Abstract
Improving the ecological resilience in the Yellow River Basin is a crucial way to achieve ecological conservation and high-quality development in the region. Based on the panel data from 2011 to 2023 of 57 cities in the Yellow River Basin, the ecological resilience of each city was measured by using the Catastrophe Progression Model, and its spatial differences and dynamic evolution characteristics were analyzed by the Dagum Gini coefficient and kernel density estimation. At the same time, the STIRPAT model was integrated with the random forest model to identify the key factors influencing urban ecological resilience. The results demonstrated the following: (1) The urban ecological resilience in the Yellow River Basin exhibited a slight upward trend during 2011–2020 and presented a gradient spatial pattern with “high in the east and low in the west”. (2) Hypervariation density is the main source of spatial difference in urban ecological resilience, with trailing and polarization phenomena across the entire basin and its three major subregions. (3) There was significant regional heterogeneity of influences in the urban ecological resilience, with upstream, midstream, and downstream regions characterized by low interference intensity, high sensitivity, and strong adaptability, respectively.
1. Introduction
Ecological resilience is closely tied to sustainable development Urban ecological resilience, as socio-ecological resilience defined by Sterk [1] in spatial manifestation drives cities to break the lock-in of unsustainable development paths by maintaining core functions and restructuring, thus facilitating sustainable development. During urbanization, changes in ecological conditions like watershed pollution, biodiversity loss, and climate change severely compromise ecosystem services and environmental carrying capacity [2]. However, urban ecological systems have historically received less attention [3], exacerbating these issues. Improving urban ecological resilience (UER) helps climate change mitigation and adaptation, reduces natural disaster risks, and protects biodiversity, thereby enhancing the overall quality of urban environments [4]. The Yellow River Basin (YRB), known as a cradle of civilization and a critical ecological security barrier, has suffered localized degradation of ecosystems, including grasslands, lakes, and wetlands, over the past two decades, resulting in a general increase in ecological vulnerability [5]. Although the YRB Ecological Protection and High-Quality Development Plan has provided strategic guidelines for ecological conservation and sustainable development, rapid urbanization in the basin has generated compounded stresses from climate change, resource shortages, and environmental pressures, with the result that the vulnerability in eco-logical resilience has become increasingly obvious [6,7]. Against such a backdrop, it is crucial to enhance ecological resilience to safeguard regional ecological security and foster harmonious coexistence between humans and nature during the modernization process [8].
Asadzadeh et al. [9] put together four key areas in resilience research, including vulnerability and adaptation to climate change, urban-regional disaster resilience, sustainability management with institutional transformation, and the far-reaching impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic. These fields are closely related to UER. They highlighting the im-portance of UER in the study of resilience. To date, academic studies have mainly concentrated on conceptual frameworks, influencing factors, and measurement methods.
Ecological resilience is defined as the ability of an ecosystem to maintain its structure and functionality in the face of disturbances [10]. Urban ecosystems emerge from the multi-scale dynamic interactions of socio-economic and biophysical factors across time and space [11]. Alberti and Marzluff [2] conceptualized UER as the threshold of perturbation absorption before reorganization of urban patterns, human systems, and ecological functions. The Resilience Alliance [12] further identified core principles in socio-ecological resilience frameworks, including thresholds/tipping points, adaptive cycles, cross-scale interactions, and adaptive governance. To better understand these concepts, Shamsipour et al. [13] systematically analyzed urban ecological components, spanning biodiversity conservation, green infrastructure, habitat restoration, and ecosystem services.
Resilience theory acknowledges the multi-layered complexity of socio-ecological systems and the strong interdependencies among their components [1]. In light of this, scholars have comprehensively considered climatic, environmental, socio-demographic, physical, urban form, and infrastructural variables to analyze various factors affecting the ecological resilience of different global cities [14,15,16].
To more clearly identify gaps in actionable and measurable aspects of UER, a range of methods have been developed, including qualitative and quantitative approaches such as participatory assessment, statistical analysis, modeling, and measurement criteria [17,18,19,20]. However, it is crucial to note that resilience is an emergent property, not a single number or outcome, manifesting differentially across subsystems [21]. Thus, current models are not suitable for all urban ecosystems. More research anchored in specific urban and cultural contexts is needed, thereby enabling the formulation of context-specific frameworks attuned to regional peculiarities.
Despite progress in ecological resilience research, three main problems still remain. The first is conceptual ambiguity. No consensus exists on the definition of ecological resilience, and the corresponding theoretical system is not yet complete. The second is methodological rigidity. Prevailing measurement methods emphasize static changes in the ecosystem’s internal factors, ignoring its dynamic characteristics and the comprehensive influence of social, economic, and cultural factors [19]. Although spatiotemporal patterns of ecological resilience have been partially revealed, its internal driving mechanism still requires deeper mechanistic exploration [22]. The third problem is contextual insensitivity. The existing research and practice often lack customized solutions for regional characteristics. In an attempt to fill these gaps, based on Holling’s [10] ecological resilience theory, a three-dimensional evaluation system for UER composed of resistance, adaptability, and recovery is constructed. The catastrophe progression model is employed to quantify its nonlinear dynamic characteristics and threshold effects. Meanwhile, the interaction mechanisms and spatial heterogeneity contributions of multidimensional influencing factors are analyzed through an integrated STIRPAT and random forest approach. Closely integrating the gradient characteristics of urban agglomerations, differentiated development pressures, and ecological vulnerability patterns in the upstream, midstream, and downstream of the YRB, a context-adapted spatial assessment framework is established. By quantifying the spatiotemporal evolution patterns of UER across the basin and identifying driving pathways of key influencing factors, this study provides a spatially targeted decision-making basis for enhancing ecological resilience in cities of the YRB through region-specific and tiered strategies.
