Grazing Exclusion Affects Alpine Meadow Plants’ Root Morphological Traits and Reduces Their Cold Resistance on the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site and Experimental Plots
2.2. Soil Temperature and Moisture Measurements
2.3. Sampling and Analysis
2.4. Comprehensive Evaluation of Cold Resistance
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
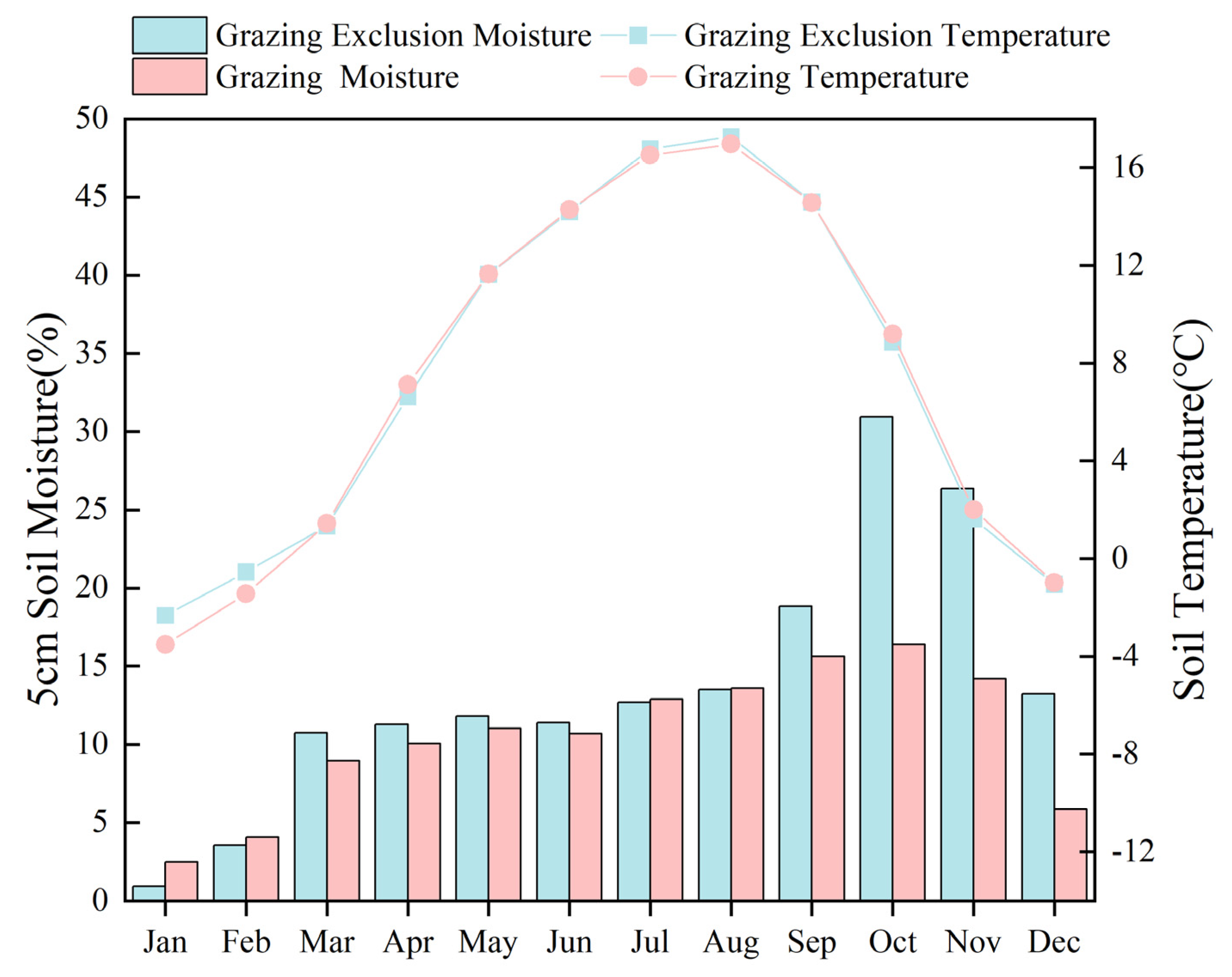
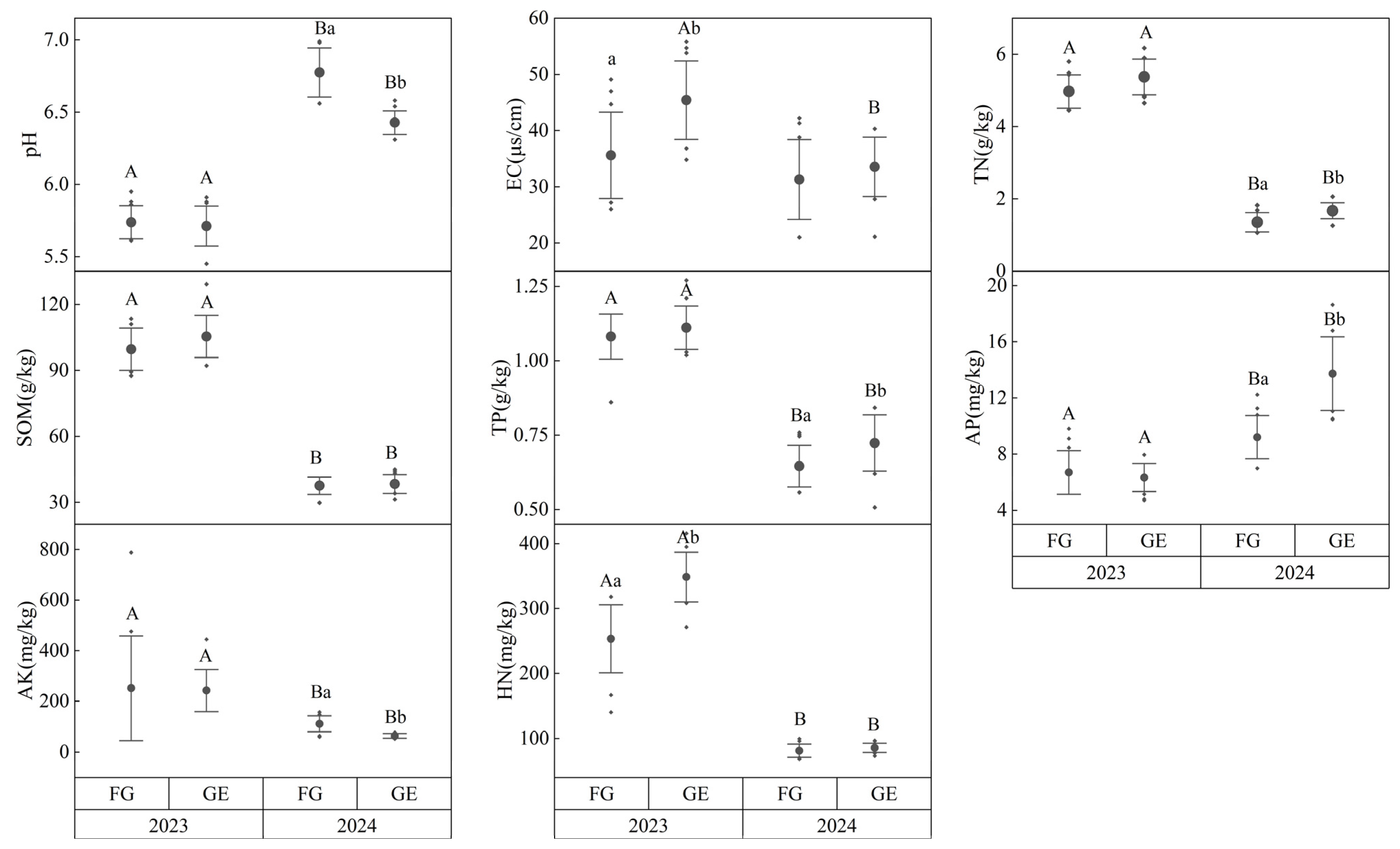
3.1. Results of Soil Temperature, Humidity, and Soil Properties in Grazing Exclusion and Grazing Grasslands
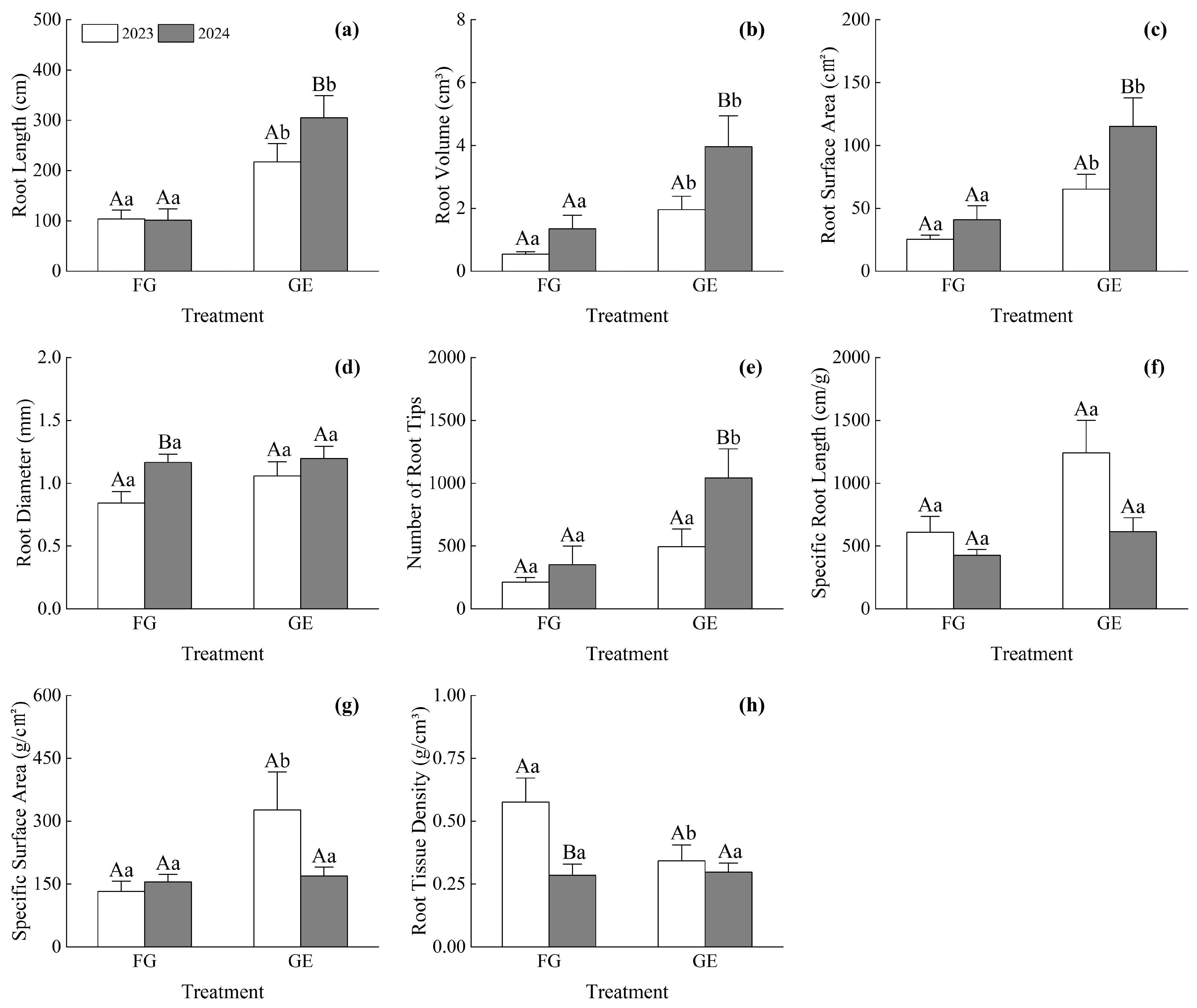
3.2. Differences in Root Morphological Traits
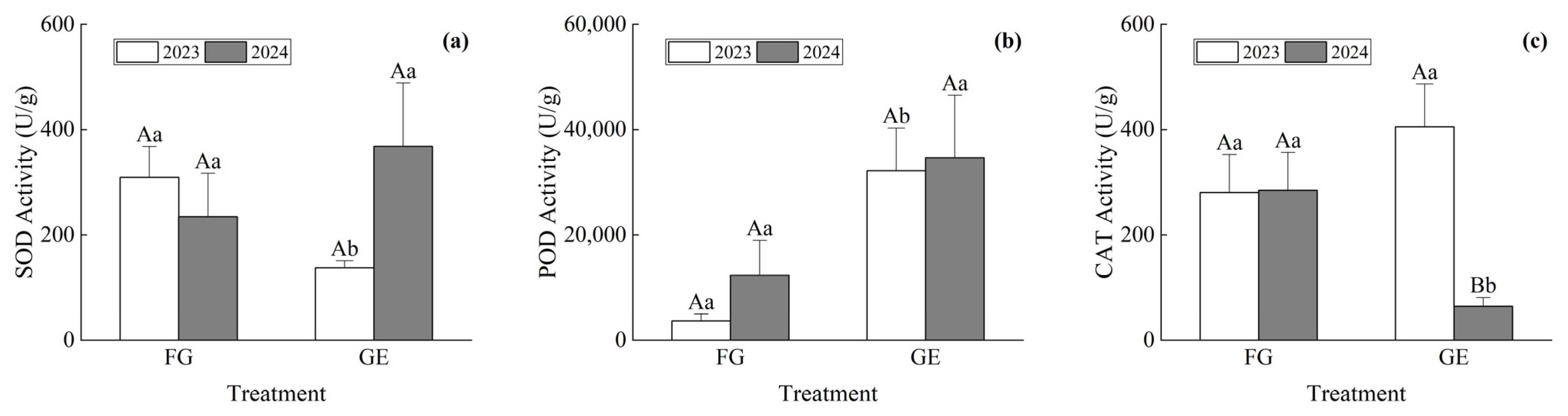
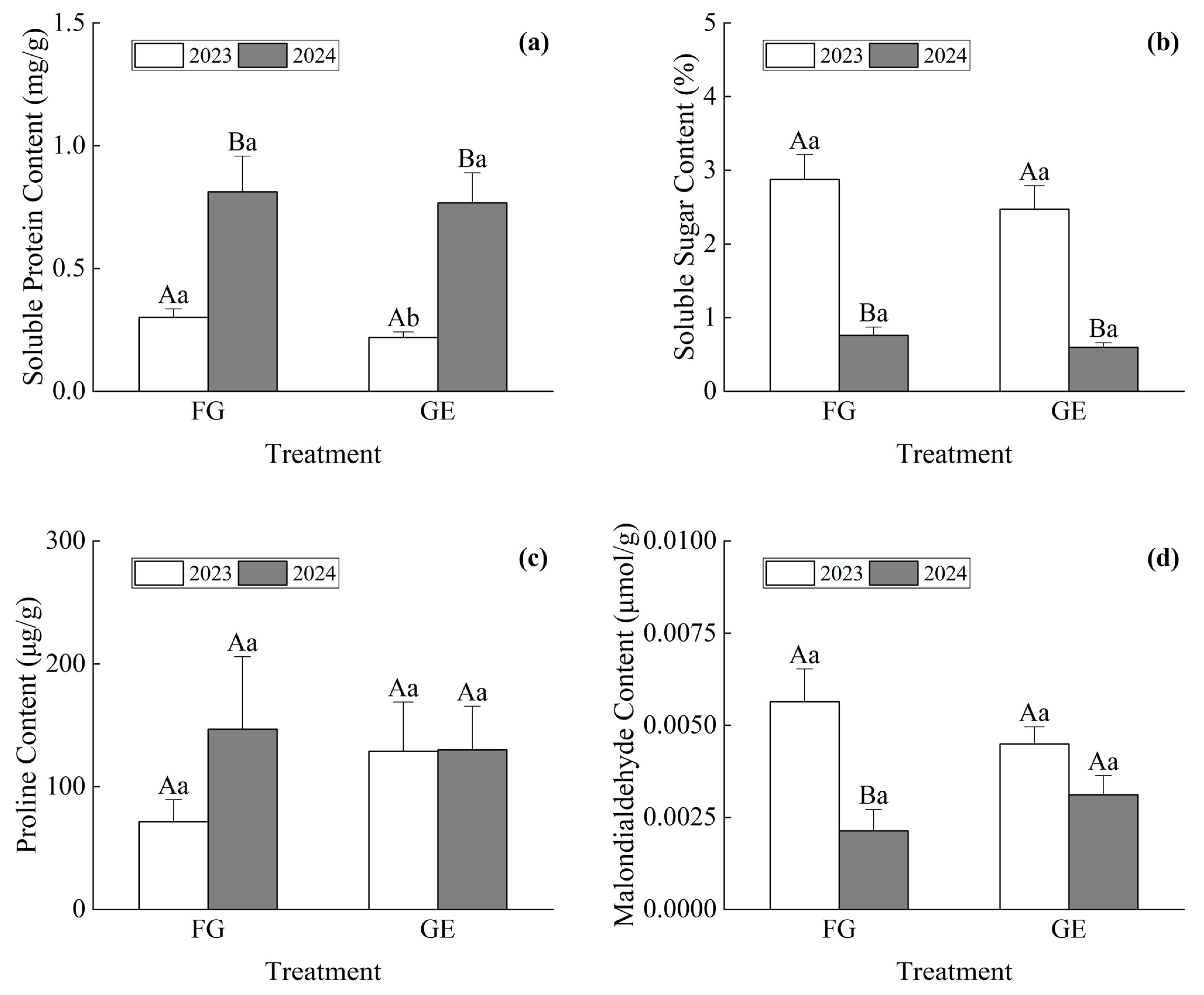
3.3. Plant Cold Resistance Difference
3.4. Comprehensive Evaluation of Plant Cold Resistance
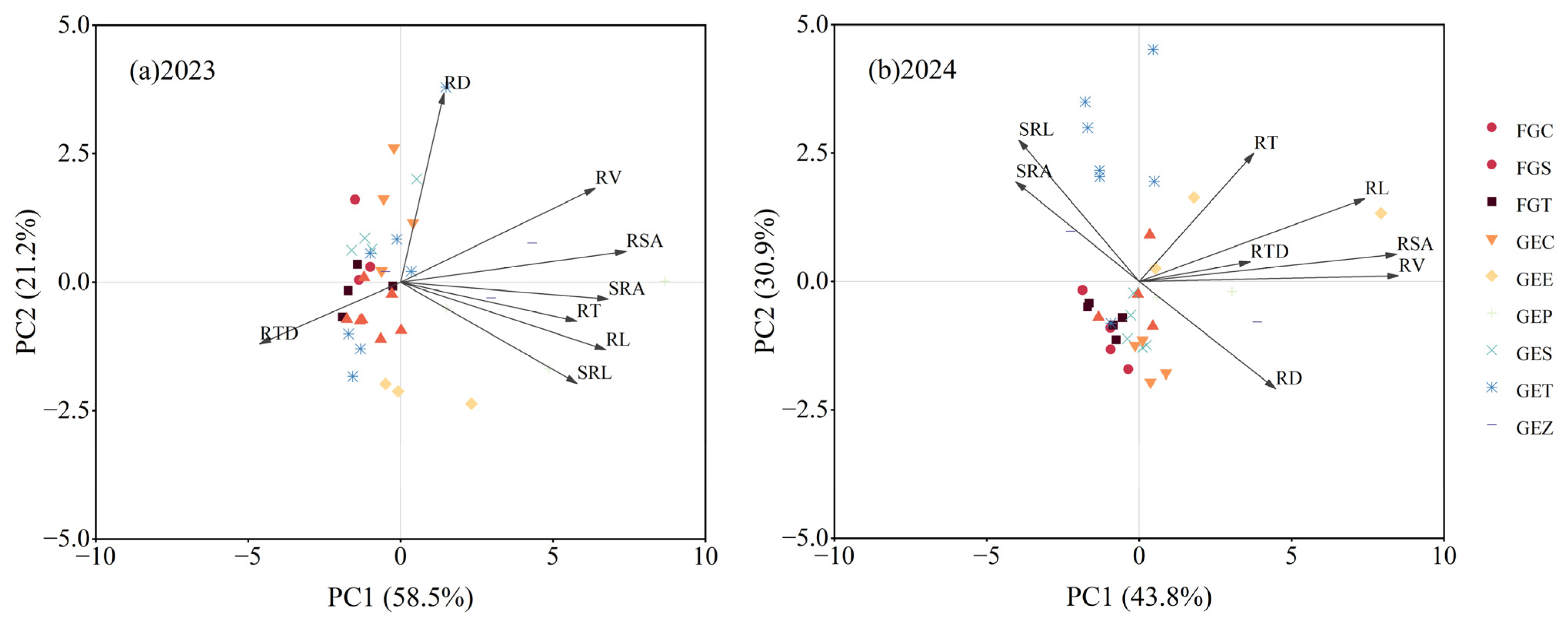
3.5. Correlation Analysis and Redundancy Analysis Between Root Properties and Cold Resistance
4. Discussion
4.1. Changes in Plant Root Characteristics and Trade-Offs Between Root Morphological Traits
4.2. Difference in Cold Resistance and Comprehensive Evaluation
4.3. Relationship Between Physiological Indices of Plant Cold Resistance, Root Morphological Traits, and Soil Properties
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FG | Grazing grasslands | SS | Soluble sugar |
| GE | Grazing exclusion grasslands | SP | Soluble protein |
| EC | Electrical conductance | PRO | Proline |
| SOM | Soil organic matter | MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| TN | Total nitrogen | RL | Root length |
| TP | Total phosphorus | RT | Number of root tips |
| AP | Available phosphorus | RD | Root mean diameter |
| AK | Available potassium | RSA | Root surface area |
| HN | Hydrolyzable nitrogen | RV | Root volume |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase | SRL | Specific root length |
| POD | Peroxidase | SRA | Specific root area |
| CAT | Catalase | RTD | Root tissue density |
References
- Han, Y.; Wu, Y.T.; Cui, J.H.; Li, H.Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.H.; Miao, B.L.; Wang, L.X.; Li, Z.Y.; Liang, C.Z. Temporal Stability of Grazed Grassland Ecosystems Alters Response to Climate Variability, While Resistance Stability Remains Unchanged. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, S.; Bai, Y. Ecosystem structure, functioning and stability under climate change and grazing in grasslands: Current status and future prospects. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2018, 33, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odriozola, I.; García-Baquero, G.; Laskurain, N.A.; Aldezabal, A. Livestock grazing modifies the effect of environmental factors on soil temperature and water content in a temperate grassland. Geoderma 2014, 235–236, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Li, P.; Li, T.; Zhou, X.L.; Liu, Z.L.; Zou, Z.Y.; Zhu, Q.A.; Peng, C.H. Grazing alters vegetation phenology by regulating regional environmental factors on the Tibetan Plateau. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 351, 108479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrallah, H.A.; Balling, R.C. The effect of overgrazing on historical temperature trends. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1994, 71, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarov, V.; Savvinov, G.; Gavrilieva, L.; Gololobova, A. The Effect of Grazing on the Temperature Regime of the Alas Soils of Central Yakutia. Land 2020, 9, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.E.; Meacham-Hensold, K.; Lemonnier, P.; Slattery, R.A.; Benjamin, C.; Bernacchi, C.J.; Lawson, T.; Cavanagh, A.P. The effect of increasing temperature on crop photosynthesis: From enzymes to ecosystems. J. Exp. Bot. 2021, 72, 2822–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saharan, B.S.; Brar, B.; Duhan, J.S.; Kumar, R.; Marwaha, S.; Rajput, V.D.; Minkina, T. Molecular and Physiological Mechanisms to Mitigate Abiotic Stress Conditions in Plants. Life 2022, 12, 1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, X.; Li, F.; Tao, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Q. Response of Alfalfa Root Traits to Fall Dormancy and Its Effect on Winter Hardiness. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2015, 48, 1689–1701. [Google Scholar]
- Castonguay, Y.; Laberge, S.; Brummer, E.C.; Volenec, J.J. Alfalfa winter hardiness: A research retrospective and integrated perspective. In Advances in Agronomy; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; Volume 90, pp. 203–265. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Wan, L.; Li, S.; Li, X.; He, F.; Tong, Z. Plastic response of Medicago sativa L. root system traits and cold resistance to simulated rainfall events. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velikova, V.; Yordanov, I.; Edreva, A. Oxidative stress and some antioxidant systems in acid rain-treated bean plants—Protective role of exogenous polyamines. Plant Sci. 2000, 151, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Shi, F. Dynamic Analysis of Physiological and Biochemical Substances in Two Types of Root Type Alfalfa during Overwintering Period. Legume Res.-Int. J. 2024, 11, 1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janmohammadi, M.; Zolla, L.; Rinalducci, S. Low temperature tolerance in plants: Changes at the protein level. Phytochemistry 2015, 117, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janska, A.; Marsik, P.; Zelenkova, S.; Ovesna, J. Cold Stress Acclim—What Is Important Metab. Adjust? Plant Biol. 2010, 12, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cong, B.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Du, X.; Tian, Y. Correlation Analysis of Cold Resistance and Antioxidant Enzyme Activities in Alfalfa Roots. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2021, 29, 244–249. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, J. Carbon storage in grasslands of China. J. Arid. Environ. 2002, 50, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahmen, S.; Poschlod, P.; Schreiber, K.-F. Conservation management of calcareous grasslands. Changes in plant species composition and response of functional traits during 25 years. Biol. Conserv. 