Thinking Green: A Place Lab Approach to Citizen Engagement and Indicators for Nature-Based Solutions in a Case Study from Katowice
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Eco-sensitisation, which refers to the process of raising awareness, promoting an understanding of ecological issues, and fostering environmentally responsible behaviour;
- Social benefits of NbSs, including improved health and well-being, enhanced quality of life, and increased social interaction ands community engagement;
- Gender-based NbSs: NbSs can have significant implications for gender by promoting equal access to and participation in decision-making processes related to green spaces, ensuring women’s safety in urban parks, and providing economic opportunities through green jobs;
- NbS economic opportunities, as implementing NbSs extends beyond urban greening; they also have the potential to generate economic opportunities by creating jobs and fostering economic growth;
- Enabling NbS-supporting political capital: this refers to the process of creating favourable political conditions and securing resources to promote the implementation and advancement of NbSs.
- Identify the reasons why people are not convinced to uptake adaptation measures and the factors that can be considered obstacles to adaptation;
- Develop indicator(s) for future studies to evaluate how citizen engagement (CE) promotes the effective uptake and integration of nature-based solutions (NbSs) within broader climate-change-mitigation strategies.
- By developing such tools, this study aims to provide a valuable framework for future assessments of the effectiveness of citizen engagement in promoting climate adaptation and NbS implementation.
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
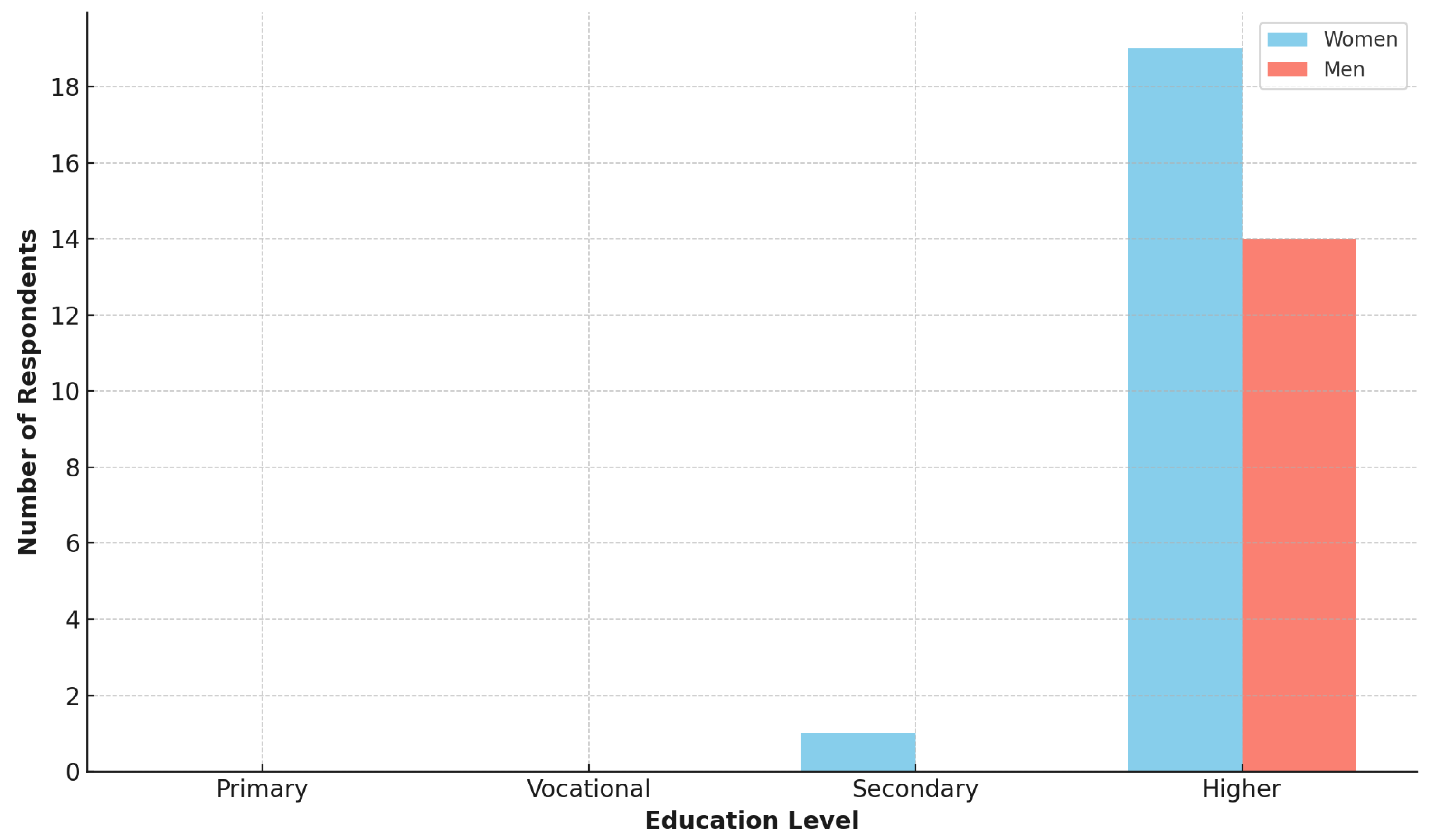
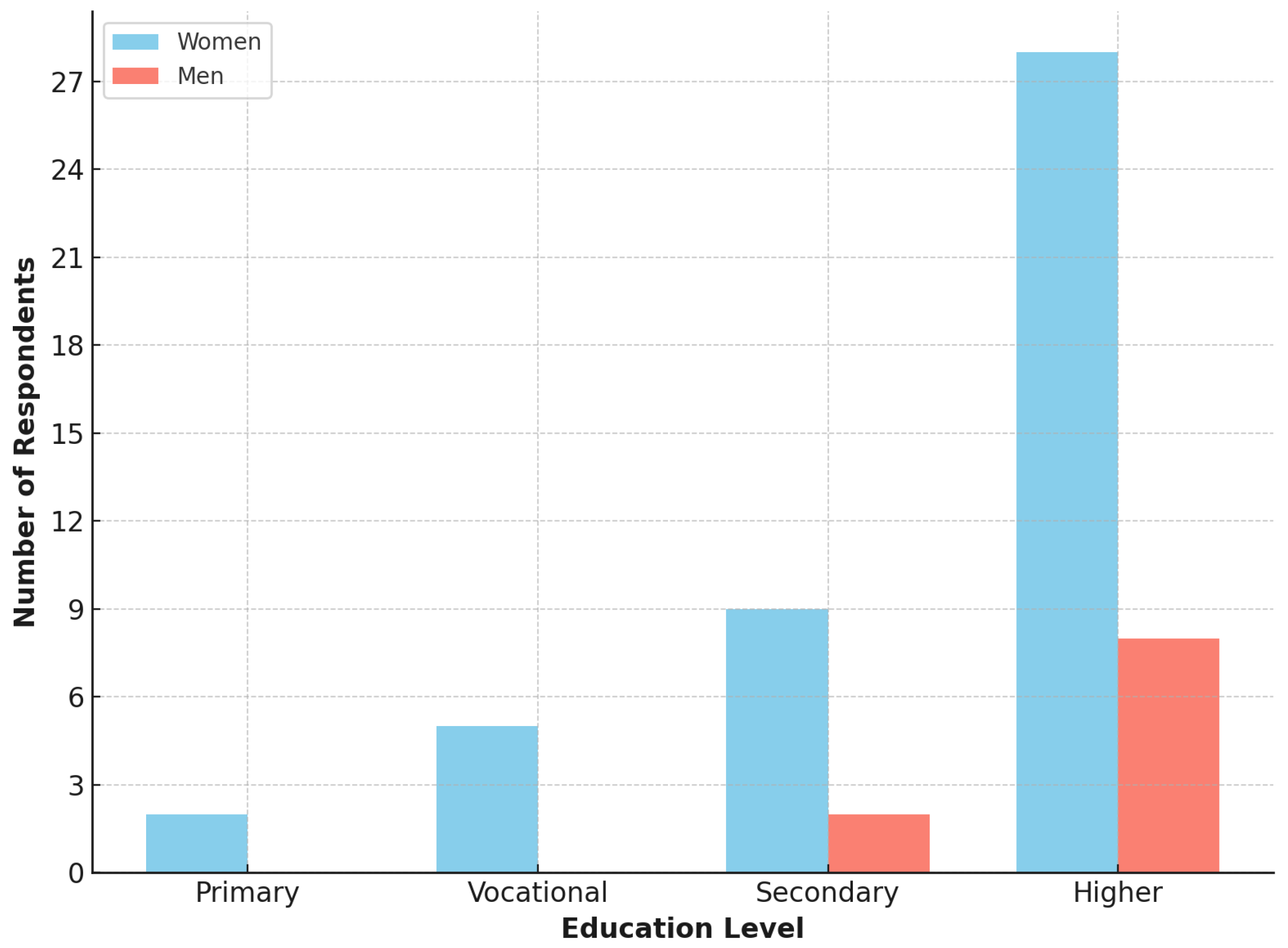
3.1. General Information About Participants
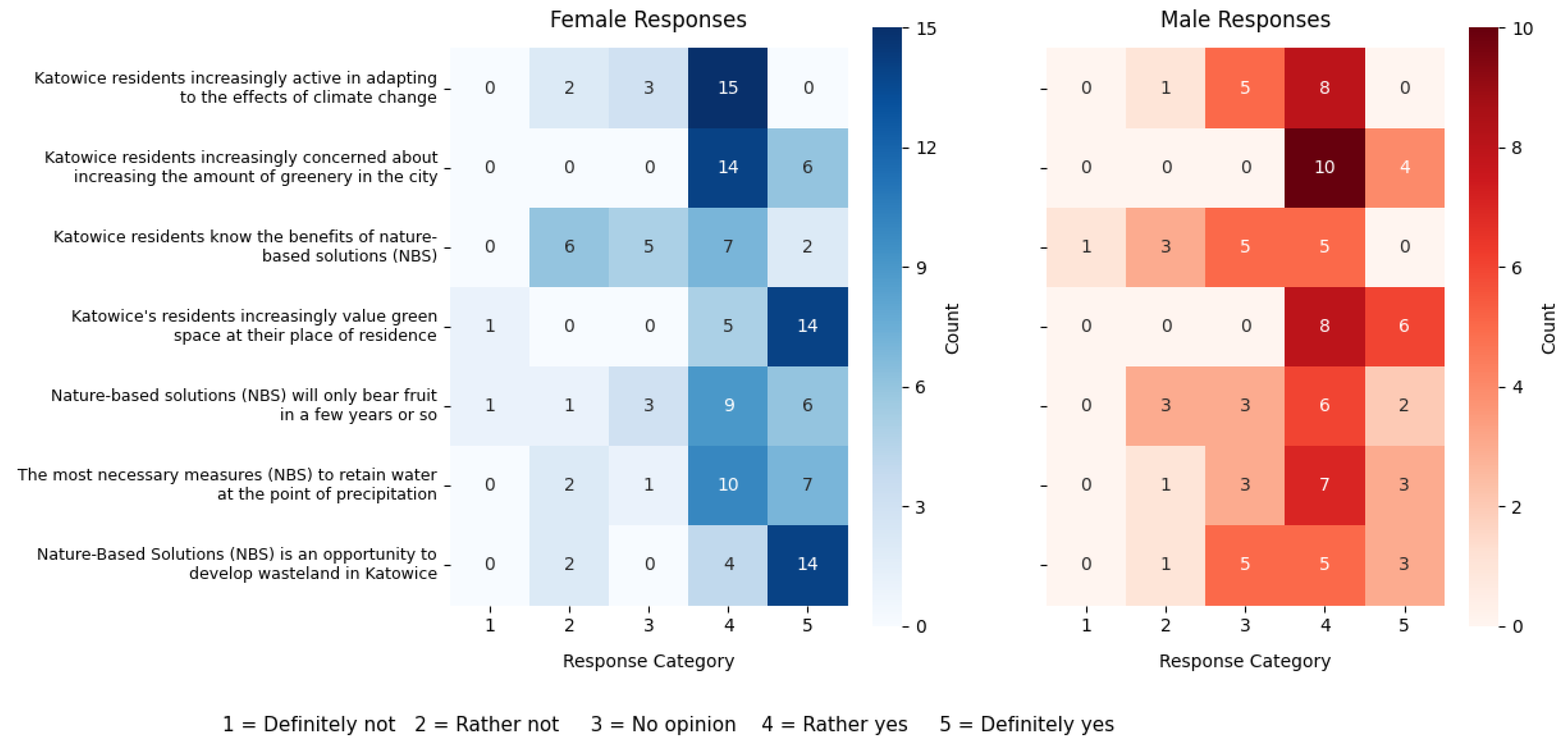
3.2. The Results of the First Survey
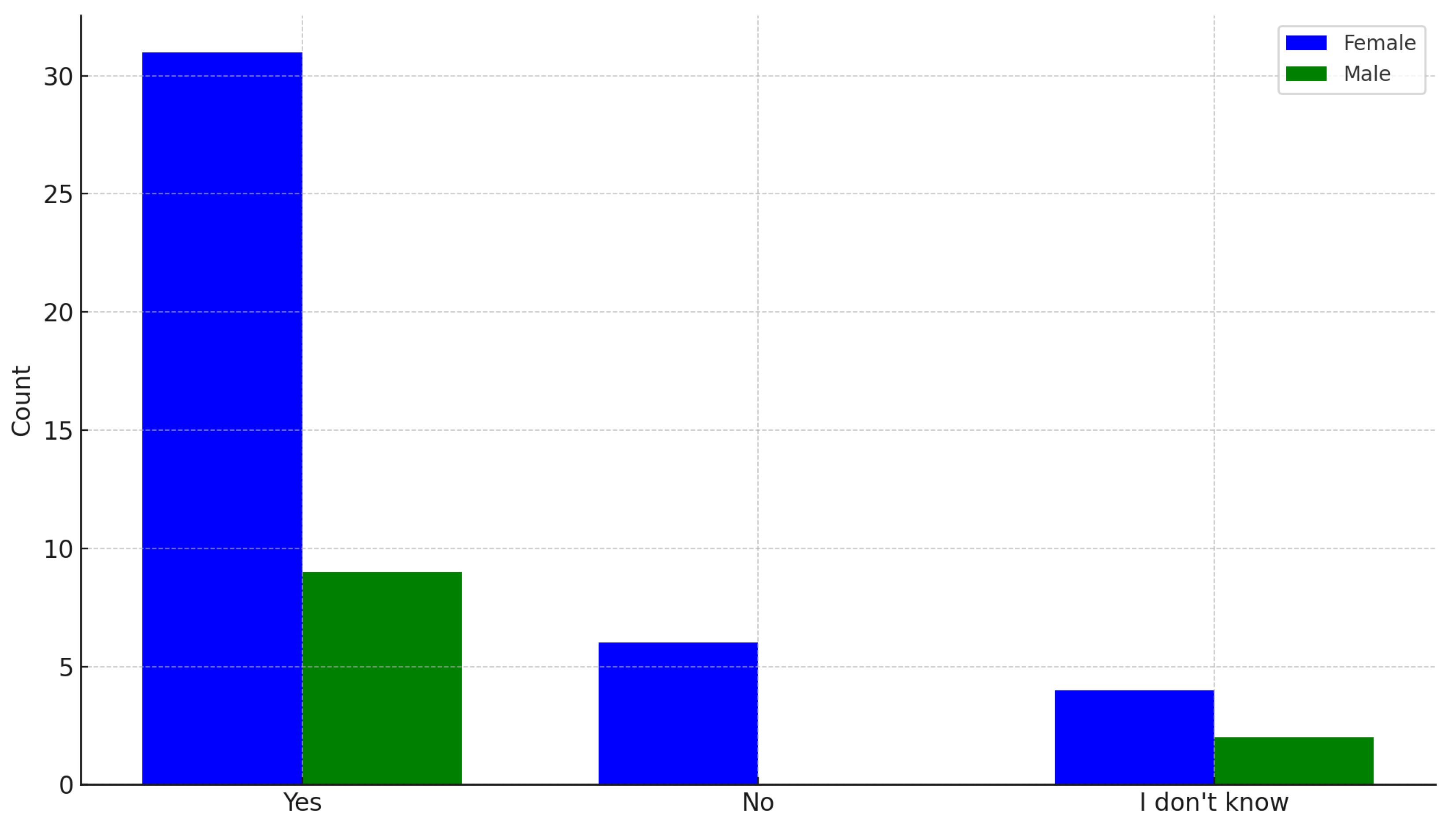
3.2.1. Opinions on the Implementation of the City Adaptation Plan
