Spatiotemporal Evolution of Ecosystem Service Value and Its Tradeoffs and Synergies in the Liaoning Coastal Economic Belt
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data Sources
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
3. Research Methods
3.1. Land Use Dynamic Changes
3.1.1. Land Use Dynamic Index
- (1)
- Single land use dynamics
- (2)
- Comprehensive land use dynamics
3.1.2. Land Use Composite Index
3.2. Estimation of ESV
3.3. Construction of the Geo-Information Tupu
- (1)
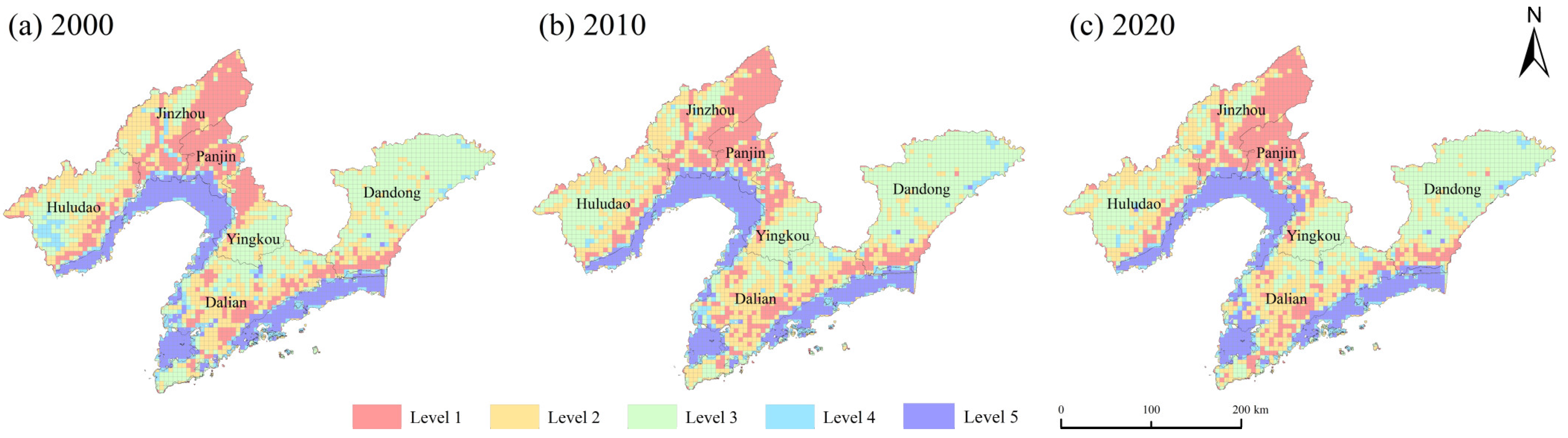
- ESV’s spatiotemporal evolution Tupu. ArcMap 10.2 software is employed to create a 5 km × 5 km regular grid covering the study area, and the ESV of each grid is calculated [8,36]. According to relevant studies [37,38], the natural breakpoint grading approach is used to set the ESV classification criterion as follows: Level 1 (0, 1831.24 ten thousand yuan), Level 2 (1831.25, 3364.69 ten thousand yuan), Level 3 (3364.70, 5125.87 ten thousand yuan), Level 4 (5125.88, 7552.16 ten thousand yuan), and Level 5 (7552.17, 14,716.19 ten thousand yuan). Thus, we obtained the ESV’s spatial distribution maps in the LCEB.
- (2)
- Transfer of ESV Tupu. The Markov transition model is a statistical framework grounded in probability theory, designed to capture the dynamics of system states transitioning from time T0 to T1. It operates under the assumption that the state at T1 depends solely on the conditions at T0, without influence from earlier periods [39]. In this study, the model is utilized to generate a transition matrix for the ESV, where each matrix element represents the area transferred between ESV levels. This approach facilitates a more detailed understanding of the spatial and temporal evolution of ESVs and provides a quantitative depiction of transitions among different ESV levels. The related formulas are as follows:In Formula (7), represents the transfer probability of the ESV changing from level to level , indicating either the quantity of area converted or the proportional relationship between levels. This probability satisfies the conditions 0 < < 1 and = 1, meaning that the sum of each row’s elements equals one.
- (3)
- The rise-and-fall Tupu of the ESV is derived from the ESV transfer Tupu. Areas where the ESV level at time are defined as rising Tupu units, whereas those where the ESV level at is lower than at are identified as falling Tupus.
