterns can effectively predict short-term tourist arrivals and help destinations better prepare for visitor fluctuations [33]. The formula is as follows:
where T is the intra-week distribution skewness index; Xi is the percentage of network attention on day i to the total number of network attention in the week. T value is less than 0, indicating that the network attention in the first half of the week is more centralized; T value is greater than 0, indicating that the network attention in the second half of the week is more centralized; T value is equal to 0, indicating that the network attention in the front and back half of the week is symmetrically distributed.
3.3.2. Spatial Analysis Methods
- (4)
- Geographic Concentration Index
The geographic concentration index is analyzing spatial distribution patterns of tourism attention, which effectively measures the degree of spatial agglomeration in tourism markets, analyzing spatial concentration helps identify core tourist source markets and evaluate market penetration across different regions [34]. The formula is as follows:
where G is the geographic concentration index, Pa is the network attention of province a, and P is the total network attention of the whole country; the larger the value of G is, the higher the spatial concentration of network attention is.
- (5)
- Primacy Index
The primacy index originally developed in urban studies, has been widely adopted in tourism research to measure market concentration patterns, which effectively reveals the spatial hierarchy of tourism markets and can intuitively reflect the degree of concentration of the network attention of the tourism network of Zhangjiajie National Forest Park, which evaluates whether attention is disproportionately focused on a few leading regions, reflecting market dynamics [35]. The formula is as follows:
Among them, P is the first degree index, P1, P2 represents the regional scale in the first and second place in the region Zhangjiajie National Forest Park tourism network attention, respectively. It is usually believed that P ≧ 2, indicating that the regional attention is too concentrated; P < 2, indicating that the regional attention is relatively balanced, the degree of agglomeration is moderate.
- (6)
- Coefficient of Variation
The coefficient of variation is a statistical measure used to compare the degree of dispersion of different data sets, which has been widely used in tourism research to measure spatial disparities in tourism development. It effectively captures the degree of spatial dispersion in tourism attention across different regions [36]. The formula is as follows:
where i is the provincial administrative region; Xi is the ith provincial administrative region to Zhangjiajie National Forest Park tourism network attention; is the average network attention of Zhangjiajie National Forest Park tourism; CV value that is, the larger the coefficient of variation, indicating that the spatial distribution of Zhangjiajie National Forest Park tourism network attention is more uneven, the more obvious the difference, and vice versa.
- (7)
- Herfindahl–Hirschman Index
The Herfindahl–Hirschman index (HHI), originally developed for measuring market concentration in industrial economics, which effectively measures the spatial concentration of tourism markets across different regions, and helps evaluate the evolution of market structure and competition patterns in tourism destinations, indicating potential monopolistic behaviors [37]. The formula is as follows
The formula is as follows: H is Herfindahl–Hirschman index, Sa is the ratio of a province’s network attention to the national total attention, and the closer the value of H is to 1, the higher the market concentration is.
- (8)
- Geodetector
The geographical detector is an innovative spatial statistical method for detecting spatial stratified heterogeneity and revealing its driving factors. This method’s unique strengths in analyzing spatial differentiation mechanisms make it ideal for this study. The geographical detector has several distinct advantages, including (1) it can detect both linear and nonlinear relationships between factors and spatial patterns; (2) it effectively reveals interaction effects between different factors; and (3) it quantifies the relative importance of each factor through factor detection q-values [38]. In this study, we employ two core functions of the geographical detector:
- 1.
- Factor Detection
Factor detection: It is used to measure the explanatory power of individual influencing factors on the spatial divergence of network attention. This analysis helps to pinpoint which factors significantly influence tourism attention patterns.
Among them, q is the explanatory power of detection factor X, i = 1, 2, …, L is the number of layers of detection factor X, N and Ni are the number of units in the study area and layer i, and respectively, and represent the variance of the network attention in the study area and layer i, respectively. q takes the value of 0~1, and the closer to 1, the stronger the influence of the detection factor on spatial differentiation of the network attention in tourism; conversely, the weaker the influence of the detection factor. The closer the value of q is to 1, the stronger the influence of the detection factor on the spatial differentiation of tourism network attention.
- 2.
- Interaction Detection
Interaction detection: It is used to analyze the effect of the interaction of two factors on the spatial variance of online attention. The interaction of the two factors is q(X1 ∩ X2), and by comparing q(X1), q(X2) and q(X1 ∩ X2), we can determine the strength of the interaction and the type of interaction of each probe factor (Table 1). This analysis provides insight into how factors interact with each other to shape tourism attention patterns.

