Bee Products as a Bioindicator of Radionuclide Contamination: Environmental Approach and Health Risk Evaluation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
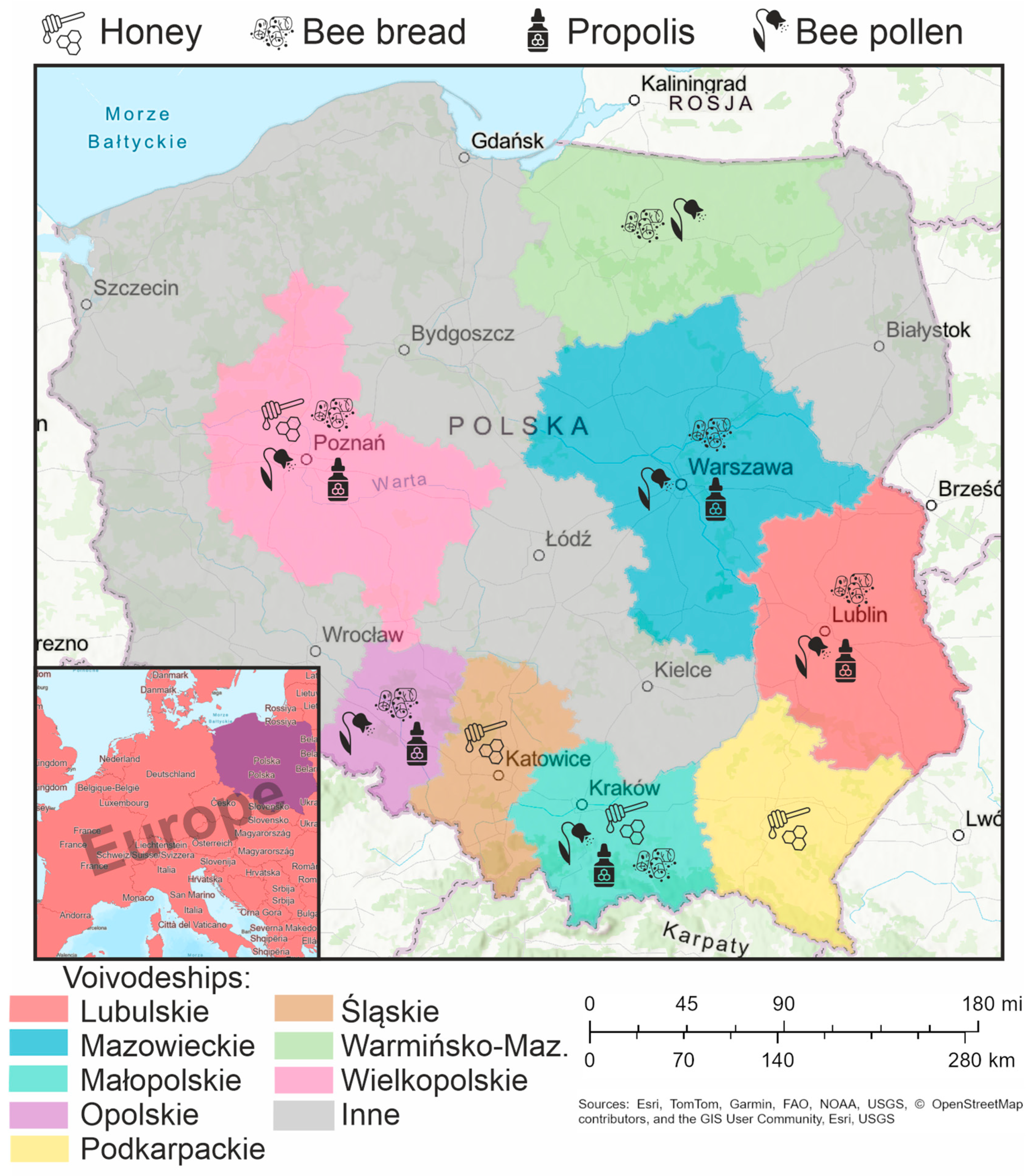
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling and Measurements
2.3. Reference Soil Data
2.4. Health Risk Calculation
3. Results and Discussion
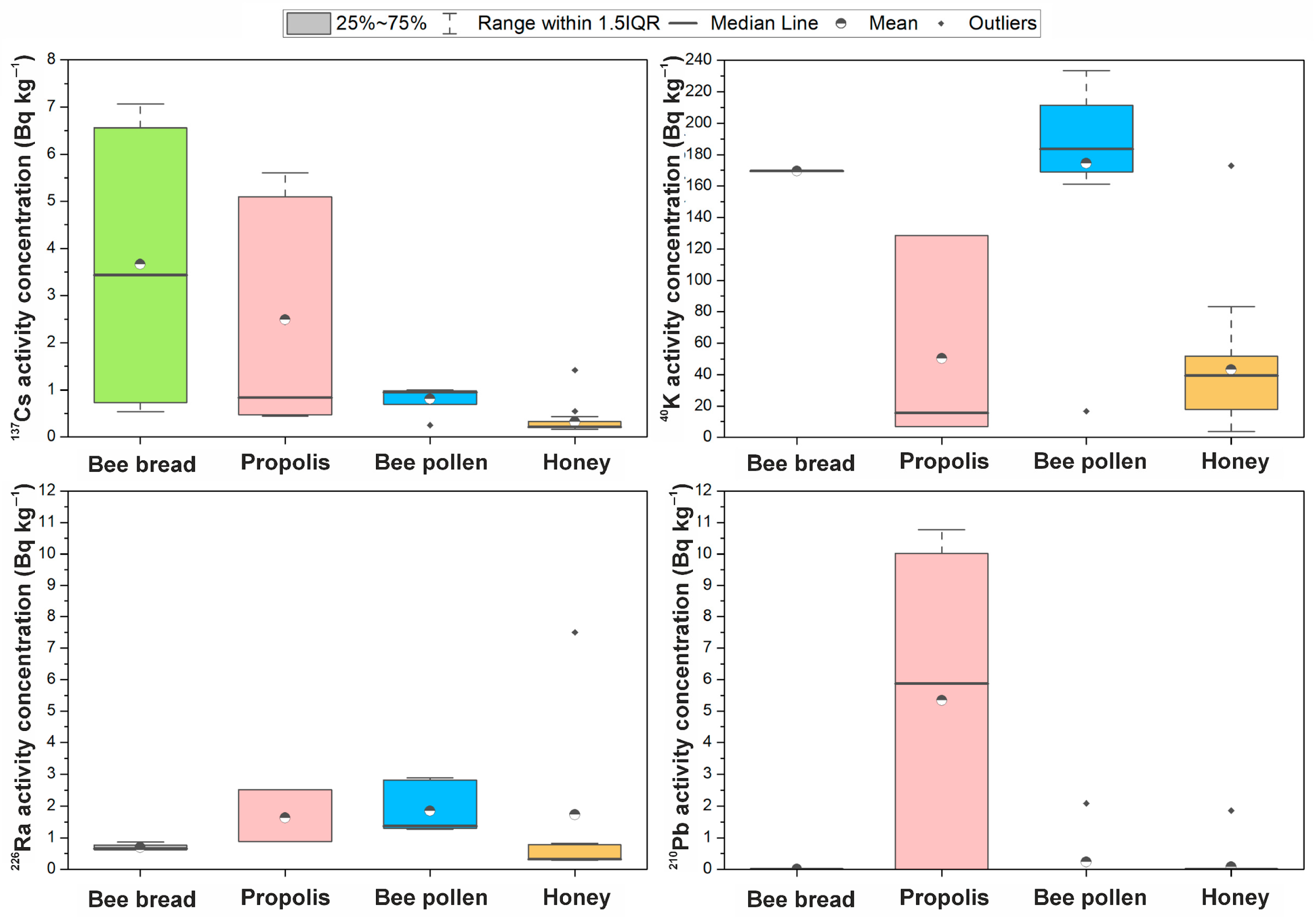
3.1. General Radioisotopic Characterization of Bee Products
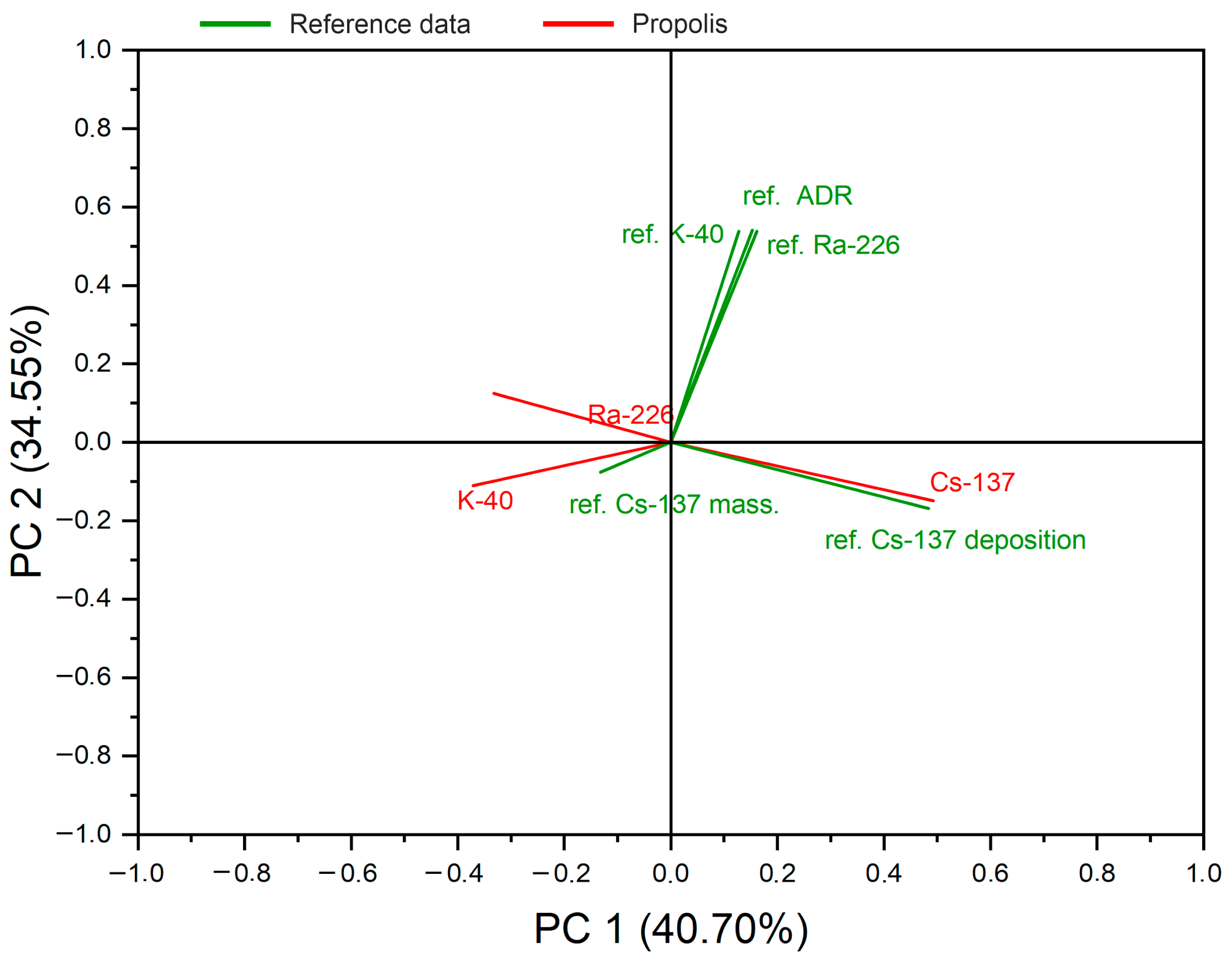
3.2. Principal Component Analysis for Environmental Radioisotopic Correlations
3.3. Health Risk Assessment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADR | Absorbed dose rate |
| CR | Cancer risk |
| MDA | Minimum detectable activity |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Al-Waili, N.S.; Salom, K.; Butler, G.; Al Ghamdi, A.A. Honey and Microbial Infections: A Review Supporting the Use of Honey for Microbial Control. J. Med. Food 2011, 14, 1079–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livia Persano, O.; Lucia, P.; Stefan, B.; Antonio, B.; Panagiota, G.; Jacob, K.; Peter, M.; Monique, M.; Alberto Ortiz, V.; Kaspar, R.; et al. Botanical species giving unifloral honey in Europe. Apidologie 2004, 35, S82–S93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, M.D.; Bryan, C.R. Radioactivity, Geochemistry, and Health. In Treatise on Geochemistry, 2nd ed.; Holland, H.D., Turekian, K.K., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2014; Volume 11, pp. 191–256. [Google Scholar]
- Sljivic-Ivanovic, M.; Smičiklas, I. Radioactive Contamination of the Soil: Assessments of Pollutants Mobility with Implication to Remediation Strategies. In Soil Contamination—Current Consequences and Further Solutions; Larramendy, M.L., Soloneski, S., Eds.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, K.C. Honey as an indicator of heavy metal contamination. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1987, 33, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casula, M.; Corrias, F.; Atzei, A.; Milia, M.; Arru, N.; Satta, A.; Floris, I.; Pusceddu, M.; Angioni, A. Multiresidue Methods Analysis to Detect Contamination of Selected Metals in Honey and Pesticides in Honey and Pollen. Foods 2024, 13, 4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godebo, T.R.; Stoner, H.; Taylor, P.; Jeuland, M. Metals in honey from bees as a proxy for environmental contamination in the United States. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 364, 125221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek, J.; Kaczor, M.; Romańczyk, G.; Grońska, M.; Boryło, A. Radioactivity of honey in central and southern Poland. J. Environ. Radioact. 2020, 222, 106376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihaljev, Ž.; Jakšić, S.; Živkov Baloš, M.; Popov, N. Radioactive Residue in Honey. Arch. Vet. Med. 2021, 14, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meli, M.A.; Desideri, D.; Roselli, C.; Benedetti, C.; Feduzi, L. Essential and toxic elements in honeys from a region of central Italy. J Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2015, 78, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meli, M.A.; Desideri, D.; Roselli, C.; Feduzi, L.; Benedetti, C. Radioactivity in honey of the central Italy. Food Chem. 2016, 202, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panatto, D.; Gasparini, R.; Lai, P.; Rovatti, P.; Gallelli, G. Long-term decline of 137Cs concentration in honey in the second decade after the Chernobyl accident. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 382, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molzahn, D.; Assmann-Werthmüller, U. Caesium radioactivity in several selected species of honey. Sci. Total Environ. 1993, 130, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barišić, D.; Lulić, S.; Kezić, N.; Vertačnik, A. 137Cs in flowers, pollen and honey from the Republic of Croatia four years after the Chernobyl accident. Apidologie 1992, 23, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borawska, M.H.; Kapała, J.; Puścion-Jakubik, A.; Horembała, J.; Markiewicz-Żukowska, R. Radioactivity of Honeys from Poland After the Fukushima Accident. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2013, 91, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misiak, R.; Hajduk, R.; Stobinski, M.; Bartyzel, M.; Szarlowicz, K.; Kubica, B. Self-absorption correction and efficiency calibration for radioactivity measurement of environmental samples by gamma-ray spectrometry. Nukleonika 2011, 56, 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore, G.R. Practical Gamma-Ray Spectrometry; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 251–277. [Google Scholar]
