Simulating the Impacts of Climate Change on the Hydrology of Doğancı Dam in Bursa, Turkey, Using Feed-Forward Neural Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Artificial Neural Networks and Their Requisites
2.2. Data Attainment
2.3. The Selection of the ANN Model
2.4. Training of a Feed-Forward Neural Network
2.5. Performance Evaluation
2.6. ANN Application
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cooper, S.D.; Lake, P.S.; Sabater, S.; Melack, J.M.; Sabo, J.L. The effects of land use changes on streams and rivers in mediterranean climates. Hydrobiologia 2013, 719, 383–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondolf, G.M.; Gao, Y.; Annandale, G.W.; Morris, G.L.; Jiang, E.; Zhang, J.; Cao, Y.; Carling, P.; Fu, K.; Guo, Q.; et al. Sustainable sediment management in reservoirs and regulated rivers: Experiences from five continents. Earth’s Future 2014, 2, 256–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogeboom, R.J.; Knook, L.; Hoekstra, A.Y. The blue water footprint of the world’s artificial reservoirs for hydroelectricity, irrigation, residential and industrial water supply, flood protection, fishing and recreation. Adv. Water Resour. 2018, 113, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamoglou, M.; Papadimitriou, T.; Kagalou, I. Key-descriptors for the functioning of a Mediterranean reservoir: The case of the new Lake Karla-Greece. Environ. Process. 2014, 1, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, R.; Pielke Sr, R.A.; Hubbard, K.G.; Niyogi, D.; Dirmeyer, P.A.; McAlpine, C.; Carleton, A.M.; Hale, R.; Gameda, S.; Beltrán-Przekurat, A.; et al. Land cover changes and their biogeophysical effects on climate. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 929–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casserly, C.M.; Turner, J.N.; O’sullivan, J.J.; Bruen, M.; Bullock, C.; Atkinson, S.; Kelly-Quinn, M. Impact of low-head dams on bedload transport rates in coarse-bedded streams. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 716, 136908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ye, M.; Yang, J. Developing a Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) based model for predicting water table depth in agricultural areas. J. Hydrol. 2018, 561, 918–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, M.; Zaid-Alkelani, M. Prediction of water demand using artificial neural networks models and statistical model. Int. J. Intell. Syst. Appl. 2019, 11, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshorbagy, A.; Simonovic, S.; Panu, U. Performance evaluation of artificial neural networks for runoff prediction. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2000, 5, 424–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McJannet, D.; Cook, F.; Burn, S. Comparison of techniques for estimating evaporation from an irrigation water storage. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 1415–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouali, D.; Chebana, F.; Ouarda, T.B. Fully nonlinear statistical and machine-learning approaches for hydrological frequency estimation at ungauged sites. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2017, 9, 1292–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaseen, Z.M. A new benchmark on machine learning methodologies for hydrological processes modelling: A comprehensive review for limitations and future research directions. Knowl.-Based Eng. Sci. 2023, 4, 65–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourani, V.; Molajou, A.; Najafi, H.; Danandeh Mehr, A. Emotional ANN (EANN): A new generation of neural networks for hydrological modeling in IoT. In Artificial Intelligence in IoT; Springer: Cham, Switzerland; Geneva, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 45–61. [Google Scholar]
- Tabbussum, R.; Dar, A.Q. Performance evaluation of artificial intelligence paradigms—Artificial neural networks, fuzzy logic, and adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system for flood prediction. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 25265–25282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaseen, Z.M.; Naganna, S.R.; Sa’adi, Z.; Samui, P.; Ghorbani, M.A.; Salih, S.Q.; Shahid, S. Hourly river flow forecasting: Application of emotional neural network versus multiple machine learning paradigms. Water Resour. Manag. 2020, 34, 1075–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyebode, O.; Stretch, D. Neural network modeling of hydrological systems: A review of implementation techniques. Nat. Resour. Model. 2019, 32, e12189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y. Advances in artificial neural networks–methodological development and application. Algorithms 2009, 2, 973–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Üneş, F.; Demirci, M.; Kişi, Ö. Prediction of millers ferry dam reservoir level in USA using artificial neural network. Period. Polytech. Civ. Eng. 2015, 59, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valipour, M.; Banihabib, M.E.; Behbahani, S.M.R. Comparison of the ARMA, ARIMA, and the autoregressive artificial neural network models in forecasting the monthly inflow of Dez dam reservoir. J. Hydrol. 2013, 476, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadiyan, P.P.; Moeini, R.; Ehsanzadeh, E. Application of static and dynamic artificial neural networks for forecasting inflow discharges, case study: Sefidroud Dam reservoir. Sustain. Comput. Inform. Syst. 2020, 27, 100401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, S.; Parekh, F. Application of artificial neural network (ANN) for reservoir water level forecasting. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2014, 3, 1077–1082. [Google Scholar]
- Üneş, F.; Demirci, M.; Başar, B.; Kaya, Y.Z.; Varçın, H. Estimating dam reservoir level fluctuations using data-driven techniques. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2019, 28, 3451–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benzaghta, M.A.; Mohammed, T.A.; Ghazali, A.H.; Soom, M.A.M. Prediction of evaporation in tropical climate using artificial neural network and climate based models. Sci. Res. Essays 2012, 7, 3133–3148. [Google Scholar]
- Rungee, J.; Kim, U. Long-term assessment of climate change impacts on Tennessee Valley Authority reservoir operations: Norris Dam. Water 2017, 9, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salami, A.W.; Ibrahim, H.; Sojobi, A.O. Evaluation of impact of climate variability on water resources and yield capacity of selected reservoirs in the north central Nigeria. Environ. Eng. Res. 2015, 20, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, A.; Bormann, H.; Casper, M. Climate change impact assessment on a German lowland river using long short-term memory and conceptual hydrological models. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2025, 59, 102426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katip, A.; Anwar, A. Modeling the Influence of Climate Change on the Water Quality of Doğancı Dam in Bursa, Turkey, Using Artificial Neural Networks. Water 2025, 17, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Shin, J.-Y.; Kim, H.; Kim, S.; Heo, J.-H. The use of large-scale climate indices in monthly reservoir inflow forecasting and its application on time series and artificial intelligence models. Water 2019, 11, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J. A Study on the Improvement of Flood Season in Korea Considering the 21st Century Observations. Master’s Thesis, Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, College of Engineering, Seoul National University, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2022. Available online: https://dcollection.snu.ac.kr/common/orgView/000000173218 (accessed on 26 February 2025).