Table 1.
Types of interaction between two factors.
4. Results
To test whether inter-provincial and inter-annual differences in tourism network attention are statistically significant, two one-way ANOVA tests were conducted. The first treated provinces as groups (each containing 11 yearly observations), while the second considered years as groups (each with 31 provincial observations). The province-based ANOVA yielded a highly significant result (F = 28.29, p < 0.001), indicating substantial spatial disparities in online tourism interest across China’s provinces. Similarly, the year-based ANOVA was also statistically significant (F = 7.86, p < 0.001), suggesting that tourism network attention has undergone notable fluctuations over time from 2013 to 2023. This discovery provides a solid foundation for the subsequent use of methods such as geographic concentration index, coefficient of variation, and geographic detectors in this study to deeply analyze its spatial pattern characteristics and reveal the underlying driving mechanisms.
4.1. Temporal Evolution Analysis
Network attention for Zhangjiajie National Forest Park demonstrated three distinct phases over 2013–2023 (Figure 1). During the rapid rise phase (2013–2017), annual searches increased from 5.45 to 11.93 million (118.86% growth). Mobile usage expanded from 35.17% to 56.42%, reflecting broader digitalization trends. The fluctuation adjustment phase (2018–2020) maintained high attention levels (7.11–10.70 million) but with increased volatility. COVID-19 reduced 2020 attention by 33.6% compared to 2019, demonstrating the destination’s vulnerability to external shocks. The recovery phase (2021–2023) saw attention rebound to 9.35 million by 2023, with mobile searches reaching 82.61%. Notably, 2023 marked the first year when spring attention exceeded traditional summer peaks, indicating evolving tourist preferences toward off-peak travel.
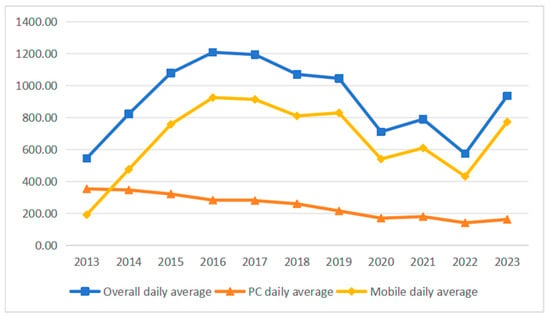
Figure 1.
Inter-annual change in attention network in Zhangjiajie National Forest Park from 2013 to 2023 (million).
Seasonal Evolution Patterns. The temporal analysis reveals a consistent “bimodal” distribution with primary peaks in July–August (averaging 12.96% of annual attention) and secondary peaks in April–May (Figure 2). However, 2023 marked a significant shift with spring attention (13.67% in April, 16.39% in May) exceeding summer levels for the first time. This change possibly reflects post-pandemic travel preference shifts toward avoiding peak-season crowds and the influence of extended holiday policies such as the five-day Labor Day holiday (Table 2).
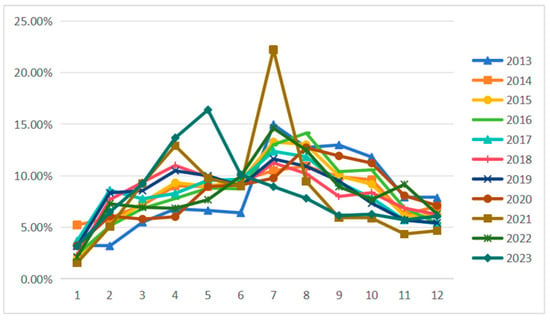
Figure 2.
Monthly attention network accounts for the proportion of the whole year from 2013 to 2023.

Table 2.
Seasonal intensity index of network attention in each month from 2013 to 2023 (ten thousand).
Holiday Effect Analysis. Long holidays consistently generated the highest attention levels, with National Day periods showing peak activity. National Day 2016 reached the highest recorded daily attention of 243,800 searches (Figure 3). The pandemic temporarily disrupted these patterns in 2020, with all holiday attention declining significantly before recovering to pre-pandemic levels by 2021–2023 (Table 3).
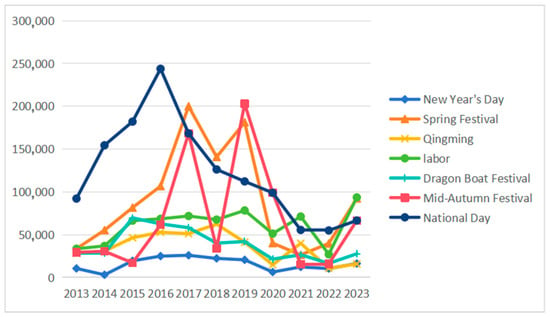
Figure 3.
