Digital Enablers of Sustainability: Insights from Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Research Mapping
Abstract
1. Introduction
- RQ 1: How have research trends in the SDGs and their associations with DTs evolved in recent decades?
- RQ 2: How have the SDG–DT research pairs evolved? Which DTs are most frequently associated with each SDG? What differences exist between the DTs regarding their associations with specific goals?
- RQ 3: What are the emerging areas of research at the intersection of the SDGs and DTs?
2. Relevant Studies
3. Data Collection
4. Results
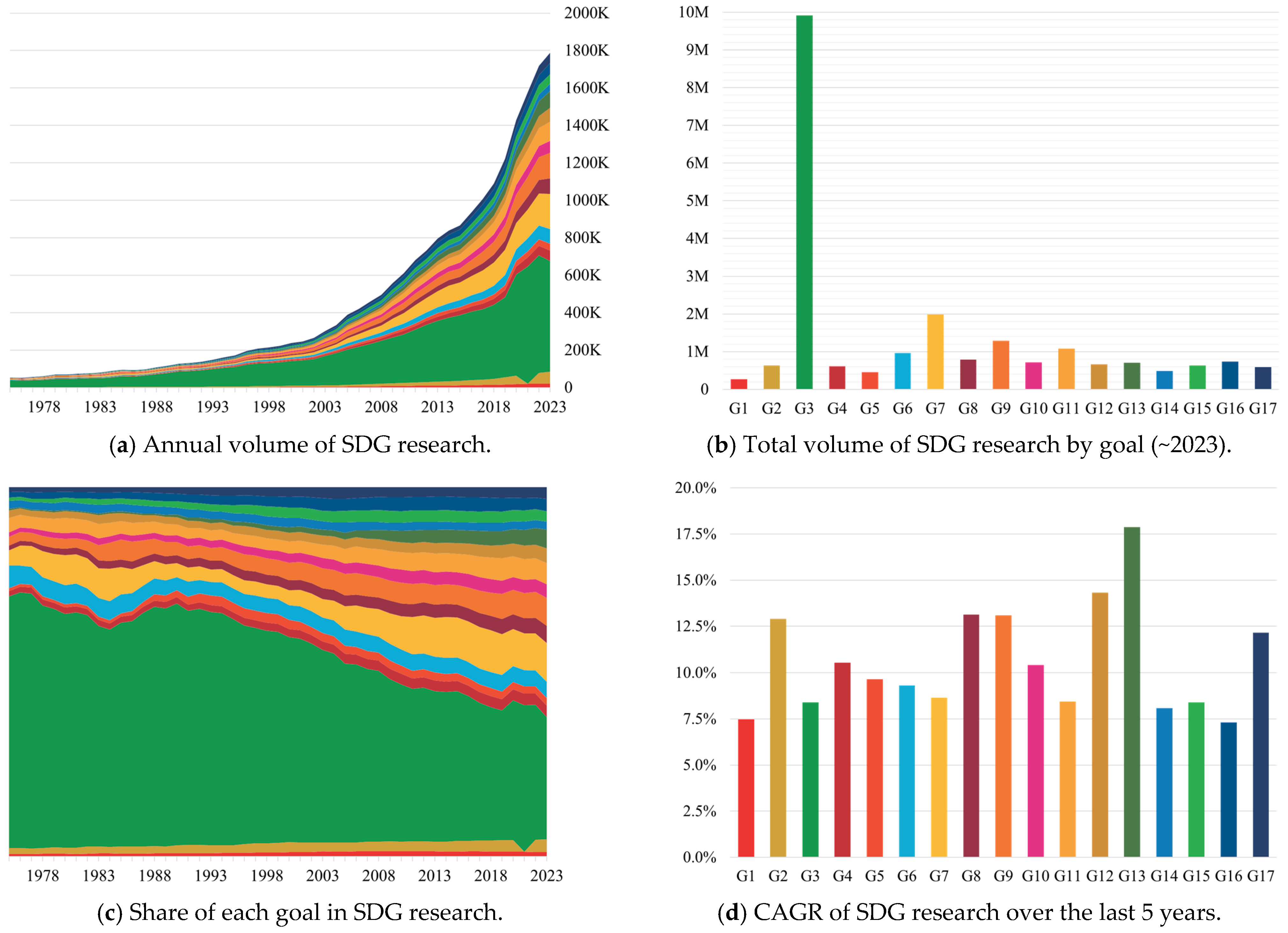
4.1. SDG Research: Overall Trends in the Volume of Research by Goal
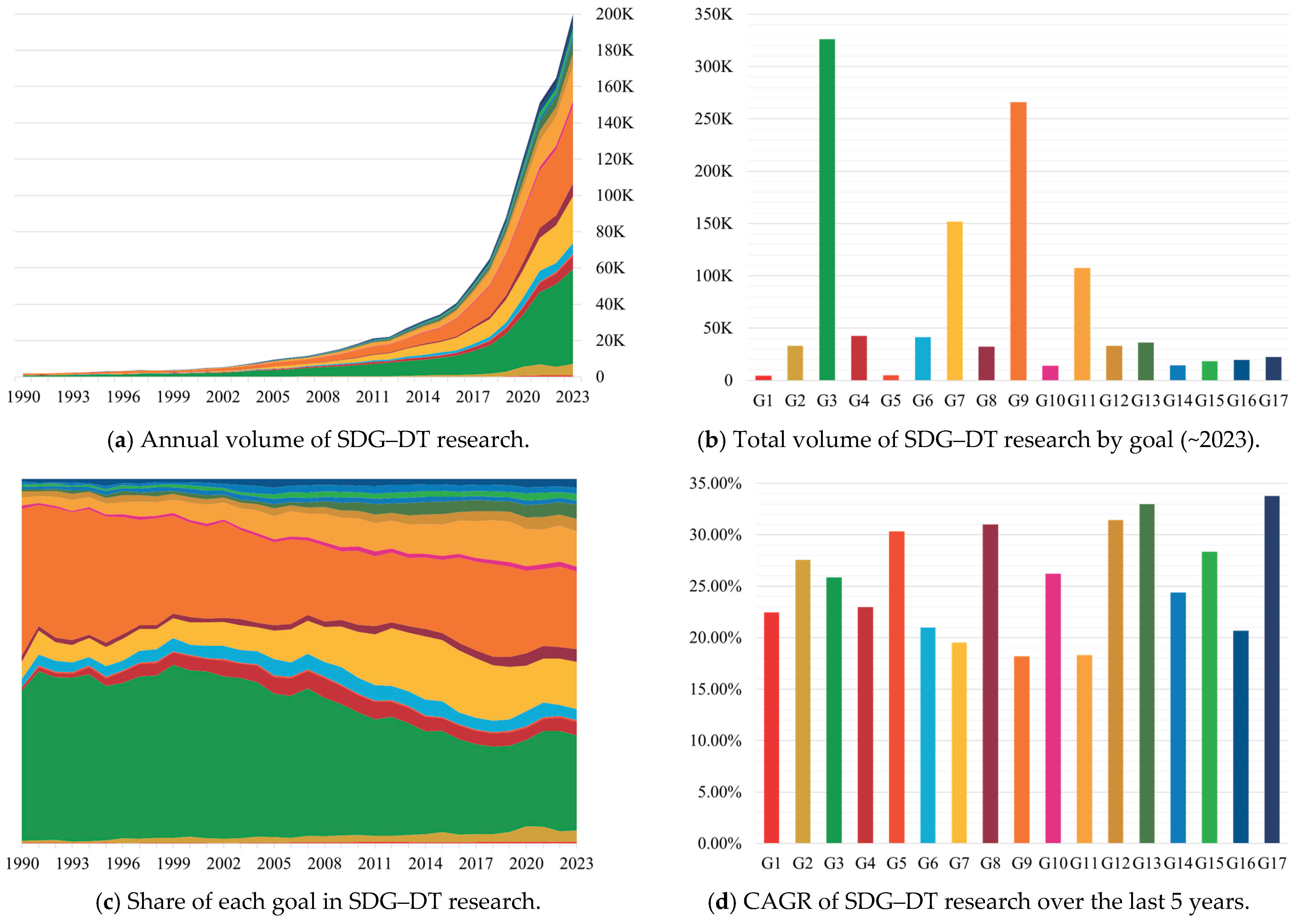
4.2. SDG–DT Research: Overall Trends in Volume and Its Share Within Total SDG Research
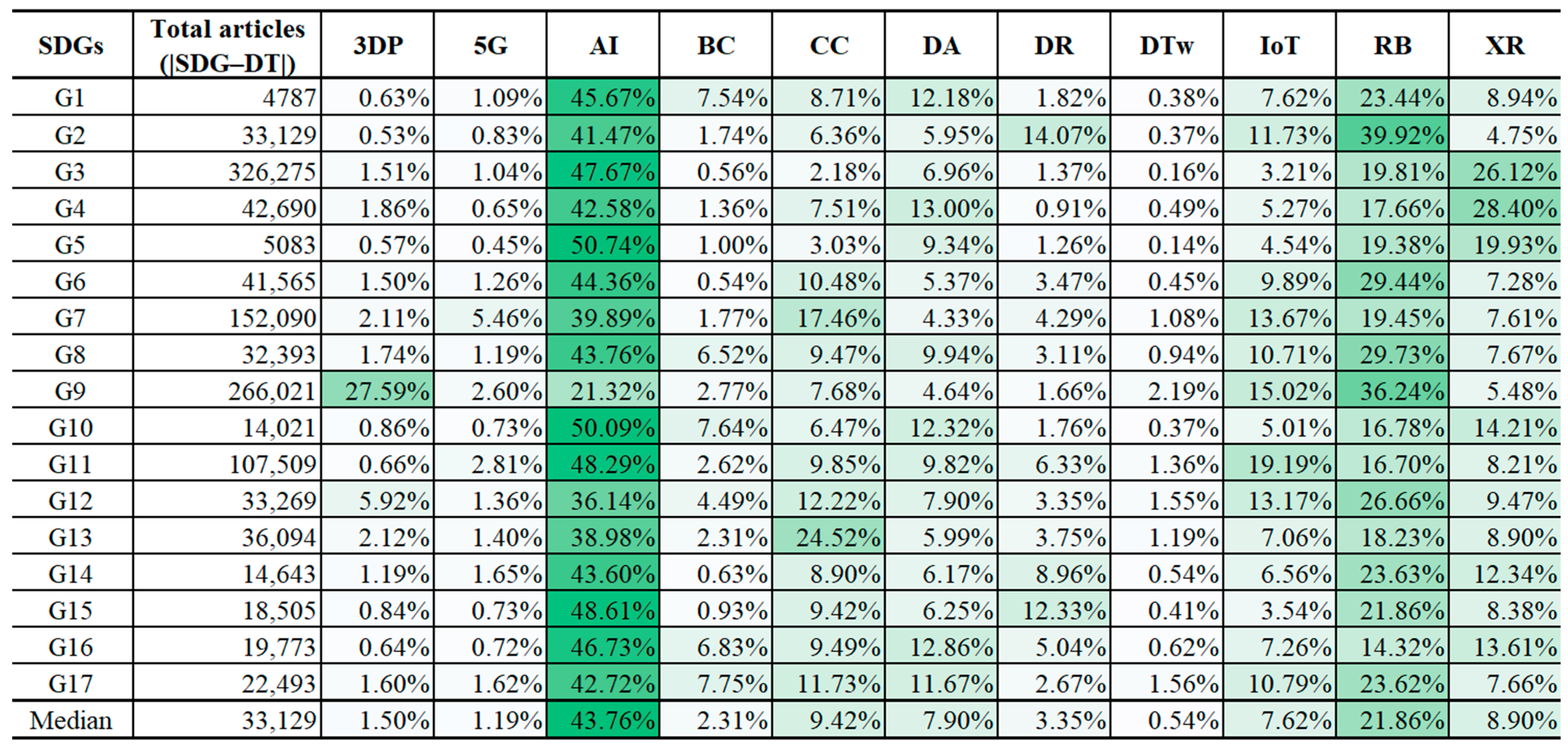
4.3. Most Associated Linkages Between the SDGs and DTs
4.3.1. Most Associated DTs for Each SDG
4.3.2. Most Associated SDGs for Each DT
4.4. Emerging Areas in SDG–DT Research
5. Discussion
5.1. Key Findings and Implications of RQ 1: Trends in the Volume of SDG–DT Research