3.4. Standard Deviation Ellipse
3.5. Ecosystem Service Tradeoff Degree (ESTD) Index
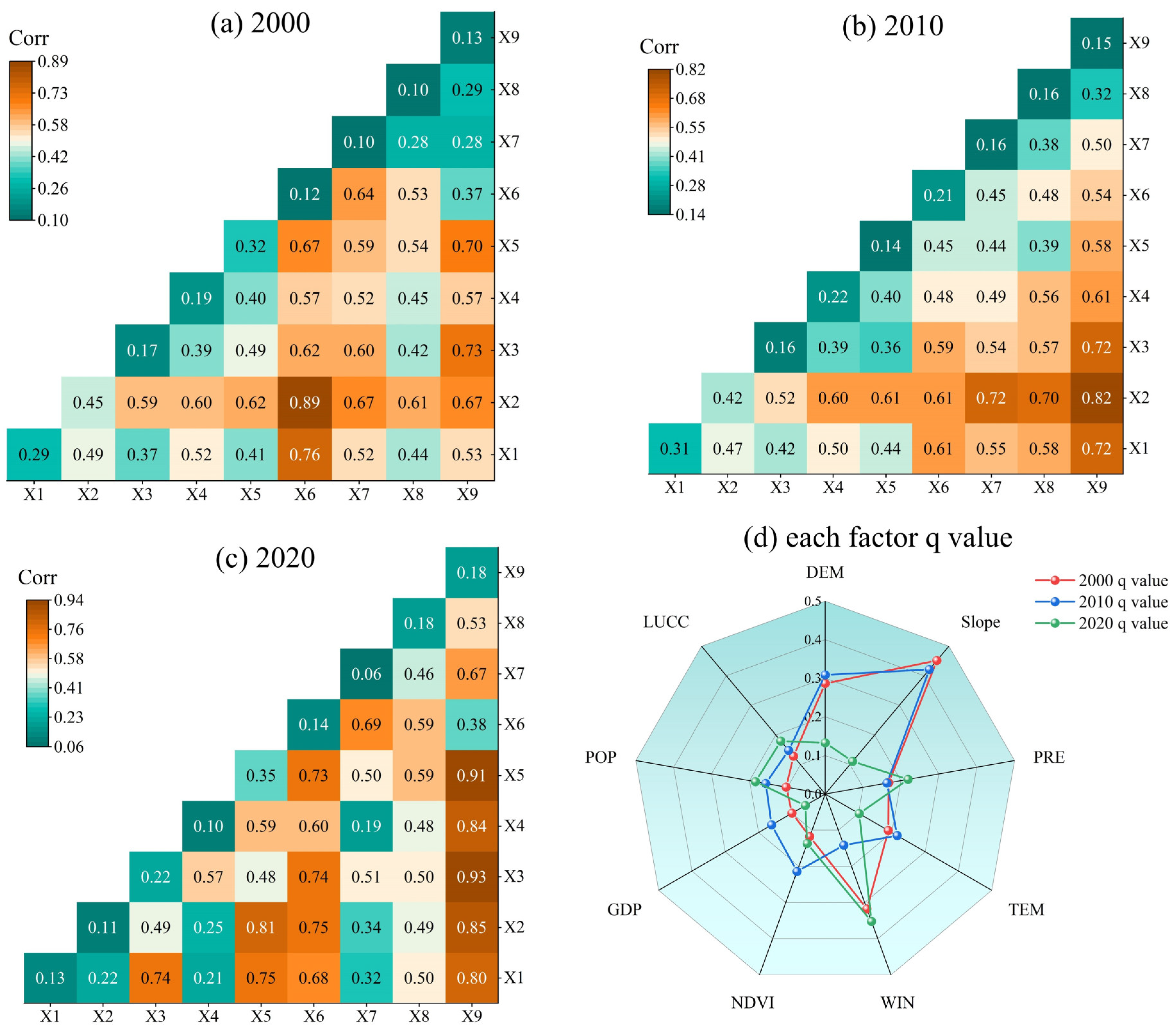
3.6. Geographical Detector
4. Results
4.1. Land Use Change Characteristics
4.2. Characteristics of Changes in ESV
4.2.1. Spatiotemporal Evolution of ESV
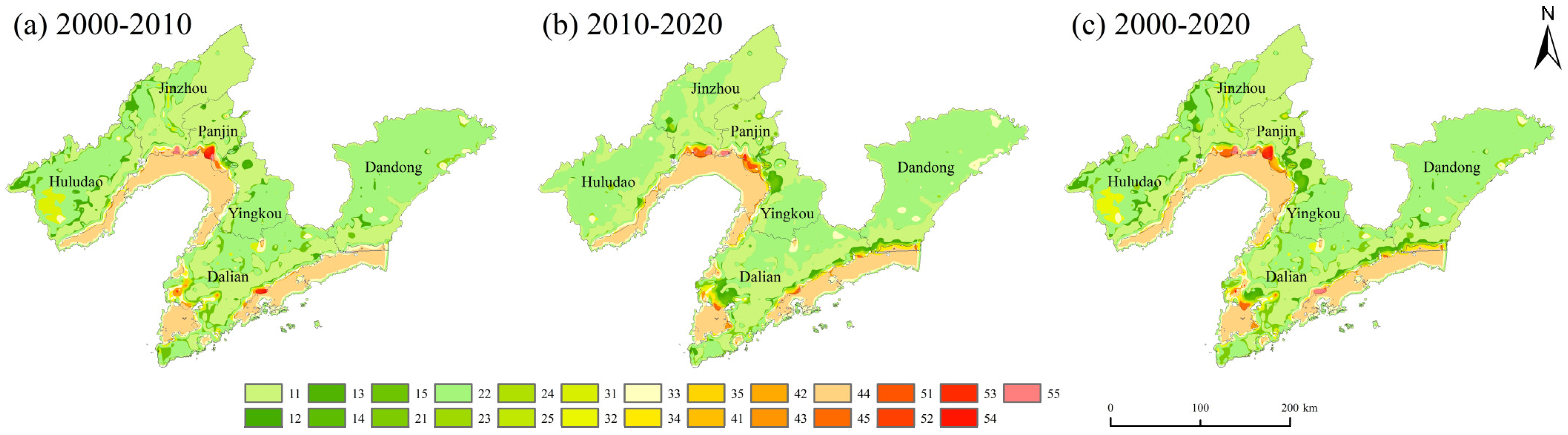
4.2.2. Characteristics of Transfer Tupu of ESV Levels
4.2.3. Characteristics of the Rise and Fall of Each ESV Level
4.3. Standard Deviation Ellipse Analysis of ESV
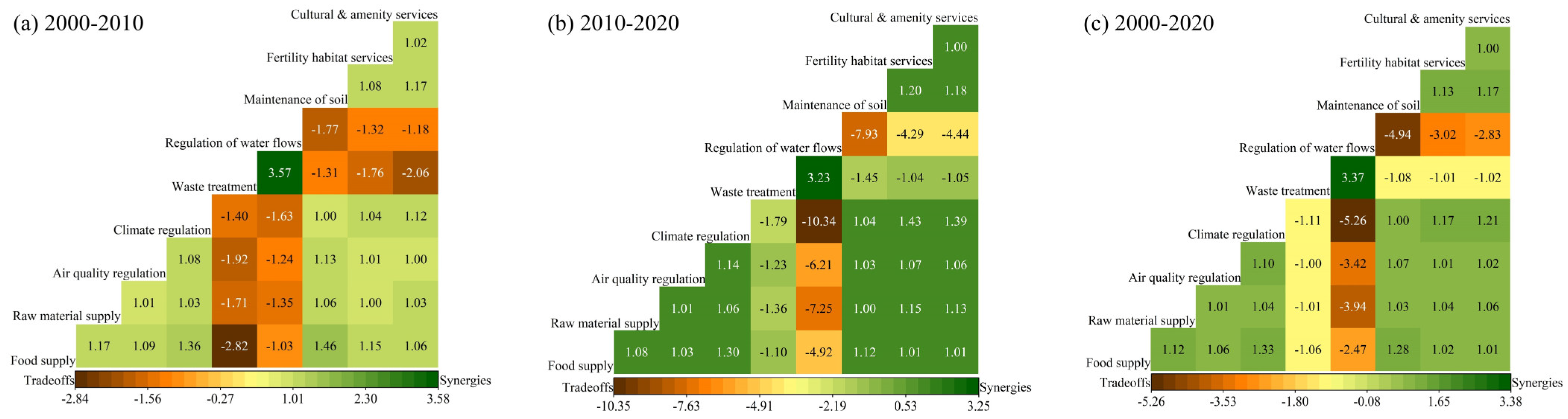
4.4. Analysis of Tradeoffs/Synergies Between ESs
4.5. Spatial Heterogeneity of ESV
5. Discussion
5.1. ESV Responses to Land Use
5.2. Complex Interactions Between ESs
5.3. Policy Suggestions
5.4. Research Limitations and Perspectives
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ESV | Ecosystem service value |
| ESTD | Ecosystem service tradeoff degree |
| LCEB | Liaoning Coastal Economic Belt |
| ES | Ecosystem services |
| InVEST | Integrated Valuation of Ecosystem Services and Tradeoffs |
| NDVI | Normalized vegetation index |
| DEM | Digital Elevation Model |
| PRE | Average annual precipitation |
| TEM | Average annual temperature |
| WIN | Average annual wind speed |
| POP | Population density |
References
- Liu, L.; Wu, J. Space Cannot Substitute for Time in the Study of the Ecosystem Services-Human Wellbeing Relationship. Geogr. Sustainability 2025, 6, 100221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daily, G.C. Nature’s Service: Societal Dependence Onnatural Ecosystems; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, L.; Geng, M.; Li, F.; Xie, Y.; Tian, T.; Chen, Q. Spatiotemporal Characteristics and Drivers of Ecosystem Service Interactions in the Dongting Lake Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 926, 172012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Chen, Y.; Wan, Z.; Chen, Z.; Lin, J.; Chen, P.; Sun, W.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, Y. Cross-Sensitivity Analysis of Land Use Transition and Ecological Service Values in Rare Earth Mining Areas in Southern China. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 22817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Zhen, L.; Lu, C.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, C. Expert knowledge based valuation method of ecosystem services in China. J. Nat. Rescour. 2008, 154, 911–919. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, G.; Zhang, C.; Zhen, L.; Zhang, L. Dynamic Changes in the Value of China’s Ecosystem Services. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 26, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lai, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, S.; Lv, L.; Fan, Y. Optimization of Territorial Ecological Space under the Constraint of Ecosystem Service Externalities. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 168, 112752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Zhang, F.; Wang, H. The Response of Ecosystem Service Value to Land Use Change in the Middle and Lower Yellow River: A Case Study of the Henan Section. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 140, 109019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yu, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, J.; Yang, W.; Wang, X. Research on the Value of County-Level Ecosystem Services in Highly Mountainous Canyon Areas Based on Land Use Change: Analysis of Spatiotemporal Evolution Characteristics and Spatial Stability. Land 2025, 14, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Liu, D.; Zhang, J.; Xie, Y.; Cao, E.; Li, H. Tradeoffs/Synergies of Multiple Ecosystem Services Based on Land Use Simulation in a Mountain-Basin Area, Western China. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 99, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lu, B.; Li, J.; Liu, Q.; He, L.; Lv, S.; Yu, S. Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Ecological Service Value Driven by Land Use Changes: A Case Study with Danjiangkou, Hubei Section. Resour. Environ. Sustain. 2024, 15, 100146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Jia, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Z. Evaluating Ecosystem Service Value Changes in Mangrove Forests in Guangxi, China, from 2016 to 2020. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Tian, G.; Liu, G.; Ye, J.; Yao, X.; Liu, Q.; Lou, W.; Wu, S. Tupu Methods of Spatial-Temporal Pattern on Land Use Change: A Case Study in the Yellow River Delta. J. Geogr. Sci 2004, 14, 131–142. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Hu, B.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, G. Research on the Spatiotemporal Evolution and Mechanism of Ecosystem Service Value in the Mountain-River-Sea Transition Zone Based on “Production-Living-Ecological Space”—Taking the Karst-Beibu Gulf in Southwest Guangxi, China as an Example. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 148, 109889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, L.; Zhao, F.; Teng, Y.; Teng, J.; Zhan, J.; Zhang, F.; Liu, W.; Wang, L. Scale Dependency of Trade-Offs/Synergies Analysis of Ecosystem Services Based on Bayesian Belief Networks: A Case of the Yellow River Basin. J. Environ. Manage. 2025, 375, 124410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, E.; Wang, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, D. Methods, Tools and Research Framework of Ecosystem Service Trade-Offs. Geogr. Res. 2016, 35, 1005–1016. [Google Scholar]
- Howe, C.; Suich, H.; Vira, B.; Mace, G.M. Creating Win-Wins from Trade-Offs? Ecosystem Services for Human Well-Being: A Meta-Analysis of Ecosystem Service Trade-Offs and Synergies in the Real World. Glob. Environ. Change 2014, 28, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Yang, H.; Gong, H.; Shi, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, R.; Chen, Y. Spatiotemporal Changes and Trade-Offs/Synergies of Waterfront Ecosystem Services Globally. Sustainability 2025, 17, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Yang, J.; Tang, Z.; Xue, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J. Driving Mechanisms of Ecosystem Services and Their Trade-Offs and Synergies in the Transition Zone between the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and the Loess Plateau. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 171, 113148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Li, Z.; Gibson, J. A Review on Trade-off Analysis of Ecosystem Services for Sustainable Land-Use Management. J. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 953–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, L.; Wu, Q.; Du, P. Analysis of Spatial and Temporal Evolution of Ecosystem Service Value Based on the Framework of “Risk-Association-Driver”: A Case Study of Panjin City. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Jian, S. Synergies and Trade-Offs of Ecosystem Services Affected by Land Use Structures of Small Watershed in the Loess Plateau. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 350, 119589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wu, W.; Yang, M.; Gao, Y.; Shao, J.; Yang, W.; Ma, G.; Yu, F.; Yao, N.; Jiang, H. Exploring the Complex Trade-Offs and Synergies of Global Ecosystem Services. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2024, 21, 100391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Jia, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z. Analysis of Trade-off and Synergy Effects of Ecosystem Services in Hebei Province from the Perspective of Ecological Function Area. ACTA Geogr. Sin. 2023, 78, 2833–2849. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Luo, H. Trade-off/Synergistic Changes in Ecosystem Services and Geographical Detection of Its Driving Factors in Typical Karst Areas in Southern China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Song, F. Quantifying the Independent Contributions of Climate and Land Use Change to Ecosystem Services. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 153, 110411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, P.; Jiang, X.; Lo, K. Measuring Sustainable Urbanization in China: A Case Study of the Coastal Liaoning Area. Sustain. Sci. 2013, 8, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Fang, S.; Geng, X.; Yuan, Y.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, D.; Li, R.; Sun, W.; Wang, X. Coastal Ecosystem Service in Response to Past and Future Land Use and Land Cover Change Dynamics in the Yangtze River Estuary. J. Cleaner Prod. 2023, 385, 135601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Hao, R. Research Progress and Prospect of Ecosystem Services. Adv. Earth Sci. 2020, 35, 804. [Google Scholar]
- Chuai, X.; Huang, X.; Wu, C.; Li, J.; Lu, Q.; Qi, X.; Zhang, M.; Zuo, T.; Lu, J. Land Use and Ecosystems Services Value Changes and Ecological Land Management in Coastal Jiangsu, China. Habitat Int. 2016, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Bao, Y. Study on the Methods of Land Use Dynamic Change Research. Prog. Geogr. 1999, 18, 81–87. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Zhou, J.; Zhan, D. Spatial and Temporal Changes and Driving Factors of Cultivated Land in Heilongjiang Province. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2021, 41, 1266–1275. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, J.; Qian, B.; Chen, G.; Shi, F.; Cao, X.; Zhu, C. Land Use Change and Evolution of Ecosystem Service Value in Maduo County of Source Region of the Yellow River. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 510–521. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, D.; Liu, J. Study on the Model of Regional Differentiation of Land Use Degree in China. J. Nat. Resour. 1997, 12, 105–111. [Google Scholar]