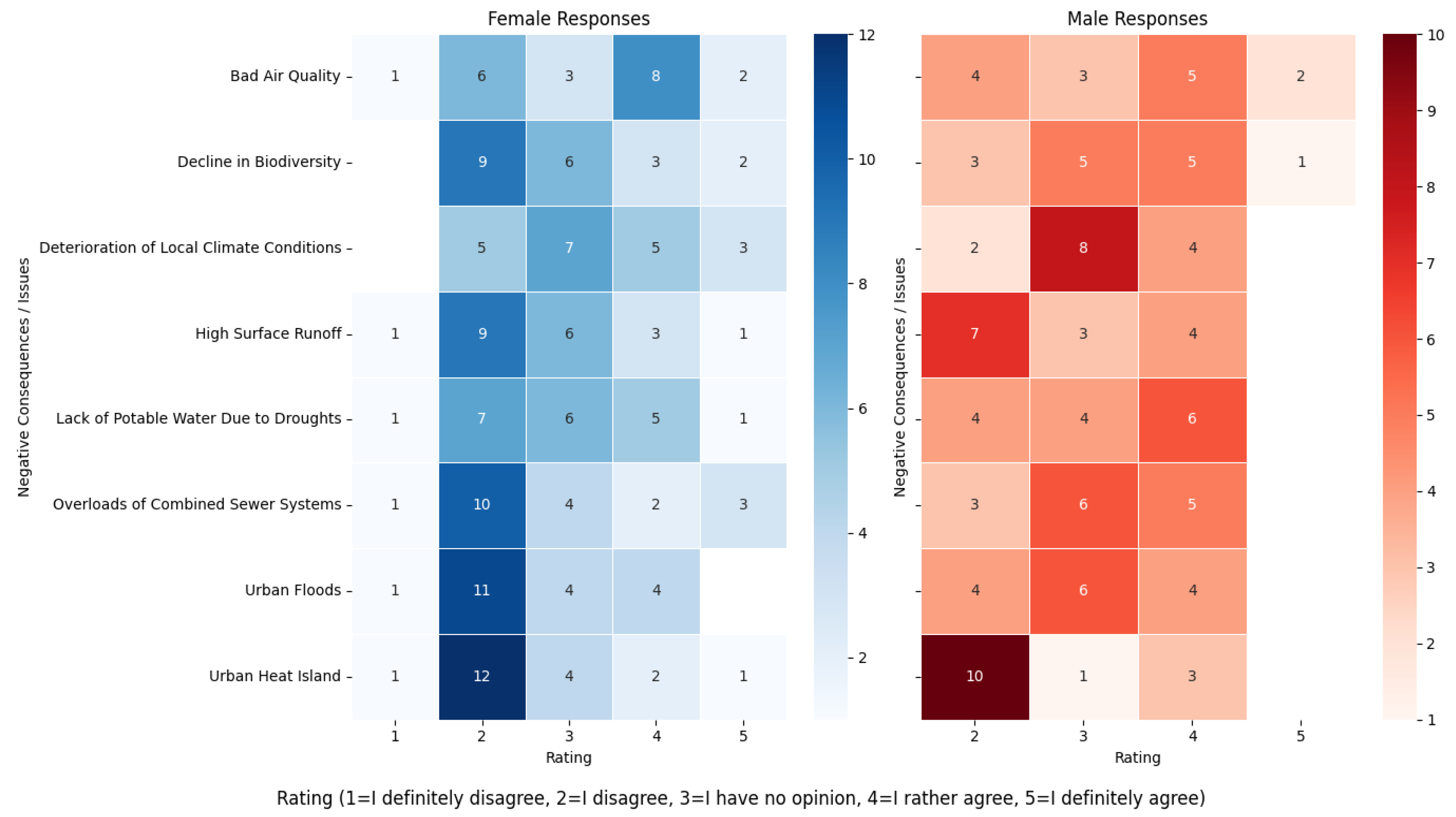
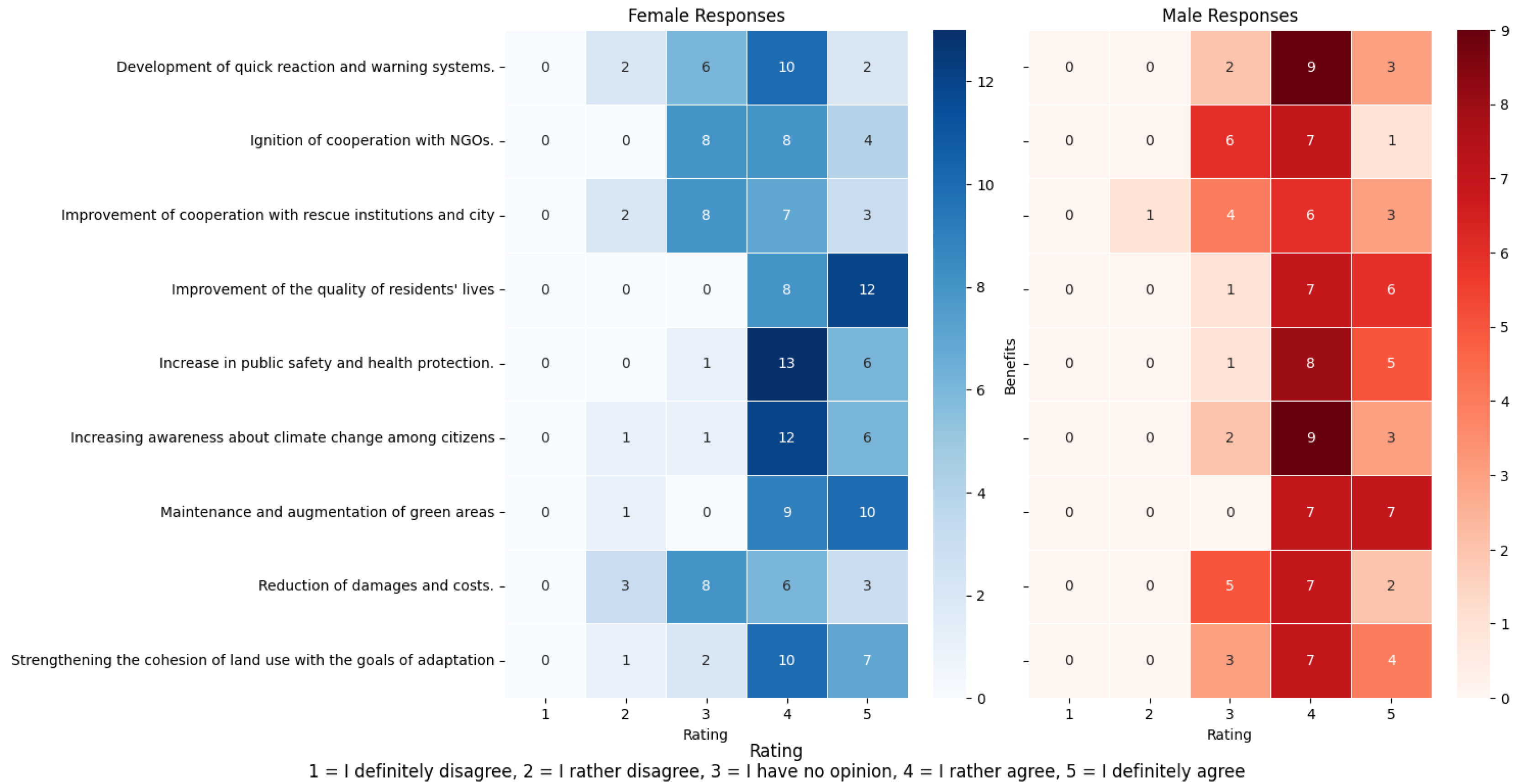
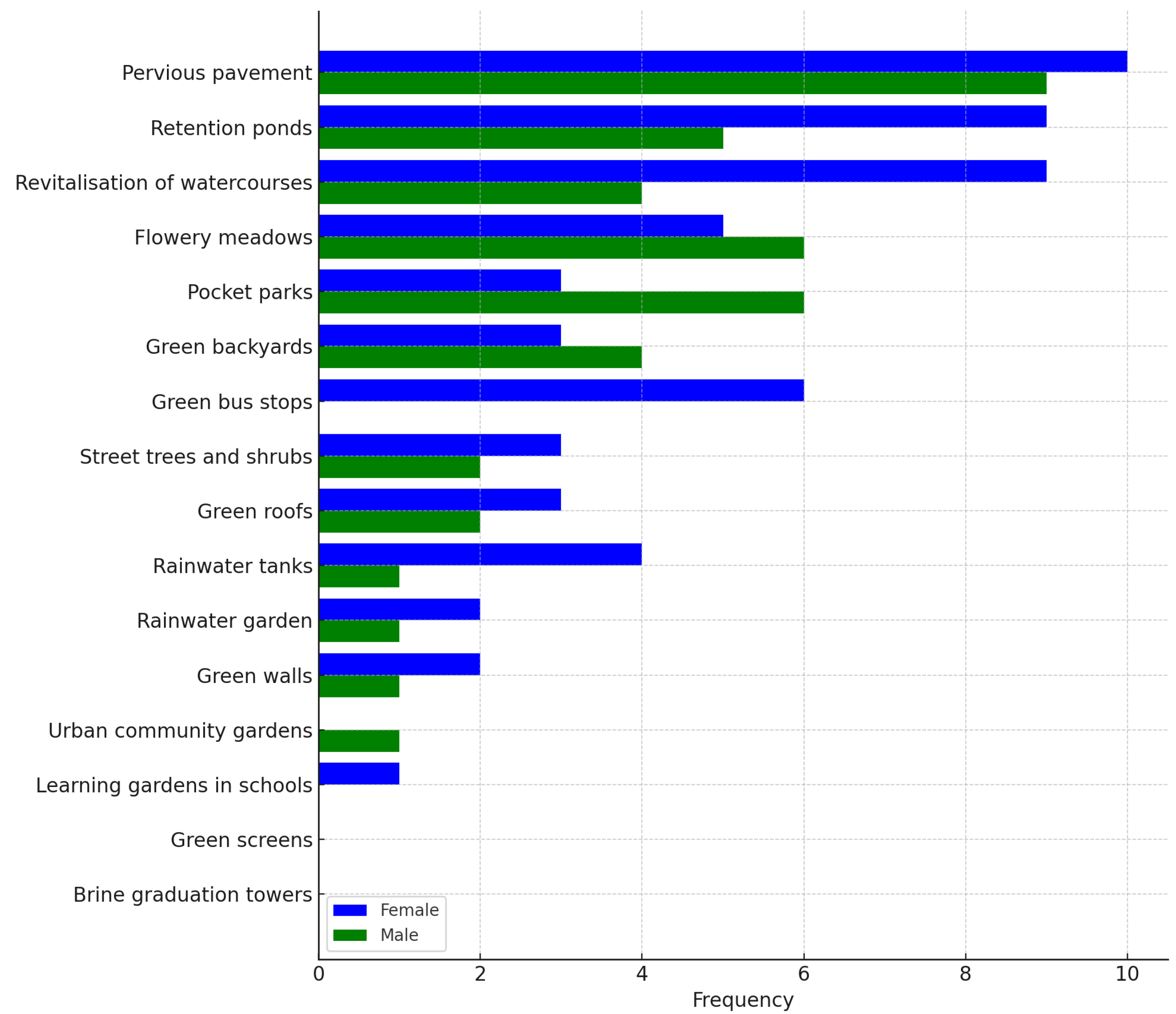
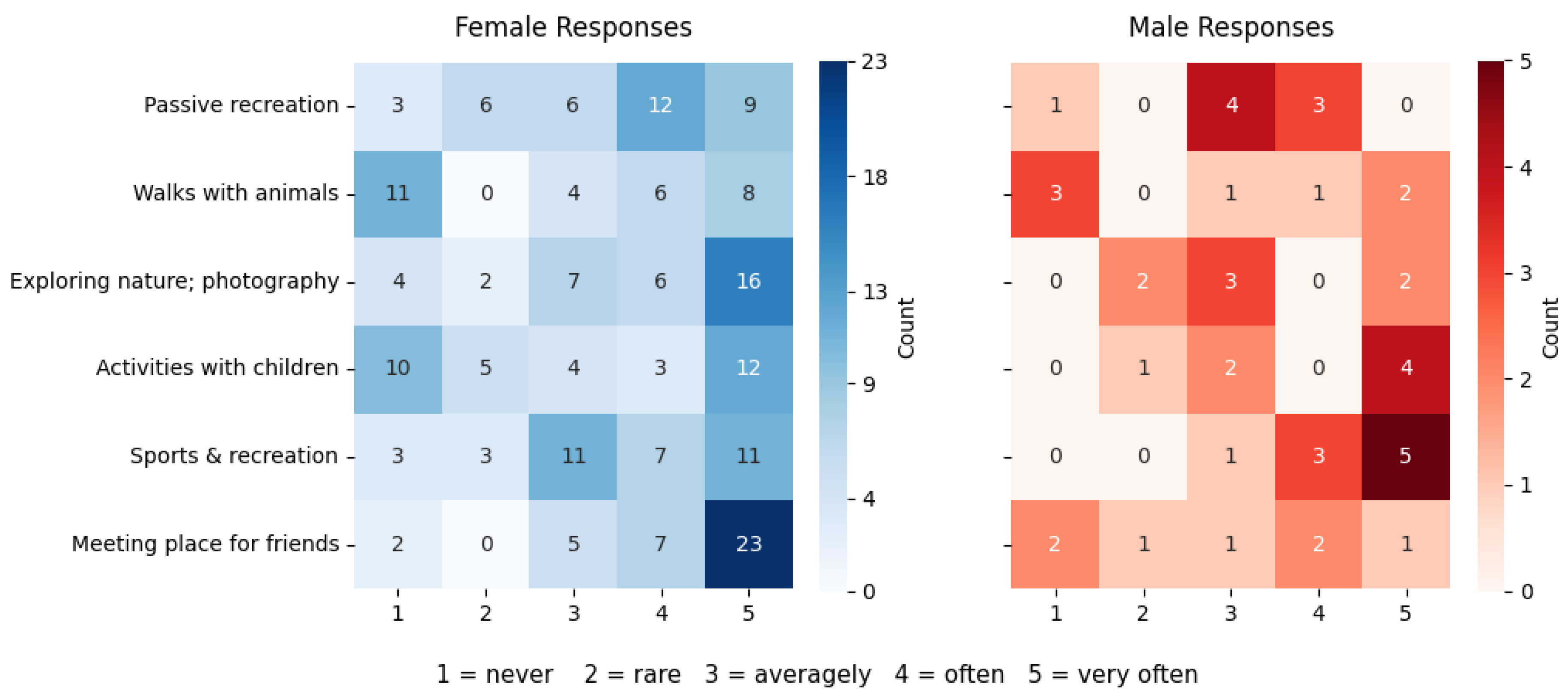
3.2.2. Knowledge and Engagement of Residents in the Dissemination of Nature-Based Solutions (NbSs)
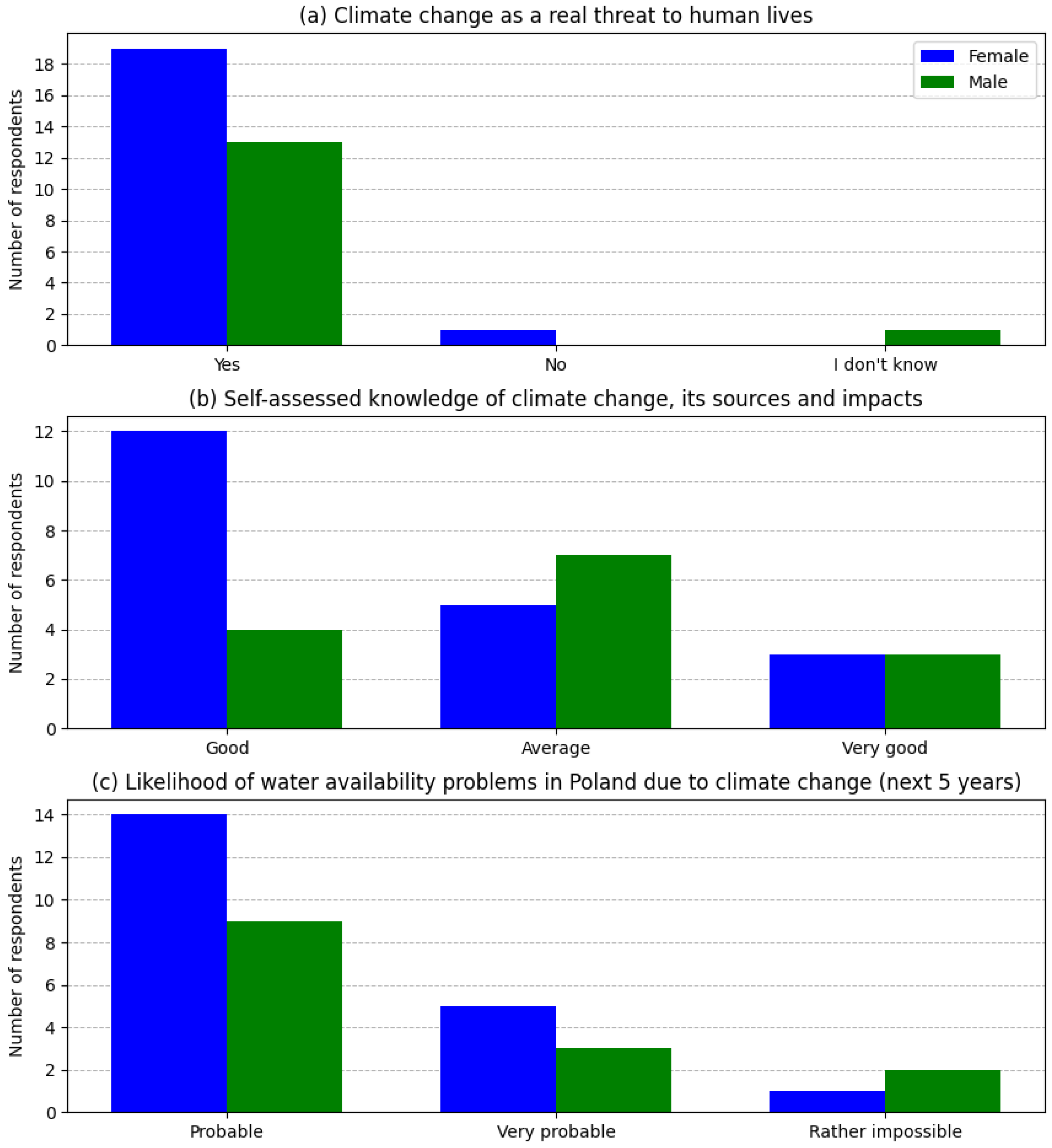
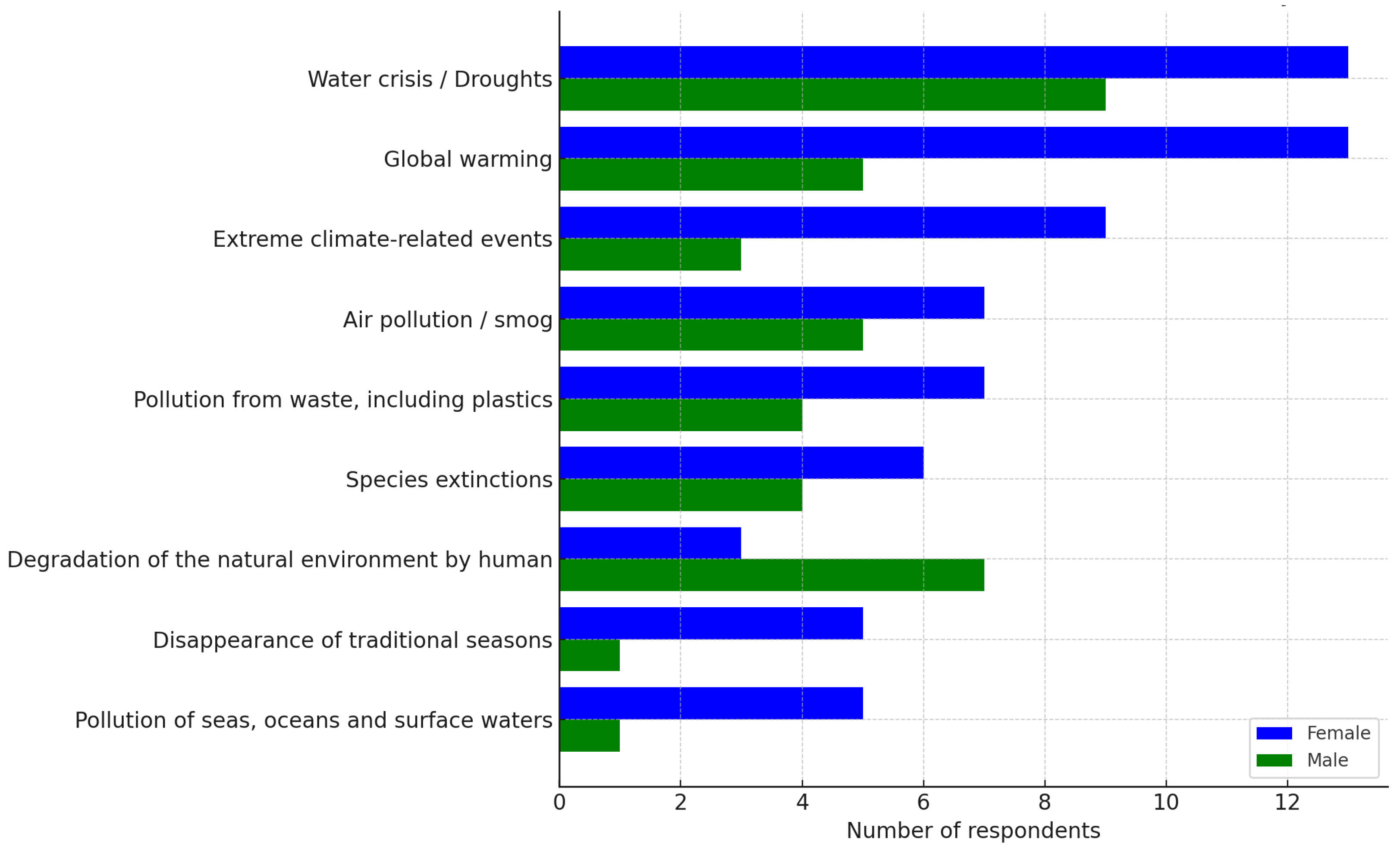
3.2.3. Civic Awareness of Climate Change and Environmental Conservation
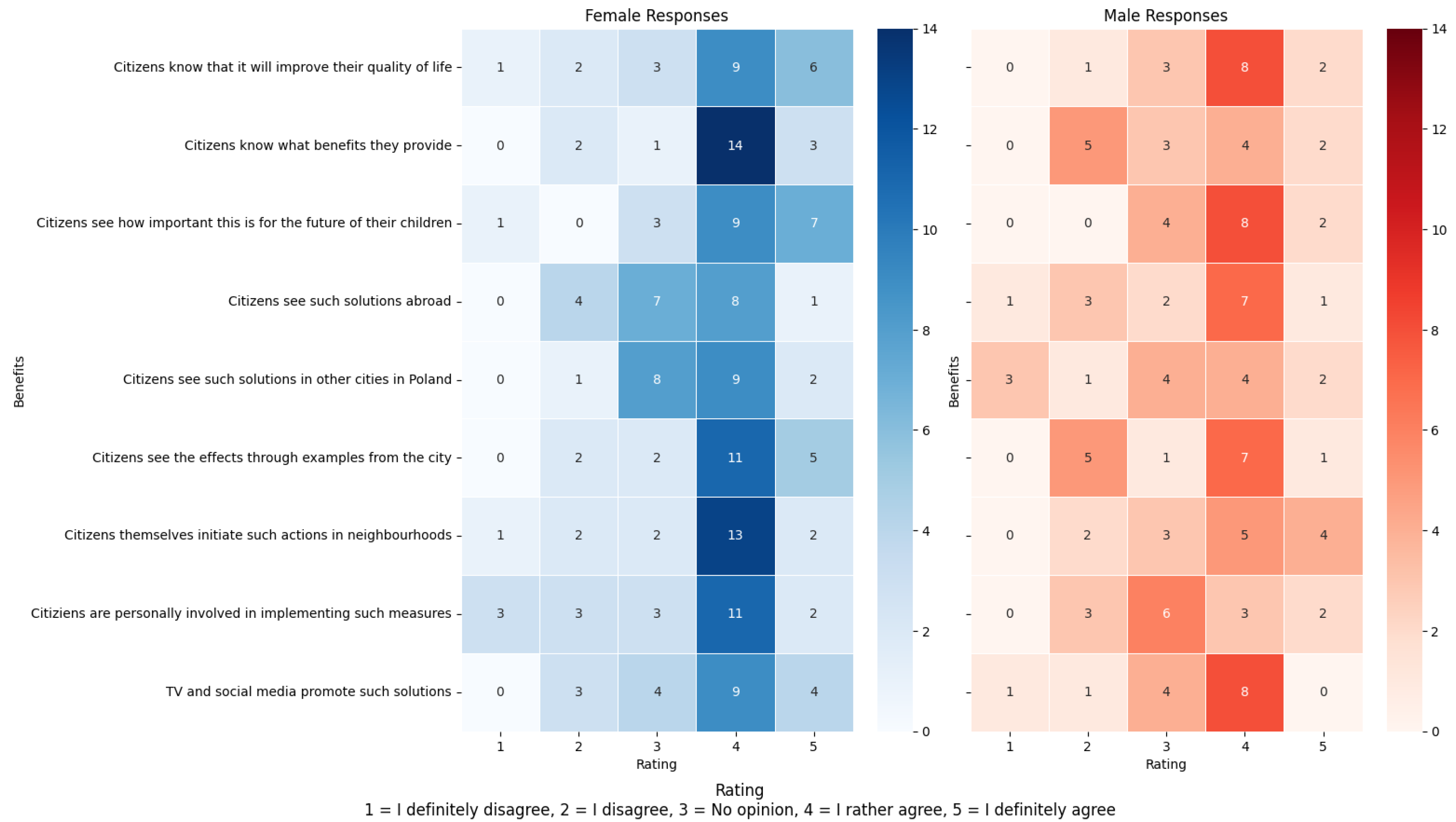
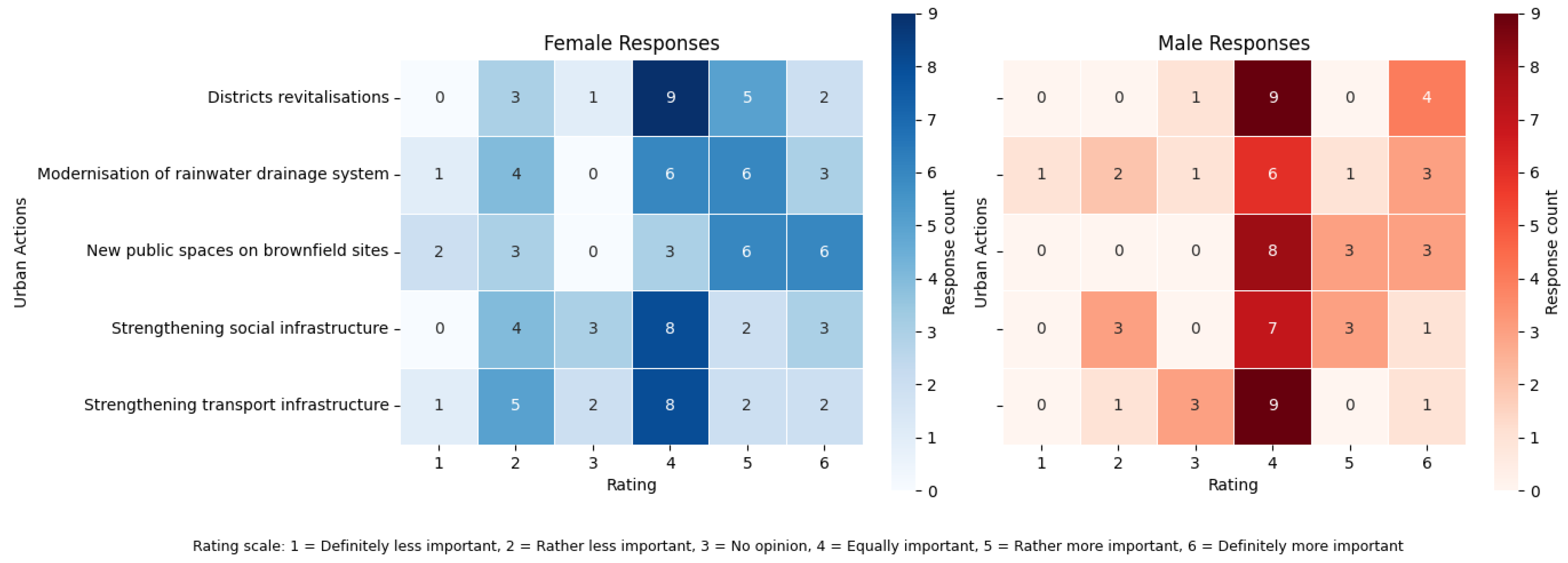
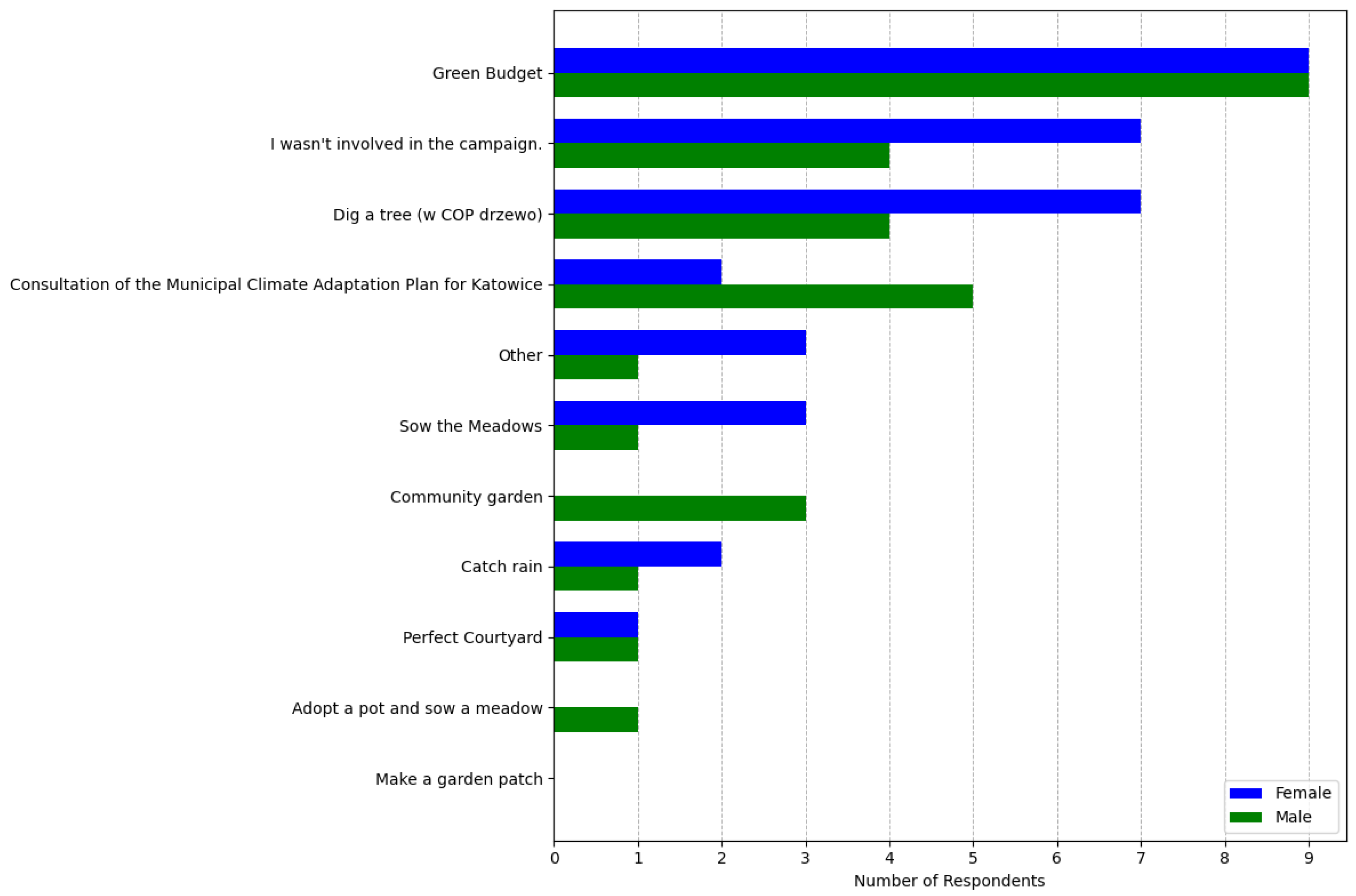
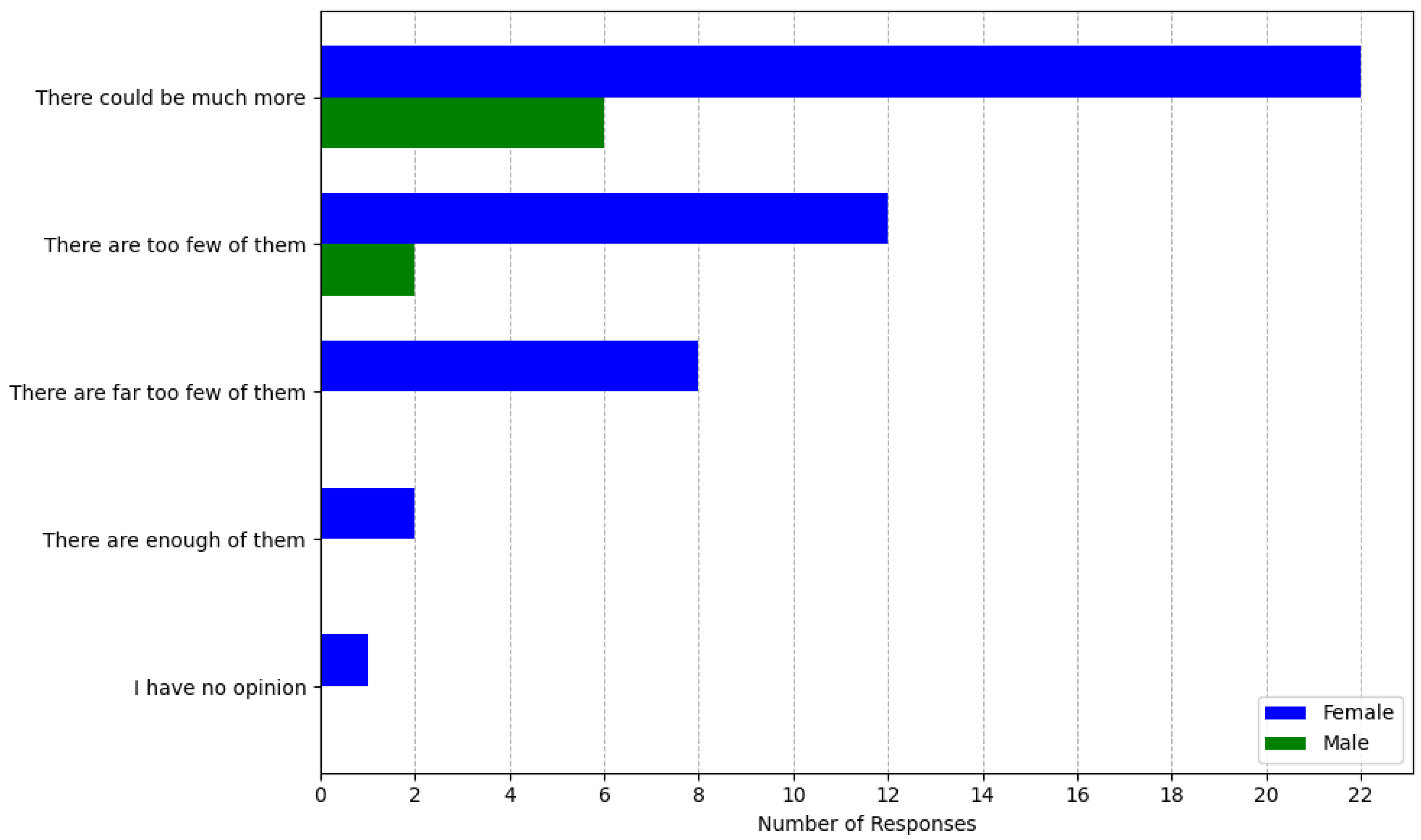
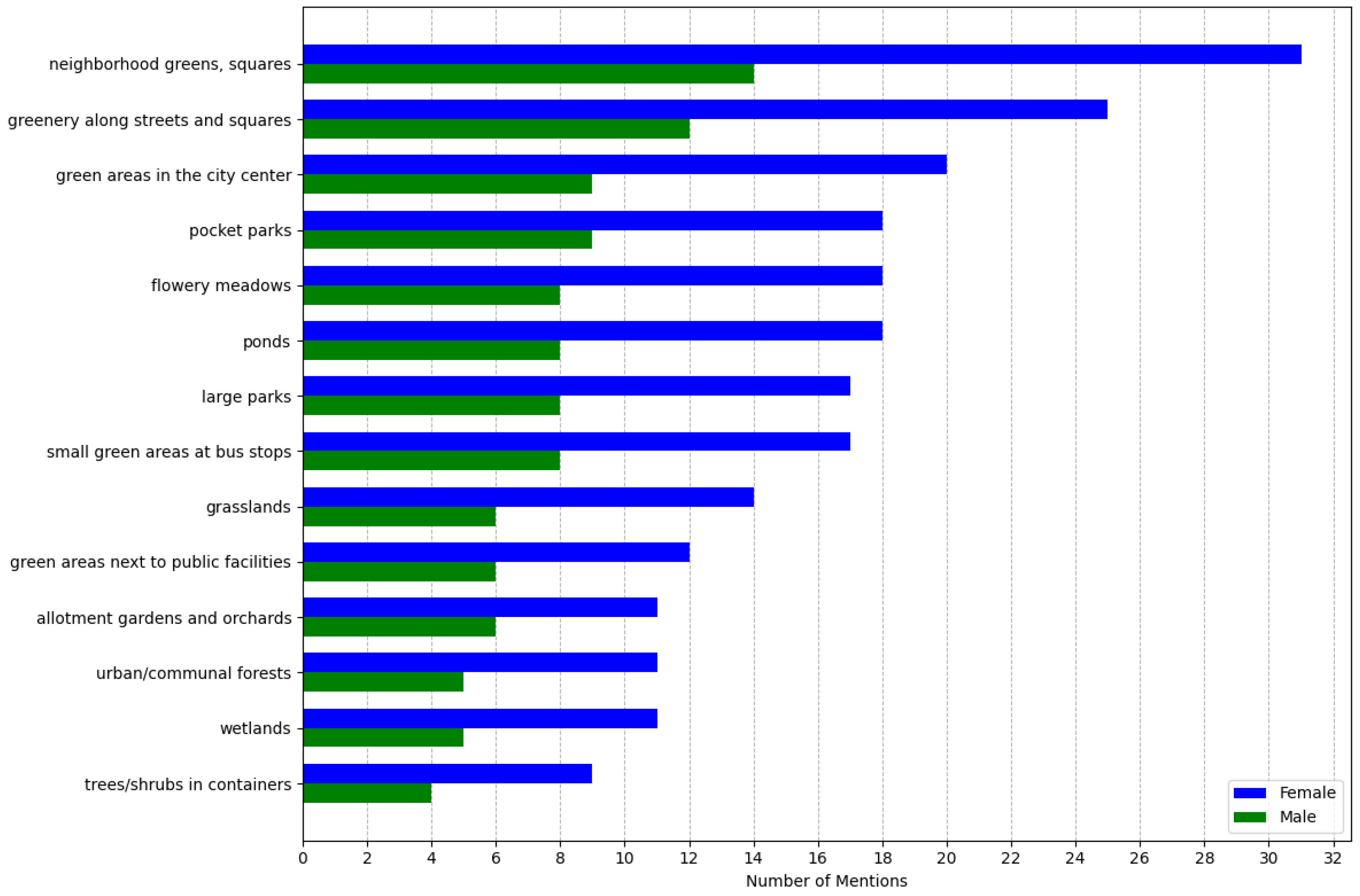
3.3. The Results of the Second Survey
Attitude and Responsibility Towards Green Spaces
3.4. The Illustrative Application of Indicators
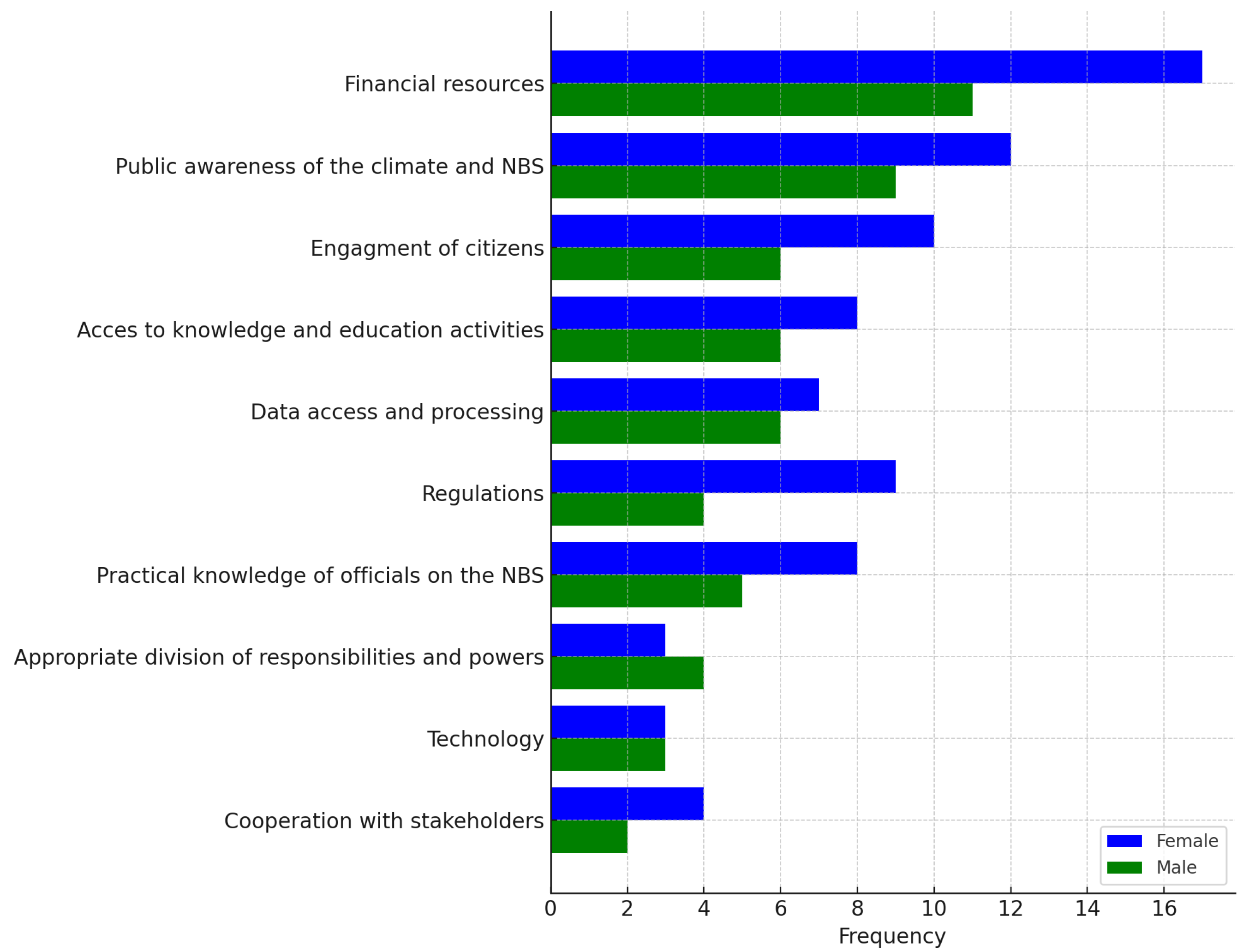
4. Discussion
- Limited public knowledge and scepticism: While many respondents recognise climate change and the need for adaptation measures, they doubt whether the wider public in Katowice has the same level of understanding. This perceived knowledge gap breeds scepticism, makes it harder for planners to secure community buy-in, and can stall participation in co-creation workshops [155,156,157];
- Competing priorities and time constraints limit participation: Younger residents, particularly those who juggle multiple jobs and family duties, often lack the time or energy to attend engagement events. To widen involvement, planners could design some activities for retirees, who usually have more flexible schedules, or organise family friendly events that allow parents to participate without sacrificing time with their children [160,161,162];
- Perceived inequity or exclusion: NbS projects can be seen as benefiting only certain neighbourhoods or demographic groups. If residents believe that new green spaces will not address their needs, whether because they live in a less affluent district or speak a different language, they may opt out of participating altogether [162,163,164];