Holidays changes in attention network from 2013 to 2023.

Table 3.
Skewness index of intra-week distribution.
4.2. Spatial Distribution Evolution
Spatial analysis reveals progressive geographic convergence in tourism attention distribution despite persistent regional hierarchies (Table 4). The coefficient of variation decreased from 0.6849 (2013) to 0.5382 (2023), while the geographic concentration index declined from 4.7390 to 4.1603, indicating reduced spatial concentration. The Herfindahl–Hirschman index remained stable around 0.04 with primacy indices below 2.0, confirming no regional monopoly exists.

Table 4.
Spatial differences of network attention from 2013 to 2023 (ten thousand).
The spatial evolution over the full study period is presented in Appendix A Figure A1, while key representative years are shown below.
The spatial pattern maintains a persistent “East High, West Low” structure throughout the study period (Figure 4). Eastern coastal provinces (Guangdong, Jiangsu, Zhejiang) and central provinces (Hunan, Henan, Hubei) consistently dominate attention levels due to three causal factors: superior transportation infrastructure providing direct access, higher economic capacity enabling tourism consumption, and concentrated digital marketing presence. Western provinces (Tibet, Qinghai, Xinjiang) and northeastern regions show substantially lower engagement primarily due to distance barriers, limited direct connectivity, and lower per-capita disposable income. COVID-19 temporarily increased spatial concentration in 2020 (CV: 0.5758), but the long-term decentralization trend resumed by 2021–2023.
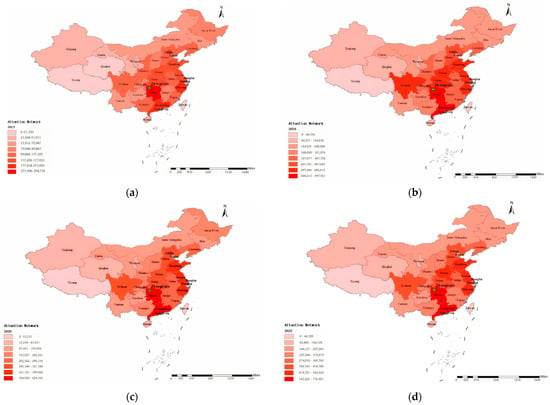
Figure 4.
Spatial distribution evolution of tourism network attention across four critical periods: (a) 2013 baseline; (b) 2016 growth peak; (c) 2020 pandemic impact; (d) 2023 recovery phase.
Regional growth patterns demonstrate spatial convergence despite persistent hierarchical differences. Western and central provinces achieved faster growth rates (19.65% and 13.01% respectively) than eastern provinces (5.84%), yet absolute attention levels remain concentrated in economically developed regions, with Guangdong maintaining market leadership throughout the study period (Table 5). Detailed provincial-level data (Appendix A Table A1).

Table 5.
Regional summary statistics.
4.3. Geodetection of Impact Factors
4.3.1. The Factor Detection Framework
Geodetector analysis was applied to identify key drivers of spatial differentiation in tourism attention using data from 2014 and 2023, representing periods of significant spatial variation. Eight factors across four dimensions were examined: economic development (per-capita disposable income, GDP), urbanization level, informatization degree (internet users), geographical accessibility (distance, flight time), and ecological environment quality (forest coverage, air quality index) (Table 6).

Table 6.
Influencing factor index system of spatial differentiation.
4.3.2. Single-Factor Detection Results
Geodetector analysis reveals significant shifts in factor influence between 2014 and 2023. In 2014, six factors passed significance testing (p < 0.05), led by per-capita disposable income (q = 0.465), internet users (q = 0.420), and flight time (q = 0.419). By 2023, only three factors remained significant: GDP (q = 0.801), internet users (q = 0.781), and geographic distance (q = 0.757). This convergence indicates that tourism attention patterns have become increasingly driven by fundamental structural advantages—regional economic capacity, digital infrastructure, and spatial accessibility—rather than diverse individual factors, suggesting systematic causal mechanisms rather than random influences (Table 7).

Table 7.
Detection results of impact factors.
