Abstract
Straw removal is a method used to reduce cadmium (Cd) concentration in contaminated farmland. Experiments in Hunan Province tested different stubble heights (0, 15, 30, 45 cm) in three Cd-polluted paddy fields with different contamination levels. The results showed that lower stubble heights resulted in larger straw biomass and more Cd removed from the field, while the residual biomass and Cd returned to the field decreased accordingly. At stubble heights of 0, 15, 30, and 45 cm, the removed straw biomass accounted for 100%, 69.19%, 48.84%, and 28.17% of the total straw biomass, respectively. The corresponding Cd removal amounts were 12.89, 7.18, 4.18, and 1.83 g ha−1, which constituted 100%, 54.06%, 29.85%, and 12.54% of the total Cd accumulation in straw for the season, respectively. According to the fitted curve, the biomass of returned and removed straw was equal at a stubble height of 31 cm, while at 23 cm, the Cd return and removal amounts were balanced. Rice varieties Huanghuazhan and Nongxiang 42 had better Cd removal but risked grain Cd exceeding limits. Since Cd concentration in straw determines removal efficiency, varieties with high straw Cd accumulation and low grain Cd are more suitable for remediation, rather than high-Cd-accumulating types.
1. Introduction
The 2021 Bulletin on the State of China’s Ecological Environment identifies heavy metals as the predominant pollutants in the country’s agricultural soils, with cadmium (Cd) being the most critical contaminant [1]. Cd is readily absorbed by rice plants and bioaccumulates in grains [2]. Chronic consumption of Cd-contaminated rice exceeding safety thresholds predisposes humans to severe health risks, including nephrotoxicity, osteoporosis, and carcinogenesis [3]. Concomitantly, Cd pollution disrupts soil ecological equilibrium, exerts toxic effects on microbiota and crops, and disseminates via hydrological pathways, ultimately compromising environmental integrity and ecosystem security [4]. According to the Soil Pollution Prevention and Control Action Plan issued by the State Council in 2016, China aims to achieve a safe utilization rate of over 95% for polluted arable land by 2030. Nevertheless, vast contaminated farmland and protracted remediation make sole fiscal dependence unsustainable [5]. Therefore, it is imperative to explore technologies that not only control heavy metal pollution in farmland but also potentially enhance rice yield and increase farmers’ income. This dual-benefit approach represents a feasible option for addressing heavy metal pollution in farmland.
The concept of natural remediation, a cornerstone in ecological restoration, involves reducing the bioavailability of heavy metals or removing them through biological, physical, and chemical processes. Straw removal from heavy-metal-contaminated farmland is an environmentally friendly phytoremediation technology. In paddy fields, rice is one of the primary candidate plants for phytoremediation. Different rice types and growing seasons exhibit varying capacities for Cd absorption and accumulation. Generally, indica rice and hybrid rice accumulate more Cd in their aboveground parts compared to japonica rice [6,7], and late-season rice typically contains higher Cd concentrations than early-season rice in all parts of the plant [8]. Studies confirm that using high-Cd-accumulating rice varieties for remediation consistently reduces soil Cd content [9,10,11]. Notably, the Cd removal through removed straw removal during crop harvest is significantly higher than that through leaching losses, accounting for over 93% of total Cd output [12]. This underscores the feasibility and effectiveness of employing high-Cd-accumulating rice for remediating contaminated farmland [6]. However, there is a lack of quantitative evidence on remediation efficiency across different pollution levels and regions, particularly concerning stubble height, highlighting the need for further research. Understanding the impact of stubble height on straw removal efficiency is crucial for evaluating remediation technologies and implementing site-specific interventions.
Stubble height plays a decisive role in the removal of soil Cd through straw harvesting. It not only influences Cd removal efficiency but also affects subsequent crops, as residual Cd in stubble can pose risks. For instance, Shi Hanzhi et al. found that in moderately Cd-contaminated farmland, the Cd content in the aboveground parts of the succeeding rice crop was significantly higher when both stubble and straw were returned to the field compared to treatments where only stubble was returned [13]. Conversely, Zhao Fangjie et al. argued that straw removal has limited effects on reducing soil Cd levels [14]. Thus, a scientific understanding of how straw removal affects the total and bioavailable Cd in soil is essential for accurately assessing remediation efficiency. Balancing soil Cd remediation with the safe production of subsequent crops is a key challenge for natural remediation pathways. Straw biomass and cadmium (Cd) concentration are governing factors determining Cd accumulation in straw. However, the relative contribution of these factors to Cd loading in the returned straw versus removed straw remains to be elucidated. This study investigates the effects of varying rice stubble heights on soil Cd removal potential and residual Cd levels. By quantifying the impact of stubble height on straw removal efficiency, this research provides a theoretical foundation for the orderly removal of Cd-contaminated straw and the safe utilization of straw in subsequent applications.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
The experiment was conducted in three Cd-contaminated paddy fields with varying levels of contamination located in Yiyang (28°30′17″ N, 112°36′54″ E), Zhuzhou (27°34′13″ N, 113°16′8″ E), and Hengyang (26°59′52″ N, 112°22′58″ E), Hunan Province. The average temperatures during the rice-growing season were 28.63 °C, 28.80 °C, and 29.04 °C, with accumulated effective temperatures of 3092.32 °C, 3110.25 °C, and 3136.72 °C, and precipitation levels of 92.47 mm, 92.37 mm, and 63.51 mm, respectively. The soils at the three test sites were all waterloggogenic paddy soil. The basic soil properties of the experimental sites are detailed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Basic physicochemical properties of test soils.