- Unclear roles and responsibilities: Successful nature-based solutions (NbSs) require ongoing maintenance. If it is not clearly defined who will be responsible for these tasks (e.g., city agencies, community volunteers, or a hybrid arrangement), residents may hesitate to invest their time in the planning process. They may fear that the initiative will eventually be neglected or become overgrown. A clean and aesthetically pleasing project is crucial for community acceptance and uptake [167,168];
- Insufficient resources for engagement: Effective social engagement requires adequate funding for facilitators, translators, materials, and, in some cases, modest stipends to compensate participants for lost wages. Moreover, nature-based solutions also demand resources such as land, vegetation, and the involvement of experts who are willing to share their knowledge with participants [110,169,170];
- Inadequate feedback and follow-through: When authorities hold a few workshops but then fail to show how community input influenced the final designs, citizens become sceptical. The perception that “engagement is a checkbox” undermines participation in future projects and erodes social capital [173,174];
- Legal and institutional constraints: Sometimes regulations make it difficult to transfer responsibility for green-space stewardship to community groups (e.g., liability concerns, permitting hurdles). If co-management agreements are legally cumbersome, agencies may avoid offering genuine co-creation or co-management roles, which limits social engagement [175,176].
5. Conclusions
- Residents are generally aware of the negative effects of climate change; however, they remain sceptical about the city’s and authorities’ preparedness to address these impacts. Notably, opinions vary according to gender and more detailed responses, suggesting that scepticism and lack of trust constitute key obstacles;
- The majority of respondents acknowledge the positive role of urban greenery and nature-based solutions and express a sense of responsibility for green spaces. Nevertheless, they demonstrate limited willingness to take the initiative or express uncertainty regarding what actions they could personally undertake. This may reflect concerns about the long-term maintenance of such interventions;