- Overall growth and diversification in SDG research: Research on SDGs has experienced substantial growth, beginning to rise notably in the 1990s and accelerating sharply after 2000. A significant surge occurred between 2017 and 2023, likely fueled by the heightened global awareness of sustainability challenges and the UN’s formal adoption of the SDGs. In 2023, the annual number of publications reached nearly 1.8 million, and this upward trend is expected to continue as sustainability remains a key research priority. Although Goal 3 continues to dominate, the research landscape is rapidly diversifying. Many other goals are now experiencing accelerated growth, suggesting a broader and more balanced focus across the full spectrum of SDGs.
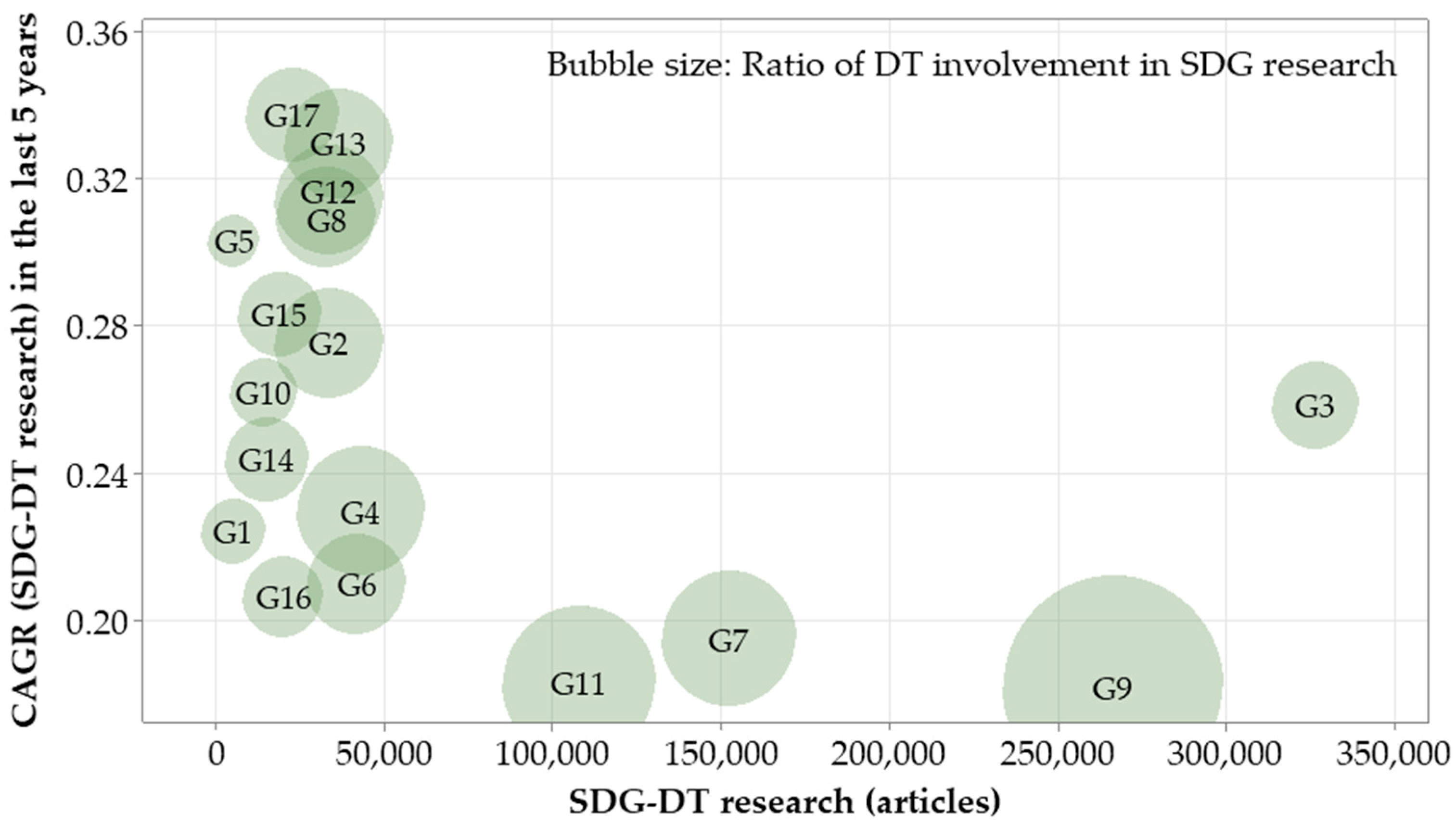
- Rapid expansion of SDG–DT research: Although the level of digital integration varies across SDGs, there is an overall trend of consistent growth across all goals. Notably, SDG–DT research has expanded at a much faster rate than general SDG research, with a median CAGR of 25.86% over the past five years, significantly outpacing the average 9.65% CAGR of general SDG research. Consequently, the proportion of SDG–DT research within the total body of SDG publications has increased.
