Abstract
Due to the lack of research on the temporal variation in As in the lower Yellow River and the extreme rainfall during the 2021 rainy season, this study aimed to investigate the As distribution patterns and their evolution driven by water level changes. Principal component analysis (PCA) revealed that As mobilization was predominantly controlled by redox conditions and mineral dissolution/desorption processes. The distribution of high-As water exhibited significant spatial variability, mainly located in the alluvial fan plain (14.97 μg/L) and marine-alluvial plain (22.5 μg/L). The average As concentrations in the study area decreased by 3.78 μg/L(11.55 μg/L in May and 7.77 μg/L in September). High-As groundwater was highly sensitive to water level fluctuations, while low-As groundwater was less affected. In the alluvial fan plain, As decreased with a 0–2 m groundwater level rise but increased when the level exceeded 4 m. A sedimentary zone–As distribution–water level sensitivity response model was proposed, which provides important reference value for developing groundwater exploitation and utilization plans.
1. Introduction
When the As concentration in groundwater exceeds the drinking water standard proposed by the World Health Organization (WHO) of 10 μg/L, it is considered high-As groundwater. High-As groundwater is distributed in more than 70 countries worldwide [1,2] and is drunk by 100–200 million people, with severely affected countries including Bangladesh, India, Myanmar, Vietnam, Argentina, the United States, and China [3,4,5,6,7,8,9]. The distribution of high-As water poses a serious health threat to local residents. Since its initial discovery in the early 20th century, high-As groundwater has become an urgent global environmental geological issue [10].
The formation mechanisms of natural high-As groundwater mainly include the mineral oxidative dissolution of sulfide, the reduction mechanisms of As (V), the reductive dissolution of iron–manganese oxides, and ion competitive adsorption mechanisms [11,12]. In specific environments, the enrichment process of As in groundwater is not determined by a single mechanism but by the combined action of several mechanisms [13]. Globally, high-As groundwater in reducing environments is widely distributed and has the highest level of research, with the commonly accepted As enrichment mechanism being the reductive dissolution of iron minerals, leading to the release of As adsorbed on them [14,15,16]. In general, three conditions lead to high-As groundwater in reducing environments: the presence of As sources in the area, hydrogeochemical conditions that release solid-phase As into groundwater, and relatively closed hydrogeological conditions that allow As enrichment [17].
As distribution is highly heterogeneous, mainly due to differences in topography, landforms, and sedimentology [1,18]. High-As groundwater is generally found in areas with small topographic gradients, such as lacustrine sediments, fluvial sediments, and basin subsidence center areas [19,20,21,22,23,24,25]. High-As groundwater has also been found in other sedimentary facies, such as the alluvial–diluvial sediments in front of mountains in Kuitun City, the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, and coastal sediments in Chiayi County, Taiwan [26]. Critical controls on As concentration distributions include the distribution of organic matter in sediments, groundwater recharge sources and rates, groundwater flow velocity, and the flushing time of sediments [27,28,29,30]. Human activities also influence As spatial distributions to some extent, with irrigation infiltration and runoff washing being important processes controlling As release in groundwater systems [31,32,33].
The temporal variation in As concentrations is a notable concern. As is very sensitive to redox conditions, and changes in water levels can alter these conditions, thus affecting As concentrations in groundwater. Existing research shows that seasonal variations in As concentrations differ significantly across areas due to variations in primary geological settings. In particular areas, As concentrations do not exhibit clear seasonal changes. As concentrations in some areas are higher during the rainy season than in the dry season, and the reverse applies in some other places [34,35,36,37]. Some studies have found that As concentrations increase with the age of the groundwater well [38,39].
The Yellow River Basin is home to several high-As inland basins, including the Guide Basin, Yinchuan Basin, Hetao Basin, Hohhot Basin, the Guanzhong–Yuncheng Basin, and so on [40]. The lower Yellow River shows lower As concentrations [41], but it has detected sporadic cases of arsenicosis, indicating certain risks [42,43]. The groundwater pollution survey results in the North China Plain (2006–2009) showed that high-As groundwater was widely distributed in the Yellow River alluvial–diluvial plain area [44]. Studies on groundwater As in the North Henan Plain [45,46,47,48] revealed that high-As water was distributed in sedimentary environments, such as the fan-front depression, and areas with sand–mud interbedded layers in the alluvial plain. Liu Chunhua et al. (2013) [49] analyzed the distribution characteristics and controlling factors of As in groundwater in the North Shandong Plain, revealing high As heterogeneity and variability.
From 2019 to 2021, our research team conducted hydrogeological surveys in the lower Yellow River mainstream area, which spans Henan and Shandong provinces. The area, with a variety of sedimentary types, exhibits different As distribution characteristics in different sedimentary zones, with complex and unclear variation mechanisms. Ren Yu et al. (2021) [45] compared As variations in the North Henan Plain over a decade (2010–2020), finding that As concentrations increased in high-As areas and decreased in low-As areas. However, no quantitative analysis of the variation mechanisms was conducted. Due to the lack of research on temporal variation in As in the lower Yellow River and the extreme rainfall during the 2021 rainy season, this study aimed to investigate the As distribution characteristics in groundwater and its evolution driven by water level changes by sampling groundwater in the low-water-level period (May) and high-water-level period (September) of 2021. Understanding the formation mechanism of and temporal variation in high-As groundwater is critical for ensuring the sustainable use of groundwater resources, especially for safe rural decentralized drinking water.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The study area was located in the northern part of Henan Province and southern Shandong Province, extending from Zhengzhou–Jiaozuo in the west to the Dongying Kenli District in the east. Centered along the Yellow River, the area stretches up to 35 km on both sides, covering about 20,800 km2. The area is part of the lower Yellow River alluvial plain, with a general west-to-east trend of higher terrain in the west and lower terrain in the east. The elevation ranges from 95 m to 2 m. The main landforms are the Yellow River alluvial fan plain, the Yellow River floodplain, the marine-alluvial plain, and the delta plain. Characterized by a warm-temperate monsoon climate, the area exhibits distinct seasonal variations and an uneven rainfall distribution throughout the year, which is concentrated from July to September. The major water bodies within the study area include the main channel of the Yellow River and its tributaries, including the Qin River, the Tianran-Wenyan Canal, and the Jindi River.
To intuitively reflect the distribution patterns of As in different sedimentary environments, the area was divided into four sedimentary zones based on the available data: the alluvial fan plain, floodplain, marine-alluvial plain, and delta plain (Figure 1) [50,51,52,53]. The shallow groundwater system’s aquifer group is mainly formed by Yellow River alluvium, with the bottom surface buried at depths between 60 and 120 m. Since the formation of the Yellow River, multiple stages of alluvial fan have been deposited in layers. The grain size of aquifers decreases from the top of the alluvial fan to downstream, and the thickness increases. In the Wenmengtan area, the aquifer consists of gravelly coarse sand, coarse sand, and medium sand. In the Zhengzhou–Xinxiang area, the aquifer consists of various types of sand layers interbedded with silty soil, with coarse layers below and finer ones on top, forming multiple sedimentary patterns. In the Kaifeng–Puyang area, the aquifer varies greatly both horizontally and vertically, which is why in Fengqiu County, Kaifeng is used as the boundary between the Yellow River alluvial fan and floodplain. The aquifer in the floodplain, with a thickness of 10–30 m, consists mainly of medium sand, fine sand, and silty sand. The particles are coarse and thick in the main river channel and become finer and their thickness decreases toward the downstream or flood-prone areas. The marine-alluvial plain and delta plain are characterized by a well-developed marine-alluvial layer, with a composition of silty fine sand, fine particles, thin aquifers, and semi-saline water in the marine-alluvial plain and fully saline water in the delta plain. In the insets of the figures below, A presents the alluvial fan plain, B presents the floodplain, C presents the marine-alluvial plain, and D presents the delta plain.
