Abstract
This study adopts a dynamic Expectancy–Disconfirmation framework to investigate the evolving nature of user satisfaction across three product categories: durable goods, fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG), and digital products. A 25-day longitudinal experiment involving 128 participants was conducted, during which users engaged with their most recently purchased products and provided repeated subjective evaluations over time. The findings reveal dynamic changes in the influence of expectations and perceived performance on satisfaction throughout the product usage cycle. For durable goods and FMCG, both expectations and perceived performance gradually declined, accompanied by a weakening effect of expectations on satisfaction. In contrast, digital products exhibited greater volatility, lacking a stable experiential baseline and resulting in greater fluctuations in satisfaction trajectories. Moreover, external contextual and emotional factors were found to play a more significant role in shaping satisfaction with physical products, beyond the scope of the traditional expectancy–performance model. These insights offer theoretical and managerial implications for sustainable product and experience design. In particular, they highlight the importance of implementing experience-stabilizing strategies in digital consumption contexts to support user well-being and enhance continuous product utilization, thereby maximizing product potential and reducing waste.
1. Introduction
User satisfaction has been extensively examined in marketing, human factors, and psychology to develop more effective marketing and service strategies by elucidating its underlying mechanisms [1]. The Expectancy–Disconfirmation Theory is the most widely applied among the various theoretical models. It explains satisfaction as the result of a cognitive comparison between a user’s expectation and the product’s perceived performance [2]. Due to its flexibility, this theory has been widely employed in research on user satisfaction in product experiences [3]. A comprehensive understanding of user satisfaction is critical for achieving business success and maintaining a sustainable competitive advantage in today’s market environment [4].
Despite considerable efforts to understand user satisfaction, most existing models predominantly rely on static approaches, typically measuring satisfaction at a single point in time. However, product experience is inherently dynamic, and static models often fail to capture the continuity and evolution of user experience over the product lifecycle [5,6]. In contrast, dynamic satisfaction models better reflect the evolving complexity of ongoing product interactions, enabling a more nuanced understanding of how user satisfaction develops over time. This approach facilitates a more accurate assessment of users’ experiences and improves the predictive accuracy of future satisfaction. Furthermore, satisfaction dynamics may vary across different product categories [7]. Products are generally categorized as either tangible or virtual [8,9]. Virtual products primarily include digital products [10], while tangible products can be subdivided based on consumption characteristics and usage duration into durable goods and fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) [11,12]. These distinct product types offer unique user experience patterns, leading to different satisfaction trajectories. For example, using durable goods often involves long-term interaction, during which satisfaction may shift gradually as users’ expectations and perceptions evolve. In contrast, FMCG experiences are usually short-term and directly influenced by immediate use and initial impressions [13,14]. Meanwhile, digital products exhibit a fundamentally different experience pattern, marked by frequent updates and iterative changes, which can cause fluctuations in user satisfaction throughout the product lifecycle [15]. These variations in experiential dynamics across product categories highlight the need for satisfaction models that account for the temporal specificities of each type [16].
To address this, our study examines the dynamic characteristics of user satisfaction across different product types through experimental validation. First, we categorized participants’ purchased products into three types based on a review of the existing literature and theoretical frameworks: durable goods, FMCG, and digital products [17,18,19]. Reflecting the distinct temporal patterns of user satisfaction across these categories, we proposed corresponding hypotheses to capture their dynamic trajectories. Using the Expectancy–Disconfirmation Theory as a foundation, we developed a dynamic satisfaction framework to test these hypotheses. Participants’ product experiences were tracked under natural daily conditions, with satisfaction data collected at several time points during usage to compare dynamic satisfaction trajectories across different product categories. The results confirmed our hypotheses and provided empirical support for a dynamic understanding of user satisfaction. Importantly, these findings have direct implications for sustainability by highlighting how fostering positive and sustained user experiences can maximize product utilization and reduce premature abandonment or underuse. By understanding the evolving satisfaction patterns across product types, designers can better promote continuous engagement and responsible consumption, thereby minimizing waste and enhancing resource efficiency, especially within digital products where user experience volatility is higher.
2. Related Work
2.1. Dynamic Expectancy–Disconfirmation Framework
User satisfaction refers to an overall evaluation based on users’ cumulative experiences over time, rather than a single service encounter. It reflects an aggregated perception shaped by multiple interactions and contextual factors [20]. Therefore, its measurement should account for evolving expectations and the influence of prior experiences on evaluations. However, Expectancy–Disconfirmation Theory is typically applied from a static perspective when describing customer satisfaction. Most studies using this framework conceptualize satisfaction as a one-time comparison between expectations and performance [21]. Such a static view may overlook the temporal fluctuations and cumulative nature of user satisfaction in product experience. It may also fail to capture situations in which users report satisfaction despite unmet expectations due to compensatory factors such as emotional value, convenience, or contextual fit. Adopting a dynamic perspective enables a more comprehensive understanding of how satisfaction transforms over time, capturing both cognitive and emotional shifts across the user journey.
First, expectations and perceived performance, fundamental components of the satisfaction evaluation system, evolve dynamically throughout the product experience. From a dynamic expectations perspective, each instance of perceived service quality may generate new expectations that subsequently influence future perceptions of quality [22]. Second, the product usage process consists of two alternating phases: usage and non-usage units. A usage unit refers to a period during which the user actively engages with the product to fulfill a specific task or purpose, such as using a computer during working hours. In contrast, a non-usage unit refers to the interval when the product is not in use, such as after work, when the user is no longer interacting with the computer. These two types of units alternate over time to form the complete product experience. During usage units, satisfaction is determined by the interaction between expectations and perceived performance. In turn, the perceived performance and satisfaction experienced during these phases influence expectations for subsequent usage. Based on expectation uncertainty theory, each interaction can be conceptualized as a unit that includes expectations, perceived performance, and satisfaction. The overall product experience is thus composed of a series of sequential units, each influencing the next. This process is illustrated in Figure 1.
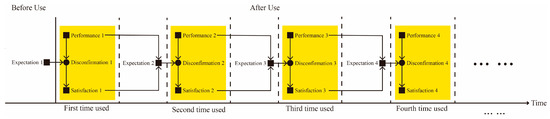
Figure 1.
Dynamic Expectancy–Disconfirmation Framework.
2.2. Factors of the User Experience
The Dynamic Expectancy–Disconfirmation Framework posits that expectations and perceived performance are central internal factors shaping user satisfaction. In addition to these internal elements, external factors such as social support, pricing, and other aspects of the user’s perceived experience also play a significant role in shaping satisfaction. The relative influence of these internal and external factors on satisfaction evaluation may vary across different product categories.
Keshavarz and Jamshidi [23] argue that price is frequently a proxy for quality, directly through perceived value rather than prior expectations. Similarly, Hepola, Karjaluoto and Hintikka [24] suggest that for tangible goods, external cues such as brand reputation and packaging exert a more substantial influence on satisfaction than pre-consumption expectations, as these cues shape perceived utility during and after product use. These findings highlight the decisive role of external factors in the satisfaction evaluation process. However, Anifa and Sanaji [25] found that due to the intangible nature of digital products, users primarily rely on the product’s presented content to form satisfaction judgments, thereby amplifying the influence of expectations. Through their Information Systems Success Model, DeLone and McLean [26] further demonstrated that for digital products, internal factors such as system quality and information quality play a more dominant role in shaping user satisfaction, in contrast to physical products, where tangible attributes are more salient.