5.2. Key Findings and Implications of RQ 2: Associations Between the SDGs and DTs
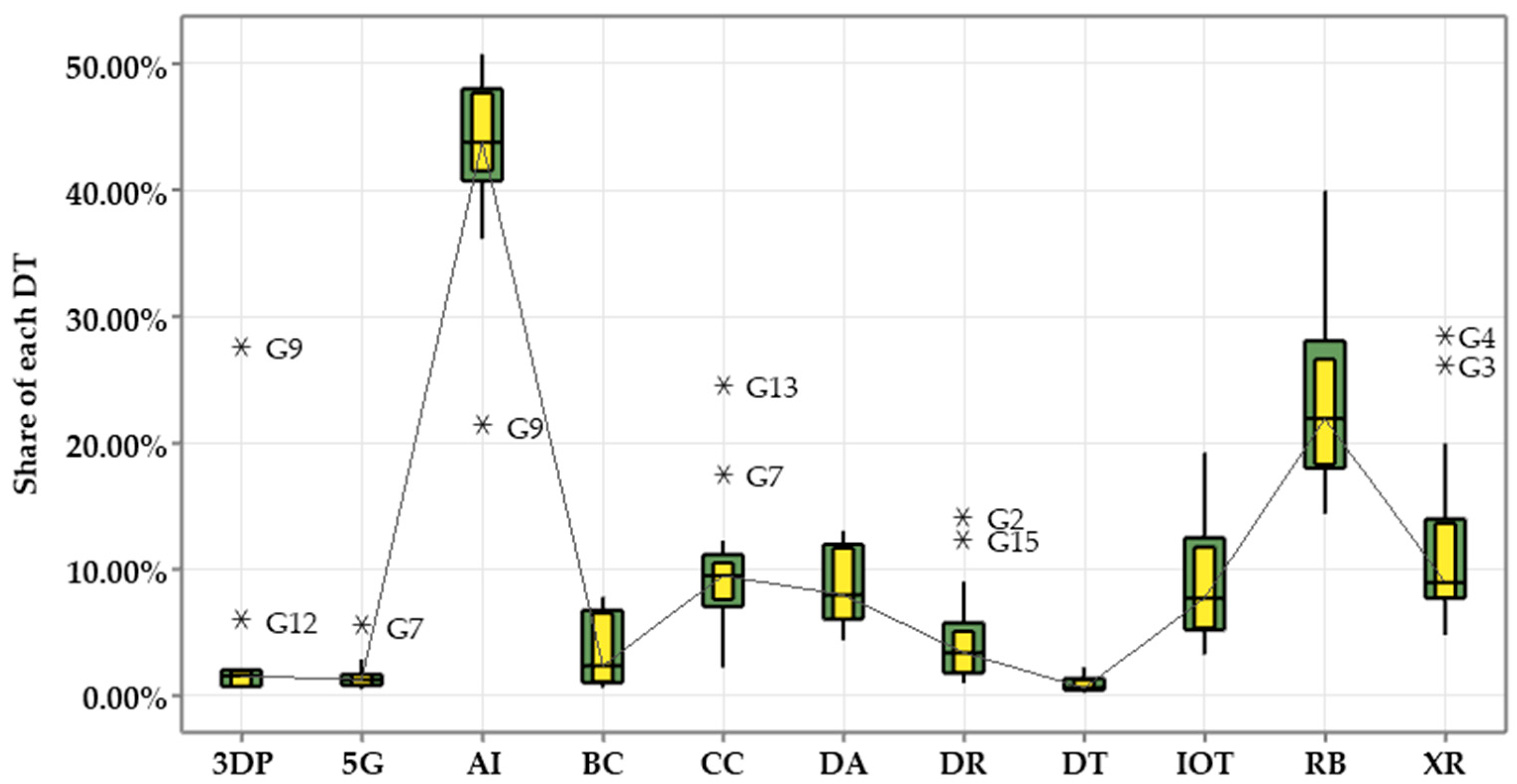
- DTs most associated with each SDG: AI and RB (robotics) show dominant associations across nearly all goals, indicating their widespread applicability. Goal-specific associations are also observed, such as 3DP for Goal 9, XR for Goals 3 to 5, IoT for Goal 11, and CC for Goal 13. These results suggest that such technologies are particularly relevant for addressing specific sustainability issues.
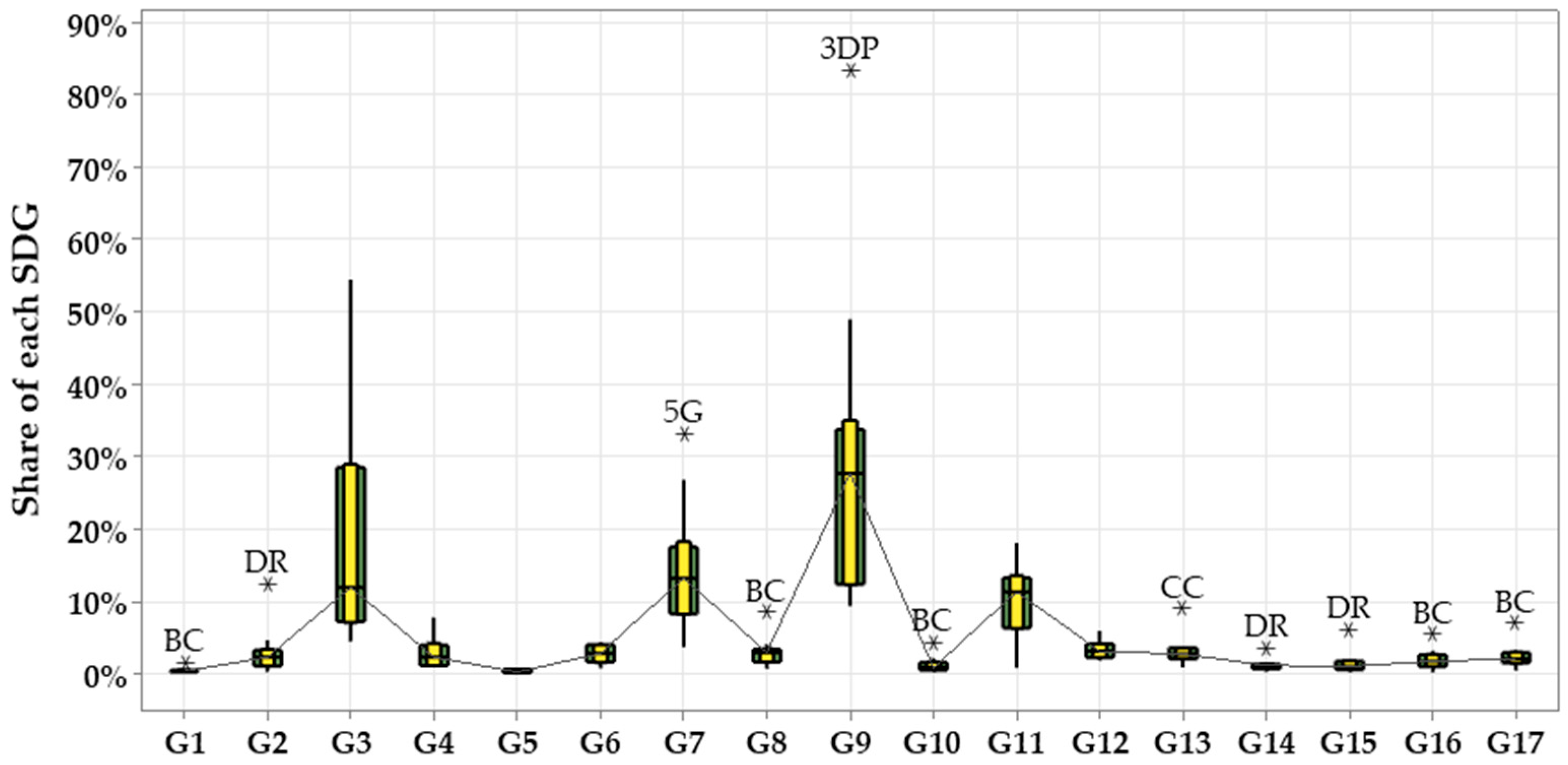
- SDGs most associated with each DT: From the perspective of each DT, the most frequently targeted goals are Goals 9, 3, 7, and 11. These goals serve as focal points in digital applications. Additionally, some DTs have revealed unique priorities, such as BC for Goal 8, CC for Goal 13, DA and XR for Goal 4, and DR and RB for Goal 2. The results imply that each DT has focused primarily on addressing these goals.
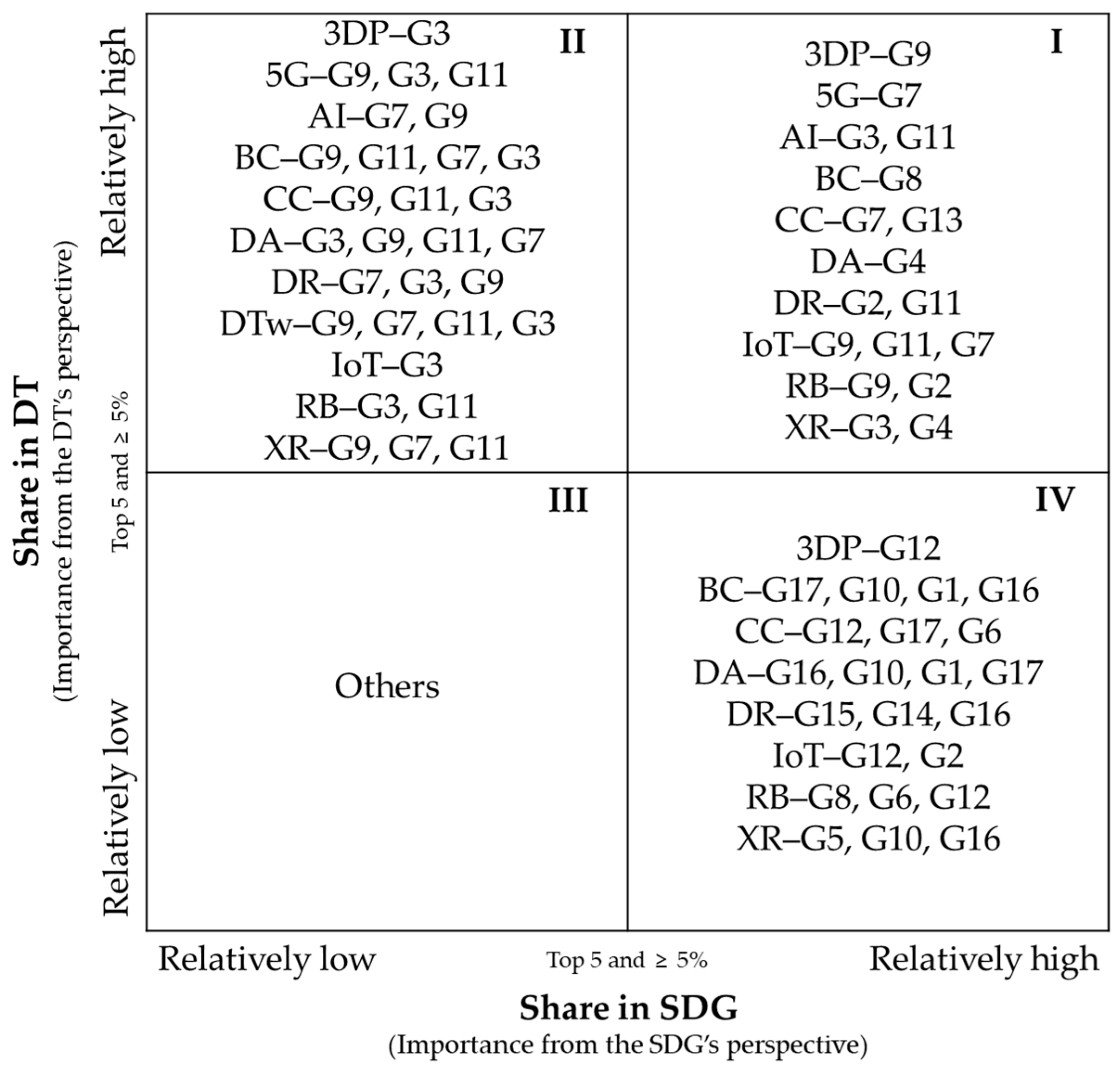
- Quadrant I (strong mutual relevance): These SDG–DT pairs demonstrate fairly high shares from both perspectives. The DT is widely adopted within the SDG domain and represents a key application area for the DT. This reflects strategically aligned and mature research intersections, offering high potential for integrated innovation and policy development.