The tested rice varieties included Huanghuazhan (HHZ), Nongxiang 42 (NX42), Taiyou 398 (TY398), and Xiangwanxian 12 (XWX12), widely cultivated in Hunan Province. Among these, HHZ and NX42 are conventional varieties, while TY398 and XWX12 are hybrid varieties. The experiment consisted of four treatments with three replicates each. The plots were randomized, with areas of 30 m2 and 0.5 m buffer zones. The plots were separated by film-covered ridges, 35 cm above the field surface, to prevent cross-contamination. Fertilization and water management were carried out according to local practices. During harvest, rice was cut at different stubble heights (0, 15, 30, and 45 cm). For each treatment, straw below the respective stubble height (15, 30, or 45 cm) was returned to the field, while straw above these heights was removed.
2.2. Sample Collection
Before rice planting, soil samples were collected using the five-point sampling method. The samples were air-dried in a well-ventilated location, ground, and sieved through 20-mesh and 100-mesh sieves. Basic physical and chemical properties of the soil were analyzed (Table 1). During harvest, plant samples were collected and separated into roots, grains, and straw according to stubble height: 0–15 cm, >15 cm, 0–30 cm, >30 cm, 0–45 cm, and >45 cm. The samples were first rinsed with tap water and then with ultrapure water, blanched at 105 °C for 30 min, and dried at 70 °C to a constant weight. Biomass and Cd content in each plant part were measured to calculate heavy metal bioconcentration factors (BCFs), translocation factors (TFs), and Cd removal amounts under different stubble height treatments.
2.3. Measurement of Indicators
Cd content in plant tissues was determined by HNO3-HClO4 digestion followed by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS, iCap-Q, Thermo Scientific (Wilmington, DE, USA)). Total Cd content in soil was measured using aqua regia extraction and ICP-MS. The bioavailable Cd in the soil was extracted with a 0.01 mol/L CaCl2 solution and quantified by ICP-MS. The reagents used in the sample analysis were all of high-grade purity, the national standard reference substance (rice: GSB-22) was added as the internal standard for quality control, and the analytical vessels were soaked in 5% nitric acid solution overnight and washed with clean deionized water. Basic soil physicochemical properties were analyzed according to methods outlined in Soil Agrochemical Analysis.
2.4. Data Analysis
Key indices were calculated according to Liu’s method [15] as follows:
Returned straw translocation factors (TF) = Returned straw Cd concentration/Root Cd concentration.
Removed straw TF = Removed straw Cd concentration/Returned straw Cd concentration for same treatment.
Grain TF = Grain Cd concentration/Removed straw Cd concentration for same treatment.
Returned straw bioconcentration factor (BCF) = Returned straw Cd concentration/Total Cd content of soil.
Removed straw BCF = Removed straw Cd concentration/Total Cd content of soil.
Grain BCF = Grain Cd concentration/Total Cd content of soil.
Data analysis and visualization were performed using Excel 2016 and SPSS 20.0. The statistical differences among the treatment groups were evaluated using one-way ANNOVA and the least significant difference (LSD) method. The significance level was set at p < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Straw Biomass
The straw biomass varied significantly among rice varieties. NX42 had the highest biomass, followed by XWX12 and HHZ, while TY398, being a dwarf variety, had the lowest biomass. These trends were consistent across the test locations (Figure 1). As stubble height increased, the biomass of returned straw significantly increased, while the biomass of removed straw significantly decreased. At a stubble height of 15 cm, the average biomass of removed straw was 4660.86 kg ha−1 (range: 3407.54–6155.45 kg ha−1), accounting for 69.19% (57.83–77.70%) of the total straw biomass. At 30 cm, the average biomass of removed straw was 3422.54 kg ha−1 (range: 2131.13–5169.20 kg ha−1), accounting for 48.84% (40.07–59.67%). At 45 cm, the average biomass of removed straw dropped to 2101.89 kg ha−1 (range: 763.21–3640.76 kg ha−1), representing 28.17% (13.75–43.67%) of the total straw biomass. Thus, at stubble heights of 15, 30, and 45 cm, the returned straw biomass accounted for approximately 1/5–2/5, 2/5–3/5, and 3/5–4/5 of the total straw biomass, respectively. There was no obvious rule for the influence of stubble height on the biomass of returned/removed straw.
