Harnessing an Algae–Bacteria Symbiosis System: Innovative Strategies for Enhancing Complex Wastewater Matrices Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Basic Concept and Classification of the ABS System
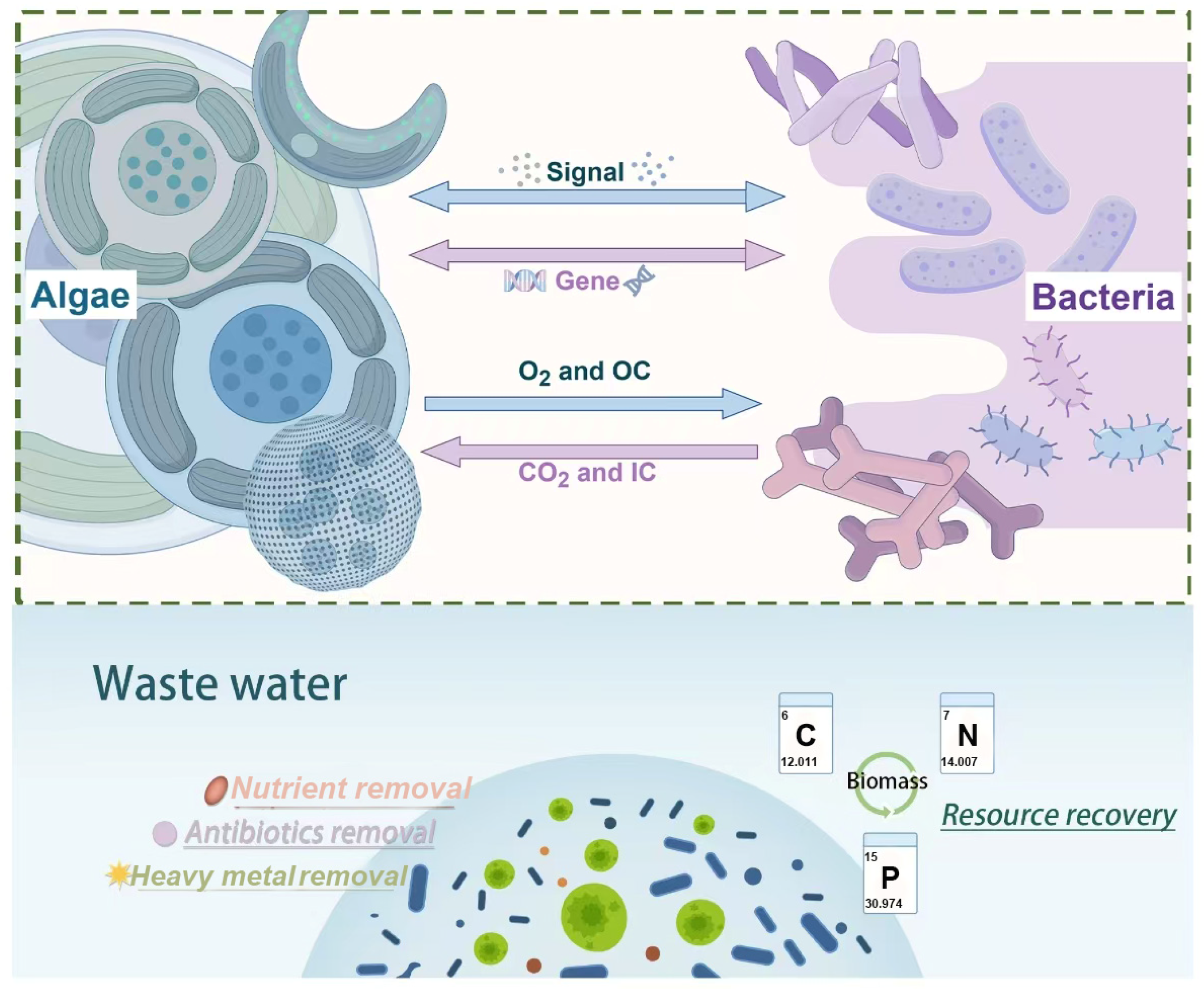
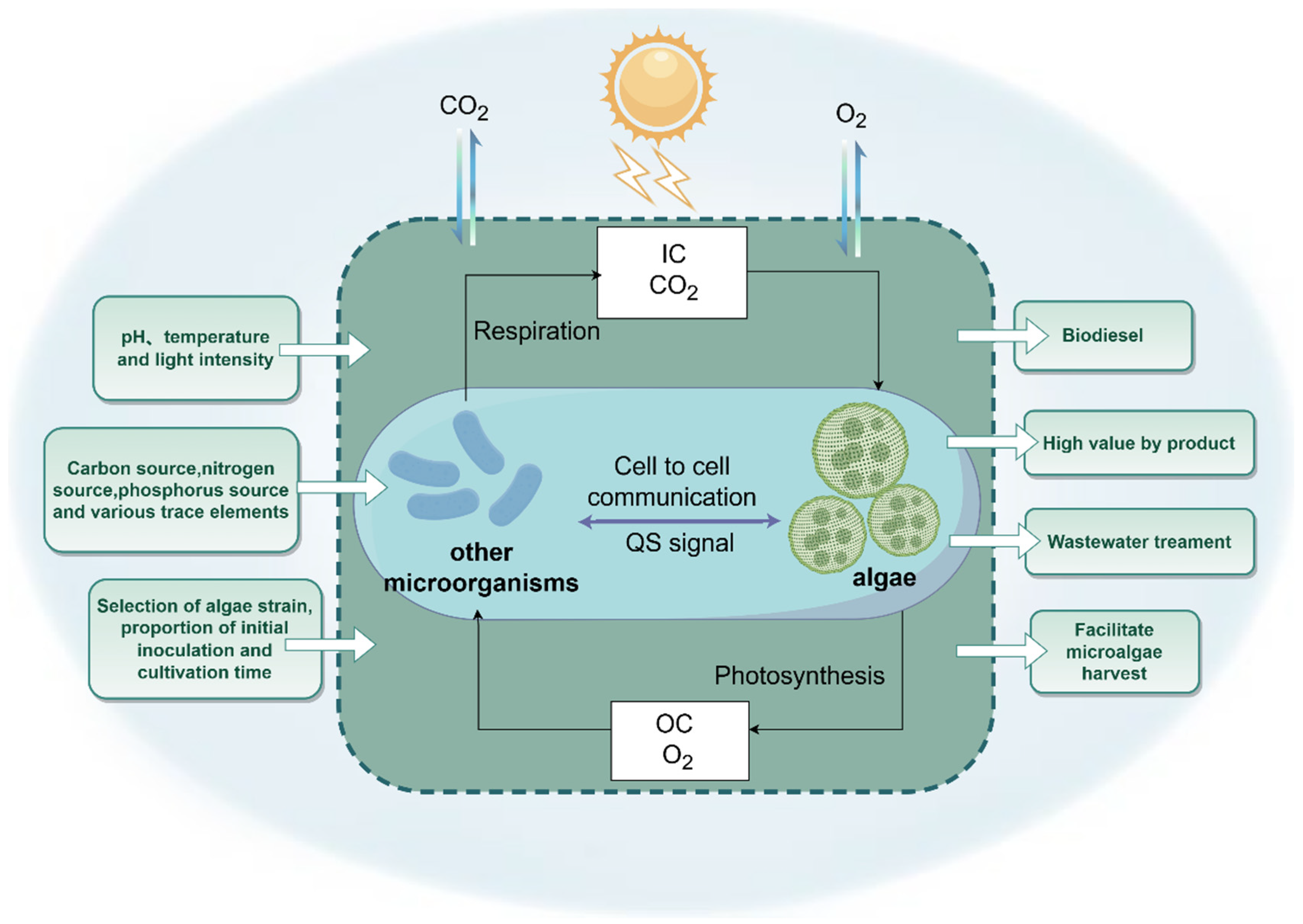
2.1. Basic Concepts
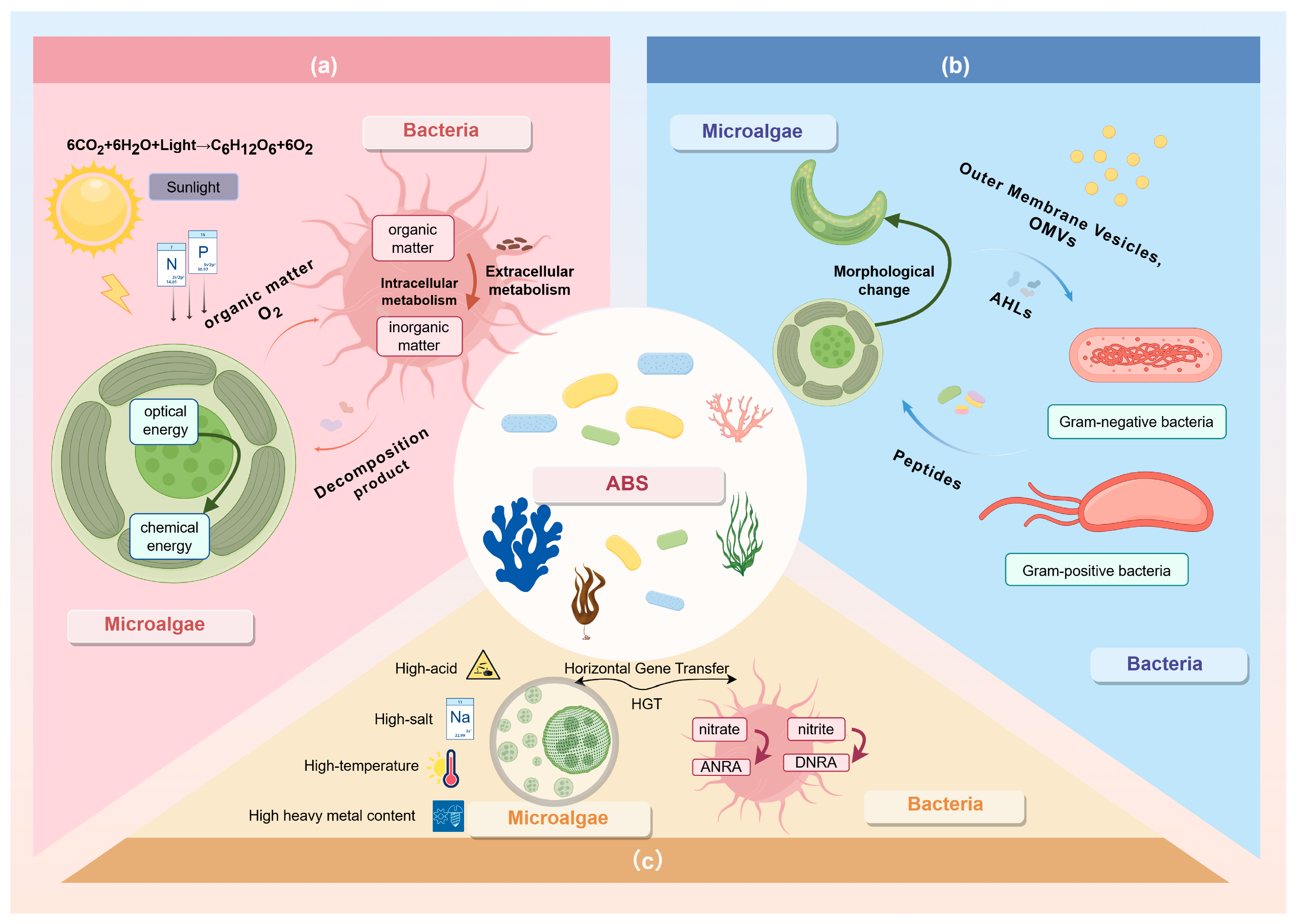
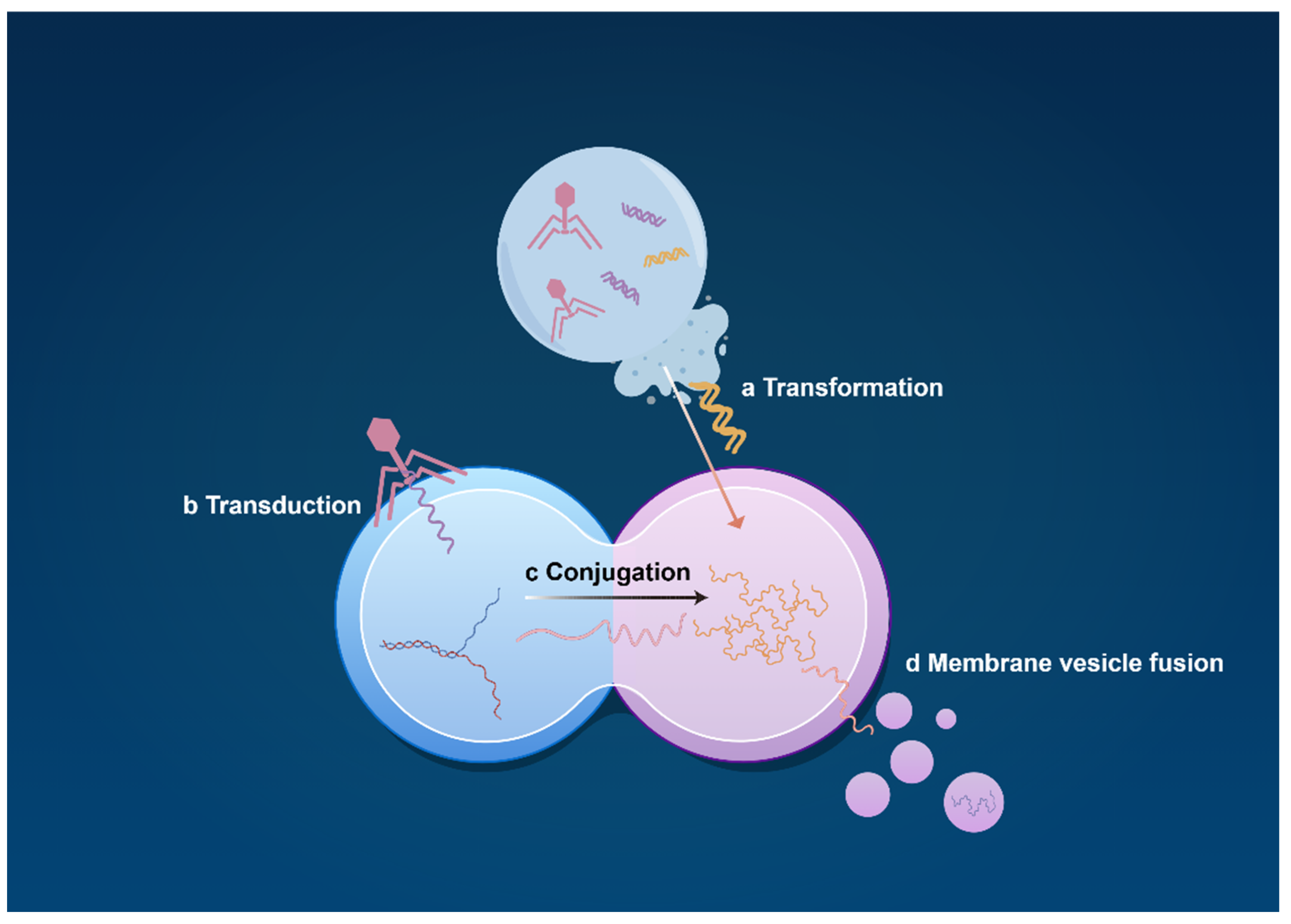
2.2. Interaction and Mechanism of the ABS System
2.3. Taxonomy of the ABS System
2.3.1. Classification by Symbiotic Bacteria
- (1)
- Organic pollutant-degrading bacteria
- (2)
- Heavy metal removal bacteria
- (3)
- Nitrogen-converting bacteria
- (4)
- Phosphate-solubilizing bacteria
2.3.2. Classification by Operational Mode
- (1)
- Batch and fed-batch operation:
- (2)
- Continuous operation:
- (3)
- Semi-continuous operation:
2.3.3. Classification by System Configuration
- (1)
- Open systems
- (2)
- Closed systems
- (3)
- Hybrid systems
3. Applications and Influencing Factors of the ABS System
3.1. Applications
3.1.1. Laboratory-Level Multi-HM Wastewater
3.1.2. Laboratory-Level Multi-POP Wastewater
3.1.3. Laboratory-Level POP-HM Composite Wastewater
3.1.4. Wastewater Under Extreme Conditions
3.1.5. Actual Wastewater
3.2. Influencing Factors
3.2.1. Proportion of Inoculation of Algae and Bacteria
3.2.2. Aeration Duration and Intensity
3.2.3. Light Intensity and Wavelength
3.2.4. Carbon Source and Interaction Between Algae and Bacteria
3.2.5. Application Cases and Practical Operation
4. Summary and Prospect
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jain, K.; Patel, A.S.; Pardhi, V.P.; Flora, S.J.S. Nanotechnology in Wastewater Management: A New Paradigm Towards Wastewater Treatment. Molecules 2021, 26, 1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Prasad, S.M.; Bashri, G. Fate and toxicity of nanoparticles in aquatic systems. Acta Geochim. 2023, 42, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Liu, X.; Jiang, J. Enhanced bioremediation of organic pollutant contaminated environment by microbial consortia: Current situations and challenges. J. Nanjing Agric. Univ. 2020, 43, 10–17. [Google Scholar]
- Behera, S.; Das, S. Potential and prospects of Actinobacteria in the bioremediation of environmental pollutants: Cellular mechanisms and genetic regulations. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 273, 127399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, F.; Wang, P.; Li, Y.; Ling, J.; Ruan, Y.; Yu, J.; Zhang, L. Bioremediation of environmental organic pollutants by Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Mechanisms, methods and challenges. Environ. Res. 2023, 239, 117211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Song, W.; Li, N.; Lu, J.; Niu, X.; Ma, Y.; Ding, J.; Wang, M. Ultraviolet-B radiation of Haematococcus pluvialis for enhanced biological contact oxidation pretreatment of black odorous water in the symbiotic system of algae and bacteria. Biochem. Eng. J. 2020, 157, 107553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, S.A.; Machado, C.A.; Esteves, A.F.; Salgado, E.M.; Dias, J.M.; Vilaça, J.S.; Pires, J.C.M. Microalgae-based wastewater remediation: Linking N:P ratio and nitrogen sources to treatment performance by Chlorella vulgaris and biomass valorisation. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 518, 164701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousa, S.; Ali Mohsin, M.E. Bioprocess modeling of microalgae in treating domestic wastewater via fermentation to convert pollutants into hydrogen. J. Mol. Struct. 2025, 1345, 143022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Cao, W.; Tang, L.; Jin, C.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Guo, L. Integrated physiological and proteomic analyses reveal differential responses of microalgae to inorganic phosphate forms in wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 117137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Zhu, D.; Niu, L.; Zhang, J. Chlorella-actinomycetes symbiotic system for heavy metal wastewater remediation: Influence of initial heavy metal concentration and remediation time. J. Water Process Eng. 2025, 76, 108183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zheng, W.; Tran, K.; Kamilar, E.; Bariwal, J.; Ma, H.; Liang, H. Hydrophilic nanoparticles that kill bacteria while sparing mammalian cells reveal the antibiotic role of nanostructures. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Feng, L.; Zhang, Y. Heavy metals in a typical industrial area-groundwater system: Spatial distribution, microbial response and ecological risk. Chemosphere 2024, 360, 142339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Wu, F.; Zhang, J.; Ai, S.; Liu, Z. Microbial community composition and degradation potential of petroleum-contaminated sites under heavy metal stress. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 457, 131814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, E.R.; Van Vliet, M.T.H.; Qadir, M.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Country-level and gridded estimates of wastewater production, collection, treatment and reuse. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 237–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, L.; Qiang, X.; Song, Y.; Gu, W.; Ma, Z.; Wang, G. Design, construction and application of algae-bacteria synergistic system for treating wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 366, 121720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, M.; Feng, K.; He, Q.; Yang, X.; Hou, W.; Li, F.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, B.; et al. Metabolic interdependencies in thermophilic communities are revealed using co-occurrence and complementarity networks. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 8166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepehri, A. Interaction between Chlorella vulgaris and nitrifying-enriched activated sludge in the treatment of wastewater with low C/N ratio. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 247, 119164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Cui, B.; Guo, D. Towards advanced mariculture wastewater treatment by bacterial-algal symbiosis system with different bacteria and algae inoculation ratios. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 53, 103826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.H.; Kumar, M.; Selvaraj, S.; Samuel, M.S.; Ethiraj, S.; Senthilkumar, A.; Dong, C.D.; Shkir, M. Green energy breakthroughs: Harnessing nano-catalysts and enzymatic catalysts for bioenergy generation. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2024, 215, 118527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eheneden, I.; Wang, R.; Zhao, J. Antibiotic removal by microalgae-bacteria consortium: Metabolic pathways and microbial responses. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 891, 164489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Ji, B.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y. Auto-floating oxygenic microalgal-bacterial granular sludge. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 856, 159175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Xie, Y.; Qiu, S.; Li, M.; Ge, S. Enriched functional exoproteins and increased exopolysaccharides with altered molecular conformation mutually promoted indigenous microalgal-bacterial consortium biofilm growth under high light intensity. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 480, 148056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, B.; Liu, C. CO2 improves the microalgal-bacterial granular sludge towards carbon-negative wastewater treatment. Water Res. 2022, 208, 117865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Peng, S.; Zhao, D.; Miao, L. Autotrophic biological nitrogen removal in a bacterial-algal symbiosis system: Formation of integrated algae/partial-nitrification/anammox biofilm and metagenomic analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 439, 135689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ji, B.; Tian, J.; Liu, Y. Development, performance and microbial community analysis of a continuous-flow microalgal-bacterial biofilm photoreactor for municipal wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 338, 117770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ji, B.; Liu, Y. Microalgal-bacterial granular sludge process: A game changer of future municipal wastewater treatment? Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 141957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Zheng, R.; Feng, Y.; Du, W.; Xie, C.; Gu, Y.; Liu, S. Anammox bacteria adapt to long-term light irradiation in photogranules. Water Res. 2023, 241, 120144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, B.; Shi, Y.; Yılmaz, M. Microalgal-bacterial granular sludge process for sustainable municipal wastewater treatment: Simple organics versus complex organics. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 46, 102613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q. Study on Pollution Reduction and Carbon Reduction Performance of Wastewater Treatment Process in Algae-Bacteria Symbiosis System. Master’s Thesis, Jianzhu University, Jinan, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, T.; Shan, Y.; Huang, B.; Tang, T.; Gao, M.; Wei, W. Effects of algae-bacteria co-culture of on Chlorella sp. growth and phenol degradation. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2020, 14, 1679–1687. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Li, X.; Tang, S.; Lin, K.; Zhao, T.; Chen, X. A review on algal-bacterial symbiosis system for aquaculture tail water treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 847, 157620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, A.; Kumar, P.S.; Varjani, S.; Jeevanantham, S.; Yaashikaa, P.R.; Thamarai, P.; Abirami, B.; George, C.S. A review on algal-bacterial symbiotic system for effective treatment of wastewater. Chemosphere 2021, 271, 129540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.J.; Li, X.; Wang, J.H.; Qi, S.S.; Dai, Z.C.; Du, D.L. Effect of nitrogen-fixing bacteria on resource investment of the root system in an invasive clonal plant under low nutritional environment. Flora 2022, 297, 152166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Gong, Y.; He, Y.; Xin, Y.; Lv, N.; Du, X.; Li, Y.; Jeong, B.; Xu, J. Genome engineering of Nannochloropsis with hundred-kilobase fragment deletions by Cas9 cleavages. Plant J. 2021, 106, 1148–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Huang, F.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liao, X.; Feng, Y.; Ma, J.; Lan, T. Nitrogen removal characteristics of heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification bacterium Acinetobacter ZQ-A1 and community characteristics analysis of its application in pig farm wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 104029–104042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ali, A.; Su, J.; Huang, T.; Wang, Z. Ammonium nitrogen and phosphorus removal by bacterial-algal symbiotic dynamic sponge bioremediation system in micropolluted water: Operational mechanism and transformation pathways. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 947, 174636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, J.; Naduthodi, M.I.S.; Mao, Y.; Dégut, C.; Musiał, S.; Salter, A.; Leake, M.C.; Plevin, M.J.; McCormick, A.J.; Blaza, J.N.; et al. A promiscuous mechanism to phase separate eukaryotic carbon fixation in the green lineage. Nat. Plants 2024, 10, 1801–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Chai, W.; Sun, C.; Huang, L.; Sheng, T.; Song, Z.; Fang, M. Role of microalgae-bacterial consortium in wastewater treatment: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 360, 121226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tirichine, L.; Piganeau, G. Editorial: Algal symbiotic relationships in freshwater and marine environments. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1155759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teplitski, M.; Rajamani, S. Signal and Nutrient Exchange in the Interactions Between Soil Algae and Bacteria. In Biocommunication in Soil Microorganisms; Witzany, G., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 23, pp. 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Hu, Y.; He, Z.; Li, Z.; Tian, Y.; Wang, X. Promoting symbiotic relationship between microalgae and bacteria in wastewater treatment processes: Technic comparison, microbial analysis, and future perspectives. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 498, 155703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Zhang, K.; Liu, Z.; Liu, C.; Kang, J. Study on wastewater treatment characteristics and microbial ecosystem of bacteria-algae symbiosis coupling under carbon neutralization background. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 383, 125331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowruzi, B.; Shishir, M.A.; Porzani, S.J.; Ferdous, U.T. Exploring the Interactions Between Algae and Bacteria. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2022, 22, 2596–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Lyu, S.; An, Y.; Lu, J.; Gjermansen, C.; Schramm, A. Microalgae-bacteria symbiosis in microalgal growth and biofuel production: A review. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 126, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Li, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J. The interactions of an algae–fungi symbiotic system influence nutrient removal from synthetic wastewater. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2019, 94, 3993–3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Zou, Y.; Zheng, J.; Qiu, S.; Liu, L.; Wei, C. Quorum sensing-mediated microbial interactions: Mechanisms, applications, challenges and perspectives. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 273, 127414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Wu, L.; Shi, W.; Zhang, Z.; Lens, P.N.L. A novel strategy for rapid development of a self-sustaining symbiotic algal-bacterial granular sludge: Applying algal-mycelial pellets as nuclei. Water Res. 2022, 214, 118210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Cheng, H.X.; Wang, P.; Fan, R.; Luo, L.Z.; Lin, G.H.; Tian, G.M. Promotion of growth and biological state of microalgae-bacteria consortia during swine wastewater treatment doped with nano-sized iron. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 22876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Song, M.; Yin, D.; Li, R.; Yu, J.; Ye, X.; Chen, X. Sustainable transforming toxic sludge into amino acids via bacteria-algae consortium. Environ. Res. 2024, 263, 120079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, D.; Sharma, U.; Poria, P.; Finlan, A.; Parker, B.; Sharma, R.S.; Mishra, V. Iron-dependent mutualism between Chlorella sorokiniana and Ralstonia pickettii forms the basis for a sustainable bioremediation system. ISME Commun. 2022, 2, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, E.; Dittami, S.M. Maintaining beneficial alga-associated bacterial communities under heat stress: Insights from controlled co-culture experiments using antibiotic-resistant bacterial strains. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2023, 99, fiad130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nef, C.; Dittami, S.; Kaas, R.; Briand, E.; Noël, C.; Mairet, F.; Garnier, M. Sharing Vitamin B12 between Bacteria and Microalgae Does Not Systematically Occur: Case Study of the Haptophyte tisochrysis lutea. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassan, F.D.; Coniglio, A.; Amavizca, E.; Maroniche, G.; Cascales, E.; Bashan, Y.; de-Bashan, L.E. The Azospirillum brasilense type VI secretion system promotes cell aggregation, biocontrol protection against phytopathogens and attachment to the microalgae Chlorella sorokiniana. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 6257–6274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calatrava, V.; Tejada-Jimenez, M.; Sanz-Luque, E.; Fernandez, E.; Galvan, A.; Llamas, A. Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, a Reference Organism to Study Algal–Microbial Interactions: Why Can’t They Be Friends? Plants 2023, 12, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumder, S.; Bhattacharya, D.; Nag, M.; Lahiri, D. Bioactive compounds from marine algae and fungi in down-regulating quorum sensing. Blue Biotechnol. 2024, 1, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Wu, Y.; Liu, C.; Wan, L.; Han, R. Research progress on quorum sensing enhanced denitrification performance of biofilm based on exogenous acyl homoserine lactone. J. Dalian Ocean. Univ. 2023, 38, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boominathan, R.; Devanesan, S.; AlSalhi, M.S.; Balasubramanian, A.; Alkhalid, I.Z.; Paul, P.; Singh, A.J.A.R. Quorum quenching action of marine red alga Halemenia durvillei on biofilm forming Gram negative bacterial isolates from contact lens. Algal Res. 2022, 64, 102693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, C.Y.; Honda, K.; Derek, C.J.C. A review on microalgal-bacterial co-culture: The multifaceted role of beneficial bacteria towards enhancement of microalgal metabolite production. Environ. Res. 2023, 228, 115872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Wei, Y.; Salam, M.; Yuan, X.; Liu, B.; He, Q.; Hu, X.; Li, H.; He, Y. Potassium supplement enhanced cadmium removal in a Microcystis aeruginosa photobioreactor: Evidence from actual and simulated wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zeng, T.