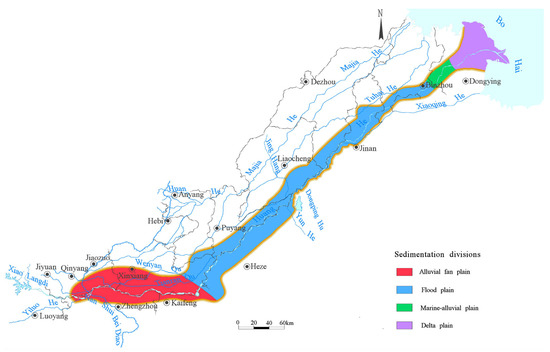
Figure 1.
Sedimentary zones of the study area.
Shallow groundwater flow is controlled by topography and recharge sources. The Yellow River flows from west to east through the central part of the area and turns northeast at Dongbatou in Lankao. The riverbed is higher than the surrounding floodplain, making it the watershed of the north and south plains. The groundwater to the south of the river flows from the northwest to the southeast, while that to the north of the river flows from the southwest to the northeast. After the river turns at Dongbatou, the groundwater to the north of the Yellow River gradually flows from the southeast to the northwest, while the groundwater south of the river flows from the northwest to the southeast. The groundwater level is generally at depths of 0–4 m, and it goes deeper in parts of Jiaozuo, Zhengzhou, and Xinxiang. Groundwater levels are mainly influenced by rainfall recharge, river infiltration, artificial extraction, and evaporation, with significant seasonal variations, reaching their lowest in May and highest in September.
2.2. Sample Collection and Testing Analysis
During May and September 2021, the project team conducted hydrogeological investigations and sample collection in the lower Yellow River’s mainstream area. In total, 141 groundwater samples were collected in May and 113 in September, with 100 identical samples. Shallow drilling was implemented to collect samples from depths of 3–4 m in the delta plain due to the lack of operational wells. Other sampling points utilized wells spanning 10–80 m depths. Despite the vertical variability, the wells all belonged to the same aquifer system, with no stable impermeable layers, resulting in close hydraulic connectivity. Therefore, all samples collected from wells of different depths belonged to the same shallow aquifer system.
The wells were purged to ensure water quality stability, and sample bottles were rinsed 3–4 times. For trace element analysis, the water samples were acidified with 50% nitric acid for preservation and stored in a temperature-controlled box at 0–4 °C. After transport to the laboratory, the samples were stored in a freezer for long-term preservation. The water samples were analyzed by the Institute of Hydrogeology and Environmental Geology, the Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences. The detection limits, standard method, and detailed analytical protocol of the test items are listed in Table 1. Quality control involved using 5% duplicate samples, and all duplicate sample errors were less than 5%.

Table 1.
Detection limits, standard method, and detailed analytical protocol of test items.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Groundwater Hydrochemical Characteristics in Different Sedimentary Zones
The September sampling campaign collected fewer total samples compared with May but achieved a more balanced spatial distribution across the sedimentary zones. Therefore, the September data were selected to analyze the groundwater hydrochemical characteristics.
From the statistical results (Table 2), the pH values of the groundwater in the four regions were quite similar, with a small coefficient of variation. The mean pH ranged from 7.18 to 7.50, and the pH test values ranged from 6.79 to 8, indicating a neutral-to-slightly alkaline environment. The other indicators showed increasing ionic concentrations, excluding HCO3, from the alluvial fan plain, floodplain, and marine-alluvial plain to the delta plain. The TDS (total dissolved solids) statistics showed that, except for the alluvial fan plain, where the average value was less than 1000 mg/L (indicating fresh water), other regions had an average TDS greater than 1000 mg/L, with the marine-alluvial plain being brackish water and the delta plain being saline water. The data show that in the floodplain, the groundwater dominated by the anion HCO3− had TDS values of less than 1000 mg/L. Compared with the WHO guidelines for drinking water quality, the groundwater in the alluvial fan plain and floodplain is suitable for drinking, while in the marine-alluvial plain and delta plain, it is not. According to the Gibbs diagram (Figure 2) [62], the alluvial fan plain and floodplain are more influenced by rock weathering, while the marine-alluvial plain and delta plain are more controlled by evaporation and concentration. The coefficient of variation for SO42− in the alluvial fan plain and floodplain was relatively high, while the coefficient of variation for Cl− was higher in the floodplain and marine-alluvial plain, indicating significant spatial variations.

Table 2.
Main ion concentration statistics of groundwater in September 2021.
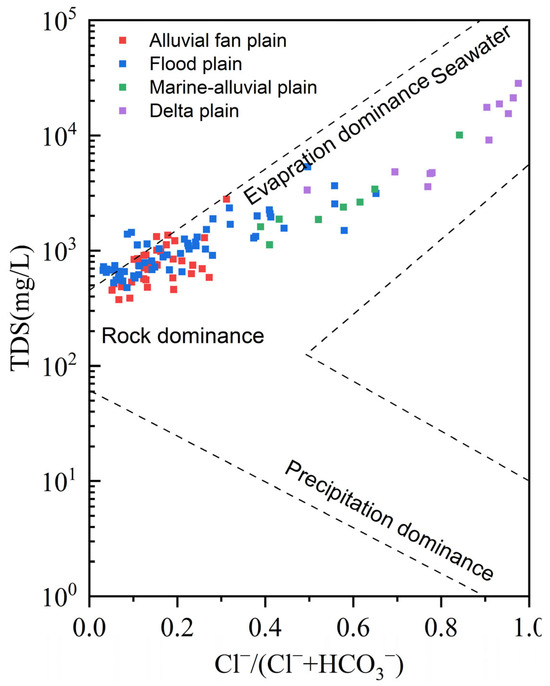
Figure 2.
Gibbs diagram of shallow groundwater in the study area.
According to previous studies comparing groundwater chemistry types in the North Shandong Plain in 1989 and 2005, the chemistry type of the western mining area has shifted to the HCO3 type, while the Cl type in the eastern area has expanded westward [64]. The groundwater chemistry types in the study area demonstrate a regular distribution along the groundwater aquifer systems and show that human activities have had an influence, resulting in point-like or zonal changes. From southwest to northeast, the distribution of water chemistry anions follows the pattern from the HCO3−type to the HCO3.Cl type, and then to the Cl.HCO3 type, and finally to the Cl type.
In the alluvial fan plain, the groundwater anion is predominantly HCO3−, with a more complex cation composition, with Ca.Mg.Na and Na.Mg being the most common in the floodplain. The anions are mainly HCO3 and HCO3.Cl, with the main cations being Ca.Mg and Mg.Na. There are scattered distributions of Cl.HCO3 and Cl.HCO3.SO4, with the corresponding main cations being Na.Mg, Na.Ca.Mg, and Na.Mg; downstream, there is a Cl.SO4-Na.Mg type. The groundwater chemistry type in the marine-alluvial plain is mainly Cl.HCO3-Na, and in the delta plain, it is mainly Cl-Na.