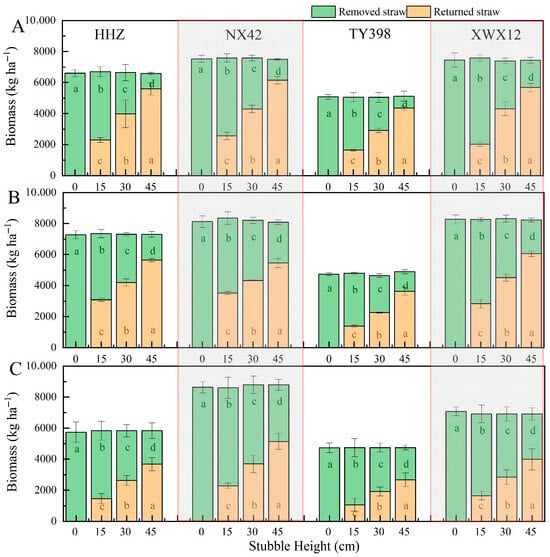
Figure 1.
The effect of stubble height on biomass of returned/removed straw. Figures (A–C), respectively, represent the three experimental sites: Yiyang, Zhuzhou, and Hengyang. HHZ, NX42, TY398, and XWX12 represent the four rice varieties Huanghuazhan, Nongxiang 42, Taiyou 398, and Xiangwanxian 12, respectively. In the column chart, the bright cyan and light apricot colors, respectively, represent the removed straw and returned straw. Different lowercase letters of the same color indicate significant differences at the 0.05 level for straw biomass across stubble heights within the same variety.
3.2. Straw Cd Concentration
At the same stubble height, the Cd concentration in returned straw was consistently higher than in removed straw. Moreover, lower stubble heights were associated with higher Cd concentration in returned straw. Across treatments, the Cd concentration followed the following trend: 15 cm > 30 cm > 45 cm (Figure 2). At stubble heights of 15, 30, and 45 cm, the average Cd concentration in returned straw was 2.88, 2.75, and 2.62 mg kg−1, respectively, while in removed straw, the values were 1.68, 1.35, and 0.83 mg kg−1. Returned straw Cd concentration was 1.71 (15 cm), 2.03 (30 cm), and 3.17 (45 cm) times higher than that of removed straw. Regardless of the height of the stubble, the Cd concentration of returned straw was higher than that of all removed straws, and the difference in Cd concentration between straws below 15 cm and below 45 cm was generally significant. Apart from at the Zhuzhou site, significant differences in removed straw Cd concentration were observed across treatments. When all straw was removed (0 cm), the Cd concentration was slightly higher than that with straw above 15 cm, but the difference was not significant. Grain Cd concentration was the lowest, significantly below that of straw. Among the test locations, straw Cd concentration at Hengyang was significantly higher than at the other two locations, particularly for XWX12, which showed notable differences across locations.
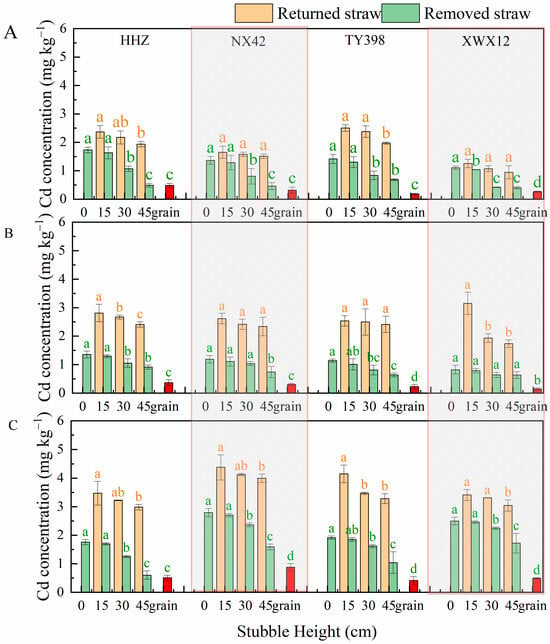
Figure 2.
The straw Cd concentration at different stubble heights. Figures (A–C), respectively, represent the three experimental sites: Yiyang, Zhuzhou, and Hengyang. HHZ, NX42, TY398, and XWX12 represent the four rice varieties Huanghuazhan, Nongxiang 42, Taiyou 398, and Xiangwanxian 12, respectively. In the column charts, the bright cyan, light apricot, and red colors, respectively, represent the removed straw, returned straw, and grain. Different lowercase letters of the same color indicate significant differences at the 0.05 level for Cd concentration of removed (grain)/returned straw across stubble heights within the same variety.
