Upscaling Soil Salinization in Keriya Oasis Using Bayesian Belief Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Field Soil Sampling and Laboratory Analysis
2.4. Modeling Approach
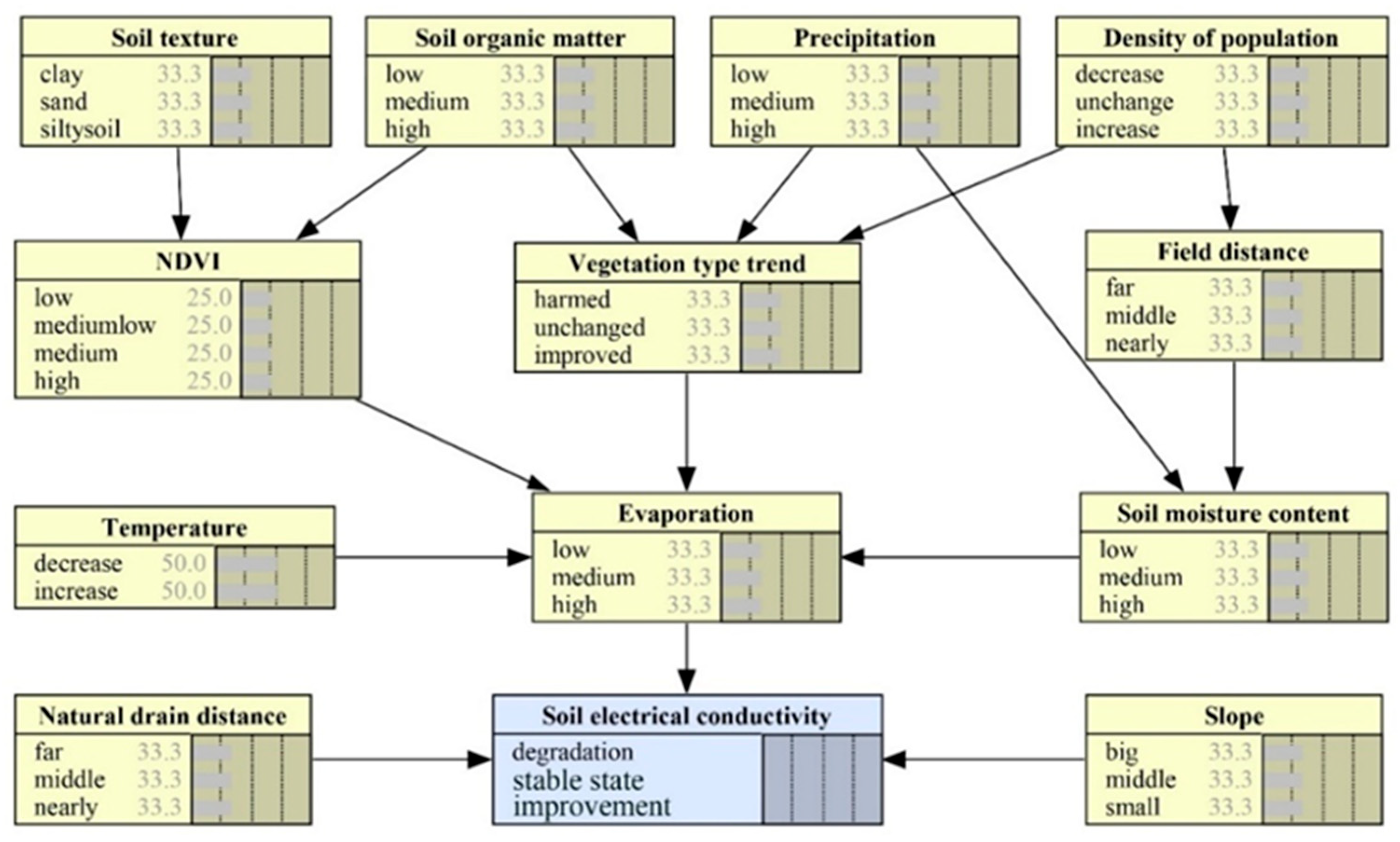
2.4.1. Indicator Selection
2.4.2. Bayesian Network
2.4.3. Model Validation
2.4.4. Tension Spline Function
2.4.5. PLS-SEM Model
3. Results
3.1. Model Sensitivity Analysis
3.2. Spatio-Temporal Changes of Soil Salinization
3.2.1. Temporal Changes of Soil Salinization
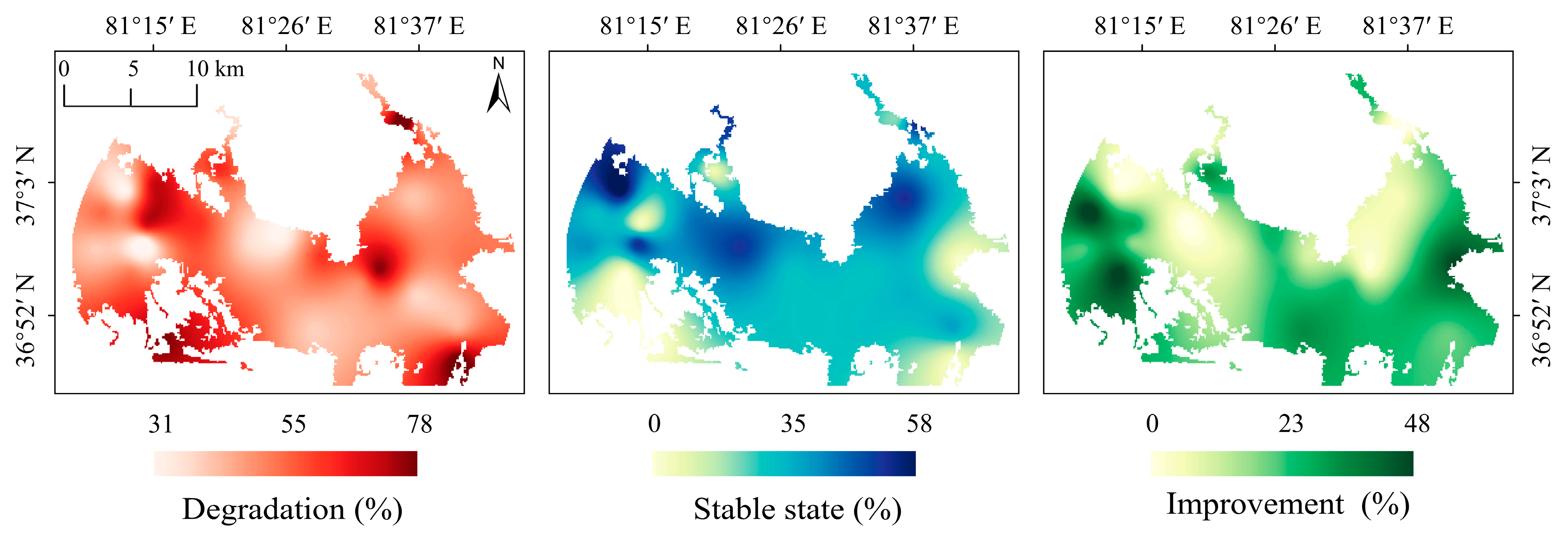
3.2.2. Spatial Characteristics of Salinization Probability Trend
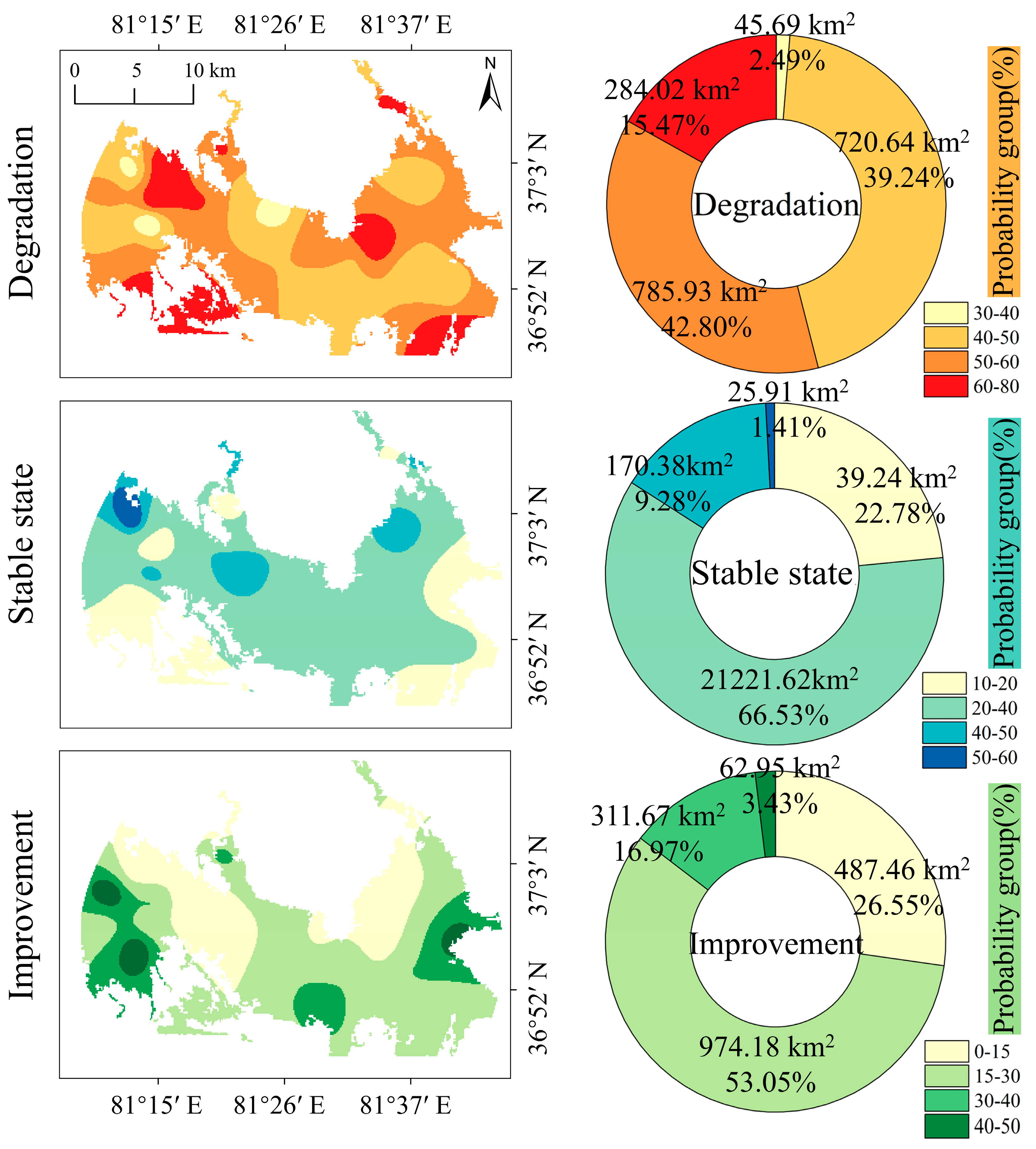
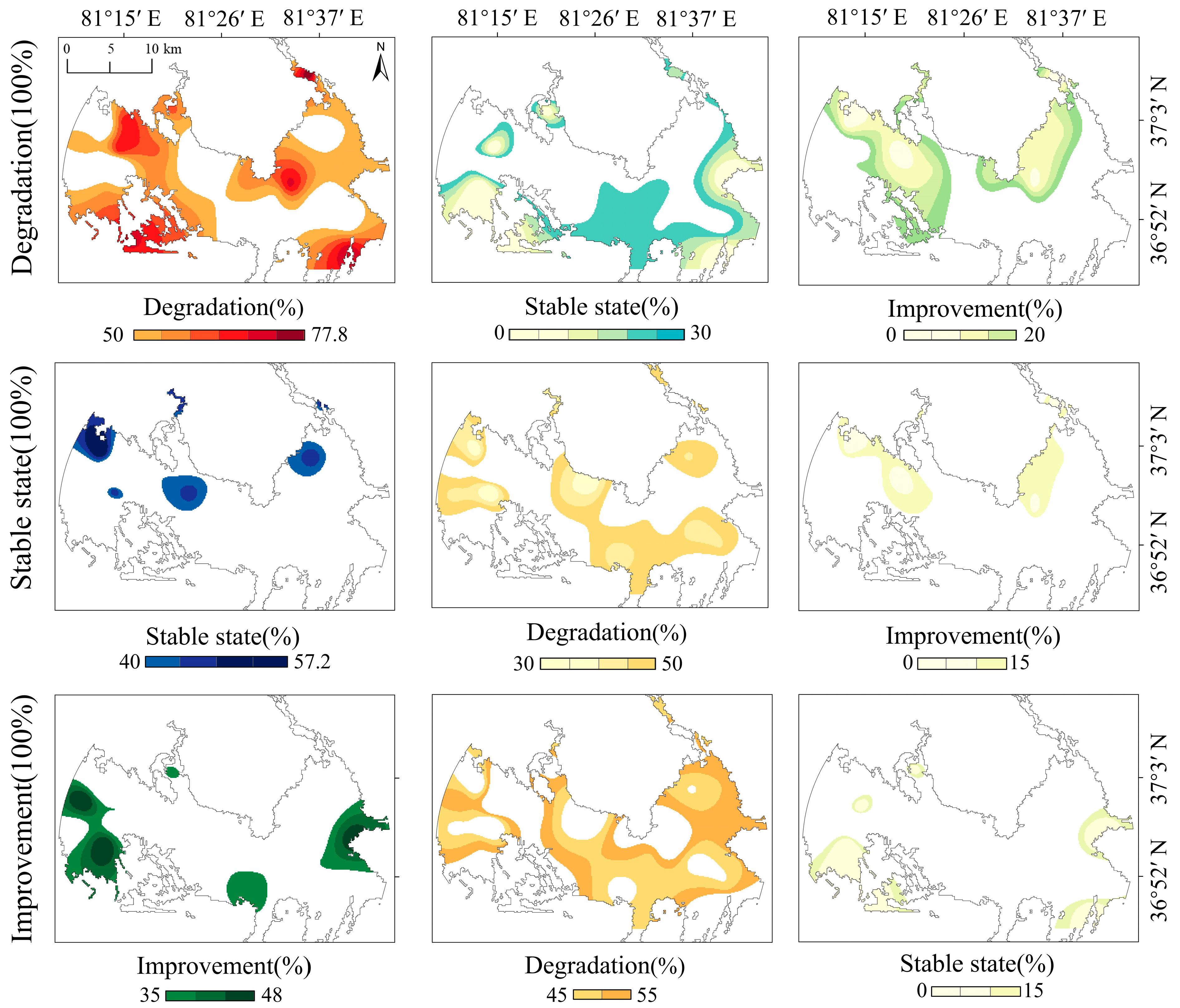
3.3. Area Analysis of Salinization Probability Trend
3.4. Analysis of Spatial Superposition with Different Probabilities
4. Discussion
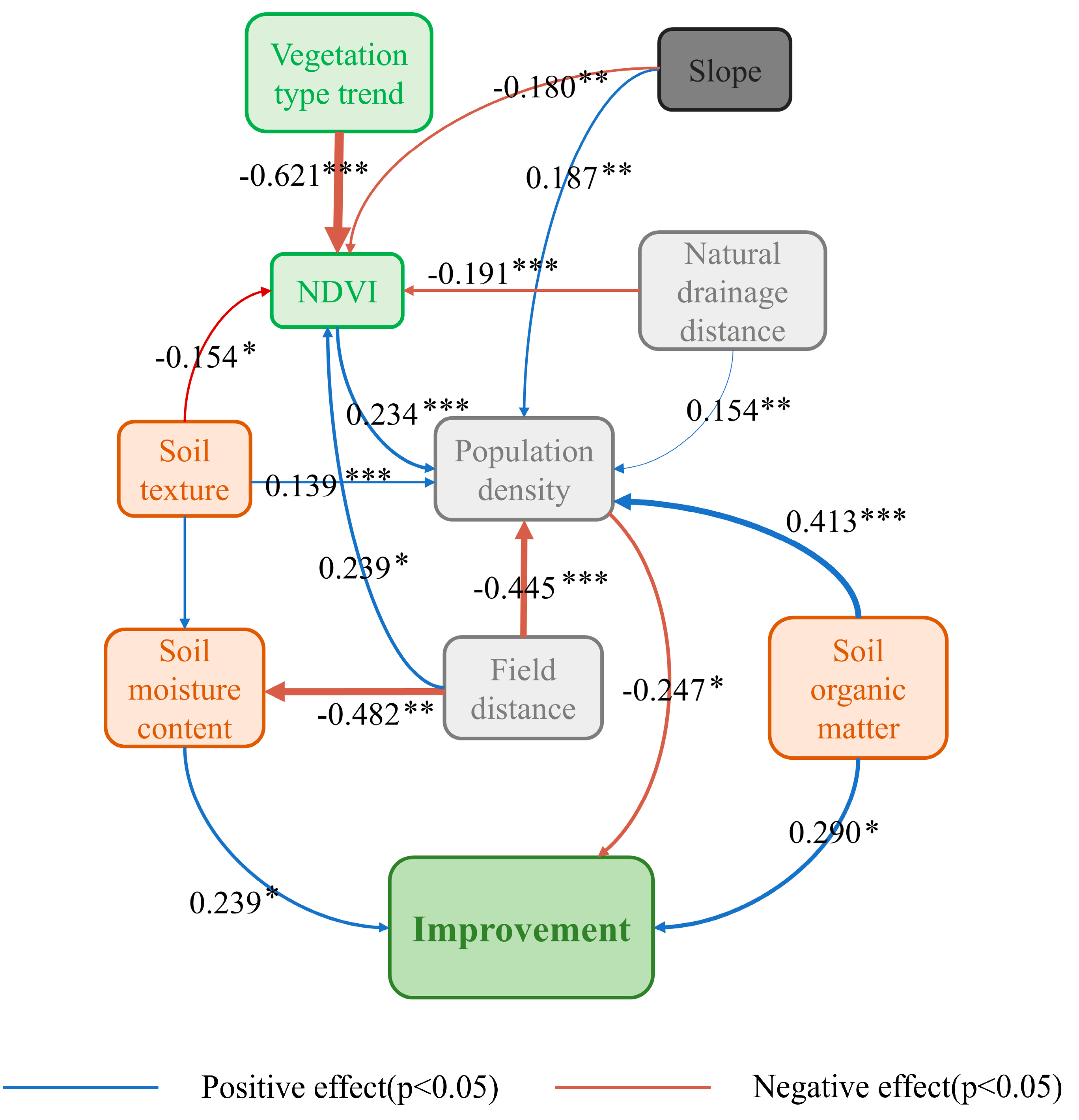
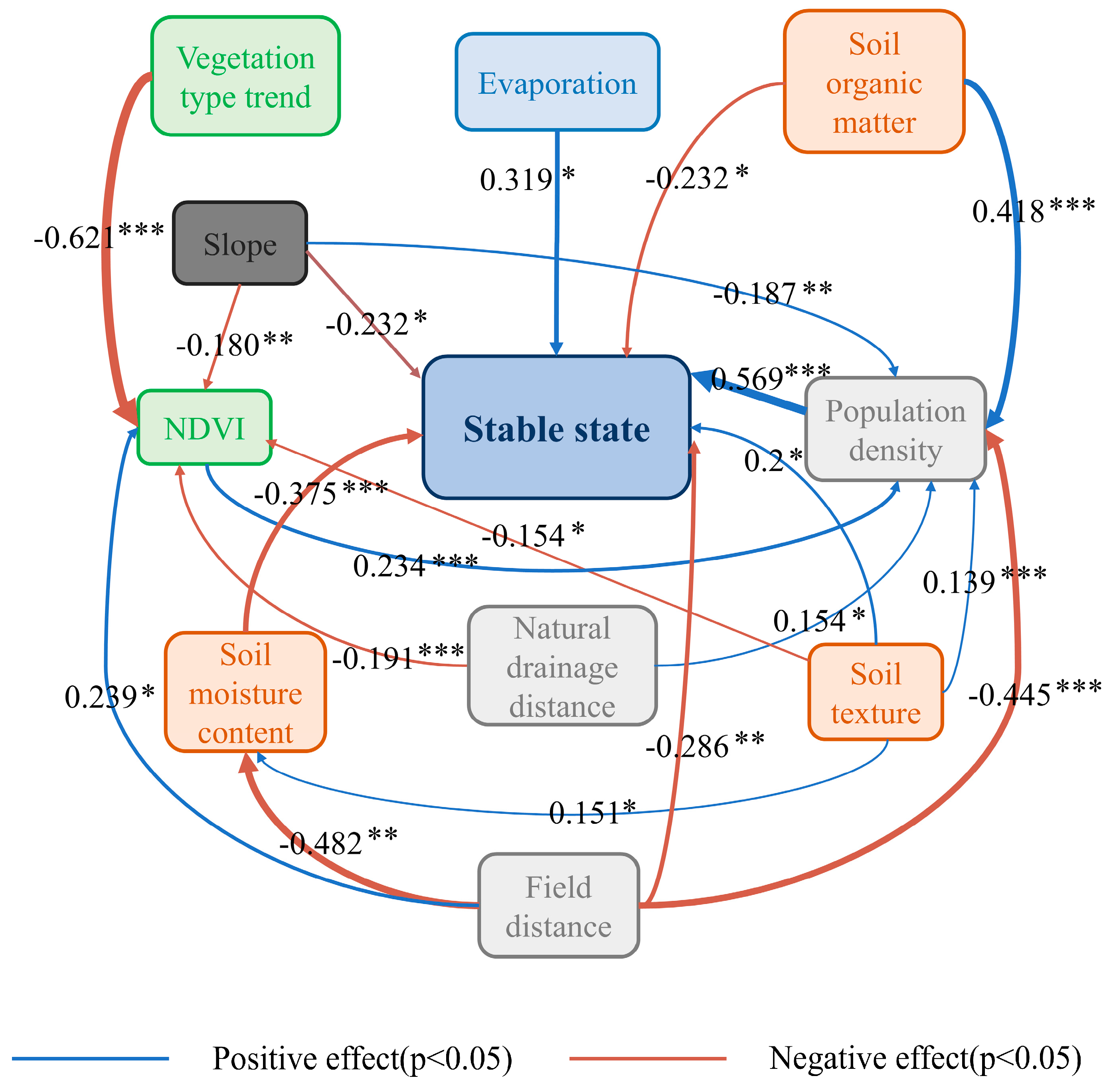
4.1. Mechanism of Drivers Coupling the Salinization Spatiotemporal Probability
4.2. Regional Differences in Soil Salinization in the Keriya Oasis
4.3. Implications for Land Use Policy and Management
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hertwich, E.G.; Pease, W.S.; Koshland, C.P. Evaluating the environmental impact of products and production processes: A comparison of six methods. Sci. Total Environ. 1997, 196, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisladottir, G.; Stocking, M. Land degradation control and its global environmental benefits. Land Degrad. Dev. 2005, 16, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakadevan, K.; Nguyen, M.-L. Extent, impact, and response to soil and water salinity in arid and semiarid regions. Adv. Agron. 2010, 109, 55–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopmans, J.W.; Qureshi, A.; Kisekka, I.; Munns, R.; Grattan, S.; Rengasamy, P.; Ben-Gal, A.; Assouline, S.; Javaux, M.; Minhas, S.P.; et al. Critical knowledge gaps and research priorities in global soil salinity. Adv. Agron. 2021, 169, 1–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hasini, A.; El Amrani, A.; Bouri, H. Soil Salinity under Climate Change: Challenges for Sustainable Agriculture and Food Security. Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 287, 106786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Fan, Y.; Ning, Y.; Wei, J.; Yong, C. Analysis and Prospects of Saline-alkali Land in China from the Perspective of Utilization. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2023, 54, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, M.V. Climate extremes and impacts on agriculture. Agroclimatol. Link. Agric. Clim. 2020, 60, 621–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillel, D. An overview of soil and water management: The challenge of enhancing productivity and sustainability. Soil Manag. Build. A Stable Base Agric. 2011, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondrasek, G.; Rengel, Z. Environmental salinization processes: Detection, implications & solutions. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 142432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y. Monitoring the Seasonal Dynamics of Soil Salinization in the Yellow River Delta of China Using Landsat Data. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 19, 1499–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitman, M.G.; Läuchli, A. Global impact of salinity and agricultural ecosystems. In Salinity: Environmental Plants-Molecules; Lauchli, A., Luttge, U., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Ling, H.; Xu, H.; Guo, B. Study of suitable oasis scales based on water resource availability in an arid region of China: A case study of Hotan River Basin. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A. Soil salinization and waterlogging: A threat to environment and agricultural sustainability. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 57, 128–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A. Soil salinity: A global threat to sustainable development. Soil Use Manag. 2022, 38, 39–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wan, S.; Kang, Y.; Dou, C. Assessment of secondary soil salinity prevention and economic benefit under different drip line placement and irrigation regime in northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 131, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Subasinghe, R.; Malik, R.; Triantafilis, J. Salinity hazard and risk mapping of point source salinisation using proximally sensed electromagnetic instruments. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2015, 113, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besma, Z.; Christian, W.; Didier, M.; Pierre, M.J.; Mohamed, H. Soil salinization monitoring method evolution at various spatial and temporal scales in arid context: A review. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarolli, P.; Luo, J.; Park, E.; Barcaccia, G.; Masin, R. Soil salinization in agriculture: Mitigation and adaptation strategies combining nature-based solutions and bioengineering. iScience 2024, 27, 108830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codling, E.A.; Dumbrell, A.J. Bridging the Gap between Theory and Data in Ecological Models. Ecol. Complex. 2013, 16, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachshon, U. Cropland soil salinization and associated hydrology: Trends, processes and examples. Water 2018, 10, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Kang, S.; Du, T.; Ding, R.; Zou, M. Optimal groundwater depth and irrigation amount can mitigate secondary salinization in water-saving irrigated areas in arid regions. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 302, 109007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, J.; Daliakopoulos, I.N.; del Moral, F.; Hueso, J.J.; Tsanis, I.K. A review of soil-improving cropping systems for soil salinization. Agronomy 2019, 9, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhao, C.; Zheng, J.; Zhu, J.; Gui, Z.; Yu, Z. Evolution of soil salinity and the critical ratio of drainage to irrigation (CRDI) in the Weigan Oasis in the Tarim Basin. Catena 2021, 201, 105210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Luo, P.; Wang, J.; Lu, Y.; Huo, A.; Liu, L. Soil salinity accumulation and groundwater degradation due to overexploitation over recent 40-year period in Yaoba Oasis, China. Soil Tillage Res. 2025, 248, 106398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Rawy, M.; Sayed, S.Y.; AbdelRahman, M.A.; Makhloof, A.; Al-Arifi, N.; Abd-Ellah, M.K. Assessing and segmenting salt-affected soils using in-situ EC measurements, remote sensing, and a modified deep learning MU-NET convolutional neural network. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 81, 102652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hou, K.; Qian, H.; Gao, Y.; Fang, Y.; Xiao, S.; Tang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Qu, W.; Ren, W. Characterization of soil salinization and its driving factors in a typical irrigation area of Northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 837, 155808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaddad, S.M.; Buttafuoco, G.; Castrignanò, A. Assessment and mapping of soil salinization risk in an Egyptian field using a probabilistic approach. Agronomy 2020, 10, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafzadeh, A.; Roshandel, F.; Khaledian, M.; Vazifedoust, M.; Rezaei, M. Assessment of groundwater salinity risk using kriging methods: A case study in northern Iran. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 178, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grafius, D.R.; Corstanje, R.; Warren, P.H.; Evans, K.L.; Norton, B.A.; Siriwardena, G.M.; Pescott, O.L.; Plummer, K.E.; Mears, M.; Zawadzka, J.; et al. Using GIS-linked Bayesian Belief Networks as a tool for modelling urban biodiversity. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2019, 189, 382–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yuan, X.; Li, J.; Qian, K.; Yan, W.; Yang, X.; Ma, X. Trade-offs and synergistic relationships of ecosystem services under land use change in Xinjiang from 1990 to 2020: A Bayesian network analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 160015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Duan, Q.; Zhao, W.; Wang, L.; Zhong, Y.; Zhuang, Y.; Chang, X.; Dong, C.; Du, W.; Luo, L. Oasis sustainability is related to water supply mode. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 290, 108589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Erath, A. A Bayesian network approach for population synthesis. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2015, 61, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaikkonen, L.; Parviainen, T.; Rahikainen, M.; Uusitalo, L.; Lehikoinen, A. Bayesian networks in environmental risk assessment: A review. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2020, 17, 62–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Bai, Y.; Xue, J.; Gong, L.; Zeng, F.; Sun, H.; Hu, Y.; Huang, H.; Ma, Y. Software. Dynamic Bayesian networks with application in environmental modeling and management: A review. Environ. Model. Softw. 2023, 170, 105835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, D.N.; Kuikka, S.; Varis, O.; Uusitalo, L.; Henriksen, H.J.; Borsuk, M.; de la Hera, A.; Farmani, R.; Johnson, S.; Linnell, J.D.; et al. Bayesian networks in environmental and resource management. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2012, 8, 418–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.; Peña-Arancibia, J.L.; Siyal, A.A. Three-dimensional soil salinity mapping with uncertainty using Bayesian Hierarchical Modelling, Random Forest Regression and remote sensing data. Agric. Water Manag. 2025, 309, 109318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Hagare, D.; Maheshwari, B. Bayesian Belief Network analysis of soil salinity in a peri-urban agricultural field irrigated with recycled water. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 176, 280–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Hagare, D.; Maheshwari, B. Framework to assess sources controlling soil salinity resulting from irrigation using recycled water: An application of Bayesian Belief Network. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 105, 406–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seydehmet, J.; Lv, G.H.; Nurmemet, I.; Aishan, T.; Abliz, A.; Sawut, M.; Abliz, A.; Eziz, M. Model Prediction of Secondary Soil Salinization in the Keriya Oasis, Northwest China. Sustainability. 2018, 10, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.Y. To reduce soil salinity: The role of irrigation and water management in global arid regions across development phases. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2204.02029. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, F.; Luo, G.; Guo, Y.; Zheng, J.; Wu, S.; Wang, D.; Liu, S.; Shi, Q. Factors influencing seasonal changes in inundation of the Daliyaboyi Oasis, lower Keriya River valley, central Tarim Basin, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, F.; Luo, G.; Guo, Y.; Zheng, J.; Wu, S.; Keram, Q.; Liu, S.; Shi, Q. Influence of natural and anthropogenic controls on runoff in the Keriya River, central Tarim Basin, China. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0269132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Nurmemet, I.; Lv, X.; Yu, X.; Gu, A.; Aihaiti, A.; Li, S. Multi-Source Attention U-Net: A Novel Deep Learning Framework for the Land Use and Soil Salinization Classification of Keriya Oasis in China with RADARSAT-2 and Landsat-8 Data. Land 2025, 14, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X. The oases along the Keriya River in the Taklamakan Desert, China, and their evolution since the end of the last glaciation. Environ. Geol. 2001, 41, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhu, Z.; Jaekel, D.; Owen, L.; Han, J. Late Quaternary palaeoenvironment change and landscape evolution along the Keriya River, Xinjiang, China: The relationship between high mountain glaciation and landscape evolution in foreland desert regions. Quat. Int. 2002, 97, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurmemet, I.; Sagan, V.; Ding JianLi, D.J.; Halik, Ü.; Abliz, A.; Yakup, Z. A WFS-SVM model for soil salinity mapping in Keriya Oasis, Northwestern China using polarimetric decomposition and fully PolSAR data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Nurmemet, I.; Seydehmet, J.; Lv, X.; Aili, Y.; Yu, X. Spatiotemporal Dynamics and Driving Factors of Soil Salinization: A Case Study of the Yutian Oasis, Xinjiang, China. Land 2024, 13, 1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamat, Z.; Halik, U.; Muhtar, P.; Nurmamat, I.; Abliz, A. Temporal variation of significant soil hydrological parameters in the Yutian oasis in Northwest China from 2001 to 2010. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, J.; Keeler-Wolf, T.; Thomas, K.A.; Shaari, D.A.; Stine, P.A.; Michaelsen, J.; Miller, J. Stratified sampling for field survey of environmental gradients in the Mojave Desert Ecoregion. In GIS and Remote Sensing Applications in Biogeography and Ecology; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2001; pp. 229–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boschetti, L.; Stehman, S.V.; Roy, D.P. A stratified random sampling design in space and time for regional to global scale burned area product validation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 186, 465–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Liu, Y.; Fan, J.; Lu, M.; Zang, W.; Liu, C.; Wang, B.; Huang, X.; Lai, J.; Wu, H. The salinization process and its response to the combined processes of climate change—Human activity in the Yellow River Delta between 1984 and 2022. Catena 2023, 231, 107301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eswar, D.; Karuppusamy, R.; Chellamuthu, S. Drivers of soil salinity and their correlation with climate change. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2021, 50, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmas, C.; Kairis, O.; Karavitis, C.; Acikalin, S.; Alcalá, M.; Alfama, P.; Atlhopheng, J.; Barrera, J.; Belgacem, A.; Solé-Benet, A.; et al. An exploratory analysis of land abandonment drivers in areas prone to desertification. Catena 2015, 128, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Ju, X.; Han, C.; Liu, L.; Zhang, H.; Adilai, S.; Li, C. Spatiotemporal Dynamics and Driving Mechanism of Ecological Environment Quality in Piedmont-Oasis-Desert Ecotone Based on Long-term Harmonized Remote Sensing Ecological Index-Take Korla-Tiemenguan Oasis in Xinjiang as an Example. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 2025, 26, 100611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessoa, L.G.; Freire, M.B.d.S.; Green, C.H.; Miranda, M.F.; de A Filho, J.C.; Pessoa, W.R. Assessment of soil salinity status under different land-use conditions in the semiarid region of Northeastern Brazil. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 141, 109139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garvey, M.D.; Carnovale, S.; Yeniyurt, S. An analytical framework for supply network risk propagation: A Bayesian network approach. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2015, 243, 618–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.