Sustainable Management of Fruit By-Products Through Design Thinking: Development of an Innovative Food Product
Abstract
1. Introduction
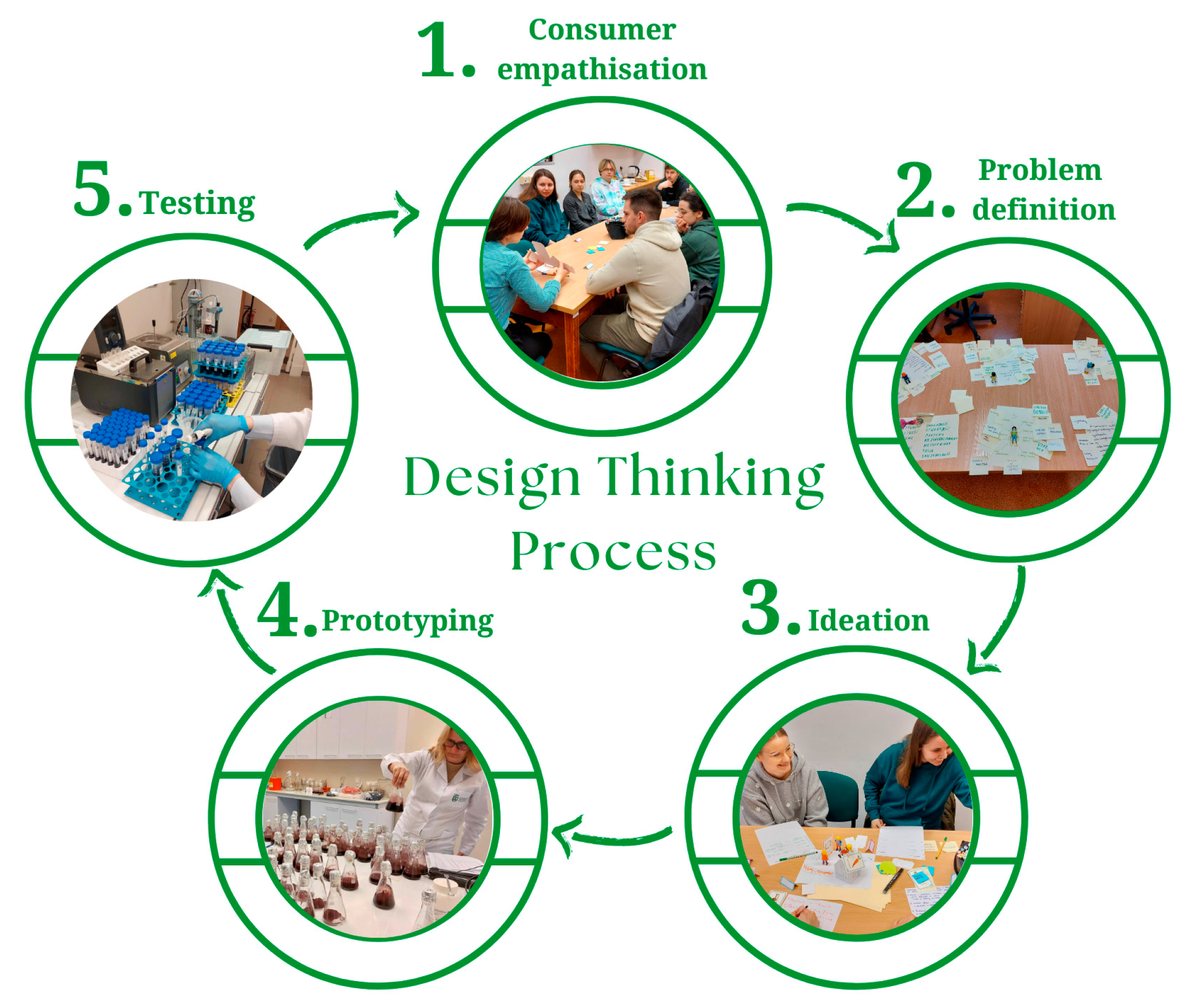
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Empathising with the Consumer and Defining the Problem
2.2. Generation of Ideas
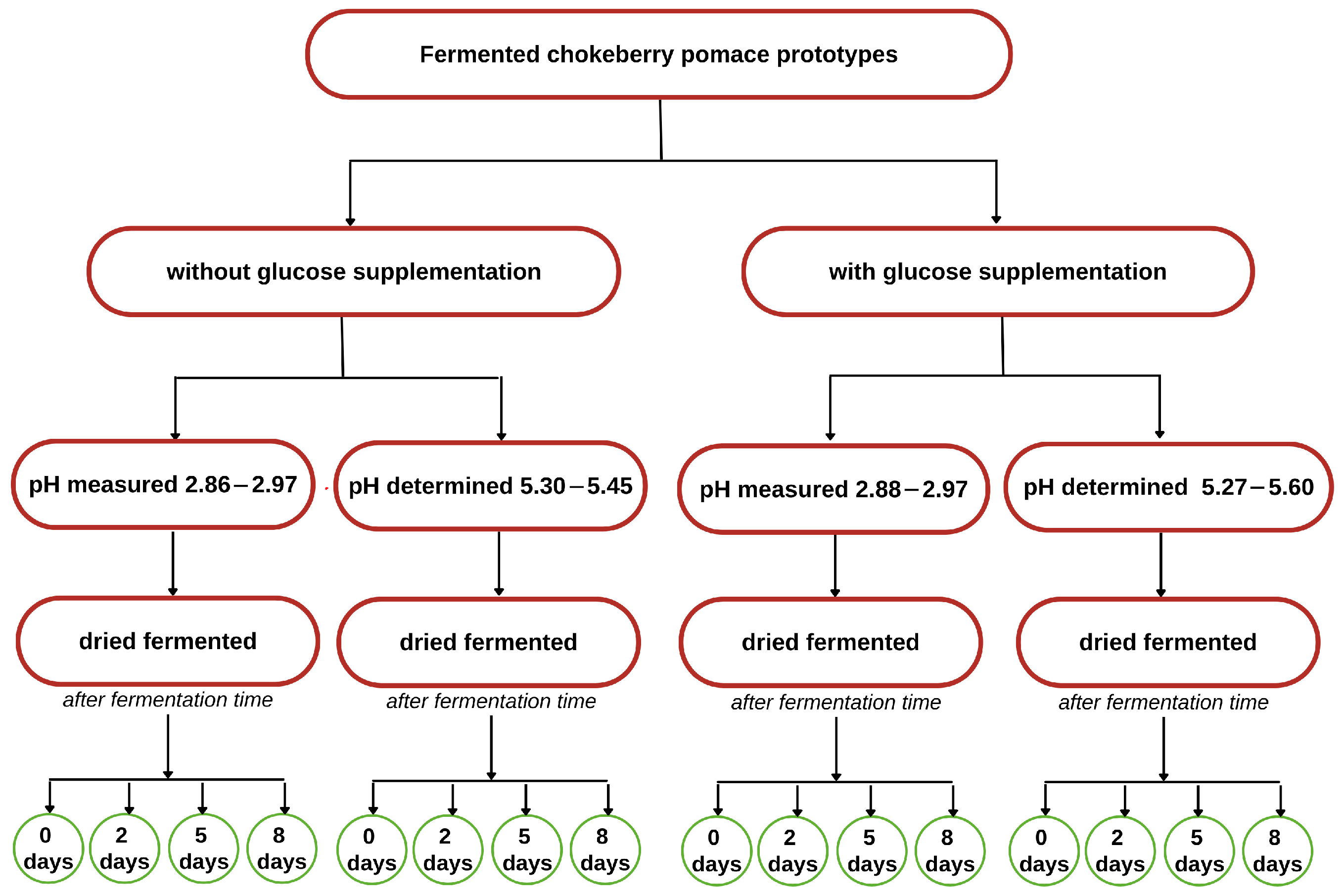
2.3. Development of Prototypes
2.4. Methods of Prototype Testing
2.4.1. Total Polyphenol Content (TPC)
2.4.2. Total Anthocyanin Content (TAC)
2.4.3. Total Proanthocyanidins (TPAC)
2.4.4. ABTS Assay
2.4.5. FRAP Assay
2.4.6. CUPRAC Assay
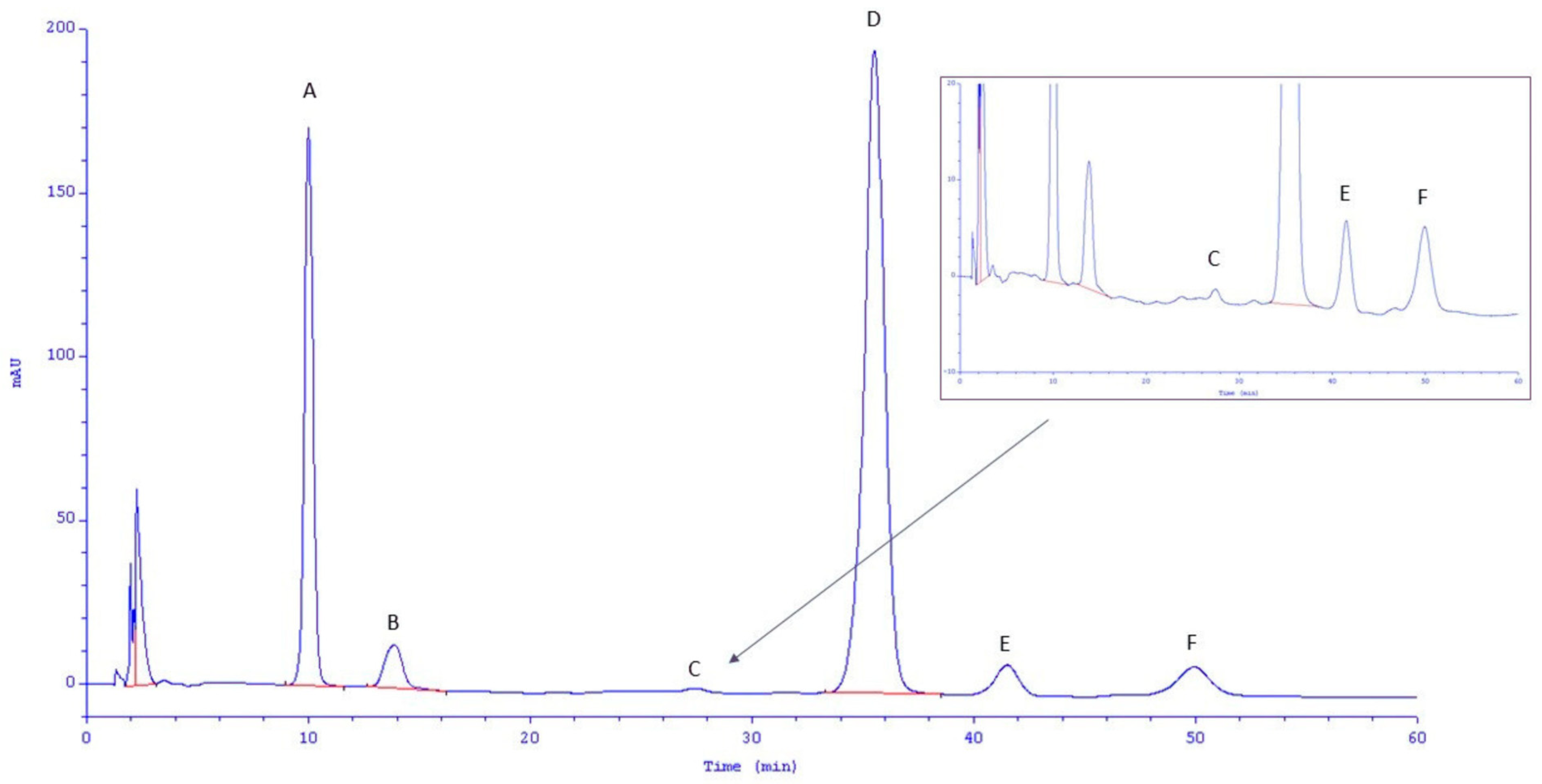
2.4.7. HPLC Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Empathising with the Consumer
3.2. Problem Definition
- The product should consist of natural ingredients and limited food additives whenever possible while remaining attractive to consumers in line with the ‘clean label’ trend;
- The product should be characterised by a sustainable approach to using chokeberry processing by-products, encouraging the use of a circular bioeconomy;
- The product should have a higher antioxidant potential than a conventional product;
- The product should maintain a low processing degree.
3.3. Ideation
3.4. Prototyping
3.5. Testing
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Horvat, A.; Granato, G.; Fogliano, V.; Luning, P.A. Understanding consumer data use in new product development and the product life cycle in European food firms–An empirical study. Food Qual. Prefer. 2019, 76, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachołek, B. Produkty Uboczne Przetwórstwa Owoców w Projektowaniu Żywności, 1st ed.; Wydawnictwo Uniwersytetu Ekonomicznego w Poznaniu: Poznan, Poland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tkaczewska, J.; Kulawik, P.; Morawska-Tota, M.; Zając, M.; Guzik, P.; Tota, Ł.; Pająk, P.; Duliński, R.; Florkiewicz, A.; Migdał, W. Protocol for designing new functional food with the addition of food industry by-products, using design thinking techniques—A case study of a snack with antioxidant properties for physically active people. Foods 2021, 10, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bebek Markovinović, A.; Putnik, P.; Bosiljkov, T.; Kostelac, D.; Frece, J.; Markov, K.; Žigolić, A.; Kaurinović, J.; Pavlić, B.; Duralija, B.; et al. 3D printing of functional strawberry snacks: Food design, texture, antioxidant bioactive compounds, and microbial stability. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costantini, E.; Boakye-Yiadom, K.A.; Ilari, A.; Foppa Pedretti, E.; Duca, D. Environmental impact assessment of new sea fennel-based food products: Spice and fermented pickles. Sustainability 2025, 17, 1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, M.K.; Zahid, A.; Shah, F.-H. Role of food product development in increased food consumption and value addition. In Food Processing for Increased Quality and Consumption, 1st ed.; Grumezescu, A.M., Holban, A.M., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2018; Volume 18, pp. 455–479. [Google Scholar]