- Quadrant II (SDG-side adoption opportunity): These pairs are prominent within the DT research landscape but remain underutilized within corresponding SDG research. This asymmetry suggests an opportunity to promote technology adoption on the side of the SDGs. The SDG community may benefit from greater awareness and integration of these digital tools.
- Quadrant III (peripheral or emerging linkages): These pairs show low engagement on both sides, indicating limited current research activity. While some may reflect weak synergies, others may represent nascent or underexplored frontiers in SDG–DT integration, offering promising avenues for interdisciplinary exploration and innovation.
- Quadrant IV (DT-side expansion opportunity): The DT is heavily referenced in a particular SDG, but that SDG accounts for only a small fraction of the DT’s broader research applications. Broadening the impact horizons for SDGs is recommended for the DT research community.
5.3. Key Findings and Implications of RQ 3: Emerging SDG–DT Research
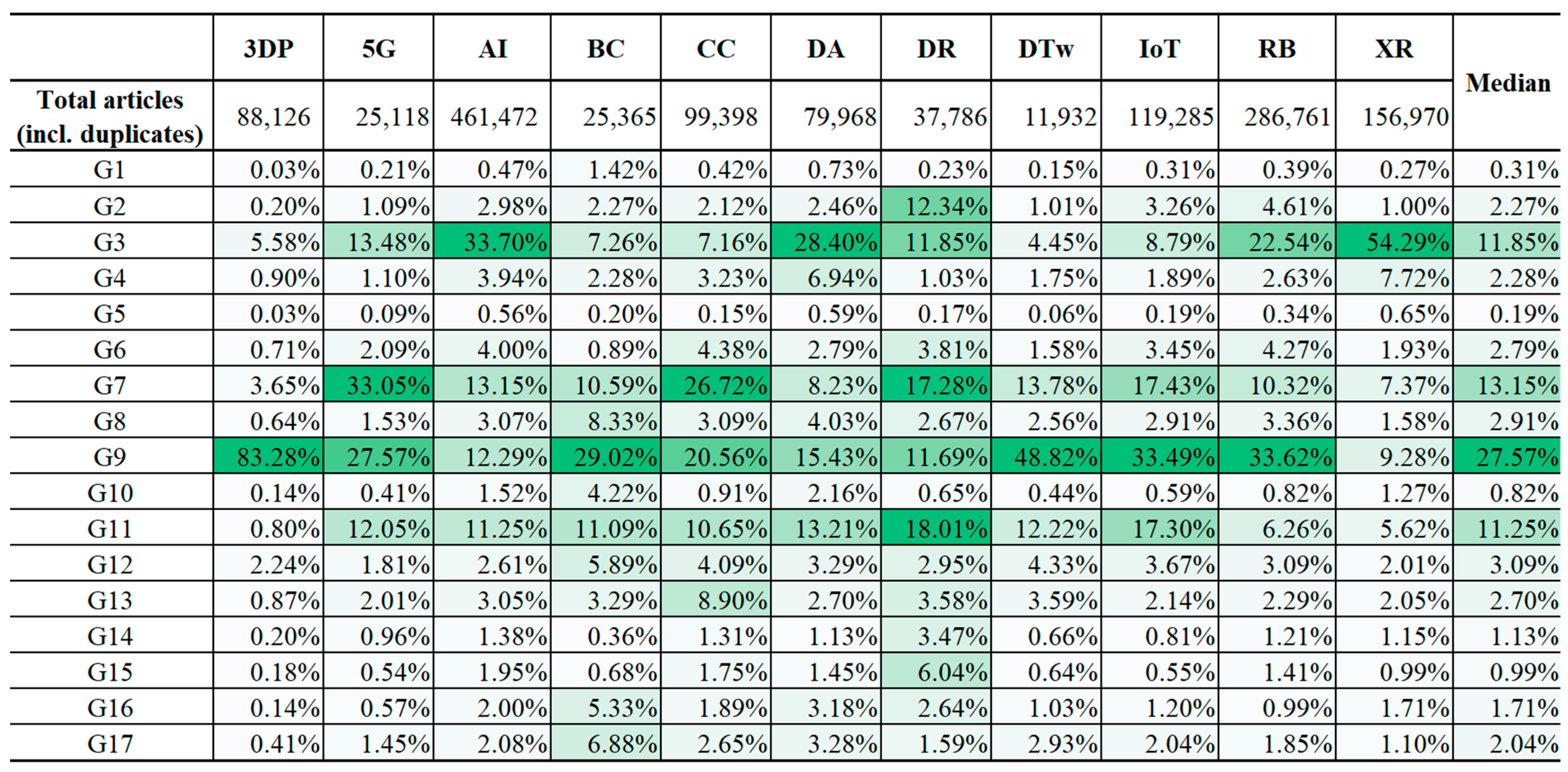
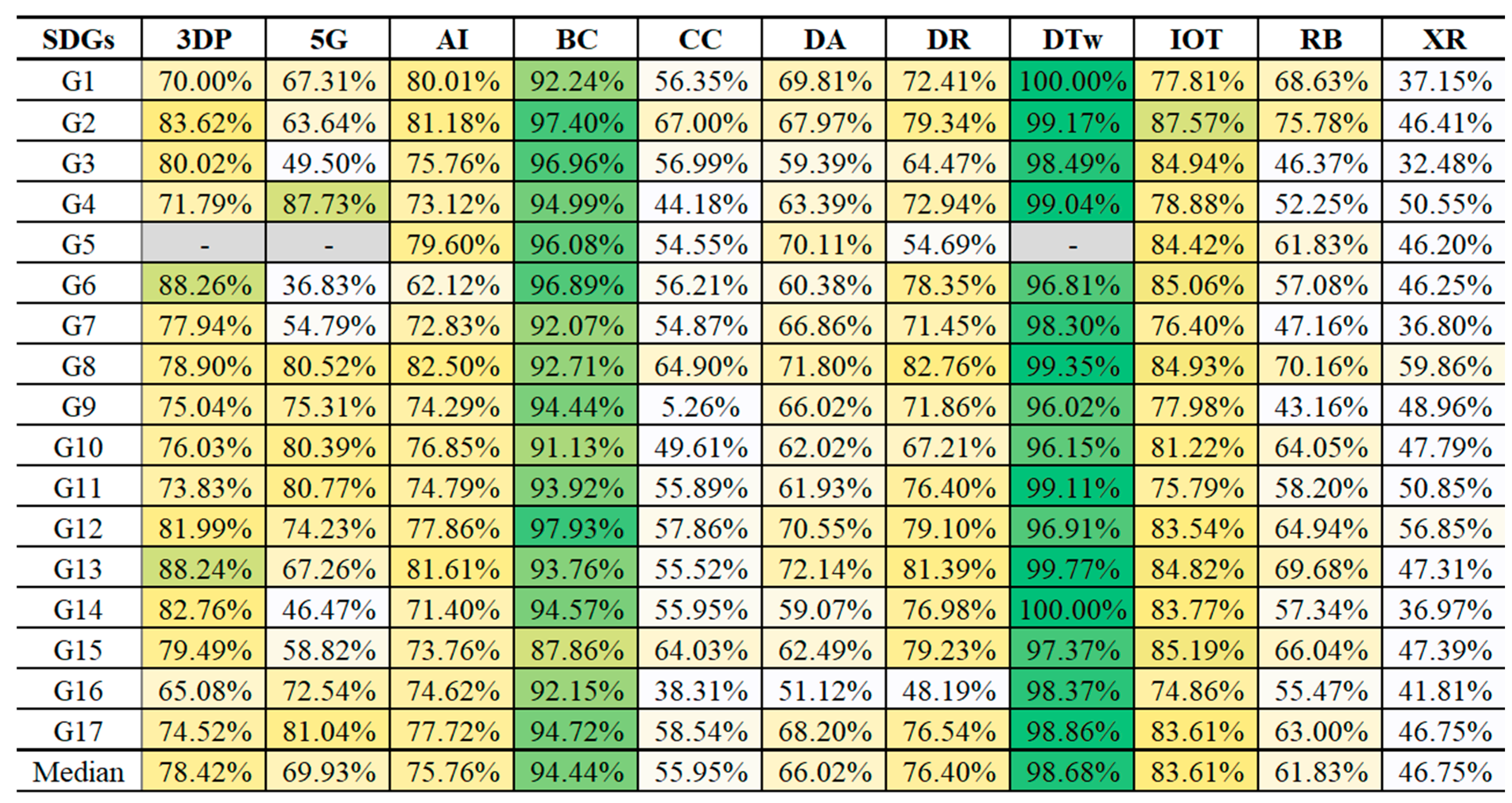
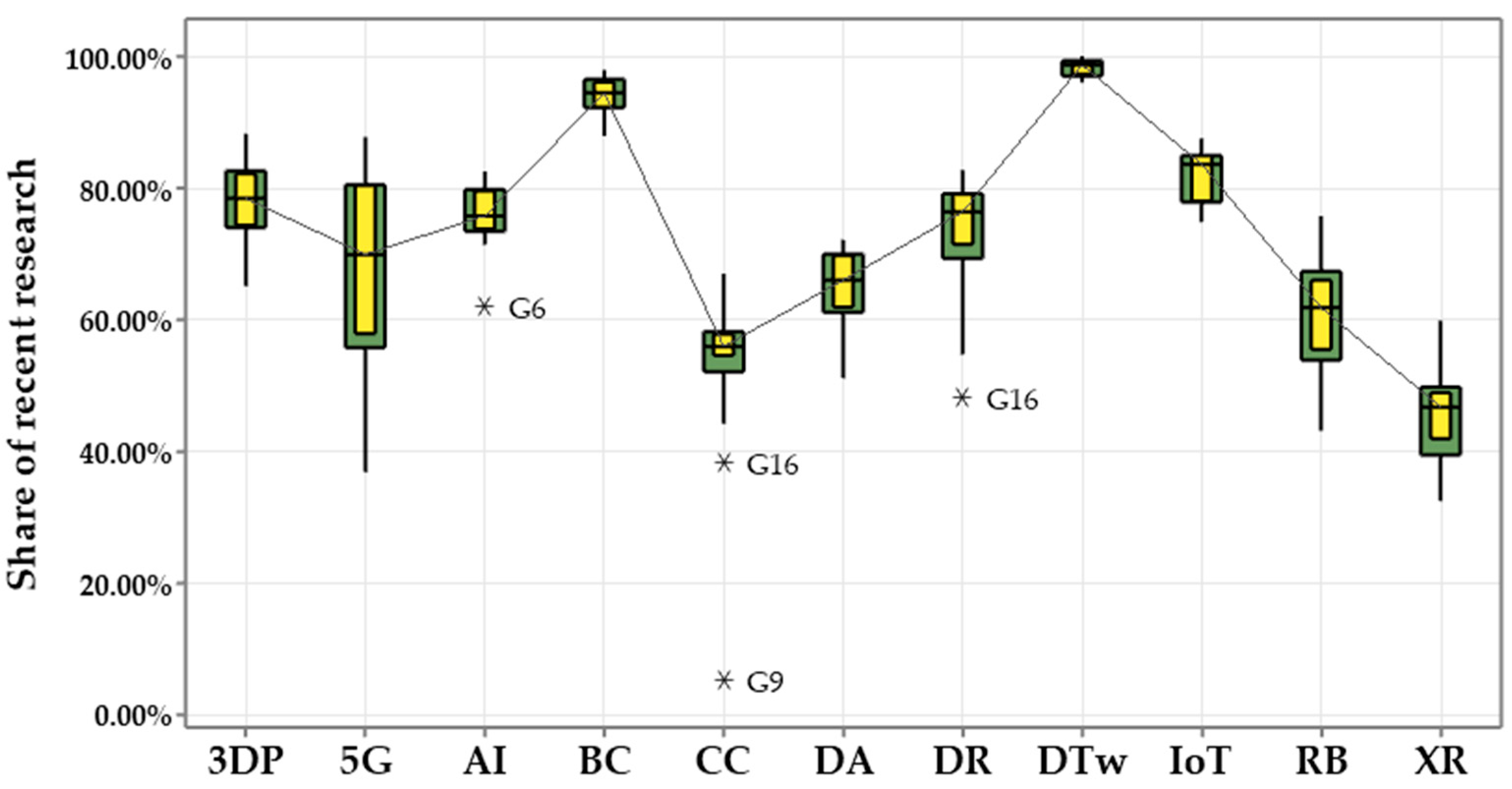
- Emergence of DTw and BC across broad SDGs: The analysis revealed that DTw and BC have emerged as the fastest-growing technologies in SDG research. DTw leads, with 98.68% of related publications occurring in the past five years, followed by BC with 94.44%. Their rapid growth underscores their emerging application for various SDGs, with DTw focusing on simulation and predictive modeling, and BC enhancing secure data sharing and transparency.
- Emerging linkages in a specific goal: Several SDG-specific emerging linkages are also identified, showcasing the dynamic integration of the SDGs and DTs. 3D printing is prominent in Goals 6 and 13, with over 88% of recent publications focusing on these areas. 5G technology has emerged in Goal 4, with more than 87% of its publications appearing in the past five years. The IoT is also emerging in various SDG studies, especially in Goals 2 and 15.
5.4. Methodological and Practical Implications
- Methodological implications and limitations: This study introduces a novel methodological framework that combines automated SDG mapping with pairwise SDG–DT analysis. This approach enables the systematic identification of trends, concentrations, and gaps in SDG–DT research. Such a structural mapping-based bibliometric analysis provides valuable insights into how digital transformation evolves across sustainability domains. Furthermore, this method is easily transferable to other interdisciplinary contexts linking SDGs with technologies, industry sectors, or academic disciplines, such as SDG–biotechnology, SDG–liberal arts, and SDG–education.However, the limitations of this approach must be acknowledged. The analysis relies on keyword-based bibliometric data, which are inherently subject to false positives and false negatives, despite being informed by carefully curated queries. The selection of DT categories and associated keywords reflects subjective decisions that may not fully or precisely capture the nuances of digital integration. In addition, SDG-mapping tools primarily identify quantitative associations and do not assess the depth, context, or quality of SDG–DT relevance within articles.The strength of this method lies in its ability to reveal macrolevel patterns. With future improvements and complementary research (such as the incorporation of NLP, topic modeling, and expert validation), SDG mapping–based bibliometric methods can serve as powerful tools for diagnosing research priorities and guiding cross-sector collaboration.