In summary, physical products rely heavily on observable external cues such as pricing, brand reputation, packaging, and measurable quality indicators, significantly shaping user satisfaction [27]. These products typically deliver a fixed and immediately consumable experience, making satisfaction more dependent on external perceptions. In contrast, virtual products such as digital platforms, applications, and streaming content are characterized by their dynamic, interactive, and adaptive nature. Satisfaction with such products is formed through ongoing experiential evaluations, including interface usability, flow, personalization, and emotional engagement [28]. Therefore, satisfaction with digital products is more significantly influenced by internal factors within the user experience evaluation system. Based on these insights, the following hypothesis is proposed:
H1:
Throughout the entire experience process, satisfaction with digital products is more heavily influenced by internal evaluation factors than is the case with physical products.
2.3. Expectation and Experience
Comparative research on digital and physical product experiences has revealed notable differences in the continuous formation of user expectations and the factors influencing satisfaction. In the context of digital products, Wixom and Todd [29] demonstrated that perceived quality and expectation confirmation are critical determinants of user satisfaction with information systems. This is mainly due to the frequent updates and improvements of software applications and online services, which enable more rapid and flexible adjustments to user expectations [20]. The intangibility and interactivity of digital products also lead users to develop heightened expectations for functionality and convenience [30]. Moreover, digital product experiences are often continuous and dynamic, allowing users to adjust their expectations in real-time during usage. This dynamic adjustment process directly and significantly impacts satisfaction formation [31]. In contrast, tangible attributes and functional performance generally shape user expectations for physical products [32]. Given the relatively infrequent updates associated with physical products, expectations remain stable throughout usage. As a result, satisfaction is primarily determined by initial product quality and performance [33]. Although after-sales services and quality guarantees can enhance user satisfaction, the mechanisms available to adjust user expectations after purchase are comparatively limited. Consequently, changes in perceived satisfaction with physical products occur more slowly [34]. Furthermore, the features of physical products are typically well-defined and concrete, enabling users to form relatively accurate expectations before purchase based on product descriptions, user reviews, and physical displays [35]. As a result, the discrepancy between expected and actual performance tends to be smaller, reducing the impact of expectation disconfirmation on satisfaction [36].
In summary, the flexibility and adaptability of digital products allow for continuous refinement based on user feedback, often leading to elevated expectations and a more dynamic satisfaction formation process [37,38]. Conversely, the fixed nature of physical products after manufacturing makes it more challenging to adjust to user expectations over time, potentially resulting in weaker satisfaction outcomes [39,40]. Therefore, the following hypothesis is proposed:
H2:
During the use of physical products, the impact of user expectations on satisfaction may be less significant than for services or digital products.
2.4. Experience Baseline
We define the experience baseline as a user’s internalized reference point, formed through early but repeated interactions with a product, against which subsequent experiences are evaluated. This concept is distinct from initial expectations, which are formed before any actual use based on marketing or prior beliefs [41], and from first-use impressions, which reflect immediate reactions during the first encounter. In contrast, the experience baseline develops through accumulated early interactions and serves as a more stable and enduring benchmark in the user’s evaluative framework [42]. The differences in user experience between physical and digital products can be attributed to fundamental distinctions in their interaction design and post-deployment flexibility. Physical products are generally static; once manufactured, their features and quality are mainly fixed and not easily modified [43]. As a result, users’ initial interactions with physical products tend to exert a long-lasting influence on their overall satisfaction [44]. In contrast, digital products are inherently dynamic, enabling designers to collect real-time user feedback and implement iterative updates that continuously enhance usability, functionality, and perceived value [39]. Prior research has shown that such iterative refinements can significantly reshape users’ perceptions of digital products, particularly about perceived ease of use and usefulness [45]. Furthermore, Ntoa [46] emphasized the importance of user-centered design and continuous testing in optimizing digital interfaces. These findings suggest that, unlike physical products, satisfaction with digital products may not be firmly anchored to initial experiences. Instead, satisfaction may evolve through prolonged engagement with updated versions, diminishing the influence of early evaluations. Nevertheless, while existing studies have offered valuable insights into product evolution and user adaptation, they have not explicitly examined whether a stable experiential baseline exists across different product types. Addressing this gap and considering the inherently dynamic nature of digital interaction, we propose the following hypothesis:
H3:
A critical experience baseline affects satisfaction in the experience of physical products, whereas such a baseline does not exist in the experience of digital products.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Participants
Through the university’s social network, we recruited 128 participants from diverse academic disciplines and backgrounds (68 males and 60 females). The average age of the participants was 28.62 years (SD = 6.22), and all were cognitively healthy. To control for the influence of native cultural factors on product experience cognition, all participants were either Chinese nationals or individuals born and primarily educated in China. Moreover, recruitment was limited to individuals who had already purchased the new products to ensure that participants had substantial prior engagement with the target products. All participants provided informed consent and completed a demographic questionnaire, which included information on age and gender and a self-report measure confirming no usage of similar products within the past month, to ensure that recent comparable experiences did not shape participants’ expectations and that the satisfaction data reflected authentic responses. It is important to note that this study focused on users’ current subjective experiences across different product types. Therefore, a single participant could contribute data for multiple product categories.
3.2. Experimental Materials and Grouping
The experimental materials were selected from everyday industrial products in daily life. These products were divided into two major categories and three subgroups [47]. Group I is Durable Goods; Group II is FMCG; and Group III is Digital Products. Groups I and II are categorized as physical products, while Group III represents digital products. To support this classification, we established a product evaluation mechanism based on three key dimensions: (1) physical characteristics and forms of existence, (2) usage cycle and durability, and (3) consumer interaction methods. Each dimension was assessed using a Likert-scale questionnaire to evaluate how strongly each product type exhibited the relevant features. Three product design experts were consulted to review the item scores and offer classification suggestions. Final product groupings were determined by combining quantitative evaluation results and expert consensus, ensuring both theoretical validity and practical relevance. Specifically, as follows:
1. Physical characteristics and forms of existence: Durable Goods: These products are physical entities that can be touched and perceived [48]. They are typically made of metal, plastic, and wood, with a defined volume and weight, and they physically occupy space [49]. That characteristic allows users to perceive durable goods’ quality and physical comfort [50]. FMCG: Although also physical items, FMCG are generally smaller in size, lower in cost, and shorter in life cycle. Their physical characteristics often require simple manufacturing processes, allowing mass production and rapid distribution. These products focus more on fulfilling immediate or short-term needs, with frequent usage [51]. Digital Products: They have no physical form; they exist entirely in virtual form and are typically delivered via the Internet [52]. Users access these products through hardware like smartphones or computers, but the products are based on code, data, and content, and cannot be physically touched or perceived [53]. Digital products depend on users’ devices and network connections, lacking a physical presence but offering rich content and interactive experiences [54].