2002, 104, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.A.; Xiong, W.; Xu, Y.Y.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, E.X.; Zhan, W.; He, Y.X.; Zhu, D.; Zhu, Q.A.; Peng, C.H.; et al. Soil properties and species composition under different grazing intensity in an alpine meadow on the eastern Tibetan Plateau, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.Y.; Xu, G.P.; Chao, Z.G.; Wang, S.P.; Lin, X.W.; Hu, Y.G.; Zhang, Z.H.; Duan, J.C.; Chang, X.F.; Su, A.L.; et al. Effect of warming and grazing on litter mass loss and temperature sensitivity of litter and dung mass loss on the Tibetan plateau. Glob. Change Biol. 2010, 16, 1606–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.A.; Zhu, Q.A.; Zhan, W.; Xu, Y.Y.; Zhu, E.X.; Gao, Y.H.; Li, S.Q.; Zheng, Q.Y.; Zhu, D.; He, Y.X.; et al. The linkage between vegetation and soil nutrients and their variation under different grazing intensities in an alpine meadow on the eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 110, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.K.; Shang, Z.H.; Gao, J.X.; Boone, R.B. Enhancing sustainability of grassland ecosystems through ecological restoration and grazing management in an era of climate change on Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 287, 106684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, R.B. Rangeland degradation on the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau: A review of the evidence of its magnitude and causes. J. Arid. Environ. 2010, 74, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.Z.; Giese, M.; Lin, S.; Sattelmacher, B.; Zhao, Y.; Brueck, H. Belowground net primary productivity and biomass allocation of a grassland in Inner Mongolia is affected by grazing intensity. Plant Soil. 2008, 307, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.B.; Ding, W.Q. Grazing led to an increase in the root: Shoot ratio and a shallow root system in an alpine meadow of the Tibetan plateau. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1348220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, W.M.; Fang, Y.; Zhou, M.; Xie, T.; Li, L.H.; Zhang, W.H. Heavily intensified grazing reduces root production in an Inner Mongolia temperate steppe. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 200, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.T.; Zhong, M.Y.; Liu, Y.H.; Wu, R.X.; Shao, X.Q. Covariation in root traits of Leymus chinensis in response to grazing in steppe rangeland. Rangel. J. 2019, 41, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, X.; Liang, C.Z.; Liang, M.W.; Han, W.H.; Li, Z.Y.; Miao, B.L.; Wang, W.; Wang, L.X. Seasonal dynamics of belowground biomass and productivity and potential of carbon sequestration in meadow steppe and typical steppe, in Inner Mongolia, China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2014, 34, 5530–5540. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, G.; Zhou, X.; He, Y.; Shao, J.; Hu, Z.; Liu, R.; Zhou, H.; Hosseinibai, S. Grazing intensity significantly affects belowground carbon and nitrogen cycling in grassland ecosystems: A meta-analysis. Glob. Change Biol. 2017, 23, 1167–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Sweeney, S.; Shangguan, Z.P. Grassland responses to grazing disturbance: Plant diversity changes with grazing intensity in a desert steppe. Grass Forage Sci. 2014, 69, 524–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.M.; Ding, K.Y.; Li, Z.W. Comparison of soil carbon and nitrogen stocks at grazing-excluded and yak grazed alpine meadow sites in Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau, China. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 87, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.J.; Wei, C.; Adamowski, J.F.; Biswas, A.; Li, Y.M.; Zhu, G.F.; Liu, C.F.; Feng, Q. On China’s Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, duration of grazing exclosure alters R:S ratio, root morphology and attending root biomass. Soil. Tillage Res. 2021, 209, 104969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.S.; Jing, G.H.; Jin, J.W.; Wei, L.; Liu, J.; Cheng, J.M. Identifying drivers of root community compositional changes in semiarid grassland on the Loess plateau after long-term grazing exclusion. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 99, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.H.; Wu, Q.G.; Hu, J.Y.; Yu, L.F.; Bie, P.F.; Wang, H.; Deng, D.Z. Changes in Soil Physical and Chemical Properties During the Process of Alpine Meadow Degradation along the Eastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Eurasian Soil. Sci. 2018, 51, 1440–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhu, Q.A.; Peng, C.H.; Wu, N.; Wang, Y.F.; Fang, X.Q.; Gao, Y.H.; Zhu, D.; Yang, G.; Tian, J.Q.; et al. The impacts of climate change and human activities on biogeochemical cycles on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Glob. Change Biol. 2013, 19, 2940–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadauria, T.; Li, Z.; Xie, Y.; Ning, X.; Zhang, X.; Hai, Q. Spatial distributions of salt-based ions, a case study from the Hunshandake Sandy Land, China. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0271562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Yang, C.; Wang, P.; Bao, A.; Ma, Q. Effect of low-temperature stress on the physiological responses of six gramineous forages in alpine regions and evaluation of their cold resistance. Pratacultural Sci. 2021, 38, 2019–2028. [Google Scholar]
- Schönbach, P.; Wan, H.W.; Gierus, M.; Bai, Y.F.; Müller, K.; Lin, L.J.; Susenbeth, A.; Taube, F. Grassland responses to grazing: Effects of grazing intensity and management system in an Inner Mongolian steppe ecosystem. Plant Soil. 2011, 340, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wu, G.L.; Zhu, Y.J.; Shi, Z.H. Grazing exclusion effects on above- and below-ground C and N pools of typical grassland on the Loess Plateau (China). Catena 2014, 123, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.B.; Deng, L.; Ren, Z.P.; Li, J.P.; Shangguan, Z. Grazing exclusion significantly improves grassland ecosystem C and N pools in a desert steppe of Northwest China. Catena 2016, 137, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.L.; Liu, Z.H.; Zhang, L.; Chen, J.M.; Hu, T.M. Long-term fencing improved soil properties and soil organic carbon storage in an alpine swamp meadow of western China. Plant Soil. 2010, 332, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardgett, R.D.; Mommer, L.; De Vries, F.T. Going underground: Root traits as drivers of ecosystem processes. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2014, 29, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.R.; Lin, L.; Pang, S.; Guo, X.W.; Cao, G.M.; He, J.S.; Wang, Q.B. Early season precipitation accounts for the variability of fine-root traits in a Tibetan alpine grassland. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2020, 172, 103991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.S.; Wang, L.Q.; Zhang, P.; Liang, J.H.; Wang, X.F. Responses of the root architecture of Stipa grandis to grassland degradation. Pratacultural Sci. 2011, 28, 1962–1966. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.J.; Dong, T.; Gu, C.; Xue, W.J.; Zhao, M.L. Effect of Different Grazing Intensities on Root Characteristics of Stipa grandis. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2015, 37, 86–91. [Google Scholar]
- Glimskär, A. Estimates of root system topology of five plant species grown at steady-state nutrition. Plant Soil. 2000, 227, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.D.; Ma, J.L.; Ma, H.B.; Zhou, Y.; Li, C.; Dong, C. Effects of grazing exclusion on root trait characteristics of dominant plants in the desert steppe. Pratacultural Sci. 2023, 40, 1507–1517. [Google Scholar]
- Beniston, M. Mountain Weather and Climate: A General Overview and a Focus on Climatic Change in the Alps. Hydrobiologia 2006, 562, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.C.; Yan, R.R.; Chen, J.Q.; Xin, X.P.; Eldridge, D.J.; Shao, C.L.; Wang, X.; Lv, S.J.; Jin, D.Y.; Chen, J.Q.; et al. Grazing modulates soil temperature and moisture in a Eurasian steppe. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 262, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.L.; Chen, J.Q.; Li, L.H.; Dong, G.; Han, J.J.; Abraha, M.; John, R. Grazing effects on surface energy fluxes in a desert steppe on the Mongolian Plateau. Ecol. Appl. 2017, 27, 485–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Peth, S.; Reszkowska, A.; Gan, L.; Krümmelbein, J.; Peng, X.H.; Horn, R. Response of soil moisture and temperature to grazing intensity in a Leymus chinensis steppe, Inner Mongolia. Plant Soil. 2011, 340, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.X.; Zhao, R.D.; Zhang, C.; Li, R.; Shao, P. Responses of physiological parameters in plants on sub-alpine meadow to slope aspects. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2017, 28, 2863–2869. [Google Scholar]
