From Solid Waste to Technosols: Evaluation of Aggregate Stability, Microbial Community and Biotoxicity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Analytical Methods
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Aggregate Classification
2.5. Calculation of Fractal Dimension
2.6. SOC Mineralization
2.7. Seed Germination Assay
2.8. Bacterial Community Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physical and Chemical Properties of Technosols
3.2. Microscopic Morphology of Technosols
3.3. Formation and Influencing Factors of Aggregates in Technosols
3.3.1. Distribution and Stability of Aggregates
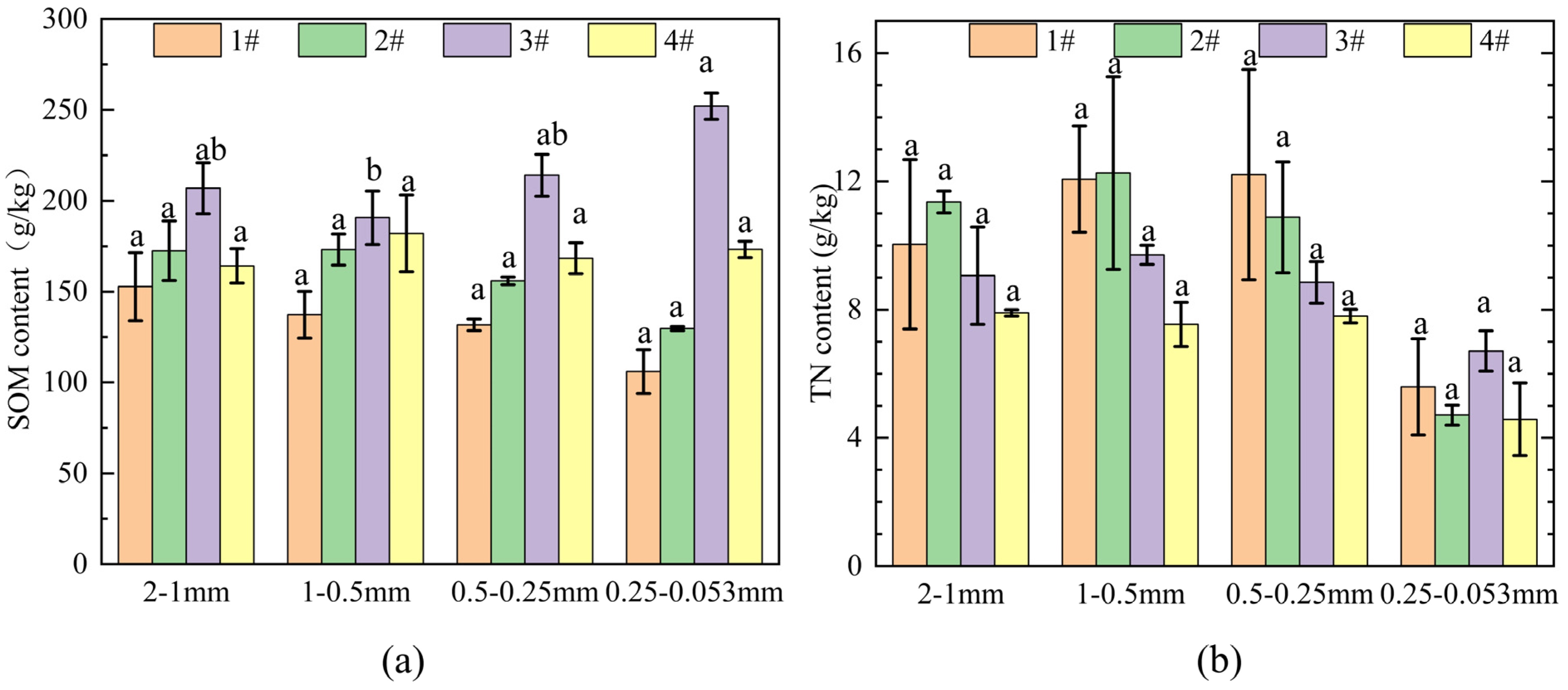
3.3.2. Distribution Characteristics of SOM and TN in Aggregates
3.3.3. Correlation Analysis Between Physicochemical Properties of Technosols and Their Aggregate Stability
3.4. Bacteria Community and Their Mineralization Characteristics in Technosols
3.4.1. Bacteria Community Characteristics
3.4.2. Mineralization Characteristics of Organic Carbon in Technosols
3.5. Biological Toxicity of Technosols
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statements
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SOM | Soil organic matter |
| TN | Total nitrogen |
| SOC | Soil organic carbon |
| R0.25 | The percentage of >0.25 mm aggregates |
| MWD | Mean weight diameter |
| GMD | Mean geometric diameter |
| PAD | Proportion of aggregates destruction |
| FD | Fractal dimension |
| RSG | Relative seed germination |
| RRG | Relative root elongation |
| GI | Germination index |
| pH | Electrical conductivity |
| WHC | Water holding capacity |
References
- Jin, H.X.; Wang, S.J.F.; Xiao, Y.D.; Guo, Y.L.; Song, H.H. Study on the characteristics and collaborative utilization of red mud and fly ash resources. J. Guizhou Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2022, 39, 18–26. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.B.; Liu, J.; Xin, H.J.; Chen, J.; Xu, S.; Liu, J.X.; Hou, X. Present status and prospect of fly ash utilization in China. Energy Res. Manag. 2022, 41, 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- Government, People of Republic of China. Guiding Opinions on the Comprehensive Utilization of Bulk Solid Wastes in the 14th Five-Year Plan. 2021. Available online: https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2021-03/25/content_5595566.htm (accessed on 25 March 2021).
- Rossiter, D.G. Classification of urban and industrial soils in the world reference base for soil resources. J. Soil Sediment. 2007, 7, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, J.; Gérard, A.; Séré, G.; Morel, J.L.; Guimont, S.; Simonnot, M.O.; Pons, M.N. Life cycle impacts of soil construction, an innovative approach to reclaim brownfields and produce nonedible biomass. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 211, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiler, J.; Firpo, B.A.; Schneider, I.A.H. Technosol as an integrated management tool for turning urban and coal mining waste into a resource. Miner. Eng. 2020, 147, 106179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otremba, K.; Kozlowski, M.; Tatusko-Krygier, N.; Pajak, M.; Kolodziej, B.; Bryk, M. Impact of alfalfa and NPK fertilization in agricultural reclamation on the transformation of technosols in an area following lignite mining. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 1179–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, F.J.R.; Firpo, B.A.; Broadhurst, J.L.; Harrison, S.T.L. On the feasibility of South African coal waste for production of ‘FabSoil’, a Technosol. Miner. Eng. 2020, 146, 106059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Xu, M.; Liu, G.; Yao, X.; Tuo, D.; Zhang, R.; Xiao, T.; Peng, G. Quantification of soil aggregate microstructure on abandoned cropland during vegetative succession using synchrotron radiation-based micro-computed tomography. Soil Till. Res. 2017, 165, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, X.; Neal, A.L.; Crawford, J.W.; Mooney, S.J.; Bacq-Labreuil, A. Evolution of the transport properties of soil aggregates and their relationship with soil organic carbon following land use changes. Soil Till. Res. 2022, 215, 105226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.D. Soil Agro-Chemistrical Analysis, 3rd ed.; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2007; pp. 183–185. [Google Scholar]
- Ravikumar, P.; Somashekar, R.K. Spatial distribution of macronutrients in soils of Markandeya river basin, Belgaum(d), Karnataka(s), India. Proc. Int. Acad. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2014, 4, 81–94. [Google Scholar]
- Pronk, G.J.; Heister, K.; Ding, G.-C.; Smalla, K.; Kögel-Knabner, I. Development of biogeochemical interfaces in an artificial soil incubation experiment; aggregation and formation of organo-mineral associations. Geoderma 2012, 189–190, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sher, Y.; Baker, N.R.; Herman, D.J.; Fossum, C.; Firestone, M.K. Microbial extracellular polysaccharide production and aggregate stability controlled by Switchgrass (Panicum virgatum) root biomass and soil water potential. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 143, 107742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.M.; Fan, H.; Wang, J.Q.; Ippolite, J.; Li, Y.B.; Feng, S.; An, M.J.; Zhang, F.H.; Wang, K.Y. Effect of polymer materials on soil structure and organic carbon under drip irrigation. Geoderma 2019, 340, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, K.; Qian, H.; Zhang, Y.; Qu, W.; Ren, W.; Wang, H. Relationship between fractal characteristics of grain-size and physical properties: Insights from a typical loess profile of the loess Plateau. Catena 2021, 207, 105653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.M.; Liao, C.L.; Xie, L.H.; Dai, Q.; Tang, R.; Sun, Y.X.; Li, N.; Yin, L.C. Effects of groundwater tables and long-term fertilization on mineralization of organic carbon in red paddy soil. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2019, 5, 1414–1423. [Google Scholar]