- Costanza, R.; De Groot, R.; Sutton, P.; Van der Ploeg, S.; Anderson, S.J.; Kubiszewski, I.; Farber, S.; Turner, R.K. Changes in the Global Value of Ecosystem Services. Glob. Environ. Change 2014, 26, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayila, R.; Mamat, S.; Nigela, T.; Yikiliman, A.; Ma, C.; Yierxiati, A. The Ecosystem Service Value Spatial-Temporal Changes in the Ugan-Kuqa River Delta Oasis Based on RS and GIS. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 5938–5951. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Adam, N.A.; Mirzaliev, S.; Saydullaev, S.; Bai, H. An Integrated Approach for Evaluating the Spatial and Temporal Dynamics of Ecosystem Services and Ecological Risk Urban Agglomerations in China. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 172, 113248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Liu, X.; Liu, J. Construction and Optimization of Ecological Security Patterns in Chinese Black Soil Areas Considering Ecological Importance and Vulnerability. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 12142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Xu, J.; Zang, J.; Huang, T. Simulation and Prediction of Land Use Change in Guangxi Based on Markov-FLUS Model. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 29, 249–254. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Qin, T.; Yan, D.; Liu, S.; Feng, J.; Wang, Q.; Liu, H.; Gao, H. Analysis of the Evolution of Ecosystem Service Value and Its Driving Factors in the Yellow River Source Area, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefever, D.W. Measuring Geographic Concentration by Means of the Standard Deviational Ellipse. Am. J. Sociol. 1926, 32, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wei, J.; Wang, X.; Cai, Y. Temporal and Spatial Variation of Ecosystem Service Value and Its Trade-Offs and Synergies in the Peripheral Region of the Poyang Lake. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2022, 42, 1229–1238. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Ren, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J. Tradeoffs-synergies Analysis among Ecosystem Services in Northwestern Valley Basin: Taking Yinchuan Basin as an Example. J. Desert Res. 2016, 36, 1731–1738. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Xu, C.D. Geodetector: Principle and Prospective. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 116–134. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Yin, Q.; Zheng, Z.; Sun, S.; Huang, J. Dynamic Changes and Key Drivers of Ecosystem Service Values in Populous Zones on the Tibetan Plateau: A 35-Year Analysis. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 167, 112620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Song, Y.; Xue, Y.; Jian, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, G. Spatial-Temporal Variations and Mechanism of Ecosystem Services Value from Land Ues Perspective: A Case Study of Liaoning Coastal Zones. Areal Res. Dev. 2024, 43, 153–159. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, H.; Yuan, S.; Prishchepov, A.V. Spatial-Temporal Heterogeneity of Ecosystem Service Interactions and Their Social-Ecological Drivers: Implications for Spatial Planning and Management. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 189, 106767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Wu, Z. Spatiotemporal Coupling Analysis between Human Footprint and Ecosystem Service Value in the Highly Urbanized Pearl River Delta Urban Agglomeration, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 148, 110033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hou, X.; Li, X.; Song, B.; Wang, C. Assessing and Predicting Changes in Ecosystem Service Values Based on Land Use/Cover Change in the Bohai Rim Coastal Zone. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 111, 106004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Wang, X.H.; Wu, W. Assessment of coastal eco- environmental sustainable development under multiple pressures: A Case Study of Jiaozhou Bay, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 363, 121230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, L.; Li, B.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Sun, X. Quantifying the climatic and hydrological effects of land use/cover change based on Weather Research and Forecasting model. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 917–925. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Cheng, H.; Wang, N.; Huang, C.; Zhang, K.; Qiao, B.; Wang, Y.; Wen, P. Trade-off and Synergy Relationships and Spatial Bundle Analysis of Ecosystem Services in the Qilian Mountains. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, C.; Ren, H.; Xu, D.; Gao, Y. Spatial Scale Effects on the Value of Ecosystem Services in China’s Terrestrial Area. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 366, 121745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Li, W.; Wang, S.; Wang, J. Assessing Heterogeneity of Trade-Offs/Synergies and Values among Ecosystem Services in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 140, 109026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, E.M.; Peterson, G.D.; Gordon, L.J. Understanding Relationships among Multiple Ecosystem Services. Ecol. Lett. 2009, 12, 1394–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cord, A.F.; Bartkowski, B.; Beckmann, M.; Dittrich, A.; Hermans-Neumann, K.; Kaim, A.; Lienhoop, N.; Locher-Krause, K.; Priess, J.; Schröter-Schlaack, C.; et al. Towards Systematic Analyses of Ecosystem Service Trade-Offs and Synergies: Main Concepts, Methods and the Road Ahead. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 28, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, E.P.; Lin, H.; Wang, G.X.; Xia, C. Analysis of Evolution and Driving Force of Ecosystem Service Values in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region during 1990–2011. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2014, 34, 5962–5973. [Google Scholar]



| Primary Classification | Secondary Classification | Farmland | Forest | Grassland | Inland Freshwater | Saltwater Wetland | Shallow Water | Unused Land |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Provisioning services | Food supply | 2320.77 | 530.31 | 490.06 | 840.10 | 1071.13 | 28,877.33 | 105.01 |
| Raw material supply | 514.56 | 1218.14 | 721.08 | 241.53 | 1050.12 | 479.28 | 31.50 | |