- Bowler, C.; Montagu, M.V.; Inze, D. Superoxide Dismutase and Stress Tolerance. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 1992, 43, 83–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridovich, I. Superoxide Dismutases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1975, 44, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kučerová, K.; Henselová, M.; Slováková, Ľ.; Hensel, K. Effects of plasma activated water on wheat: Germination, growth parameters, photosynthetic pigments, soluble protein content, and antioxidant enzymes activity. Plasma Process. Polym. 2019, 16, 1800131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.J.; Liu, X.L.; Hsu, C.C.; Du, Y.Y.; Sang, T.; Zhu, C.; Wang, Y.B.; Satheesh, V.; et al. A RAF-SnRK2 kinase cascade mediates early osmotic stress signaling in higher plants. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.R.; Jantalia, C.P.; Reis, V.M.; Döwich, I.; Polidoro, J.C.; Alves, B.J.R.; Boddey, R.M.; Urquiaga, S. Impact of plant growth-promoting bacteria on grain yield, protein content, and urea-15 N recovery by maize in a Cerrado Oxisol. Plant Soil. 2018, 422, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forlani, G.; Bertazzini, M.; Cagnano, G. Stress-driven increase in proline levels, and not proline levels themselves, correlates with the ability to withstand excess salt in a group of 17 Italian rice genotypes. Plant Biol. 2019, 21, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, A.; Yamauchi, A. Root Osmotic Adjustment under Osmotic Stress in Maize Seedlings. 2. Mode of Accumulation of Several Solutes for Osmotic Adjustment in the Root. Plant Prod. Sci. 2006, 9, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.Y.; Pan, Y.; Gong, J.R.; Li, X.B.; Liu, M.; Yang, B.; Zhang, Z.H.; Baoyin, T.G.T. Physiology of Leymus chinensis under seasonal grazing: Implications for the development of sustainable grazing in a temperate grassland of Inner Mongolia. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 271, 110984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, L.L.; Shi, S.L.; Chen, J.G.; Zhu, X.Q.; Guo, Q.E.; Zhao, W.H. Field evaluation of the response and resistance to low temperature of alfalfa root with different root types during over-wintering. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2011, 19, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.B.; Yang, S.Q.; Xin, R.G.; Feng, Y.Z.; Zhang, Q.; Li, P. Changes analysis in physiological properties of several gramineous grass species and cold-resistance comparison on under cold stress. Ecol. Front. 2009, 29, 1341–1347. [Google Scholar]
- Navas, M.L.; Roumet, C.; Bellmann, A.; Laurent, G.; Garnier, E. Suites of plant traits in species from different stages of a Mediterranean secondary succession. Plant Biol. 2010, 12, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitman, T.; Aarssen, L.W. The leaf size/number trade-off in herbaceous angiosperms. J. Plant Ecol. 2009, 3, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasse, J.; Martinoia, E.; Northen, T. Feed Your Friends: Do Plant Exudates Shape Root Microbiome? Trends Plant Sci. 2018, 23, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.D.; Ye, Y.Q.; Guan, Q.W.; Jones, D.L. Organic mulching masks rhizosphere effects on carbon and nitrogen fractions and enzyme activities in urban greening space. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 1621–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.H.; Yu, Z.P.; Wang, M.J.