- Saez, J.; Aguilar, M.I.; Ortuno, J.F.; Meseguer, V.F. Phytotoxicity and heavy metals speciation of stabilised sewage sludges. J. Hazard. Mater. 2004, A108, 161–169. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Li, W.X.; Zuo, W.G.; Qiu, M.H.; Zhang, L.; Fan, X.H.; Chen, M.; Wang, X.K.; Bo, Y.C. Spatial and temporal variation of cropland pH and the driving factors in Jiangsu over the past 40 years. J. Plant Nutr. Fert. 2023, 29, 264–272. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yu, S.; Wang, C.; Yin, W.; Xu, Q.; Wang, S.; Xiaoye, W. Construction of technosols by aggregating various inorganic and organic solid wastes. J. Agric. Res. 2023, 40, 445–454. [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann, J.; Kleber, M. The contentious nature of soil organic matter. Nature 2015, 528, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Xu, Y.; Cui, Y.; Meng, Y.D.; Dong, Y.; Li, R.; Ma, Y.B. Variation of soil organic matter content in croplands of China over the last three decades. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2017, 54, 1047–1056. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.Q.; Yue, T.X.; Fan, Z.M.; Du, Z.P.; Chen, C.F.; Lu, Y.M. Spatial simulation of topsoil TN at the national scale in China. Geogr. Res. 2010, 29, 1981–1992. [Google Scholar]
- He, L.L.; Qiang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, B.; Xy, P. Effect of secondary succession on soil water holding capacity of subalpine coniferous forest in western Sichuan. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 2021, 27, 639–647. [Google Scholar]
- Hamllam, J.; Hodson, M.E. Impact of different earthworm ecotypes on water stable aggregates and soil water holding capacity. Biol. Fert. Soils 2020, 56, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jozedaemi, E.; Golchin, A. Changes in aggregate-associated carbon and microbial respiration affected by aggregate size, soil depth, and altitude in a forest soil. Catena 2024, 234, 107567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Ma, W.M.; Wang, C.T.; Deng, Z.Z.M.; Tang, S.H.; Hou, C. Effects of shrub-encroached grassland on the stability of soil aggregates and cementing materials in alpine grassland of Qinghai-Tibet plateau. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2023, 60, 151–163. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.M.; Gao, X.F.; Jiang, H.T. Content of five main soil water-stable aggregates in China. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2013, 373, 32–35. [Google Scholar]
