Iterative Learning Control for Virtual Inertia: Improving Frequency Stability in Renewable Energy Microgrids
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. System Configuration and Modeling
2.1. Fundamental Frequency Regulation
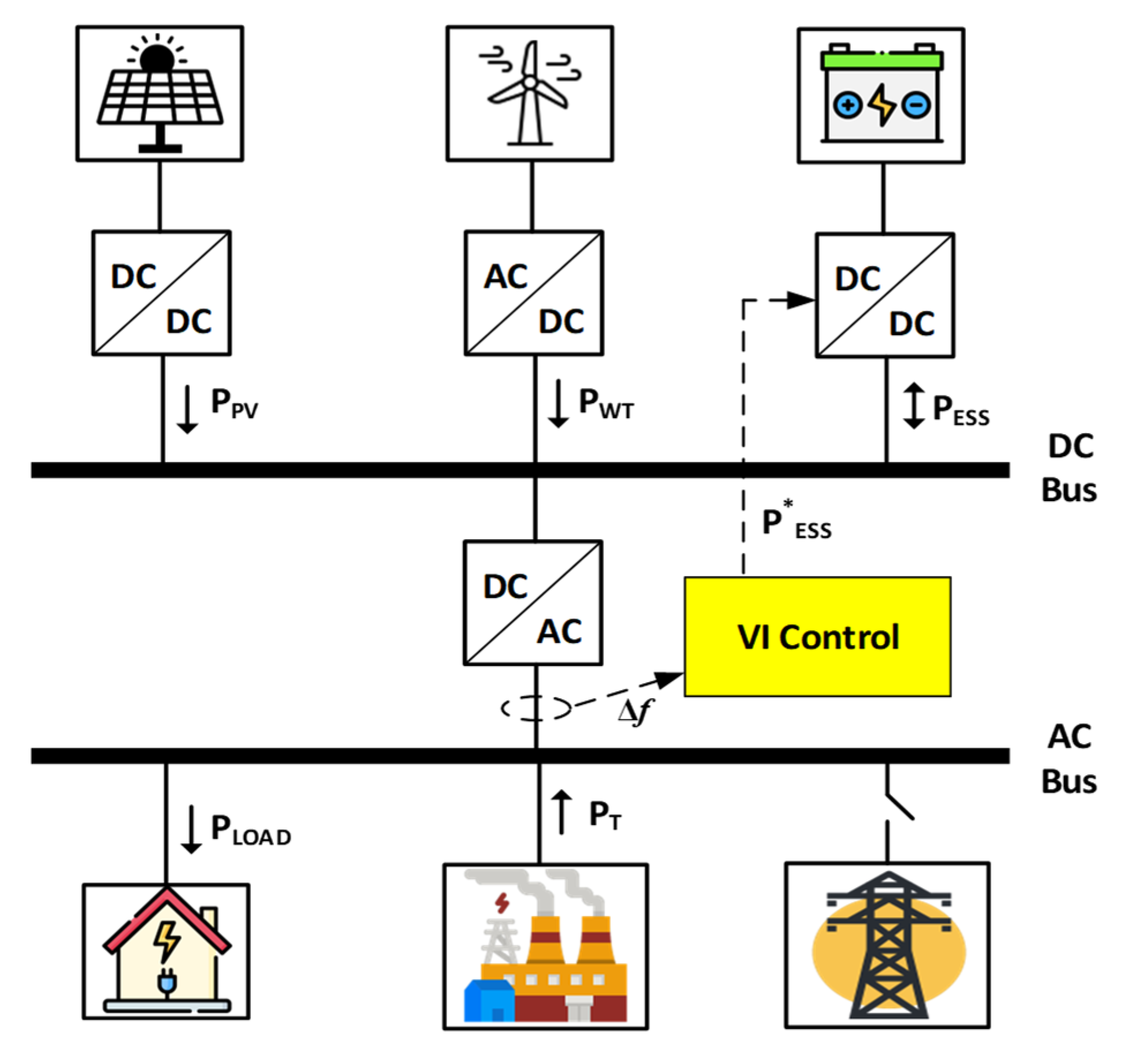
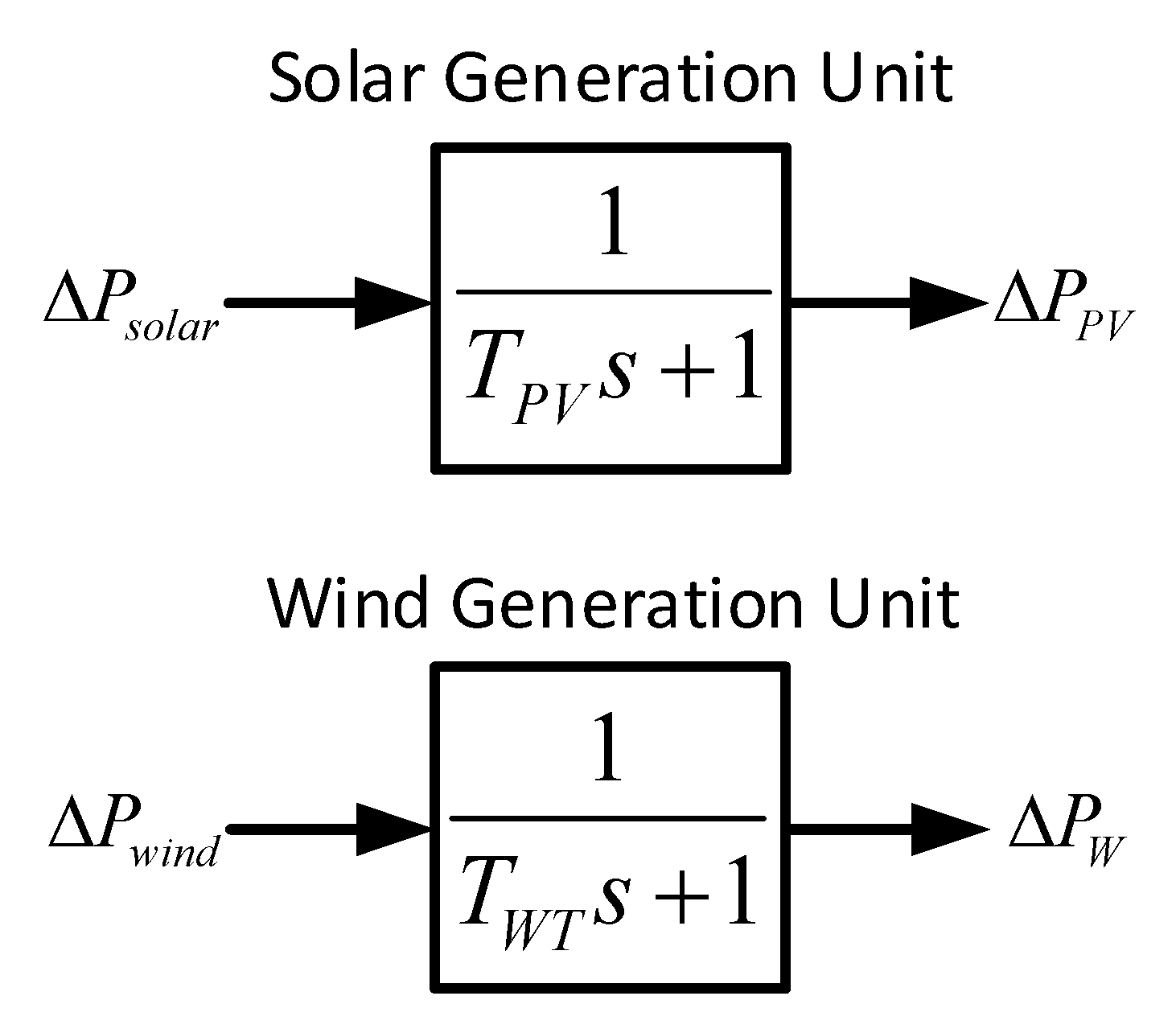
2.2. Microgrid Dynamic and Modeling
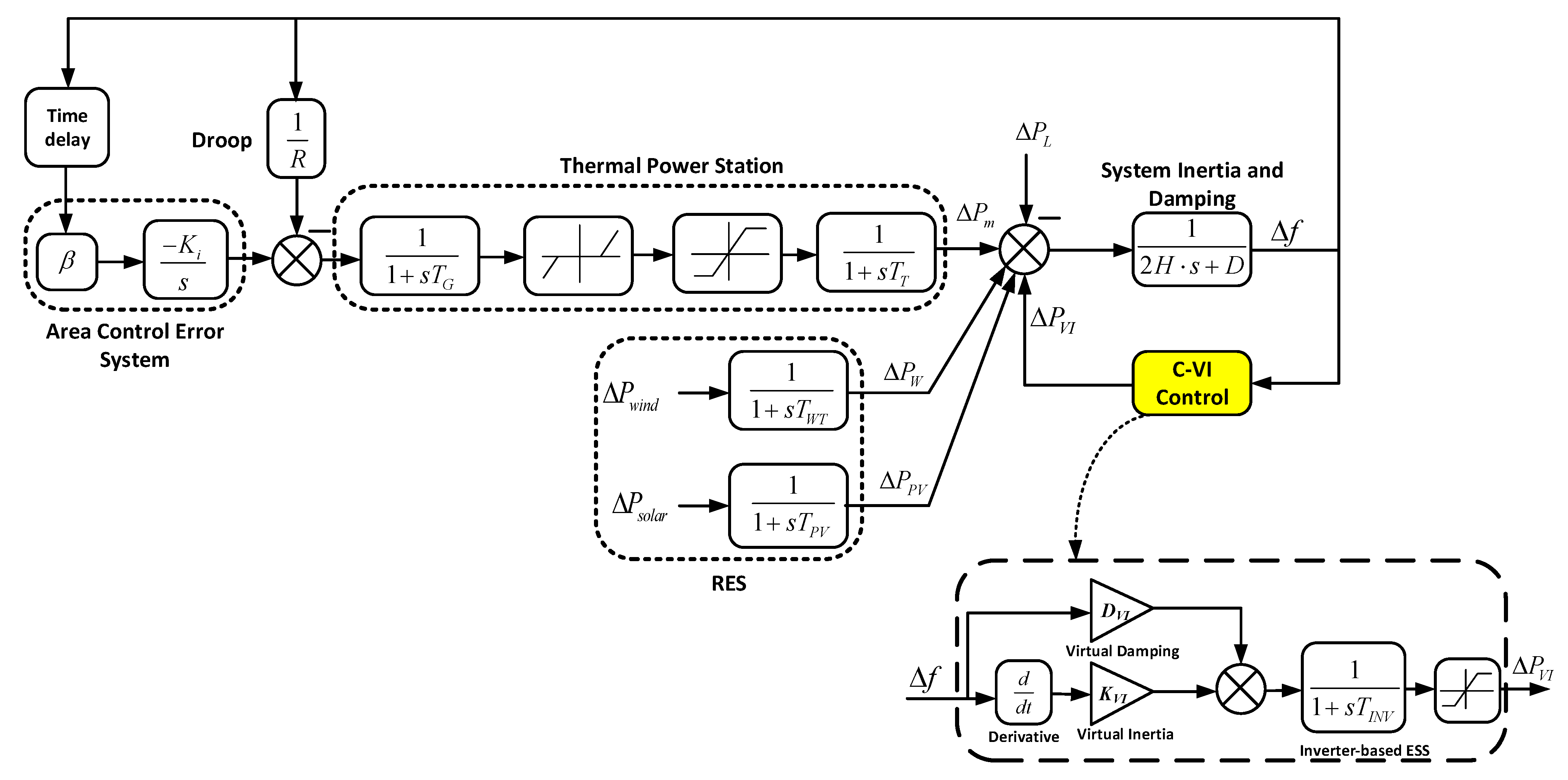
2.3. Conventional Virtual Inertia Control for Islanded Microgrids
2.4. State-Space Modeling of Microgrid
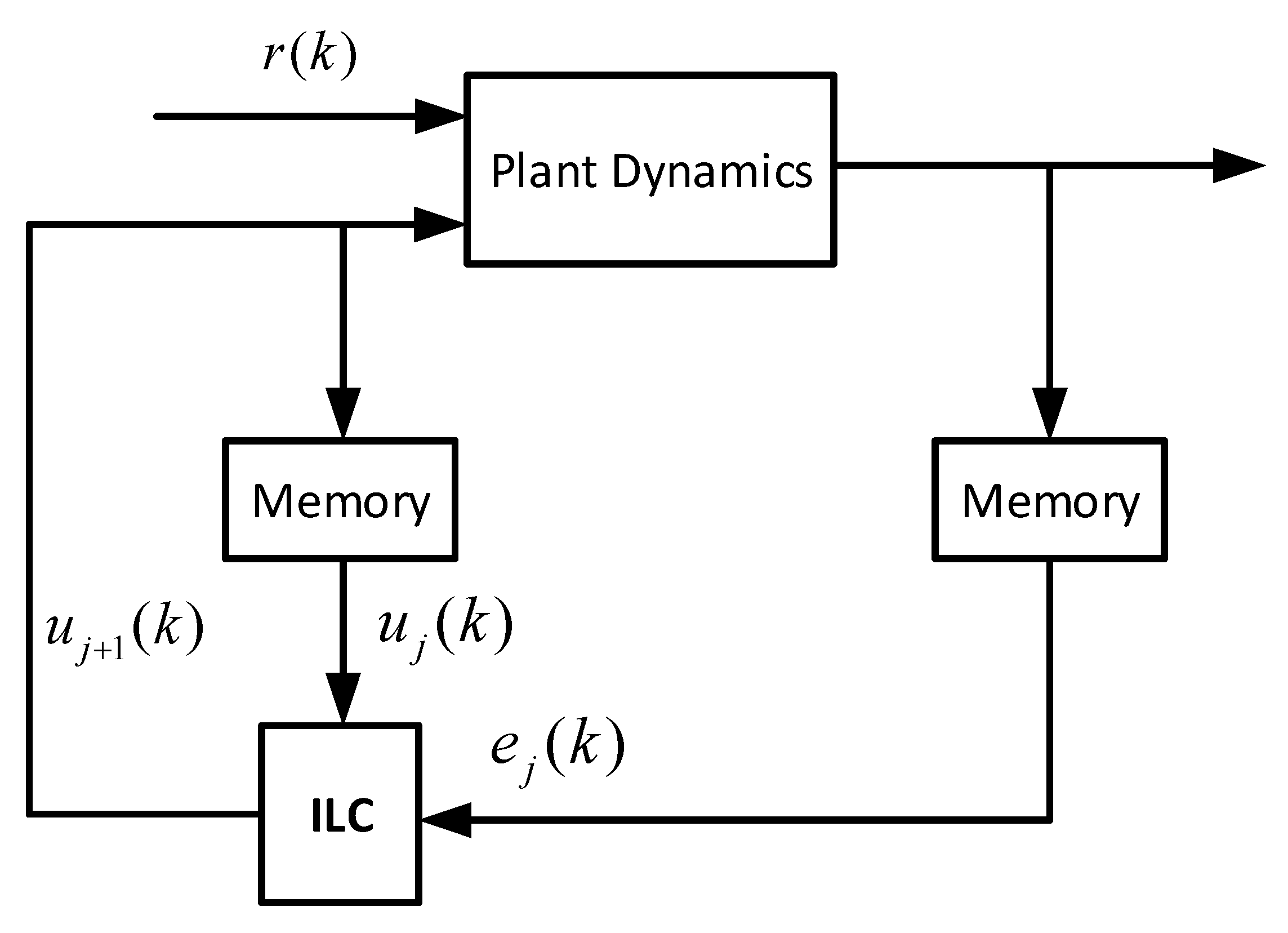
3. Designing Iterative Learning Control for Frequency Regulation
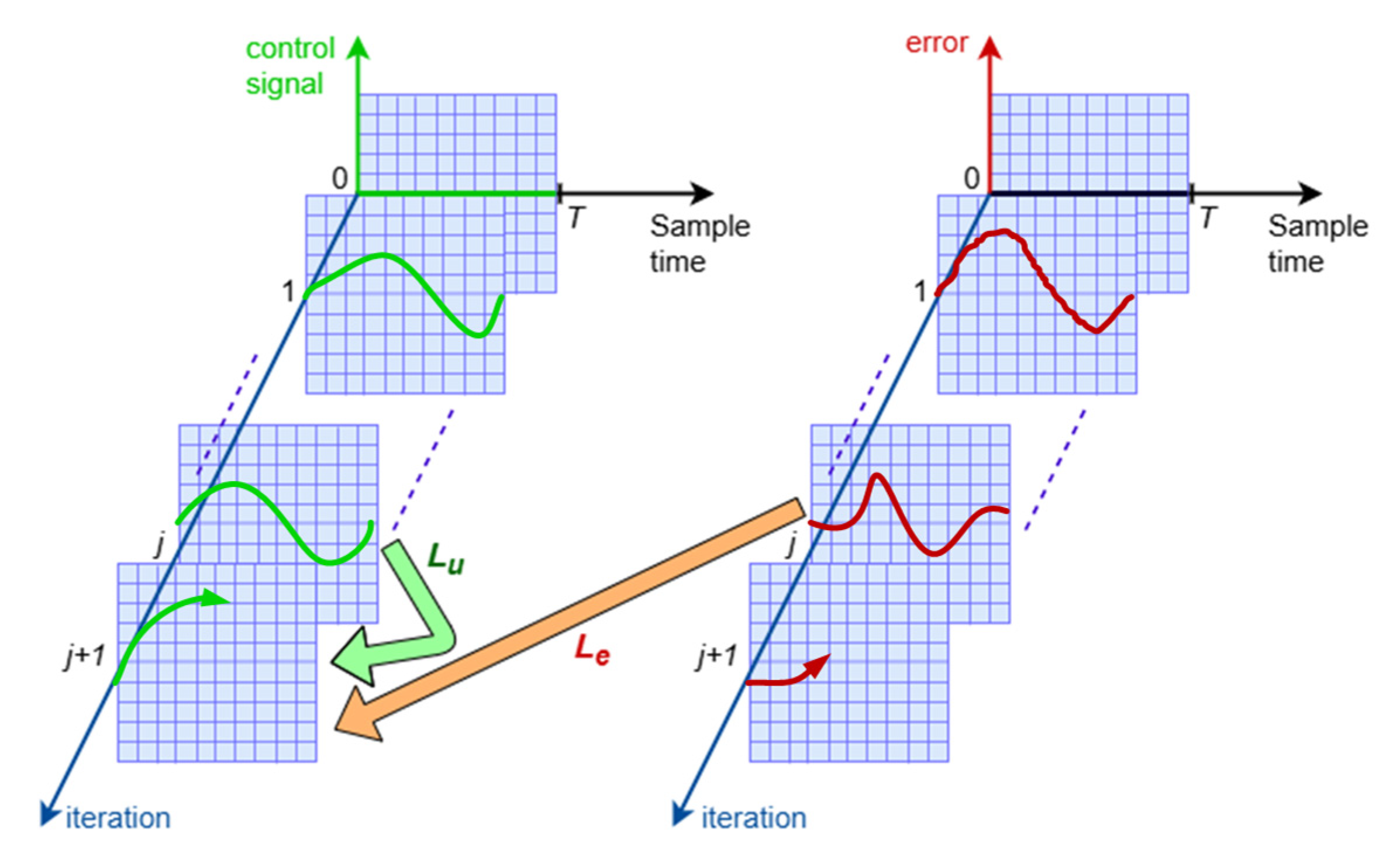
3.1. Basic Concept of Iterative Learning Control
- The system must incorporate ILC within a fixed time interval;
- In each iteration, ILC must generate an output signal to the same reference setpoint;
- The initial state of each iteration should be reset to the same value.
3.2. Virtual Inertia Control Based Iterative Learning Control
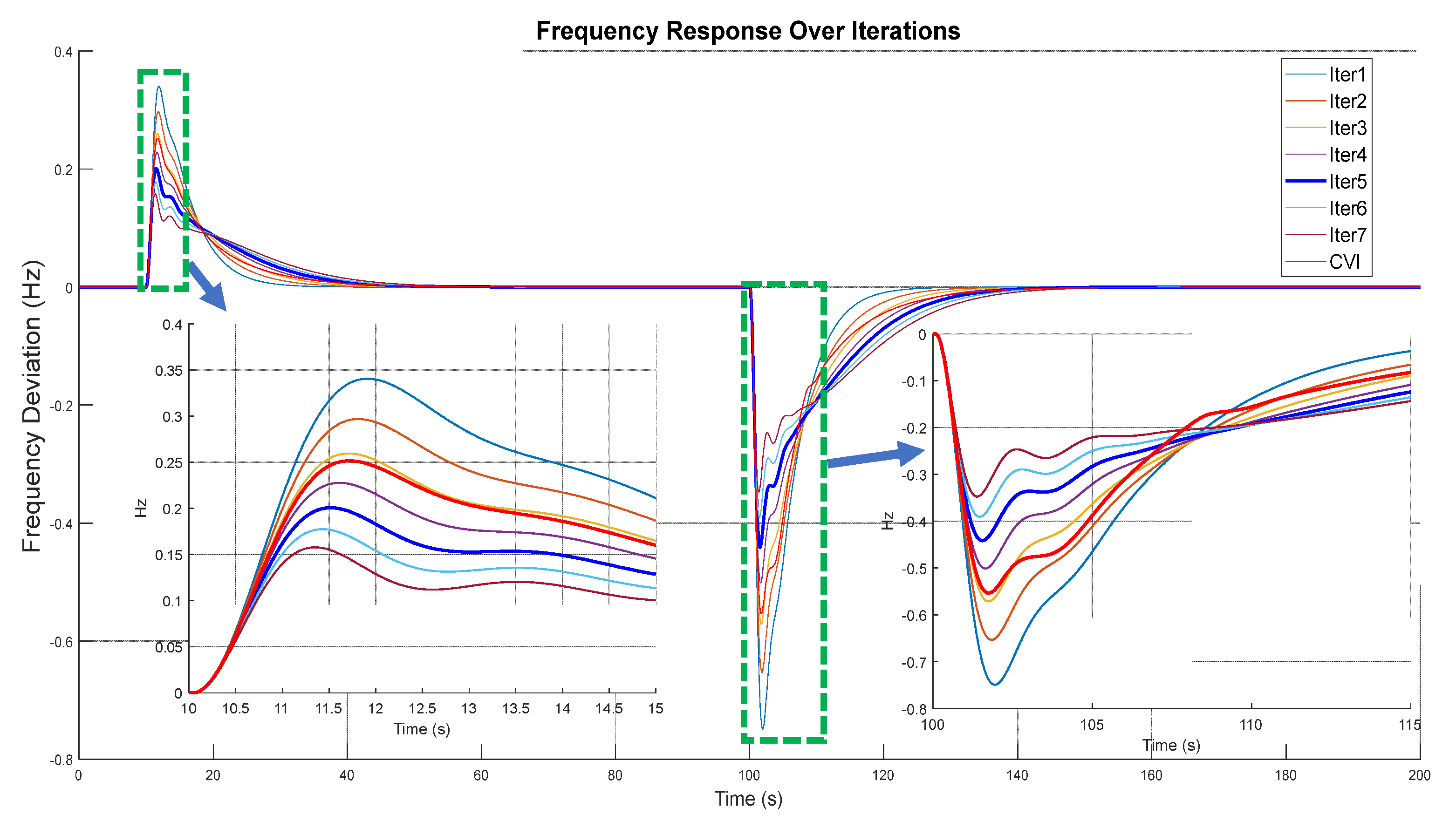
4. Simulation Results and Discussions
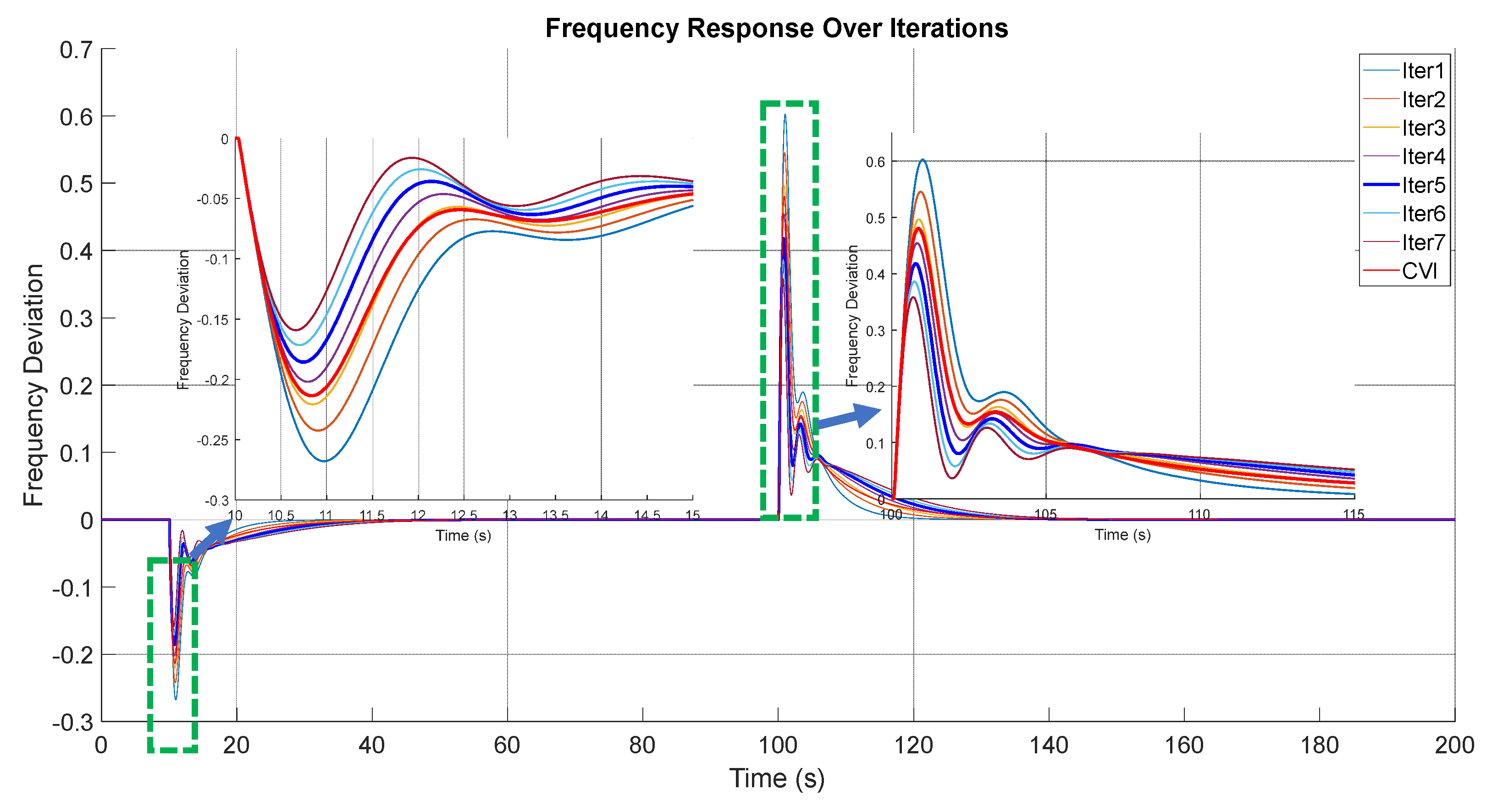
4.1. Scenario 1: Unit Step Load Power and Constant RES Power
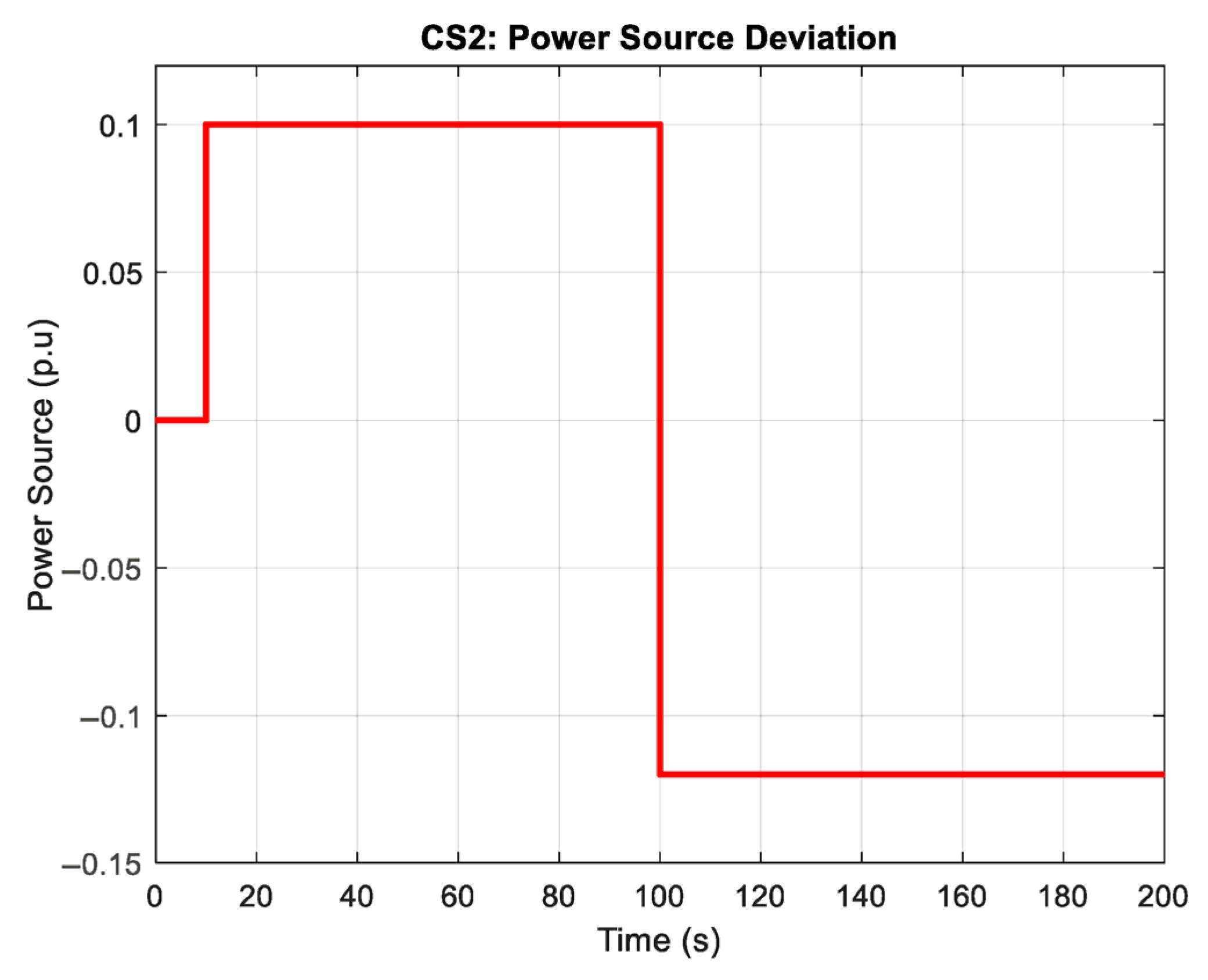
4.2. Scenario 2: Unit Step RES Power and Constant Load Power
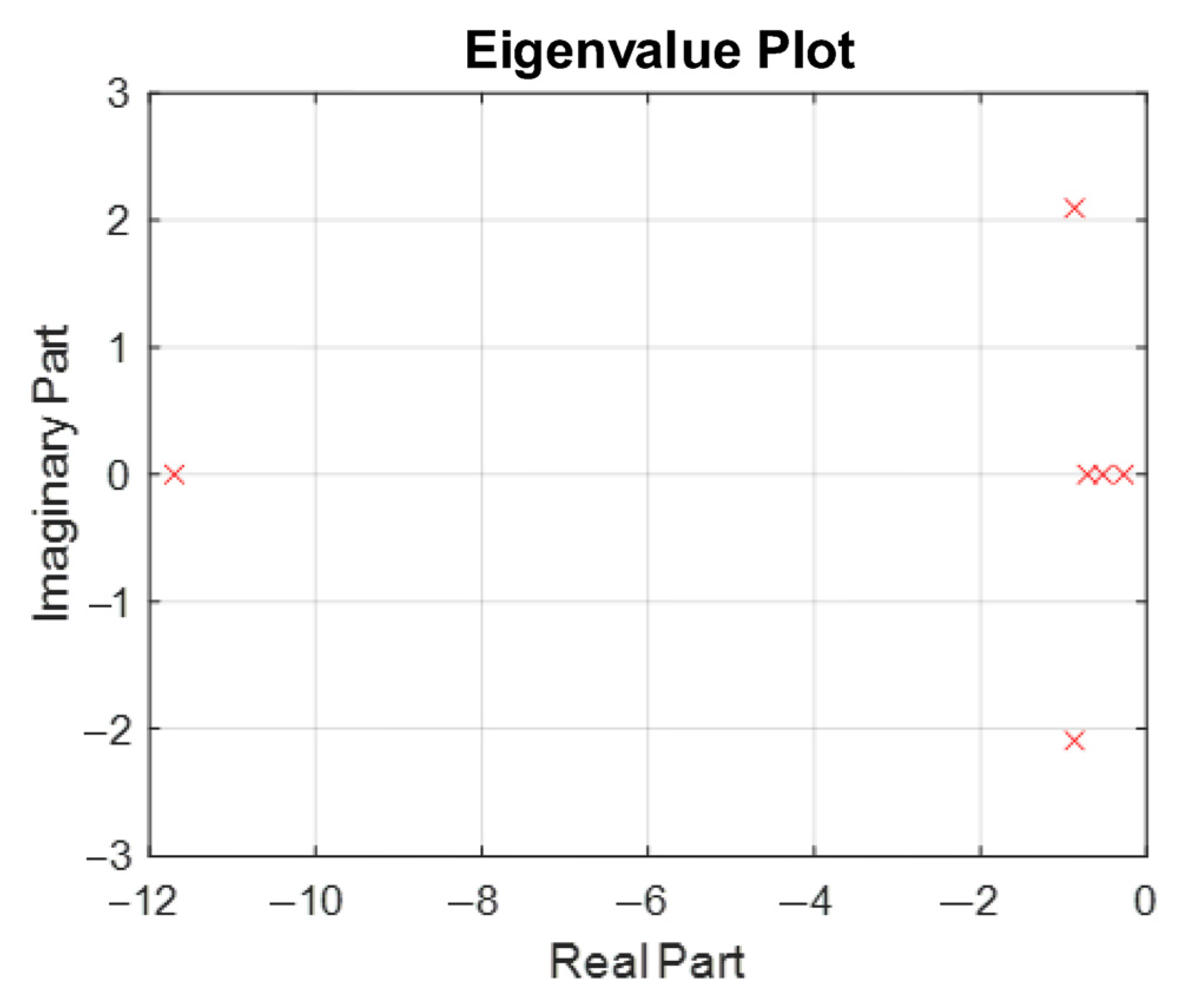
4.3. Parameter Selection Methodology and Sensitivity Analysis
4.4. Discussion on Complex Scenarios, Scalability, and Implementation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ILC | Iterative Learning Control |
| P | Proportional |
| PD | Proportional–Derivative |
| VI | Virtual Inertia |
| C-VI | Conventional Virtual Inertia |