- Pinna, C.; Galati, F.; Rossi, M.; Saidy, C.; Harik, R.; Terzi, S. Effect of product lifecycle management on new product development performances: Evidence from the food industry. Comput. Ind. 2018, 100, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinel, C.; Leifer, L.; Plattner, H. Design Thinking: Understand–Improve–Apply, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Buhl, A.; Schmidt-Keilich, M.; Muster, V.; Blazejewski, S.; Schrader, U.; Harrach, C.; Schäfer, M.; Süßbauer, E. Design thinking for sustainability: Why and how design thinking can foster sustainability-oriented innovation development. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 231, 1248–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolniak, R.; Łyp-Wrońska, K. Wykorzystanie metody QFD w koncepcji Design Thinking. Zesz. Nauk.-Polit. Śl. Organ. Zarz. 2018, 131, 549–559. [Google Scholar]
- Massari, S. Food design and food studies: Discussing creative and critical thinking in food system education and research. Int. J. Food Des. 2017, 2, 117–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikelsone, E.; Cirule, I. Design thinking approach to create impact assessment tool: Cities2030 case study. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veflen Olsen, N. Design thinking and food innovation. In Proceedings of the 8th International European Forum on System Dynamics and Innovation in Food Networks, Innsbruck-Igls, Austria, 17–21 February 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Batat, W.; Addis, M. Designing food experiences for well-being: A framework advancing design thinking research from a customer experience perspective. Eur. J. Mark. 2021, 55, 2392–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panghal, A.; Janghu, S.; Virkar, K.; Gat, Y.; Kumar, V.; Chhikara, N. Potential non-dairy probiotic products–A healthy approach. Food Biosci. 2018, 21, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, M.; Bunt, C.R.; Mason, S.L.; Hussain, M.A. Non-dairy probiotic food products: An emerging group of functional foods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 2626–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-Y.; Chen, J.; Li, X.-L.; Yi, K.; Ye, Y.; Liu, G.; Wang, S.-F.; Hu, H.-L.; Zou, L.; Wang, Z.-G. Dynamic changes in antioxidant activity and biochemical composition of tartary buckwheat leaves during Aspergillus niger fermentation. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 32, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verni, M.; Verardo, V.; Rizzello, C. How fermentation affects the antioxidant properties of cereals and legumes. Foods 2019, 8, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erskine, E.; Ozkan, G.; Lu, B.; Capanoglu, E. Effects of fermentation process on the antioxidant capacity of fruit byproducts. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 4543–4553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hur, S.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, Y.-C.; Choi, I.; Kim, G.-B. Effect of fermentation on the antioxidant activity in plant-based foods. Food Chem. 2014, 160, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sady, S. Wytłoki Aronii Jako Komponent Innowacyjnych Osłonek Jadalnych, 1st ed.; Wydawnictwo Uniwersytetu Ekonomicznego w Poznaniu: Poznan, Poland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kapci, B.; Neradova, E.; Cizkova, H.; Voldrich, M.; Rajchl, A.; Capanoglu, E. Investigating the antioxidant potential of chokeberry (Aronia melanocarpa) products. J. Food Nutr. Res. 2013, 52, 219–229. [Google Scholar]