- Citizens express a strong desire for more green spaces, particularly in the city centre, and many are even willing to accept trade-offs, such as converting parking areas into green infrastructure;
- While residents of Katowice are increasingly concerned with expanding greenery in urban areas and value green spaces in their immediate surroundings, their perception of other citizens’ knowledge and awareness of the benefits of nature-based solutions appears less certain and requires further improvement.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FFEM-DB | Database of Flood Fatalities in the Euro-Mediterranean Region |
| SuDS | Sustainable Drainage Systems |
| EASAC | European Academies’ Science Advisory Council |
| LID | Low-Impact Development |
| BMP | Best Management Practices |
| UHI | Urban Heat Island |
| CE | Citizen Engagement |
| NbS | Nature-Based Solutions |
| NGOs | Non-Governmental Organizations |
References
- UNDESA. World Population Prospect 2024: Release Note About Major Differences in Total Population Estimates for Mid-2023 Between 2022 and 2024 Revisions. 2024. Available online: https://population.un.org/wpp/assets/Files/WPP2024_Release-Note.pdf (accessed on 9 February 2025).
- Lutz, W.; Stilianakis, N.; Stonawski, M.; Goujon, A.; Samir, K.C. (Eds.) Demographic and Human Capital Scenarios for the 21st Century—2018 Assessment for 201 Countries; Joint Research Centre (Publications Office of European Commission): Luxembourg, 2018; Available online: https://data.europa.eu/doi/10.2760/835878 (accessed on 9 February 2025).