| ESS | Energy Storage System |
| MG | Microgrid |
| DG | Distributed Generation |
| ACE | Area Control Error |
| RoCoF | Rate of Change of Frequency |
| RESs | Renewable Energy Sources |
| GRC | Generation Rate Constraint |
| GDB | Governor Dead Band |
| LQ | Linear–Quadratic |
References
- Ulbig, A.; Borsche, T.S.; Andersson, G. Analyzing rotational inertia, grid topology and their role for power system stability. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2015, 48, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, M.Q.; Tran, N.T.N.; Sava, G.N.; Leva, S.; Mussetta, M. The Impact of 150 MWp PhoAn Solar Photovoltaic Project into Vietnamese QuangNgai-Grid. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference and Exposition on Electrical and Power Engineering (EPE), Iasi, Romania, 18–19 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bevrani, H. Robust Power System Frequency Control; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kerdphol, T.; Rahman, F.S.; Watanabe, M.; Mitani, Y. Virtual Inertia Synthesis and Control; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, P.; Alimi, O.A.; Abu-Siada, A. A Review of System Strength and Inertia in Renewable-Energy-Dominated Grids: Challenges, Sustainability, and Solutions. Challenges 2025, 16, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevrani, H.; Ise, T.; Miura, Y. Virtual synchronous generators: A survey and new perspectives. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2014, 54, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harasis, S. Controllable transient power sharing of inverter-based droop controlled microgrid. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2024, 155, 109565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Yang, G.; Yao, L. Transient Frequency Modeling and Characteristic Analysis of Virtual Synchronous Generator. Energies 2025, 18, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harasis, S.; Sozer, Y. Improved Transient Frequency Stabilization of Grid Feeding Distributed Generation Systems Using Active Damping Control. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Baltimore, MD, USA, 29 September–3 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, V.T.; Nguyen, H.V.P.; Truong, T.B.T.; Truong, Q.V. A virtual synchronous generator control method in microgrid with vehicle-to-grid system. J. Electr. Eng. 2023, 74, 492–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesse, R.; Turschner, D.; Beck, H.P. Microgrid stabilization using the Virtual Synchronous Machine (VISMA). In Proceedings of the International Conference on Renewable Energies and Power Quality (ICREPQ’09), Valencia, Spain, 15–17 April 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Shadoul, M.; Ahshan, R.; AlAbri, R.S.; Al-Badi, A.; Albadi, M.; Jamil, M.A. A comprehensive review on a virtual-synchronous generator: Topologies, control orders and techniques, energy storages, and applications. Energies 2022, 15, 8406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakimoto, K.; Miura, Y.; Ise, T. Stabilization of a power system with a distributed generator by a Virtual Synchronous Generator function. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Power Electronics—ECCE Asia, Jeju, Republic of Korea, 30 May–3 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Tamrakar, U.; Shrestha, D.; Maharjan, M.; Bhattarai, B.P.; Hansen, T.M.; Tonkoski, R. Virtual inertia: Current trends and future directions. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerdphol, T.; Rahman, F.S.; Mitani, Y.; Hongesombut, K.; Küfeoğlu, S. Virtual Inertia Control-Based Model Predictive Control for Microgrid Frequency Stabilization Considering High Renewable Energy Integration. Sustainability 2017, 9, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, A.; Hasanien, H.M.; Turky, R.A.; Turdybek, B.; Alharbi, M.; Jurado, F.; Omran, W.A. Optimal Model Predictive Control for Virtual Inertia Control of Autonomous Microgrids. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaid, S.A.; Bakeer, A.; Magdy, G.; Albalawi, H.; Kassem, A.M.; El-Shimy, M.E.; AbdelMeguid, H.; Manqarah, B. A New Intelligent Fractional-Order Load Frequency Control for Interconnected Modern Power Systems with Virtual Inertia Control. Fractal Fract. 2023, 7, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerdphol, T.; Rahman, F.S.; Mitani, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Küfeoǧlu, S.K. Robust Virtual Inertia Control of an Islanded Microgrid Considering High Penetration of Renewable Energy. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, A.; Omran, W.A.; Hasanien, H.M.; Tostado-Véliz, M.; Alkuhayli, A.; Jurado, F. Manta Ray Foraging Optimization for the Virtual Inertia Control of Islanded Microgrids Including Renewable Energy Sources. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skiparev, V.; Machlev, R.; Chowdhury, N.R.; Levron, Y.; Petlenkov, E.; Belikov, J. Virtual Inertia Control Methods in Islanded Microgrids. Energies 2021, 14, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunnarsson, S.; Norrlöf, M. A Short Introduction to Iterative Learning Control; Linköping University Electronic Press: Linköping, Sweden, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, X.; Mo, R.; Wang, P.; Chen, J.; Nan, D.; Liu, M. Review of RoCoF Estimation Techniques for Low-Inertia Power Systems. Energies 2023, 16, 3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Li, H.; Tang, Y.; Blaabjerg, F. On the Inertia of Future More-Electronics Power Systems. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2019, 7, 2130–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Sahu, P.R.; Prusty, R.C.; Panda, S.; Ustun, T.S.; Onen, A. Application of Enhanced Self-Adaptive Virtual Inertia Control for Efficient Frequency Control of Renewable Energy-Based Microgrid System Integrated with Electric Vehicles. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 43520–43531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Wu, Z.; Dinavahi, V. Dynamic Analysis and Model Order Reduction of Virtual Synchronous Machine Based Microgrid. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 106585–106600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamanah, W.M.; Shafiullah, M.; Alhems, L.M.; Alam, M.S.; Abido, M.A. Realization of Robust Frequency Stability in Low-Inertia Islanded Microgrids with Optimized Virtual Inertia Control. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 58208–58221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerdphol, T.; Rahman, F.S.; Watanabe, M.; Mitani, Y.; Turschner, D.; Beck, H.