2. Conceptual Model and Methods
2.1. Theoretical Framework of UER in the YRB
Although the concept of resilience originated from materials science, Holling [10] introduced it into ecology and redefined it as the ability of a system to absorb disturbances and maintain its core functions, criticizing the traditional view of pursuing equilibrium-based stability. Subsequently, Holling [23] further clarified that the core of ecological resilience lies in the disturbance threshold a system can withstand before crossing a critical point rather than merely pursuing recovery efficiency. Walker and Salt [21] further developed evolutionary resilience, stressing the systems’ capacity for self-organization and innovation to achieve structural and functional evolution amid prolonged and complex external changes. With resilience theory expanding, its applications extended to sociology and urban planning, forming the social-ecosystem resilience and UER. The former is the ability of social and ecological systems to maintain functionality despite external disturbances [24], and the latter refers to the capacity of urban ecosystems to sustain their structure and function in the face of external disturbances through the interaction of society, economy, and ecology [2]. Overall, resilience is a multidimensional capacity encompassing resistance, i.e., withstanding disturbances with minimal equilibrium shift; adaptability, i.e., adjusting processes to changing conditions; and recovery, i.e., returning to functionality postdisturbance. Given the complex nature of ecosystems and the interconnectedness of society and ecosystems, analyzing ecological resilience requires consideration of population, economy, technology, and other factors. The above theories provide the theoretical basis for the measurement and influencing factors of UER in the YRB.
2.1.1. Nonlinearity and Threshold Effects in UER
Ecosystems’ responses to disturbances do not follow a simple linear pattern. When the intensity of the disturbance exceeds the ecological resilience threshold of the system, the ecosystem may irreversibly transition to a new stable state after losing its ability to maintain its original state [10], which reflects the nonlinearity and threshold effects of ecosystems. Dakos and Kéfi [19] applied potential function theory, analyzing changes in the shape of potential functions to identify critical thresholds and abrupt transition risks in ecosystems. On this basis, we use the catastrophe progression method with potential functions f (x, u) to identify the critical point of the ecosystem in the YRB by quantifying the three dimensions of resistance, adaptability, and recovery (Figure 1). This method evaluates UER in the YRB, thereby providing a scientific basis for its measurement and management.
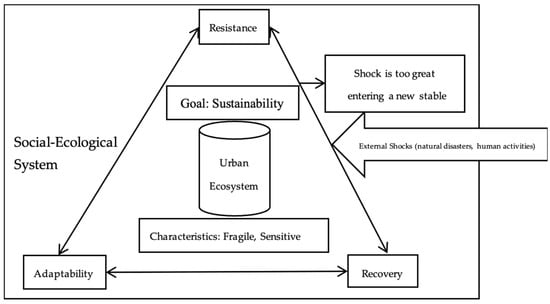
Figure 1.
Map of UER mechanisms.
2.1.2. Complexity of Influencing UER
UER is the product of interactions between natural systems and human societies, influenced by natural, economic, social, and other multidimensional factors. Moreover, both natural and human interventions exert nonlinear effects on ecological resilience [25]. Specifically, natural factors include climate conditions, landforms, vegetation types, and water resources, among others, which constitute the basic elements of ecosystems and directly impact ecosystem structure and function. Beyond these direct natural impacts, economic and social factors have equally profound effects. Economic factors are represented by utilization in human activities, including the levels of economic development, industrial structure, and market mechanisms, among others. While resource consumption and environmental pollution caused by economic activities drive ecosystem degradation, technological innovation and management improvements driven by economic development enhance ecological resilience and adaptive capacity. Social factors are reflected in the regulatory capacity of institutions and behaviors, including population size, social structure, policies, and regulations. To holistically dissect these influences, it is essential to transcend single-discipline perspectives and adopt a multidimensional analytical method to quantify their impacts on ecological resilience, thereby providing a scientific basis for its management and policy formulation.
2.2. Determination of the Evaluation Indicator System
2.2.1. Study Area
According to the China Administrative Division Handbook (1995), the YRB encompassed 69 administrative regions, including prefectures, leagues, and cities. In view of the availability of data and to ensure the geographical continuity within the Yellow River Watershed, some regions (prefectures, leagues, and cities), such as Sichuan Province, which has severe data deficiencies and is located on the outer edge of the watershed, have been excluded. This resulted in 57 regions in the core watershed being selected as study areas.
2.2.2. Data Sources
A4 data were collected from NASA EarthData (https://www.earthdata.nasa.gov/ accessed on 30 November 2024), B3 data from China’s air quality monitoring online platforms, and all other data from the China City Statistical Yearbook (2011–2023) and statistical yearbooks/bulletins of province-level cities within the basin. Missing values in the dataset were interpolated using linear or spatial-proportional methods.
2.2.3. Construction of UER Assessment Index System
In developing ecological resilience assessment frameworks, existing studies primarily focus on the natural–economic–social complex system [26] and adaptive cycles within socio-ecological systems [27] to analyze urban spatial features. These efforts have led to frameworks such as scale–density–morphology [28], potential–connectivity–resilience [29], PSR/PPSR/DPSR/DPSIR/DPWSIR [30,31,32,33,34], and resistance–adaptability–resilience [35]. Current research predominantly employs multidimensional composite indicator systems. Given the complexity of UER, this study adopts a multidimensional approach to construct an evaluation framework that fully captures its definition while ensuring accuracy, scientific rigor, and data accessibility. Drawing on research by He et al. [36], Li et al. [37], and Lu, Liu, and Wang [20] and incorporating regional characteristics such as soil erosion and water pollution in the YRB as well as high-quality development requirements for improving living standards and environmental quality [38], this study decomposes UER in the YRB into three components, namely resistance, adaptability, and recovery, and selects thirteen relatively independent indicators as specific evaluation criteria, where indicators of each dimension indirectly characterize resistance, adaptability, and recovery through the quantitative performance of environmental pressure, system response, and resource endowment rather than directly measuring their dynamic attributes so as to make up for the limitation of the lack of internal state data. (Table 1).

Table 1.
Evaluation index system of UER in the YRB.