2. Usage cycle and durability: Durable Goods: These products typically have a longer usage cycle. They are designed for long-term use, usually lasting at least 6 months without frequent replacement [55]. Due to their higher cost and durability, durable goods require more consideration and planning when purchasing [56,57]. FMCG: These products have a shorter usage cycle compared to durable goods. They are usually single-use or quickly consumed items, are purchased more frequently, and typically have lower costs and shorter usage cycles, leading consumers to buy and replace them often [58]. Digital Products: These products do not have a clearly defined physical usage cycle because they are virtual products based on content and services, accessed by consumers through devices. Their “lifespan” usually depends on the frequency of updates and ongoing interaction with the content [59]. There is no physical wear, but user engagement decreases if the content becomes outdated or loses appeal [60,61].
3. Consumer interaction methods: Durable Goods: Consumer interaction with durable goods primarily occurs through physical operations during usage [55], such as a chair’s comfort or the sound quality of headphones. Consumers typically perceive the product’s performance and quality through long-term use, meaning the interaction is based on the actual use and operation of the product [57]. FMCG: The interaction is more immediate and consumable [62]. The usage of FMCG is often brief, focusing on quickly satisfying needs, such as using tissues or beverages. Consumers may not profoundly consider the long-term performance or sustainability of the product but instead focus on its instant effect and convenience [63]. Digital Products: Consumer interaction with digital products is highly virtual, typically facilitated through screens and digital interfaces [64]. Users interact by clicking, browsing, watching, or gaming. The depth of interaction depends on the product’s design [65]; for example, some digital products like video games offer immersive experiences, whereas videos or e-books are more oriented toward content consumption. This interaction is based on the content’s continued appeal and the user’s emotional resonance [66,67].
3.3. Experimental Procedure
This experiment was conducted in real-world settings rather than controlled laboratory environments to ensure the authenticity of user satisfaction responses. Laboratory settings tended to make participants feel nervous or observed, which may alter their natural behavior and emotional responses. Moreover, the complexity and dynamics of actual usage scenarios are challenging to reproduce in the lab. Thus, ecological validity was prioritized over experimental controllability to reflect genuine user experiences better. Participants were free to choose their own usage contexts; however, they were instructed to engage with the product in a calm and undisturbed emotional state to ensure that situational mood did not confound their satisfaction evaluations. Participants were recruited and asked to report any products they had purchased or started using within the past three days, based on their needs and preferences. Participants were required to provide basic information for each reported product, including product type, brand, price, and materials. In addition, they completed a questionnaire developed to assess product’s characteristics across three key dimensions. Based on the questionnaire scores, each product (and its user) was assigned to one of the three predefined product categories: Durable Goods, FMCG, or Digital Products. They were explicitly required to immediately record their satisfaction and perceived product performance after each use via an online platform with automatic timestamping. This ensured that usage evaluations were made in real time, minimizing recall bias. To further enhance experimental control without compromising naturalistic user behavior, participants were required to submit a short context description (e.g., time, location, emotional state) along with each satisfaction entry. This allowed us to monitor potential contextual factors influencing satisfaction ratings and conduct robustness checks during data analysis. The initial product use was mandatorily recorded. Afterward, participants could continue using the product freely and were instructed to complete a self-report questionnaire every 3 to 5 days, to document their subjective experiences, for five reporting sessions. To minimize external interference, after each product usage record, participants were asked whether they had used similar products or had been exposed to any promotional materials for similar products during the interval. Any violations led to the exclusion of the corresponding cycle’s data from the primary analysis. Although this less restrictive setting reduced experimental control compared to traditional laboratory experiments, it allowed for capturing more authentic and dynamic user experiences, which was essential for verifying the specific hypotheses about satisfaction development over time rather than isolating all potential influencing factors.
Although the three product categories differ in usage frequency and consumption cycles, the 25-day observation period was sufficient to capture meaningful dynamics in user satisfaction across all types. According to adaptation theory, durable goods typically exhibit notable shifts in satisfaction during the early stages of use, after which evaluations stabilize. Therefore, this initial usage window is critical for capturing expectation adjustment and early performance appraisal. FMCG products, by contrast, are consumed more frequently and provide immediate feedback, enabling satisfaction changes to emerge over shorter time frames. Digital products, while used continuously, are characterized by high interaction frequency and content variability, often resulting in more rapid and volatile satisfaction fluctuations. The use of a unified time window across all product categories thus enabled a direct and consistent comparison of temporal satisfaction patterns, while still capturing the most relevant phase of user experience for each type. This design choice ensured both internal coherence and theoretical validity across the experimental groups.
3.4. Measures
To determine participants’ subjective perceptions of different product experiences, we used a 7-point Likert scale to assess their satisfaction with the experience. This scale consists of three questions related to the elements of satisfaction formation in the Expectancy–Disconfirmation Theory. The questionnaire includes three questions: Q1 shows the user’s expectations before using the product; they choose the option that fits their feelings from 1–7, where 1 represents no expectations, and 7 represents very high expectations. Q2 is based on the post-use perception of product performance evaluation, where 1 represents poor product performance, and 7 represents good product performance. In Q3, satisfaction with the user experience is shown, where 1 represents very dissatisfied, and 7 represents very satisfied. Q1 was designed to capture users’ expectations before using the product, while Q2 and Q3 recorded post-use perceptions of performance and satisfaction. Although conceptually separated, all three questions were answered in a single session after product use, allowing participants to simultaneously reflect on their pre-use expectations and post-use experiences. All questionnaires and data entries were distributed and collected via an online survey platform, and all data were automatically uploaded and timestamped to verify compliance with the experimental protocol. Participants were instructed to complete a usage report every 3 to 5 days, ensuring sufficient intervals between product interactions to capture temporal dynamics without inducing participant fatigue or memory decay. A semi-structured interval design was employed to balance the need for temporal spacing with the preservation of naturalistic behavior. This approach is commonly used in longitudinal field studies [68]. A protocol compliance rule was implemented to ensure consistency across data points: if a usage instance occurred outside the designated 3–5-day interval, the corresponding data point was flagged and excluded from the primary hypothesis-testing analyses. Across the 128 participants, a total of 115 unique products were included in the final analysis. Among them, 40 were classified as durable goods (n = 40 for Group I), 38 as FMCG (n = 38 for Group II), and 37 as digital products (n = 37 for Group III). These products covered various subtypes, including home appliances, skincare items, beverages, mobile apps, and digital games. This variety enhanced the generalizability of findings within each product category. A reliability analysis was conducted on relevant items, where the Cronbach’s α coefficients were 0.82 for Group I, 0.865 for Group II, and 0.801 for Group III. Both were >0.8, indicating high reliability. Investigation locations: Guangdong and Hunan provinces in China.