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Z.Q. Litter and root traits control soil microbial composition and enzyme activities in 28 common subtropical tree species. J. Ecol. 2022, 110, 3012–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Gong, J.R.; Baoyin, T.G.T.; Luo, Q.P.; Zhai, Z.W.; Xu, S.; Wang, Y.H.; Liu, M.; Yang, L.L. Effect of Seasonal Grazing on Trade-off Among Plant Functional Traits in Root, Stem and Leaf of Leymus chinensis in the Temperate Grassland of Inner Mongolia, China. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2017, 52, 307–321. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Yan, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Cheng, G. Short-term grazing exclusion has no impact on soil properties and nutrients of degraded alpine grassland in Tibet, China. Solid. Earth 2015, 6, 1195–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffens, M.; Kölbl, A.; Totsche, K.U.; Kögel-Knabner, I. Grazing effects on soil chemical and physical properties in a semiarid steppe of Inner Mongolia (P.R. China). Geoderma 2008, 143, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Xu, X.; Pang, B.; Ma, X.; Wang, X. Significant soil acidification caused by grazing exclusion across China’s grassland areas. Land. Degrad. Dev. 2020, 32, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.-Q.; Epstein, H.; Li, G.-Y. Grazing exclusion did not affect soil properties in alpine meadows in the Tibetan permafrost region. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 147, 105657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Shangguan, Z.-P.; Wu, G.-L.; Chang, X.-F. Effects of grazing exclusion on carbon sequestration in China’s grassland. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2017, 173, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Li, S.; Guo, Q.; Niu, S.; He, N.; Li, L.; Yu, G. A synthesis of the effect of grazing exclusion on carbon dynamics in grasslands in China. Glob. Change Biol. 2016, 22, 1385–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ji, C.; Ma, W.; Wang, S.; Wang, S.; Han, W.; Mohammat, A.; Robinson, D.; Smith, P. Significant soil acidification across northern China’s grasslands during 1980s–2000s. Glob. Change Biol. 2012, 18, 2292–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poschenrieder, C.; Gunse, B.; Corrales, I.; Barcelo, J. A glance into aluminum toxicity and resistance in plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 400, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Treatment | Botanical Name | Frequency | Height (cm) | Abbreviation | Group |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FG | Carex muliensis Hand-Mazz. | 84% | 2 | FGT | non-Gramineae |
| Kobresia pygmaea (C. B. Clarke) C. B. Clarke | 88% | 1 | FGC | ||
| Saussurea pulchra Lipsch. | 60% | 1.5 | FGS | ||
| GE | Carex muliensis Hand-Mazz. | 96% | 10 | GET | |
| Kobresia pygmaea (C. B. Clarke) C. B. Clarke | 96% | 5 | GEC | ||
| Saussurea pulchra Lipsch. | 20% | 20 | GES | ||
| Poa pratensis L. | 50% | 60 | GEZ | Gramineae | |
| Polypogon fugax Nees ex Steud. | 30% | 45 | GEB | ||