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. Catastrophe Progression Model
Given the confirmed nonlinear threshold effects in the ecosystem of the YRB’s ecosystem [6], we adopt the catastrophe progression model. Unlike the PSR model’s linear approach or TOPSIS’s distance-based limitations, this model quantifies discontinuous catastrophic behaviors through topological singularity theory, which can quantify discontinuous catastrophic behaviors under the influence of multiple control variables [39] and is more in line with the nonlinear dynamic characteristics of resilient systems. It has been applied to social science fields through morphological analysis and equation transformation [40]. It is applied to UER evaluation in the YRB through three steps: index optimization, model selection, and normalization. The method for each step is described below.
In the first step, the relative importance of resistance, adaptability, and restoration capacity subindicators was objectively ranked using entropy weighting to minimize subjectivity.
Positive indicators:
Negative indicators:
where is the standardized index, and and represent the maximum and minimum values of index j across all years and all regions, respectively.
Proportion of indicator j:
We thus obtain the observed value of UER indicator j for city i within the YRB.
Information entropy of j:
Entropy redundancy:
Weight assignment:
In the second step, we detail the following: criterion layer (resistance, adaptability, and restoration): swallowtail catastrophe model; resistance/adaptability sublayers (four indicators each): butterfly catastrophe model; restoration sublayer (five indicators): wigwam catastrophe model.
Based on the two steps, following complementary principles (inter-indicator correlation < 0.5), total membership values were calculated as follows:
Sublayer normalization:
Mainly derived from the normalization principle of the bifurcation equation of the mutation theory [39], the core mechanism is to uniformly map the original values of different priority indicators to the [0,1] interval through power function transformation, where n denotes the priority rank of indicator i. The smaller the n, the higher the priority of the indicator.
Criterion/target layer aggregation:
The essence of this arithmetic mean aggregation is the first-order collaborative quantification of the equilibrium state of the mutant system that, while retaining the threshold mutation characteristics, achieves an overall representation of the ecological resilience level of multiple subsystems through linear dimensionality reduction.
2.3.2. Dagum Gini Coefficient Decomposition
Dagum’s method decomposes spatial disparities into intra-regional and inter-regional contributions [41] and was employed to measure UER disparities across the YRB, enabling precise identification of regional and city-level differences and their impact on uneven UER development, calculated as follows:
where k: total number of regions; : number of provinces (or cities) within region j; : value of UER across all regions; : UER value of province i (r) in region j (h).
Intra-regional Gini ():
Inter-regional Gini ():
2.3.3. Kernel Density Estimation
Kernel density estimation (KDE) is a nonparametric method used to estimate the probability density functions of variables. It enables analysis of the overall distribution pattern of UER in the YRB and captures its dynamic characteristics over time [8]. It is calculated as follows:
where k: Gaussian kernel; h: bandwidth; : observed resilience values.
2.3.4. STIRPAT Model
The stochastic model extends IPAT for multifactorial analysis:
This formula is a logarithmic equivalent transformation of the original multiplicative form of STIRPAT. The logarithmic transformation merely linearizes the nonlinear multiplicative elastic relationship for easier estimation. Essentially, it retains the nonlinear causal mechanism through which variables influence changes in resilience via proportional effects, where R represents UER; P, A, and T denote population scale, wealth level, and technological level, respectively; X is the matrix of other important variables; a is the constant term; b, c, and d are variable coefficients; i represents cities, t represents time; and ε is the random error term.
Given the YRB cities’ ecological characteristics and prior research, we selected the following impact factors:
Population scale (P) is measured by land use intensity, calculated by the proportion of urban construction land to total urban area. Demographic complexity renders population distribution more environmentally impactful and universal than population scale [42,43], while land use data provides cost-effective, reliable regional population estimation through effectively predicting small-scale population distribution and dynamically monitoring changes [44,45,46]. This approach directly links to ecological resilience focus, as unreasonable land use demonstrably affects UER [47].
Wealth scale (A) is operationalized by per capita GDP. On one hand, economic development indirectly increases energy consumption and pollution emissions, exerting negative impacts on UER [48]. On the other hand, the achievements of economic development can also be applied to ecological protection and construction to enhance UER.
Technological level (T) is measured by the number of patents granted per 10,000 people. Technological innovation provides new solutions to ecological protection and resource consumption issues, which can not only realize the greening of production but also guide the greening of consumption concepts [3]. However, the environmental impacts of technological innovation are complex and may increase environmental pollution [49]. The patents granted per 10,000 people can reflect a region’s capacity for independent innovation and the important role of technology in the ecosystem.
Other important factors (X): Two factors, industrial structure (In) and environmental regulation (ER), were further selected to reflect the impacts of human activities on UER. Industrial structure serves as a vital link between economic activities and the ecological environment. Rational industrial structure adjustment can enhance the stability, adaptability, and resilience of ecosystems, while backward industrial structures impose negative impacts on ecosystems and weaken their resilience. Industrial structure is measured by the proportion of tertiary industry output value. Environmental regulation has significant positive and negative effects on ecosystems. The “Porter hypothesis” suggests that scientific environmental regulation can stimulate the “innovation effect”, while the “compliance cost” theory argues that it increases enterprises’ green production costs. Following the approaches of Chen and Chen [50], Deng and Zhao [51], and Yin and Wu [52], environmental regulation-related word frequencies in government work reports were used to capture local governments’ environmental protection priorities, policy orientations, and focal concerns, providing a policy-relevant and operational textual basis for quantifying environmental regulation intensity. Specifically, Python 3.10 was used for word segmentation of government work reports, and regular expressions were employed to measure the intensity of environmental regulation by counting the proportion of 15 environmental regulation-related word frequencies in the work reports of prefecture-level city governments.
2.3.5. Random Forest Model
The random forest model combines tree predictors, each of which depends on an independently sampled random vector. As the number of trees increases, its generalization error converges to a limit. Compared with the Adaboost algorithm, it has a lower error rate and is more robust to noise. The internal estimates of the random forest model can not only monitor error, strength, and correlation but also measure the importance of variables [53]. Specifically, taking the UER in the YRB as the dependent variable and the influencing factors as the independent variables, based on the STIRPAT model, the random forest model was applied to rank the importance of the influencing factors, aiming to explain the main factors affecting the UER in the YRB.