- Practical implications for stakeholders: The findings have meaningful implications for various stakeholders, including researchers, policymakers, businesses, and educators.Researchers can leverage these results to identify underexplored opportunities. In particular, the SDG–DT pairs situated in Quadrants II and III of the positioning matrix represent areas where novel academic contributions are both needed and feasible.Policymakers can use these findings to facilitate more balanced digital integration across the SDGs. In cases where particular SDGs show weak DT engagement (Quadrant II), efforts may be directed toward encouraging greater adoption of the corresponding DTs. Conversely, when DTs have not yet deeply engaged with specific SDGs (Quadrant IV), strategies may be developed to promote DT-side involvement. For pairs in Quadrant III, that remain underexplored on both sides, policymakers can initiate discourse and funding to explore their potential as emerging frontiers.Businesses and technology developers can identify digital solutions that align with sustainability goals. Well-established SDG–DT linkages can inform strategic roadmaps for deploying technologies to address clearly defined sustainability challenges. At the same time, SDG–DT pairs with emerging momentum highlight areas with high potential for innovation and market development.Educators and academic institutions can align their curricula with the technologies most relevant to the SDG agenda. Emphasizing DTs with strong linkages to SDGs—such as AI, RB, IoT, or XR—within sustainability-focused programs will better prepare students for leadership roles in addressing complex global challenges. In addition, strengthening education for sustainable development (ESD) within DT-related disciplines can help equip the next generation of professionals with both technical expertise and sustainability awareness.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SDG | Sustainable Development Goal |
| DT | Digital Technology |
| 3DP | 3D Printing |
| 5G | 5th-Generation Mobile Network |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| BC | Blockchain |
| CC | Cloud Computing |
| DA | Data Analytics |
| DTw | Digital Twin |
| DR | Drones |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| RB | Robotics |
| XR | Extended Reality |
Appendix A
| DT | Query |
|---|---|
| 3DP | (TITLE-ABS-KEY(“3D Printing”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“3D-printing”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Three Dimensional Printing”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Additive Manufacturing”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Additive Layer Manufacturing”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“3D Manufacturing”)) |
| 5G | (TITLE-ABS-KEY(“5G”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“5th Generation Mobile Networks”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Next-Generation Networks”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“5G Communication Technology”)) |
| AI | (TITLE-ABS-KEY(“AI”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Artificial Intelligence”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Machine Learning”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Deep Learning”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Neural Networks”)) |
| BC | (TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Blockchain”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Digital Distributed Ledger”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Block Technology”)) |
| CC | (TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Cloud-computing”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Cloud Computing”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Cloud Technology”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Online Computing”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Remote Servers”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Digital Storage”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Distributed Computer Systems”)) |
| DA | (TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Data Analytics”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Data Science”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Big Data Analytics”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Data Mining”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Predictive Analytics”)) |
| DR | (TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Drones”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Drone”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“UAV”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Unmanned Aerial Vehicles”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Unmanned Aerial Systems”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Autonomous Aircraft”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Drone Technology”)) |
| DTw | (TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Digital Twin”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Digital Twins”)) |
| IoT | (TITLE-ABS-KEY(“IOT”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Internet of things”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Internet of thing”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“IoT”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Smart Devices”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Connected Devices”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Machine-to-Machine (M2M) Communication”)) |
| RB | (TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Robotics”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Robot”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Robots”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Robot Programming”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Automation”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Robot Technology”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Robotic Engineering”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Autonomous Systems”)) |
| XR | (TITLE-ABS-KEY(“XR(MR,VR,AR)”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“XR”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Mixed Reality”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Virtual Reality”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Augmented Reality”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“MR”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“VR”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“AR”)) |
| All DTs | Combine all queries above in series with “OR” |
Appendix B
| SDG | Volume of SDG Research (|SDG|) | Volume of SDG–DT Research (|SDG–DT|) | Ratio of DT-Related Research (|SDG–DT|/|SDG|) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total in All Years | Past 5 Years | Total in All Years | Past 5 years | All Years | Before Last 5 Years | Last 5 Years | |||
| Volume | CAGR | Volume | CAGR | ||||||
| G1 | 268,153 | 93,691 | 7.47% | 4787 | 3341 | 22.43% | 1.79% | 0.83% | 3.57% |
| G2 | 632,428 | 256,118 | 12.90% | 33,129 | 24,634 | 27.55% | 5.24% | 2.26% | 11.63% |
| G3 | 9,911,209 | 2,820,028 | 8.40% | 326,275 | 186,787 | 25.86% | 3.29% | 1.97% | 6.62% |
| G4 | 608,162 | 236,921 | 10.54% | 42,690 | 25,608 | 22.97% | 7.02% | 4.60% | 10.81% |
| G5 | 452,721 | 155,175 | 9.65% | 5083 | 3435 | 30.32% | 1.12% | 0.55% | 2.21% |
| G6 | 963,508 | 339,493 | 9.31% | 41,565 | 24,831 | 21.00% | 4.31% | 2.68% | 7.31% |
| G7 | 1,982,122 | 789,410 | 8.66% | 152,090 | 92,708 | 19.50% | 7.67% | 4.98% | 11.74% |
| G8 | 784,518 | 329,343 | 13.14% | 32,393 | 24,028 | 30.99% | 4.13% | 1.84% | 7.30% |
| G9 | 1,285,695 | 539,735 | 13.09% | 266,021 | 159,580 | 18.20% | 20.69% | 14.27% | 29.57% |
| G10 | 712,342 | 276,171 | 10.41% | 14,021 | 9493 | 26.20% | 1.97% | 1.04% | 3.44% |
| G11 | 1,081,855 | 443,156 | 8.44% | 107,509 | 72,012 | 18.33% | 9.94% | 5.56% | 16.25% |
| G12 | 669,161 | 284,773 | 14.33% | 33,269 | 23,270 | 31.44% | 4.97% | 2.60% | 8.17% |
| G13 | 706,537 | 338,469 | 17.88% | 36,094 | 25,064 | 32.97% | 5.11% | 3.00% | 7.41% |
| G14 | 490,088 | 170,740 | 8.09% | 14,643 | 9093 | 24.40% | 2.99% | 1.74% | 5.33% |
| G15 | 636,693 | 229,904 | 8.40% | 18,505 | 12,649 | 28.34% | 2.91% | 1.44% | 5.50% |
| G16 | 737,067 | 257,381 | 7.31% | 19,773 | 12,060 | 20.65% | 2.68% | 1.61% | 4.69% |
| G17 | 590,748 | 226,518 | 12.14% | 22,493 | 15,505 | 33.76% | 3.81% | 1.92% | 6.84% |
| Median | 706,537 | 276,171 | 9.65% | 33,129 | 24,028 | 25.86% | 4.13% | 1.92% | 7.30% |
| 3DP | 5G | AI | BC | CC | DA | DR | DTw | IoT | RB | XR | Total (|SDG–DT|) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | 30 | 52 | 2186 | 361 | 417 | 583 | 87 | 18 | 365 | 1122 | 428 | 4787 |
| G2 | 177 | 275 | 13,737 | 577 | 2106 | 1970 | 4661 | 121 | 3886 | 13,224 | 1573 | 33,129 |
| G3 | 4920 | 3386 | 155,531 | 1841 | 7117 | 22,707 | 4478 | 531 | 10,480 | 64,637 | 85,226 | 326,275 |
| G4 | 794 | 277 | 18,179 | 579 | 3207 | 5551 | 388 | 209 | 2249 | 7539 | 12,125 | 42,690 |
| G5 | 29 | 23 | 2579 | 51 | 154 | 475 | 64 | 7 | 231 | 985 | 1013 | 5083 |
| G6 | 622 | 524 | 18,438 | 225 | 4357 | 2234 | 1441 | 188 | 4111 | 12,235 | 3025 | 41,565 |
| G7 | 3214 | 8302 | 60,669 | 2685 | 26,561 | 6581 | 6529 | 1644 | 20,795 | 29,581 | 11,572 | 152,090 |
| G8 | 564 | 385 | 14,175 | 2112 | 3068 | 3220 | 1009 | 306 | 3470 | 9629 | 2484 | 32,393 |
| G9 | 73,395 | 6925 | 56,722 | 7362 | 20,436 | 12,339 | 4417 | 5825 | 39,952 | 96,404 | 14,574 | 266,021 |
| G10 | 121 | 102 | 7023 | 1071 | 907 | 1727 | 247 | 52 | 703 | 2353 | 1992 | 14,021 |
| G11 | 707 | 3026 | 51,911 | 2813 | 10,588 | 10,562 | 6805 | 1458 | 20,632 | 17,954 | 8822 | 107,509 |
| G12 | 1971 | 454 | 12,022 | 1494 | 4067 | 2628 | 1115 | 517 | 4381 | 8868 | 3152 | 33,269 |
| G13 | 765 | 504 | 14,071 | 834 | 8851 | 2161 | 1354 | 428 | 2550 | 6579 | 3213 | 36,094 |
| G14 | 174 | 241 | 6384 | 92 | 1303 | 904 | 1312 | 79 | 961 | 3460 | 1807 | 14,643 |
| G15 | 156 | 136 | 8996 | 173 | 1743 | 1157 | 2282 | 76 | 655 | 4046 | 1551 | 18,505 |
| G16 | 126 | 142 | 9240 | 1351 | 1877 | 2543 | 996 | 123 | 1436 | 2832 | 2691 | 19,773 |
| G17 | 361 | 364 | 9609 | 1744 | 2639 | 2626 | 601 | 350 | 2428 | 5313 | 1722 | 22,493 |
References
- United Nations. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2015; Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/2030agenda (accessed on 26 June 2025).