- IPCC. Climate Change 2022: Mitigation of Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Biswas, A.; Zhao, Y.; Niu, B.; Siddique, K.H. Assessing climate change and human impacts on runoff and hydrological droughts in the Yellow River Basin using a machine learning-enhanced hydrological modeling approach. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 380, 125091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Hu, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, C.; Lu, X.; Cheng, H. Exploring the temporal and spatial effects of city size on regional economic integration: Evidence from the Yangtze River Economic Belt in China. Land Use Policy 2023, 132, 106770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Pombo, N.; Pires, I.M.; Garcia, N.M. Is Overfitting in a Neural Network a Reliable Model for the Recognition of Activities of Daily Living? In Proceedings of the 5th EAI International Conference on Smart Objects and Technologies for Social Good, Valencia, Spain, 25–27 September 2019; pp. 223–226. [Google Scholar]
- Pachauri, R.K.; Pachauri, R.K.; Allen, M.R.; Barros, V.R.; Broome, J.; Cramer, W.; Christ, R.; Church, J.A.; Clarke, L.; Dahe, Q.; et al. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change in Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- BUSKI. Baraj Doluluk Oranları. Available online: https://www.buski.gov.tr/baraj-detay (accessed on 7 January 2025).
- Koç, A.A.; Codron, J.M.; Tekelioğlu, Y.; Lemeilleur, S.; Tozanli, S.; Aksoy, Ş.; Bignebat, C.; Demirer, R.; Mencet, N. Restructuring of Agrifood Chains in Turkey. In Regoverning Markets Agrifood Sector Studies (A); IIED: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Apaydin, H.; Feizi, H.; Sattari, M.T.; Colak, M.S.; Shamshirband, S.; Chau, K.-W. Comparative analysis of recurrent neural network architectures for reservoir inflow forecasting. Water 2020, 12, 1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okkan, U. Aylık Yağış ve Sıcaklık Değişimlerinin İzmir Içme Suyu Havzalarının Akımlarına Etkileri. Master’s Thesis, Fen Bilimleri Enstitüsü, Dokuz Eylül Üniversitesi, İzmir, Turkey, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Raşit, A. Namazgâh Barajında Meteorolojik Veriler Kullanılarak Yapay Sinir Ağları ile Akışın Tahmin Edilmesi. Master’s Thesis, Fen Bilimleri Enstitüsü, Kocaeli Üniversitesi, İzmit, Turkey, 2019. Available online: http://dspace.kocaeli.edu.tr:8080/xmlui/handle/11493/16790 (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Mata, J. Interpretation of concrete dam behaviour with artificial neural network and multiple linear regression models. Eng. Struct. 2011, 33, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozsoy, G.; Aksoy, E.; Karaata, E. Estimating soil loss of Doganci Dam watershed, northwest Turkey and lifetime analyze of Doganci Dam using multi-year remotely sensed data and GIS techniques. Soil-Water J. 2013, 2, 927–934. [Google Scholar]
- Stotz, C.L. The Bursa region of Turkey. Geogr. Rev. 1939, 29, 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erünal, E. Examining age structure and estimating mortality rates in Ottoman Bursa using mid-nineteenth-century population registers. Middle East. Stud. 2020, 57, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, R.M.; Ahmad, Z.; Don, M.M.; Uzir, M. Modelling and control of different types of polymerization processes using neural networks technique: A review. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2010, 88, 1065–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabari, H.; Talaee, P.H. Reconstruction of river water quality missing data using artificial neural networks. Water Qual. Res. J. Can. 2015, 50, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, G.; Bezuidenhout, C.; Bezuidenhout, J. Artificial neural networks: Applications in the drinking water sector. Water Supply 2018, 18, 1869–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najah, A.; El-Shafie, A.; Karim, O.A.; El-Shafie, A.H. Application of artificial neural networks for water quality prediction. Neural Comput. Appl. 2013, 22, 187–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.; Kim, Y.D.; Lee, J.M.; Kim, S.J. Hydro-environmental runoff projection under GCM scenario downscaled by artificial neural network in the Namgang Dam watershed, Korea. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2015, 19, 434–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruczyk, M. Long series of GNSS integrated precipitable water as a climate change indicator. Rep. Geod. Geoinform. 2015, 99, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mahdy, M.E.-S.; El-Abd, W.A.; Morsi, F.I. Forecasting lake evaporation under a changing climate with an integrated artificial neural network model: A case study Lake Nasser, Egypt. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2021, 179, 104191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svozil, D.; Kvasnicka, V.; Pospichal, J. Introduction to multi-layer feed-forward neural networks. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 1997, 39, 43–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad, R.N.M.R.; Ishak, W.H.W. Forecasting the flood stage of a reservoir based on the changes in upstream rainfall pattern. J. Technol. Oper. Manag. 2019, 14, 46–52. [Google Scholar]
- Damla, Y.; Temiz, T.; Keskin, E. Yapay sinir ağı kullanılarak su seviyesinin tahmin edilmesi: Yalova Gökçe barajı örneği. Kırklareli Üniversitesi Mühendislik Fen Bilim. Derg. 2020, 6, 32–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çalım, M.M. Estimation of Dam Reservoir Level with Artificial Neural Network Method. Master’s Thesis, Mustafa Kemal Üniversitesi, Antakya, Turkey, 2008. Available online: https://tez.yok.gov.tr/UlusalTezMerkezi/tezDetay.jsp?id=tPtS_heSMyicaKWhD0vd6w&no=hXyjBcHCUojyy4SSrKgk7A (accessed on 16 January 2025).