- Redmile-Gordon, M.; Gregory, A.S.; White, R.P.; Watts, C.W. Soil organic carbon extracellular polymeric substances EPS and soil structural stability as affected by previous and current land use. Geoderma 2020, 363, 114143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.Y.; Sheng, X.F. Effect of exopolysaccharide-producing bacteria on water-stable macro-aggregate formation in soil. Geomicrobiol. J. 2020, 37, 738–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhya, V.; Ali, S.Z. The production of exopolysaccharide by Pseudomonas putida GAP-P45 under various abiotic stress conditions and its role in soil aggregation. Microbiology 2015, 84, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.L.; Tan, W.F.; Chen, X.H. Arbuscular mycorrhizal mycelial networks and glomalin-related soil protein increase soil aggregation in Calcaric Regosol under well-watered and drought stress conditions. Soil Till. Res. 2019, 185, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.L.; Wei, Y.X.; Liu, J.Z.; Yuan, J.C.; Liang, Y.; Ren, J.; Cai, H.G. Effects of maize straw and its biochar application on organic and humic carbon in water-stable aggregates of a Mollisol in Northeast China: A five-year field experiment. Soil Till. Res. 2019, 190, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisdall, J.M.; Oades, J.M. Organic matter and water-stable aggregates in soils. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 1982, 33, 141–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodhi, G.P.S.; Beri, V.; Benbi, D.K. Soil aggregation and distribution of carbon and nitrogen in different fractions under long-tern application of compost in rice–wheat system. Soil Till. Res. 2009, 103, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.R.; Hasi, E.; Han, X.J.; Qingda, M. Fractal characterization of soil particle size distribution under different land use patterns on the north slope of Wula Mountain in China. J. Soil Sediment. 2024, 24, 1148–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Qu, J.J.; Tan, L.H.; Fan, Q.B.; Niu, Q.H. Fractal features of sandy soil particle-size distributions during the rangeland desertification process on the eastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Soil Sediment. 2020, 20, 472–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.F.; Xu, Y.; Shi, Z.H.; Cai, P.; Huang, Q.Y. The formation process and stabilization mechanism of soil aggregates driven by binding materials. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2023, 60, 1297–1308. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, C.; Wu, L.J.; Yan, Q.Y.; Yan, S.D.; Dong, F.; Li, F.; Cheng, Y.G.; Huang, X. Effects of green manure application on soil organic carbon and nitrogen content among aggregates fraction in dryland wheat fields. J.Soil Water Conserv. 2023, 37, 304–312. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, Y.Y.; Jan, D.F.; Guo, Z.Y.; Chen, R.R.; Wu, M.; Li, Z.P.; Lin, X.G.; Feng, Y.Z. Important ecophysiological roles of nondominant Actinobacteria in plant residue decomposition, especially in less fertile soils. Microbiome 2021, 9, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z.; Li, S.; Bol, R.; Zhu, P.; Wang, J. Differential long-term fertilization alters residue-derived labile organic carbon fractions and the microbial community during straw residue decomposition. Soil Till. Res. 2021, 213, 105120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.M.; Zhang, L.; Bai, M.X.; Zhou, Y.; Qin, H.; Xu, Q.F.; Chen, J.H. Effects of single application of organic amendments and their combination with biochar on microbial community Composition in a red soil. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2024, 16, 3333–3339. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.W.; Yu, G.R.; Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, R.L.; Wang, Q.F. Plant functional traits determined the latitudinal variations in soil microbial functions: Evidence from a forest transect in China. Biogeosci. Discuss. 2019, 16, 3333–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Lv, D.T.; Jiang, S.Y.; Lin, H.; Sun, J. Soil salinity regulation of soil microbial carbon metabolic function in the Yellow River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 79, 148258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, C.C.; Zhou, J.H.; Wang, T.T.; Zheng, J.Y. Effects of biochar addition on soil bacterial community in semi-arid region. China Environ. Sci. 2019, 39, 2170–2179. [Google Scholar]
- Figueroa-López, A.M.; Cordero-Ramírez, J.D.; Martínez-álvarez, J.C.; López-Meyer, M.; Lizárraga-Sánchez, G.J.; Félix-Gastélum, R.; Castro-Martínez, C.; Maldonado-Mendoza, I.E. Rhizospheric bacteria of maize with potential for biocontrol of Fusarium verticillioides. Springerplus 2016, 5, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangir, M.; Pathak, R.; Sharma, S.; Sharma, S. Biocontrol mechanisms of Bacillus sp., isolated from tomato rhizosphere, against Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici. Biol. Control 2018, 123, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, C.A.A.; Bettiol, W. Multifaceted intervention of Bacillus spp. against salinity stress and Fusarium wilt in tomato. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 131, 2387–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, Z.R.; Ma, S.T.; Liu, Q.Y.; Liu, B.Y.; Virk, A.L.; Qi, J.Y.; Zhao, X.; Lal, R.; Zhang, H.L. Carbon sequestration and mineralization in soil aggregates under long-term conservation tillage in the North China Plain. Catena 2020, 188, 104428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, Z.R.; Virk, A.L.; He, C.; Liu, Q.Y.; Qi, J.Y.; Dang, Y.P.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, H.L. Characteristics of carbon mineralization and accumulation under long-term conservation tillage. Catena 2020, 193, 104636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Y.; Zhang, H.P.; Vinay, N.G.; Wang, D.; Mo, F.; Liao, Y.C.; Wen, X.X. Microbial functional genes within soil aggregates drive organic carbon mineralization under contrasting tillage practices. Land Degrad. Dev. 2023, 34, 3618–3635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebrom, T.H.; Woldesenbet, S.; Bayabil, H.K.; Garcia, M.; Gao, M.; Ampim, P.; Awal, R.; Fares, A. Evaluation of phytotoxicity of three organic amendments to collard greens using the seed germination bioassay. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 5454–5462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Liang, J.; Zeng, G.; Chen, M.; Mo, D.; Li, G.; Zhang, D. Seed germination test for toxicity evaluation of compost: Its roles, problems and prospects. Waste Manag. 2017, 71, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
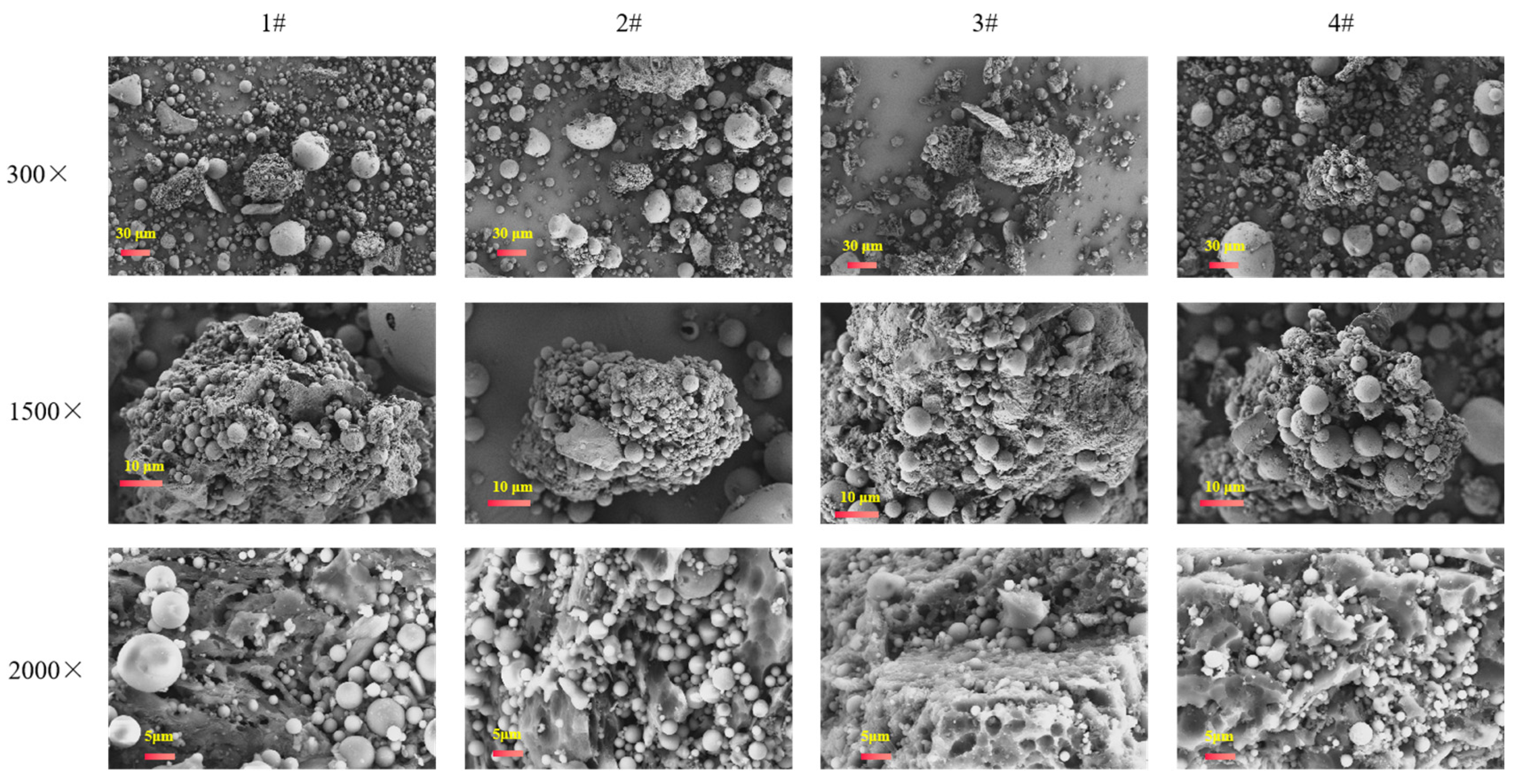






| Treatment | Sewage Sludge | Earthworm Manure | Straw | Fly Ash | Organic:Inorganic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1# | 40 | 10 | 0 | 50 | 50:50 |
| 2# | 36 | 24 | 0 | 40 | 60:40 |
| 3# | 36 | 0 | 24 | 40 | 60:40 |
| 4# | 40 | 0 | 10 | 50 | 50:50 |
| Treatment | pH | EC (ms/cm) | TN (g/kg) | SOM (g/kg) | Soil WHC (g Water/g Soil) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1# | 7.60 ± 0.03 a | 3.48 ± 0.46 a | 5.02 ± 0.35 b | 64.79 ± 6.68 c | 0.668 ± 0.041 c |
| 2# | 7.38 ± 0.04 b | 3.32 ± 0.42 a | 6.61 ± 0.17 ab | 79.02 ± 5.47 c | 0.697 ± 0.007 c |
| 3# | 7.02 ± 0.01 c | 3.51 ± 0.16 a | 7.19 ± 0.97 a | 179.00 ± 1.16 a | 1.197 ± 0.014 a |
| 4# | 7.30 ± 0.05 b | 2.84 ± 0.36 a | 5.06 ± 0.34 b | 136.46 ± 5.06 b | 0.859 ± 0.091 b |
| Treatment | Co (mg CO2/kg Soil) | K (d−1) | Co/SOC (%) | Initial Potential Mineralization Rate Co × k (mg CO2/(kg Soil·d)) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1# | 1328.2 | 0.039 | 0.547 | 51.8 |
| 2# | 847.7 | 0.096 | 0.466 | 81.4 |
| 3# | 6505.1 | 0.022 | 0.781 | 143.6 |
| 4# | 1509.2 | 0.078 | 0.471 | 117.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ge, C.; Zhang, D.; He, J.; Huo, Y.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, X. From Solid Waste to Technosols: Evaluation of Aggregate Stability, Microbial Community and Biotoxicity. Sustainability 2025, 17, 5393. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125393
Ge C, Zhang D, He J, Huo Y, Jiang L, Zhang X. From Solid Waste to Technosols: Evaluation of Aggregate Stability, Microbial Community and Biotoxicity. Sustainability. 2025; 17(12):5393. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125393
Chicago/Turabian StyleGe, Chenglong, Denghui Zhang, Jinhao He, Yueshuai Huo, Lei Jiang, and Xuan Zhang. 2025. "From Solid Waste to Technosols: Evaluation of Aggregate Stability, Microbial Community and Biotoxicity" Sustainability 17, no. 12: 5393. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125393
APA StyleGe, C., Zhang, D., He, J., Huo, Y., Jiang, L., & Zhang, X. (2025). From Solid Waste to Technosols: Evaluation of Aggregate Stability, Microbial Community and Biotoxicity. Sustainability, 17(12), 5393. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125393