3. Results
3.1. Spatiotemporal Evolution Analysis Based on Catastrophe Theory
UER levels in the YRB were quantified from 2011 to 2023 using the catastrophe progression model. The basin was divided into upstream, midstream, and downstream regions to evaluate UER at three scales: basin-wide, inter-regional, and prefecture-level (Table 2).

Table 2.
UER Levels in the YRB (2011–2023).
UER in the YRB shows distinct spatiotemporal divergence, exhibiting a downstream > midstream > upstream gradient distribution. The overall UER fluctuates around 0.8, remaining at a relatively low level. Upstream cities saw a steady upward trend in average UER before 2020, with an accumulative increase of 4.7%, reflecting the positive effects of ecological protection policies. However, this dropped abruptly by 7.0% in 2023 due to extreme drought, highlighting ecological fragility. The UER of midstream cities has declined most significantly, dropping from the peak in 2013 to the record low point in 2023, with a cumulative decline of 12.3%. This trajectory primarily originated from the dual impact of both the path dependence of highly polluting industries and the cost shifting of environmental regulations. Downstream cities maintained the basin’s highest resilience levels with minimal fluctuation yet still recorded measurable 2023 declines, confirming basin-wide climate pressures. The basin-wide UER showed a slight upward trend during 2011–2020 but declined abruptly by 7.5% in 2023, mainly attributed to water shortages caused by historic droughts, pollution surges during post-pandemic industrial recovery, and systemic risks from ecological overload in megacities such as Zhengzhou.
3.2. Natural Breaks Classification and Regional Disparities
UER in the YRB was rated based on the natural break method to precisely characterize its gradient differentiation pattern (Table 3). Although 70.18% of cities across the basin achieved good or excellent UER levels, there are obvious regional differences. Although no cities received poor ratings in the upstream, plateau ecological fragility constrained the good-to-excellent rate to only 53.33%, with a scarcity of high-resilience cities. Due to energy industry dependence, the midstream was trapped in a dilemma of coexisting high and low resilience, where 72% of cities were classified as good or excellent but accounted for 41.78% of the basin’s moderately medium or poor rated cities. Resource-based cities like Yangquan, hindered by lagging industrial upgrading, became typical UER collapse zones. The downstream region exhibited an 82.35% good-to-excellent rate, significantly higher than the upstream, confirming the UER support from eastern economic advantages. However, internal differentiation was severe. As a core city, Zhengzhou became a UER collapse zone due to deteriorating indicators, including high industrial wastewater discharge, population density exceeding international warning lines, as well as ecological space constraints such as scarce per capita water resources and insufficient green space. This conclusion aligns with the “prominent structural pollution” noted in Central Environmental Protection Inspection bulletins and the red alerts in China Urban Carrying Capacity Report, not only revealing the unsustainability of overloaded development in developed regions but also validating the evaluation system’s effectiveness in warning ecological crises in high-load cities. Conversely, some cities with excellent UER levels, such as Ordos and Dongying, offset the environmental pressures they face through advantages in dimensions including vegetation restoration (A4) and sewage treatment (B1), which demonstrates multidimensional resilience and dynamic adaptability.

Table 3.
Resilience Tier Classification by Natural Breaks.
3.3. Spatial Heterogeneity Analysis via Dagum Gini Coefficient
The spatial differences and sources of UER in the YRB were revealed by using the Dagum Gini coefficient (Table 4).

Table 4.
Dagum Gini Coefficients and Contribution Rates.
3.3.1. Overall and Intra-Regional Differences
The average Gini coefficient of UER across the entire region was 0.050, reflecting the effectiveness of basin-wide collaborative governance, though significant internal differentiation persisted. Constrained by geographical conditions and water resource allocation, the upstream region exhibited the largest internal disparities, yet its Gini coefficient showed a declining trend before 2022, indicating the initial success of cross-provincial ecological compensation mechanisms. The midstream region had the smallest regional differences due to the convergence of energy economic paths, but it rose at an average annual rate of 1.2% in the opposite direction. Especially after 2020, the growth rate accelerated, reflecting the differentiation and transformation of industries. Energy cities like Ordos and Yulin enhanced UER through green technology upgrades, while traditional industrial cities such as Baotou and Yangquan, with a large proportion of polluting industries, faced dual pressures of ecological governance and industrial upgrading, causing persistent expansion of intercity gaps. Relying on technological spillover from developed cities, the downstream region maintained a suboptimal equilibrium in Gini coefficient and showed an overall trend of stability with a slight decline.
3.3.2. Inter-Regional Disparities
Regional disparities are jointly driven by geographical and economic factors. The UER Gini coefficient between upstream and downstream cities is as high as 0.058, which is attributed to differences in natural conditions between the fragile ecology of upstream highland canyons and the ecological redundancy of downstream alluvial plains, combined with the economic advantages of the downstream region.
Temporally, the evolution of differences exhibited dual-cycle fluctuations driven by policy and climate factor. Before 2019, the South-to-North Water Diversion Project and promotion of clean coal technology drove regional convergence; after 2019, implementation of the “Double Carbon” policy enabled the downstream to accelerate green industry undertaking with industrial base advantages, while midstream traditional industrial capacity shrank. Combined with intensified extreme climate, regional differences expanded again, exhibiting an evolutionary pattern of “divergence–convergence–redivergence”.
3.3.3. Contributions to Spatial Heterogeneity
Hypervariable density with 46.1% contribution has become the dominant factor of spatial disparity, which is primarily due to UER gaps resulting from disparities in natural conditions, negative effects of economic agglomeration, and shocks from extreme events like the 2021 Zhengzhou floods. Notably, the interregional contribution rate dropped to 7.86% in 2017, significantly lower than other years, which was primarily attributed to interprovincial compensation disputes triggered by the Sanjiangyuan National Park pilot. Although central emergency intervention temporarily adjusted statistical data, it did not fundamentally resolve the weaknesses of regional collaboration mechanisms.
3.4. Dynamic Evolution of UER in the YRB
KDE was further applied to analyze the spatiotemporal dynamic evolution of UER in the YRB (Figure 2).
