The Interactive Coercive Relationship Between Urbanization and Eco-Environmental Quality in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. EEQ Data
2.3. Quantifying Urbanization
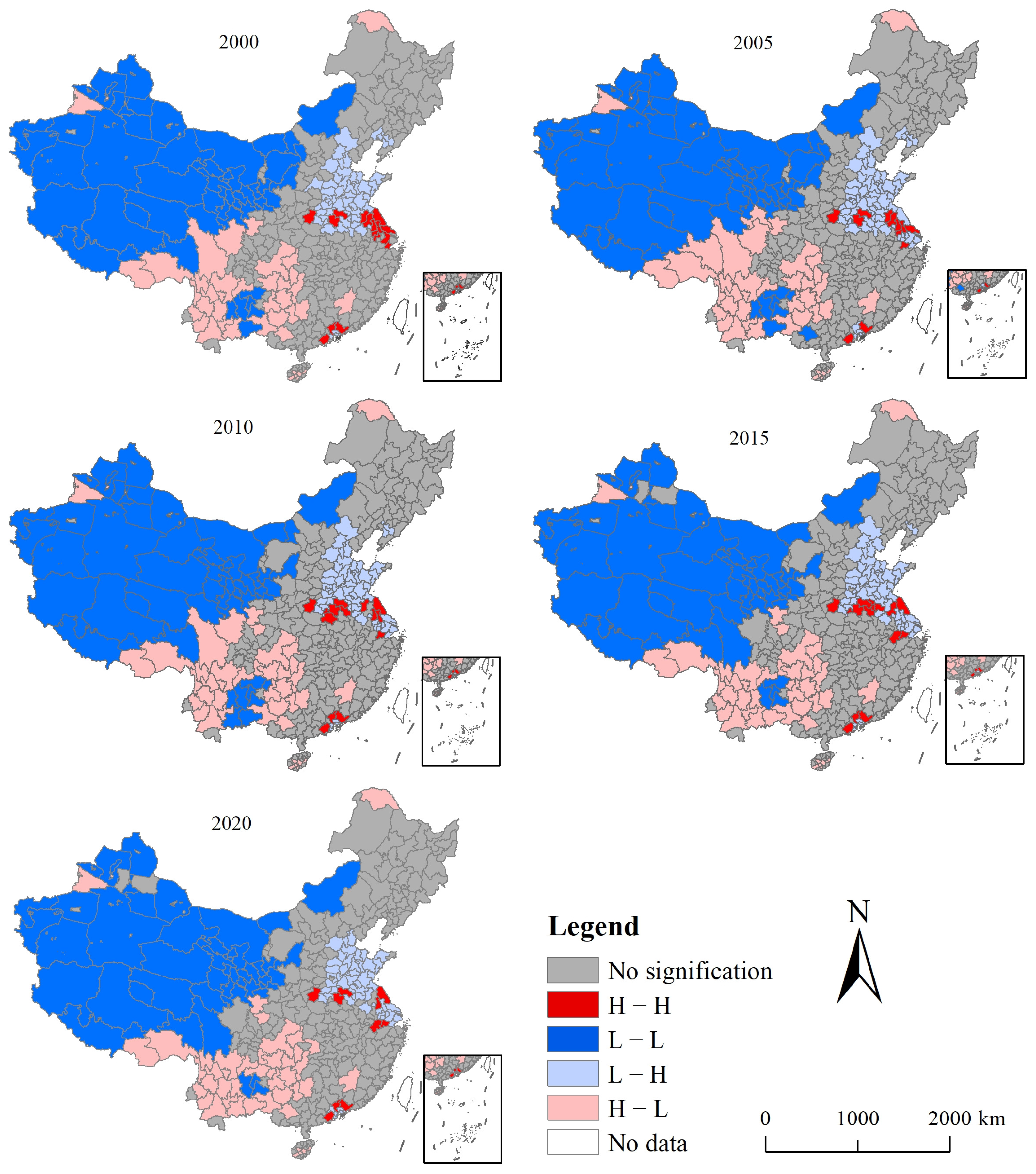
2.4. Spatial Autocorrelation
2.5. CCD Model
3. Results
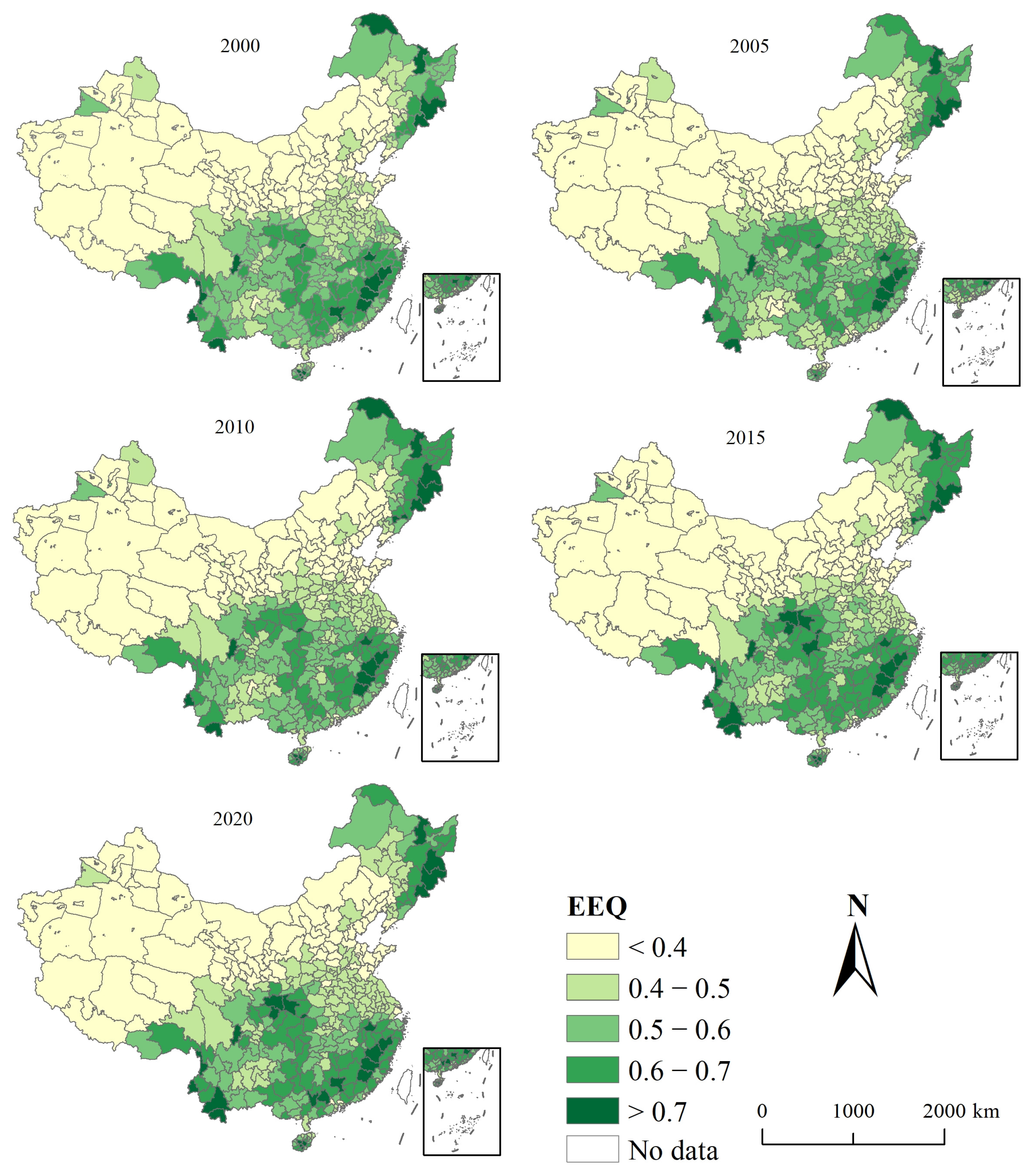
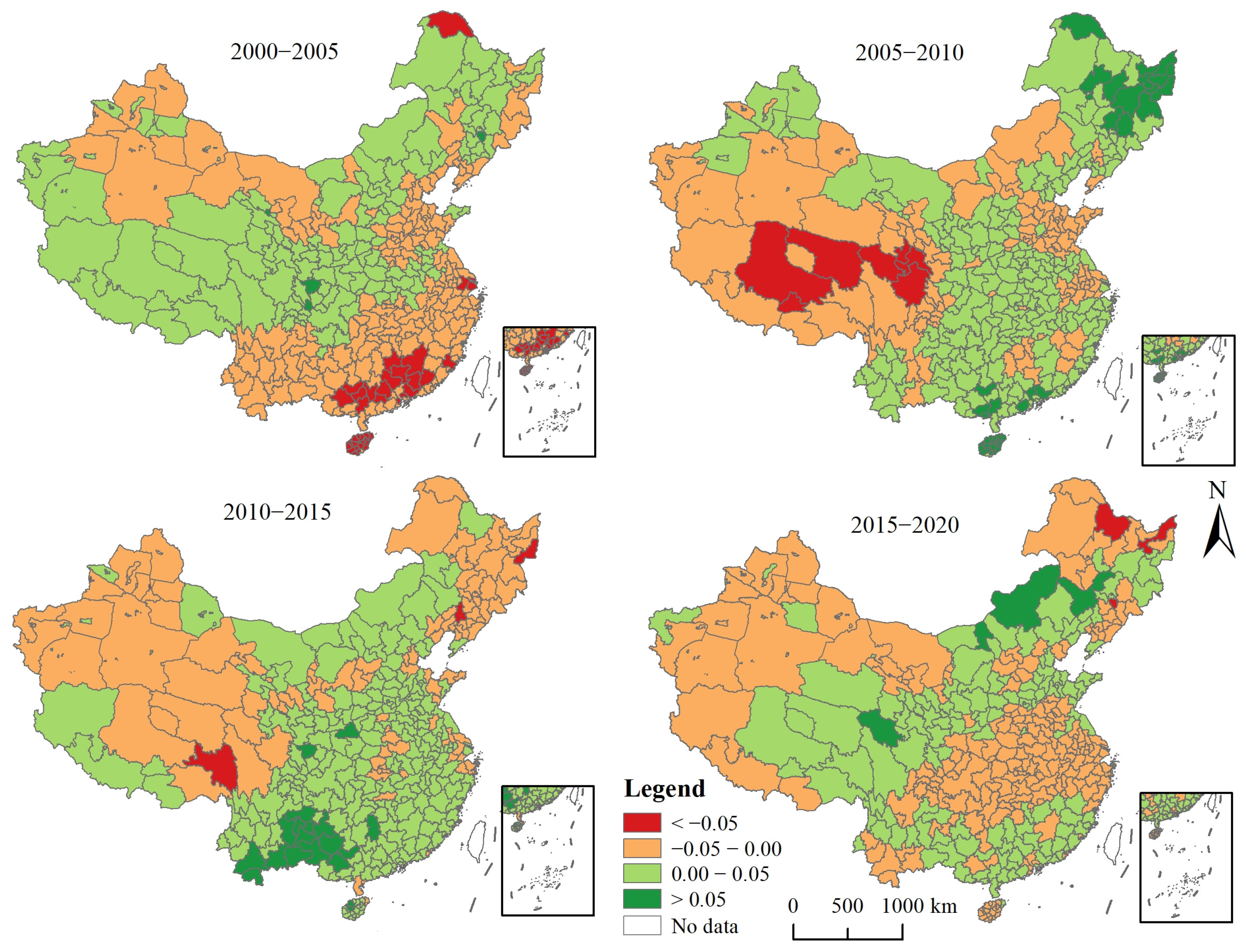
3.1. Spatio-Temporal Characteristics of EEQ
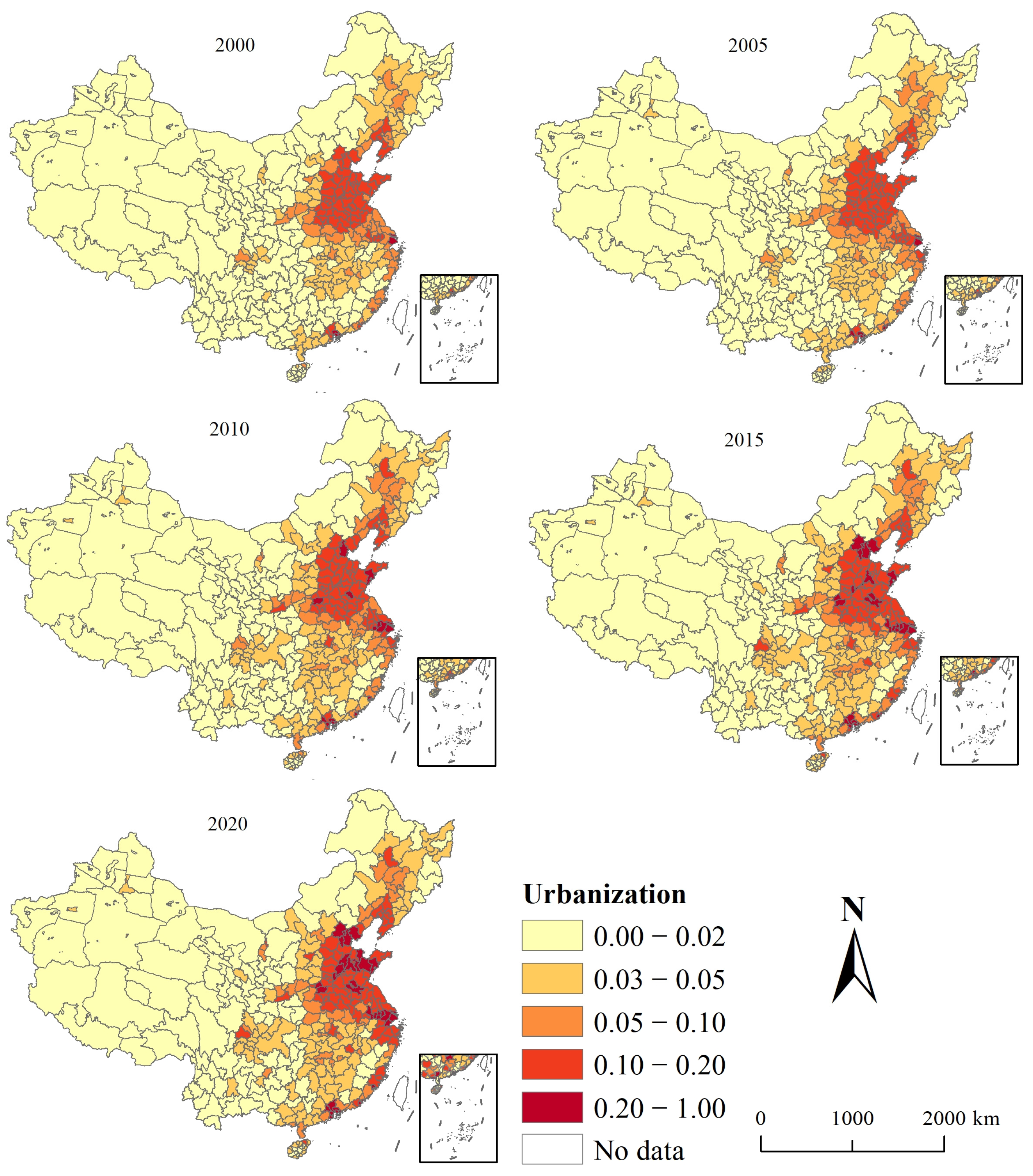
3.2. Spatio-Temporal Characteristics of Urbanization
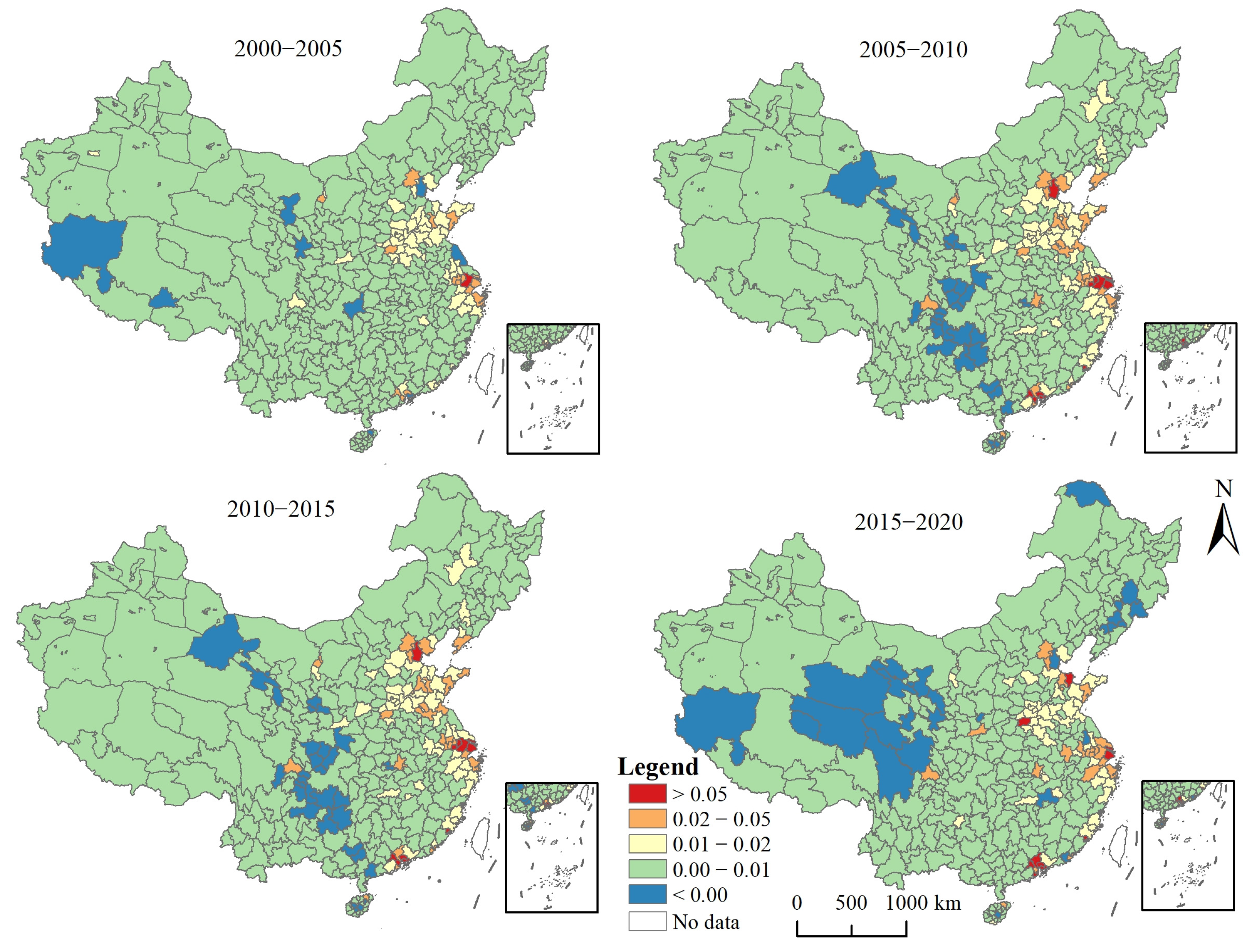
3.3. Spatial Autocorrelation of Urbanization and EEQ
3.4. Coupled Coordination Degree of EEQ and Urbanization
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatio-Temporal Characteristics of EEQ and Urbanization in China from 2000 to 2020
4.2. Spatio-Temporal Differences in the Impact of Urbanization on EEQ
4.3. Policy Implications
4.4. Limitation and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bi, Y.; Zheng, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, H.; Zhang, B. Coupling relationship between urbanization and water-related ecosystem services in China’s Yangtze River economic Belt and its socio-ecological driving forces: A county-level perspective. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.; Wu, Y.; Wong, S.W.; Shen, L. Provincial perspective analysis on the coordination between urbanization growth and resource environment carrying capacity (RECC) in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 730, 138964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Liu, H.; Gou, P.; Xu, N. Conflict