- Vollset, S.E.; Goren, E.; Yuan, C.-W.; Cao, J.; Smith, A.E.; Hsiao, T. Fertility, mortality, migration, and population scenarios for 195 countries and territories from 2017 to 2100: A forecasting analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet 2020, 396, 1285–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callegari, B.; Stoknes, P.E. People and Planet: 21st Century Sustainable Population Scenarios and Possible Living Standards within Planetary Boundaries. Earth4All Working Paper, 1 March 2023. Available online: https://earth4all.life/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/E4A_People-and-Planet_Report.pdf (accessed on 9 February 2025).
- Rockström, J.; Steffen, W.; Noone, K.; Persson, A.; Chapin, F.S., III; Lambin, E.; Lenton, T.M.; Scheffer, M.; Folke, C.; Schellnhuber, H.; et al. Planetary boundaries: Exploring the safe operating space for humanity. Ecol. Soc. 2009, 14, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AFP. 10 Billion Global Population ‘Unsustainable’: US Climate Envoy Kerry. The Business Standard, 8 June 2023. Available online: https://www.tbsnews.net/world/10-billion-global-population-unsustainable-645870 (accessed on 9 February 2025).
- World Group Bank. 2023. Available online: https://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/urbandevelopment/overview?utm_source=chatgpt.com (accessed on 9 February 2025).
- Franklin, D.; Andrews, J. The World in 2050; The Economist: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno-Monroy, A.I.; Schiavina, M.; Veneri, P. Metropolitan areas in the world. Delineation and population trends. J. Urban Econ. 2021, 125, 103242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, L.; Florczyk, A.J.; Freire, S.; Kemper, T.; Melchiorri, M.; Pesaresi, M.; Schiavina, M. Applying the degree of urbanisation to the globe: A new harmonised definition reveals a different picture of global urbanisation. J. Urban Econ. 2021, 125, 103312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kötter, T. Risks and opportunities of urbanisation and megacities. In Proceedings of the FIG Working Week, Athens, Greece, 22–27 May 2004. [Google Scholar]
- UN HABITAT. Envisaging the Future of Cities. World Cities Report 2022. Available online: https://unhabitat.org/world-cities-report-2022-envisaging-the-future-of-cities (accessed on 19 December 2024).