Comparison of q-values of individual factors in 2014 and 2023 reveals: Most notably, GDP has displaced individual income as the dominant influence factor, with its explanatory power surging from q = 0.390 to q = 0.801. This shift reflects a fundamental change in tourism dynamics, where regional economic capacity now serves as the primary driver through interconnected mechanisms. This transformation suggests that structural economic forces have gained precedence over individual wealth considerations in shaping tourism attention patterns. Equally significant is the intensification of informatization’s influence, rising from q = 0.420 to q = 0.781. This evolution demonstrates how digital infrastructure has become a fundamental enabler of tourism attention rather than merely a communication tool. Enhanced information accessibility reduces search costs for potential visitors, while social media platforms exponentially multiply marketing reach and impact.
4.3.3. Factor Interaction Detection Analysis
Factor interaction analysis reveals that all two-factor combinations exhibit higher q-values than individual factors, indicating significant synergistic effects in determining spatial differentiation (Table 8). The analysis demonstrates that tourism attention patterns result from multiple factor interactions rather than single-factor influences.

Table 8.
Detection results of factor interaction.
Three key interaction patterns emerged: First, economic factors (X1, X2) demonstrate consistently strong interactions with other variables, with GDP × Forest coverage showing enhanced synergy (q: 0.895→0.978). Second, informatization interactions intensified significantly, particularly Internet users × Forest coverage (q: 0.854→0.976), reflecting digitalization’s growing role in nature-based tourism promotion. Third, traditional accessibility advantages weakened, as evidenced by declining Income × Flight time interactions (q: 0.949→0.701), potentially reflecting transportation infrastructure improvements reducing spatial differentiation. The results confirm that spatial patterns emerge from complex factor interdependencies, with economic development serving as the primary catalyst that amplifies the effects of informatization, accessibility, and environmental quality factors.
5. Discussion
In the evolving tourism landscape, the push–pull theory illustrates a complex interplay, where economic development and digital engagement are pivotal. This interaction signals that travelers today weigh economic strength and digital accessibility more heavily than before.
5.1. Theoretical Contributions
This study significantly contributes to tourism geography by revealing that network attention is not only a proxy for ecological tourism demand in forest park settings but also indicates profound shifts in consumer behavior driven by digital engagement strategies. Specifically, our findings reveal that push factors, especially GDP, play a more substantial role in tourist decision making compared to pull factors like ecological appeal. This challenges the conventional push–pull balance, suggesting that economic motivations such as employment and wealth may create greater demand for tourism than ecological factors alone. Moreover, the interaction effects among multiple factors exceed the influence of individual components (q > 0.85), reinforcing the notion that destination attention results from complex interdependencies, where synergies across various elements (like economic capacity and digital engagement) play a crucial role in shaping consumer perceptions. Acknowledging the limitations of a single-case study, this methodological framework offers transferable tools that can be adapted to analyze tourism trends across diverse natural destinations, thereby enhancing the broader applicability of the results.
5.2. Push–Pull Dynamics and Causal Mechanisms
The ‘East high, West low’ pattern underscores the intricate interplay of push–pull dynamics shaped by systemic factors. This suggests that while environmental quality attracts visitors equally, regional economic capabilities and infrastructure primarily determine attention levels [39]. Although Zhangjiajie’s ecological quality creates universal appeal, this insight reveals that effectively addressing regional disparities requires a more focused approach on improving digital infrastructure and economic conditions in less developed areas. Specifically, eastern regions benefit from multiplicative advantages: economic capacity (higher GDP) combines with infrastructure accessibility (direct flights) and digital connectivity (higher internet penetration) to create disproportionate attention levels compared to western regions, where these enabling conditions are limited. The paradoxical increase in geographic distance influence (q: 0.257→0.757) despite transportation improvements reveals a causal mechanism, where improved connectivity paradoxically increases distance sensitivity. Enhanced transportation infrastructure creates awareness of travel possibilities in distant regions, but simultaneously elevates travelers’ sensitivity to costs associated with travel, complicating their decision-making processes. This suggests that while connectivity enhances awareness of distant areas, it also elevates travelers’ sensitivity to costs associated with travel, complicating their decision-making processes. The augmented distance-attention relationship highlights the complexity of consumer behavior in the context of improved connectivity.