3.2. Characteristics of as Spatial Distribution
In September 2021, 112 groundwater samples were collected. The As concentrations ranged from 0 to 156 μg/L, with an average value of 8.8 μg/L. In total, 22 samples (19.6%) exceeded 10 μg/L. The spatial distribution of high-As groundwater showed significant variability, especially in the alluvial fan plain and floodplain, with coefficients of variation of 2.24 and 1.95, respectively.
The Yellow River alluvial fan plain had 36 groundwater sampling points with an average As concentration of 14.97 μg/L. Nine of the points had As concentrations exceeding 10 μg/L, with an exceeding standard rate of 25%. These high-As samples were concentrated along Xinxiang County–Xingyang City to Dongming County. The floodplain had 57 samples, with an average As concentration of 4.17 μg/L. The statistics of eight samples exceeded 10 μg/L, with an exceeding standard rate of 14%, scattered within the region. The marine-alluvial plain, with eight samples, had an average As concentration of 22.5 μg/L, with statistics of 5 points exceeding 10 μg/L, and an exceeding standard rate of 62.5%. In the delta plain, all 11 samples had As concentrations below 10 μg/L, averaging 2.73 μg/L. According to the statistics above, the marine-alluvial plain had the highest average As concentrations, followed by the alluvial fan plain, while the delta plain had the lowest.
From the above analysis and the September As concentration distribution (Figure 3), two high-As areas were identified: one was from Xinxiang County–Xingyang City to Dongming County in the alluvial fan plain, and the other was Lijin County in the marine-alluvial plain. The water chemistry types in these two areas were distinctly different. Three groups of samples had As concentrations greater than 50 μg/L, and the water chemistry characteristics were distributed at two extremes: two groups had HCO3− milliequivalent percentages greater than 60% and were located in Xinxiang City and Yuanyang County in the alluvial fan plain, while the other group had a Cl− milliequivalent percentage of 61.43% and was located in Lijin County in the marine-alluvial plain. Among the 19 samples with As concentrations between 10 and 50 μg/L, the water chemistry characteristics were also mainly at two extremes. Except for samples from Dongchangfu District in Liaocheng City and Lijin County in Dongying City, the percentage of Cl− was either below 26% or greater than 60%, while HCO3− was either above 48% or below 27%. The water chemistry conditions in the high-As groundwater distribution areas differed between the alluvial fan plain and the marine-alluvial plain, yet both showed similar As accumulation effects, which will be analyzed in the subsequent sections.
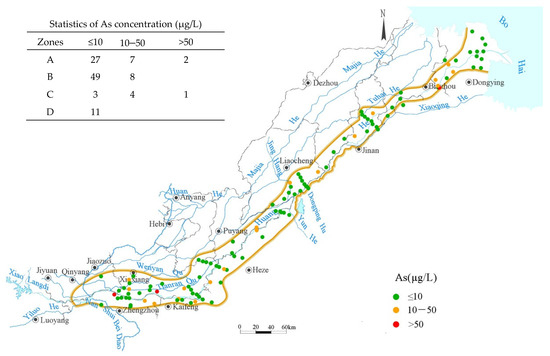
Figure 3.
As concentration distribution map in September 2021.
From a vertical distribution perspective, the groundwater with As concentrations exceeding 10 μg/L had well depths ranging from 10 to 60 m, with those exceeding 50 μg/L concentrated between 20 and 40 m. The two samples with the highest As concentrations (156 μg/L and 139 μg/L) were located in the alluvial fan plain, with well depths of 35 m and 30 m, respectively.
3.3. Formation Mechanism of High-As Groundwater
As originates from the sedimentary environment. The sediments in the lower reaches of the Yellow River contain relatively high As concentrations [65], primarily sourced from the Loess Plateau [66,67]. As-bearing minerals (such as As-bearing sandstone [68], sulfide ore deposits [69], etc.) undergo weathering, erosion, and transportation, and are ultimately deposited. High-As groundwater is mainly distributed in the alluvial fan plain area from Xinxiang County–Xingyang City to Dongming and in the combined fluvial-marine plain of Lijin County. The former area has experienced multiple Yellow River levee breaches, forming several sand-mud interlayers characterized by coarse-over-fine sedimentary interlayers. The latter features silt-dominated strata with a high organic matter content, low permeability, and slow groundwater flow [50]. Studies have shown that in sand–mud interlayered structures with weak groundwater flow, the aquifer maintains a strong reducing environment. As the clay-to-sand ratio increases, the groundwater becomes more reducing, which favors the formation of high-As groundwater [70].
To analyze the formation and evolution process of As, 11 parameters from groundwater samples were selected for PCA. Using the SPSS 20.0 software, three principal components were extracted, with a cumulative variance contribution rate of 78.52%. The factor loadings for each principal component are summarized in Table 3. Factor 1 (F1) explained 48.39% of the total variance, with Mg2+ (0.977), TDS (0.975), Cl− (0.963), Na+ (0.935), Ca2+ (0.854), and SO42− (0.848) showing a high positive loading and pH (−0.531) a high negative loading, indicating that F1 is related to groundwater salinity and primarily influenced by evaporation concentration processes. Therefore, F1 represented the evaporation concentration effect [71]. Factor 2 (F2) explained 15.43% of the total variance, with As (0.856) and Fe (0.780) having high positive loadings, representing redox processes [72]. Factor 3 (F3) explained 14.7% of the total variance, with F− (0.597) and pH (0.522) showing high positive loadings and HCO3− (−0.456) a high negative loading. Both pH and HCO3− indirectly affect element concentrations through their influence on mineral adsorption/desorption behavior. Hence, F3 is associated with mineral dissolution/desorption processes [73].

Table 3.
Factor loadings of hydrogeochemical parameters.
As had a very low loading (0.013) in F1, indicating that As in the study area was essentially unaffected by evaporation concentration. However, it had a high loading (0.856) in F2, indicating that it was mainly influenced by redox processes. The moderate loading (0.365) in F3 suggests that As was also affected, to some extent, by mineral dissolution/desorption. Therefore, the following section will explain the formation mechanism of high-As groundwater from the perspectives of redox conditions and mineral dissolution/desorption processes.
3.3.1. Redox Conditions
As showed a positive correlation with Fe (r = 0.671; p < 0.001; Figure 4a). In the aquifer medium, iron oxides are considered the primary carrier of As [74]. In reducing environments, the reduction of iron oxides leads to the dissolution of iron and the release of arsenate or arsenite adsorbed on the surface into the groundwater, resulting in rising As concentrations [16,75]. However, since sulfate (SO42−) is reduced to sulfide (S2−), which may co-precipitate with iron, manganese, and As, the positive correlation between iron and As is not always significant [76].