- Igel, C.; Toussaint, M.; Weishui, W. Rprop using the natural gradient. Trends Appl. Constr. Approx. 2005, 151, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavin, H.P. The Levenberg-Marquardt Algorithm for Nonlinear Least Squares Curve-Fitting Problems. Master’s Thesis, Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Duke University, Durham, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, R. Interpretation of the correlation coefficient: A basic review. J. Diagn. Med. Sonogr. 1990, 6, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; McAuley, K.; Harris, T. Selection of simplified models: I. Analysis of model-selection criteria using mean-squared error. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2011, 89, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicco, D.; Warrens, M.J.; Jurman, G. The coefficient of determination R-squared is more informative than SMAPE, MAE, MAPE, MSE and RMSE in regression analysis evaluation. Peerj Comput. Sci. 2021, 7, e623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathworks. Deep Learning Toolbox-Design, Train, Analyze, and Simulate Deep Learning Networks. In Deep Learning Toolbox; The Mathworks, Inc.: Natick, MA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wahir, N.; Nor, M.; Rusiman, M.; Gopal, K. Treatment of outliers via interpolation method with neural network forecast performances. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 995, 012025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaeianzadeh, M.; Stein, A.; Cox, J.P. Drought forecasting using Markov chain model and artificial neural networks. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 2245–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Üneş, F.; Varçın, H.; Dindar, K.K. Yapay sinir ağları yaklaşımı ile tahtaköprü barajındaki aylık buharlaşma tahmini. Eng. Sci. 2011, 6, 114–125. [Google Scholar]
- Khosravi, K.; Farooque, A.A.; Karbasi, M.; Ali, M.; Heddam, S.; Faghfouri, A.; Abolfathi, S. Enhanced water quality prediction model using advanced Hybridized resampling alternating tree-based and deep learning algorithms. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2025, 32, 6405–6424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khosravi, K.; Farooque, A.A.; Naghibi, A.; Heddam, S.; Sharafati, A.; Hatamiafkoueieh, J.; Abolfathi, S. Enhancing pan evaporation predictions: Accuracy and uncertainty in hybrid machine learning models. Ecol. Inform. 2025, 85, 102933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, J.A.; Bae, D.-H. Improving ANFIS based model for long-term dam inflow prediction by incorporating monthly rainfall forecasts. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 1185–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldardiry, H.; Hossain, F. The value of long-term streamflow forecasts in adaptive reservoir operation: The case of the High Aswan Dam in the transboundary Nile River basin. J. Hydrometeorol. 