- Błaszczyk, A.; Sady, S.; Pachołek, B.; Jakubowska, D.; Grzybowska-Brzezińska, M.; Krzywonos, M.; Popek, S. Sustainable management strategies for fruit processing byproducts for biorefineries: A review. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oszmiański, J.; Wojdyło, A. Aronia melanocarpa phenolics and their antioxidant activity. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2005, 221, 809–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer-Miebach, E.; Adamiuk, M.; Behsnilian, D. Stability of chokeberry bioactive polyphenols during juice processing and stabilization of a polyphenol-rich material from the by-product. Agriculture 2012, 2, 244–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulf, F.V.; Vodnar, D.C.; Dulf, E.-H.; Diaconeasa, Z.; Socaciu, C. Liberation and recovery of phenolic antioxidants and lipids in chokeberry (Aronia melanocarpa) pomace by solid-state bioprocessing using Aspergillus niger and Rhizopus oligosporus strains. Lebensm.-Wiss. Technol. 2018, 87, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez-Sanchez, E.; Quiles, A.; Hernando, I. Use of berry pomace to design functional foods. Food Rev. Int. 2023, 39, 3204–3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maison, D. Zogniskowane Wywiady Grupowe: Jakościowa Metoda Badań Marketingowych, 1st ed.; Wydawnictwo Naukowe PWN: Warszawa, Poland, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Meini, M.-R.; Cabezudo, I.; Galetto, C.S.; Romanini, D. Production of grape pomace extracts with enhanced antioxidant and prebiotic activities through solid-state fermentation by Aspergillus niger and Aspergillus oryzae. Food Biosci. 2021, 42, 101168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sady, S.; Matuszak, L.; Błaszczyk, A. Optimisation of ultrasonic-assisted extraction of bioactive compounds from chokeberry pomace using response surface methodology. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 2019, 18, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, B.; Muzykiewicz-Szymańska, A.; Ossowicz-Rupniewska, P.; Klimowicz, A.; Janus, E. The application of amino acid ionic liquids as additives in the ultrasound-assisted extraction of plant material. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 25983–25994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giusti, M.M.; Wrolstad, R.E. Characterization and measurement of anthocyanins by UV-visible spectroscopy. Curr. Protoc. Food Anal. Chem. 2001, 1, F1.2.1–F1.2.13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prior, R.L.; Fan, E.; Ji, H.; Howell, A.; Nio, C.; Payne, M.J.; Reed, J. Multi-laboratory validation of a standard method for quantifying proanthocyanidins in cranberry powders: Cranberry proanthocyanidin quantification. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90, 1473–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, A.; Duchnik, W.; Muzykiewicz-Szymańska, A.; Kucharski, Ł.; Zielonka-Brzezicka, J.; Nowak, A.; Klimowicz, A. The changes of antioxidant activity of three varieties of ‘Nalewka’, a traditional polish fruit alcoholic beverage during long-term storage. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, A.; Zagórska-Dziok, M.; Ossowicz-Rupniewska, P.; Makuch, E.; Duchnik, W.; Kucharski, Ł.; Adamiak-Giera, U.; Prowans, P.; Czapla, N.; Bargiel, P.; et al. Epilobium angustifolium L. extracts as valuable ingredients in cosmetic and dermatological products. Molecules 2021, 26, 3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Avila, G.C.; Aguilera-Carbo, A.F.; Rodriguez-Herrera, R.; Aguilar, C.N. Fungal enhancement of the antioxidant properties of grape waste. Ann. Microbiol. 2012, 62, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, I.L.F.; Haren, G.R.; Magnussen, E.L.; Dragsted, L.O.; Rasmussen, S.E. Quantification of anthocyanins in commercial black currant juices by simple high-performance liquid chromatography. Investigation of their pH stability and antioxidative potency. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 5861–5866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.Y.; Zhang, A.; Tsang, D.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Z.-Y. Stability of green tea catechins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 4624–4628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitao, M.; Ferreira, B.; Guedes, B.; Moreira, D.; Garcia, P.A.; Barreiros, L.; Correia, P. Screening of antioxidant effect of spontaneous and bioinoculated with Gluconobacter oxydans fermented papaya: A comparative study. Fermentation 2023, 9, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, P.; Idris, Z.M.; Alam, M.Z. Effects of physicochemical parameters on the production of phenolic acids from palm oil mill effluent under liquid-state fermentation by Aspergillus niger IBS-103ZA. Food Chem. 2011, 124, 1595–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.-H.; Chou, C.-C. Distribution profiles of isoflavone isomers in black bean kojis prepared with various filamentous fungi. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 1309–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vries, R.P.; Visser, J. Aspergillus enzymes involved in degradation of plant cell wall polysaccharides. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2001, 65, 497–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Werner, M.; Winterhalter, P.; Esatbeyoglu, T. Phenolic composition, radical scavenging activity and an approach for authentication of Aronia melanocarpa berries, juice, and pomace. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 1791–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitryte, V.; Kraujaliene, V.; Sulniute, V.; Pukalskas, A.; Venskutonis, P.R. Chokeberry pomace valorization into food ingredients by enzyme-assisted extraction: Process optimization and product characterization. Food Bioprod. Process. 2017, 105, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajila, C.M.; Gassara, F.; Brar, S.K.; Verma, M.; Tyagi, R.D.; Valero, J.R. Polyphenolic antioxidant mobilization in apple pomace by different methods of solid-state fermentation and evaluation of its antioxidant activity. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2012, 5, 2697–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesage-Meessen, L.; Delattre, M.; Haon, M.; Thibault, J.-F.; Ceccaldi, B.C.; Brunerie, P.; Asther, M. A two-step bioconversion process for vanillin production from ferulic acid combining Aspergillus niger and Pycnoporus cinnabarinus. J. Biotechnol. 1996, 50, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, P.L.; Hassan, O. Bioconversion of ferulic acid attained from pineapple peels and pineapple crown leaves into vanillic acid and vanillin by Aspergillus niger I-1472. BMC Chem. 2020, 14, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karegoudar, T.B.; Kim, C.-K. Microbial degradation of monohydroxybenzoic acids. J. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 53–61. [Google Scholar]
- Phang, L.Y.; Abd-Aziz, S.; Gozan, M.; Ibrahim, M.F. Sustainability of Chemical Substitutes from Agricultural and Industrial By-products. In Chemical Substitutes from Agricultural and Industrial By-Products; Abd-Aziz, S., Gozan, M., Ibrahim, M.F., Phang, L.-Y., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 355–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzywonos, M.; Difonzo, G.; Pasqualone, A. Challenges and technological requirements in agri-food waste upcycling: The case study of olive leaf extract. Future Foods 2025, 11, 100547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorvari, J.; Wahlström, M. Industrial By-Products. In Handbook of Recycling: State-of-the-Art for Practitioners, Analysts, and Scientists; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 259–285. [Google Scholar]
- Ueda, J.M.; Pedrosa, M.C.; Heleno, S.A.; Carocho, M.; Ferreira, I.C.; Barros, L. Food additives from fruit and vegetable by-products and bio-residues: A comprehensive review focused on sustainability. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tița, M.A.; Moga, V.M.; Constantinescu, M.A.; Bătușaru, C.M.; Tița, O. Harnessing the potential of Whey in the creation of innovative Food products: Contributions to the Circular Economy. Recycling 2024, 9, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boruah, B.; Ray, S. Current progress in the valorization of food industrial by-products for the development of functional food products. Food Sci. Appl. Biotechnol. 2024, 7, 289–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilas-Franquesa, A.; Montemurro, M.; Casertano, M.; Fogliano, V. The food by-products bioprocess wheel: A guidance tool for the food industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 6, 104652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal Filho, W.; Schmidberger, I.; Sharifi, A.; Vargas, V.R.; Rampasso, I.S.; Dibbern, T.; Liakh, O.; Aina, Y.A.; Trevisan, L.V.; Mbah, M.F.; et al. Design thinking for sustainable development: A bibliometric analysis and case study research. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 455, 142285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, L.; Parker, L.; Lockrey, S.; Verghese, K.; Chin, S.; Langley, S.; Hill, A.; Phan-Le, N.T.; Francis, C.; Ryder, M.; et al. The wicked problem of packaging and consumers: Innovative approaches for sustainability research. In Sustainable Packaging; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 137–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.R. Harmonizing sustainability, functionality, and cost: Navigating responsible packaging innovations in modern supply chains. Am. J. Econ. Manag. Bus. 2023, 2, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, D.; Lermen, F.H.; Echeveste, M.E. Circular product development strategies for sustainable production and consumption based on waste valorization. Manag. Environ. Qual. 2025, 36, 470–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijassi, W.; Evrard, D.; Zwolinski, P. Development of a circularity design methodology for urban factories based on systemic thinking and stakeholders engagement. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2024, 46, 600–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regulation (EC) No 178/2002 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 28 January 2002 Laying Down the General Principles and Requirements of Food Law, Establishing the European Food Safety Authority and Laying Down Procedures in Matters of Food Safety (OJ L 31, 1.2.2002, pp. 1–24). Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2002/178/oj/eng (accessed on 3 August 2025).
- Regulation (EU) 2015/2283 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 25 November 2015 on Novel Foods, Amending Regulation (EU) No 1169/2011 of the European Parliament and of the Council and Repealing Regulation (EC) No 258/97 of the European Parliament and of the Council and Commission Regulation (EC) No 1852/2001 (OJ L 327, 11.12.2015, pp. 1–22). Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2015/2283/oj/eng (accessed on 3 August 2025).
| Consumer Experience | Consumer Behaviour | Consumer Needs | Generative Questions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Functional food consumers rarely associate food products with sustainable features. They understand functional food as a supplement to vitamins, minerals, and proteins (they do not see other bioactive substances). | Functional food consumers are aware, care about their health, and seek opportunities to increase their body immunity. | Functional food consumers feel the need to enrich products with bioactive substances that benefit their well-being. | How can consumers of functional foods benefit from the addition of chokeberry pomace, which positively impacts their well-being by increasing their knowledge about the health-promoting ingredients present in this product? |
| Functional food consumers consume foods with functional properties (beneficial health effects); however, in some categories, product propositions are too boring and require variety. | Functional food consumers buy foods that benefit the health and are looking for intriguing foods. | Functional food consumers need to consume intriguing foods. | How can functional food consumers provide products containing the addition of chokeberry pomace with new taste sensations to lower their dietary monotony? |