or Coordination? measuring the relationships between urbanization and vegetation cover in China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 147, 109993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, C.; Li, Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, F. Spatio-temporal characteristics and coupling coordination relationship between urbanization and atmospheric particulate pollutants in the Bohai Rim in China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 153, 110387. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, I.; Hou, F.J.; Zakari, A.; Tawiah, V.; Ali, S.A. Energy use and urbanization as determinants of China’s environmental quality: Prospects of the Paris climate agreement. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2022, 65, 2363–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.L.; Zhou, J.F.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, B.L.; Zhu, Z.B. What is the spatiotemporal relationship between urbanization and ecosystem services? A case from 110 cities in the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 321, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, L.; Hanif, I.; Rasul, F. How are urbanization, energy consumption and globalization influencing the environmental quality of the G-7? Green Financ. 2022, 4, 231–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhou, T.; Liang, J. Urbanization, ecosystem services, and their interactive coercive relationship in Hunan Province, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 3416–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, N.B.; Faeth, S.H.; Golubiewski, N.E.; Redman, C.L.; Wu, J.G.; Bai, X.M.; Briggs, J.M. Global change and the ecology of cities. Science 2008, 319, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wang, G.; Xu, N.; Ji, M.; Zeng, J. Promoting or inhibiting? New-type urbanization and urban carbon emissions efficiency in China. Cities 2023, 140, 104429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Jiang, Q.O.; Shao, Y.; Sun, S.; Xiao, L.; Guo, J. Ecological environment assessment based on land use simulation: A case study in the Heihe River Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 697, 133928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Kong, Q.; Zhang, M.; Huang, H. New-type urbanization and ecological well-being performance: A coupling coordination analysis in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River urban agglomerations, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 159, 111678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Liu, W.; Lu, D.; Chen, H.; Ye, C. Progress of China’s new-type urbanization construction since 2014: A preliminary assessment. Cities 2018, 78, 180–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Dong, H.; Liu, X. Research on the coupling coordination and driving mechanisms of new-type urbanization and the ecological environment in China’s Yangtze River Delta. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loredana, C.; Rehman, A.; Maria Mirabela, F.I.; Pinzon, S.; Cismaș, L.M. What implications do primary energy use, urban population agglomeration, and economic development rendered to Romania’s environmental sustainability? Energy Strategy Rev. 2024, 53, 101399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Nahid, S.; Sharma, M.; Sannigrahi, S.; Anees, M.M.; Sharma, R.; Shekhar, R.; Basu, A.S.; Pilla, F.; Basu, B.; et al. A long-term and comprehensive assessment of urbanization-induced impacts on ecosystem services in the capital city of India. City Environ. Interact. 2020, 7, 100047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, N.; Bibi, F.U.N.; Junaid, A.; Alvi, S. Impact of urbanization and human development on ecological footprints in OECD and non-OECD countries. Heliyon 2024, 10, e38058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatmawati, A.; Aurora, R.M.; Thong, T.D.; Furuya, K. Impact of urbanization on the vegetation dynamic in Tama River Basin. Int. Rev. Spat. Plan. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 12, 119–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.B.; Fang, Y.L.; Jin, X.B.; Zhou, Y.K. Monitoring the effects of land consolidation on the ecological environmental quality based on remote sensing: A case study of Chaohu Lake Basin, China. Land Use Policy 2020, 95, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, W.; Jin, X.B.; Ren, J.; Wang, Y.C.; Xu, Z.G.; Fan, Y.T.; Gu, Z.M.; Hong, C.Q.; Lin, J.H.; Zhou, Y.K. Ecological environment quality assessment based on remote sensing data for land consolidation. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 239, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. A remote sensing urban ecological index and its application. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2013, 33, 7853–7862. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H. A remote sensing index for assessment of regional ecological changes. China Environ. Sci. 2013, 33, 889–897. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Xie, T.; Lyu, D.; Cui, L.; Liu, Q. Analyzing the spatiotemporal dynamics and driving forces of ecological environment quality in the Qinling Mountains, China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, L.; Yin, S.; Jin, J.; Wu, W. Assessment and simulation of urban ecological environment quality based on geographic information system ecological index. Land 2024, 13, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Q. Analysis of Spatiotemporal Changes of ecological environment quality and its coupling coordination with urbanization in the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Hua, L.; Tang, J.; Jiang, L.; Wang, Q.; Cao, Y.; Wang, T.; Cai, C. Advancing ecological quality assessment in China: Introducing the ARSEI and identifying key regional drivers. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 163, 112109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Yang, F.; Yu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Li, H.; Ma, J.; Huang, J.; Wei, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, C.; et al. Quantization of the coupling mechanism between eco-environmental quality and urbanization from multisource remote sensing data. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 321, 128948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Peng, X.; Tang, R.; Geng, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, D.; Bai, T. Spatial and temporal variation characteristics of ecological environment quality in China from 2002 to 2019 and influencing factors. Land 2024, 13, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yu, J.; Xu, W.; Wu, Y.; Lei, X.; Ye, J.; Geng, J.; Ding, Z. Long-time series ecological environment quality monitoring and cause analysis in the Dianchi Lake Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 148, 110084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Han, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, R.; Qu, C.; Zhang, P.; Martin, S.; Zhuang, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J.; et al. Spatial-temporal variation and influencing factors of ecological environment quality in Jilin Province (China). Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1446313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, T.; Yu, W. Analysis of changes in ecological environment quality and influencing factors in Chongqing based on a Remote-Sensing Ecological Index mode. Land 2024, 13, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Earth System Science Data Center (NESDC). Available online: https://www.geodata.cn/main/face_science_detail?typeName=face_science&guid=190747515712302 (accessed on 15 December 2024).