2021, 22, 1099–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amnatsan, S.; Yoshikawa, S.; Kanae, S. Improved forecasting of extreme monthly reservoir inflow using an analogue-based forecasting method: A case study of the Sirikit Dam in Thailand. Water 2018, 10, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beale, M.H.; Hagan, M.T.; Demuth, H.B. Neural network toolbox. In User’s Guide, MathWorks; The Mathworks, Inc.: Natick, MA, USA, 2010; Volume 2, pp. 77–81. [Google Scholar]
- Adeloye, A.; De Munari, A. Artificial neural network based generalized storage–yield–reliability models using the Levenberg–Marquardt algorithm. J. Hydrol. 2006, 326, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goss-Sampson, M. Statistical analysis in JASP: A Guide for Students; JASP: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
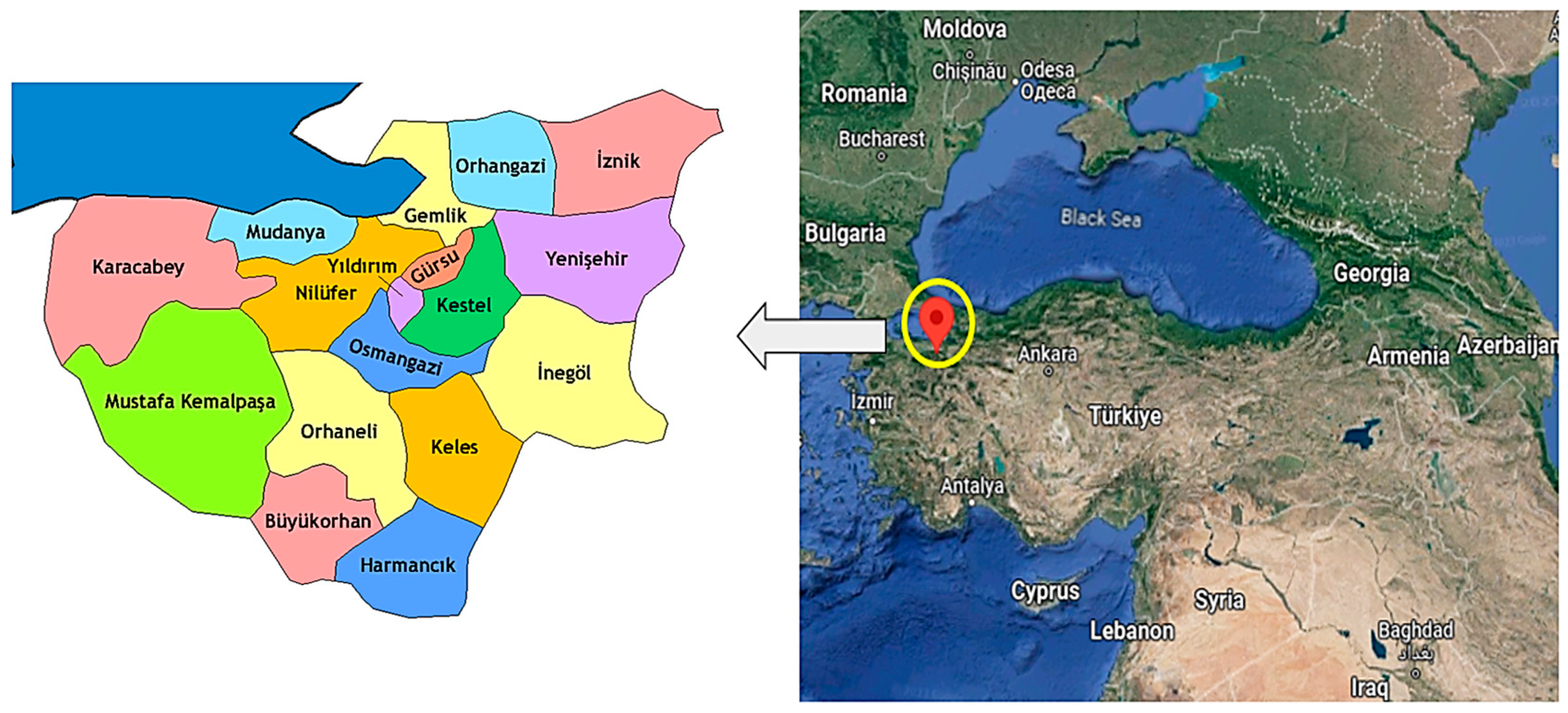

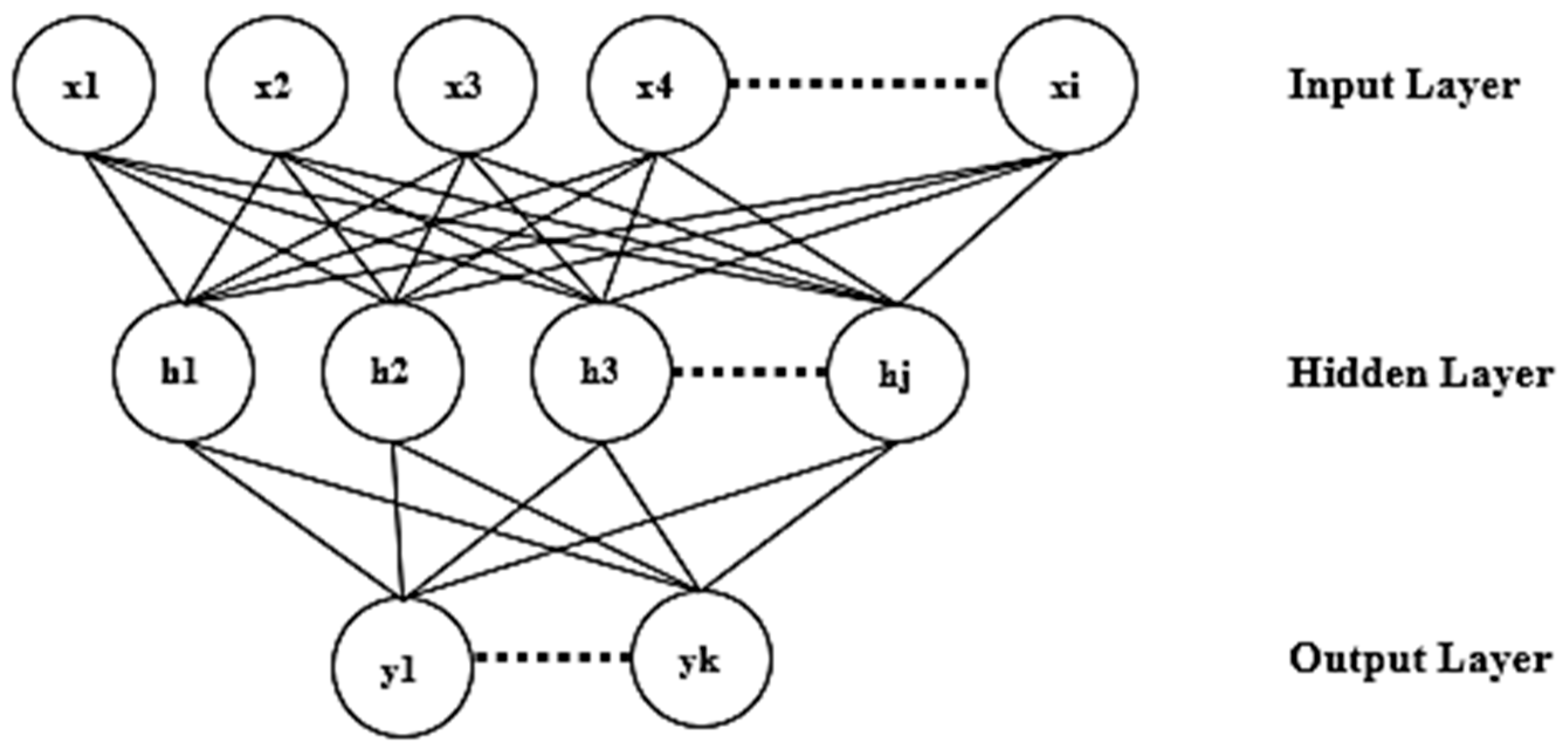
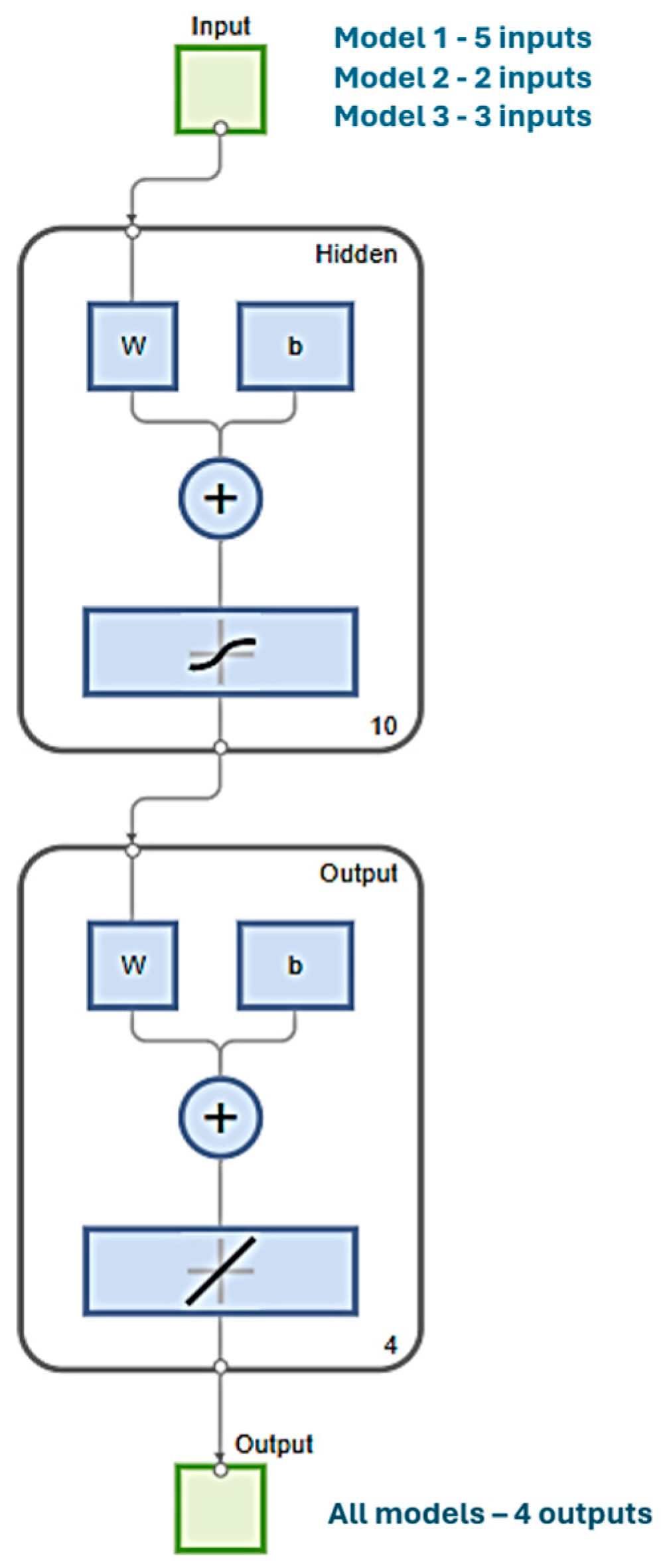
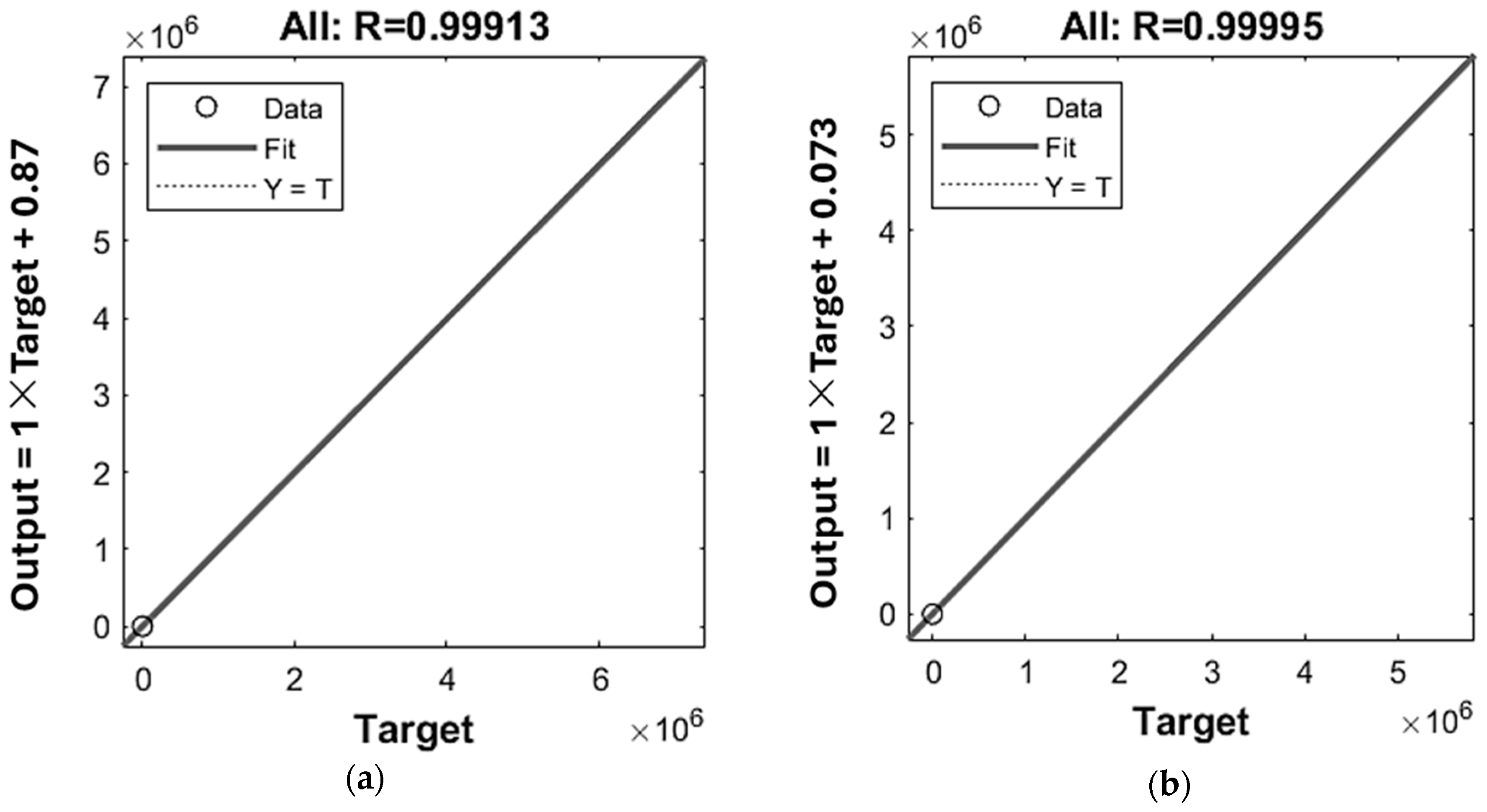
| Parameters | Average ± Standard Deviation | Range (Minimum–Maximum) |
|---|---|---|
| Meteorological Parameters of Bursa | ||
| Monthly Average Vapor Pressure (hPa) | 12.09 ± 4.59 | 5.01–22.52 |
| Monthly Average Air Temperature (°C) | 15.24 ± 7.23 | 2.18–27.64 |
| Monthly Average Relative Humidity (%) | 69.56 ± 7.56 | 50.13–87.86 |
| Monthly Average Wind Speed (m/s) | 2.06 ± 0.46 | 0.77–3.30 |