| Functional food consumers eat natural and minimally processed food products because they are aware that they are of higher quality and positively impact human health. | Functional food consumers look for products that do not contain artificial ingredients. | Functional food consumers feel a need to balance the organoleptic characteristics and the low degree of processing associated with the addition of chokeberry pomace. | How can functional food consumers provide high-palatability products with the addition of chokeberry pomace while maintaining the advantages of colour and low degree of product processing? |
| pH | Measured pH (2.86–2.97) | Determined pH (5.30–5.45) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fermentation Time (Days) | 0 | 2 | 5 | 8 | 0 | 2 | 5 | 8 |
| TPC (mg GA/L) | 1405.45 ± 70.37 a;A | 2765.99 ± 45.33 b;B | 3406.05 ± 70.37 c;B | 2739.18 ± 105.60 b;B | 1666.83 ± 46.07 a;B | 2739.18 ± 95.55 b;B | 2538.12 ± 98.67 b;A | 1898.06 ± 217.72 a;A |
| TAC (mg Cy-3-Glu/L) | 321.58 ± 3.89 b;B | 506.18 ± 4.37 d;B | 339.06 ± 2.40 c;A | 279.24 ± 3.10 a;B | 257.32 ± 3.47 b;A | 471.68 ± 3.13 d;A | 290.81 ± 4.34 c;A | 145.91 ± 11.32 a;A |
| TPAC (mg Cat/L) | 170.41 ± 6.87 a;B | 564.25 ± 1.95 b;B | 912.37 ± 27.98 d;B | 761.49 ± 9.70 c;B | 142.42 ± 1.70 a;A | 496.97 ± 12.25 c;A | 722.45 ± 10.03 d;A | 422.53 ± 4.88 b;A |
| ABTS (mmol Trolox/L) | 7.32 ± 0.80 a;A | 14.52 ± 0.72 c;A | 16.96 ± 0.34 d;B | 12.79 ± 0.54 b;B | 7.75 ± 0.24 a;A | 12.99 ± 0.74 c;A | 11.31 ± 0.68 b;A | 7.43 ± 0.30 a;A |
| FRAP (mmol FeSO4/L) | 17.31 ± 0.22 a;B | 27.47 ± 0.44 b;B | 35.81 ± 0.76 c;B | 25.32 ± 0.73 d;B | 14.82 ± 0.22 a;A | 25.90 ± 0.56 b;A | 25.09 ± 0.68 b;A | 14.91 ± 0.38 a;A |
| CUPRAC (mmol Trolox/L) | 13.84 ± 0.65 a;A | 35.87 ± 0.06 c;B | 37.57 ± 0.90 c;B | 33.78 ± 0.77 b;B | 14.87 ± 0.81 a;A | 33.45 ± 0.75 b;A | 32.10 ± 0.84 b;A | 16.15 ± 0.68 a;A |
| pH | Measured pH (2.88–2.97) | Determined pH (5.27–5.60) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fermentation Time (Days) | 0 | 2 | 5 | 8 | 0 | 2 | 5 | 8 |
| TPC (mg GA/L) | 1944.98 ± 72.73 a;A | 3677.49 ± 53.20 c;B | 2786.10 ± 68.92 b;B | 1747.26 ± 46.07 a;A | 1465.77 ± 34.83 a;B | 2380.62 ± 46.07 c;A | 2461.04 ± 92.14 c;A | 1800.88 ± 35.75 b;A |
| TAC (mg Cy-3-Glu/L) | 300.33 ± 31.73 b;B | 804.92 ± 10.52 c;B | 319.25 ± 5.65 b;B | 151.08 ± 2.23 a;A | 246.17 ± 7.25 b;A | 424.81 ± 20.87 d;A | 279.63 ± 3.38 c;A | 193.91 ± 7.47 a;A |
| TPAC (mg Cat/L) | 199.07 ± 1.84 a;A | 733.96 ± 21.71 d;B | 521.44 ± 9.00 c;A | 297.36 ± 6.01 b;A | 144.94 ± 8.34 a;A | 334.24 ± 12.22 b;A | 578.05 ± 11.41 d;B | 396.51 ± 9.27 c;B |
| ABTS (mmol Trolox/L) | 7.89 ± 0.41 a;B | 19.15 ± 0.67 d;B | 11.05 ± 0.34 c;A | 9.47 ± 0.50 b;A | 6.07 ± 0.34 a;A | 10.01 ± 0.17 b;A | 13.35 ± 0.41 c;B | 9.03 ± 0.58 b;A |
| FRAP (mmol FeSO4/L) | 16.78 ± 0.67 a;B | 44.68 ± 0.78 c;B | 25.16 ± 0.88 b;A | 16.57 ± 0.77 a;A | 12.57 ± 0.70 a;A | 21.61 ± 0.04 c;A | 23.29 ± 0.95 c;A | 16.96 ± 0.78 b;A |
| CUPRAC (mmol Trolox/L) | 43.38 ± 1.05 c;B | 59.90 ± 1.09 d;B | 33.49 ± 1.00 b;A | 21.12 ± 0.57 a;A | 14.12 ± 0.74 a;A | 24.74 ± 0.69 b;A | 31.74 ± 0.81 c;A | 23.43 ± 0.97 b;B |
| FRAP (mM FeSO4/L) | CUPRAC (mM Trolox/L) | ABTS (mM Trolox/L) | TAC (mg Cy-3-Glu/L) | TPAC (mg Cat/L) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPC (mg GA/L) | 0.953 | 0.838 | 0.948 | 0.704 | 0.877 |