- Kücükgül, E.; Cerin, P.; Liu, Y. Enhancing the value of corporate sustainability: An approach for aligning multiple SDGs guides on reporting. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 333, 130005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocelík, V.; Kolk, A.; Ciulli, F. Multinational enterprises, Industry 4.0 and sustainability: A multidisciplinary review and research agenda. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 413, 137434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobakhloo, M.; Iranmanesh, M.; Foroughi, B.; Babaee Tirkolaee, E.B.; Asadi, S.; Amran, A. Industry 5.0 implications for inclusive sustainable manufacturing: An evidence-knowledge-based strategic roadmap. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 417, 138023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, M.; Haleem, A.; Singh, R.P.; Suman, R.; Gonzalez, E.S. Understanding the adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies in improving environmental sustainability. Sustain. Oper. Comput. 2022, 3, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Song, H.; Jara, A.J.; Bie, R. Internet of things and big data analytics for smart and connected communities. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 766–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, R.Y.; Xu, X.; Klotz, E.; Newman, S.T. Intelligent manufacturing in the context of Industry 4.0: A review. Engineering 2017, 3, 616–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vărzaru, A.A.; Bocean, C.G.; Gheorghe, M.; Simion, D.; Mangra, M.G.; Cioabă, A.A. Assessing the impact of digital technologies on the sustainable development goals within the European Union. Electronics 2024, 13, 4695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariyani, D.; Hariyani, P.; Mishra, S. Digital technologies for the Sustainable Development Goals. Green Technol. Sustain. 2025, 3, 100202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancuso, I.; Petruzzelli, A.M.; Panniello, U.; Vaia, G. The bright and dark sides of AI innovation for sustainable development: Understanding the paradoxical tension between value creation and value destruction. Technovation 2025, 143, 103232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedard-Vallee, A.; Chris, J.; Guillaume, R. Elsevier 2023 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Mapping; Elsevier Data Repository; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, R.; Leal Filho, W.; Martin, H.; Ray, S.; Das, D.; Nedungadi, P. Exploring sustainable development goal research trajectories in Small Island developing states. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashnitsky, Y.; Roberge, G.; Mu, J.; Kang, K.; Wang, W.; Vanderfeesten, M.; Rivest, M.; Chamezopoulos, S.; Jaworek, R.; Vignes, M.; et al. Evaluating approaches to identifying research supporting the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals. Quant. Sci. Stud. 2024, 5, 408–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoosain, M.S.; Paul, B.S.; Ramakrishna, S. The impact of 4IR digital technologies and circular thinking on the United Nations sustainable development goals. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Despeisse, M.; Johansson, B. Environmental sustainability of digitalization in manufacturing: A review. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio-Gómez, O.Y.; Ortiz, O.L.O.; von Feigenblatt, O.F. Building a sustainable future: The role of digital resources in achieving the sustainable development goals (SDGs). Rev. Lusófona Educ. 2024, 61, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dionisio, M.; de Souza Junior, S.J.; Paula, F.; Pellanda, P.C. The role of digital social innovations to address SDGs: A systematic review. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 26, 5709–5734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, S.; Song, Y. Role of digital technology in achieving the sustainable development goals: Focus on the efforts of the international community. J. Int. Dev. Coop. 2021, 16, 31–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinuesa, R.; Azizpour, H.; Leite, I.; Balaam, M.; Dignum, V.; Domisch, S.; Felländer, A.; Langhans, S.D.; Tegmark, M.; Fuso Nerini, F.F. The role of artificial intelligence in achieving the Sustainable Development Goals. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, I.S.; Ahmad, M.O.; Majava, J. Industry 4.0 and sustainable development: A systematic mapping of triple bottom line, circular economy, and sustainable business models perspectives. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 297, 126655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhammadi, A.; Semeraro, C.; Obaideen, K.; Alsyouf, I. Industry 4.0 technologies and sustainable development goals (SDGs): Covered publications and ranking. In ISIEA 2023. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems; Borgianni, Y., Matt, D.T., Molinaro, M., Orzes, G., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; Volume 745, pp. 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhammadi, A.; Alsyouf, I.; Semeraro, C.; Obaideen, K. The role of industry 4.0 in advancing sustainability development: A focus review in the United Arab Emirates. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2024, 18, 100708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.S.; Ahmad, M.O.; Majava, J. Industry 4.0 innovations and their implications: An evaluation from a sustainable development perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 405, 137006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzi, S.; Caputo, A.; Corvino, A.; Venturelli, A. Management research and the UN sustainable development goals (SDGs): A bibliometric investigation and systematic review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 276, 124033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, I.; Riccotta, R.; Montini, P.; Stefani, E.; de Souza Goes, R.; Gaspar, M.A.; Martins, F.S.; Fernandes, A.A.; Machado, C.; Loçano, R.; et al. The degree of contribution of digital transformation technology on company sustainability areas. Sustainability 2022, 14, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, N.; Tripathi, S.; Brunner, M.; Jodlbauer, H. The contribution of data-driven technologies in achieving the sustainable development goals. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feroz, A.K.; Zo, H.; Chiravuri, A. Digital transformation and environmental sustainability: A review and research agenda. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Shevchenko, T.; Yannou, B.; Ranjbari, M.; Shams Esfandabadi, Z.S.; Saidani, M.; Bouillass, G.; Bliumska-Danko, K.; Li, G. Exploring how digital technologies enable a circular economy of products. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariyani, D.; Hariyani, P.; Mishra, S.; Kumar Sharma, M.K. Leveraging digital technologies for advancing circular economy practices and enhancing life cycle analysis: A systematic literature review. Waste Manag. Bull. 2024, 2, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivest, M.; Kashnitsky, Y.; Bédard-Vallée, A.; Campbell, D.; Khayat, P.; Labrosse, I.; Pinheiro, H.; Provençal, S.; Roberge, G.; James, C. Improving the Scopus and Aurora Queries to Identify Research That Supports the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) 2021; Elsevier Data Repository; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; Volume 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsevier. SDG Research Mapping Initiative. 2023. Available online: https://www.elsevier.com/about/sustainability/sdg-research-mapping-initiative (accessed on 26 June 2025).
- Pereira, A.C.; Romero, F. A review of the meanings and the implications of the Industry 4.0 concept. Procedia Manuf. 2017, 13, 1206–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüßmann, M.; Lorenz, M.; Gerbert, P.; Waldner, M.; Engel, P.; Harnisch, M.; Justus, J. Industry 4.0: The Future of Productivity and Growth in Manufacturing Industries; Boston Consulting Group: Boston, MA, USA, 2015; Available online: https://web-assets.bcg.com/img-src/Industry_40_Future_of_Productivity_April_2015_tcm9-61694.pdf (accessed on 26 June 2025).
- Emeritus. Top 12 Technologies Used for Digital Transformation; Emeritus: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2023; Available online: https://emeritus.org/in/learn/digital-transformation-technologies/ (accessed on 19 June 2024).
- PwC. The New Essential Eight Technologies; PwC: New York, NY, USA, 2023; Available online: https://www.pwc.com/us/en/tech-effect/emerging-tech/essential-eight-technologies.html (accessed on 19 June 2024).
- Bong, J.; Yu, M.; Ga, J.; Kwak, M. Analyzing the contribution of digital technologies to sustainable development using Scopus SDG research mapping. In Proceedings of the Spring Joint Conference of the Korean Institute of Industrial Engineers, Yeosu, Republic of Korea, 2–4 May 2024; Available online: https://www.dbpia.co.kr/journal/articleDetail?nodeId=NODE11800687 (accessed on 4 May 2024).
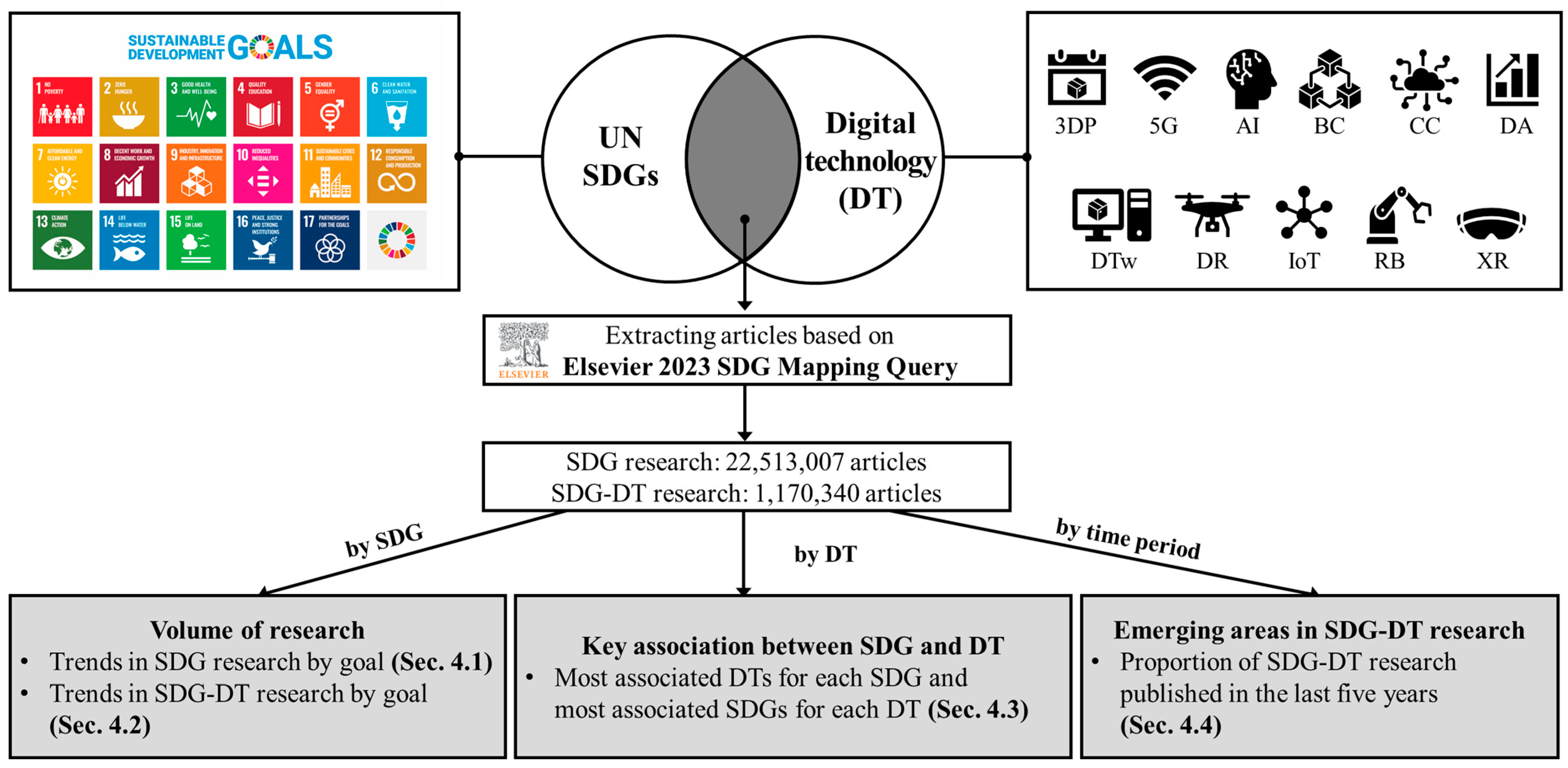




| SDGs | Details | |
|---|---|---|
| Goal 1 (G1) | No Poverty | End poverty in all its forms everywhere. |