| Monthly Average Total Precipitation (mm) | 1.94 ± 2.20 | 0.00–26.70 |
| Monthly Average Total Daily Global Solar Radiation (kWh/m2) | 3.38 ± 2.09 | 0.05–7.16 |
| Monthly Average Total Daily Solar Intensity (cal/cm2) | 323.12 ± 161.83 | 53.13–644.72 |
| Monthly Average Total Evapotranspiration (mm) | 4.60 ± 4.05 | 0.09–30.15 |
| Monthly Average Total Evaporation (mm) | 5.26 ± 2.55 | 1.00–13.30 |
| Monthly Average Total Snow Depth (cm) | 0.98 ± 3.18 | 0.00–30.75 |
| Hydrological Parameters of Doğancı Dam | ||
| Monthly Average Volume (hm3) | 29.80 ± 7.88 | 8.92–41.35 |
| Monthly Average Incoming Water Flow Rate (m3/day) | 497,783.67 ± 530,709.90 | 1555.20–2,959,638.17 |
| Monthly Average Outgoing Water Flow Rate (m3/day) | 239,507.67 ± 57,012.68 | 44,250.00–398,533.68 |
| Monthly Average Water Level (m) | 325.40 ± 6.05 | 305.38–333.35 |
| Model | Inputs | Outputs | ANN Layout | Checks | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | MSE | MAPE (%) | |||||||
| Training | Testing | Validation | Whole Dataset | ||||||
| 1 | Monthly average:
| Monthly average:
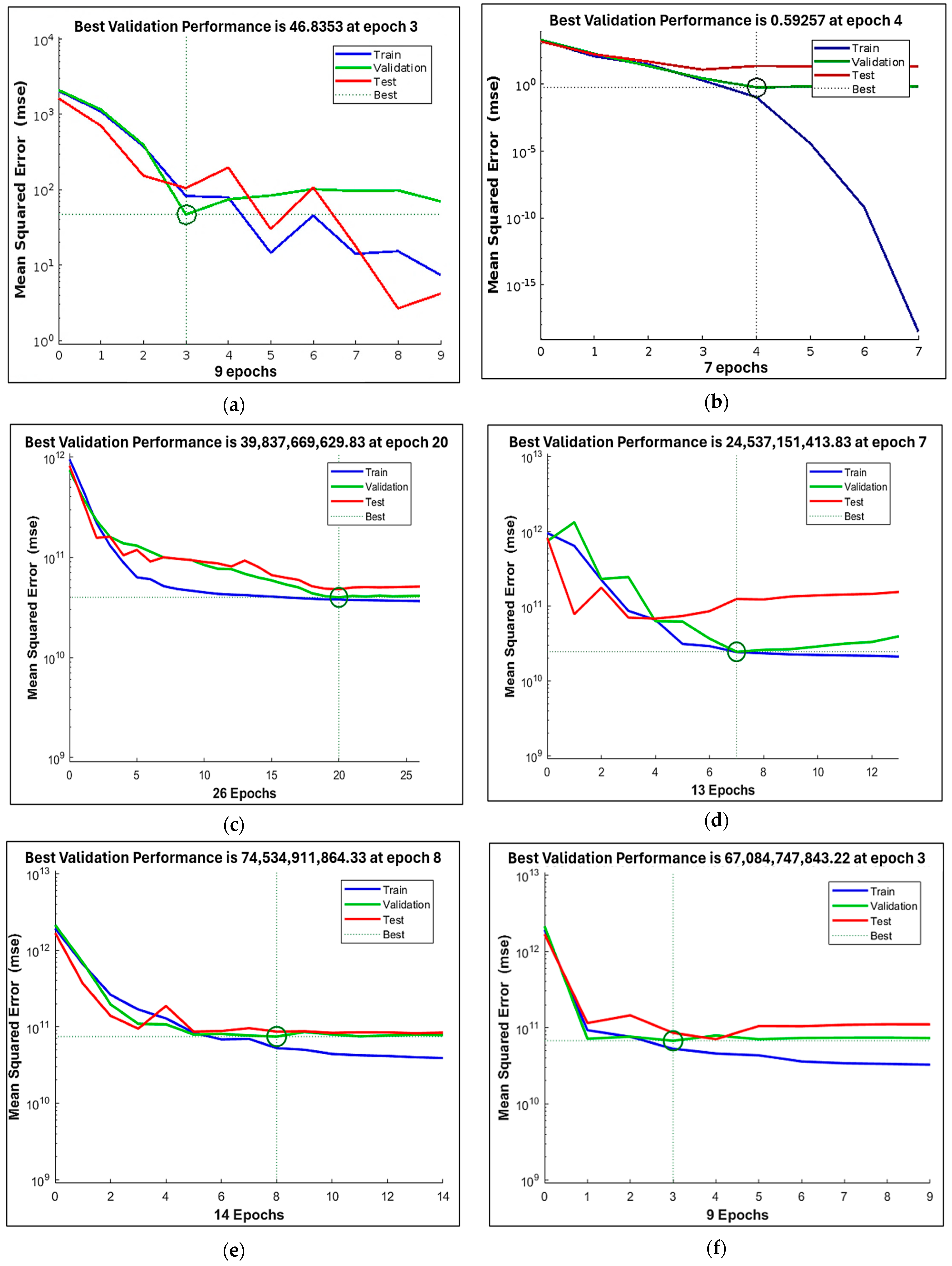
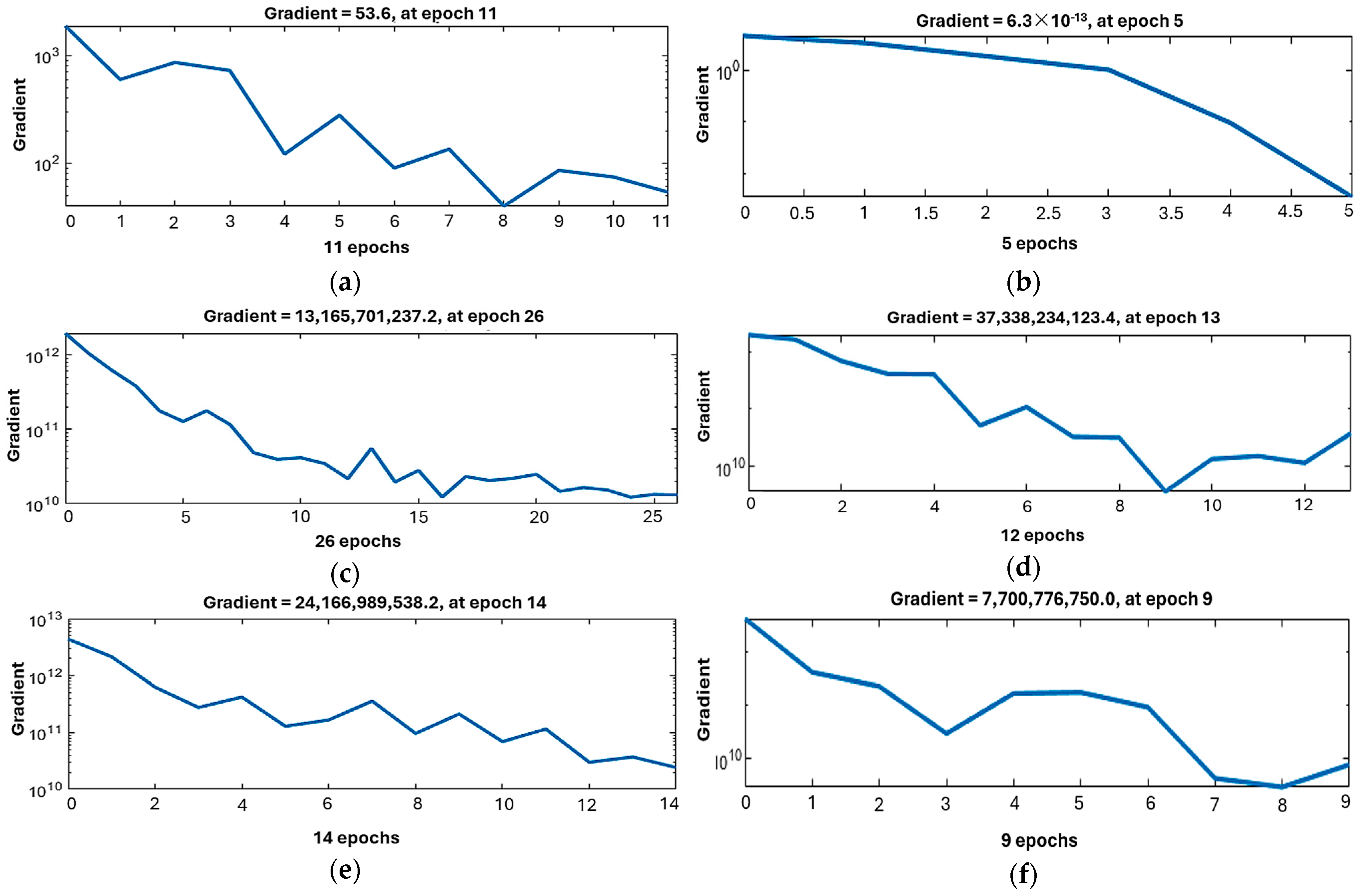
| 5-10-4 | RProp: 0.9908 LM: 1 | RProp: 1 LM: 1 | RProp: 1 LM: 1 | RProp: 0.99913 LM: 0.99995 | RProp: 46.8353 LM: 0.59257 | RProp: 13.5 LM: 1.31 |
| 2 | Monthly average:
| Monthly average:
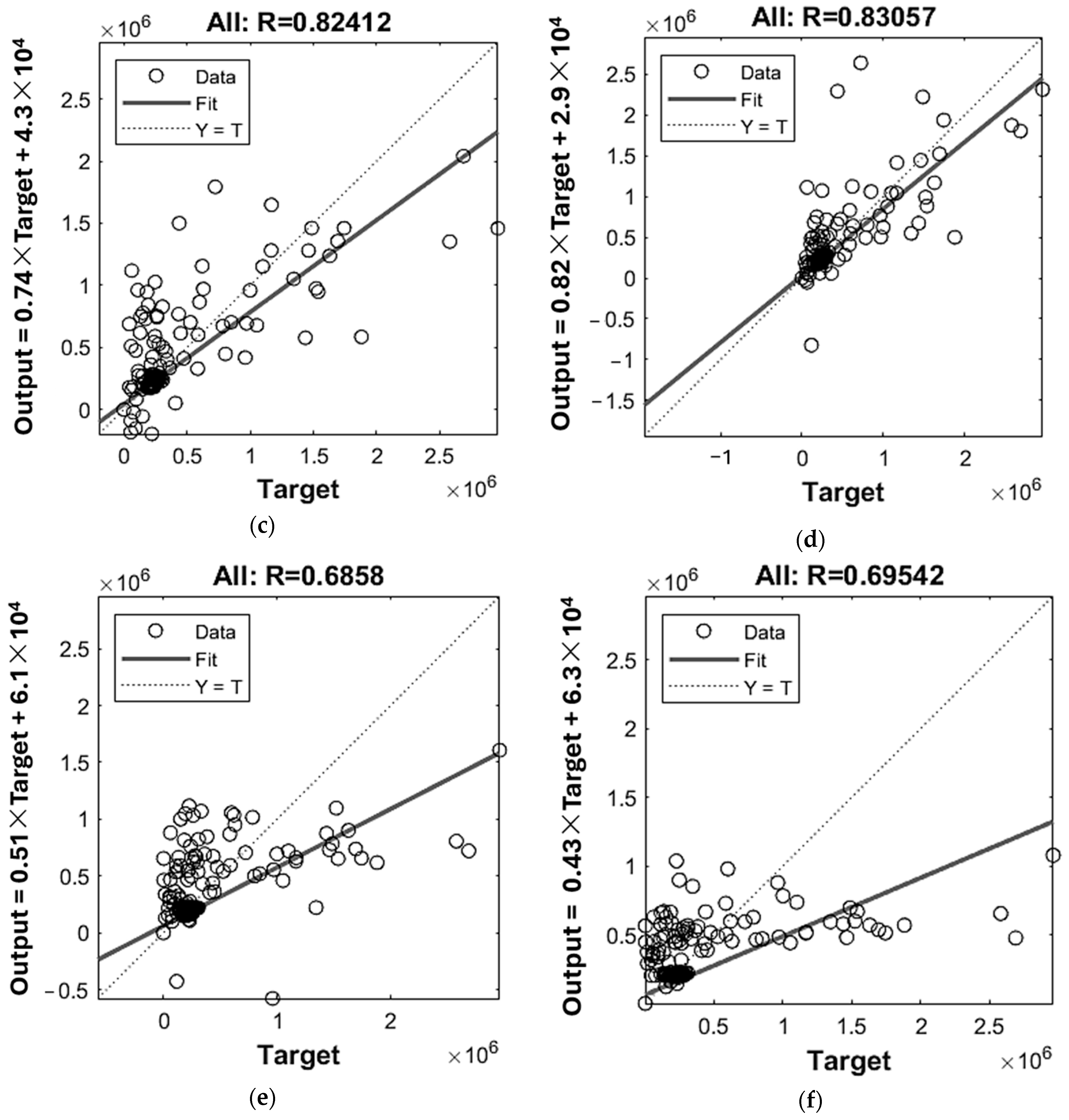