- Sohail, A.; Abbasi, B.N.; Ahmed, Z. New insights into the nexus between international trade, urbanization, nonrenewable energy consumption, and environmental quality in China: Evidence from Multivariate Threshold Regression. Nat. Resour. Forum 2025, 49, 1148–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Cheng, J.; Xu, S.; Geng, J.; Yang, F.; Fang, H.; Xu, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; et al. Understanding the relationship between China’s eco-environmental quality and urbanization using multisource remote sensing data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Liu, H.; Li, S.; Luo, Q.; Cheng, S.; Hu, G.; Wang, X.; Bai, W. Coupling coordination analysis of urbanization and ecological environment in Chengdu-Chongqing urban agglomeration. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 161, 111969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadashpoor, H.; Azizi, P.; Moghadasi, M. Land use change, urbanization, and change in landscape pattern in a metropolitan area. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 707–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, G.M.; Krueger, A.B. Economic growth and the environment. Q. J. Econ. 1995, 110, 353–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, B.; Fang, C.; Huang, J. The coupling law and its validation of the interaction between urbanization and eco-environment in arid area. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2006, 7, 2183–2190. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neill, D.W.; Fanning, A.L.; Lamb, W.F.; Steinberger, J.K. A good life for all within planetary boundaries. Nat. Sustain. 2018, 1, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beloin-Saint-Pierre, D.; Rugani, B.; Lasvaux, S.; Mailhac, A.; Popovici, E.; Sibiude, G.; Benetto, E.; Schiopu, N. A review of urban metabolism studies to identify key methodological choices for future harmonization and implementation. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 163, S223–S240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.G.; Cao, D.; Lo, K.V. Analyzing and optimizing the impact of economic restructuring on Shanghai’s carbon emissions using STIRPAT and NSGA-II. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 40, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.L.; Liu, H.M.; Li, G.D. International progress and evaluation on interactive coupling effects between urbanization and the eco-environment. J. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 1081–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Pi, J.; Chen, H. Coupling coordination development of the logistics industry, new urbanization and the ecological environment in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, X.; Shi, S.; Xu, L. Exploring the relationship between the eco-environmental quality and urbanization by utilizing sentinel and landsat data: A case study of the Yellow River Basin. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, L.; Wang, L.F.; Zhang, X.R.; Du, Y.D.; Liu, J. Key indicators of high-quality urbanization affecting eco-environmental quality in emerging urban agglomerations: Accounting for the importance variation and spatiotemporal heterogeneity. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 376, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, B. Research on the synergistic effects of urbanization and ecological environment in the Chengdu–Chongqing urban agglomeration based on the Haken model. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, Z.; Qin, K.; Dai, S.; Lu, H.; Lu, M.; Ji, J.; Yang, Z.; Chen, C.; Jia, P. Long-term dynamic monitoring and driving force analysis of eco-environmental quality in China. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.P.; Huang, R.Y.; Li, D. China’s high-quality economic development: A study of regional variations and spatial evolution. Econ. Change Restruct. 2024, 57, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resources and Environmental Sciences Data Center (RESDC). Available online: https://www.resdc.cn/DOI/DOI.aspx?DOIID=54 (accessed on 15 December 2024).
- National Geomatics Center of China. Available online: https://www.ngcc.cn/dlxxzy/gjjcdlxxsjk/ (accessed on 15 December 2024).
- Zheng, L.; Wu, J.; Chen, Q.; Wang, J.; Chen, W.; Pan, S. Identifying the interactive coercive relationships between urbanization and eco-environmental quality in the Yangtze and Yellow River Basins, China. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Chen, W.; Zeng, J.; Wang, G.; Yuan, T. Gradient differences of the impact of urbanization on habitat quality in the Yangtze River Basin. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 44, 4038–4050. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, M.; Liu, Q.; Hu, X. Understanding the county-level relationship between population change and ecological environment quality dynamic in China, 2000–2020. Front. Environ. Sci. 2025, 13, 1513998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Tian, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, M.; Hu, Y.; Wu, J. Ecosystem services response to urbanization in metropolitan areas: Thresholds identification. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607–608, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Wang, G.; Zeng, J. Impact of urbanization on ecosystem health in Chinese urban agglomerations. Environ. Impact Asses. 2023, 98, 106964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, W.; Zha, N.; Feng, Y.; Qiu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhang, R. Spatially heterogeneity response of critical ecosystem service capacity to address regional development risks to rapid urbanization: The case of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration in China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L. Local indicators of spatial association—LISA. Geogr. Anal. 1995, 27, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L. A test for spatial autocorrelation in seemingly unrelated regressions. Econ. Lett. 1988, 28, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhong, Q.; Cheng, D.; Xu, C.; Chang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Li, B. Coupling coordination analysis and prediction of landscape ecological risks and ecosystem services in the Min River Basin. Land 2022, 11, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.M.; Fan, H.B.; Liu, F.; Lv, T.G.; Sun, L.; Li, Z.L.; Shang, W.L.; Xu, G.L. Coupling coordination between the ecological environment and urbanization in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River urban agglomeration. Urban Clim. 2023, 52, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhang, N.; Cao, Y.; Xia, Z.; Bao, C.; Fan, L.; Xue, S. Analysis of the temporal and spatial changes of ecological environment quality using the optimization remote sensing ecological index in the middle Yellow River Basin, China. Earth Sci. Inform. 