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, D.; Wei, J.; Peng, Y.; Miao, L. AHL-mediated quorum sensing drives microbial community succession and metabolic pathway in algal-bacterial biofilm system. Water Res. 2025, 282, 123702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Momani, H.; Aolymat, I.; Ibrahim, L.; Albalawi, H.; Al Balawi, D.; Albiss, B.A.; Almasri, M.; Alghweiri, S. Low-dose zinc oxide nanoparticles trigger the growth and biofilm formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A hormetic response. BMC Microbiol. 2024, 24, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; You, G.; Hou, J.; Wang, C.; Xu, Y.; Miao, L.; Feng, T.; Zhang, F. Responses of wastewater biofilms to chronic CeO2 nanoparticles exposure: Structural, physicochemical and microbial properties and potential mechanism. Water Res. 2018, 133, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Sublethal Concentrations of Silver Nanoparticles Stimulate Biofilm Development. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2015, 2, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schatz, D. Extracellular vesicles—New players in cell–cell communication in aquatic environments. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2018, 43, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schatz, D.; Rosenwasser, S.; Malitsky, S.; Wolf, S.G.; Feldmesser, E.; Vardi, A. Communication via extracellular vesicles enhances viral infection of a cosmopolitan alga. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 1485–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husnik, F.; McCutcheon, J.P. Functional horizontal gene transfer from bacteria to eukaryotes. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Jiang, H.; Liu, B.; Qing, T.; Feng, B.; Ma, T.; Tang, W.; Zhang, P. Toward nitrogen recovery: Co-cultivation of microalgae and bacteria enhances the production of high-value nitrogen-rich cyanophycin. Water Res. 2024, 256, 121624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rappaport, H.B.; Oliverio, A.M. Extreme environments offer an unprecedented opportunity to understand microbial eukaryotic ecology, evolution, and genome biology. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, X.; Wu, Z. Dinoflagellate–Bacteria Interactions: Physiology, Ecology, and Evolution. Biology 2024, 13, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abate, R.; Oon, Y.L.; Oon, Y.S.; Bi, Y.; Mi, W.; Song, G.; Gao, Y. Diverse interactions between bacteria and microalgae: A review for enhancing harmful algal bloom mitigation and biomass processing efficiency. Heliyon 2024, 10, e36503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanan, R.; Kim, B.H.; Cho, D.H.; Oh, H.M.; Kim, H.S. Algae–bacteria interactions: Evolution, ecology and emerging applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInnes, R.S.; McCallum, G.E.; Lamberte, L.E.; van Schaik, W. Horizontal transfer of antibiotic resistance genes in the human gut microbiome. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2020, 53, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.; Song, M.; Ko, D.; Lee, J.; Go, S.; Kim, S.; Kyung, D.; Kim, J.; Bae, H. Enhanced carbon sequestration of biological phenol degradation using wastewater-originated microalgae-bacteria coculture system. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 502, 157882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Lu, R.; Liu, Y.; Cui, X.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Ruan, R.; Zhang, Q. Development of microalgae-bacteria symbiosis system for enhanced treatment of biogas slurry. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 354, 127187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Ren, H.; Jin, Y.; Chai, Z.; Liu, B. The bioremediation of the typical persistent organic pollutants (POPs) by microalgae-bacteria consortia: A systematic review. Chemosphere 2024, 355, 141852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, F.; Liu, S.; Zhang, X.; Li, M. Molecular characteristics of microalgal extracellular polymeric substances were different among phyla and correlated with the extracellular persistent free radicals. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowicka, B. Heavy metal–induced stress in eukaryotic algae—Mechanisms of heavy metal toxicity and tolerance with particular emphasis on oxidative stress in exposed cells and the role of antioxidant response. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 16860–16911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dziuba, J.; Nowicka, B. Unravelling the Mechanisms of Heavy Metal Tolerance: Enhancement in Hydrophilic Antioxidants and Major Antioxidant Enzymes Is Not Crucial for Long-Term Adaptation to Copper in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plants 2024, 13, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mir, I.S.; Riaz, A.; Roy, J.S.; Fréchette, J.; Morency, S.; Ponce Gomes, O.; Dumée, L.F.; Greener, J.; Messaddeq, Y. Removal of cadmium and chromium heavy metals from aqueous medium using composite bacterial cellulose membrane. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 490, 151665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, S.; Poluri, K.M. Heavy metal detoxification mechanisms by microalgae: Insights from transcriptomics analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 285, 117443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, A.; Molnárová, M.; Šotek, P.E.; Fargašová, A. Toxicity assessment of Cd and Cu on physicochemical parameters of green microalga Scenedesmus quadricauda. J. Appl. Phycol. 2025, 37, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balta, I.; Lemon, J.; Gadaj, A.; Cretescu, I.; Stef, D.; Pet, I.; Stef, L.; McCleery, D.; Douglas, A.; Corcionivoschi, N. The interplay between antimicrobial resistance, heavy metal pollution, and the role of microplastics. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1550587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathivanan, K.; Chandirika, J.U.; Vinothkanna, A.; Yin, H.; Liu, X.; Meng, D. Bacterial adaptive strategies to cope with metal toxicity in the contaminated environment—A review. Ecotox Environ. Safe. 2021, 226, 112863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Chen, J.; Ye, M.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, C.; Ge, Y. N-acyl homoserine lactones (AHLs) enhanced removal of cadmium and other pollutants by algae-bacteria consortia. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 366, 121792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Su, B.; Fei, X.; Che, J.; Yao, T.; Zhang, R.; Yi, S. Enhanced microalgal biomass and lipid production with simultaneous effective removal of Cd using algae-bacteria-activated carbon consortium added with organic carbon source. Chemosphere 2024, 350, 141088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, A.; Singh, P.; Gupta, N. Chapter 20—A key player in nutrient cycling. In Cyanobacteria; Mishra, A.K., Singh, S.S., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 579–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, W.; Sun, S.; Yang, J.; Liu, Z.; He, K.; Song, C.; Yang, S.; Wang, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, W.; et al. Operational characteristics in varied gradients of low carbon-to-nitrogen ratios utilizing a novel integrated bacteria-algae synergistic biofilm reactor for wastewater treatment. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 60, 105188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankston, E.; Wang, Q.; Higgins, B.T. Algae support populations of heterotrophic, nitrifying, and phosphate-accumulating bacteria in the treatment of poultry litter anaerobic digestate. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 398, 125550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaedig, E.; Cantrell, M.; Urban, C.; Zhao, X.; Greene, D.; Dancer, J.; Gross, M.; Sebesta, J.; Chou, K.J.; Grabowy, J.; et al. Isolation of phosphorus-hyperaccumulating microalgae from revolving algal biofilm (RAB) wastewater treatment systems. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1219318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aburai, N.; Tsukagoshi, T.; Sekiguchi, S.; Arakawa, H.; Imamura, Y.; Abe, K. Mutual supply of carbon and nitrogen sources in the co-culture of aerial microalgae and nitrogen-fixing bacteria. Algal Res. 2023, 70, 103001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Liu, W.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, X.; Duan, H.; Zhou, L.; Xu, T.; Ruan, R. Improvement of phosphate solubilizing bacteria Paenibacillus xylanexedens on the growth of Chlorella pyrenoidosa and wastewater treatment in attached cultivation. Chemosphere 2022, 306, 13560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chang, Y.; Wang, F.; Niu, D.; Zheng, W. A novel real-time optimization compensation method based on POPOA for the gold hydrometallurgy process. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2021, 171, 367–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayre, J.M.; Mickan, B.S.; Jenkins, S.N.; Moheimani, N.R. Batch cultivation of microalgae in anaerobic digestate exhibits functional changes in bacterial communities impacting nitrogen removal and wastewater treatment. Algal Res. 2021, 57, 102338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Liu, R.; Li, K.; Sun, J.; Wang, K.; Shao, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhu, J.; Pan, Z.; Nakhla, G. Microalgae-bacteria symbiosis enhanced nitrogen removal from wastewater in an inversed fluidized bed bioreactor: Performance and microflora. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1591974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zeng, Z.; Bee, M.; Gibson, V.; Wei, L.; Huang, X.; Liu, C. Characteristics and performance of aerobic algae-bacteria granular consortia in a photo-sequencing batch reactor. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 349, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, S.S.; Miranda, A.L.; Assis, D.d.J.; Souza, C.O.; de Morais, M.G.; Costa, J.A.V.; Druzian, J.I. Efficacy of Spirulina sp. polyhydroxyalkanoates extraction methods and influence on polymer properties and composition. Algal Res. 2018, 33, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.T.; Eng, R.; Zuniga, C.; Huang, K.W.; Chen, Y.; Zengler, K.; Betenbaugh, M.J. Optimization of nutrient utilization efficiency and productivity for algal cultures under light and dark cycles using genome-scale model process control. npj Syst. Biol. Appl. 2023, 9, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fields, F.J.; Ostrand, J.T.; Mayfield, S.P. Fed-batch mixotrophic cultivation of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii for high-density cultures. Algal Res. 2018, 33, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdovinos-García, E.M.; Petriz-Prieto, M.A.; Olán-Acosta, M.D.L.Á.; Barajas-Fernández, J.; Guzmán-López, A.; Bravo-Sánchez, M.G. Production of Microalgal Biomass in Photobioreactors as Feedstock for Bioenergy and Other Uses: A Techno-Economic Study of Harvesting Stage. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purba, L.D.A.; Zahra, S.A.; Yuzir, A.; Iwamoto, K.; Abdullah, N.; Shimizu, K.; Lei, Z.; Hermana, J. Algal-bacterial aerobic granular sludge for real municipal wastewater treatment: Performance, microbial community change and feasibility of lipid recovery. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 333, 117374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altimari, P.; Brasiello, A.; Di Caprio, F.; Pagnanelli, F. Production of microalgae biomass in a continuous stirred bioreactor: Analysis of microalgae-bacteria competition mediated by nitrogen and organic carbon. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2022, 260, 117826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, E.; Babaei, A.; Mehrnia, M.R.; Shayegan, J.; Safdari, M.S. Municipal wastewater treatment by semi-continuous and membrane algal-bacterial photo-bioreactors. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 36, 101274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Ling, J.; Wan, M.; Zhang, J.; Fan, F.; Wang, W.; Li, Y. Semi-continuous cultivation strategy for improving the growth of Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 based on the growth model of volume average light intensity. Algal Res. 2022, 67, 102839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Linares, L.C.; Gutiérrez-Márquez, A.; Guerrero-Barajas, C. Semi-continuous culture of a microalgal consortium in open ponds under greenhouse conditions using piggery wastewater effluent. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 12, 100597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, J.; Feng, X.; Zhao, F. Algal–Bacterial Symbiotic Granular Sludge Technology in Wastewater Treatment: A Review on Advances and Future Prospects. Water 2025, 17, 1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patidar, S.K. Metabolic interactions between microalgae and bacteria: Multifunctional ecological interplay and environmental applications. Algal Res. 2025, 86, 103904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanquia, S.N.; Vernet, G.; Kara, S. Photobioreactors for cultivation and synthesis: Specifications, challenges, and perspectives. Eng. Life Sci. 2022, 22, 712–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, Y.; Wong, Y.; Rao, R. Astaxanthin production from Haematococcus pluvialis by using illuminated photobioreactor. In Global Perspectives on Astaxanthin; Academic Press: Hongkong, China, 2021; pp. 209–224. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues de Assis, L.; Calijuri, M.L.; Assemany, P.P.; Silva, T.A.; Teixeira, J.S. Innovative hybrid system for wastewater treatment: High-rate algal ponds for effluent treatment and biofilm reactor for biomass production and harvesting. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 274, 111183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubar, A.A.; Mehmood, S.; Schagerl, M.; Kumar, S.; Hu, X.; Zhu, F.; Xu, X.; Ni, J.; Huo, S. Integrated hybrid Nested-bottled photobioreactor for enhanced mixing, mass transfer, and CO2 fixation in Arthrospira platensis raceway pond cultivation systems. Biotechnol. Biofuels Bioprod. 2025, 18, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Lu, T.; Liu, W.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, W.; Yang, C.; Qin, Y. The coupling of anammox with microalgae-bacteria symbiosis: Nitrogen removal performance and microbial community. Water Res. 2024, 252, 121214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Wang, L.; Feng, P.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, S. Treatment of mixed wastewater by vertical rotating microalgae-bacteria symbiotic biofilm reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 393, 130057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, D.; Lee, D.J.; Varjani, S.; Lam, S.S.; Allakhverdiev, S.I.; Chang, J.S. Microalgae-based wastewater treatment -microalgae-bacteria consortia, multi-omics approaches and algal stress response. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 845, 157110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Shang, Z.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, H.; Ni, Z.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, X. Tolerance Mechanisms and Removal Efficiency of Chlorella pyrenoidosa in Treating 3-Fluorophenol Pollution. Metabolites 2024, 14, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göncü, S.; Şimşek Uygun, B.; Atakan, S. Nitrogen and phosphorus removal from wastewater using Chlorella vulgaris and Scenedesmus quadricauda microalgae with a batch bioreactor. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, V.R.; Lebron, Y.A.R.; Lange, L.C.; Santos, L.V.S. Simultaneous biosorption of Cd (II), Ni (II) and Pb (II) onto a brown macroalgae Fucus vesiculosus: Mono and multi-component isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 251, 109587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qader, M.Q.; Shekha, Y.A. Bioremediation of Heavy Metals by using Aspergillus niger and Candida albicans. Zanco J. Pure Appl. Sci. 2023, 35, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, C.E.M.; Lima, V.d.S.; Rodrigues, K.; Pereira, L.; Silva, G.M.M. Bioremediation of Endocrine Disruptors (EDs): A Systematic Review of Fungal Application in ED Removal from Wastewater. Water 2025, 17, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajamanickam, R.; Selvasembian, R. Insights into the potential of Chlorella species in the treatment of hazardous pollutants from industrial effluent. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2025, 41, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Gu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Lu, R.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y. Biomass Accumulation, Contaminant Removal, and Settling Performance of Chlorella sp. in Unsterilized and Diluted Anaerobic Digestion Effluent. Fermentation 2024, 10, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhithya, S.; Nithya, K.; Sathish, A.; Kumar, V. Uncovering the feasibility of using live Chlorella microbiomes in domestic and industrial wastewater treatment: Insights into monoculture and synergistic mixed co-cultured system. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2025, 149, 140–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Zhao, L.; Li, Y.; Xing, G.; Chen, D.; Yang, Y. Glucose as a Metabolic Enhancer: Promoting Nonylphenol Detoxification by Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Water 2025, 17, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesbani, A.; Ahmad, N.; Wibiyan, S.; Wijaya, A.; Hanifah, Y.; Royani, I.; Mohadi, R. Improving congo red dye removal by modification layered double hydroxide with microalgae and macroalgae: Characterization and parametric optimation. Colloid. Surf. A 2025, 706, 135770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ñañez, K.B.; Rios Ramirez, K.D.; Cordeiro de Oliveira, O.M.; Reyes, C.Y.; Andrade Moreira, Í.T. Removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) from produced water using the microalgae Chlorella vulgaris cultivated in mixotrophic and heterotrophic conditions. Chemosphere 2024, 356, 141931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Sun, Y.; Lu, W.; Chen, X.; Mosa, A.; Minkina, T.; Gao, Y.; Ling, W. A novel remediation strategy of mixed calcium peroxide and degrading bacteria for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contaminated water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 470, 134122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasir, M.W.; Capozzi, S.L.; Kjellerup, B.V.; Mahmood, S.; Mahmood, T.; Khalid, A. Simultaneous biotreatment of hexavalent chromium Cr(VI) and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) by indigenous bacteria of Co-polluted wastewater. Int. Biodeter. Biodegrad. 2021, 161, 105249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Sun, H.; Li, X.; Lu, Q.; Qin, P.; Yang, Y.; Lai, D.; Luo, L.; Peng, X.; et al. Accelerated removal and mechanism of tetracycline from water using immobilized bacteria combined with microalgae. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 115424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Gu, L.; Hua, Z.; Wang, D.; Xu, R.; Ge, X.; Chu, K. Removal of Per-, Poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) and multi-biosphere community dynamics in a bacteria-algae symbiotic aquatic ecosystem. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 314, 120266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva Rodrigues, D.A.; da Cunha, C.C.R.F.; Freitas, M.G.; de Barros, A.L.C.; e Castro, P.B.N.; Pereira, A.R.; de Queiroz Silva, S.; da Fonseca Santiago, A.; de Cássia Franco Afonso, R.J. Biodegradation of sulfamethoxazole by microalgae-bacteria consortium in wastewater treatment plant effluents. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 749, 141441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Cui, D.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, L.; Chen, H.; Qiu, G.; Xiong, Z.; Shao, P.; Luo, X. Enhanced ammonia nitrogen removal from actual rare earth element tailings (REEs) wastewater by microalgae-bacteria symbiosis system (MBS): Ratio optimization of microalgae to bacteria and mechanism analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 367, 128304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, L.; Lian, L.; Zhang, X.; Qi, Y. Treatment of compound pollution in simulated livestock and poultry wastewater by algae-bacteria symbiosis system. Chemosphere 2025, 370, 143927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safonova, E.; Kvitko, K.V.; Iankevitch, M.I.; Surgko, L.F.; Afti, I.A.; Reisser, W. Biotreatment of industrial wastewater by selected algal-bacterial consortia. Eng. Life Sci. 2004, 4, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Jin, W.; Tu, R. Selection of Microalgae for Biofuel Using Municipal Wastewater as a Resource. Environ. Sci. 2017, 38, 3347–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhimwal, M.; Srivastava, R.K. Microcosmic plant and fungi synergism-based filter to remediate the pollutants from industrial wastewater. Mater. Today 2023, 77, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Du, H.; Zhou, M.; Li, D.; Song, Q.; Hou, N.; Zhao, X. Electrogenic microorganisms enhance synergistic interactions between algae and bacteria through electron release: Insights from niche succession and nitrogen metabolism. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 520, 146137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, S.; Sanyal, D.; Dasgupta, S.; Sapre, A.; Banik, A. Heavy metal mitigation with special reference to bioremediation by mixotrophic algae-bacterial protocooperation. In Nanotechnology in the Life Sciences; Faisal, M., Saquib, Q., Alatar, A.A., Al-Khedhairy, A.A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 305–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhu, L. Performances of Simulated Livestock Wastewater Resource Recovery by the Co Cultivation of Oleaginous Microalgae and Fungi. Res. Environ. Sci. 2023, 36, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Talukdar, A.; Dey, S.; Bhattacharya, S. Role of fungi, bacteria and microalgae in bioremediation of emerging pollutants with special reference to pesticides, heavy metals and pharmaceuticals. Discov. Environ. 2025, 3, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montreemuk, J.; Stewart, T.N.; Prapagdee, B. Bacterial-assisted phytoremediation of heavy metals: Concepts, current knowledge, and future directions. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2024, 33, 103488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cao, P.; Wang, S.; Xu, X. Research on the treatment mechanism of anthraquinone dye wastewater by algal-bacterial symbiotic system. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 347, 126691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirizadeh, S.; Solisio, C.; Converti, A.; Casazza, A.A. Efficient removal of tetracycline, ciprofloxacin, and amoxicillin by novel magnetic chitosan/microalgae biocomposites. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 329, 125115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottie, A.; Mousavi, S.M.; Saljoughi, E.; Kiani, S. Preparation and characterization of biodegradable polybutylene succinate/polyurethane membrane for harvesting of Chlorella sorokiniana microalgae. Algal Res. 2022, 63, 102658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ethiraj, S.; Samuel, M.S. A comprehensive review of the challenges and opportunities in microalgae-based wastewater treatment for eliminating organic, inorganic, and emerging pollutants. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2024, 60, 103316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Jaiswal, K.K.; Verma, M.; Vlaskin, M.S.; Nanda, M.; Chauhan, P.K.; Singh, A.; Kim, H. Algae-based sustainable approach for simultaneous removal of micropollutants, and bacteria from urban wastewater and its real-time reuse for aquaculture. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 774, 145556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oruganti, R.K.; Katam, K.; Show, P.L.; Gadhamshetty, V.; Upadhyayula, V.K.K.; Bhattacharyya, D. A comprehensive review on the use of algal-bacterial systems for wastewater treatment with emphasis on nutrient and micropollutant removal. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 10412–10453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Yoon, Y.; Ngo, H.H.; Jang, A. The application of microalgae in removing organic micropollutants in wastewater. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 51, 1187–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; DeGroot, C.T.; Bassi, A. Biofilm growth enhancement in microalgae biofilm reactors: Parameters, configurations, and modeling. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 65, 105780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.; Liu, X.; Ma, J.; Li, T.; Fan, H.