5.3. Comparative Analysis with Other Natural Tourism Destinations
The comparative analysis positions Zhangjiajie uniquely among Chinese natural destinations, illuminating distinct characteristics that underscore its reliance on promotional efforts. This analysis reveals that Zhangjiajie’s unique branding and marketing strategies are crucial for its visibility in a competitive landscape. Unlike established sites such as Jiuzhaigou which benefit from stable temporal patterns due to mature brand recognition, Zhangjiajie’s attention volatility indicates a pronounced reliance on marketing strategies, suggesting that this volatility emphasizes the need for Zhangjiajie to reinforce its branding through innovative marketing strategies to achieve consistency akin to more established destinations [40]. The observed spatial concentration in eastern provinces (73.2%) aligns with broader Chinese tourism patterns, where network attention correlates with regional economic development [41]. While this study focuses on Zhangjiajie as a representative case, it demonstrates consistency with broader Chinese forest park tourism characteristics documented in recent studies [6]. However, Zhangjiajie’s seasonal shift toward spring dominance differs from traditional summer peak patterns, indicating successful temporal diversification compared to conventional Chinese forest tourism destinations. This shift indicates successful strategic adaptation, suggesting the importance of diversifying marketing efforts to capture off-peak travelers. The findings highlight key strategic implications for tourism management and marketing, specifically the necessity to leverage digital engagement to enhance outreach while optimizing marketing expenditure across different seasons.
5.4. Limitations and Future Research
The findings offer practical guidance for forest park management and marketing strategies. The insights derived from this study can inform strategic decisions and operational improvements in forest park management. Given informatization’s growing influence, destinations should prioritize digital engagement initiatives over traditional marketing approaches. Destinations should invest resources in enhancing their digital presence, utilizing social media and mobile platforms to connect with potential visitors. The spatial analysis reveals significant opportunities for western market expansion through targeted accessibility improvements and region-specific promotional campaigns. Future studies might investigate methodologies for utilizing social media analytics to track and predict shifts in tourist preferences over time. We advocate for interdisciplinary approaches, such as leveraging Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and big data analysis, to gain a comprehensive understanding of visitor behavior. While this single-case study of Zhangjiajie provides detailed insights, direct generalizability requires careful consideration. However, several factors support broader applicability of the results. The analytical framework combining temporal indices, spatial analysis, and geodetector methods offers methodological transferability to other forest destinations. Future comparative studies involving multiple forest parks would strengthen these theoretical contributions, while the methodological approach provides researchers with a tested framework for such investigations.
6. Conclusions
This study investigates the evolution of tourism network attention for Zhangjiajie National Forest Park from 2013 to 2023,uncovering significant patterns and implications. The analysis underscores the pivotal role of economic conditions and digital accessibility in influencing tourist behavior, demonstrating that these factors may overshadow traditional ecological considerations. Among the factors examined, the findings reveal that both regional GDP and internet user numbers significantly influence attention trends, highlighting the correlation between economic power and digital accessibility. This study significantly contributes to tourism geography by revealing that digital search data are not only an effective indicator of interest in ecological tourism but also a tool for predicting future tourism trends. Using the push–pull theoretical framework, the results indicate that while ecological quality at the destination remains relatively even, differences in market characteristics at the origin play a greater role in shaping spatial attention patterns. Furthermore, this study finds that interactions between multiple factors have a stronger impact than any single factor, suggesting that future research should examine these nonlinear mechanisms behind changes in digital attention.
These findings lead to actionable strategies for effective tourism planning and promotion. Effective digital marketing strategies should incorporate mobile search trends to promote targeted outreach, especially focusing on spring tourism, as our study indicates that this season is becoming increasingly favored by travelers. This study recognizes several limitations. While this study provides significant insights, attention must be given to the discrepancies between online interest and actual travel behavior. Future research should expand the scope of study, adopt multiple data sources, compare the results of multiple national forest parks in China, and improve the general applicability of the research results.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.W. and S.B.; methodology, Y.W.; software, Y.W.; validation, Y.W.; formal analysis, Y.W.; investigation, Y.W.; data curation, Y.W.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.W.; writing—review and editing, S.B.; visualization, S.B. and S.J.; supervision, S.B. and S.J.; project administration, S.B. and S.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original data can be provided at any time during the review process as requested by the reviewers.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Network attention in various regions from 2013 to 2023 (ten thousand).
Table A1.