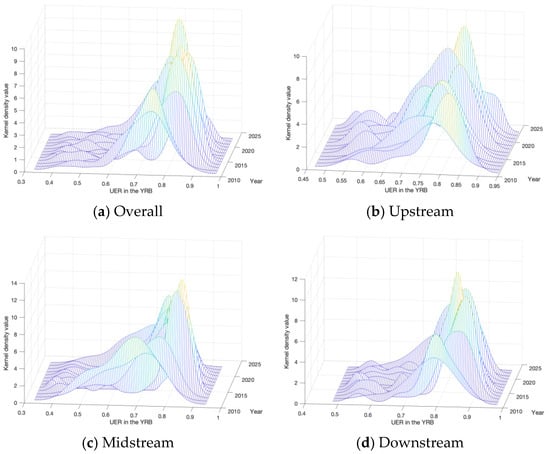
Figure 2.
Dynamic evolution of UER in the YRB.
The kernel density curve of the entire basin showed a continuous rightward shift of the main peak from 2011 to 2023, stabilizing in the 0.6–0.9 range. Particularly, after the implementation of initiatives such as the South-to-North Water Diversion, Grain for Green Program (2013), and the Double Carbon Policy (2022), the main peak notably sharpened and narrowed, reflecting the strengthening impacts of major projects and policies on UER. However, the curve’s tailing and “main-secondary peak” pattern revealed developmental imbalance between developed cities and mid-upstream regions.
The upstream region maintained its main peak within 0.65–0.85. Due to the constraints of geographical factors like the Liupan Mountains, the ecological background is fragile. Coupled with the incomplete cross-provincial ecological compensation mechanism, the peak exhibits a flat profile with a pronounced secondary peak. In the midstream region, driven by clean coal technologies, the kernel density curve shifted upward from 0.5–0.8 (pre-2012) to 0.7–0.9. Post 2013, the main peak sharpened and narrowed, reflecting reduced intercity disparities in ecological governance via industrial–technological convergence. The downstream region showed continuous rightward main peak migration, indicating rapid resilience improvements through industrial upgrading. Nevertheless, the pronounced right-tail extension highlighted how technological and capital agglomeration exacerbate intra-regional development divergence.
3.5. Analysis of Influencing Factors on UER in the YRB
3.5.1. STIRPAT Model Results
The descriptive statistics of key variables are presented in Table 5. Based on Table 6, population (P) and affluence (A) significantly inhibited ecological resilience in the downstream region, indicating that high population density and intensive economic activities exacerbate ecological carrying pressure. Although no significant impacts were observed in the upstream and midstream region, potential risks still exist. Industrial structure (In) also showed a significant negative effect in the downstream region, revealing that energy-intensive segments in the tertiary industry pose potential threats to UER. Technology (T) played a positive role in both upstream and downstream region, highlighting the restorative effect of scientific and technological innovation on UER. Environmental regulation (ER) demonstrated a double-edged sword effect. The midstream region, as a concentrated area of energy and heavy chemical industry, saw enterprises cutting environmental protection investments to save costs, resulting in significant negative effects of environmental regulations. In contrast, the downstream region’s economic strength mitigated policy shocks, resulting in statistically insignificant effects.

Table 5.
Descriptive Statistics of Key Variables.

Table 6.
STIRPAT Model Results for the YRB and Subregions.
3.5.2. Random Forest Model Analysis
To further assess the relative importance of influences, a random forest model was applied to rank influencing factors (Figure 3).
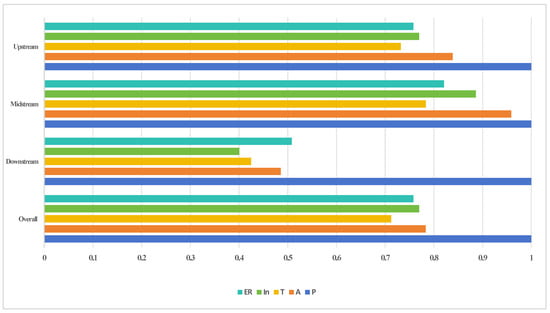
Figure 3.
Importance of Influencing Factors on UER in the YRB and Subregions.
Population (P) is the primary influencing factor, with a significantly higher importance score than other influencing factors, confirming it is the core factor leading to ecological overload. The importance of environmental regulation (ER) and industrial structure (In) exhibited regional differentiation, with the order of midstream > upstream > downstream. As the core area of energy and chemical industries, the midstream region, combined with the fragile ecological background of the Loess Plateau, exhibited high sensitivity to all factors under the dual pressures of nature and human activities. Although the downstream region has intense economic activities, it relies on ecological barriers such as the Dongying Yellow River Delta Wetland. With its powerful ecological service functions and strong buffering capacity, the impact intensity of various factors on UER is weakened.
The analytical results of the STIRPAT and random forest models regarding population factors are mutually complementary. The STIRPAT model demonstrated that population pressure exerted a significant inhibitory effect only in downstream ecologically overloaded areas, indicating that high population density triggered explicit crises once it exceeded local ecological carrying thresholds. Meanwhile, the random forest model identified population as the primary early-warning factor for ecological risks across the entire basin, revealing that mid-upstream regions harbor potential systemic risks despite lacking statistical significance. This divergence precisely validates the transmission mechanism whereby population pressure evolves from cumulative basin-wide risks to localized explosive impacts. The midstream region, dominated by energy and heavy chemical industries and constrained by fragile ecological conditions, is highly sensitive to various influencing factors such as environmental regulation (ER). Although the downstream region is economically developed and weakens the direct ecological impacts of most factors, the development of energy-intensive service industries still poses hidden risks to UER.