- Caprotti, F. Future cities: Moving from technical to human needs. Palgrave Commun. 2018, 4, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, N. Uneven Development: Nature, Capital, and the Production of Space; University of Georgia Press: Athens, GA, USA, 2010; p. 345. [Google Scholar]
- Lees, L.; Shin, H.B.; Morales, E.L. (Eds.) Global Gentrifications: Uneven Development and Displacement; Policy Press/Bristol University Press: Bristol, UK, 2015; p. 416. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Chen, J.; Li, Q.; Huang, D. Dramatic uneven urbanization of large cities throughout the world in recent decades. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rawas, G.; Nikoo, M.R.; Janbehsarayi, S.F.M.; Hassani, M.R.; Imani, S.; Niksokhan, M.H.; Nazari, R. Near future flash flood prediction in an arid region under climate change. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 25887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashley, R.; Garvin, S.; Pasche, E.; Vassilopoulos, A.; Zevenbergen, C. (Eds.) Advances in Urban Flood Management; Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK; Leiden, The Netherlands; New York, NY, USA; Philadelphia, PA, USA; Singapore, 2007; p. 499. [Google Scholar]
- Gaume, E.; Bain, V.; Bernardara, P.; Newinger, O.; Barbuc, M.; Bateman, A.; Blaškovičová, L.; Blöschl, G.; Borga, M.; Dumitrescu, A.; et al. A compilation of data on European flash floods. J. Hydrol. 2009, 367, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papagiannaki, K.; Petrucci, O.; Diakakis, M.; Kotroni, V.; Aceto, L.; Bianchi, C.; Brázdil, R.; Gelabert, M.G.; Inbar, M.; Kahraman, A.; et al. Developing a large-scale dataset of flood fatalities for territories in the Euro-Mediterranean region, FFEM-DB. Sci. Data 2022, 9, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kron, W.; Eichner, J.; Kundzewicz, Z.W. Reduction of flood risk in Europe–Reflections from a reinsurance perspective. J. Hydrol. 2019, 576, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Su, B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, G.; Wang, G.; Huang, J.; Jiang, T. Flood risk in a range of spatial perspectives–from global to local scales. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 19, 1319–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myhre, G.; Alterskjær, K.; Stjern, C.W.; Hodnebrog, Ø.; Marelle, L.; Samset, B.H.; Sillmann, J.; Schaller, N.; Fischer, E.; Schulz, M.; et al. Frequency of extreme precipitation increases extensively with event rareness under global warming. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Pińskwar, I.; Brakenridge, G.R. Changes in river flood hazard in Europe: A review. Hydrol. Res. 2018, 49, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraghavan, K.; Basanta, K.B.; Adam, M.G.; Soh, S.H.; Tsen-Tieng, D.L.; Davis, A.P.; Chew, H.S.; Tan, P.Y.; Babovic, V.; Balasubramanian, R. Bioretention systems for stormwater management: Recent advances and future prospects. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 292, 112766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, E.C.; Netusil, N.R.; Chan, F.K.S.; Dolman, N.J.; Gosling, S.N. International Perceptions of Urban Blue-Green Infrastructure: A Comparison across Four Cities. Water 2021, 13, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, J.E.; Burns, M.J.; Fletcher, T.D.; Sanders, B.F. A framework for the case-specific assessment of Green Infrastructure in mitigating urban flood hazards. Adv. Water Resour. 2017, 108, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennino, M.J.; McDonald, R.I.; Jaffe, P.R. Watershed-scale impacts of stormwater green infrastructure on hydrology, nutrient fluxes, and combined sewer overflows in the mid-Atlantic region. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 1044–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastien, N.; Arthur, S.; Wallis, S.; Scholz, M. The best management of SuDS treatment trains: A holistic approach. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercruysse, K.; Dawson, D.; Wright, N. Interoperability: A conceptual framework to bridge the gap between multi-functional and multi-system urban flood management. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2019, 12, e12535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Oppenheimer, M.; Zhu, Q.; Baldwin, J.W.; Ebi, K.L.; Bou-Zeid, E.; Guan, K.; Liu, X. Interactions between urban heat islands and heat waves. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 034003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, S.H.; Alam, K.; Iqbal, M.J. Spatio-temporal variations in urban heat island and its interaction with heat wave. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2019, 185, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, C. Influence of the proportion, height and proximity of vegetation and buildings on urban land surface temperature. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 95, 102265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, X.; Yang, Q.; Cao, Y. The turning point between urban vegetation and artificial surfaces for their competitive effect on land surface temperature. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 292, 126034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renc, A.; Łupikasza, E.; Błaszczyk, M. Spatial structure of the surface heat and cold islands in summer based on Landsat 8 imagery in southern Poland. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 142, 109181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perini, K.; Magliocco, A. Effects of vegetation, urban density, building height, and atmospheric conditions on local temperatures and thermal comfort. Urban For. Urban Green. 2014, 13, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Mayer, H.; Chen, L. Contribution of trees and grasslands to the mitigation of human heat stress in a residential district of Freiburg, Southwest Germany. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2016, 148, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzaghmanesh, M.; Beecham, S.; Salemi, T. The role of green roofs in mitigating Urban Heat Island effects in the metropolitan area of Adelaide, South Australia. Urban For. Urban Green. 2016, 15, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balany, F.; Ng, A.W.; Muttil, N.; Muthukumaran, S.; Wong, M.S. Green infrastructure as an urban heat island mitigation strategy—A review. Water 2020, 12, 3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Pitman, A.; Yang, J.; Carouge, C.; Evans, J.P.; Hart, M.; Green, D. Evaluating the effectiveness of mitigation options on heat stress for Sydney, Australia. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2018, 57, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardi, U. The outdoor microclimate benefits and energy saving resulting from green roofs retrofits. Energy Build. 2016, 121, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Berardi, U.; Akbari, H. Comparing the effects of urban heat island mitigation strategies for Toronto, Canada. Energy Build. 2016, 114, 2–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, E.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, C. A study on the cooling effects of greening in a high-density city: An experience for Hong Kong. Build. Environ. 2012, 47, 256–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventriglio, A.; Torales, J.; Castaldelli-Maia, J.M.; De Berardis, D.; Bhugra, D. Urbanization and emerging mental health issues. CNS Spectr. 2021, 26, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cianconi, P.; Hanife, B.; Hirsch, D.; Janiri, L. Is climate change affecting mental health of urban populations? Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2023, 36, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrissey, S.A.; Reser, J.P. Natural disasters, climate change and mental health considerations for rural Australia. Aust. J. Rural Health 2007, 15, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, S.; Verheij, R.A.; Groenewegen, P.P.; Spreeuwenberg, P. Natural environments—Healthy environments? An exploratory analysis of the relationship between greenspace and health. Environ. Plan. A 2003, 35, 1717–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Berg, M.; Wendel-Vos, W.; van Poppel, M.; Kemper, H.; van Mechelen, W.; Maas, J. Health benefits of green spaces in the living environment: A systematic review of epidemiological studies. Urban For. Urban Green. 2015, 14, 806–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, V.; Bamkole, O. The relationship between social cohesion and urban green space: An avenue for health promotion. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, L.V.; Inácio, M.; Pereira, P. Green and blue infrastructure (GBI) and urban nature-based solutions (NbS) contribution to human and ecological wellbeing and health. Oxf. Open Infrastruct. Health 2023, 1, ouad004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Bommel, M.N.; Derkzen, M.L.; Vaandrager, L. Greening for meaning: Sense of place in green citizen initiatives in The Netherlands. Wellbeing Space Soc. 2025, 8, 100240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harman, J.; Sharland, R.; Bell, G. Local Agenda 21 in action. RSA J. 1996, 144, 41–52. [Google Scholar]
- Olwig, K.R. The practice of landscape ‘Conventions’ and the just landscape: The case of the European landscape convention. In Justice, Power and the Political Landscape; Olwig, K.R., Mitchell, D., Eds.; Routledge: London, UK, 2009; pp. 197–212. [Google Scholar]
- Osae, I.B.; Mardiste, P.; Stober, D.; Eiter, S.; Buchecker, M.; Suškevičs, M. Access to information and public participation: Evaluating the implementation of the Aarhus Convention in Europe. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2024, 32, 2449–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, E.L. A midterm report: Will habitat III make a difference to the world’s urban development? J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 2016, 82, 398–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hales, R.; Birdthistle, N. The sustainable development goals–SDG# 11 sustainable cities and communities. In Attaining the 2030 Sustainable Development Goal of Sustainable Cities and Communities; Birdthistle, N., Hales, R., Eds.; Emerald Publishing Limited: Bingley, UK, 2023; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Arnstein, S.R. A ladder of citizen participation. J. Am. Inst. Plan. 1969, 35, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarzynski, A. Public participation, civic capacity, and climate change adaptation in cities. Urban Clim. 2015, 14, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tippett, J.; Handley, J.F.; Ravetz, J. Meeting the challenges of sustainable development—A conceptual appraisal of a new methodology for participatory ecological planning. Prog. Plan. 2007, 67, 9–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilker, J.; Rusche, K.; Rymsa-Fitschen, C. Improving participation in green infrastructure planning. Plan. Pract. Res. 2016, 31, 229–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everett, G.; Adekola, O.; Lamond, J. Developing a blue-green infrastructure (BGI) community engagement framework template. Urban Des. Int. 2021, 28, 172–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brink, E.; Aalders, J.T.; Ádám, D.; Feller, R.; Henselek, Y.; Hoffmann, A.; Ibe, K.; Matthey-Doret, A.; Meyer, M.; Negrut, N.L.; et al. Cascades of green: A review of ecosystem-based adaptation in urban areas. Glob. Environ. Change 2016, 36, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puskás, N.; Abunnasr, Y.; Naalbandian, S. Assessing deeper levels of participation in nature-based solutions in urban landscapes—A literature review of real-world cases. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2021, 210, 104065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mees, H.L.; Uittenbroek, C.J.; Hegger, D.L.; Driessen, P.P. From citizen participation to government participation: An exploration of the roles of local governments in community initiatives for climate change adaptation in The Netherlands. Environ. Policy Gov. 2019, 29, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uittenbroek, C.J.; Mees, H.L.; Hegger, D.L.; Driessen, P.P. The design of public participation: Who participates, when and how? Insights in climate adaptation planning from The Netherlands. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2019, 62, 2529–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrao-Neumann, S.; Harman, B.; Leitch, A.; Low Choy, D. Public engagement and climate adaptation: Insights from three local governments in Australia. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2015, 58, 1196–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brink, E.; Wamsler, C. Citizen engagement in climate adaptation surveyed: The role of values, worldviews, gender and place. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 209, 1342–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fors, H.; Hagemann, F.A.; Sang, Å.O.; Randrup, T.B. Striving for inclusion—A systematic review of long-term participation in strategic management of urban green spaces. Front. Sustain. Cities 2021, 3, 572423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvejić, R.; Železnikar, Š.; Nastran, M.; Rehberger, V.; Pintar, M. Urban agriculture as a tool for facilitated urban greening of sites in transition: A case study. Urbani Izziv 2015, 26, S84–S97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackie, H.; Macmillan, A.; Witten, K.; Baas, P.; Field, A.; Smith, M.; Hosking, J.; King, K.; Sosene, L.; Woodward, A. Te Ara Mua—Future Streets suburban street retrofit: A researcher–community–government co-design process and intervention outcomes. J. Transp. Health 2018, 11, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazeau-Béliveau, N.; Cloutier, G. Citizen participation at the micro-community level: The case of the green alley projects in Quebec City. Cities 2021, 112, 103065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, C.A.; Pownall, M.; Harris, R.; Blundell-Birtill, P. Is the grass always greener? Access to campus green spaces can boost students’ sense of belonging. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2023, 24, 1841–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinescu, M.; Orîndaru, A.; Căescu, Ș.-C.; Pachițanu, A. Sustainable development of urban green areas for quality of life improvement—Argument for increased citizen participation. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaas, E.; Neset, T.-S.; Kjellström, E.; Almås, A.-J. Increasing house owners adaptive capacity: Compliance between climate change risks and adaptation guidelines in Scandinavia. Urban Clim. 2015, 14, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegger, D.L.; Mees, H.L.; Driessen, P.P.; Runhaar, H.A. The roles of residents in climate adaptation: A systematic review in the case of The Netherlands. Environ. Policy Gov. 2017, 27, 336–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mees, H.; Crabbé, A.; Driessen, P.P. Conditions for citizen co-production in a resilient, efficient and legitimate flood risk governance arrangement. A tentative framework. J. Environ. Policy Plan. 2017, 19, 827–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Schertzer, D.; Tchiguirinskaia, I. Assessing cost-effectiveness of nature-based solutions scenarios: Integrating hydrological impacts and life cycle costs. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 329, 129740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, C.S.; Mourato, S.; Kasanin-Grubin, M.; Ferreira, A.J.; Destouni, G.; Kalantari, Z. Effectiveness of nature-based solutions in mitigating flood hazard in a mediterranean peri-urban catchment. Water 2020, 12, 2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Possantti, I.; Marques, G. A modelling framework for nature-based solutions expansion planning considering the benefits to downstream urban water users. Environ. Model. Softw. 2022, 152, 105381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akopov, A.S.; Beklaryan, L.A.; Saghatelyan, A.K. Agent-based modelling of interactions between air pollutants and greenery using a case study of Yerevan, Armenia. Environ. Model. Softw. 2019, 116, 7–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wamsler, C.; Alkan-Olsson, J.; Björn, H.; Falck, H.; Hanson, H.; Oskarsson, T.; Simonsson, E.; Zelmerlow, F. Beyond participation: When citizen engagement leads to undesirable outcomes for nature-based solutions and climate change adaptation. Clim. Change 2020, 158, 235–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistical Office in Katowice. 2025. Available online: https://katowice.stat.gov.pl/en/ (accessed on 14 June 2025).