Network attention in various regions from 2013 to 2023 (ten thousand).
| 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peking | 22.54 | 44.28 | 53.00 | 58.28 | 51.80 | 48.90 | 44.58 | 36.28 | 40.70 | 23.91 | 41.48 |
| Tianjin | 11.29 | 21.79 | 25.51 | 26.69 | 23.46 | 21.70 | 21.57 | 15.59 | 17.60 | 12.46 | 19.02 |
| Hebei | 11.59 | 30.97 | 41.80 | 45.02 | 44.71 | 41.19 | 41.76 | 28.95 | 34.06 | 23.36 | 38.97 |
| Shanghai | 15.93 | 33.49 | 47.83 | 49.70 | 48.70 | 42.68 | 39.27 | 30.13 | 34.79 | 23.31 | 32.71 |
| Jiangsu | 17.70 | 47.98 | 62.71 | 68.66 | 68.46 | 60.11 | 55.68 | 39.99 | 53.54 | 34.21 | 54.26 |
| Zhejiang | 19.98 | 42.82 | 55.70 | 63.91 | 57.98 | 52.07 | 54.16 | 34.65 | 39.46 | 28.66 | 45.53 |
| Fujian | 10.52 | 26.68 | 33.38 | 40.18 | 40.16 | 34.54 | 35.48 | 22.05 | 23.74 | 17.62 | 27.68 |
| Shandong | 14.53 | 40.28 | 52.75 | 57.31 | 57.54 | 55.07 | 53.34 | 37.80 | 45.28 | 31.78 | 52.25 |
| Guangdong | 27.31 | 65.50 | 85.06 | 99.76 | 93.16 | 80.42 | 76.63 | 54.79 | 54.04 | 42.87 | 71.56 |
| Hainan | 4.17 | 9.74 | 11.42 | 12.76 | 13.04 | 12.78 | 11.84 | 8.74 | 9.54 | 7.61 | 12.18 |
| Shanxi | 7.88 | 21.49 | 29.17 | 32.19 | 33.21 | 30.10 | 30.14 | 18.90 | 21.98 | 15.48 | 25.65 |
| Anhui | 9.67 | 24.54 | 31.79 | 35.67 | 40.84 | 36.66 | 33.69 | 23.94 | 27.22 | 20.30 | 32.27 |
| Jiangxi | 8.99 | 22.98 | 32.86 | 36.92 | 38.12 | 34.03 | 30.65 | 21.63 | 21.19 | 16.43 | 27.36 |
| Henan | 16.84 | 40.87 | 57.92 | 64.17 | 59.93 | 54.35 | 48.55 | 32.12 | 37.19 | 25.73 | 46.92 |
| Hubei | 16.98 | 37.29 | 54.01 | 57.66 | 55.46 | 46.82 | 43.63 | 27.57 | 30.54 | 23.32 | 39.05 |
| Hunan | 39.47 | 80.86 | 103.8 | 96.06 | 94.32 | 76.89 | 74.23 | 62.92 | 66.15 | 54.62 | 71.47 |
| Inner Mongolia | 6.21 | 14.66 | 17.18 | 20.66 | 21.07 | 20.27 | 20.29 | 13.56 | 15.53 | 11.80 | 19.41 |
| Guangxi | 9.39 | 21.91 | 28.03 | 31.51 | 31.19 | 32.41 | 32.05 | 17.50 | 17.97 | 14.25 | 26.38 |
| Chongqing | 8.13 | 22.62 | 30.70 | 35.48 | 37.65 | 28.45 | 30.94 | 19.84 | 21.40 | 14.37 | 25.52 |
| Sichuan | 10.13 | 27.34 | 46.42 | 68.26 | 59.78 | 45.95 | 46.70 | 30.90 | 32.73 | 21.55 | 38.93 |
| Guizhou | 6.45 | 17.71 | 24.00 | 29.36 | 32.54 | 27.93 | 32.77 | 15.35 | 14.83 | 11.37 | 21.04 |
| Yunnan | 6.25 | 14.76 | 18.70 | 22.81 | 24.89 | 23.00 | 24.80 | 15.18 | 15.72 | 12.13 | 21.68 |
| Xizang | 1.10 | 2.56 | 3.66 | 4.04 | 4.32 | 4.66 | 4.32 | 3.32 | 3.50 | 2.93 | 4.24 |
| Shaanxi | 10.09 | 26.27 | 35.70 | 40.15 | 38.03 | 33.14 | 31.31 | 20.26 | 23.00 | 17.59 | 27.18 |
| Gansu | 5.11 | 12.75 | 15.06 | 18.34 | 18.99 | 18.78 | 18.40 | 12.06 | 12.18 | 9.13 | 16.74 |
| Qinghai | 2.15 | 6.46 | 7.44 | 8.53 | 8.67 | 8.44 | 7.86 | 5.98 | 6.10 | 4.24 | 7.20 |
| Ningxia | 3.19 | 8.82 | 9.70 | 11.32 | 10.80 | 10.38 | 9.99 | 6.91 | 7.59 | 5.88 | 9.30 |
| Xinjiang | 5.19 | 11.90 | 12.05 | 14.48 | 15.98 | 13.47 | 13.06 | 8.38 | 10.38 | 8.60 | 14.41 |
| Liaoning | 11.72 | 24.48 | 34.09 | 36.47 | 41.41 | 38.52 | 40.19 | 24.53 | 28.58 | 20.14 | 34.28 |
| Jilin | 7.09 | 16.46 | 19.64 | 24.11 | 25.18 | 23.67 | 24.89 | 15.20 | 17.73 | 12.53 | 20.67 |
| Amur River | 7.67 | 17.12 | 20.29 | 24.80 | 26.07 | 24.02 | 26.83 | 17.11 | 18.91 | 13.84 | 22.59 |
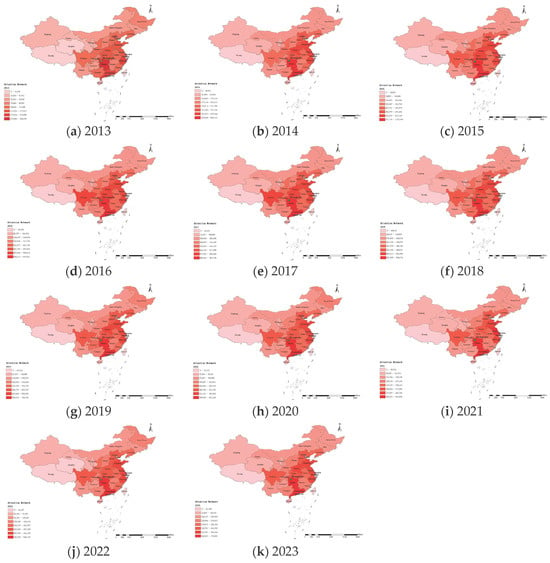
Figure A1.
Provincial distribution of network attention from 2013 to 2023.
References
- Zhang, G.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y. Spatio-temporal evolution characteristics and spatial interaction of tourism network attention: A case study of 5A-level tourist attractions in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Dai, Y. China afforested 2.783 million hectares of desertified and rocky land in 2024, according to the National Greening Bulletin. Tencent News, 12 March 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Xu, L.; Tang, L.; Wang, S.; Li, L. Big data in tourism research: A literature review. Tour. Manag. 2018, 68, 301–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, L.; Ding, Y. The Baidu Index: Uses in predicting tourism flows—A case study of the Forbidden City. Tour. Manag. 