4. Discussion
4.1. Gradient Spatial Patterns
The YRB presented a distinct “high in the east and low in the west” gradient spatial pattern in UER, consistent with spatial distributions concluded in the Yangtze River Basin [35,37] and corroborated by some conclusions in YRB [3]. However, methodological variations caused conflicting results, with a “high in the west and low in the east” pattern identified through energy ecological footprint modeling [31] and an upstream > downstream > midstream hierarchy by PSR frameworks [20]. This divergence stems not only from the basin-specific indicators (water stress/vegetation factors) incorporated in this study but also from the extreme 2023 drought’s impact on the basin. These differences highlight the sensitivity of resilience assessments to both data selection and analytical approaches as well as to spatiotemporal context. Notably, the UER of the YRB is still at a low level. Despite methodological discrepancies, the majority of studies converge on this conclusion [7,20], while some studies even document a slight decrease [30,37]. This confirms that in the process of urbanization, the YRB faced multiple pressures and challenges; thus, the UER vulnerability is prominent [7]. Although some studies have shown that the UER of the YRB had a fluctuating upward trend [20], this contradicts our findings, likely due to the expansion of our study period and the significant perturbations caused by recent exogenous shocks like the COVID-19 pandemic, which disrupted ecosystem stability [3]. This underscores the nonlinear interplay between regional development models and resilience thresholds.
4.2. Multi-Scale Governance Implications
To unravel the spatiotemporal evolution characteristics of UER in the YRB, Gini coefficient and KDE methods were used [54], while some scholars also carried out analysis through Theil index [3]. Despite methodological differences, studies consistently identify pronounced spatial imbalances in resilience development [37,54]. Hypervariation density serves as a primary source of spatial inequality [20], and it is compounded by trailing distribution features [31], reflecting regional disparities widening and polarization. Urban patterns (e.g., urban morphology, land use distribution, and connectivity) exert differential impacts on ecosystem dynamics and their resilience [2,12]. The YRB is a large area with great ecological diversity. Regional development is unbalanced, and each region has its unique resource factor endowment, leading to the spatial distribution of UER disparities showing specific spatial curing characteristics [5,20]. These findings underscore the necessity of differentiated governance strategies. While basin-wide policies are essential for macro-scale coordination, micro-scale interventions must account for regional heterogeneity to address resilience challenges [7,54].
4.3. Determinants of Ecological Resilience
The concept of resilience inherently acknowledges the multi-tiered structure of socio-ecological systems and the strong interdependencies among its influencing factors [1]. Most existing studies have employed spatial econometric models, geographical detectors, geographically weighted regression (GWR), and its variants (e.g., GTWR), among others, to dissect ecological resilience influences [3,15,28,35,55]. However, the nonlinear mechanism of natural and anthropogenic factors on ecological resilience remains unclear [25]. To address this gap, the STIRPAT model was used to analyze the effects of population (P), affluence (A), technology (T), industrial structure (In), and environmental regulation (ER) on UER in the YRB. This model is more compatible with the nonlinear and dynamic characteristics of complex systems and more flexible than IPAT/ImPACT model, which can effectively reduce subjective bias and integrate multi-dimensional driving factors [20]. Key findings reveal that population (P) and affluence (A) exerted negative impacts on UER, with greater effects on the downstream region due to high population density and economic intensity. Such patterns support the conclusion that ecosystems in areas with intensive human activities are more vulnerable [26,30,32,42,47,48]. Technology (T) positively influences UER by improving resource efficiency and reducing pollution loads, consistent with prior research [15,16,49]. Contradicting theoretical expectations, industrial structure (In) and environmental regulation (ER) significantly reduce resilience. While theoretical studies suggest that industrial optimization enhances ecological resilience through technological upgrading and resource integration [4,17,25] and that environmental regulations improve ecological performance through market incentives and command-and-control mechanisms [50,52], this discrepancy can be attributed to two mechanisms. The first mechanism is resource misallocation and path locking; the excessive agglomeration of high-polluting industries (e.g., chemicals and metallurgy) in the tertiary industry, coupled with extensive management practices, drives resource allocation beyond ecological carrying capacity thresholds, entrenching a “pollution–growth” dependence [3,52]. The second mechanism is regulatory distortions. Low-intensity administrative orders suppress short-term ecological investments, while stringent regulations trigger “policy escape” behaviors, exacerbating interregional resilience disparities [3,28]. Spatial heterogeneity analysis by random forest modeling further reveals that the upstream region exhibits the lowest factor sensitivity, the midstream region demonstrates the highest sensitivity, and upstream ecosystems possess strong adaptability.
4.4. Research Limitations
While this study advances understanding of UER in the YRB, several limitations warrant acknowledgment.
4.4.1. Temporal and Spatial Data Constraints
Constrained by short-term data from 2011 to 2023 and the scale of prefecture-level cities, this study cannot fully capture decadal climate cycles, lagging ecological responses, or the 2023 drought impacts. Additionally, prefecture-level aggregation masks differences in resilience within cities. Future studies can further enhance the depth and comprehensiveness of studies by integrating data across multiple time scales and utilizing high-resolution spatiotemporal modeling.
4.4.2. Model Simplifications
The STIRPAT model and random forest model adopted in this study are limited by the additive interaction hypothesis and the defects of black box interpretation, which fail to fully analyze the multi-factor synergistic effect and threshold pathways. To deepen the analysis, the coupled system dynamics model and the hybrid modeling framework integrating machine learning screening and structural equation modeling can be further adopted.
5. Conclusions
This study evaluates the spatiotemporal evolution and influencing factors of UER in the YRB from 2011 to 2023 based on the catastrophe progression model. UER across the YRB manifests a stepwise spatial pattern characterized by higher values in eastern regions and lower in western areas. The upstream reaches maintain a low-level equilibrium state with no high-resilience exemplar cities. Midstream cities exhibit marked fluctuations in resilience levels. While the downstream region demonstrates relative advantages overall, core urban centers like Zhengzhou experience resilience deterioration due to excessive industrial pollution and population density surpassing ecological carrying thresholds. The spatial differentiation of UER in the basin presents a fluctuating polarization trend. Influenced by climate and economy, regional disparities have undergone changes of “divergence–convergence–redivergence”, and hypervariable density dominates spatial differentiation, revealing the interactive effects of natural conditions and human activities. The midstream region achieves resilience convergence and difference narrowing through clean technology promotion, while geographical barriers in the upstream and ecological overload in the downstream economic clusters lead to coexisting local improvements and collapses. These findings confirm that the UER of the YRB is dually constrained by natural conditions and human activities. Under the influence of various factors, UER in the upstream, midstream, and downstream regions demonstrates differences of low disturbance, high sensitivity, and high adaptability, respectively. Population emerges as the core factor affecting UER in the YRB.