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, E.; Zhang, X. Two-stage anoxic-oxic (A/O) system for the treatment of coking wastewater: Full-scale performance and microbial community analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 417, 129204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Gong, W.; Zeng, W.; Chen, R.; Lin, D.; Li, G.; Liang, H. Bacterial-algae biofilm enhance MABR adapting a wider COD/N ratios wastewater: Performance and mechanism. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 781, 146663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, T.K.Q.; Hoang, Q.H.; Ngo, H.H.; Tran, C.S.; Ninh, T.N.N.; Le, S.L.; Nguyen, A.T.; Pham, T.T.; Nguyen, T.B.; Lin, C.; et al. Influence of salinity on microalgae-bacteria symbiosis treating shrimp farming wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 902, 166111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Long, H.; Zeng, Y.; Ren, W.; Huang, A.; Xie, Z. Screening of microalgae and bacteria from shrimp farming systems and their water treatment efficiency. Nat. Sci. Hainan Univ. 2025, 43, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Parida, V.K.; Majumder, A.; Gupta, B.; Gupta, A.K. Treatment of saline wastewater using physicochemical, biological, and hybrid processes: Insights into inhibition mechanisms, treatment efficiencies and performance enhancement. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Ge, F.; Xu, Y.; Tao, N.; Peng, F.; Wong, M. Efficiency assessment and pH effect in removing nitrogen and phosphorus by algae-bacteria combined system of Chlorella vulgaris and Bacillus licheniformis. Chemosphere 2013, 92, 1383–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, A.K.; Ul Gani Mir, T.; Akhtar, N.; Chopra, C.; Bashir, S.M.; Hassan, S.; Kumar, V.; Singh, R.; Américo-Pinheiro, J.H.P. Algae-Mediated Removal of Prevalent Genotoxic Antibiotics: Molecular Perspective on Algae-Bacteria Consortia and Bioreactor-Based Strategies. Curr. Microbiol. 2024, 81, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Lu, Z.; Xie, T.; Wang, L.; Mo, C. Nitrogen and phosphorus removal by coupling Anaerobic ammonia oxidation reaction with algal-bacterial symbiotic system. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Song, J.; Gu, H.; Zhen, X. Mechanism of contaminant removal by algae-bacteria symbiosis in a PBR system during the treatment of anaerobic digestion effluents. Agric. Water. Manag. 2021, 247, 106556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutić, A.; Miloloža, M.; Cvetnić, M.; Ukić, Š.; Kučić Grgić, D. Phenol, Cyanide, and Thiocyanate in Aquatic Media: The Ecotoxicity of Individual Substances and Their Mixtures. Environments 2025, 12, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Zhang, C.; Fu, L.; Xu, L.; Cui, X.; Li, Q.; Crittenden, J.C. Responses of the Microalga Chlorophyta sp. to Bacterial Quorum Sensing Molecules (N-Acylhomoserine Lactones): Aromatic Protein-Induced Self-Aggregation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 3490–3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elmaksoud, S.; Abdo, S.M.; Gad, M.; Hu, A.; El-Liethy, M.A.; Rizk, N.; Marouf, M.A.; Hamza, I.A.; Doma, H.S. Pathogens Removal in a Sustainable and Economic High-Rate Algal Pond Wastewater Treatment System. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedige, D.; Munasinghe, A.; Zhang, Y.; Nirmalakhandan, N.; Srimali, P. Bacteria and virus reduction in secondary treatment: Potential for minimizing post disinfectant demand. Water Res. 2020, 177, 115802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hong, Y. Microalgae Biofilm and Bacteria Symbiosis in Nutrient Removal and Carbon Fixation from Wastewater: A Review. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2022, 8, 128–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Cui, L.; Liu, J.; You, G.; Chen, Q.; Hou, J.; Fan, X.; Yang, Y. Study on the treatment of livestock and poultry wastewater using algae-bacteria symbiotic system: Effect of inoculation proportion and performance. Environ. Technol. 2025, 46, 2597–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, J.; Li, W.; Wang, F. Carbon sequestration performance, enzyme and photosynthetic activity, and transcriptome analysis of algae-bacteria symbiotic system after antibiotic exposure. Sci. Total. Environ. 2023, 902, 166486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, F.P.; Farias Silva, C.E.; Medeiros, J.A.; Vieira, R.C.; de Sá Filho, M.L.F.; Santos, G.K.S. Consortium between microalgae and other microbiological groups: A promising approach to emphasise the sustainability of open cultivation systems for wastewater treatment. J. Water. Process. Eng. 2022, 50, 103211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Teng, J.; Huang, J.; Shen, L.; Lin, H.; Li, R.; Cai, X.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, M. Glycerol-driven optimization of algae-bacteria symbiosis systems for enhanced lipid production and self-flocculation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 115540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Czajka, J.J.; Daiek, C.; Yang, Z.; Sun, L.; Tang, Y.J.; Liu, Y.; Liao, W. An algal-bacterial symbiotic system of carbon fixation using formate as a carbon source. Algal Res. 2023, 72, 103103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; Cai, G.; Zhan, J. Nitrogen and phosphorus removal efficiency and algae viability in an immobilized algae and bacteria symbiosis system with pink luminescent filler. Water Sci. Technol. 2022, 85, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bååth, E.; Kritzberg, E.S. Temperature Adaptation of Aquatic Bacterial Community Growth Is Faster in Response to Rising than to Falling Temperature. Microb. Ecol. 2024, 87, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mekkawi, S.A.; Abdo, S.M.; Youssef, M.; Ali, G.H. Optimizing performance efficiency of algal-bacterial-based wastewater treatment system using response surface methodology. Groundw. Sust. Dev. 2024, 26, 101273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, S.; Kaur, A.; Singh, G.; Arya, S.K. Integrating biosorption and machine learning for efficient remazol red removal by algae-bacteria co-culture and comparative analysis of predicted models. Chemosphere 2024, 355, 141791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Ping, W.; Ge, G.J.; Lin, Y. Advances in the co-culture of microalgae with other microorganisms and applications. J. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 38, 518–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.-H.; Cao, H.; Cai, P.; Sørensen, S.J. The initial inoculation ratio regulates bacterial coculture interactions and metabolic capacity. ISME J. 2021, 15, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrashekharaiah, P.S.; Gupte, Y.; Sarkar, P.; Prasad, S.; Sanyal, D.; Dasgupta, S.; Banik, A. Algae-bacterial aquaculture can enhance heavy metals (Pb2+ and Cd2+) remediation and water re-use efficiency of synthetic streams. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 180, 106211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L. Influence of inoculation ratio on the performance and microbial community of bacterial-algal symbiotic system for rural wastewater treatment. Water Environ. Res. 2023, 95, e10838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Gong, W.; Bai, L.; Chen, R.; Zeng, W.; Yan, Z.; Li, G.; Liang, H. Aeration-induced CO2 stripping, instead of high dissolved oxygen, have a negative impact on algae–bacteria symbiosis (ABS) system stability and wastewater treatment efficiency. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 382, 122957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.C.; Zuo, W.; Tian, Y.; Sun, N.; Wang, Z.W.; Zhang, J. Effect of aeration rate on performance and stability of algal-bacterial symbiosis system to treat domestic wastewater in sequencing batch reactors. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 222, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.D.; Nguyen, T.T.; An Binh, Q.; Bui, X.T.; Ngo, H.H.; Vo, H.N.P.; Andrew Lin, K.Y.; Vo, T.D.H.; Guo, W.; Lin, C.; et al. Co-culture of microalgae-activated sludge for wastewater treatment and biomass production: Exploring their role under different inoculation ratios. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 314, 123754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Xu, S.; Zou, S.