| Regulating services | Air quality regulation | 1869.22 | 4006.22 | 2534.30 | 808.59 | 3990.47 | 3957.91 | 136.52 |
| Climate regulation | 976.61 | 11,987.15 | 6699.79 | 2404.78 | 7560.89 | 5255.24 | 105.01 | |
| Waste treatment | 283.53 | 3512.66 | 2212.26 | 5828.18 | 7560.89 | 0.00 | 430.55 | |
| Regulation of water flows | 3139.87 | 7844.42 | 4907.58 | 107,364.58 | 50,888.96 | 711.35 | 252.03 | |
| Supporting services | Maintenance of soil | 1092.13 | 4877.82 | 3087.36 | 976.61 | 4851.57 | 0.00 | 157.52 |
| Fertility habitat services | 357.04 | 4442.02 | 2807.33 | 2677.81 | 16,528.94 | 19,206.75 | 147.02 | |
| Cultural services | Cultural and amenity services | 157.52 | 1947.98 | 1239.15 | 1984.73 | 9934.16 | 17,955.21 | 63.01 |
| Total | 10,711.26 | 40,366.73 | 24,698.89 | 123,126.93 | 103,437.12 | 76,443.08 | 1428.17 |
| Land Use Type | Year | Farmland | Forest | Grassland | Inland Freshwater | Saltwater Wetland | Shallow Water | Construction Land | Unused Land |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area (km2) | 2000 | 24,059.44 | 23,838.51 | 1656.20 | 1933.10 | 281.66 | 12,914.67 | 4071.27 | 1061.12 |
| 2010 | 23,232.16 | 23,848.24 | 1090.90 | 2090.75 | 425.98 | 12,529.30 | 5673.83 | 1099.46 | |
| 2020 | 22,787.49 | 23,716.01 | 1052.00 | 3113.82 | 135.62 | 12,277.52 | 5918.17 | 1010.18 | |
| Area percentage (%) | 2000 | 34.46 | 34.14 | 2.37 | 2.77 | 0.40 | 18.50 | 5.83 | 1.52 |
| 2010 | 33.19 | 34.07 | 1.56 | 2.99 | 0.61 | 17.90 | 8.11 | 1.57 | |
| 2020 | 32.55 | 33.87 | 1.50 | 4.45 | 0.19 | 17.54 | 8.45 | 1.44 | |
| Volume of change (km2) | 2000–2010 | −827.28 | 9.73 | −565.29 | 157.65 | 144.31 | −385.37 | 1602.56 | 38.34 |
| 2010–2020 | −444.67 | −132.23 | −38.90 | 1023.08 | −290.36 | −251.79 | 244.33 | −89.29 | |
| 2000–2020 | −1271.95 | −122.50 | –604.19 | 1180.72 | −146.05 | −637.15 | 1846.89 | −50.95 | |
| Single-motion attitude (%) | 2000–2010 | −0.34 | 0.004 | −3.41 | 0.82 | 5.12 | −0.30 | 3.94 | 0.36 |
| 2010–2020 | −0.19 | −0.06 | −0.36 | 4.89 | −6.82 | −0.20 | 0.43 | −0.81 | |
| 2000–2020 | −0.26 | −0.03 | −1.82 | 3.05 | −2.59 | −0.25 | 2.27 | −0.24 |
| Land Use Type | Year | Farmland | Forest | Grassland | Inland Freshwater | Saltwater Wetland | Shallow Water | Unused Land | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ESV (RMB 100 million yuan) | 2000 | 257.71 | 962.28 | 40.91 | 238.02 | 29.13 | 987.24 | 1.52 | 2516.80 |
| 2010 | 248.85 | 962.68 | 26.94 | 257.43 | 44.06 | 957.78 | 1.57 | 2499.30 | |
| 2020 | 244.08 | 957.34 | 25.98 | 383.40 | 14.03 | 938.53 | 1.44 | 2564.80 | |
| Contribution rate (%) | 2000 | 10.24 | 38.23 | 1.63 | 9.46 | 1.16 | 39.23 | 0.06 | 100.00 |
| 2010 | 9.96 | 38.52 | 1.08 | 10.30 | 1.76 | 38.32 | 0.06 | 100.00 | |
| 2020 | 9.52 | 37.33 | 1.01 | 14.95 | 0.55 | 36.59 | 0.06 | 100.00 | |
| Volume of change (RMB 100 million yuan) | 2000–2010 | −8.86 | 0.39 | −13.96 | 19.41 | 14.93 | −29.46 | 0.05 | −17.50 |
| 2010–2020 | −4.76 | −5.34 | −0.96 | 125.97 | −30.03 | −19.25 | −0.13 | 65.50 | |
| 2000–2020 | −13.62 | −4.95 | −14.92 | 145.38 | −15.11 | −48.71 | −0.07 | 48.00 | |
| Average annual rate of change (%) | 2000–2010 | −0.35 | 0.004 | −4.09 | 0.79 | 4.22 | −0.30 | 0.36 | −0.07 |