Based on these findings, three governance pathways are proposed.
Firstly, the government must adjust regional development strategies according to local conditions. In upstream ecological barrier areas like the Three-River-Source Region, strict conservation measures must prioritize water retention and salinization control through scientific water resource management. Midstream industrial hubs such as Yulin should initiate concrete demonstration projects that integrate carbon capture with coal chemical processes while also forming cross-city technology alliances to phase out obsolete facilities and scale hydrogen energy production. Downstream economic centers including Zhengzhou need binding land development restrictions coupled with targeted river rehabilitation and wetland restoration programs to resolve ecological overloading, using their financial advantage to accelerate green industrial upgrading across manufacturing and services.
Secondly, a problem-oriented and regionally linked comprehensive governance system should be established. Concrete solutions must bridge midstream energy volatility and downstream ecological collapse by transforming upstream conservation efforts into economic value through formal Payment for Ecosystem Services programs and green industry incentives. Midstream cities require dynamic production capacity adjustment systems paired with transformation subsidies for clean technology adoption. Downstream cities should gain land development rights through verified off-site carbon sink forest investments while contributing to a basin-wide ecological restoration fund. A dedicated cross-provincial coordination body must standardize compensation, manage pollution discharge trading markets, and integrate environmental monitoring data across jurisdictions to enable resource sharing and balanced development.
Thirdly, the government should implement zoned and classified source governance and construct an intelligent sensitive collaborative prevention and control system. Downstream areas must enforce binding urban growth boundaries and construction density limits to reduce ecological pressure while midstream areas mandate comprehensive energy–chemical sector transitions through circular production models and emission capture retrofits. Basin-wide green technology investments should target water efficiency and pollution control. A unified intelligent early warning network must synthesize satellite imagery, aerial surveillance, ground sensors, and hydrological data with ecological models to generate dynamic vulnerability assessments. This enables adaptive management, where downstream industries face graded operational restrictions during pollution crises and midstream areas adjust to environmental enforcement based on real-time production data, shifting governance from disaster response to proactive risk mitigation that sustains ecological–economic equilibrium.
Author Contributions
Z.Z., conceptualization, funding acquisition, methodology, project administration, resources, supervision, validation, and writing—review and editing; Y.W., data curation, formal analysis, investigation, software, visualization, and writing—original draft. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by (1) The Key Project of the National Social Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 24AJL008); (2) The Soft Science Project of Gansu Province (Grant No. 24JRZA090); (3) The Excellent Doctoral Project of Gansu Province (Grant No. 25JRRA237); (4) The Innovative Project of Scientific Research for Doctoral Students of Lanzhou University of Finance and Economics (Grant No. 2023D05).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author, upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We appreciate the comments of the reviewers.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| UER | Urban ecological resilience |
| YRB | Yellow River Basin |
| KDE | Kernel density estimation |
References
- Sterk, M.; van de Leemput, I.A.; Peeters, E.T. How to conceptualize and operationalize resilience in socio-ecological systems? Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2017, 28, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, M.; Marzluff, J.M. Ecological resilience in urban ecosystems: Linking urban patterns to human and ecological functions. Urban Ecosyst. 2004, 7, 241–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.S.; Chen, Y.; Xie, H.Q. Spatiotemporal pattern and driving factors of urban agglomeration ecological resilience in the Yellow River Basin. Ecol. Econ. 2024, 40, 99–108. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bush, J.; Doyon, A. Building urban resilience with nature-based solutions: How can urban planning contribute? Cities 2019, 95, 102483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.S. Systematic identification and prospect of eco-environmental issues in the Yellow River Basin. Res. Environ. Sci. 2024, 37, 1–10. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Li, L.; Wang, S.; Huang, J.; Xie, X.; Wang, Y. What are the dominant drivers and optimal thresholds for a healthy ecosystem in the Yellow River Basin, China? From a perspective of nonlinear nexus. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 162, 111997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Luo, M. Spatiotemporal evolution characteristics and driving factors of water-energy-food-carbon system vulnerability: A case study of the Yellow River Basin, China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.N.; Ru, S.F.; Xue, F. Spatiotemporal pattern and dynamic evolution of ecological resilience in the Yellow River Basin: Analysis based on emergy ecological footprint model. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2024, 34, 136–147. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Asadzadeh, A.; Khavarian-Garmsir, A.R.; Sharifi, A.; Salehi, P.; Kötter, T. Transformative resilience: An overview of its structure, evolution, and trends. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holling, C.S. Resilience and stability of ecological systems. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1973, 4, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, M. Modeling the urban ecosystem: A conceptual framework. In Urban Ecology: An International Perspective on the Interaction Between Humans and Nature; Marzluff, J.M., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 623–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alliance, R. Assessing Resilience in Social-Ecological Systems: Workbook for Practitioners; Resilience Alliance: Ontario, ON, Canada, 2010; Available online: http://www.resalliance.org (accessed on 10 October 2024).