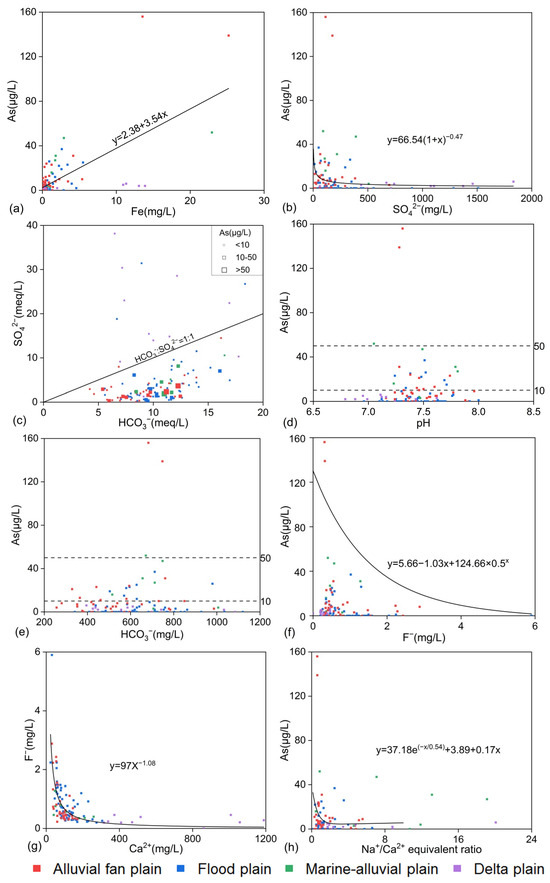
Figure 4.
Relationship between Fe and As (a), SO42− and As (b), HCO3− and SO42− (c), pH and As (d), HCO3− and As (e), F− and As (f), Ca2+ and F− (g), Na+/Ca2+ ratio and As, and concentrations (h) in groundwater.
The high-As groundwater in the lower Yellow River is in a reducing environment [45,46,47,48]. Under reducing conditions, SO42− is reduced to S2−, and there is a negative correlation between As and SO42− (Figure 4b). The HCO3− content gradually increases under microbial activity, and the HCO3−/SO42− ratio increases. The larger the HCO3−/SO42− ratio, the stronger the groundwater reducibility [70]. As shown in Figure 4c, points with As concentrations greater than 10 μg/L are mostly distributed below the line where HCO3−– SO42− = 1:1. Points with As concentrations greater than 50 μg/L have significantly higher HCO3−/SO42− ratios compared with others, indicating that stronger reducing conditions correspond to higher As concentrations. The delta plain samples, with HCO3−/SO42− ratios mostly above the 1:1 line, reflect an oxidative environment.
3.3.2. Mineral Dissolution/Desorption Processes
pH plays a decisive role in determining the ionic speciation and transport behavior of groundwater constituents. As primarily exists in groundwater as two anionic species: arsenate (AsO43−) and arsenite (AsO33−) [77,78]. As shown in Figure 4d, depicting the relationship between As and pH values, the high-As groundwater had pH values concentrated between 7.05 and 7.81. In alkaline environments, the negative charge on clay minerals increases, leading to competitive adsorption, unfavorable for the adsorption of arsenate or arsenite, creating conditions for As enrichment [75]. The pH values of the two points with extreme values of As content were 7.28 and 7.31, respectively.
Competitive adsorption by HCO3− is another important factor causing As release [46]. HCO3− displaces arsenate or arsenite adsorbed on iron oxide surfaces, causing As to dissolve into the water [79]. As shown in Figure 4e, As concentrations increased with rising HCO3− levels (200–700 mg/L) but decreased beyond 700 mg/L. This is partly because the increased salinity reduces the activity of reducing bacteria, hindering the reduction reaction. Another reason is that the strong adsorption capacity of bicarbonate minerals can adsorb As on their surfaces and form complexes, thus reducing As concentrations in the water [76].
In the study area, F− concentrations showed a negative correlation with As concentrations (Figure 4f), and groundwater F− concentrations showed a strong negative (r = −0.684; p < 0.001) correlation with Ca2+ concentrations (Figure 4g). Lower concentrations of Ca2+ are typically associated with higher concentrations of F in groundwater. Figure 4h reflects that there was a negative correlation between As and the Na/Ca equivalent ratio, and cation exchange processes happened under sluggish high-As groundwater flow conditions, where Na+ depletion and Ca2+ enrichment dominated, consistent with the findings in the North Henan Plain obtained by Ren Yu et al. [45]. This explains why As and F− concentrations showed opposing trends in their distribution. The contrasting distribution of groundwater As and F− was analogous to that in the Datong Basin [80] and the Hetao Basin [81,82], while it was different from the co-occurring high As and F− concentrations in the Yuncheng Basin [83] in China and the Chandrapur district in India [84], which can be attributed to the geogenic origin. The Na+/Ca2+ ratios in the marine-alluvial plain and delta plain were significantly higher than those in the alluvial fan plain and floodplain, which aligned with the previously mentioned groundwater chemical characteristics and flow features. The marine-alluvial plain near the delta had several points with high Na+/Ca2+ ratios, primarily because of high Na2+ and low Ca2+ concentrations in some groundwater samples.
The distribution map of As content showed no regular pattern in the direction of the groundwater flow, nor in the vertical profiles across the Yellow River’s channel (e.g., Xinxiang, Lankao, Dongming, Dong’a, and Jiyang). Liu Chunhua et al. (2013) [49] analyzed the variability in As in shallow groundwater in the North Shandong Plain of the lower Yellow River, finding that As exhibits spatial anisotropy, with the greatest variability in the southwest–northeast direction. This indicates that the As content is not strongly related to the groundwater flow direction, consistent with the findings of this study.
In summary, As sources in sedimentary environments (e.g., sand–mud interbeds in alluvial fan plains and silty fine sand layers in marine-alluvial plains) contribute to the reduced environments of aquifers that are foundational for high-As water. The reduction of iron oxides releases As, making it the main process responsible for high-As groundwater distribution. The stronger the reduction, the higher the As concentration. At the same time, ion competitive adsorption also plays a role in high-As groundwater formation.
3.4. Analysis of as Concentration Changes During High and Low Water Levels
The As concentration distribution in May and September is shown in Figure 5. Among the 100 sample points, 25 exhibited high-As groundwater in May, and 18 did in September. The average As concentrations decreased by 3.78 μg/L (11.55 μg/L in May and 7.77 μg/L in September), with 38 sample points showing a decrease, 36 remaining stable, and 26 showing an increase. The significant rainfall in 2021 near the lower Yellow River during the rainy season [85,86] led to a general rise in groundwater levels, ranging from 0 to 9 m (Figure 6). The alluvial fan plain saw the largest increase in water levels, while the delta plain experienced a rise of 0–1 m.
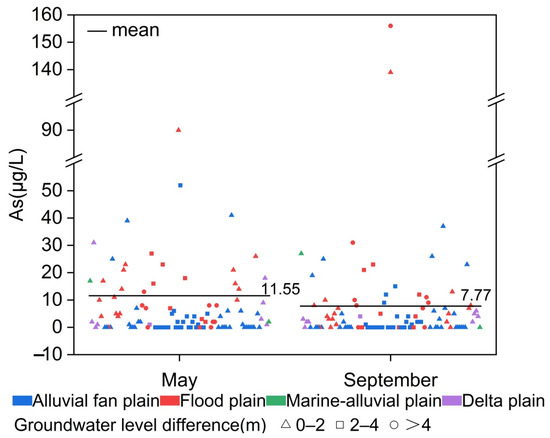
Figure 5.
Distribution of groundwater As concentrations.
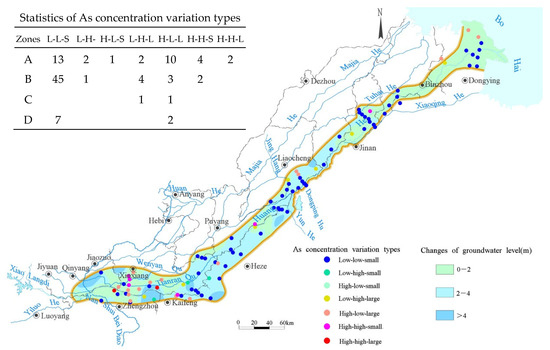
Figure 6.