-K.; Wang, X.; Xiao, J. Inferring parent–child relationships by a node-remove centrality framework in online social networks. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2018, 505, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowell, R.G.; Verrall, R.J.; Yoon, Y.K. Modeling operational risk with Bayesian networks. J. Risk Insur. 2007, 74, 795–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcot, B.G. Metrics for evaluating performance and uncertainty of Bayesian network models. Ecol. Model. 2012, 230, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrés-Hernández, L.; Baten, A.; Azman Halimi, R.; Walls, R.; King, G.J. Knowledge representation and data sharing to unlock crop variation for nutritional food security. Crop Sci. 2020, 60, 516–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaruddin, S.A.; Zainolabdin, S.N.; Abd. Aziz, K.N.; Roslani, M.A.; Zohir, N.S.A.M.; Al-Bakri, N.Y.M. A comparative study of the accuracy of regularized and tension spline interpolation methods to map the surface water temperature of Pulau tuba, Langkawi, Kedah. In Proceedings of the Charting the Sustainable Future of ASEAN in Science and Technology: Proceedings from the 3rd International Conference on the Future of ASEAN (ICoFA) 2019-Volume 2; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 285–295. [Google Scholar]
- Ajvazi, B.; Czimber, K. A comparative analysis of different DEM interpolation methods in GIS: Case study of Rahovec, Kosovo. Geod. Cartogr. 2019, 45, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perperoglou, A.; Sauerbrei, W.; Abrahamowicz, M.; Schmid, M. A review of spline function procedures in R. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2019, 19, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, M.A.; Ramayah, T.; Cheah, J.-H.; Ting, H.; Chuah, F.; Cham, T.H. PLS-SEM statistical programs: A review. J. Appl. Struct. Equ. Model. 2021, 5, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhang, S.; Guo, L.; Yang, J. The influence of traditional ethnic villages on forest structure based on PLS-SEM: A case study of Miao inhabited area. Forests 2023, 14, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, N.; Wang, W. Spatiotemporal dynamics of wetlands and their driving factors based on PLS-SEM: A case study in Wuhan. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 151310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Aishan, T.; Ma, X. Coupled water-habitat-carbon nexus and driving mechanisms in the Tarim River Basin: A multi-scenario simulation perspective. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 167, 112649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Li, M.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, C. An ensemble learning approach for land use/land cover classification of arid regions for climate simulation: A case study of Xinjiang, Northwest China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 2413–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Banerjee, S.; White, J.F.; Liu, J.-J.; Zhou, N.; Tian, C.-Y. High salt stress increases archaeal abundance and network connectivity in saline agricultural soils. Catena 2022, 217, 106520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Ma, B.; Hou, Z.a.; Liang, X.; Cui, Y.; Li, F. Seasonal transpiration dynamics and water use strategy of a farmland shelterbelt in Gurbantunggut Desert oasis, northwestern China. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 295, 108777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahab, S.; Suhani, I.; Srivastava, V.; Chauhan, P.S.; Singh, R.P.; Prasad, V. Potential risk assessment of soil salinity to agroecosystem sustainability: Current status and management strategies. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 764, 144164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Yu, R.; Chen, X.; Yu, G.; Gan, M.; Disse, M. Agricultural water allocation strategies along the oasis of Tarim River in Northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 187, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, E.; Zhang, H. Complex network and redundancy analysis of spatial–temporal dynamic changes and driving forces behind changes in oases within the Tarim Basin in northwestern China. Catena 2021, 201, 105216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chang, S.X.; Salifu, K.F. Soil texture and layering effects on water and salt dynamics in the presence of a water table: A review. Environ. Rev. 2014, 22, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seydehmet, J.; Lv, G.-H.; Abliz, A. Landscape design as a tool to reduce soil salinization: The study case of Keriya oasis (NW China). Sustainability 2019, 11, 2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madureira, H.; Pacheco, M.; Sousa, C.; Monteiro, A.; De-Sario, M. Sustainability. Evidences on adaptive mechanisms for cardiorespiratory diseases regarding extreme temperatures and air pollution: A comparative systematic review. Geogr. Sustain. 2021, 2, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Gao, S.; Pei, D.; Wen, Y.; Mu, X.; Liu, M.; Wang, Z. Spatio-temporal evolution and simulation of soil salinization in typical oasis water-saving irrigation area based on long series data. Agric. Water Manag. 2025, 307, 109275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Jiang, X.; Ma, M.; Zhou, B.; Guan, D.; Zhao, B.; Zhou, J.; Cao, F.; Li, L.; Li, J. Effect of 35 years inorganic fertilizer and manure amendment on structure of bacterial and archaeal communities in black soil of northeast China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 105, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ding, J.; Han, L.; Tan, J.; Ge, X.; Nan, Q. Biochar addition reduces salinity in salt-affected soils with no impact on soil pH: A meta-analysis. Geoderma 2024, 443, 116845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Luo, M.; Tan, J.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Huang, J.; Tan, Y.; Xiao, L.; Xu, Z. Salt-tolerant plant moderates the effect of salinity on soil organic carbon mineralization in a subtropical tidal wetland. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 837, 155855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, E.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Y. Exploring land reclamation history: Soil organic carbon sequestration due to dramatic oasis agriculture expansion in arid region of Northwest China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 108, 105746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Tariq, A.; Zeng, F.; Sardans, J.; Peñuelas, J.; Zhang, Z.; Islam, W.; Xu, M. “Fertile islands” beneath three desert vegetation on soil phosphorus fractions, enzymatic activities, and microbial biomass in the desert-oasis transition zone. Catena 2022, 212, 106090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, B.; Cheng, W. Sustainable land-use patterns for arid lands: A case study in the northern slope areas of the Tianshan Mountains. J. Geogr. Sci. 2010, 20, 510–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookes, I.A. Geomorphology and Quaternary geology of the Dakhla Oasis region, Egypt. Quat. Sci. Rev. 1993, 12, 529–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Boer, A.; Volkov, V. Logistics of water and salt transport through the plant: Structure and functioning of the xylem. Plant Cell Environ. 