| FRAP (mM FeSO4/L) | 0.841 | 0.963 | 0.804 | 0.814 | |
| CUPRAC (mM Trolox/L) | 0.810 | 0.741 | 0.640 | ||
| ABTS (mM Trolox/L) | 0.724 | 0.851 | |||
| TAC (mg Cy-3-Glu /L) | s.i. |
| pH | Measured pH (2.86–2.97) | Determined pH (5.30–5.45) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fermentation Time (Days) | 0 | 5 | 0 | 2 |
| Protocatechuic acid | 0.57 ± 0.32 a;A | 7.52 ± 0.05 b;B | 0.74 ± 0.05 a;A | 3.84 ± 0.11 b;A |
| Gentisic acid | 2.74 ± 0.47 a;A | 7.72 ± 0.35 b;B | 3.51 ± 0.37 a;A | 5.90 ± 0.34 b;A |
| m-Salicylic acid | 0.12 ± 0.08 a;A | 0.06 ± 0.04 a;A | 0.94 ± 0.26 a;B | 0.11 ± 0.06 b;A |
| Vanillic acid | 2.62 ± 0.11 a;B | 28.55 ± 0.35 b;A | 0.95 ± 0.12 a;A | 14.35 ± 0.56 b;A |
| Caffeic acid | n.d. | 1.89 ± 0.03 a;B | 0.72 ± 0.03 a;A | 1.48 ± 0.07 b;A |
| Chlorogenic acid | 1.51 ± 0.13 a;A | 2.95 ± 0.10 b;B | n.d. | 2.41 ± 0.19 b;A |
| pH | Measured pH (2.88–2.97) | Determined pH (5.27–5.60) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fermentation Time (Days) | 0 | 5 | 0 | 2 |
| Protocatechuic acid | 2.58 ± 0.10 a;B | 5.38 ± 0.08 b;B | 0.68 ± 0.04 a;A | 4.87 ± 0.06 b;A |
| Gentisic acid | 9.01 ± 0.65 a;B | 11.30 ± 0.89 b;B | 2.60 ± 0.51 a;A | 2.24 ± 0.60 a;A |
| m-Salicylic acid | 2.19 ± 0.11 b;A | 0.12 ± 0.08 b;A | n.d. | 0.06 ± 0.04 a;A |
| Vanillic acid | 4.75 ± 0.06 a;B | 20.56 ± 0.36 b;B | 0.82 ± 0.12 a;A | 15.91 ± 0.11 b;A |
| Caffeic acid | 1.32 ± 0.13 a;B | 1.09 ± 0.10 a;A | 0.77 ± 0.01 a;A | 1.09 ± 0.11 b;A |
| Chlorogenic acid | 3.31 ± 0.11 a;B | 4.62 ± 0.40 b;B | 1.04 ± 0.06 a;A | 1.35 ± 0.11 b;A |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sady, S.; Błaszczyk, A.; Pachołek, B.; Muzykiewicz-Szymańska, A.; Nowak, A.; Syguła-Cholewińska, J.; Sawoszczuk, T.; Popek, S.; Krzywonos, M.; Piekara, A.; et al. Sustainable Management of Fruit By-Products Through Design Thinking: Development of an Innovative Food Product. Sustainability 2025, 17, 7164. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17157164
Sady S, Błaszczyk A, Pachołek B, Muzykiewicz-Szymańska A, Nowak A, Syguła-Cholewińska J, Sawoszczuk T, Popek S, Krzywonos M, Piekara A, et al. Sustainable Management of Fruit By-Products Through Design Thinking: Development of an Innovative Food Product. Sustainability. 2025; 17(15):7164. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17157164
Chicago/Turabian StyleSady, Sylwia, Alfred Błaszczyk, Bogdan Pachołek, Anna Muzykiewicz-Szymańska, Anna Nowak, Justyna Syguła-Cholewińska, Tomasz Sawoszczuk, Stanisław Popek, Małgorzata Krzywonos, Agnieszka Piekara, and et al. 2025. "Sustainable Management of Fruit By-Products Through Design Thinking: Development of an Innovative Food Product" Sustainability 17, no. 15: 7164. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17157164
APA StyleSady, S., Błaszczyk, A., Pachołek, B., Muzykiewicz-Szymańska, A., Nowak, A., Syguła-Cholewińska, J., Sawoszczuk, T., Popek, S., Krzywonos, M., Piekara, A., & Jakubowska, D. (2025). Sustainable Management of Fruit By-Products Through Design Thinking: Development of an Innovative Food Product. Sustainability, 17(15), 7164. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17157164