Distribution of As concentration variation types and changes in groundwater level.
The As concentration distribution and variation types were defined as “May As concentration–September As concentration–absolute As concentration change.” As concentrations of greater than 10 μg/L were classified as high, while concentrations of less than 10 μg/L were classified as low. An absolute difference in the As concentration of greater than 10 μg/L was considered large, and one less than 10 μg/L was considered small. Based on the statistical analysis, there were seven types of variations (as shown in Figure 6): low–low–small (L-L-S), low–high–small (L-H-S), high–low–small (H-L-S), low–high–large (L-H-L), high–low–large (H-L-L), high–high–small (H-H-S), and high–high–large (H-H-L), with the most common types being low–low–small and high–low–large. Water sample points where both May and September As concentrations were less than 10 μg/L were considered low-As points, while those with at least one period having As concentrations greater than 10 μg/L were referred to as high-As points.
In the 34 water samples from the alluvial fan plain, 13 points exhibited the variation type of low–low–small, while 21 points were high-As groundwater, with 14 points showing an absolute As concentration change of greater than 10 μg/L. This indicated that the alluvial fan plain had high As concentrations and was greatly influenced by water level changes. Among the 55 water samples from the floodplain, 45 points showed the variation type of low–low–small, indicating that the As concentrations in the floodplain were low and less sensitive to water level changes; additionally, 10 points were high-As groundwater, among which 7 groups exhibited As concentration variations exceeding 10 μg/L. In the marine-alluvial plain, both common points showed As concentration changes of greater than 10 μg/L, with one point being high–low–large and the other being low–high–large. In the delta plain, there were nine common water sample points, with seven points showing the variation type of low–low–small and two points being high–low–large. From this, it can be concluded that the majority of high-As groundwater in the region was highly sensitive to water level changes, with As concentrations being significantly affected by water level fluctuations. Meanwhile, low-As groundwater was less influenced by water level changes. This is consistent with Duan Yanhua’s findings in the Jianghan Plain [19], demonstrating the strong sensitivity of high-As zones to redox conditions.
Points with increased As concentrations were mostly concentrated in the southern part of the alluvial fan plain and the delta plain, with increases of greater than 10 μg/L generally near the Yellow River channel or its tributaries. Points with decreased As concentrations were mostly found in the northern part of the alluvial fan plain. The distribution of As concentration variations and water level changes, along with the correlation analysis, revealed no significant relationship between these two factors. This reflected the complexity of As concentration changes in different sedimentary environments under rising water levels. The relationship between water level changes and As concentrations in each hydrogeological division should be analyzed to explore the mechanisms behind the water-level-driven changes in As concentrations.
3.5. As Concentration Change Mechanism Driven by Water Level
The relationship between water level differences in May and September and As concentration changes in the study area is shown in Figure 7. The As concentration change characteristics were analyzed for four sedimentary regions at water level changes of 0–2 m, 2–4 m, and greater than 4 m, clarifying the impact of water level changes on As concentrations.
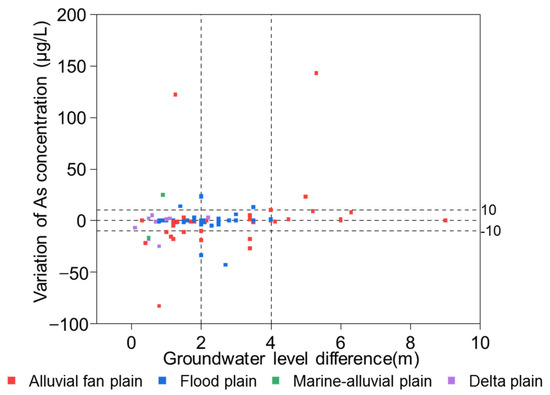
Figure 7.
Relationship between groundwater level differences and As concentration changes.
In the alluvial fan plain, As concentrations were high and were significantly affected by water level changes.
1. Water level rise of 0–2 m: Seventeen water samples exhibited an average As concentration decrease of 4.471 µg/L. Except for three samples, the As concentration decreased in the remaining samples. Eight samples showed a high–low–large change type, and one showed a high–high–large change type, with As concentrations dropping by more than 10 µg/L. Five samples showed a low–low–small change type, one showed a high–low–small type, and two showed a high–high–small type.
2. Water level rise of 2–4 m: Eight water samples exhibited an average As concentration decrease of 3.875 µg/L. Two samples showed a high–low–large change type, one showed a low–high–large type, three showed a low–low–small type, and two showed a high–high–small type.
3. Water level rise exceeding 4 m: There were nine water samples, except for one sample, where the As concentration decreased by 1 µg/L, while the others either increased or remained stable, with the average concentration increasing by 20.444 µg/L. Among these, five samples showed a low–low–small change type, one showed a low–high–large type, two showed a low–high–small type, and one showed a high–high–large type. Except for the low-As samples, the As concentration in the samples with water levels rising by more than 4 m generally increased.
In summary, in the alluvial fan plain, As concentrations tended to decrease when the water level rose by 0–2 m, but increased when the water level rose above 4 m. The Yellow River and several other rivers pass through the study area. During the rainy season, river water replenishes the groundwater, promoting an increase in the water level. This is consistent with the previously noted observation that As concentrations are notably higher near river channels. Compared with May, in September, sulfate concentrations increased by an average of 17.77 µg/L when the water level rose by 0–2 m and decreased by 11.84 µg/L when the water level rose by more than 4 m, reflecting the change in the redox environment of the aquifer. When the water level rise is minor, rainwater and surface water containing oxygen and other oxidants infiltrate into the groundwater, increasing the oxidation conditions that inhibit As release. When the water level rise is substantial, the aquifer becomes saturated, resulting in a reduced environment that leads to an increase in the As concentration [19]. The change in the As concentration in the alluvial fan plain was highly correlated with the iron concentration (0.913), while the correlations with the other indicators were relatively low, indicating that the As in the groundwater originated from the dissolution of iron oxide compounds.
In the floodplain, of the 55 water samples, only 7 had a change greater than 10 µg/L; the other points either remained stable or showed slight fluctuations. Most of the low-As points were distributed in areas with less sensitivity to water level changes.
1. Water level rise of 0–2 m: There were 30 water samples, with 24 showing a low–low–small change type (1 increased, 8 decreased, and 15 remained stable), 3 showing a low–high–large change type, 1 showing a high–low–large type, and 2 showing a high–high–small type (1 decreased by 2 µg/L, and 1 remained stable).
2. Water level rise of 2–4 m: There were 25 water samples, with 21 showing a low–low–small change type (2 increased, 4 decreased, and 15 remained stable), 1 showing a low–high–small type, 2 showing a high–low–large type, and 1 showing a low–high–large type.
In the marine-alluvial plain, two common water samples collected in May and September showed water level increases of less than 1 m, yet the As concentration changes were greater than 10 µg/L. Based on the As distribution characteristics in September, the marine-alluvial plain is considered a high-As area. From the response of the high-As groundwater in the alluvial fan plain to water level changes, it is inferred that the marine-alluvial plain is significantly affected by water level changes and can be regarded as a sensitive area for water level variations.