- CLOR. Annual Report 2021; Centralne Laboratorium Ochrony Radiologicznej: Warszawa, Poland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- ICRP. ICRP Publication 119: Compendium of dose coefficients based on ICRP Publication 60. Ann. ICRP 2012, 41, 1–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA. Cancer Risk Coefficients for Environmental Exposure to Radionuclides. In Federal Guidance Report No. 13; United States Environment Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2015; pp. 83–104. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Tuo, F.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Pang, C. Dietary exposure of radionuclides and heavy metals in adult residents in a high background natural radiation area using duplicate diet method. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Różański, H. Propolis—Właściwości Lecznicze. 2015. Available online: https://rozanski.li/16/propolis-wlasciwosci-lecznicze/ (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- Kieliszek, M.; Piwowarek, K.; Kot, A.M.; Błażejak, S.; Chlebowska-Śmigiel, A.; Wolska, I. Pollen and bee bread as new health-oriented products: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 71, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polska Izba, M. Polska Izba Miodu: Polacy Kupują Coraz Więcej Miodu. 2025. Available online: https://www.portalspozywczy.pl/slodycze-przekaski/wiadomosci/polska-izba-miodu-polacy-kupuja-coraz-wiecej-miodu,273842.html (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- Beňová, K.; Dvořák, P.; Špalková, M. Radiocaesium in Honey from Košice and Prešov Regions in Eastern Slovakia. Folia Vet. 2019, 63, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djuric, G.; Popovic, D.; Todorovic, D. Activity variations and concentration factors for natural radionuclides in a “soil-plant-honey” system. Environ. Int. 1996, 22, 361–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, A. Effect of toxicological condition of honey on cumulation level of selected toxic elements in bee (Apis mellifera L.) bodies. Acta Agroph. 2003, 1, 295–300. [Google Scholar]