-P. Enhanced virtual inertia control based on derivative technique to emulate simultaneous inertia and damping properties for microgrid frequency regulation. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 14422–14433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsali, J.; Zare, K.; Hagh, M.T. Appropriate generation rate constraint (GRC) modeling method for reheat thermal units to obtain optimal load frequency controller (LFC). In Proceedings of the 2014 5th Conference on Thermal Power Plants (CTPP), Tehran, Iran, 10–11 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Shobug, M.A.; Chowdhury, N.A.; Hossain, M.A.; Sanjari, M.J.; Lu, J.; Yang, F. Virtual Inertia Control for Power Electronics-Integrated Power Systems: Challenges and Prospects. Energies 2024, 17, 2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, A.; Iravani, R. Voltage-Sourced Converters in Power Systems: Modeling, Control, and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, K.S. Iterative learning control applied to batch processes: An overview. Control Eng. Pract. 2007, 15, 1306–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estakhrouieh, M.R.; Gharaveisi, A.A. Optimal iterative learning control design for generator voltage regulation system. Turk. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2013, 21, 1909–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza-Alikhani, H.-R.; Madady, A. Monotonic convergence conditions in PD type iterative learning control. In Proceedings of the 2011 19th Mediterranean Conference on Control & Automation (MED), Corfu, Greece, 20–23 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bristow, D.A.; Tharayil, M.; Alleyne, A.G. A survey of iterative learning control. IEEE Control Syst. Mag. 2006, 26, 96–114. [Google Scholar]