In the delta plain, of the nine water samples, most experienced a water level increase of 0–1 m. Among these, seven samples showed low–low–small changes (five increased and two decreased), while two samples showed high–low–large changes. The sensitivity of the As concentration changes due to groundwater level increases was between the sensitivity of the alluvial fan plain and the marine-alluvial plain.
Based on the hydrogeological conditions of the sedimentary areas, the distribution characteristics of the As content, and the sensitivity to water level influences, the following four models are proposed: alluvial fan with multi-layered sand and silt intercalations rich in organic matter–high As–significant water level influence zone; floodplain in the Yellow River’s floodwater zone–low As–low sensitivity to water level influence zone; marine-alluvial plain with slow runoff and evaporation concentration–high As–sensitive to water level influence zone; and delta with extensive saline water distribution–low As–moderate sensitivity to water level influence zone. For the alluvial fan plain where groundwater development and utilization are relatively high, the distribution of high-As groundwater should be given attention.
4. Conclusions and Suggestions
As mobilization is predominantly controlled by redox conditions and mineral dissolution/desorption processes. As showed a positive correlation with Fe but negative correlations with SO₄2−, F−, and the Na+/Ca2+ equivalent ratio. The high-As groundwater in the lower Yellow River exhibited significant spatial variability, and the reductive dissolution of iron oxides was the primary cause of high-As water formation, accompanied by ion competitive adsorption.
The comparative analysis of As concentration variations and water level fluctuations between May and September revealed that high-As groundwater was significantly influenced by water level fluctuations, while low-As groundwater was less affected by water level changes. In the alluvial fan plain, As concentrations tended to decrease when the water level rose by 0–2 m, but they increased when the water level rose over 4 m.
Future research priorities include (1) the systematic characterization of sediment matrix components (e.g., Fe/Mn oxides and organic matter) in vertical profiles and (2) the real-time monitoring of redox parameters (Eh, DO, and Fe2+/Fe3+ ratios) to elucidate the As mobilization mechanism across sediment–water interfaces.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.M., X.L. and X.Z.; data curation, S.M. and X.C.; formal analysis, S.M. and X.Z.; funding acquisition, X.Z.; investigation, S.M., X.C., C.S. and S.L.; methodology, S.M. and X.L.; project administration, X.Z.; resources, X.Z. and Y.F.; software, S.M. and K.L.; supervision, X.L., X.Z. and Y.F.; validation, S.M. and X.Z.; visualization, S.M. and K.L.; writing—original draft, S.M.; writing—review and editing, S.M., X.L., X.Z. and J.C. All authors will be updated at each stage of manuscript processing, including submission, revision, and revision reminders, via emails from our system or the assigned Assistant Editor. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences Basal Research Fund (JKYZD202411) and China Geological Survey (DD20221773-3; DD20193035).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Jia, Y.F.; Guo, H.M. Hot topics and trends in the study of high arsenic groundwater. Adv. Earth Sci. 2013, 28, 51–61. [Google Scholar]
- Podgorski, J.; Berg, M. Global threat of arsenic in groundwater. Science 2020, 368, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaubey, Y.P.; Zhang, Q. Contamination severity index: An analysis of Bangladesh groundwater arsenic. Environmetrics 2024, 35, e2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, S.; Dokania, P.; Goenka, M.; Patil, P.B.; Sarkar, A. Health-Risk Assessment of Groundwater Arsenic Levels in Bhagalpur, India, and Development of a Cost-Effective Paper-Based Arsenic Testing-Kit. Clean-Soil Air Water 2025, 53, e202300291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khant, N.A.; Kim, H.; Moon, J.; Lumongsod, R.M. Groundwater contamination by arsenic in Myanmar and their sustainability: A review. Episodes 2024, 47, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, N.N.; Tran, L.L.; Nguyen, A.L.; Nguyen, T.K.N.; Nguyen, T.H.T. Groundwater arsenic pollution in Vietnam: Current opinion on the mobilization and remediation. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2025, 44, 100596. [Google Scholar]
- Sosa, N.N.; Kulkarni, H.V.; Datta, S.; Beilinson, E.; Porfido, C.; Spagnuolo, M.; Zárate, M.A.; Surber, J. Occurrence and dis-tribution of high arsenic in sediments and groundwater of the Claromecó fluvial basin, southern Pampean plain (Argentina). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 695, 133673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yue, F.-J.; Wong, W.W.; Lin, S.-C.; Guo, T.-L.; Li, S.-L. Arsenic toxicity exacerbates China’s groundwater and health crisis. Environ. Int. 2025, 198, 109435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayotte, J.D.; Belaval, M.; Olson, S.A.; Burow, K.R.; Flanagan, S.M.; Hinkle, S.R.; Lindsey, B.D. Factors affecting temporal variability of arsenic in groundwater used for drinking water supply in the United States. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 505, 1370–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y. Global solutions to a silent poison. Science 2020, 368, 818–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.G.; Zhang, Q.H.; Zhang, P.; Liu, W. Study on distribution characteristics and formation mechanism of high arsenic groundwater. GR Water 2022, 44, 16–18+23. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Guo, H.M.; Liu, H.Y.; Zhang, W.M. Source, migration, distribution, toxicological effects and remediation technologies of arsenic in groundwater in China. China Geol. 2023, 6, 476–493. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.M.; Ni, P.; Jia, Y.F.; Guo, Q.; Jiang, Y.X. Types, chemical characteristics and genesis of geogenic high arsenic groundwater in the world. Earth Sci. Front. 2014, 21, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.P.; Jia, Y.F.; Guo, H.M.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, B. Quantifying Geochemical Processes of Arsenic Mobility in Groundwater From an Inland Basin Using a Reactive Transport Model. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2019WR025492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stopelli, E.; Duyen, V.T.; Mai, T.T.; Trang, P.T.K.; Viet, P.H.; Lightfoot, A.; Kipfer, R.; Schneider, M.; Eiche, E.; Kontny, A.; et al. Spatial and temporal evolution of groundwater arsenic contamination in the Red River delta, Vietnam: Interplay of mobilisation and retardation processes. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 137143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Sun, Y.; Li, Z.; Duan, Y.; Han, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, M.; Zheng, Y. Beyond the geological origin of sediment arsenic in groundwater systems: Arsenic redux by redox. Sci. Bull. 2023, 68, 1616–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.B. Groundwater Hydro-Chemical Characteristics Study in Hetao Plain. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Geosciences (Beijing), Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee, A.; Coomar, P.; Sarkar, S.; Johannesson, K.H.; Fryar, A.E.; Schreiber, M.E.; Ahmed, K.M.; Alam, M.A.; Bhattacharya, P.; Bundschuh, J.; et al. Arsenic and other geogenic contaminants in global groundwater. Nature Rev. Earth Environ. 2024, 5, 312–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.H. Seasonal Variations of Groundwater Arsenic Concentration in Shallow Aquifers at Jianghan Plain. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Wuhan, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Anawar, H.M.; Komaki, K.; Akai, J.; Takada, J.; Ishizuka, T.; Takahashi, T.; Yoshioka, T.; Kato, K. Diagenetic control on arsenic partitioning in sediments of the Meghna River delta, Bangladesh. Environ. Geol. 2002, 41, 816–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, B.; Berner, Z.; Mallik, S.B.; Chatterjee, D.; Charlet, L.; Stueben, D. Characterization of aquifers conducting groundwaters with low and high arsenic concentrations: A comparative case study from West Bengal, India. Mineral. Mag. 2005, 69, 841–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.R. Research on the mechanism of arsenic pollution in groundwater in the Hetao Plain, Inner Mongolia, China. China J. Geol. Hazard Control 1999, 10, 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, J.M.; Tang, J.; Feng, L.; Zha, E.S. Hydrogeochemical characteristics in the arsenic poisoning area in western Jilin Province. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2009, 36, 80–83. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.P.; Xie, X.J.; Li, J.X.; Wang, Y.X. Spatial Variation, Speciation and Enrichment of Arsenic in Groundwater from the Da-tong Basin, Northern China. Geol. Sci. Technol. Inf. 2014, 33, 178–184. [Google Scholar]