| Elymus atratus (Nevski) Hand.-Mazz. | 88% | 50 | GEE |
| Principal Component | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| SOD | 0.280 | 0.670 | 0.120 |
| PRO | 0.500 | −0.030 | 0.310 |
| POD | 0.270 | −0.660 | 0.310 |
| SP | 0.500 | −0.090 | −0.310 |
| CAT | 0.510 | 0.160 | 0.230 |
| MDA | 0.220 | 0.130 | −0.560 |
| SS | −0.210 | 0.250 | 0.580 |
| Contribution rate (%) | 37.569 | 19.462 | 18.481 |
| Eigenvalue | 2.630 | 1.362 | 1.294 |
| Cumulative contribution rate (%) | 37.569 | 57.031 | 75.512 |
| CI1 | CI2 | CI3 | U (X1) | U (X2) | U (X3) | D | Order | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FGT | 2.232 | 1.335 | −0.004 | 1.005 | 0.804 | 0.418 | 0.809 | 1 |
| FGC | 0.694 | 0.496 | −0.691 | 0.670 | 0.558 | 0.150 | 0.514 | 4 |
| FGS | −2.892 | 0.431 | 1.577 | −0.110 | 0.539 | 1.036 | 0.338 | 5 |
| GET | 0.908 | 0.780 | 1.221 | 0.716 | 0.642 | 0.897 | 0.741 | 2 |
| GES | −1.194 | 0.830 | −1.037 | 0.259 | 0.656 | 0.015 | 0.302 | 6 |
| GEZ | −0.562 | −1.257 | −0.694 | 0.397 | 0.044 | 0.149 | 0.245 | 7 |
| GEP | −0.531 | −0.597 | −1.415 | 0.403 | 0.238 | −0.133 | 0.229 | 8 |
| GEE | 1.345 | −2.018 | 1.045 | 0.812 | −0.178 | 0.828 | 0.561 | 3 |
| Weight | 0.498 | 0.258 | 0.245 |
| SOD | PRO | POD | SP | CAT | MDA | SS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RL | −0.128 | 0.011 | 0.373 * | 0.094 | −0.165 | 0.081 | −0.205 |
| RV | −0.176 | −0.216 | 0.089 | 0.117 | −0.254 | 0.026 | −0.335 * |
| RSA | −0.166 | −0.123 | 0.192 | 0.131 | −0.279 * | 0.028 | −0.326 * |
| RD | −0.157 | −0.335 * | −0.137 | 0.080 | −0.147 | −0.104 | −0.309 * |
| RT | −0.045 | −0.049 | 0.197 | 0.256 | −0.238 | −0.027 | −0.396 * |
| SRL | −0.026 | 0.107 | 0.314 * | −0.281 * | 0.260 | 0.129 | 0.144 |
| SRA | −0.055 | 0.009 | 0.292 * | −0.212 | 0.212 | 0.118 | 0.006 |
| RTD | 0.091 | 0.199 | −0.089 | 0.045 | 0.008 | −0.003 | 0.256 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.; Yan, Y. Grazing Exclusion Affects Alpine Meadow Plants’ Root Morphological Traits and Reduces Their Cold Resistance on the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Sustainability 2025, 17, 5010. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17115010
Chen J, Yan Y. Grazing Exclusion Affects Alpine Meadow Plants’ Root Morphological Traits and Reduces Their Cold Resistance on the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Sustainability. 2025; 17(11):5010. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17115010
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Jiuyun, and Yan Yan. 2025. "Grazing Exclusion Affects Alpine Meadow Plants’ Root Morphological Traits and Reduces Their Cold Resistance on the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau" Sustainability 17, no. 11: 5010. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17115010
APA StyleChen, J., & Yan, Y. (2025). Grazing Exclusion Affects Alpine Meadow Plants’ Root Morphological Traits and Reduces Their Cold Resistance on the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Sustainability, 17(11), 5010. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17115010