2003, 26, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapiya, M.; Ramoelo, A. Groundwater–Vegetation Interactions in Rangeland Ecosystems: A Review. Water 2025, 17, 1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhabra, R. Nature and origin of salts, classification, area and distribution of salt-affected soils. In Salt-affected Soils and Marginal Waters: Global Perspectives and Sustainable Management; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, P.W.; Howell, T.A. Agricultural water conservation-A global perspective. J. Crop Prod. 2000, 2, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanavelu, A.; Naganna, S.R.; Al-Ansari, N. Irrigation induced salinity and sodicity hazards on soil and groundwater: An overview of its causes, impacts and mitigation strategies. Agriculture 2021, 11, 983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.M.; Salem, H.M. Salinity-induced desertification in oasis ecosystems: Challenges and future directions. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xue, J.; Gui, D.; Lei, J.; Sun, H.; Lv, G.; Zhang, Z. Agricultural oasis expansion and its impact on oasis landscape patterns in the southern margin of Tarim basin, Northwest China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askri, B.; Khodmi, S.; Bouhlila, R. Impact of subsurface drainage system on waterlogged and saline soils in a Saharan palm grove. Catena 2022, 212, 106070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebrehiwot, K.A. A review on waterlogging, salinization and drainage in Ethiopian irrigated agriculture. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2018, 4, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhu, C.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, T. Water quality and interaction between groundwater and surface water impacted by agricultural activities in an oasis-desert region. J. Hydrol. 2023, 617, 128937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aishan, T.; Song, J.; Halik, Ü.; Betz, F.; Yusup, A. Predicting Land-Use Change Trends and Habitat Quality in the Tarim River Basin: A Perspective with Climate Change Scenarios and Multiple Scales. Land 2024, 13, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiam, H.I.; Owusu, V.; Villamor, G.B.; Schuler, J.; Hathie, I. Farmers’ intention to adapt to soil salinity expansion in Fimela, Sine-Saloum area in Senegal: A structural equation modelling approach. Land Use Policy 2024, 137, 106990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, R.; Wang, Z. Rationale saline-water irrigation also serves as enhancing soil aggregate stability, regulating carbon emissions, and improving water use efficiency in oasis cotton fields. Ind. Crops Prod. 2025, 223, 120144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

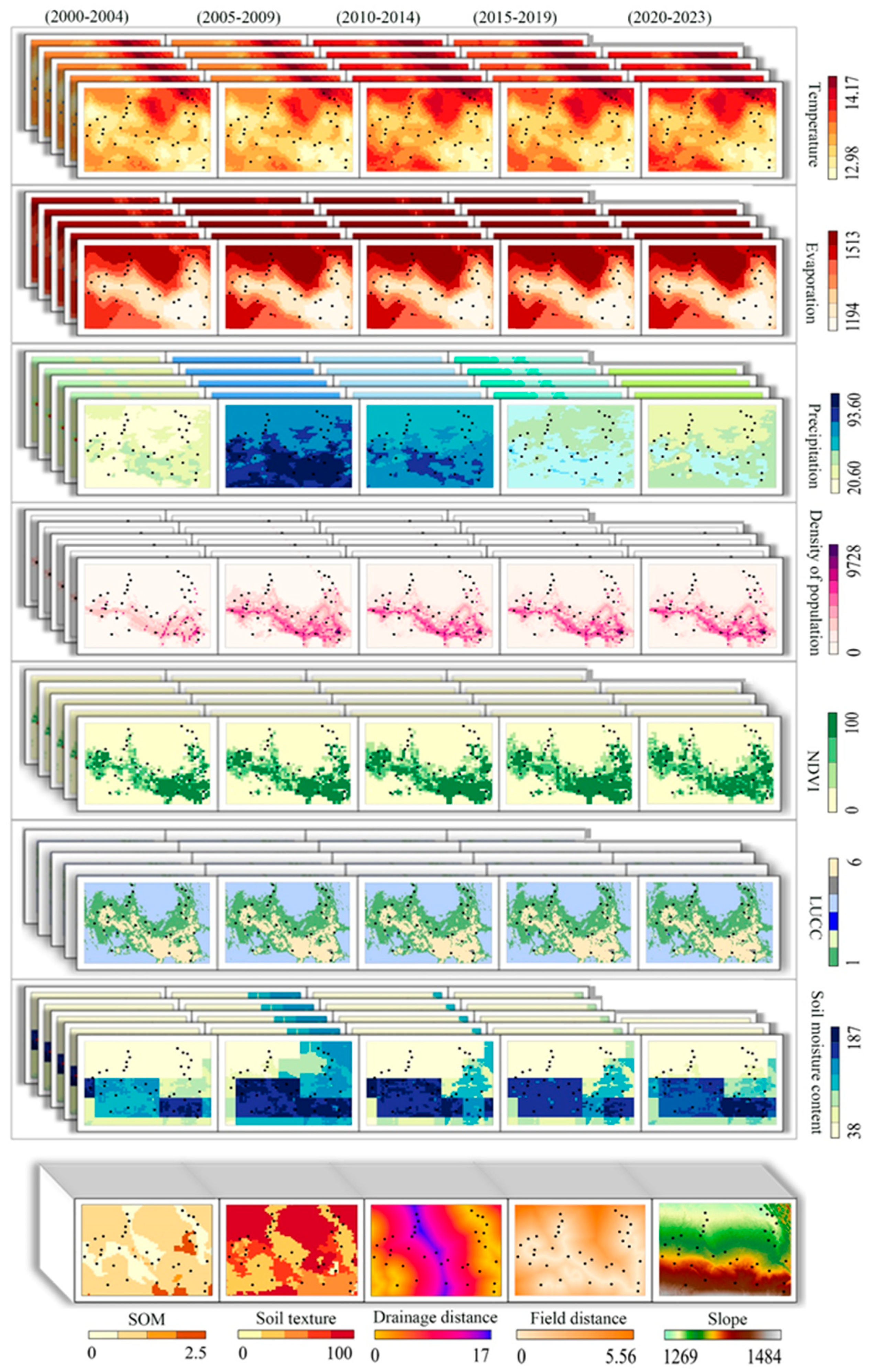


| Data Types | Indicator | Time Scale | Resolution | Data Quantity | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Meteorological | Temperature (°C) | 2000–2023 | 1 km | 24 | http://www.gis5g.com/data/dzsjj (accessed on 21 April 2024) |
| Evaporation (mm) | 2000–2023 | 1 km | 24 | http://www.gis5g.com/data/dzsjj (accessed on 21 April 2024) | |
| Precipitation(mm) | 2000–2023 | 1 km | 24 | https://data.tpdc.ac.cn/home (accessed on 1 April 2024) | |
| Socioeconomic | Density of population (person/km2) | 2000–2023 | 1 km | 24 | https://landscan.ornl.gov/ (accessed on 15 April 2024) |
| LUCC | Vegetation type trend | 2000–2023 | 300 m | 24 | European Space Agency |
| Biophysical | Soil moisture content (g/kg) | 2000–2022 | 100 m | 23 | https://data.tpdc.ac.cn/home (accessed on 1 April 2024) |
| Natural drainage distance (km) | 2020 | 1 km | 1 | https://www.openstreetmap.org/ (accessed on 20 April 2024) | |
| Slope (°) | 2020 | 12.5 m | 1 | https://www.gscloud.cn/search (accessed on 23 April 2024) | |
| Field distance (km) | 2020 | 300 m | 1 | European Space Agency | |
| NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index) | 2000–2023 | 30 m | 24 | http://www.gis5g.com/data/dzsjj (accessed on 21 April 2024) | |
| Soil texture | 2019 | 250 m | 1 | http://www.gis5g.com/data/dzsjj (accessed on 21 April 2024) | |
| Soil organic matter (SOM) (mg/kg) | 2019 | 1 km | 1 | https://data.tpdc.ac.cn/home (accessed on 1 April 2024) | |