| 2-10-4 | RProp: 0.83633 LM: 0.89876 | RProp: 0.79397 LM: 0.62345 | RProp: 0.85413 LM: 0.93957 | RProp: 0.82412 LM: 0.83057 | RProp: 4.0 × 1010 LM: 2.4 × 1010 | RProp: 38.88 LM: 37.3 |
| 3 | Monthly average:
| Monthly average:
| 3-10-4 | RProp: 0.69929 LM: 0.69352 | RProp: 0.70283 LM: 0.7626 | RProp: 0.60448 LM: 0.65079 | RProp: 0.6858 LM: 0.69542 | RProp: 7.4 × 1010 LM: 6.7 × 1010 | RProp: 152.52 LM: 184.27 |
| Study No. | Dam (Location) | Inputs (Meteorological Parameters) | Outputs (Hydrological Parameters) | Errors | Correlation Coefficient | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Yalova Gökçe (Turkey) | Annual precipitation | Dam’s water level | 0.11 | 0.87 | [53] |
| 2 | Norris (America) | Annual precipitation and air temperature | Inflow volume to the dam and water level | 11 | 0.81 | [24] |
| 3 | Doroozdan (Iran) | Monthly precipitation | Inflow volume to the dam | 34.60 × 106 | 0.64 | [62] |
| 4 | Asa and Kampe (Nigeria) | Annual air temperature, precipitation, and evapotranspiration | Inflow rate to the dam | - | 0.99 | [25] |
| 5 | Batu (Malaysia) | Daily air temperature, wind speed, relative humidity, precipitation, sunshine duration, and solar radiation | Evaporation from the dam | 1.22 | 0.96 | [23] |
| 6 | Yarseli (Turkey) | Daily precipitation | Dam’s water level | 0.135 | 0.99 | [54] |
| Cases | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F | p | η2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Algorithms | 5.298 × 10−5 | 1 | 5.298 × 10−5 | 0.002 | 0.965 | 5.541 × 10−4 |