2017, 58, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.B. Spatio-temporal Characterization of Potential Demand for Tourist Attractions Based on Internet Search. SAGE Open 2025, 15, 21582440251323550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Dong, D.; Ji, F.; Tai, Y.; Li, N.; Huang, R.; Xiao, T. A Study on Spatiotemporal Evolution and Influencing Factors of Chinese National Park Network Attention. Land 2024, 13, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Moreno, S.; González-Fernández, A.M.; Muñoz-Gallego, P.A. Big data in tourism marketing: Past research and future opportunities. Span. J. Mark.-Esic 2024, 28, 266–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbai, I.; Krichen, S.; Elgammal, I. An Adapted NSGA-II Algorithm for Integrated Timetabling and Bus Packing Problems: A Case of Pilgrims Transportation Problem. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Decision Aid and Artificial Intelligence (ICODAI 2024); Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2025; Volume 12, p. 78. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Wang, J.; Xu, C.; Song, Y. Modeling of spatial stratified heterogeneity. GIScience Remote Sens. 2022, 59, 1660–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cheng, Y.; Mao, Y.; Cai, W.; Zhao, B. What are the factors influencing recreational visits to national forest parks in China? Experiments using crowdsourced geospatial data. Urban For. Urban Green. 2022, 72, 127570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Li, H.; Song, H.; Li, X. Tourism demand forecasting using short video information. Ann. Tour. Res. 2024, 109, 103838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Wang, L.; Sun, M.; Jiang, J. Analysis of spatial patterns and driving factors of provincial tourism demand in China using big data from web search engines. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2260. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.F.; Xu, C.D. Geodetector: Principle and prospective. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 116–134. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Chi, L.; Zhang, T.; Ju, H. Spatio-temporal pattern and influencing factors of border tourism efficiency in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2024, 34, 2288–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Hu, T.; Wu, H. Tourism demand with subtle seasonality: Recognition and forecasting. Tour. Econ. 2023, 29, 1865–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Haining, R.; Zhang, T.; Xu, C.; Hu, M.; Yin, Q.; Li, L.; Zhou, C.; Li, G.; Chen, H. Statistical modeling of spatially stratified heterogeneous data. Ann. Am. Assoc. Geogr. 2024, 114, 499–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Sun, H.; Lin, Q.; Lin, K.; Chong, K.M. Public network attention to hiking in China and its influencing factors. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0306726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, W. Spatiotemporal characteristics and influencing factors of network attention to resort hotels in China. Heliyon 2024, 10, e35314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Zhao, B.; Feng, Y. Spatial distribution and influencing factors of rural tourism: A case study of Henan Province. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Liang, S. Structural characteristics and influencing factors of a spatial correlation network for tourism environmental efficiency in China. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Pan, C.; Xu, F. The spatial structure and influencing factors of the tourism economic network in the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration. Tour. Hosp. 2024, 5, 60–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dann, G.M.S. Anomie, ego-enhancement and tourism. Ann. Tour. Res. 1977, 4, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crompton, J.L. Motivations for pleasure vacation. Ann. Tour. Res. 1979, 6, 408–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, S.; Morelli, M.; Mubushar, M.; Centobelli, P.; Cerchione, R. Encouraging user-generated content to engage travellers in rural tourism of developing countries. Curr. Issues Tour. 2025, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Niu, S.; Miao, M. Urban economic resilience within the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration: Exploring spatially correlated network and spatial heterogeneity. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 103, 105270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgammal, I.; Jones, E. Using discourse analysis to explore the achievability of triple bottom line sustainability (TBLS): The case of the bluestone holiday village. Acad. Renew. Innov. Leis. Tour. Theor. Methods 2007, 2, LSA-97. [Google Scholar]
- Zhangjiajie National Forest Park Administration. (n.d.). Scenic Area Introduction. Available online: http://www.hnzjj.com/index.php/Product/list/7.html (accessed on 29 June 2024).
- Song, Z.; Coupé, T. Predicting Chinese consumption series with Baidu. J. Chin. Econ. Bus. Stud. 2023, 21, 429–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, R.X.; Wu, C.; Liang, H.M. Exploring Appropriate Search Engine Data for Interval Tourism Demand Forecasting Responding a Public Crisis in Macao: A Combined Bayesian Model. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics. [China Statistical Yearbook]. National Bureau of Statistics Official Website. 2025. Available online: https://www.stats.gov.cn/sj/ndsj/ (accessed on 20 May 2025).
- Rutty, M.; Scott, D.; Matthews, L.; Burrowes, R.; Trotman, A.; Mahon, R.; Charles, A. An inter-comparison of the Holiday Climate Index (HCI: Beach) and the Tourism Climate Index (TCI) to explain Canadian tourism arrivals to the Caribbean. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogowski, M.; Zawilińska, B.; Hibner, J. Managing tourism pressure: Exploring tourist traffic patterns and seasonality in mountain national parks to alleviate overtourism effects. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 373, 123430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Wei, Y.; Tsui, K.L.; Wang, S. Forecasting tourist arrivals with machine learning and internet search index. Tour. Manag. 2019, 70, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, K.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Z. Analysis of tourist market structure and its driving factors in small cities before and after COVID-19. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2023, 12, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jefferson, M. Why geography? The law of the primate city. Geogr. Rev. 1989, 79, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Zhang, L.; Sun, H.; Chen, F.; Zhou, C. Spatiotemporal difference characteristics and influencing factors of tourism urbanization in China’s major tourist cities. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 10414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solarin, S.A. Convergence of tourism market diversification: Evidence from a new indicator based on Herfindahl–Hirschman index. Qual. Quant. 2025, 59, 663–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Li, X.H.; Christakos, G.; Liao, Y.L.; Zhang, T.; Gu, X.; Zheng, X.Y. Geographical detectors-based health risk assessment and its application in the neural tube defects study of the Heshun Region, China. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 107–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Chen, W.; Wu, D.; Zheng, L.; Li, J. Spatiotemporal evolution and influencing factors of tourism development efficiency in the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 379, 134722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.W.; Liu, Y.; Fan, Z.P.; Zhang, J. Daily tourism volume forecasting for tourist attractions. Ann. Oper. Res. 2020, 287, 411–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ge, Q. Spatial association network of economic resilience and its influencing factors: Evidence from 31 Chinese provinces. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2023, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).