- Kulpa, J.; Kamiński, P.; Stecuła, K.; Prostański, D.; Matusiak, P.; Kowol, D.; Kopacz, M.; Olczak, P. Technical and economic aspects of electric energy storage in a mine shaft—Budryk case study. Energies 2021, 14, 7337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vöröš, D.; Řimnáčová, D.; Medvecká, L.; Geršlová, E.; Díaz-Somoano, M. The impact of saline mine water on fate of mineral elements and organic matter: The case study of the Upper Silesian Coal Basin. Chemosphere 2021, 284, 131397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janson, E. Multi-Decadal Impact of Mine Waters in Przemsza River Basin, Upper Silesian Coal Basin, Southern Poland. Water 2024, 16, 3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulias, R. Upper Silesian Region—An example of large-scale transformation of relief by mining. In Landscapes and Landforms of Poland; Migoń, P., Jancewicz, K., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 371–383. [Google Scholar]
- Murzyn-Kupisz, M.; Gwosdz, K. The changing identity of the Central European city: The case of Katowice. J. Hist. Geogr. 2011, 37, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łukaszkiewicz, J.; Fortuna-Antoszkiewicz, B.; Długoński, A.; Wiśniewski, P. From the heap to the park–reclamation and adaptation of degraded urban areas for recreational functions in Poland. Sci. Rev. Eng. Environ. Sci. 2019, 28, 664–681. [Google Scholar]
- Pancewicz, A.; Anczykowska, W.; Żak, N. Climate change adaptation activities planning and implementation in large cities: Results of research carried out in Poland and selected European cities. Clim. Change 2023, 176, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janiszek, M.; Krzysztofik, R. Green infrastructure as an effective tool for urban adaptation—Solutions from a big city in a postindustrial region. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etzkowitz, H.; Leydesdorff, L. The dynamics of innovation: From National Systems and “Mode 2” to a Triple Helix of university–industry–government relations. Res. Policy 2000, 29, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carayannis, E.G.; Campbell, D.F. ‘Mode 3’ and ‘Quadruple Helix’: Toward a 21st century fractal innovation ecosystem. Int. J. Technol. Manag. 2009, 46, 201–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carayannis, E.G.; Barth, T.D.; Campbell, D.F. The Quintuple Helix innovation model: Global warming as a challenge and driver for innovation. J. Innov. Entrep. 2012, 1, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahour, K. Role of women in environment conservation. J. Adv. Lab. Res. Biol. 2016, 7, 17–26. [Google Scholar]
- Labaris, A. Women involvement in environmental protection and management: A case of Nasarawa state. J. Sustain. Dev. Afr. 2009, 10, 179–191. [Google Scholar]
- Mohai, P. Men, women, and the environment: An examination of the gender gap in environmental concern and activism. In Women Working in the Environment; Sachs, C.E., Ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 2014; pp. 215–239. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, J.; Xia, B.; Barker, J.; Skitmore, M. Green buildings for greying people: A case study of a retirement village in Australia. Facilities 2014, 32, 365–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillemer, K.; Wells, N.M.; Meador, R.H.; Schultz, L.; Henderson, C.R., Jr.; Cope, M.T. Engaging older adults in environmental volunteerism: The retirees in service to the environment program. Gerontologist 2017, 57, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Family, Labour and Social Policy. 2025. Available online: https://www.gov.pl/web/rodzina/biuletyn-europejski-rok-umiejetnosci (accessed on 15 July 2025).
- Hornsey, M.J.; Lewandowsky, S. A toolkit for understanding and addressing climate scepticism. Nat. Hum. Behav. 2022, 6, 1454–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steentjes, K.; Pidgeon, N.; Poortinga, W.; Corner, A.; Arnold, A.; Böhm, G.; Mays, C.; Poumadère, M.; Ruddat, M.; Scheer, D.; et al. European Perceptions of Climate Change (EPCC): Topline Findings of a Survey Conducted in Four European Countries in 2016; Cardiff University: Cardiff, UK, 2017; Available online: https://orca.cardiff.ac.uk/id/eprint/98660/7/epcc.pdf (accessed on 17 June 2025).
- Insurance Journal. Available online: https://www.insurancejournal.com/news/east/2024/10/24/798217.htm (accessed on 17 June 2025).
- Gensler Institute Research Survey. 2022. Available online: https://www.gensler.com/gri/us-climate-action-survey-2022 (accessed on 17 June 2025).
- Sapiains, R.; Azócar, G.; Moraga, P.; Valenzuela, C.; Aldunce, P.; Cornejo, C.; Rojas, M.; Pulgar, A.; Medina, L.; Bozkurt, D. Are citizens ready for active climate engagement or stuck in a game of blame? Local perceptions of climate action and citizen participation in Chilean Patagonia. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donahue, A.K.; Eckel, C.C.; Wilson, R.K. Ready or not? How citizens and public officials perceive risk and preparedness. Am. Rev. Public Adm. 2014, 44 (Suppl. S4), 89–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doorn, N. Distributing responsibilities for safety from flooding. In Proceedings of the E3S Web of Conferences, 3rd European Conference on Flood Risk Management (FLOODrisk 2016), Lyon, France, 17–21 October 2016; EDP Sciences: Les Ulis, France, 2016; Volume 7, p. 24002. [Google Scholar]
- Skarzauskiene, A.; Mačiulienė, M.; Kovaitė, K. Citizen engagement in climate adaptation surveyed: Identifying challenges in education and capacity building. Eur. J. Educ. 2024, 59, e12732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabisch, N.; Frantzeskaki, N.; Pauleit, S.; Naumann, S.; Davis, M.; Artmann, M.; Haase, D.; Knapp, S.; Korn, H.; Stadler, J.; et al. Nature-based solutions to climate change mitigation and adaptation in urban areas: Perspectives on indicators, knowledge gaps, barriers, and opportunities for action. Ecol. Soc. 2016, 21, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Bosch, M.; Sang, Å.O. Urban natural environments as nature-based solutions for improved public health—A systematic review of reviews. Environ. Res. 2017, 158, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seddon, N.; Chausson, A.; Berry, P.; Girardin, C.A.; Smith, A.; Turner, B. Understanding the value and limits of nature-based solutions to climate change and other global challenges. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2020, 375, 20190120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seddon, N.; Smith, A.; Smith, P.; Key, I.; Chausson, A.; Girardin, C.; House, J.; Srivastava, S.; Turner, B. Getting the message right on nature-based solutions to climate change. Glob. Change Biol. 2021, 27, 1518–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folkard-Tapp, H.; Banks-Leite, C.; Cavan, E.L. Nature-based Solutions to tackle climate change and restore biodiversity. J. Appl. Ecol. 2021, 58, 2344–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Y.; Jay, M.; Chen, X. The role of nature-based solutions for improving environmental quality, health and well-being. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, A.S.; Dee, L.E.; Gonzalez, A.; Ohashi, H.; Cowles, J.; Wright, A.J.; Loreau, M.; Hautier, Y.; Newbold, T.; Reich, P.B.; et al. Biodiversity–productivity relationships are key to nature-based climate solutions. Nat. Clim. Change 2021, 11, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, R.; Pluchinotta, I.; Pagano, A.; Scrieciu, A.; Nanu, F. Enhancing nature-based solutions acceptance through stakeholders’ engagement in co-benefits identification and trade-offs analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, C.C.; Renaud, F.G.; Hanscomb, S.; Munro, K.E.; Gonzalez-Ollauri, A.; Thomson, C.S.; Pouta, E.; Soini, K.; Loupis, M.; Panga, D.; et al. Public acceptance of nature-based solutions for natural hazard risk reduction: Survey findings from three study sites in Europe. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 678938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depietri, Y.; McPhearson, T. Integrating the Grey, Green, and Blue in Cities: Nature-Based Solutions for Climate Change Adaptation and Risk Reduction. In Nature-Based Solutions to Climate Change Adaptation in Urban Areas: Linkages Between Science, Policy and Practice; Kabisch, N., Korn, H., Stadler, J., Bonn, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 91–109. [Google Scholar]
- Frantzeskaki, N. Seven lessons for planning nature-based solutions in cities. Environ. Sci. Policy 2019, 93, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chausson, A.; Turner, B.; Seddon, D.; Chabaneix, N.; Girardin, C.A.J.; Kapos, V.; Key, I.; Roe, D.; Smith, A.; Woroniecki, S.; et al. Mapping the effectiveness of nature-based solutions for climate change adaptation. Glob. Change Biol. 2020, 26, 6134–6155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giachino, C.; Pattanaro, G.; Bertoldi, B.; Bollani, L.; Bonadonna, A. Nature-based solutions and their potential to attract the young generations. Land Use Policy 2021, 101, 105176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macháč, J.; Brabec, J.; Arnberger, A. Exploring public preferences and preference heterogeneity for green and blue infrastructure in urban green spaces. Urban For. Urban Green. 2022, 75, 127695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Agudelo, N.A.; Porcar Anento, R.; Villares, M.; Roca, E. Nature-based solutions for water management in peri-urban areas: Barriers and lessons learned from implementation experiences. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarlett, R.D.; Subramaniam, M.; McMillan, S.K.; Ingermann, A.T.; Clinton, S.M. Stormwater on the margins: Influence of race, gender, and education on willingness to participate in stormwater management. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 290, 112552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lampinen, J.; García-Antúnez, O.; Lechner, A.M.; Olafsson, A.S.; Gulsrud, N.M.; Raymond, C.M. Mapping public support for urban green infrastructure policies across the biodiversity-climate-society-nexus. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2023, 239, 104856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, J.; Borne, K.E.; Semadeni-Davies, A.; Tanner, C.C. Selection, Planning, and Modelling of Nature-Based Solutions for Flood Mitigation. Water 2024, 16, 2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, I.; Grosinger, J.; Bauer, S.; de Francisco, J.C.R.; Negacz, K.; Hein, J. Time in and for nature-based solutions. No quick fix solutions for complex ecological and social processes. Nat.-Based Solut. 2025, 7, 100219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Center for Industry Analysis. 2023. Available online: https://cab-badania.pl/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/Rynek-kostki-brukowej-w-Polsce-edycja-2023.pdf (accessed on 18 June 2023).
- Anderson, C.C.; Renaud, F.G. A review of public acceptance of nature-based solutions: The ‘why’, ‘when’, and ‘how’ of success for disaster risk reduction measures. Ambio 2021, 50, 1552–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loder, A. “There’s a meadow outside my workplace”: A phenomenological exploration of aesthetics and green roofs in Chicago and Toronto. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 126, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poje, M.; Vukelić, A.; Židovec, V.; Prebeg, T.; Kušen, M. Perception of the Vegetation Elements of Urban Green Spaces with a Focus on Flower Beds. Plants 2024, 13, 2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steadman, S.; Smith, H.M.; Jeffrey, P.; Wheat, P. Exploring public perceptions and support for green infrastructure funding mechanisms: A study of the Oxford-Cambridge Arc, England. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2024, 67, 2502–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Völker, S.; Kistemann, T. The impact of blue space on human health and well-being—Salutogenetic health effects of inland surface waters: A review. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2011, 214, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckstein, G.; D’Andrea, A.; Marshall, V.; O’Donnell, E.; Talbot-Jones, J.; Curran, D.; O’Bryan, K. Conferring legal personality on the world’s rivers: A brief intellectual assessment. Water Int. 2019, 44, 804–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayward, P.; Fisiak, T.; Fleury, C. Resurrecting riverine identity. Civic symbolism, ghostly traces and waterway restoration in 21st century Łódź (Poland). Anthr. Hum. Inhuman Posthuman 2024, 5, 1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilczyńska, A.; Niin, G.; Vassiljev, P.; Myszka, I.; Bell, S. Perceptions and patterns of use of blue spaces in selected European cities: Tartu, Tallinn, Barcelona, Warsaw and Plymouth. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bąkowska-Waldmann, E.; Piniarski, W. Gender-specific preferences regarding urban green areas. Quaest. Geogr. 2023, 42, 23–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.L.; Yuen, B.; Briffett, C.; Sodhi, N.S. Nature and nurture, danger and delight: Urban women’s experiences of the natural world. Landsc. Res. 1997, 22, 245–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braçe, O.; Garrido-Cumbrera, M.; Correa-Fernández, J. Gender differences in the perceptions of green spaces characteristics. Soc. Sci. Q. 2021, 102, 2640–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Luo, Y.; Furuya, K. Gender differences and optimizing women’s experiences: An exploratory study of visual behavior while viewing urban park landscapes in Tokyo, Japan. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, H.; Cao, Y.; Almomani, A.; Akmeel, L.; Wang, L. Exploring Safety Perceptions Among Women Using Factor and Cluster Analysis: A Case Study of Neighborhood Parks in Jordan. Land 2025, 14, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Transportation Alternatives. Available online: https://transalt.org/blog/clear-majority-of-new-york-city-voters-support-removing-car-parking-to-build-streets-for-people#:~:text=Eighty,even%20if%20it%20results%20in (accessed on 17 June 2025).
- Eurocities. Available online: https://eurocities.eu/latest/there-is-a-will-and-a-way-to-green-paris/ (accessed on 17 June 2025).