4. Results
4.1. Descriptive Statistics
Descriptive statistics of the data are shown in Table 1. It shows where I represents the durable goods (n = 40), II represents the FMCG (n = 37), and III represents the digital products (n = 38), where SATIt, PERt, and EXPt stand for satisfaction, perceived performance, and expectation, and t = 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 denote the first time to fifth time using the product. Indicators that can effectively reflect differences in the data are calculated, including the mean, variance, and variant coefficients [69]. It is observed that both the expected average value and perceived performance of durable goods and FMCG exhibit a gradual decline, whereas this trend is not pronounced in digital products. The satisfaction variability of physical products is lower than that of digital products, with the coefficient of variation primarily ranging between 0.2 and 0.3, whereas digital products show broader variation and larger ranges. These findings suggest that physical product experiences tend to stabilize more quickly, possibly due to their fixed characteristics. In contrast, digital product experiences remain more volatile and adaptable, potentially reflecting the influence of iterative design and evolving user expectations. This variability may serve as an early indicator of users’ sensitivity to product updates in digital environments—a key consideration for sustainable interaction design.

Table 1.
Mean, variance, and coefficient of variation between groups.
4.2. Explanatory Power and Correlation
The data were analyzed using linear regression. The meanings of SATIt, PERt and EXPt are the same as in Table 1. The results are divided into two parts; the first part uses SATIt as the dependent variable and PERt, and EXPt as the independent variables in a usage unit, which is the relationship between the user expectations and perceived performance on satisfaction when using the product. In the second part, PERt and SATIt within a usage unit were treated as independent variables, while EXPt+1 in the subsequent non-usage unit was the dependent variable. A regression analysis was conducted to examine how prior experiences influence users’ persistent expectations across the continuum of product use [70].
To evaluate the independence of residuals in the regression models, the Durbin–Watson (D-W) statistic was used to test for first-order autocorrelation. The values fell within acceptable ranges, indicating that residuals were independent and the regression results statistically valid. F-tests for all three product categories were significant (p < 0.001), suggesting that at least one predictor had a significant effect on satisfaction and expectation, with differences likely driven by product-type factors [71]. As shown in Table 2, adjusted R2 values exceeded 0.5 across all models, indicating substantial explanatory power. Notably, digital product models exhibited the highest explanatory strength in both satisfaction and expectation prediction [69]. Across all product types, perceived performance consistently had a stronger positive effect on satisfaction than expectation, while expectations were negatively correlated with satisfaction. These findings support the Expectancy–Disconfirmation Framework and suggest that actual performance plays a more decisive role than expectation alignment. From a design perspective, especially for digital products, enhancing real-time performance is more effective for sustaining satisfaction than relying on pre-use expectation management. In sustainable design contexts, this reinforces the importance of continuous functionality improvement to maintain long-term user engagement.

Table 2.
Linear regression results within groups.
5. Discussion
5.1. Changes in the Impact of Elements Within the Group
This section focuses on intra-group observations, examining how the influence of user expectations and perceived performance evolves within each product category over time. Figure 2 presents normalized adjusted R2 values from Table 2 (where satisfaction was the dependent variable). Adjusted R2 quantifies the proportion of variance in the dependent variable explained by the independent variables [72]—in this case, user expectation and perceived performance. This visualization emphasizes the negative correlation effects, indicated by (−). As a percentage impact graph, it includes non-significant effects (p > 0.05), denoted by (☐). The portion unexplained by adjusted R2 can be attributed to other factors influencing satisfaction [73], interpreted here as influences beyond expectation and perceived performance. Similarly, Figure 3 shows normalized data with user expectations as the dependent variable.
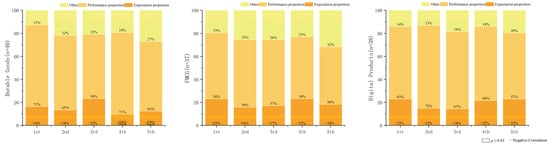
Figure 2.
Percentage chart of factors influencing satisfaction changes.
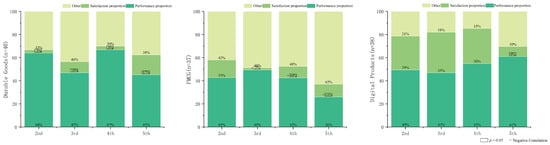
Figure 3.
Percentage chart of factors influencing expectation changes.
Figure 2 reveals that expectation and perceived performance collectively explain a high proportion (greater than 70%) of satisfaction formation. This reaffirms the high applicability of the Expectancy–Disconfirmation Theory in product experience research [74]. Two key observations emerge: First, perceived performance consistently exerts a more substantial influence on satisfaction than expectation across all stages (accounting for >50% of the explained variance). This indicates that high perceived performance is essential for user satisfaction and consistently shapes the experience across all stages [75]. In contrast, the impact of user expectations on satisfaction is consistently smaller than perceived performance. This implies that, for product experiences, enhancing product quality is a more effective strategy for boosting satisfaction than managing user expectations. Second, expectations consistently correlate negatively with satisfaction across all groups, aligning with the established finding that higher expectations can lead to lower satisfaction [76]. These findings collectively indicate that while EDT demonstrates high applicability, the relative impact weights of expectations versus performance on satisfaction differ significantly in product experience contexts. This divergence questions the direct relevance of marketing-based satisfaction models to product experience contexts, where coefficient patterns differ significantly.
Figure 3 displays results using PERn and SATIt as independent variables and EXPt+1 as the dependent variable. Two main patterns are evident: First, the independent variables explain less variance in expectation changes for durable goods and FMCG than for digital products. This suggests that factors beyond satisfaction and perceived performance play a larger role in shaping ongoing expectation changes in physical product experiences. Conversely, satisfaction and performance better explain expectation changes for digital products, suggesting users focus more intently on the digital product itself and its evolving experience [38]. Second, 7 out of 8 satisfaction measures show non-significant effects (p > 0.05) on subsequent expectations for durable goods and FMCG. This indicates that post-use satisfaction does not significantly influence pre-use expectations for subsequent usage instances in these categories. This pattern suggests a potential decay of intrinsic motivation, where repeated use fails to adjust user expectations over time [77]. User adaptation theory offers a possible explanation: users gradually recalibrate expectations based on prior experiences. As expectations stabilize or decline with repeated exposure, the influence of satisfaction on future expectations becomes weaker. This adaptation likely leads to a more stable and less responsive expectation baseline, especially for physical products where novelty diminishes quickly. For digital products, satisfaction significantly influences expectations (approximately 30% influence) in the first three periods but becomes non-significant in the final period. This shift may reflect users’ increasing focus on the product and its evolving experience, rather than prior satisfaction levels, especially in later stages [78]. In summary, throughout the entire experience, prior satisfaction, expectations, and perceived performance fluctuations significantly impact satisfaction changes for digital products. Conversely, for physical products (durable goods and FMCG), satisfaction changes depend more heavily on factors external to the core EDT variables of expectation and perceived performance. These results validate (H1).