| 2010–2020 | −0.19 | −0.06 | −0.36 | 4.06 | −10.81 | −0.20 | −0.84 | 0.26 | |
| 2000–2020 | −0.27 | −0.03 | −2.24 | 2.41 | −3.59 | −0.25 | −0.25 | 0.09 |
| Level | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Level 4 | Level 5 | Transfers Out |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level 1 | (1922.43, 28.48) | (21.23, 0.31) | (6.39, 0.09) | (0, 0) | (1950.05, 28.89) | |
| (1163.52, 21.89) | (334.4, 6.29) | (198.7, 3.74) | (113.61, 2.14) | (1810.22, 34.05) | ||
| (2551.06, 27.6) | (290.06, 3.14) | (144.87, 1.57) | (78.9, 0.85) | (3064.89, 33.16) | ||
| Level 2 | (1982.58, 29.37) | (419.35, 6.21) | (14.38, 0.21) | (6.53, 0.1) | (2422.85, 35.89) | |
| (751.45, 14.14) | (619.35, 11.65) | (222.9, 4.19) | (53.75, 1.01) | (1647.44, 30.99) | ||
| (2171.5, 23.5) | (745.67, 8.07) | (165.99, 1.8) | (38.67, 0.42) | (3121.83, 33.78) | ||
| Level 3 | (119.12, 1.76) | (1343.28, 19.9) | (237.02, 3.51) | (11.24, 0.17) | (1710.65, 25.34) | |
| (60.83, 1.14) | (315.76, 5.94) | (597.3, 11.24) | (137.4, 2.58) | (1111.29, 20.9) | ||
| (129.65, 1.4) | (1347.09, 14.58) | (590.95, 6.39) | (125.45, 1.36) | (2193.15, 23.73) | ||
| Level 4 | (46.86, 0.69) | (76.89, 1.14) | (282.98, 4.19) | (71.81, 1.06) | (478.54, 7.09) | |
| (30.68, 0.58) | (45.85, 0.86) | (341.83, 6.43) | (216.89, 4.08) | (635.25, 11.95) | ||
| (45.53, 0.49) | (70.41, 0.76) | (373.56, 4.04) | (217.16, 2.35) | (706.66, 7.65) | ||
| Level 5 | (5.07, 0.08) | (26.45, 0.39) | (71.10, 1.05) | (85.46, 1.27) | (188.08, 2.79) | |
| (50.43, 0.95) | (20.87, 0.39) | (12.02, 0.23) | (28.44, 0.53) | (111.76, 2.1) | ||
| (0.57, 0.01) | (22.21, 0.24) | (68.02, 0.74) | (64.91, 0.7) | (155.71, 1.68) | ||
| Transfers In | (2153.63, 31.9) | (3369.05, 49.91) | (794.65, 11.77) | (343.27, 5.09) | (89.59, 1.33) | (6750.18, 9.67) |
| (893.38, 16.81) | (1546, 29.08) | (1307.6, 24.6) | (1047.34, 19.7) | (521.64, 9.81) | (5315.96, 7.6) | |
| (2347.25, 25.4) | (3990.78, 43.18) | (1477.31, 15.98) | (966.73, 10.46) | (460.18, 4.98) | (9242.24, 13.2) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ke, L.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, L.; Lu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Q. Spatiotemporal Evolution of Ecosystem Service Value and Its Tradeoffs and Synergies in the Liaoning Coastal Economic Belt. Sustainability 2025, 17, 5245. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125245
Ke L, Jiang Q, Wang L, Lu Y, Zhao Y, Wang Q. Spatiotemporal Evolution of Ecosystem Service Value and Its Tradeoffs and Synergies in the Liaoning Coastal Economic Belt. Sustainability. 2025; 17(12):5245. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125245
Chicago/Turabian StyleKe, Lina, Qingli Jiang, Lei Wang, Yao Lu, Yu Zhao, and Quanming Wang. 2025. "Spatiotemporal Evolution of Ecosystem Service Value and Its Tradeoffs and Synergies in the Liaoning Coastal Economic Belt" Sustainability 17, no. 12: 5245. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125245
APA StyleKe, L., Jiang, Q., Wang, L., Lu, Y., Zhao, Y., & Wang, Q. (2025). Spatiotemporal Evolution of Ecosystem Service Value and Its Tradeoffs and Synergies in the Liaoning Coastal Economic Belt. Sustainability, 17(12), 5245. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125245