- Shamsipour, A.; Jahanshahi, S.; Mousavi, S.S.; Shoja, F.; Golenji, R.A.; Tayebi, S.; Sharifi, A. Assessing and mapping urban ecological resilience using the loss-gain approach: A case study of Tehran, Iran. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 103, 105252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, M.; Gómez-Baggethun, E.; Benayas, J.; Tilbury, D. Towards an urban resilience index: A case study in 50 Spanish cities. Sustainability 2016, 8, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Zhu, X.; Wu, H.; Li, Z. Assessment of urban ecological resilience and its influencing factors: A case study of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration of China. Land 2022, 11, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Tian, J.; Li, X. Enhancing urban ecological resilience through integrated green technology progress: Evidence from Chinese cities. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 36349–36366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, L.C.; Yao, S.M. Evaluation of urban resilience in prefecture-level cities of Yangtze River Delta from social-ecological system perspective. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2017, 27, 151–158. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ingrisch, J.; Bahn, M. Towards a comparable quantification of resilience. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2018, 33, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakos, V.; Kéfi, S. Ecological resilience: What to measure and how. Environ. Res. Lett. 2022, 17, 043003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Liu, Q.; Wang, P. Spatiotemporal characteristics of ecological resilience and its influencing factors in the Yellow River Basin of China. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 16988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, B.; Salt, D. Resilience Practice: Building Capacity to Absorb Disturbance and Maintain Function; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marini Govigli, V.; Healey, J.R.; Wong, J.L.; Stara, K.; Tsiakiris, R.; Halley, J.M. Exploring spatial and temporal resilience in socio-ecological systems: Evidence from sacred forests in Epirus, Greece. People Nat. 2024, 6, 1206–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holling, C.S. Engineering resilience versus ecological resilience. In Engineering Within Ecological Constraints; Schulze, P.C., Ed.; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1996; pp. 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folke, C. Resilience: The emergence of a perspective for social–ecological systems analyses. Glob. Environ. Change 2006, 16, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lei, F.; Zeng, H.; Xie, L.; Ouyang, X. Estimating non-linear effects of natural and anthropogenic factors on ecological resilience: Evidence from the southern hilly areas. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.J.; Wang, R.S. Social-economic-natural complex ecosystem. Acta Ecol. Sin. 1984, 4, 1–9. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Simmie, J.; Martin, R. The economic resilience of regions: Towards an evolutionary approach. Camb. J. Reg. Econ. Soc. 2010, 3, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yin, L.; Zhang, B. Potential heterogeneity of urban ecological resilience and urbanization in multiple urban agglomerations from a landscape perspective. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 342, 118129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.M.; Niu, J.L. Spatiotemporal evolution and influencing factors of urban ecological resilience in the Yellow River Basin. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 8309–8320. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Fu, X.; Li, H.; Xu, C. Ecological vulnerability assessment based on PSSR in Yellow River Delta. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 167, 1106–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Fang, C.; Liu, H.; Liu, X. Evaluating urban ecosystem resilience using the DPSIR framework and the ENA model: A case study of 35 cities in China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 72, 102997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Zhang, F.; Li, J.; Zhao, C.; Jiang, Q.; Cheng, Z. Ecosystem health assessment based on AHP-DPSR model and impacts of climate change and human disturbances: A case study of Liaohe River Basin in Jilin Province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 142, 109171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Huang, T.; Xu, S. Assessment of urban ecological resilience based on PSR framework in the Pearl River Delta urban agglomeration, China. Land 2023, 12, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Wu, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z. Research on the impact of sand and dust weather on the social-ecological system resilience based on the DPWSIR model—Taking the arid cities of Northwest China as an example. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.C.; Yan, J.; Li, T. Ecological resilience of city clusters in the middle reaches of Yangtze River. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 443, 141082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.R.; Shi, C.X.; Peng, K.J. Spatio-temporal adaptation and interaction between new urbanization and ecological resilience in urban agglomerations of the middle Yangtze River. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2024, 33, 699–714. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Qing, W.; Li, C.; Yang, Y. Differential evaluation of ecological resilience in 45 cities along the Yangtze River in China: A new multidimensional analysis framework. Land 2024, 13, 1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.S.; Qiu, C.C.; Wang, N.N.; Cao, Y.L.; Zang, Z.C. Research on the ecological protection status of the Yellow River Basin based on variable fuzzy sets. Manag. Rev. 2023, 35, 315–326. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thom, R. Stabilité structurelle et morphogenèse. Poetics 1974, 3, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamovlasis, D. Catastrophe theory: Methodology, epistemology, and applications in learning science. In Complex Dynamical Systems in Education: Concepts, Methods and Applications; Koopmans, M., Stamovlasis, D., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 141–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagum, C. A new approach to the decomposition of the Gini income inequality ratio. In Income Distribution, Inequality, and Poverty; Dagum, C., Zenga, M., Eds.; Physica-Verlag: Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; pp. 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, L.M. Population and Environment: A Complex Relationship; RAND Corporation: Santa Monica, CA, USA, 2000; Available online: https://www.rand.org/pubs/research_briefs/RB5045.html (accessed on 10 October 2024).
- Weber, H.; Sciubba, J.D. The effect of population growth on the environment: Evidence from European regions. Eur. J. Popul. 2019, 35, 379–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagan, H.; Yamagata, Y. Analysis of urban growth and estimating population density using satellite images of nighttime lights and land-use and population data. GISci. Remote Sens. 2015, 52, 765–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Gao, J.; Yuan, F. Growth type and functional trajectories: An empirical study of urban expansion in Nanjing, China. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Huang, Y.; Xu, X.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Ciais, P.; Zeng, Z. High-spatiotemporal-resolution mapping of global urban change from 1985 to 2015. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 3, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; He, M.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Tan, Y.; Li, Z.; Wei, Y. Spatio-temporal analysis and driving forces of urban ecosystem resilience based on land use: A case study in the Great Bay Area. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 159, 111769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farley, J.; Voinov, A. Economics, socio-ecological resilience and ecosystem services. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 183, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dam, M.M.; Kaya, F.; Bekun, F.V. How does technological innovation affect the ecological footprint? Evidence from E-7 countries in the background of the SDGs. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 443, 141020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y.; Chen, D.K. Haze pollution, government governance, and high-quality economic development. Econ. Res. J. 2018, 53, 20–34. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Deng, H.H.; Zhao, J.L. Herd behavior in local government economic decision-making. China Ind. Econ. 2018, 4, 59–78. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.H.; Wu, C.Q. Environmental regulation and ecological efficiency of pollution-intensive industries in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. China Soft Sci. 2021, 8, 181–192. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhong, P.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L. Spatial-temporal differentiation and driving factors of ecological resilience in the Yellow River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.M.; Ning, W.P.; Niu, J.L.; An, K. Spatiotemporal differentiation and convergence of urban ecological resilience in the Yellow River Basin: An empirical analysis based on 61 cities in seven major urban agglomerations. Arid Land Geography. 2024, 47, 93–103. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).