- Giménez-Forcada, E.; Luque-Espinar, J.A.; López-Bahut, M.T.; Grima-Olmedo, J.; Jiménez-Sánchez, J.; Ontiveros-Beltranena, C.; Díaz-Muñoz, J.Á.; Elster, D.; Skopljak, F.; Voutchkova, D.; et al. Analysis of the geological control on the spatial distribution of potentially toxic concentrations of As and F- in groundwater on a Pan-European scale. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 247, 114161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Bian, J.M.; Li, Z.Y.; Wang, N.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, H. Relationship between hydrochemical environment and arsenism in areas with arsenic poisoning drinking water in China. Asian J. Ecotoxicol. 2013, 8, 222–229. [Google Scholar]
- Harvey, C.F.; Swartz, C.H.; Badruzzaman, A.B.M.; Keon-Blute, N.; Yu, W.; Ali, M.A.; Jay, J.; Beckie, R.; Niedan, V.; Brabander, D.; et al. Arsenic Mobility and Groundwater Extraction in Bangladesh. Science 2002, 298, 1602–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Geen, A.; Zheng, Y.; Goodbred, S., Jr.; Horneman, A.; Aziz, Z.; Cheng, Z.; Stute, M.; Mailloux, B.; Weinman, B.; Hoque, M.A.; et al. Flushing History as a Hydrogeological Control on the Regional Distribution of Arsenic in Shallow Groundwater of the Bengal Basin. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 2283–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stute, M.; Zheng, Y.; Schlosser, P.; Horneman, A.; Dhar, R.K.; Datta, S.; Hoque, M.A.; Seddique, A.A.; Shamsudduha, M.; Ahmed, K.M.; et al. Hydrological control of As concentrations in Bangladesh groundwater. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 43, W09417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, Z.; van Geen, A.; Stute, M.; Versteeg, R.; Horneman, A.; Zheng, Y.; Goodbred, S.; Steckler, M.; Weinman, B.; Gavrieli, I.; et al. Impact of local recharge on arsenic concentrations in shallow aquifers inferred from the electromagnetic conductivity of soils in Araihazar, Bangladesh. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, W07416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Wang, Y.; Su, C.; Li, J.; Li, M. Influence of irrigation practices on arsenic mobilization: Evidence from isotope composition and Cl/Br ratios in groundwater from Datong Basin, northern China. J. Hydrol. 2012, 424–425, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X. Study on Migration and Enrichment of Arsenic in Groundwater Under the Influence of Irrigated Agriculture in Hetao Plain. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Wuhan, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee, R.; Adhikari, K.; Sinha, R.; Bharti, S.; Mal, U. Arsenic contamination in groundwater of moribund delta of Bengal basin: Quantitative assessment through adsorption kinetics and contaminant transport modelling. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2024, 133, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; van Geen, A.; Seddique, A.A.; Ahmed, K.M. Limited Temporal Variability of Arsenic Concentrations in 20 Wells Monitored for 3 Years in Araihazar, Bangladesh. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 4759–4766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Geen, A.; Ahmed, K.M.; Seddique, A.A.; Shamsudduha, M. Community wells to mitigate the arsenic crisis in Bangladesh. Bull. World Health Organ. 2003, 81, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, Y.; Zhao, K.; Li, Y.; Tang, X. Dynamic behaviors of water levels and arsenic concentration in shallow groundwater from the Hetao Basin, Inner Mongolia. J. Geochem. Explor. 2012, 135, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, T.; Wu, G.W.; Li, P. Effect of surface water-groundwater interaction on arsenic transport in shallow groundwater of Jianghan Plain. Earth Sci. 2023, 48, 3420–3431. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborti, D.; Basu, G.K.; Biswas, B.K.; Chowdhury, U.K.; Rahman, M.M.; Paul, K.; Ray, S.L. Characterization of arsenic bearing sediments in Gangetie delta of West Bengal-India. Arsen. Expo. Health Eff. 2001, 4, 27–52. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenboom, J.W. Arsenic in 15 Upazilas of Bangladesh: Water Supplies, Health and Behaviours-An Analysis of Available Data. In Report for the Department of Public Health Engineering (Bangladesh); The Department for International Development (UK) and UNICEF: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, W. Molecular Characteristics of Organic Matter and Their Roles in Arsenic Mobility in Typical Yellow River Basins. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Geosciences (Beijing), Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S.B.; Li, F.C.; Wang, S.; Li, H.X.; Yuan, L.; Liu, J.T.; Shen, H.Y.; Zhang, X.Q.; Li, C.Q.; Wu, X.; et al. Groundwater resource and eco-environmental problem of the Yellow River Basin. Geol. China 2021, 48, 1001–1019. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, X.G.; Gao, Z.J.; Bian, J.C.; Wang, H.J.; Wang, M. The correlation between endemic diseases and eco-geochemical environment in the lower Yellow River basin, Shandong Province. Geol. China 2010, 37, 824–830. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, T.C.; He, G.X.; Zhang, M.J. Epidemiological investigation of endemic arsenic poisoning in Xinxiang City. Henan J. Prev. Med. 2010, 21, 289–291. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.J.; Fei, Y.H.; Qian, Y.; Li, Y.S.; Wang, Z.; Meng, S.H.; Chen, J.S.; Zhang, F.E.; Guo, C.Y.; Wang, C.X.; et al. Report on the Investigation and Assessment Results of Ground-Water Pollution in North China Plain. Shijiazhuang in Hebei Province of China: Institute of Hydrogeology and Environmental Geology; Chinese Academy of Geological Science: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.; Cao, W.G.; Pan, D.; Wang, S.; Li, Z.Y.; Li, J.C. Evolution characteristics and change mechanism of arsenic and fluorine in shallow groundwater from a typical irrigation area in the lower reaches of the Yellow River (Henan) in 2010–2020. Rock Miner. Anal. 2021, 40, 846–859. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.C.; Cao, W.G.; Pan, D.; Wang, S.; Li, Z.Y.; Ren, Y. Influences of nitrogen cycle on arsenic enrichment in shallow groundwater from the Yellow River alluvial fan plain. Rock Miner. Anal. 2022, 41, 120–132. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Cao, W.G.; Pan, D.; Wang, S.; Ren, Y.; Li, Z.Y. Distribution and origin of high arsenic and fluoride in groundwater of the North Henan Plain. Rock Miner. Anal. 2022, 41, 1095–1109. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, W.; Cao, W.; Gao, Z.; Pan, D.; Ren, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Z. Contrasting behaviors of groundwater arsenic and fluoride in the lower reaches of the Yellow River basin, China: Geochemical and modeling evidences. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851, 158134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.H.; Zhang, G.H.; Yang, L.Z.; Wei, Z.R.; Liu, Z.Y.; Chen, X.L.; Zhang, Z. Variation characteristics and causes of arsenic con-centration in shallow groundwater of Northern Shandong Plain in the lower reaches of the Yellow River. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2013, 34, 470–476. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.S.; Liu, C.L.; Sun, C.Y.; Yan, Z.P.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.J.; Dong, H.; Ye, H.; Zhang, Y.B.; Zhang, L.Z.; et al. Research on Major Environmental Geological Problems in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yellow River, 1st ed.; China Land Press: Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Wang, L.L.; Cao, W.G. Evolution of groundwater hydrochemical characteristics in the influence zone of the lower Yellow River in Henan. Yellow River 2021, 43, 91–99. [Google Scholar]
- Geological Environmental Monitoring Institute of Henan Province. Evaluation Report on Groundwater Resources in Henan Province; Geological Environmental Monitoring Institute of Henan Province: Zhengzhou, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Shandong Provincial Territorial Spatial Ecological Restoration Center. Dynamic Monitoring and Evaluation Report on Groundwater Resources in Shandong Province; Shandong Provincial Territorial Spatial Ecological Restoration Center: Jinan, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- HJ 776-2015; Water Quality—Determination of 32 Elements—Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometry. Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2015.