- Longman, R.W.; Liu, S.; Elsharhawy, T.A. A Method to Speed Up the Convergence of Iterative Learning Control for High Precision Repetitive Motion. In Proceedings of the AIAA/AAS Astrodynamics Specialist Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 13–17 August 2023. [Google Scholar]





| Symbol | Quantity | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Ki | Gain of integral controller | 0.1 |
| TG | Governor time constant | 0.09 (s) |
| TT | Turbine time constant | 0.4 (s) |
| R | Governor droop constant | 2.6 (Hz/p.u.) |
| β | Bias factor | 0.98 (p.u./Hz) |
| KVI | Virtual inertia constant | 0.2 (p.u. s) |
| DVI | Virtual damping constant | 0.3 (p.u./Hz) |
| TINV | Time constant of inverter-based ESS | 3.0 (s) |
| TW | Time constant of wind turbine | 1.4 (s) |
| TPV | Time constant of solar system | 1.9 (s) |
| H | Microgrid system inertia | 0.083 (p.u. s) |
| D | Microgrid system damping | 0.016 (p.u./Hz) |
| Lu | Filter parameter of ILC | I |
| Kp | Proportional gain of ILC | 0.11 |
| Kd | Derivative gain of ILC | 0.085 |
| Scenario | Frequency Nadir/Overshoot (Hz) | RoCoF (Hz/s) | Settling Time (s) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 s | C-VI | −0.22 | 0.368 | 35.4 |
| ILC-VI (5th trial) | −0.16 | 0.361 | 35.7 | ||
| 100 s | C-VI | 0.47 | 0.752 | 60 | |
| ILC-VI (5th trial) | 0.41 | 0.729 | 40.3 | ||
| 2 | 10 s | C-VI | 0.251 | 0.125 | 45 |
| ILC-VI (5th trial) | 0.2 | 0.11 | 43 | ||
| 100 s | C-VI | −0.553 | 0.242 | 50.5 | |
| ILC-VI (5th trial) | −0.441 | 0.231 | 47.4 | ||