- Phillips, A.; Da Schio, N.; Canters, F.; Khan, A.Z. “A living street and not just green”: Exploring public preferences and concerns regarding nature-based solution implementation in urban streetscapes. Urban For. Urban Green. 2023, 86, 128034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, N. Responsibility: Distinguishing virtue from capacity. Pol. J. Philos. 2009, 3, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, H. Green citizenship. Soc. Policy Adm. 2001, 35, 490–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagers, S.C.; Matti, S. Ecological citizens: Identifying values and beliefs that support individual environmental responsibility among Swedes. Sustainability 2010, 2, 1055–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahern, J. Urban landscape sustainability and resilience: The promise and challenges of integrating ecology with urban planning and design. Landsc. Ecol. 2013, 28, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.I.; Yeom, S.J. A Social Responsibility of Landscape Architecture as a Green Infrastructure for Environmental Justice Realization. J. Environ. Sci. Int. 2017, 26, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, C.; Santo-Tomás Muro, R. Stewardship and green infrastructure in England. Planning perspectives informed through an investigation of urban green infrastructure. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2024, 67, 2748–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, C.; Lafortezza, R. Transitional path to the adoption of nature-based solutions. Land Use Policy 2019, 80, 406–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, I.; Morello, E. Co-creation pathway for urban nature-based solutions: Testing a shared-governance approach in three cities and nine action labs. In Smart and Sustainable Planning for Cities and Regions: Results of SSPCR 2019—Open Access Contributions; Bisello, A., Vettorato, D., Ludlow, D., Baranzelli, C., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 259–276. [Google Scholar]
- Carpini, M.X.D.; Cook, F.L.; Jacobs, L.R. Public deliberation, discursive participation, and citizen engagement: A review of the empirical literature. Annu. Rev. Polit. Sci. 2004, 7, 315–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, M.A.; Leahy, J.E.; Anderson, D.H.; Jakes, P.J. Building trust in natural resource management within local communities: A case study of the Midewin National Tallgrass Prairie. Environ. Manag. 2007, 39, 353–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cologna, V.; Siegrist, M. The role of trust for climate change mitigation and adaptation behaviour: A meta-analysis. J. Environ. Psychol. 2020, 69, 101428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzoni, I.; Nicholson-Cole, S.; Whitmarsh, L. Barriers perceived to engaging with climate change among the UK public and their policy implications. Glob. Environ. Change 2007, 17, 445–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syrbe, R.U.; Neumann, I.; Grunewald, K.; Brzoska, P.; Louda, J.; Kochan, B.; Macháč, J.; Dubová, L.; Meyer, P.; Brabec, J.; et al. The value of urban nature in terms of providing ecosystem services related to health and well-being: An empirical comparative pilot study of cities in Germany and the Czech Republic. Land 2021, 10, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajca, J.; Olczak, B.; Wilkosz-Mamcarczyk, M. Urban adaptation to climate change and resident awareness. A Polish perspective. Geomat. Landmanagement Landsc. 2023, 2, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, N.; Doyon, A. Increasing knowledge and trust to overcome barriers to green infrastructure implementation: A Vancouver case study. Urban Water J. 2024, 21, 802–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, M.; Overney, C.; Kamra, A.; Tepale, J.; Hamby, E.; Jasim, M.; Roy, D. Voice to Vision: Enhancing Civic Decision-Making through Co-Designed Data Infrastructure. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2505.14853. [Google Scholar]
- Waite, S.; Husain, F.; Scandone, B.; Forsyth, E.; Piggott, H. ‘It’s not for people like (them)’: Structural and cultural barriers to children and young people engaging with nature outside schooling. J. Adventure Educ. Outdoor Learn. 2023, 23, 54–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sextus, C.P.; Hytten, K.F.; Perry, P. A systematic review of environmental volunteer motivations. Soc. Nat. Resour. 2024, 37, 1591–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollmer, A.; Ceolotto, S.; Farrell, N. Nature-Based Solutions for Climate Adaptation: Review of Barriers to Adoption and Guidelines for Policymakers; ESRI Working Paper No. 794; Economic and Social Research Institute: Dublin, Ireland, 2024; Available online: https://www.esri.ie/system/files/publications/WP794.pdf (accessed on 16 June 2025).
- Walker, S.E.; Bennett, N.; Smith, E.A.; Nuckols, T.; Narayana, A.; Lee, J.; Bailey, K.M. Unintended consequences of nature-based solutions: Social equity and flood buyouts. PLoS Clim. 2024, 3, e0000328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadgar, A.; Luciani, G.; Nyka, L. Spatial allocation of nature-based solutions in the form of public green infrastructure in relation to the socio-economic district profile–a GIS-based comparative study of Gdańsk and Rome. Land Use Policy 2025, 150, 107454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, V.; Barreira, A.P.; Loures, L.; Antunes, D.; Panagopoulos, T. Stakeholders’ engagement on nature-based solutions: A systematic literature review. Sustainability 2020, 12, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Luo, A. Unravelling stakeholder narratives on nature-based solutions for hydro-meteorological risk reduction. Sustain. Sci. 2024, 19, 1677–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thodesen, B.; Time, B.; Kvande, T. Sustainable urban drainage systems: Themes of public perception—A case study. Land 2022, 11, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapik, E.; Brandimarte, L.; Usher, M. Maintenance in sustainable stormwater management: Issues, barriers and challenges. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2024, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarabi, S.; Han, Q.; Romme, A.G.L.; De Vries, B.; Valkenburg, R.; Den Ouden, E. Uptake and implementation of nature-based solutions: An analysis of barriers using interpretive structural modeling. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 270, 110749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raška, P.; Bezak, N.; Ferreira, C.S.S.; Kalantari, Z.; Banasik, K.; Bertola, M.; Bourke, M.; Cerdà, A.; Davids, P.; Madruga de Brito, M.; et al. Identifying barriers for nature-based solutions in flood risk management: An interdisciplinary overview using expert community approach. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 310, 114725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ignatieva, M.; Eriksson, F.; Eriksson, T.; Berg, P.; Hedblom, M. The lawn as a social and cultural phenomenon in Sweden. Urban For. Urban Green. 2017, 21, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Xia, Y.; Qiu, H.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, G.; Li, S.; Gao, W.; Xu, T.; et al. Exploring public attitudes toward implementing green infrastructure for sponge city stormwater management. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 24252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, M.S.; Sanders Thompson, V.L.; Arroyo Johnson, C.; Gennarelli, R.; Drake, B.F.; Bajwa, P.; Witherspoon, M.; Bowen, D. Evaluating community engagement in research: Quantitative measure development. J. Community Psychol. 2017, 45, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazy, B.; Khodeir, L.; Fathy, F. Achieving socio-economic resilience in neighborhood through nature-based solutions: A systematic review. Results Eng. 2025, 25, 104266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilt, J.H.; Ries, P.D. Constraints and catalysts influencing green infrastructure projects: A study of small communities in Oregon (USA). Urban For. Urban Green. 2021, 63, 127138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobles, E.C.; Moore, K. Barriers to equitable greening in urban environmental policies. J. Environ. Policy Plan. 2024, 26, 388–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowińska-Świerkosz, B.; García, J. A new evaluation framework for nature-based solutions (NBS) projects based on the application of performance questions and indicators approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 787, 147615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, M.; Dumitru, A.; Wendling, L.; Briega, P.; Capobianco, V.; Connop, S.; Crespo, L.; Fermoso, J.; Giannico, V.; Gómez, S.; et al. Application of the NBS impact evaluation framework: NBS performance and impact evaluation case studies. In Evaluating the Impact of Nature-Based Solutions: A Handbook for Practitioners Brussels; Dumitru, A., Wendling, L., Eds.; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2021; pp. 179–240. [Google Scholar]
- Michalina, D.; Mederly, P.; Diefenbacher, H.; Held, B. Sustainable urban development: A review of urban sustainability indicator frameworks. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Lierop, M.; Dobbs, C.; van der Jagt, A.; Skiba, A.; Flores, C.; Maselli Locosselli, G.; Duarte, D.; Zingraff-Hamed, A.; Pauleit, S. The why, how, and what of indicator-based monitoring of nature-based solutions: Perspectives from EU and LAC city practitioners. Ambio 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UPSURGE Project Site. Available online: https://www.upsurge-project.eu/index.html%3Fp=451.html (accessed on 16 July 2025).
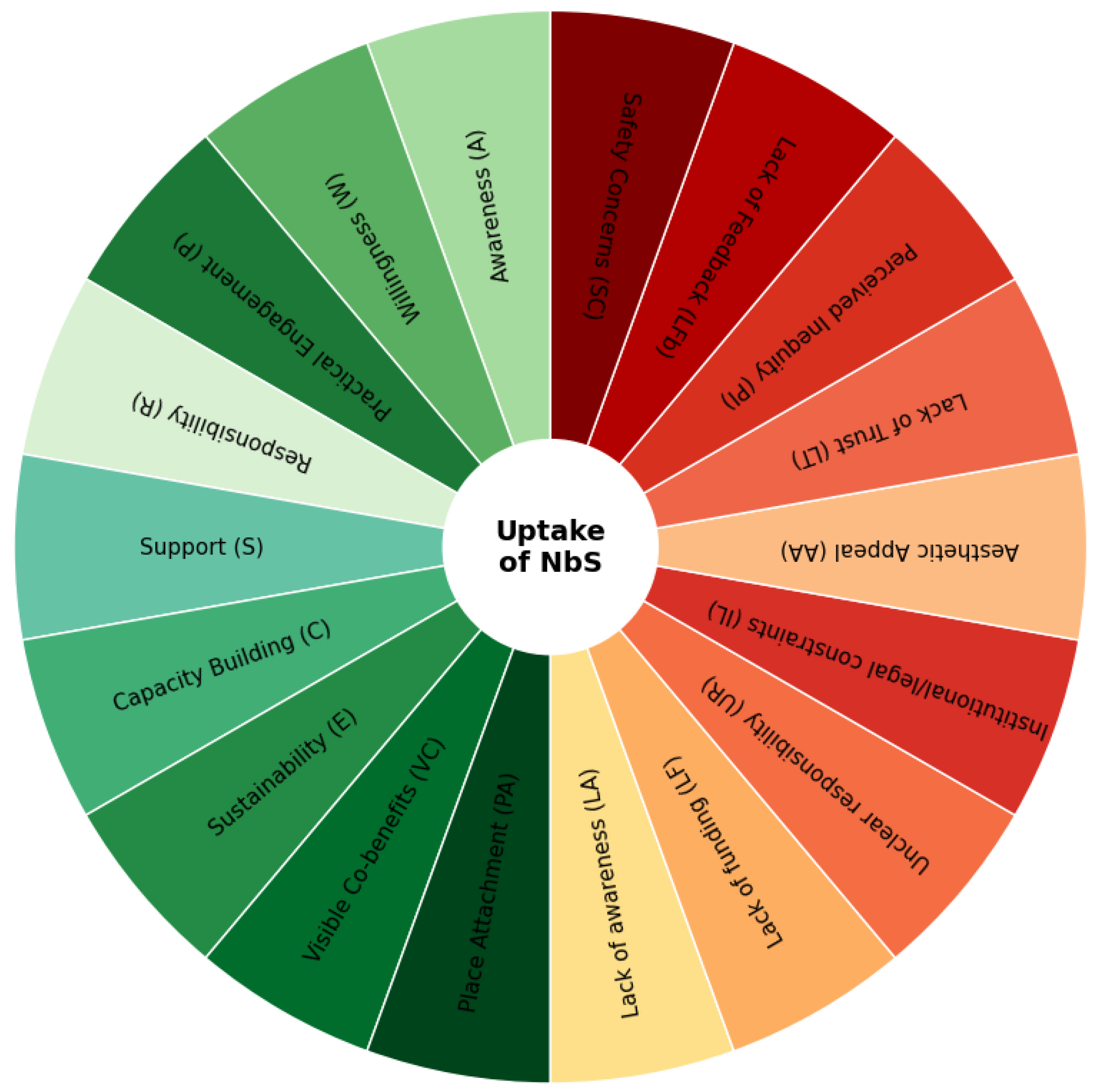







| Drivers | |
|---|---|
| Parameter | Description |
| Awareness (A) | Number or proportion of respondents self-classified as aware of the benefits of nature-based solutions. |
| Willingness (W) | Number or proportion of respondents willing to make trade-offs between grey infrastructure or land use (e.g., parking). |
| Practical Engagement (P) | Number or proportion of respondents involved in voluntary green-space care activities (e.g., planting, cleaning). |
| Responsibility (R) | Number or proportion of respondents who feel personally responsible for green areas (e.g., by taking part in green projects). |
| Support (S) | Number or proportion supporting shared governance of green spaces (e.g., involving citizens, schools, volunteers). |
| Capacity Building (C) | Number of workshops or training sessions organised for citizens. |
| Sustainability of Engagement (E) | Number or proportion of respondents willing to remain involved in the project after its official end. |
| Visible Co-benefits (VC) | Number or proportion of respondents who observe improvements such as cooling, shade, biodiversity, or recreational use due to NbSs. |
| Place Attachment (PA) | Number or proportion of respondents who feel emotionally or historically connected to local green spaces. |
| Obstacles | |
| Parameter | Description |
| Lack of Awareness (LA) | Number or proportion of respondents unaware of the benefits of nature-based solutions. |
| Lack of Funding (LF) | Number or proportion of respondents indicating withdrawal from NbS maintenance in the absence of funding |
| Unclear responsibility (UR) | Number or proportion of respondents who do not know who is responsible for managing green areas in the city. |
| Institutional/Legal Constraints (IL) | Number of legal or administrative procedures required to carry out an NbS intervention. |
| Aesthetic Appeal (AA) | Number or proportion of respondents expressing a negative perception of wild or unmanaged green spaces. |
| Lack of Trust (LT) | Number or proportion of respondents expressing low trust in local authorities or implementing institutions. |
| Perceived Inequity (PI) | Number or proportion of respondents who believe NbS projects benefit only certain areas or social groups. |
| Lack of Feedback (LFb) | Number or proportion of respondents who feel their input was ignored or not reflected in project outcomes. |
| Safety Concerns (SC) | Number or proportion of respondents expressing fears about unmanaged green spaces (e.g., pests, crime, flooding). |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Samborska-Goik, K.; Starzewska-Sikorska, A.; Obłój, P. Thinking Green: A Place Lab Approach to Citizen Engagement and Indicators for Nature-Based Solutions in a Case Study from Katowice. Sustainability 2025, 17, 6857. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17156857
Samborska-Goik K, Starzewska-Sikorska A, Obłój P. Thinking Green: A Place Lab Approach to Citizen Engagement and Indicators for Nature-Based Solutions in a Case Study from Katowice. Sustainability. 2025; 17(15):6857. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17156857
Chicago/Turabian StyleSamborska-Goik, Katarzyna, Anna Starzewska-Sikorska, and Patrycja Obłój. 2025. "Thinking Green: A Place Lab Approach to Citizen Engagement and Indicators for Nature-Based Solutions in a Case Study from Katowice" Sustainability 17, no. 15: 6857. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17156857
APA StyleSamborska-Goik, K., Starzewska-Sikorska, A., & Obłój, P. (2025). Thinking Green: A Place Lab Approach to Citizen Engagement and Indicators for Nature-Based Solutions in a Case Study from Katowice. Sustainability, 17(15), 6857. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17156857