- Bora, F.D.; Babeș, A.C.; Călugăr, A.; Jitea, M.I.; Hoble, A.; Filimon, R.V.; Bunea, A.; Nicolescu, A.; Bunea, C.I. Unravelling Heavy Metal Dynamics in Soil and Honey: A Case Study from Maramureș Region, Romania. Foods 2023, 12, 3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarić, N.M.; Ilijević, K.; Stanisavljević, L.; Gržetić, I. Use of honeybees (Apis mellifera L.) as bioindicators for assessment and source appointment of metal pollution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 25828–25838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankova, V.; Popova, M.; Trusheva, B. The phytochemistry of the honeybee. Phytochemistry 2018, 155, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabakci, D. Comparison of some biological activities of propolis and bee bread samples obtained from Apis mellifera Anatoliaca and its Muğla and Efe ecotypes. J. Hell. Vet. Med. Soc. 2024, 74, 6451–6462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsuk, G.; Sulborska, A.; Stawiarz, E.; Olszewski, K.; Wiącek, D.; Ramzi, N.; Nawrocka, A.; Jędryczka, M. Capacity of honeybees to remove heavy metals from nectar and excrete the contaminants from their bodies. Apidologie 2021, 52, 1098–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Ghouizi, A.; Bakour, M.; Laaroussi, H.; Ousaaid, D.; El Menyiy, N.; Hano, C.; Lyoussi, B. Bee Pollen as Functional Food: Insights into Its Composition and Therapeutic Properties. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisani, A.; Protano, G.; Riccobono, F. Minor and trace elements in different honey types produced in Siena County (Italy). Food Chem. 2008, 107, 1553–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Martín, M.I.; Escuredo, O.; Revilla, I.; Vivar-Quintana, A.M.; Coello, M.C.; Riocerezo, C.P.; Moncada, G.W. Determination of the Mineral Composition and Toxic Element Contents of Propolis by Near Infrared Spectroscopy. Sensors 2015, 15, 27854–27868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipiak, M.; Shields, M.W.; Cairns, S.M.; Grainger, M.N.C.; Wratten, S.D. The conserved and high K-to-Na ratio in sunflower pollen: Possible implications for bee health and plant-bee interactions. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1042348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, P.J. Chapter 2—Ion Uptake Mechanisms of Individual Cells and Roots: Short-distance Transport. In Marschner’s Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants, 3rd ed.; Marschner, P., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2012; pp. 7–47. [Google Scholar]
- Girault, F.; Perrier, F.; Ourcival, J.-M.; Ferry, R.; Gaudemer, Y.; Bourges, F.; Didon-Lescot, J.-F. Substratum influences uptake of radium-226 by plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 766, 142655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannides, K.G.; Mertzimekis, T.J.; Papachristodoulou, C.A.; Tzialla, C.E. Measurements of natural radioactivity in phosphate fertilizers. Sci. Total Environ. 1997, 196, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IAEA. The Environmental Behaviour of Radium: Revised Edition; International Atomic Energy Agency: Vienna, Austria, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bulubasa, G.; Costinel, D.; Miu, A.F.; Ene, M.R. Activity concentrations of 238U, 232Th, 226Ra 137Cs and 40K radionuclides in honey samples from Romania. Lifetime cancer risk estimated. J. Environ. Radioact. 2021, 234, 106626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dizman, S.; Hodolli, G.; Kadiri, S.; Aliu, H.; Makolli, S. Radioactivity in Kosovo Honey Samples. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2020, 29, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jędrzejek, F.; Szarłowicz, K. Evaluation and reduction of background interference caused by airborne particles in gamma spectrometry measurements. Measurement 2024, 232, 114730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulhendri, F.; Perera, C.O.; Tandean, S.; Abdulah, R.; Herman, H.; Christoper, A.; Chandrasekaran, K.; Putra, A.; Lesmana, R. The Potential Use of Propolis as a Primary or an Adjunctive Therapy in Respiratory Tract-Related Diseases and Disorders: A Systematic Scoping Review. Biomed. Pharmacoth. 2022, 146, 112595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICRP. The 2007 Recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection, ICRP publication 103. Ann. ICRP 2007, 37, 1–332. [Google Scholar]