5.2. Characterization of Trends Between Groups
This section shifts to inter-group comparisons, analyzing how the temporal trajectories of expectation, perceived performance, and satisfaction differ across product types. Given the limited number of observations (only five time points) and the need to capture both gradual changes and short-term fluctuations, we adopted triple exponential smoothing—a method particularly effective for modeling evolving patterns and seasonality in observational data [79,80]. We determined the initial value (S0) as the average of the first three observations. We systematically tested smoothing parameters (alpha) from 0.05 to 1.0 in increments of 0.05, selecting the value yielding the highest fit [81]. Applying this method to the three datasets yielded the S0 and alpha values presented in Table 3. Figure 4 displays the actual values, fitted values, and one-period-ahead forecasts for all three datasets, enabling effective discernment of different trends [82]. Previous research indicates that behavior and performance tend to be more consistent in service domains, while perceived performance in design domains is subject to slight variation. As a result, products experienced through stable design processes tend to generate more stable expectations compared to dynamic service experiences [83]. This suggests that expectations play a relatively minor role in shaping satisfaction with everyday industrial products, primarily common durable goods. These products are typically used in routine, goal-oriented scenarios where performance tends to be stable and predictable. As a result, satisfaction is more directly influenced by actual product performance than by the gap between expectations and perceived outcomes. This aligns with Hoe and Mansori [84], who found varying degrees of fit with the expectations model across product categories: Digital products closely follow the model, whereas physical products exhibit weaker expectation effects and stronger performance influences. Our experimental results support this pattern, showing that both durable goods and FMCG demonstrate a reduced role of expectations and a dominant impact of perceived performance, indicating shared characteristics within the Expectancy–Disconfirmation Theory Framework.

Table 3.
The values of S0 and Alpha.
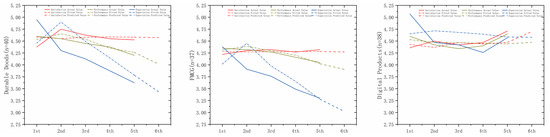
Figure 4.
Actual, fitted, and predicted values.
As illustrated in Figure 4, expectations and perceived performance for physical products decline steadily over time, while these indicators fluctuate more markedly for digital products. Furthermore, the actual values for physical products closely follow their fitted trends, whereas digital product data show greater deviations, suggesting a more dynamic and unstable user experience. This finding emphasizes the temporal instability of satisfaction in digital content usage due to frequent cognitive re-evaluation [85]. In contrast, prior research on physical products typically reports more stable trajectories of user appraisal [86]. Despite these divergent trend patterns, overall satisfaction appears similar across all three product categories. However, this surface similarity may mask different underlying mechanisms, as the intra-group analysis reveals. Relying solely on aggregate satisfaction outcomes risks the erroneous assumption that a single measurement approach suffices across diverse product experiences [87]. Specifically, in physical product experiences, expectations and perceived performance decline steadily, yet satisfaction remains relatively stable [88]. This indicates that user satisfaction becomes progressively less dependent on initial expectations and perceived performance over time, a shift less evident in digital product experiences. These findings support the hypothesis (H2).
Moreover, these trend differences have significant implications for sustainable consumption: For physical products, the gradual decline in expectations and performance—coupled with stable satisfaction—suggests users are likely to continue usage despite diminishing novelty or perceived value. This adaptive continuity can extend product lifespans, reduce replacement frequency, and consequently decrease material waste [89]. Conversely, the volatile satisfaction and performance observed in digital products may precipitate shorter usage cycles, premature abandonment, or unnecessary upgrades, increasing risks of digital resource waste [90]. Additionally, consistent satisfaction correlates with higher repeat purchase intentions, while fluctuation often reflects unmet expectations, discouraging long-term engagement. These findings imply that designers of digital products should consider adaptive feedback systems and iterative updates to maintain user engagement. At the same time, marketers of physical goods may focus on communicating long-term value and reliability. Therefore, recognizing and strategically managing satisfaction stability across product types is crucial for optimizing experience design and fostering more sustainable usage patterns.
5.3. The Disconfirmation Degree and Satisfaction
Existing research confirms that the satisfaction model’s applicability varies across product types. For instance, Guru, Paulssen and Japutra [91] found that the performance-based model is particularly relevant to durable goods, while observed that satisfaction with durables is driven more strongly by actual performance than expectations, with prior expectations or disconfirmation playing a relatively minor role. To further investigate these patterns, we calculated the disconfirmation value (DIS = perceived performance − expectation) for each usage occasion (1 to 5). Table 4 presents t-test results comparing DIS across product types. Key findings include the following: First, for durable goods and FMCG, DIS exceeded 1 only on the first usage occasion (2.131 and 2.330, respectively), signifying stronger disconfirmation early in the experience. Subsequent DIS values fell below 1. Second, for digital products, DIS remained above 1 across all five occasions, peaking at 3.090 on the fourth use and remaining relatively high (1.696) on the fifth. These results suggest the perception gap between expectations and performance diminishes rapidly for physical products, particularly durables, while disconfirmation remains more volatile and sustained throughout digital product usage.

Table 4.
Variance and mean of disconfirmation.
We further analyzed DIS distribution and fluctuation using box plots (Figure 5): Physical products: DIS fluctuation was highest during the first usage but narrowed significantly in subsequent experiences. This indicates expectations rapidly adjust and converge with perceived performance after the initial experience, acting as a correction point for forming stable expectations. Digital products: DIS values showed persistent, irregular fluctuations across all usage occasions without apparent convergence. This suggests a persistent mismatch, making user expectations harder to stabilize and increasing the risk of dissatisfaction. A positive disconfirmation value (DIS > 0) means the product outperforms the user’s prior expectations, often leading to enhanced satisfaction and reinforcing engagement. In contrast, a negative value (DIS < 0) indicates a shortfall in perceived performance, which may result in disappointment or erosion of trust in the product. These effects also differ across product types: for instance, users purchasing a new ergonomic office chair with high expectations may initially feel disappointed if comfort falls short, but this disconfirmation often diminishes over time as they adapt their expectations or usage posture. On the other hand, a user of a digital reading app may initially find certain personalized features unexpectedly helpful, but later updates that disrupt usability or remove familiar functions can lead to repeated mismatches. This repeated volatility prevents expectation stabilization and makes satisfaction more fragile over time. This divergence implies physical product experiences exhibit two distinct phases: pre-use and post-use, with the first use critically aligning expectations. Digital products lack this clear boundary, leading to prolonged mismatches. These findings support Hypothesis (H3).
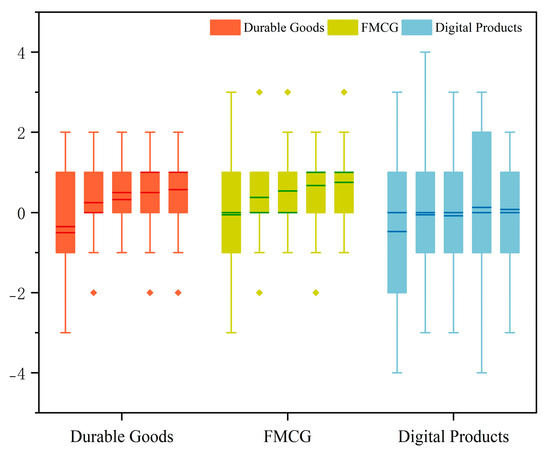
Figure 5.
Box plot of disconfirmation values.