- DZ/T0064.42-2021; Methods for Analysis of Groundwater Quality—Part 42: Determination of Calcium, Magnesium, Potassium, Sodium, Aluminium, Iron, Strontium, Barium and Manganese Contents-Inductively Coupled Plasma Atomie Emission Spectrometry. Ministry of Natural Resources of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2021.
- DZ/T 0064.49-2021; Methods for Analysis of Groundwater Quality—Part 49: Determination of Carbonate, Bicarbonate Ions, Hy-droxy—Titration. Ministry of Natural Resources of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2021.
- DZ/T0064.50-2021; Methods for Analysis of Groundwater Quality—Part 50: Determination of Chloride Argentometric—Titration. Ministry of Natural Resources of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2021.
- HJ 84-2016; Water Quality-Determination of Inorganic Anions (F−, Cl−, NO2−, Br−, NO3−, PO43−, SO32−, SO42−)-Ion Chromatography. Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- DZ/T 0064.11-2021; Methods for Analysis of Groundwater Quality—Part 11: Determination of Arsenic Content—Hydride Generation Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry. Ministry of Natural Resources of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2021.
- DZ/T 0064.5-2021; Methods for Analysis of Groundwater Quality—Part 5: Determination of pH-Glass-Electrodes Method. Ministry of Natural Resources of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2021.
- DZ/T 0064.9-2021; Methods for Analysis of Groundwater Quality—Part 9: Determination of Total Dissolved Solids—Gravimetric Method. Ministry of Natural Resources of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Gibbs, R.J. Mechanisms Controlling World Water Chemistry. Science 1970, 170, 1088–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality: Fourth Edition Incorporating the First and Second Addenda; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.J.; Fei, Y.H.; Chen, Z.Y. Investigation and Assessment of Sustainable Utilization of Groundwater Resources in the North China Plain, 1st ed.; Geology Press: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.H. Water quality evaluation of the Yellow River in Shandong. Yellow River 1992, 9, 61–62. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, W.Y. The Speciation Distribution Study of Arsenic and Mercury in the Water Body of Yellow River in Inner Mongolia sec-Tion. Master’s Thesis, Inner Mongolia University, Huhehaote, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, C.D.; Wang, Z.M. Preliminary analysis of arsenic sources in Yellow River Water and their relationship with sediments. Water Resour. Prot. 1986, 1, 14–17. [Google Scholar]
- Nan, F.C. Apples Brought Prosperity to This Once Poorest Land. 2024. Available online: https://cj.sina.com.cn/articles/view/1645578093/6215876d02701igns (accessed on 4 December 2024).
- Li, Y.; Gao, X.B.; Zhang, X.; Luo, W.T.; Hu, Q.H. Geochemistry of arsenic in sediments and groundwater in areas with arsenic polluted groundwater in Yuncheng Basin. Saf. Environ. Eng. 2017, 24, 68–74. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, W.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, R.; Li, Y.; Dong, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhao, R. Controls of paleochannels on groundwater arsenic distribution in shallow aquifers of alluvial plain in the Hetao Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613–614, 958–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Wang, W.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, C.; Sun, Y. Hydrogeochemical Characteristics and Health Effects of Iodine in Groundwater in Wei River Basin. Expo. Health 2020, 12, 369–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Das, A.; Das, N.; Goswami, R.; Singh, U.K. Co-occurrence perspective of arsenic and fluoride in the groundwater of Diphu, Assam, Northeastern India. Chemosphere 2016, 150, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondu, R.; Cloutier, V.; Rosa, E.; Roy, M. An exploratory data analysis approach for assessing the sources and distribution of naturally occurring contaminants (F, Ba, Mn, As) in (Canada). Appl. Geochem. 2020, 114, 104500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravenscroft, P.; Brammer, H.; Richards, K. Arsenic Pollution: A Global Synthesis; Wiley-Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.N.; Li, H.Q.; Wen, X.Y.; Xie, W.L.; Zhang, J.W.; Zhao, Z.Q. Arsenic enrichment mechanism of groundwater in the western Hetao Plain. Bull. Mineral. Petrol. Geochem. 2023, 42, 289–297. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y. Hydrogeochemical Evolution of High Arsenic Groundwater in the Hetao Basin, Inner Mongolia. Master’s Thesis, China University of Geosciences (Beijing), Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Li, X.; Xiu, W.; He, W.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, A. Controls of organic matter bioreactivity on arsenic mobility in shallow aquifers of the Hetao Basin, P.R. China. J. Hydrol. 2019, 571, 448–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.C.; Zhang, Z.J.; Zhao, X.Y.; Wen, M.T.; Cao, S.W.; Li, Y.S. Arsenic contamination caused by roxarsone transformation with spatiotemporal variation of microbial community structure in a column experiment. J. Groundw. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 304–316. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Su, C.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Q. Mobility of arsenic in aquifer sediments at Datong Basin, northern China: Effect of bicarbonate and phosphate. J. Geochem. Explor. 2013, 135, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, K.F.; Wang, Y.X.; Xie, X.J.; Su, C.L.; Ma, T.; Li, J.X.; Liu, Y.Q. Hydrogeochemistry of co-occurring geogenic arsenic, fluoride and iodine in groundwater at Datong Basin, northern China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 300, 652–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, T.; Gan, Y. Speciation and enrichment of arsenic in strongly reducing shallow aquifers at western Hetao Plain, northern China. Environ. Geol. 2009, 56, 1467–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xing, L.; Jia, Y. Spatial variation in arsenic and fluoride concentrations of shallow groundwater from the town of Shahai in the Hetao basin, Inner Mongolia. Appl. Geochem. 2012, 27, 2187–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currell, M.; Cartwright, I.; Raveggi, M.; Han, D. Controls on elevated fluoride and arsenic concentrations in groundwater from the Yuncheng Basin, China. Appl. Geochem. 2011, 26, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahul, K.K. Co-occurrence of arsenic and fluoride in groundwater in Chandrapur district, central India. Holist. Approach Environ. 2025, 15, 36–46. [Google Scholar]
- Water resources department of Henan province. Henan Water Resources Bulletin in 2021; Water resources department of Henan province: Zhengzhou, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Water resources department of Shandong province. Shandong Water Resources Bulletin in 2021; Water resources department of Shandong province: Jinan, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).