With increasing stubble height, the translocation factor (TF) of Cd in both returned and removed straw gradually decreased. For returned straw, the TF values were 0.57 (0–15 cm), 0.52 (0–30 cm), and 0.47 (0–45 cm). For removed straw, the TF values were 0.33 (>0 cm), 0.56 (>15 cm), 0.47 (>30 cm), and 0.35 (>45 cm), with TF (>15 cm) being significantly higher than for other heights (Table 2). This indicates that the ability of Cd to translocate from roots to returned straw and from returned straw to removed straw weakened with increasing stubble height. For grains, TF (>0 cm-grains), TF (>15 cm-grains), TF (>30 cm-grains), and TF (>45 cm-grains) were 0.23, 0.25, 0.35, and 0.50, respectively (Table 3), indicating that Cd translocation from removed straw to grains increased with stubble height. At 45 cm, the TF values for grains of HHZ and NX42 were significantly higher than at other heights, with consistent trends across test locations.

Table 2.
Effect of stubble height on Cd translocation factor (TF) of straw.

Table 3.
Effect of stubble height on TF from removed straw to grain.
Similarly, the bioconcentration factor (BCF) for both returned and removed straw decreased with an increasing stubble height (Table 4). When all straw was removed (0 cm), the BCF for straw was 3.02, while for grains, it was 0.71. At 15 cm, the BCF was highest, with returned and removed straw BCF values of 5.22 and 3.25, respectively. At 30 cm, these values were 5.20 and 2.61, and at 45 cm, they were 4.98 and 1.53. At all stubble heights, the BCF for returned straw was significantly higher than that for removed straw. The difference between stubble and removed straw BCF increased with stubble height. At 15, 30, and 45 cm, the average stubble BCF was 1.61, 1.99, and 3.25 times that of the corresponding removed straw BCF. While stubble height had no significant effect on returned straw BCF, removed straw BCF decreased significantly with increasing stubble height, and grain BCF remained significantly lower than straw BCF. Across varieties, straw BCF at the Hengyang site was higher than at Yiyang and Zhuzhou.

Table 4.
Effect of stubble height on bioconcentration factor (BCF) of straw and grain.
3.3. Accumulated Cd Content
The accumulated Cd content of returned straw increased significantly with stubble height, while the accumulated Cd content of removed straw decreased significantly (Figure 3). At stubble heights of 0, 15, 30, and 45 cm, the Cd accumulations returned to the field with the stubble were 0, 5.93, 8.57, and 10.99 g ha−1, respectively, while the corresponding removed Cd accumulations were 12.95, 7.15, 4.27, and 1.88 g ha−1. Across test locations, Hengyang had higher removed Cd accumulation values than Zhuzhou and Yiyang. Among varieties, NX42 achieved the highest removed Cd accumulation, while TY398 achieved the lowest.
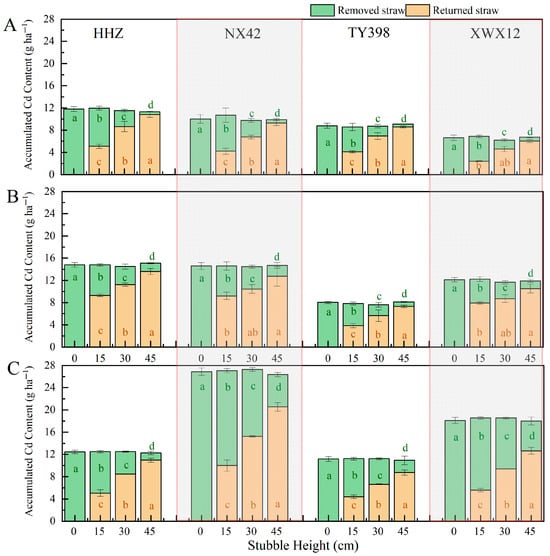
Figure 3.
The straw accumulated Cd content at different stubble heights. Figures (A–C), respectively, represent the three experimental sites: Yiyang, Zhuzhou, and Hengyang. HHZ, NX42, TY398, and XWX12 represent the four rice varieties Huanghuazhan, Nongxiang 42, Taiyou 398, and Xiangwanxian 12, respectively. In the column charts, the bright cyan and light apricot colors, respectively, represent the removed straw and returned straw. Different lowercase letters of the same color indicate significant differences at the 0.05 level for the accumulated Cd content of removed/returned straw across stubble heights within the same variety.
The proportion of removed Cd accumulation by removed straw relative to total straw Cd accumulation was significantly affected by stubble height. Lower stubble heights resulted in a higher proportion of removed Cd accumulation. At stubble heights of 15, 30, and 45 cm, the removed Cd accumulation proportion averaged 54.06%, 29.85%, and 12.54%, respectively, with significant differences across treatments and consistent trends across varieties and test locations (Table 5). Among sites, the proportion of Cd removal was highest in Hengyang, followed by Zhuzhou and Yiyang.

Table 5.
Effect of stubble height on proportion of removed Cd amount relative to total straw Cd accumulation.
In order to further clarify the effects of stubble height on the biomass and Cd accumulation of removed/returned straw, linear fitting was performed for stubble height and removed/returned straw biomass, and stubble height and removed/returned straw biomass Cd accumulation, respectively. At a stubble height of 31 cm, the biomass of removed and returned straw was equal. At a stubble height of approximately 23 cm, the removed and returned Cd accumulation were equal. Above this height, Cd return exceeded removal, and vice versa (Figure 4).