| Goal 2 (G2) | Zero Hunger | End hunger, achieve food security and improved nutrition, and promote sustainable agriculture. |
| Goal 3 (G3) | Good Health and Well-Being | Ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages. |
| Goal 4 (G4) | Quality Education | Ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all. |
| Goal 5 (G5) | Gender Equality | Achieve gender equality and empower all women and girls. |
| Goal 6 (G6) | Clean Water and Sanitation | Ensure availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all. |
| Goal 7 (G7) | Affordable and Clean Energy | Ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable, and modern energy for all. |
| Goal 8 (G8) | Decent Work and Economic Growth | Promote sustained, inclusive, and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment, and decent work for all. |
| Goal 9 (G9) | Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure | Build resilient infrastructure, promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization, and foster innovation. |
| Goal 10 G10) | Reduced Inequalities | Reduce inequality within and among countries. |
| Goal 11 (G11) | Sustainable Cities and Communities | Make cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient, and sustainable. |
| Goal 12 (G12) | Responsible Consumption and Production | Ensure sustainable consumption and production patterns. |
| Goal 13 (G13) | Climate Action | Take urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts. |
| Goal 14 (G14) | Life Below Water | Conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas, and marine resources for sustainable development. |
| Goal 15 (G15) | Life on Land | Protect, restore, and promote sustainable use of terrestrial ecosystems, sustainably manage forests, combat desertification, and halt and reverse land degradation and biodiversity loss. |
| Goal 16 (G16) | Peace, Justice, and Strong Institutions | Promote peaceful and inclusive societies for sustainable development, provide access to justice for all, and build effective, accountable, and inclusive institutions at all levels. |
| Goal 17 (G17) | Partnerships for the Goals | Strengthen the means of implementation and revitalize the Global Partnership for Sustainable Development. |
| Study | Main Interest and Scope of the Study | Evidence | Representative DTs Mentioned in the Paper | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AI | XR | IoT | DA | BC | DTw | CC | RB | 5G | 3DP | |||
| Hoosain et al. (2020) [14] | DTs for the circular economy and SDGs | Case study | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||
| Chen et al. (2020) [15] | DTs for sustainability of manufacturing | Case study | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||
| Aparicio-Gómez et al. (2024) [16] | DTs for the SDGs | Case study | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||
| Dionisio et al. (2024) [17] | DTs for social innovation for SDGs | Case study | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |
| Yoo and Song. (2021) [18] | DTs in international cooperation for SDGs | Case study | ● | ● | ● | |||||||
| Vinuesa et al. (2020) [19] | Artificial intelligence (AI) for SDGs | Case study | ● | |||||||||
| Khan et al. (2021) [20] | Industry 4.0 technologies for SDGs | 81 articles | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||
| Alhammadi et al. (2023) [21] | Industry 4.0 technologies for SDGs | 163 articles | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||
| Alhammadi et al. (2024) [22] | Industry 4.0 technology for SDGs in the United Arab Emirates | 138 articles | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |
| Khan et al. (2023) [23] | Industry 4.0 innovations and their implications in sustainable development perspective | 58 articles | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||
| Pizzi et al. (2020) [24] | Management research for SDGs | 266 articles | ● | ● | ||||||||
| Costa et al. (2022) [25] | Digital transformation for company sustainability | 70 articles | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● |
| Bachmann et al. (2022) [26] | Data-driven technologies for SDGs | 193 articles | ● | ● | ||||||||
| Feroz et al. (2021) [27] | Digital transformations for environmental sustainability | 106 articles | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||
| Hariyani et al. (2025) [9] | DTs for SDGs | 473 articles | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||
| Javaid et al. (2022) [5] | Industry 4.0 for sustainable manufacturing | 218 articles | ● | ● | ● | |||||||
| Han et al. (2023) [28] | DTs for circular economy | 79 articles | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||
| Hariyani et al. (2024) [29] | DTs for circular economy and life cycle analysis | 153 articles | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||
| Digital Technology | Synonyms and Related Terms Applied in This Study | Precision (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3D Printing (3DP) | 3D-printing, Three-Dimensional Printing, Additive Manufacturing, Additive Layer Manufacturing, 3D Manufacturing | 96% |
| 2 | 5th-Generation Mobile Network (5G) | 5G, Next-Generation Networks, 5G Communication Technology | 84% |
| 3 | Artificial Intelligence (AI) | Machine Learning, Deep Learning, Neural Networks | 94% |
| 4 | Blockchain (BC) | Block-chain, Digital Distributed Ledger, Block Technology | 90% |
| 5 | Cloud Computing (CC) | Cloud-computing, Cloud Computing, Cloud Technology, Online Computing, Remote Servers, Digital Storage, Distributed Computer Systems | 71% |
| 6 | Data Analytics (DA) | Data Science, Big Data Analytics, Data Mining, Predictive Analytics | 88% |
| 7 | Digital Twin (DTw) | Digital Twins | 94% |
| 8 | Drones (DR) | Drone, UAV, Unmanned Aerial Vehicles, Unmanned Aerial Systems, Autonomous Aircraft, Drone Technology | 100% |
| 9 | Internet of Things (IoT) | Internet of thing, IoT, Smart Devices, Connected Devices, Machine-to-Machine (M2M) Communication | 92% |
| 10 | Robotics (RB) | Robot, Robots, Robot Programming, Automation, Robot Technology, Robotic Engineering, Autonomous Systems | 86% |
| 11 | Extended Reality (XR) | Mixed Reality, Virtual Reality, Augmented Reality, MR, VR, AR | 71% |
| Query for 3D Printing and Goal 1 (No Poverty) |
|---|
| (TITLE-ABS-KEY(“3D Printing”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“3D-printing”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Three Dimensional Printing”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Additive Manufacturing”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Additive Layer Manufacturing”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(“3D Manufacturing”)) AND ((((TITLE-ABS(“unesco”) AND TITLE-ABS(“poverty”) AND TITLE-ABS(“program”)) OR(AUTHKEY(“unesco”) AND AUTHKEY(“poverty”) AND AUTHKEY(“program”)) OR(TITLE-ABS(“poverty*-reducing* polic*”) OR TITLE-ABS(“povertyreducing* polic*”)) OR(AUTHKEY(“poverty*-reducing* polic*”) OR…the rest omitted |
| SDG | Top 1 | Top 2 | Top 3 | Top 4 | Top 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | AI | RB | DA | XR | CC |
| G2 | AI | RB | DR | IoT | CC |
| G3 | AI | XR | RB | DA | - |
| G4 | AI | XR | RB | DA | CC |
| G5 | AI | XR | RB | DA | IoT |
| G6 | AI | RB | CC | IoT | XR |
| G7 | AI | RB | CC | IoT | XR |
| G8 | AI | RB | IoT | DA | CC |
| G9 | RB | 3DP | AI | IoT | CC |
| G10 | AI | RB | XR | DA | BC |
| G11 | AI | IoT | RB | CC | DA |
| G12 | AI | RB | IoT | CC | XR |
| G13 | AI | CC | RB | XR | IoT |
| G14 | AI | RB | XR | DR | CC |
| G15 | AI | RB | DR | CC | XR |
| G16 | AI | RB | XR | DA | CC |
| G17 | AI | RB | CC | DA | IoT |
| DT | Top 1 | Top 2 | Top 3 | Top 4 | Top 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3DP | G9 | G3 | - | - | - |
| 5G | G7 | G9 | G3 | G11 | - |
| AI | G3 | G7 | G9 | G11 | - |
| BC | G9 | G11 | G7 | G8 | G3 |
| CC | G7 | G9 | G11 | G13 | G3 |
| DA | G3 | G9 | G11 | G7 | G4 |
| DR | G11 | G7 | G2 | G3 | G9 |
| DTw | G9 | G7 | G11 | G3 | - |
| IoT | G9 | G7 | G11 | G3 | - |
| RB | G9 | G3 | G11 | G2 | - |
| XR | G3 | G9 | G4 | G7 | G11 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ga, J.; Bong, J.; Yu, M.; Kwak, M. Digital Enablers of Sustainability: Insights from Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Research Mapping. Sustainability 2025, 17, 7031. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17157031
Ga J, Bong J, Yu M, Kwak M. Digital Enablers of Sustainability: Insights from Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Research Mapping. Sustainability. 2025; 17(15):7031. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17157031
Chicago/Turabian StyleGa, Jeongmi, Jaewoo Bong, Myeongjun Yu, and Minjung Kwak. 2025. "Digital Enablers of Sustainability: Insights from Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Research Mapping" Sustainability 17, no. 15: 7031. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17157031
APA StyleGa, J., Bong, J., Yu, M., & Kwak, M. (2025). Digital Enablers of Sustainability: Insights from Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Research Mapping. Sustainability, 17(15), 7031. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17157031