A crucial distinction revealed here concerns post-purchase adaptation potential: Digital products: Designers can leverage real-time usage data and frequent updates to improve experience and satisfaction iteratively. This dynamic feedback loop necessitates a longitudinal understanding of satisfaction, emphasizing the sustained interaction’s role in shaping evaluations. Such ongoing engagement also supports more responsible and efficient use of digital products, helping to reduce waste associated with premature abandonment or disengagement. FMCG: Typically consumed quickly with no possibility for post-purchase modification or personalization. Consequently, FMCG satisfaction relies more heavily on immediate experience and brand familiarity than ongoing adaptation. Recognizing these structural differences clarifies satisfaction development mechanisms across categories and underscores the need for differentiated design and evaluation strategies. These insights contribute to a more nuanced understanding of how satisfaction evolves across different product domains, moving beyond the limitations of static models and highlighting pathways toward more sustainable consumption behaviors.
5.4. Implications for Design and Sustainability
The distinct satisfaction dynamics identified in this study offer valuable implications for designing sustainable product experiences across physical and digital ecosystems. For physical products, the observed gradual decline in expectations and perceived performance, alongside relatively stable satisfaction that becomes less dependent on these core factors over time, suggests that extending product lifespan and reinforcing long-term value perception are essential for sustainability. Designers should prioritize inherent durability, timeless aesthetics, and ease of repair and maintenance to mitigate declining perceptions. Moreover, marketers and sustainability advocates are encouraged to emphasize product longevity, reliability, and contextual benefits to foster emotional attachment and reduce premature replacement behaviors. In contrast, the instability of satisfaction in digital products underscores the importance of strategies that stabilize user experience and support long-term engagement. Product managers and UX designers should focus on iterative improvements informed by user feedback, ensuring consistent performance, minimizing disruptive updates, and fostering sustained engagement through personalization and value-added features. Such approaches can effectively reduce digital waste associated with underutilized applications and services. Collectively, these findings highlight the divergent sustainability pathways for physical and digital products: optimizing tangible durability and emotional connection for the former, while actively managing the dynamic user journey to promote continuous use and resource efficiency for the latter. This nuanced understanding provides critical guidance for product managers, UX designers, and sustainability advocates aiming to advance sustainable consumption through targeted design strategies tailored to each product ecosystem.
6. Conclusions
This study provides a comparative analysis of user expectations, perceived performance, and satisfaction between physical and digital products, emphasizing the dynamic evolution of user experience over time. By examining temporal patterns in these variables, we identified both convergence and divergence in the mechanisms shaping satisfaction. These findings enhance our understanding of how product type affects the stability of user experience and provide valuable implications for fostering sustained engagement in different product contexts.
- The Expectancy–Disconfirmation Theory remains a robust framework for modeling satisfaction across diverse product types. However, the influence of individual components such as expectation, perceived performance, and disconfirmation varies notably between categories. For digital products, satisfaction is more heavily shaped by users’ pre-existing mental models and expectations. This suggests that digital experiences are more cognitively driven and perception-sensitive, reinforcing the need for anticipatory design strategies that align digital performance with evolving user expectations to sustain satisfaction over time.
- While final satisfaction levels may converge across product types, the underlying temporal mechanisms differ significantly. For physical products, satisfaction tends to become increasingly influenced by external contextual factors, such as environmental conditions and social feedback. This suggests that adaptability to changing contexts and sustained functional or social relevance are critical for long-term satisfaction. In contrast, satisfaction with digital products is more dependent on internal dynamics, including interaction quality, personalization, and system adaptability. This highlights the importance of continuous optimization and implementing user-centered feedback loops in digital product design to support long-term user engagement and well-being.
- The early stages of use play a disproportionately critical role in shaping satisfaction with physical products by establishing a relatively fixed baseline for future evaluations. In contrast, digital product experiences tend to be more fluid and adaptive, allowing satisfaction to be reshaped over time. This finding highlights the potential of dynamic experience management strategies such as real-time updates, adaptive interfaces, and context-aware feedback as effective strategies for maintaining user satisfaction in digital environments.
In summary, this study contributes to sustainable design and product strategy by revealing how satisfaction evolves differently across physical and digital product types, with implications for reducing product abandonment and fostering long-term engagement. Beyond extending the Expectancy–Disconfirmation Theory, the findings align with and refine other dynamic models of user experience, such as the Peak–End Rule [92], by showing that satisfaction does not always follow a uniform trajectory over time. Furthermore, this study provides a novel perspective on hybrid products that integrate physical and digital features (e.g., smart appliances or digital subscription services embedded in hardware), suggesting that their satisfaction dynamics may combine features of both categories. These insights offer a theoretical basis for designing interventions that improve user experience continuity and sustainability across product ecosystems.
7. Limitations and Future Research
Despite its contributions, several limitations of the present study should be acknowledged. These limitations help define the boundaries of current insights and offer valuable directions for future investigation.
This study faces three key methodological limitations. First, although the design reflected real-world usage scenarios, the absence of environmental control may have introduced uncontrolled variability. The exclusive reliance on self-reported satisfaction also raises the possibility of recall bias or subjective distortion. Second, satisfaction was measured at only five time points, which limited the temporal resolution and may have obscured short-term fluctuations or nonlinear changes. Third, the study focused on overall satisfaction, expectations, and performance evaluations, without incorporating multidimensional indicators such as emotional response, trust, usability, or perceived value.
Future research should consider hybrid designs that balance ecological validity with contextual control and adopt temporally sensitive methods such as experience sampling or ecological momentary assessment to track satisfaction in real time. Increasing the number of measurement points could help reveal finer-grained dynamics. In addition, integrating behavioral data such as usage frequency, engagement duration, and interaction patterns could provide objective insights into satisfaction-related behavior. Qualitative methods such as interviews or diary studies may also help uncover the psychological mechanisms behind satisfaction development.