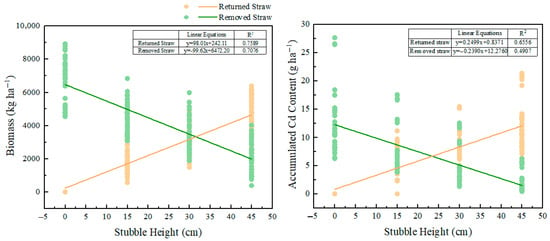
Figure 4.
Linear relationship between straw biomass, accumulated Cd content, and stubble height.
Correlation analysis (Figure 5A,B) indicated that stubble height was negatively correlated with the Cd translocation factor for both stubble and removed straw, consistent with Table 2. Returned straw biomass and returned Cd accumulation were significantly positively correlated with stubble height, while removed straw biomass and removed Cd accumulation were significantly negatively correlated, as shown in Figure 1 and Figure 3. Notably, biomass had the greatest impact on the Cd accumulation returned to field, while Cd concentration had the greatest impact on the Cd accumulation removal by removed straw. PCA analysis indicated that under the straw return scenario, a cumulative variability of 78.0% was explained by the first two principal components (Figure 5C). The first PC explained 42.7% of the variability with major contributions to BCF and concentration. The second PC explained 35.3% of the variability with a major contribution to amount (Figure 5C). Under the straw removal scenario, a cumulative variability of 87.4% was explained by the first two principal components, with PC1 and PC2 capturing 66.2% and 21.4% of the total variation, respectively (Figure 5D).
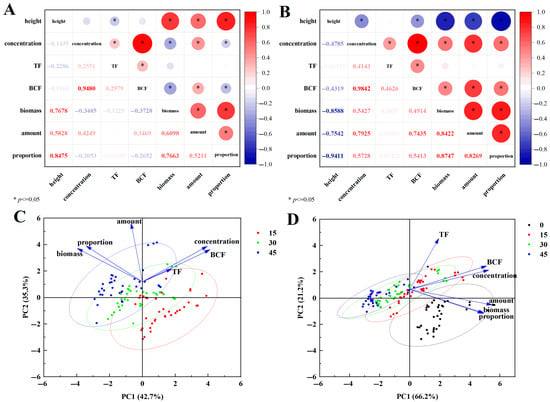
Figure 5.
Pearson correlation (A,B) and principal component analysis (C,D) among observed indicators. Figures (A,C) represent returned straw and Figures (B,D) represent removed straw. Labels 0, 15, 30, and 45 represent stubble heights of 0, 15, 30, and 45 cm. Ellipses represent 95% confidence limits. Height, stubble height; concentration, Cd concentration; amount, returned/removed accumulated Cd content; proportion, returned/removed accumulated Cd content proportion.
4. Discussion
4.1. Cd Removal Efficiency
Although the Cd bioconcentration factor (BCF) in rice is relatively low compared to Cd hyperaccumulators, rice has distinct advantages, including high biomass, strong adaptability, mature cultivation techniques, and stable genetic traits. Consequently, the use of high-Cd-accumulating rice varieties for remediating Cd-contaminated farmland has gained attention both domestically and internationally [11,16,17].
In this study, the biomasses of HHZ, NNX42, and XWX12 were higher than that of TY398 (Figure 1). However, across the three experimental sites, the Cd concentration in the straw of the four varieties showed little difference (Figure 2). Both high biomass and high Cd accumulation are critical factors for selecting rice varieties as potential phytoremediation agents for Cd-contaminated fields [9]. Due to its lower biomass, TY398 showed the lowest Cd removal efficiency among the varieties (Figure 3), making it unsuitable for remediation purposes. XWX12 was previously identified as a low-Cd-accumulating rice variety [18], and its Cd concentration varied significantly among sites (Figure 2), also making it unsuitable for remediation. Conventional varieties HHZ and NX42 demonstrated the best Cd removal efficiency through straw removal, but both pose a risk of Cd exceeding safe limits in rice grains.