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xu, H.; Wang, J.; Ma, J.; Chen, R.; Zuo, Z. Carbohydrate and lipid yield in Microcystis aeruginosa for biofuel production under different light qualities. Biotechnol. Biofuels Bioprod. 2025, 18, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Tan, Y.; Wei, Z.; He, W.; Qu, Z.; Yang, T.; Shi, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, G.; Song, C.; et al. Exploring the carbon skeleton cycling regulation mechanism of single-wavelength light quality promoting the accumulation of polysaccharides in Spirulina platensis FACHB-439: Based on transcriptomics. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 457, 142443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Sharma, N.; Jaiswal, K.K.; Vlaskin, M.S.; Nanda, M.; Tripathi, M.K.; Kumar, S. Microalgae with a truncated light-harvesting antenna to maximize photosynthetic efficiency and biomass productivity: Recent advances and current challenges. Process Biochem. 2021, 104, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Jin, W.; Xi, T.; Zhou, X.; He, Z.; Meng, X.; Naushad, M.; Jiang, G.; Li, X. Factors affect the oxygen production of chlorella pyrenoidosa in a bacterial-algal symbiotic system: Light intensity, temperature, pH and static magnetic field. Process Saf. Environ. 2024, 184, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ming, Y.; Wang, H.B.; Jin, H.L. Strategies for adaptation to high light in plants. aBIOTECH 2024, 5, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Bernard, O.; Fanesi, A.; Perré, P.; Lopes, F. The effect of light intensity on microalgae biofilm structures and physiology under continuous illumination. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, K.; Yang, R.; Zhang, S.; Fang, F.; Huo, Y.; Yan, P.; Chen, Y.; Guo, J. Extracellular polymeric substances enhanced photosynthesis over respiration in Microcystis aeruginosa. Harmful Algae 2025, 145, 102843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casagli, F.; Rossi, S.; Steyer, J.P.; Bernard, O.; Ficara, E. Balancing microalgae and nitrifiers for wastewater treatment: Can inorganic carbon limitation cause an environmental threat? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 3940–3955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, Y.; Dai, Q.; Du, W.; Zhao, Y.; Song, Q. Screening of Bacteria Promoting Carbon Fixation in Chlorella vulgaris Under High Concentration CO2 Stress. Biology 2025, 14, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Gurung, A.; Mehdi, S.E.H.; Shahzad, S.; Hussain, F.; Kang, W.; Pandey, S.; Khan, A.H.A.; Oh, S.E. Optimizing Physical Factors for the Ammonium Removal from Wastewater Using Bio-Electrochemical Systems. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Xu, Y.; Chen, S.; Liang, C.; Guo, W.; Ngo, H.H.; Peng, L. Inorganic carbon limitation decreases ammonium removal and N2O production in the algae-nitrifying bacteria symbiosis system. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 928, 172440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Zhang, X.; He, Z.; Tian, Y.; Wang, X. Role of extracellular polymeric substances on nutrients storage and transfer in algal-bacteria symbiosis sludge system treating wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 331, 125010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.; Tang, A.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Huang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wei, Y.; Su, Y.; Zhang, Y. Microbial community evolution and fate of antibiotic resistance genes along six different full-scale municipal wastewater treatment processes. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 72, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Hu, Z.; Qi, Y.; Song, C.; Chen, G. The interactions of algae-activated sludge symbiotic system and its effects on wastewater treatment and lipid accumulation. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 292, 122017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, S.; Kong, M.; Zhu, F.; Qian, J.; Huang, D.; Chen, P.; Ruan, R. Co-culture of Chlorella and wastewater-borne bacteria in vinegar production wastewater: Enhancement of nutrients removal and influence of algal biomass generation. Algal Res. 2020, 45, 101744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, D.J.; David, A.S.; Menges, E.S.; Searcy, C.A.; Afkhami, M.E. Environmental stress destabilizes microbial networks. ISME J. 2021, 15, 1722–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reji, M.; Kumar, R. Response surface methodology (RSM): An overview to analyze multivariate data. Indian J. Microbiol. 2023, 9, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfy, W.A.; Ali, A.M.; Abdou, H.M.; Ghanem, K.M. Optimization of fermentation conditions for enhanced acetylcholine and biomass production of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum AM2 using the Taguchi approach. BMC Microbiol. 2025, 25, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Li, Z.; Hu, F.; Wu, B. How does land urbanization promote urban eco-efficiency? The mediating effect of industrial structure advancement. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 272, 122798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, L.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Wan, T.; Gong, Y.; Dai, C.; Ochieng, W.A.; Nasimiyu, A.T.; Li, W.; Liu, F. Corrigendum to “Glutamate dehydrogenase plays an important role in ammonium detoxification by submerged macrophytes. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 733, 139640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Rio-Chanona, E.A.; Cong, X.; Bradford, E.; Zhang, D.; Jing, K. Review of advanced physical and data-driven models for dynamic bioprocess simulation: Case study of algae–bacteria consortium wastewater treatment. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2019, 116, 342–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Feng, L.; Liu, C. Effect of bacteria-algae ratio on treatment of anaerobic digested wastewater by symbiotic coupling of bacteria and algae under the background of carbon neutralization. Environ. Res. 2024, 251, 118771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Cao, Y.; Shi, X.; Li, H.; Shi, Q.; Zhang, Z. How China’s electricity generation sector can achieve its carbon intensity reduction targets? Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 706, 135689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballesté, E.; Pascual-Benito, M.; Martín-Díaz, J.; Blanch, A.R.; Lucena, F.; Muniesa, M.; Jofre, J.; García-Aljaro, C. Dynamics of crAssphage as a human source tracking marker in potentially faecally polluted environments. Water Res. 2019, 155, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Liao, X.; Zou, D.; Huang, B.; Liu, Z. The regulations of varied carbon-nitrogen supplies to physiology and amino acid contents in Gracilariopsis lemaneiformis (Gracilariales, Rhodophyta). Algal Res. 2020, 47, 101818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eze, V.C.; Velasquez-Orta, S.B.; Hernández-García, A.; Monje-Ramírez, I.; Orta-Ledesma, M.T. Kinetic modelling of microalgae cultivation for wastewater treatment and carbon dioxide sequestration. Algal Res. 2018, 32, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casagli, F.; Bernard, O. Simulating biotechnological processes affected by meteorology: Application to algae–bacteria systems. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 377, 134190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S.; Mantovani, M.; Marazzi, F.; Mezzanotte, V.; Ficara, E. Long-term outdoor operation of microalgae-based digestate treatment: Impact of external drivers on process performances and techno-economic assessment. Bioresour. Technol. 2025, 427, 132406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Sun, X.; Liu, X. Synergizing mechanistic and AI models for deeper insights into algal-bacterial systems in sustainable wastewater treatment. J. Water Process Eng. 2025, 76, 108169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, M.; Li, D.; Wen, Q.; Chen, Z. Electrochemical pretreatment of coal gasification wastewater with Bi-doped PbO2 electrode: Preparation of anode, efficiency and mechanism. Chemosphere 2020, 248, 126021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Saiyin, H.; Zheng, Z. The collaborative effect of Chlorella vulgaris-Bacillus licheniformis consortia on the treatment of municipal water. J. Hazar Mater. 2019, 365, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Gou, Y.; Fang, F.; Guo, J.; Lu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, H. Potential of wastewater treatment using a concentrated and suspended algal-bacterial consortium in a photo membrane bioreactor. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 335, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Wang, C.; Qi, Y.; Pang, F.; Wang, M.; Yang, G.; Ma, X. Optimizing algal-bacterial systems for efficient sugar cane wastewater treatment: Pollutant removal and biomass resource recovery. Bioresour. Technol. 2025, 429, 132497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, X.; Lin, H.; Teng, J.; Zhang, M. Harnessing diurnal dynamics: Deciphering the interplay of light cycles on algal-bacterial membrane bioreactors. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 913, 169644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Su, X.; Yang, Q.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Bao, F.; Zhang, N. Nitrogen and phosphorus removal and interactions between algae and bacteria during algal-bacterial granular sludge formation and stabilization. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 67, 106188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhary, A.K.; Kishi, M.; Toda, T. Enhanced growth of Chromochloris zofingiensis through the transition of nutritional modes. Algal Res. 2022, 65, 102723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Ali, S.; Afzal, M.; Nizami, A.S.; Han, S.; Dar, M.A.; Zhu, D. Advancements in bacterial chemotaxis: Utilizing the navigational intelligence of bacteria and its practical applications. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 931, 172967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Yang, D.; Wang, X.; Cao, W. A novel thermostable cellulase-producing Bacillus licheniformis A5 acts synergistically with Bacillus subtilis B2 to improve degradation of Chinese distillers’ grains. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 325, 124729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasani, A.A.; Esmaeili, A.; Golzary, A. Software tools for microalgae biorefineries: Cultivation, separation, conversion process integration, modeling, and optimization. Algal Res. 2022, 61, 102597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschitschko, B.; Esti, M.; Philippi, M.; Kidane, A.T.; Littmann, S.; Kitzinger, K.; Speth, D.R.; Li, S.; Kraberg, A.; Tienken, D.; et al. Rhizobia–diatom symbiosis fixes missing nitrogen in the ocean. Nature 2024, 630, 899–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, Q.; Zhang, J. Effects of static magnetic field on Chlorella vulgaris: Growth and extracellular polysaccharide (EPS) production. J. Appl. Phycol. 2020, 32, 2819–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Types of Wastewater | Algae Species | Bacterial Species | Pollutants and Removal Efficiency | Application Characteristics | Innovation | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lab-scale HM wastewater | Chlorella pyrenoidosa | / | Cu 80% | Low treatable concentration. The HM removal type is single. | / | [114] |
| Chlorella vulgaris | / | Cd 40–70% | Low removal efficiency. The HM removal type is single. | / | [115] | |
| Scenedesmus obliquus | / | Cd 60–75% | / | |||
| Fucus vesiculosus | / | Cd 143.2 ± 7.5 mg/g, Ni 70.1 ± 1.9 mg/g, Pd 516.3 ± 12.5 mg/g | Low adsorption efficiency. Greatly influenced by the environment. | / | [116] | |
| / | Aspergillus niger | Pb 85.6%, Cd 80% | Low treatable concentration. Poor adaptability of strain | / | [117] | |
| / | Trametes versicolor | Cu 88.35%, Cd 87.69%, Pb 96.8%, Zn 91.9% | Long incubation time of strain. Low removal efficiency. | / | [118] | |
| Chlorella vulgaris | Enterobacter sp. Mn17 | Cu 90%, Cd 85% | Environmentally friendly. High value-added products can be produced. |
| [119] | |
| Chlorella pyrenoidosa | Bacillus subtilis | Cu 72.9%, Cd 70% Zn 73% | High biological tolerance. Low cost and sustainability. |
| [120] | |
| Navicula seminulum | Alcaligenes faecalis | Cr 71.8%, Hg 74.8% Pb 79.6%, Cd 72.5% | High removal efficiency. Low cost and sustainability. |
| [121] | |
| Multi-POPs wastewater | Chlorella pyrenoidosa | / | Nonylpheno l90.9% | Dependent metabolic enhancement. Metabolite increase. The POP removal type is single. | / | [122] |
| Eucheuma cottonii | / | Congo red 91% | Decline in regeneration efficiency. Complex preparation process of composite materials. | / | [123] | |
| Chlorella vulgaris | / | PAHs 38–96% | Strict nutritional conditions. Unstable removal efficiency. | / | [124] | |
| / | Acinetobacter Stenotrophomonas Comamonas | Phenanthrene 88.67%, Pyrene 36.42% | Environmental condition limitation. Synergistic reagents lead to system alkalinity problems. | / | [125] | |
| / | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Bipheny l95% | Low removal efficiency. Complex practical application. | / | [126] | |
| / | Alcaligenes faecalis | Tetracycline 68.78% | Low removal efficiency. Time consuming. | / | [127] | |
| Tetradesmus obliquus | Alcaligenes faecalis | Tetracycline 93.87% | High removal efficiency. Various ways of removal. |
| [127] | |
| Chlorophyta Bacillariophyta | Fee-living biosphere | PFBA, PFPeA, PFHxA, PFHpA, PFOA, PONA, PFDA, PFUdA, PFDoA, PFTeDA, PFBS, PFHxS, PFOS | High efficiency PFASs removal ability. Multi-biosphere synergy. Alleviation of oxidative stress |
| [128] | |
| Chlorella sorokiniana | Bacteria in goldfish culture pond | Sulfamethoxazole 54.34% ± 2.35% Partial CECs removal capacity | Excellent biological synergy. Propagation of low antibiotic resistance gene (ARGs). Multi-pollutant removal potential. |
| [129] | |
| POPs-HMs Composite wastewater | Chlorella sorokiniana | / | Zn 86.14%, Etrone 84.96% | Poor long-term operation stability. Sensitive to environmental conditions. | / | [130] |
| Chlorella vulgaris | Bacteria in aerobics activated sludge | Cu 66.7% Sulfadimidine 91.3%+ | High removal efficiency. High biomass and oil content. Low ability to spread antibiotic-resistant genes. |
| [131] | |
| Chlorella sp., Scenedesmus obliquus, Stichococcus strains, Phormidium sp. | Rhodococcus sp. Kibdelosporangium aridum | Zn 90%, Cu 62%, Ni 62%, Mn 70%, Fe 64%, BOD 97%, Oil leakage 96% | High pollutant removal efficiency. Stable symbiotic system. High economic benefit. Environmentally friendly. Excellent sustainability. | Stabilization of microbial community: Fixing algae and bacteria on carriers constructs a stable microbial community. Algal secretions fix bacteria and prevent washout, enhancing system stability and impact resistance. | [132] | |
| Real wastewater | Scenedesmus Obliquus | / | COD 86.4%, TN 93.4%, TP 93.4% | Wastewater needs pretreatment. Strict operating conditions. Low economic benefit. | / | [133] |
| / | Trichoderma harzianum | COD 55.1%, BOD 40.8%, NO3-N 33.9% | Low removal efficiency. Poor long-term stability. | / | [134] | |
| Rhodotorula, Apiotrichum | Acidocella, Enterobacter, Delftia, Macellibacteroides | NH4+-N 96.4%, TN 97.3%, COD 98.6% | High removal efficiency. |
| [135] | |
| Scenedesmus, Auxenochlorella, Nitzschia | Candidatus Competibacter, Candidatus Accumulibacter, Dechloromonas, Thauera, Ferribacterium et al. | NH4+-N 99%, TN 78%, PO43-P 95%, COD 92% | Fast start-up speed. High removal efficiency. Resource recycling. Environmentally friendly. Good adaptability. |
| [120] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, W.; Tian, K.; Zhang, L.; Tang, Y.; Chen, R.; Zheng, X.; Zhao, M. Harnessing an Algae–Bacteria Symbiosis System: Innovative Strategies for Enhancing Complex Wastewater Matrices Treatment. Sustainability 2025, 17, 7104. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17157104
Zhao W, Tian K, Zhang L, Tang Y, Chen R, Zheng X, Zhao M. Harnessing an Algae–Bacteria Symbiosis System: Innovative Strategies for Enhancing Complex Wastewater Matrices Treatment. Sustainability. 2025; 17(15):7104. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17157104
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Wantong, Kun Tian, Lan Zhang, Ye Tang, Ruihuan Chen, Xiangyong Zheng, and Min Zhao. 2025. "Harnessing an Algae–Bacteria Symbiosis System: Innovative Strategies for Enhancing Complex Wastewater Matrices Treatment" Sustainability 17, no. 15: 7104. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17157104
APA StyleZhao, W., Tian, K., Zhang, L., Tang, Y., Chen, R., Zheng, X., & Zhao, M. (2025). Harnessing an Algae–Bacteria Symbiosis System: Innovative Strategies for Enhancing Complex Wastewater Matrices Treatment. Sustainability, 17(15), 7104. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17157104