| salinization | EC (mS/cm) | 2000, 2005, 2010; 2012, 2013, 2014, 2015, 2021, 2001, 2006, 2011, 2016, 2021 | - | 13 | [47,48], This study field survey experimental data |
| Indicator | Time | Maximum | Minimum | Mean | Medium | SD | Skewness | Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EC (mS/cm) | 2012 | 6.36 | 0.09 | 0.80 | 0.55 | 1.25 | 4.18 | 24 |
| 2013 | 134.3 | 0.16 | 18.63 | 3.71 | 35.74 | 2.47 | 24 | |
| 2014 | 31.5 | 0 | 8.17 | 3.88 | 8.90 | 1.16 | 36 | |
| 2015 | 26.4 | 0 | 8.65 | 5.24 | 8.86 | 0.67 | 36 | |
| 2021 | 35.7 | 0.17 | 6.48 | 3.23 | 9.10 | 2.09 | 26 |
| Category | Indicator | Indicator States and Determination of Threshold |
|---|---|---|
| Drive | Temperature | |
| Soil organic matter | Low: <0.83 g/kg; medium: 0.83–1.66 g/kg; high: >1.66 g/kg | |
| Precipitation | Low: >42.3 mm; medium: 42.3–68.1 mm; high: >68.1 mm | |
| Density of population | ||
| Slope | small: <4.73°; middle: 4.73–6.20°; big: >6.20° | |
| Natural drainage distance | nearly: <5.76 km; middle: 5.76–11.29 km; far: >11.29 km | |
| Soil texture | clay: <0.2 mm; sand: 0.05–2 mm; silt: >2 mm | |
| Pressure | Evaporation | low: >1255 mm; medium: 1255–1352 mm; high: >1352 mm |
| Soil moisture content | low: <0.080 m3; medium: 0.080–0.13 m3; high: >0.13 m3 | |
| Vegetation type trend | harmed: bare land; unchanged: cultivated land; improvement: grassland | |
| Field distance | nearly: <0.95 km; middle: 0.95–1.18 km; Far: >1.18 km | |
| NDVI | low: <30%; medium low: 30–40%; medium: 40–60%; high: >60% | |
| State | EC |
| No. | Chain of BN Nodes | Accuracy (%) | Number of Tests |
|---|---|---|---|
| a | Soil texture—NDVI | 90 | 720 |
| b | Soil organic matter—NDVI | 84 | |
| c | Soil organic matter—LUCC | 87 | |
| d | Precipitation—LUCC | 73 | |
| e | Precipitation—Soil moisture content | 66 | |
| f | Density of population—LUCC | 83 | |
| g | Density of population—Field distance | 81 | |
| h | Field distance—Soil moisture content | 83 | |
| i | Soil moisture content—Evaporation | 75 | |
| j | NDVI—Evaporation | 80 | |
| k | LUCC—Evaporation | 78 | |
| l | Temperature—Evaporation | 87 | |
| m | Evaporation—EC | 77 | |
| n | Slope—EC | 83 | |
| o | Natural drainage channels—EC | 76 | |
| Average | 80.2 | Total 10,800 |
| Sample ID | Y01 | Y02 | Y03 | Y04 | Y05 | Y06 | Y07 | Y08 | Y09 | Y10 | Y11 | Y12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EC change from 2012 to 2021 (mS/cm) | −0.02 | 0.35 | 0.15 | 14.68 | 0.16 | 5.21 | 1.19 | 16.65 | 1.34 | 0.05 | 21.44 | 2.28 |
| Sample ID | Y13 | Y14 | Y15 | Y16 | Y17 | Y18 | Y19 | Y20 | Y21 | Y22 | Y23 | Y24 |
| EC change from 2012 to 2021 (mS/cm) | −0.26 | 2.68 | 5.48 | 1.91 | 0.33 | −0.38 | 6.24 | 8.83 | −0.38 | 3.52 | 2.47 | 4.84 |
| Sample ID | Y25 | Y26 | Y27 | Y28 | Y29 | Y30 | Y31 | Y32 | Y33 | Y34 | Y35 | Y36 |
| EC change from 2012 to 2021 (mS/cm) | 5.28 | 4.89 | −0.32 | 5.58 | 2.54 | 2.47 | 1.54 | 6.04 | 1.02 | 0.96 | 8.44 | 4.61 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, H.; Seydehmet, J.; Li, X. Upscaling Soil Salinization in Keriya Oasis Using Bayesian Belief Networks. Sustainability 2025, 17, 7082. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17157082
Chen H, Seydehmet J, Li X. Upscaling Soil Salinization in Keriya Oasis Using Bayesian Belief Networks. Sustainability. 2025; 17(15):7082. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17157082
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Hong, Jumeniyaz Seydehmet, and Xiangyu Li. 2025. "Upscaling Soil Salinization in Keriya Oasis Using Bayesian Belief Networks" Sustainability 17, no. 15: 7082. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17157082
APA StyleChen, H., Seydehmet, J., & Li, X. (2025). Upscaling Soil Salinization in Keriya Oasis Using Bayesian Belief Networks. Sustainability, 17(15), 7082. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17157082