2024, 17, 5107–5122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, T.; Bai, Z.; Zheng, B. Spatiotemporal dynamics and driving forces of ecological environment quality in coastal cities: A remote sensing and land use perspective in Changle District, Fuzhou. Land 2024, 13, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airiken, M.; Li, S. The Dynamic monitoring and driving forces analysis of ecological environment quality in the Tibetan Plateau based on the Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Guo, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L. Examining the complex relationship between Urbanization and ecological environment in ecologically fragile areas: A case study in Southwest China. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1358051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, T.T.; Cheng, J.; Zheng, Z.H.; Zhang, Q.F.; Li, Z.H.; Xu, D. Drivers of eco-environmental quality in China from 2000 to 2017. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 396, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Hu, Z.; Liu, Y. Shift in the trend of browning in Southwestern Tibetan Plateau in the past two decades. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2020, 287, 107950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Chen, T.; Jia, K.; Plaza, A. Coupling analysis between ecological environment change and urbanization process in the Middle Reaches of Yangtze River Urban Agglomeration, China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 880–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, W.A.; Chao, F.B. The win-win ability of environmental protection and economic development during China’s transition. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2021, 166, 120617. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.; Deng, X.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z. Exploring the relationship between urbanization and urban eco-efficiency: Evidence from prefecture-level cities in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 195, 1487–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Yang, Z.; Ding, Z.; Wang, S.; Li, H. Spatial differentiation and influencing factors of the coupling coordination degree of urbanization and eco-environment in China at city-level from 2010 to 2020. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 44, 5040–5058. [Google Scholar]
- Ozturk, I.; Savranlar, B.; Aslan, A.; Al-mulali, U.; Artan, S. The dynamic simulation analysis of the impact of urbanization and globalization on environmental quality. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, M.K.; York, A.M.; Boone, C.G.; Zhang, S. Land fragmentation due to rapid urbanization in the Phoenix Metropolitan Area: Analyzing the spatiotemporal patterns and drivers. Appl. Geogr. 2012, 32, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Sun, W.Z.; Yang, K.; Zhao, L. China urbanization process induced vegetation degradation and improvement in recent 20 years. Cities 2021, 114, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Gu, T.; Zeng, J. Urbanisation and ecosystem health in the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River urban agglomerations, China: A U-curve relationship. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 318, 115565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Qi, R.; Cheng, J.H.; Zhu, Y.G.; Lu, P.X. The behavior and cognition of ecological civilization among Chinese university students. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 243, 118464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulfiqar, M.; Fatima, A.; Ullah, M.R.; Huo, W.D.; Pervaiz, A.; Ghafoor, S. The triple threat: How green technology innovation, green energy production, and financial development impact environmental quality? Nat. Resour. Forum 2023, 17, 12384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; He, J.; Liu, D.; Wang, J.; Guo, X. Ecosystem health assessment based on ecological integrity and ecosystem services demand in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 774, 144837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Li, X.; Li, S.; Sun, H.; Liu, H. Effect of urban fringes green space fragmentation on ecosystem service value. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0263452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhanam, H.; Majumdar, R. Quantification of green-blue ratios, impervious surface area and pace of urbanisation for sustainable management of urban lake—land zones in India -a case study from Bengaluru city. J. Urban Manag. 2022, 11, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Categories | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Severe imbalance | 16.7% | 15.1% | 12.9% | 11.3% | 10.8% |
| Moderate imbalance | 55.8% | 55.3% | 55.3% | 52.3% | 51.8% |
| Low coordination | 27.2% | 29.6% | 31.0% | 34.5% | 35.3% |
| Moderate coordination | 0.3% | 0.0% | 0.8% | 1.9% | 1.9% |
| High coordination | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.3% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhong, M. The Interactive Coercive Relationship Between Urbanization and Eco-Environmental Quality in China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 6019. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17136019
Zhong M. The Interactive Coercive Relationship Between Urbanization and Eco-Environmental Quality in China. Sustainability. 2025; 17(13):6019. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17136019
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhong, Mingxing. 2025. "The Interactive Coercive Relationship Between Urbanization and Eco-Environmental Quality in China" Sustainability 17, no. 13: 6019. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17136019
APA StyleZhong, M. (2025). The Interactive Coercive Relationship Between Urbanization and Eco-Environmental Quality in China. Sustainability, 17(13), 6019. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17136019