Finally, the cultural and contextual scope of the study should be considered. As the study was conducted entirely within a Chinese cultural and linguistic context, the findings may not be generalizable to users from other cultural backgrounds. For example, collectivist cultures may emphasize social harmony and long-term relationships with products, leading to more stable or conservative satisfaction ratings. In contrast, users in individualist cultures may value novelty and personal autonomy, which could result in more fluctuating or extreme evaluations. Future research should explore these differences through cross-cultural comparative studies or culturally grounded qualitative inquiries.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.W. and K.O.; methodology, Z.W., K.O. and Y.W.; validation, Z.W. and K.O.; formal analysis, Z.W. and Y.W.; investigation, Z.W.; resources, Z.W.; data curation, Z.W. and Y.W.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.W.; writing—review and editing, K.O. and Y.W.; visualization, Z.W.; supervision, K.O.; project administration, K.O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
According to Article 32 of the “Measures for Ethical Review of Life Science and Medical Research Involving Human” issued by the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2023-02/28/content_5743658.htm, accessed on 26 May 2025), ethical review and approval were waived for this study.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all participants involved in the study. Participation was voluntary, and all responses were anonymous.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented are available on request from the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Hult, G.T.M.; Morgeson, F.V.; Morgan, N.A.; Mithas, S.; Fornell, C. Do managers know what their customers think and why? J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2017, 45, 37–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, R.L. A cognitive model of the antecedents and consequences of satisfaction decisions. J. Mark. Res. 1980, 17, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiebler, T.; Lee, N.; Brodbeck, F.C. Expectancy-disconfirmation and consumer satisfaction: A meta-analysis. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2025, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, N.; Brierley, J. How to Measure Customer Satisfaction; Routledge: Oxfordshire, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hassenzahl, M. The thing and I: Understanding the relationship between user and product. In Funology 2: From Usability to Enjoyment; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 301–313. [Google Scholar]
- Kwortnik Jr, R.J.; Thompson, G.M. Unifying service marketing and operations with service experience management. J. Serv. Res. 2009, 11, 389–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keiningham, T.; Aksoy, L.; Bruce, H.L.; Cadet, F.; Clennell, N.; Hodgkinson, I.R.; Kearney, T. Customer experience driven business model innovation. J. Bus. Res. 2020, 116, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, Y.; Henfridsson, O.; Lyytinen, K. Research commentary—The new organizing logic of digital innovation: An agenda for information systems research. Inf. Syst. Res. 2010, 21, 724–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, M.E.; Heppelmann, J.E. How smart, connected products are transforming competition. Harv. Bus. Rev. 2014, 92, 64–88. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Fu, M.; Zhang, Z. The adoption of digital technologies in supply chains: Drivers, process and impact. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2021, 169, 120795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozari, H.; Fallah, M.; Kazemipoor, H.; Najafi, S.E. Big data analysis of IoT-based supply chain management considering FMCG industries. Бизнес-инфoрматика 2021, 15, 78–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhishek, V.; Guajardo, J.A.; Zhang, Z. Business models in the sharing economy: Manufacturing durable goods in the presence of peer-to-peer rental markets. Inf. Syst. Res. 2021, 32, 1450–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senachai, P.; Julagasigorn, P.; Chumwichan, S. The role of retail mix elements in enhancing customer engagement: Evidence from Thai fast-moving consumer goods retail sector. ABAC J. 2023, 43, 106–124. [Google Scholar]
- Niedermeier, A.; Emberger-Klein, A.; Menrad, K. Which factors distinguish the different consumer segments of green fast-moving consumer goods in Germany? Bus. Strategy Environ. 2021, 30, 1823–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazirkha, D.P.; Hom, J.; Melinda, V. Quality analysis of digital business services in improving customer satisfaction. Startupreneur Bus. Digit. (SABDA J.) 2022, 1, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shou, Z.; Wang, F.; Jia, J. The Measurement of Cumulative Satisfaction: An Analytical Model based on Dynamic Customer Expectation. Nankai Bus. Rev. 2011, 14, 142–150. [Google Scholar]
- Kerschbaumer, R.H.; Foscht, T.; Eisingerich, A.B. Is ownership of brands passe? A new model of temporary usage for durable goods. J. Bus. Strategy 2024, 45, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulyawan, A.; Alamsyah, Z. How digital platform changing people way to buy FMCG products. Proc. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 1063, 012050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramoniam, R.; Sundin, E.; Subramoniam, S.; Huisingh, D. Riding the digital product life cycle waves towards a circular economy. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemon, K.N.; Verhoef, P.C. Understanding customer experience throughout the customer journey. J. Mark. 2016, 80, 69–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jing, F. Research on Dynamic Satisfaction of Post Impulsive Buying Behavior—The Regulation Analysis of High/Low Internal Assessment Product. Soft Sci. 2012, 26, 132–136. [Google Scholar]
- Ramya, N.; Kowsalya, A.; Dharanipriya, K. Service quality and its dimensions. EPRA Int. J. Res. Dev. 2019, 4, 38–41. [Google Scholar]
- Keshavarz, Y.; Jamshidi, D. Service quality evaluation and the mediating role of perceived value and customer satisfaction in customer loyalty. Int. J. Tour. Cities 2018, 4, 220–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepola, J.; Karjaluoto, H.; Hintikka, A. The effect of sensory brand experience and involvement on brand equity directly and indirectly through consumer brand engagement. J. Prod. Brand Manag. 2017, 26, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anifa, N.; Sanaji, S. Augmented reality users: The effect of perceived ease of use, perceived usefulness, and customer experience on repurchase intention. J. Bus. Manag. Rev. 2022, 3, 252–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLone, W.H.; McLean, E.R. The DeLone and McLean model of information systems success: A ten-year update. J. Manag. Inf. Syst. 2003, 19, 9–30. [Google Scholar]
- Rehman, A.U.; Elahi, Y.A. How semiotic product packaging, brand image, perceived brand quality influence brand loyalty and purchase intention: A stimulus-organism-response perspective. Asia Pac. J. Mark. Logist. 2024, 36, 3043–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffer, D. Microinteractions: Designing with Details; O’Reilly Media, Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wixom, B.H.; Todd, P.A. A theoretical integration of user satisfaction and technology acceptance. Inf. Syst. Res. 2005, 16, 85–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V.; Thong, J.Y.; Xu, X. Consumer acceptance and use of information technology: Extending the unified theory of acceptance and use of technology. MIS Q. 2012, 36, 157–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Benbasat, I.; Cenfetelli, R.T. Integrating service quality with system and information quality: An empirical test in the e-service context. MIS Q. 2013, 37, 777–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghirov, F.; Zhang, Y. Assessment of the association between aesthetic products and perceived product quality: An analysis of customer attitudes. J. Consum. Mark. 2024, 41, 789–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hultén, B. Sensory marketing: The multi-sensory brand-experience concept. Eur. Bus. Rev. 2011, 23, 256–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, P. After-sales service shaping assortment satisfaction and online repatronage intention in the backdrop of social influence. Int. J. Qual. Serv. Sci. 2022, 14, 595–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babin, B.J.; Babin, L. Seeking something different? A model of schema typicality, consumer affect, purchase intentions and perceived shopping value. J. Bus. Res. 2001, 54, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-H.; Liu, C.-C.; Keng, C.-J. Understanding customers’ discontinuance intention toward curated subscription commerce via the expectation disconfirmation theory. Chiao Manag. Rev. 2023, 43, 65–96. [Google Scholar]
- Hassenzahl, M.; Tractinsky, N. User experience-a research agenda. Behav. Inf. Technol. 2006, 25, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, B.; Tullis, T. Measuring the User Experience: Collecting, Analyzing, and Presenting Usability Metrics; Newnes: New South Wales, Australia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Garett, J. The Elements of User Experience: User-Centered Design for the Web and Beyond, New Riders, Peachpit. Interactions 2011, 10, 49–51. [Google Scholar]