| Parameter Variation | Kp | Kd | Frequency Nadir (Hz) | RoCoF (Hz/s) | Settling Time (s) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nominal | 0.11 | 0.085 | 0.174 | −0.16 | 0.361 | 35.7 |
| Kp + 20% | 0.132 | 0.085 | 0.246 | −0.154 | 0.355 | 34.2 |
| Kp − 20% | 0.088 | 0.085 | 0.102 | −0.18 | 0.368 | 37.1 |
| Kd + 20% | 0.11 | 0.102 | 0.209 | −0.155 | 0.358 | 35.0 |
| Kd − 20% | 0.11 | 0.068 | 0.139 | −0.165 | 0.364 | 36.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, V.T.; Truong, T.B.T.; Truong, Q.V.; Nguyen, H.V.P.; Duong, M.Q. Iterative Learning Control for Virtual Inertia: Improving Frequency Stability in Renewable Energy Microgrids. Sustainability 2025, 17, 6727. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17156727
Nguyen VT, Truong TBT, Truong QV, Nguyen HVP, Duong MQ. Iterative Learning Control for Virtual Inertia: Improving Frequency Stability in Renewable Energy Microgrids. Sustainability. 2025; 17(15):6727. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17156727
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Van Tan, Thi Bich Thanh Truong, Quang Vu Truong, Hong Viet Phuong Nguyen, and Minh Quan Duong. 2025. "Iterative Learning Control for Virtual Inertia: Improving Frequency Stability in Renewable Energy Microgrids" Sustainability 17, no. 15: 6727. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17156727
APA StyleNguyen, V. T., Truong, T. B. T., Truong, Q. V., Nguyen, H. V. P., & Duong, M. Q. (2025). Iterative Learning Control for Virtual Inertia: Improving Frequency Stability in Renewable Energy Microgrids. Sustainability, 17(15), 6727. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17156727