4.2. Differences in Straw Cd Accumulation Across Ecological Zones
Generally, higher soil Cd levels result in greater Cd uptake and accumulation in rice plants. Previous studies with soil Cd levels of 0.45 mg kg−1 and 0.41 mg kg−1 reported stem Cd concentrations of 0.5–1.0 mg kg−1 and 0.45–3.34 mg kg−1, respectively [11,19]. In this study, the soil Cd content (0.49–0.66 mg kg−1) was higher than in the previous studies, and correspondingly, the straw Cd concentration was also higher (1.32–5.00 mg kg−1) (Figure 2). Interestingly, although Hengyang had the lowest soil Cd content among the three sites, it exhibited the highest straw Cd content and removal rates. This may be attributed to the high available phosphorus content at this site, which was 5–15 times higher than at the other sites, while other soil properties showed no consistent patterns (Table 1). Previous research indicates that phosphorus fertilizers can promote Cd uptake by plants [20]. Increased available phosphorus in soil enhances Cd bioavailability [21] and up-regulates the expression of the OsNramp5 gene in rice, leading to greater Cd accumulation in plant tissues under both phosphorus-deficient and phosphorus-rich conditions [22,23]. Additionally, phosphorus facilitates the formation of iron plaques on rice root surfaces, reducing Cd translocation to grain-bearing parts and promoting Cd precipitation in vegetative tissues [2,24]. Temperature also plays a role, as higher temperatures increase the bioavailability of metals, promoting their uptake and translocation within plants [25,26]. In this study, the average temperature and accumulated effective temperature during the rice-growing season were higher at the Hengyang site than at the other two sites (Section 2.1), likely contributing to the higher Cd accumulation in rice straw. Given the limited number of experimental sites and soil types, it was not possible to establish comprehensive relationships between soil physicochemical properties, ecological factors, and straw Cd accumulation. Future research should include more soil types and ecological zones to clarify these relationships and provide practical guidance for straw removal and its safe utilization.
4.3. Higher Stubble Height Reduces Removed Straw Cd Removal
The ability of rice plants to accumulate Cd is influenced by genetic traits, soil properties, and soil Cd content. However, the general pattern shows higher Cd concentrations in underground parts than in aboveground parts, with Cd concentration decreasing with plant height [15]. In this study, lower stubble heights corresponded to higher Cd contents in returned straw (Figure 2). With increasing stubble height, the Cd TF of both returned and removed straw decreased (Table 2), indicating that Cd translocation weakens with distance from the soil, consistent with previous studies [15,27]. The BCF of returned and removed straw also decreased with increasing stubble height, while the grain BCF was significantly lower than that of straw (Table 4). Although the upward Cd translocation capacity within rice plants weakens with height, the TF from removed straw to grains increased with stubble height (Table 3). One of the reasons for the above phenomenon is the different ratio of stem, stem node and leaf distribution of straw at different stubble heights. In rice plants, the vascular bundle is the element transport channel, and the stem node regulates the element transport distribution [28]. The stalk and stem nodes are the two tissues with the most accumulated Cd except for the roots [29]. The farther away from the ground, the lower the proportion of stems and nodes for the plant, and the lower the Cd accumulation, resulting in a greater TF (removed straw–grain).
In terms of stubble straw, no matter whether the height of the stubble is 15, 30, or 45 cm, there is no significant difference in Cd concentration of stubble straw (Figure 2), and biomass is the main influencing factor causing the return of Cd in returned straw (Figure 5), indicating that the stubble height should be appropriately reduced to remove more Cd. However, for removed straw, the Cd concentration varied significantly, and the Cd concentration contributed the largest contribution to Cd removal (Figure 5). The Cd accumulation by the whole plant for rice straw was 12.76 g ha−1, and although the biomass of 0–15 cm straw only accounted for 31.46% of the whole plant biomass, the returned Cd accumulation of 0–15 cm stubble straw accounted for 45.76% of the Cd accumulation of the whole plant, close to half of the whole plant’s accumulation; that is, the higher the stubble, the greater the returned Cd accumulation. At a stubble height of 23 cm, Cd removal and return were balanced at approximately 6.57 g ha−1.
While full straw removal can eliminate Cd return from stubble, lower stubble heights increase the load on harvesting machinery, extend operation times, raise fuel consumption, and increase grain loss rates [30]. Long-term straw removal can also reduce soil silicon levels, leading to lower rice yields [31]. Straw return can mitigate soil silicon loss, as silicon inhibits Cd uptake in rice and reduces Cd concentration in brown rice [32,33]. Moreover, organic carbon released during straw decomposition can adsorb Cd more effectively than it releases it [10]. Straw return also enhances soil organic matter, benefiting arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, which can mobilize unavailable Cd and increase its bioavailability for plants [34,35,36]. The impact of straw return on subsequent soil properties and crops remains unclear. Although this study established linear relationships between stubble height and the biomass and Cd accumulation of stubble and removed straw, it did not address the effects of returned straw on soil Cd levels or Cd uptake by subsequent crops. Future studies should focus on regulating Cd and silicon through stubble height adjustments and assess the implications for subsequent soil and crop health.