- California Environmental Protection Agency Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment. Cancer Risk and Noncancer Hazard Index. 2020. Available online: https://oehha.ca.gov/sites/default/files/media/downloads/risk-assessment/fact-sheet-california-human-health-screening-levels-chhsls/riskfactsheet.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- Jędrzejek, F.; Katarzyna, S.; Najman, J. Bee Products as a Bioindicators of Radionuclide Contamination, Draft Version ed.; AGH University of Krakow: Kraków, Poland, 2025. [Google Scholar]
| Element (Age) | Dose for Honey [µSv y−1] (15 kg y−1) 1 | Dose for Honey [µSv y−1] (0.83 kg y−1) 1 | Dose for Bee Bread [µSv y−1] (7.3 kg y−1) 1 | Dose for Propolis [µSv y−1] (0.05 kg y−1) 1 | Dose for Bee Pollen [µSv y−1] (1.8 kg y−1) 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 137Cs (adult) | 0.031–0.277 | 0.002–0.015 | 0.05–0.67 | 0.0003–0.0036 | 0.006–0.023 |
| 137Cs (10 y) | - | 0.001–0.012 | 0.04–0.52 | 0.0002–0.0028 | 0.005–0.018 |
| 137Cs (15 y) | - | 0.002–0.015 | 0.05–0.67 | 0.0003–0.0036 | 0.006–0.023 |
| 40K (adult) | 0.354–16.092 | 0.020–0.890 | ~7.67 | 0.002–0.040 | 0.185–2.605 |
| 40K (10 y) | - | 0.041–1.867l | ~16.08 | 0.005–0.083 | 0.388–5.461 |
| 40K (15 y) | - | 0.024–1.092 | ~9.40 | 0.003–0.049 | 0.227–3.193 |
| 226Ra (adult) | 1.23–91.36 | 0.068–5.055 | 1.27–1.75 | 0.012–0.035 | 0.635–1.455 |
| 226Ra (10 y) | - | 0.195–14.444 | 3.62–5.00 | 0.035–0.101 | 1.814–4.158 |
| 226Ra (15 y) | - | 0.365–27.082 | 6.78–9.38 | 0.066–0.189 | 3.402–7.797 |
| Product (Consumption) | Mean Total Dose [µSv y−1] (Adult) | Mean Total Dose [µSv y−1] (10 y) | Mean Total Dose [µSv y−1] (15 y) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Honey (15 kg y−1) | 10.28 | - | - |
| Honey (0.83 kg y−1) | 0.57 | 1.46 | 2.16 |
| Bee bread (7.3 kg y−1) | 2.16 | 4.81 | 5.95 |
| Propolis (0.05 kg y−1) | 0.025 | 0.060 | 0.086 |