- Norman, D.A. The Design of Everyday Things Basic Books; Perseus: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacherjee, A. Understanding information systems continuance: An expectation-confirmation model. MIS Q. 2001, 25, 351–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujala, S.; Roto, V.; Väänänen-Vainio-Mattila, K.; Sinnelä, A. Identifying hedonic factors in long-term user experience. In Proceedings of the 2011 Conference on Designing Pleasurable Products and Interfaces, Milano, Italy, 22–25 June 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Sun, X.; Yan, D.; Wen, D. Perceived sustainability and customer engagement in the online shopping environment: The rational and emotional perspectives. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shneiderman, B.; Plaisant, C. Designing the User Interface: Strategies for Effective Human-Computer Interaction; Pearson Education India: Uttar Pradesh, India, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesh, V.; Morris, M.G.; Davis, G.B.; Davis, F.D. User acceptance of information technology: Toward a unified view. MIS Q. 2003, 27, 425–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntoa, S. Usability and user experience evaluation in intelligent environments: A review and reappraisal. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Interact. 2025, 41, 2829–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, K.T.; Eppinger, S.D. Product Design and Development; McGraw-hill: Singapore, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, H.; Gertsakis, J.; Grant, T.; Morelli, N.; Sweatman, A. Design + Environment: A Global Guide to Designing Greener Goods; Routledge: Sheffield, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Koenigsberg, O.; Kohli, R.; Montoya, R. The design of durable goods. Mark. Sci. 2011, 30, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhagaiah, R.; Ezhilarasi, E. Consumer behavior regarding durable goods. Indian J. Mark. 2012, 42, 27–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, M.N.; Wang, L.; Li, Y. Study On the Design Methods of Fast Moving Consumer Goods. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 605, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sordi, J.O.; Reed, E.N.; Meireles, M.; da Silveira, M.A. Development of digital products and services: Proposal of a framework to analyze versioning actions. Eur. Manag. J. 2016, 34, 564–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koukova, N.T.; Kannan, P.; Kirmani, A. Multiformat digital products: How design attributes interact with usage situations to determine choice. J. Mark. Res. 2012, 49, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G. Digital reframing: The design thinking of redesigning traditional products into innovative digital products. J. Prod. Innov. Manag. 2022, 39, 95–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldman, M. Durable goods theory for real world markets. J. Econ. Perspect. 2003, 17, 131–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotler, P.; Armstrong, G. Principles of Marketing; Pearson Education: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Gowrisankaran, G.; Rysman, M. Dynamics of consumer demand for new durable goods. J. Political Econ. 2012, 120, 1173–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiris, T.K.A.; Jasingha, D.; Rathnasiri, M.S.H. Examining the effect of consumption values on green FMCG purchase behaviour: A focus on the theory of consumption values. Manag. Sustain. Arab Rev. 2024, 3, 385–403. [Google Scholar]
- Rusch, M.; Schöggl, J.P.; Baumgartner, R.J. Application of digital technologies for sustainable product management in a circular economy: A review. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2023, 32, 1159–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 9241-210:2010; Ergonomics of Human System Interaction-Part 210: Human-Centred Design for Interactive Systems. International Standardization Organization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- Hui, K.L.; Chau, P.Y. Classifying digital products. Commun. ACM 2002, 45, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tassell, C.; Aurisicchio, M. Refill at home for fast-moving consumer goods: Uncovering compliant and divergent consumer behaviour. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2023, 39, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.J.; Bellezza, S.; Paharia, N. Buy less, buy luxury: Understanding and overcoming product durability neglect for sustainable consumption. J. Mark. 2021, 85, 28–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pino, G.; Amatulli, C.; Nataraajan, R.; De Angelis, M.; Peluso, A.M.; Guido, G. Product touch in the real and digital world: How do consumers react? J. Bus. Res. 2020, 112, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tidwell, J. Designing Interfaces: Patterns for Effective Interaction Design; O’Reilly Media, Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Cochoy, F.; Licoppe, C.; McIntyre, M.P.; Sörum, N. Digitalizing consumer society: Equipment and devices of digital consumption. J. Cult. Econ. 2020, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, J.; Thomas, E.; Qi, J.; Tan, Y. Online group influence and digital product consumption. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2018, 46, 921–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Harris, K.; Vazire, S. Is well-being associated with the quantity and quality of social interactions? J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 2020, 119, 1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, P.C.; Steyerberg, E.W. The number of subjects per variable required in linear regression analyses. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2015, 68, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, K.; Yadav, S. Linear regression analysis study. J. Pract. Cardiovasc. Sci. 2018, 4, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, A.C.; Trivedi, P.K. Microeconometrics: Methods and Applications; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery, D.C.; Peck, E.A.; Vining, G.G. Introduction to Linear Regression Analysis; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, M.; Lin, Y. Model selection and estimation in regression with grouped variables. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 2006, 68, 49–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.J.; Kim, J.H. An empirical validation of a loyalty model based on expectation disconfirmation. J. Consum. Mark. 2000, 17, 120–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V.; Goyal, S. Expectation disconfirmation and technology adoption: Polynomial modeling and response surface analysis. MIS Q. 2010, 34, 281–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churchill Jr, G.A.; Surprenant, C. An investigation into the determinants of customer satisfaction. J. Mark. Res. 1982, 19, 491–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.; Zheng, Y. Predicting Continuance Intention to Use Learning Management Systems among Undergraduates: The Moderating Effect of Intrinsic Motivation. SAGE Open 2024, 14, 21582440241271319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyrväinen, O. The Use of Digital Technologies in Omnichannel Retailing: Understanding Integrated Customer Experience Across Diverse Touchpoints. Ph.D. Thesis, Jyväskylän yliopisto, Jyväskylä, Finland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ostertagova, E.; Ostertag, O. Forecasting using simple exponential smoothing method. Acta Electrotech. Inform. 2012, 12, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownlee, J. Introduction to Time Series Forecasting with Python: How to Prepare Data and Develop Models to Predict the Future; Machine Learning Mastery: Victoria, Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gelper, S.; Fried, R.; Croux, C. Robust forecasting with exponential and Holt–Winters smoothing. J. Forecast. 2010, 29, 285–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, D.; Mallery, P. IBM SPSS Statistics 26 Step by Step: A Simple Guide and Reference; Routledge: Sheffield, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Voorhees, C.M.; Fombelle, P.W.; Gregoire, Y.; Bone, S.; Gustafsson, A.; Sousa, R.; Walkowiak, T. Service encounters, experiences and the customer journey: Defining the field and a call to expand our lens. J. Bus. Res. 2017, 79, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoe, L.C.; Mansori, S. The effects of product quality on customer satisfaction and loyalty: Evidence from Malaysian engineering industry. Int. J. Ind. Mark. 2018, 3, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Fan, Y.; Li, Y.; Tarkoma, S.; Hui, P. Understanding the long-term evolution of mobile app usage. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2021, 22, 1213–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, R.L. Cognitive, affective, and attribute bases of the satisfaction response. J. Consum. Res. 1993, 20, 418–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaris, C.; Sarantopoulos, P.; Vrechopoulos, A.; Doukidis, G. Effects of increased omnichannel integration on customer satisfaction and loyalty intentions. Int. J. Electron. Commer. 2021, 25, 440–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blom, A.; Lange, F.; Hess, R.L. Omnichannel promotions and their effect on customer satisfaction. Eur. J. Mark. 2021, 55, 177–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, K.; Habib, R.; Hardisty, D.J. How to SHIFT consumer behaviors to be more sustainable: A literature review and guiding framework. J. Mark. 2019, 83, 22–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, V.; Kamakura, W.A. Satisfaction, repurchase intent, and repurchase behavior: Investigating the moderating effect of customer characteristics. J. Mark. Res. 2001, 38, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guru, R.R.D.; Paulssen, M.; Japutra, A. Role of brand attachment and satisfaction in driving customer behaviors for durables: A longitudinal study. Eur. J. Mark. 2024, 58, 217–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, A.M.; Rupert, A.V.; Wolford, G. Evaluations of pleasurable experiences: The peak-end rule. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2008, 15, 96–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).