5. Conclusions
Straw removal offers a sustainable strategy for simultaneous rice production and remediation in Cd-contaminated paddies. The cultivars Huanghuazhan and Nongxiang 42 demonstrated high and stable straw biomass across regions, enabling superior Cd removal at equivalent stubble heights despite similar straw Cd concentrations. At stubble heights < 45 cm, residual stubble biomass dominated Cd return to soil, while lower stubbles maximized Cd removal via harvested straw, primarily driven by straw Cd concentration. Linear relationships existed between stubble height and biomass/Cd accumulation in both harvested and residual straw. Future work should aim to achieve the following: (i) screen varieties with high straw Cd but low grain Cd accumulation, (ii) further investigate the long-term effects of straw return on soil silicon cycling and subsequent crop Cd uptake, (iii) implement strict monitoring and safe disposal of Cd-enriched straw/grains to prevent food chain entry, thereby ensuring the sustainable development of simultaneous rice production and remediation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.D. and H.P.; methodology, Y.D., M.S. and H.P.; software, Y.D. and M.S.; validation, M.S. and Y.L.; investigation, Y.L.; resources, Y.Z. and J.Z.; data curation, Y.D. and M.S.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.D.; writing—review and editing, M.S., Y.L., Y.Z., J.Z. and H.P.; visualization, Y.D. and M.S.; supervision, H.P.; project administration, H.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China, grant number 2022YFD1700103; the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 42377411 and 42407054; and the Provincial Natural Science Foundation of Hunan, grant number 2023JJ40366.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Guolong Huang and Shengliang Fang for their technical assistance during the experiments.
Conflicts of Interest
The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| Cd | Cadmium |
| TF | Translocation factor |
| BCF | Bioconcentration factor |
| HHZ | Huanghuazhan |
| NX42 | Nongxiang 42 |
| TY398 | Taiyou 398 |
| XWX12 | Xiangwanxian 12 |
References
- Report on the State of the Ecology and Environment in China 2021; Ministry of Ecology and Environment, The People’s Republic of China; Beijing, China, 2021.[Green Version]
- Zou, M.; Zhou, S.; Zhou, Y.; Jia, Z.; Guo, T.; Wang, J. Cadmium pollution of soil-rice ecosystems in rice cultivation dominated regions in China: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 280, 116965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charkiewicz, A.E.; Omeljaniuk, W.J.; Nowak, K.; Garley, M.; Nikli’nski, J. Cadmium Toxicity and Health Effects-A Brief Summary. Molecules 2023, 28, 6620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Chen, H.; Kopittke, P.M.; Zhao, F.-J. Cadmium contamination in agricultural soils of China and the impact on food safety. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J. Risk Perception and Technology Cognition on Farmers’ Behavior of Preventing and Controlling Heavy Metal Pollution in Cropland: An Evidence from Adoption of Cadmium Pollution Prevention and Control Technology for Rice Farmers. Ph.D. thesis, Sichuan Agricultural University, Yaan, Sichuan, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ibaraki, T.; Kuroyanagi, N.; Murakami, M. Practical phytoextraction in cadmium-polluted paddy fields using a high cadmium accumulating rice plant cultured by early drainage of irrigation water. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2009, 55, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Tan, C.; Cai, R.; Cheng, X.; Liu, L.; Zhang, X.; Huang, S. Potential of plant rotation patterns for phytoremediation of cadmium contaminated farmland. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2022, 41, 765–773. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.; Tu, C.; Qiu, W.; Zhu, X.; Fan, W.; Cao, Z.; Zhu, X.; Luo, Y. Cadmium accumulation and pollution reduction of different rice varieties on cadminum-contaminated. J. Ecol. Environ. 2023, 39, 547–555. [Google Scholar]
- Imseng, M.; Wiggenhauser, M.; Keller, A.; Müller, M.; Rehkämper, M.; Murphy, K.; Kreissig, K.; Frossard, E.; Wilcke, W.; Bigalke, M. Fate of Cd in agricultural soils: A stable isotope approach to anthropogenic impact, soil formation, and soil-plant cycling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 1919–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Jiang, Q.; Wen, D.; Xu, A.; Deng, T.; Du, R. Effects of straw returning on Cd transfer and transformation in rice at different growth stages. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2023, 51, 202–207. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, R.; Ito, M.; Kawamoto, T. The road to practical application of cadmium phytoremediation using rice. Plants 2021, 10, 1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morishita, T.; Fumoto, N.; Yoshizawa, T.; Kagawa, K. Varietal differences in cadmium levels of rice grains of Japonica, Indica, Javanica, and hybrid varieties produced in the same plot of a field. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 1987, 33, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, P.; Feng, X.; Jiao, H.; Li, Y.; Jiang, H. Risk research of low accumulation rice planting in Cd contaminated farmland in northern Guangdong. Environ. Sci. Manag. 2023, 48, 140–145. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, F.-J.; Zhao, X.-Y.; Tao, Y.-M.; Wang, H.; Wang, P. Straw removal has a limited effect on decreasing cadmium concentration in soil. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2021, 40, 693–699. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Chen, H.; Ji, X.; Liu, Z.; Xie, Y.; Tian, F.; Pan, S. Remediation potential of rice with high cadmium accumulation to cadmium contaminated farmland. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. (Trans. CSAE) 2021, 37, 175–181. [Google Scholar]