| Residuals | 0.096 | 4 | 0.024 | |||
| (a) | ||||||
| Algorithms | 8.627 × 1019 | 1 | 8.627 × 1019 | 0.068 | 0.807 | 0.017 |
| Residuals | 5.086 × 1021 | 4 | 1.272 × 1021 | |||
| (b) | ||||||
| Algorithms | 54.361 | 1 | 54.361 | 0.007 | 0.936 | 0.002 |
| Residuals | 29,756.237 | 4 | 7439.059 | |||
| (c) | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Katip, A.; Anwar, A. Simulating the Impacts of Climate Change on the Hydrology of Doğancı Dam in Bursa, Turkey, Using Feed-Forward Neural Networks. Sustainability 2025, 17, 6273. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146273
Katip A, Anwar A. Simulating the Impacts of Climate Change on the Hydrology of Doğancı Dam in Bursa, Turkey, Using Feed-Forward Neural Networks. Sustainability. 2025; 17(14):6273. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146273
Chicago/Turabian StyleKatip, Aslıhan, and Asifa Anwar. 2025. "Simulating the Impacts of Climate Change on the Hydrology of Doğancı Dam in Bursa, Turkey, Using Feed-Forward Neural Networks" Sustainability 17, no. 14: 6273. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146273
APA StyleKatip, A., & Anwar, A. (2025). Simulating the Impacts of Climate Change on the Hydrology of Doğancı Dam in Bursa, Turkey, Using Feed-Forward Neural Networks. Sustainability, 17(14), 6273. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146273