| Bee pollen (1.8 kg y−1) | 2.68 | 6.16 | 6.27 |
| Product | CR for 137Cs Mortality [10−8] Mean (Range) | CR for 137Cs Morbidity [10−8] Mean (Range) | CR for 40K Mortality [10−6] Mean (Range) | CR for 40K Morbidity [10−6] Mean (Range) | CR for 226Ra Mortality [10−6] Mean (Range) | CR for 226Ra Morbidity [10−6] Mean (Range) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Honey for consumption 15 kg y−1 | 16.6 (8.3–73.4) | 24.4 (12.2–107.7) | 19.0 (1.7–76.4) | 29.8 (2.6–120.2) | 12.4 (2.1–156.0) | 18.0 (3.1–226.8) |
| Honey for consumption 0.83 kg y−1 | 0.9 (0.5–4.1) | 1.4 (0.7–6.0) | 1.1 (0.1–4.2) | 1.7 (0.1–6.6) | 0.7 (0.1–8.6) | 1.0 (0.2–12.5) |
| Bee bread for consumption 7.3 kg y−1 | 92.1 (13.5–177.4) | 135.1 (19.8–260.4) | ~36.4 | ~57.3 | 2.4 (2.2–3.0) | 3.5 (3.1–4.3) |
| Propolis for consumption 0.05 kg y−1 | 0.43 (0.08–0.96) | 0.63 (0.11–1.41) | 0.07 (0.01–0.19) | 0.12 (0.02–0.30) | 0.04 (0.02–0.06) | 0.06 (0.03–0.09) |
| Bee pollen for consumption 1.8 kg y−1 | 5.0 (1.6–6.2) | 7.3 (2.3–9.1) | 9.2 (0.9–12.4) | 14.5 (1.4–19.5) | 1.6 (1.1–2.5) | 2.3 (1.6–3.6) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szarłowicz, K.; Jędrzejek, F.; Najman, J. Bee Products as a Bioindicator of Radionuclide Contamination: Environmental Approach and Health Risk Evaluation. Sustainability 2025, 17, 6798. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17156798
Szarłowicz K, Jędrzejek F, Najman J. Bee Products as a Bioindicator of Radionuclide Contamination: Environmental Approach and Health Risk Evaluation. Sustainability. 2025; 17(15):6798. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17156798
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzarłowicz, Katarzyna, Filip Jędrzejek, and Joanna Najman. 2025. "Bee Products as a Bioindicator of Radionuclide Contamination: Environmental Approach and Health Risk Evaluation" Sustainability 17, no. 15: 6798. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17156798
APA StyleSzarłowicz, K., Jędrzejek, F., & Najman, J. (2025). Bee Products as a Bioindicator of Radionuclide Contamination: Environmental Approach and Health Risk Evaluation. Sustainability, 17(15), 6798. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17156798