- Ibaraki, T.; Fujitomi, S.-I.; Ishitsuka, A.; Yanaka, M. Phytoextraction by high-Cd-accumulating rice to reduce Cd in wheat grains grown in Cd-polluted fields. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2014, 60, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-Z.; Fang, B.-H.; Teng, Z.-N.; Chen, G.-H.; Liu, Y.; Ling, W.-B.; Xiang, S.-Q.; Bai, L.-Y. Screening and verification of rice varieties with low cadmium accumulation. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2019, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.-Y.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, K.-H.; Tan, W.-T.; Jiiang, Y.; Tang, Q.; Wu, G.-F.; Gu, J.-F.; Zeng, P.; Liao, B.-H. Effects of straw removal measure on soil Cd bioavailability and rice Cd accumulation. Environ. Sci. 2023, 44, 4109–4118. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Sun, T.-H.; Sun, L.-N.; Zhou, Q.-X.; Chao, L. Influences of phosphate nutritional level on the phytoavailability and speciation distribution of cadmium and lead in soil. J. Environ. Sci. 2006, 18, 1247–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.-Q.; Wang, F.-Y.; Jiang, H.-M.; Zhang, J.-F.; Yang, J.-C.; Guo, J.-M.; Li, X.; Liu, L.; Xie, Y.-Q.; Li, L.-L. Available posphorus is a key regulator of cadmium phytoavailability in greenhouse soils. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2014, 33, 1721–1727. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, W.-T.; Huo, Y.; Zhou, H.; Qiu, Y.-Y.; Zeng, P.; Gu, J.-F.; Liao, B.-H. Effects of Phosphorus Sufficiency and Deficiency on Cadmium Uptake and Transportation by Rice. Environ. Sci. 2022, 43, 3308–3314. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, T.-T.; Wang, C.-L.; Zhao, X.-L. Effects of different phosphate fertilizers on iron plaque amount on root surface and arsenic and cadmium uptake by rice grown in a limestone yellow loamy paddy soil. China Environ. Sci. 2021, 41, 297–306. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, T.-Y.; Liu, M.-D.; Wo, X.-H.; Li, J. Effects of combined application of silicon and phosphorus on cadmium uptake and transport in rice and its mechanisms. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2020, 39, 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, C.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Z. Increasing phosphate inhibits cadmium uptake in plants and promotes synthesis of amino acids in grains of rice. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 257, 113496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.-Q.; Cang, L.; Liu, H.; Zhou, D.-M. Effects of warming on uptake and translocation of cadmium (Cd) and copper (Cu) in a contaminated soil-rice system under Free Air Temperature Increase (FATI). Chemosphere 2016, 155, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.-C.; Zheng, Y.-J.; He, X.-F.; Li, X.-F.; Zhang, X.-X. Analysis of the Report on the national general survey of soil contamination. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2017, 36, 1689–1692. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, F.; Lei, M.; Tang, Z.; Yang, R.-B.; Song, Z.-G.; Tang, S.-R.; Peng, S.; Liao, H.-Y. Accumulation characteristic and dynamic distribution of Cd in different genotypes of rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2013, 32, 1092–1098. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaji, N.; Ma, J.F. Node-controlled allocation of mineral elements in Poaceae. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2017, 39, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Bai, B.; Xie, Y.; Yao, D.; Zhang, D.; Chen, Z.; Zhuang, W.; Deng, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Wu, J. Effects of Cd uptake, translocation and redistribution in different hybrid rice varieties on grain Cd concentration. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 240, 113686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Gao, S.; Kong, X.; Xu, W.; Wu, Y.; Xu, L.; Wei, L.; Xiao, P.; She, H.; Chen, K.; et al. Research on key techniques of mechanical harvesting of hybrid rice to reduce rice yield loss. China Rice 2023, 29, 99–102. [Google Scholar]
- Savant, N.K.; Datnoff, L.E.; Snyder, G.H. Depletion of plant-available silicon in soils: A possible cause of declining rice yields. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1997, 28, 1245–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ding, H.; Dai, W.; Zhu, X.; Mu, J. Supplying amorphous silicon fertilizer reduced Cd accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) via Increasing the available Si/Cd ratio in paddy soil. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2023, 32, 5197–5210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.F.; Che, J.; Yamaji, N.; Shen, R.F.; Ma, J.F. Silicon reduces cadmium accumulation by suppressing expression of transporter genes involved in cadmium uptake and translocation in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 5641–5651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xia, X.-G.; Chen, Y.-F.; Guo, X.-F.; Yu, X.-P.; Liu, D.-H.; Zhang, Z. Effects of stubble in height and grinding degree during straw application on crop yield and soil nutrients under rice-rapeseed rotation. Soil Fertil. Sci. China 2023, 6, 122–128. [Google Scholar]
- Begum, N.; Qin, C.; Ahanger, M.A.; Raza, S.; Khan, M.I.; Ashraf, M.; Ahmed, N.; Zhang, L. Role of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in plant growth regulation: Implications in abiotic stress tolerance. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Lu, S.; Jia, C.; Liu, M. Effects of long-term straw return on soil arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and their ecological network. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2025, 62, 1523–1534. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).