1.2. Review of Literature
There are several models in the field of renewable energy prediction that are made to work with varying forecast time spans. These models include statistical models, machine learning models, mathematical–physical method models, and combined prediction models that capitalize on each model’s advantages [
3].
Numerically driven meteorological prediction systems primarily employ Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP) frameworks as their computational foundation. These systems implement atmospheric discretization by dividing the planetary surface into a three-dimensional lattice structure, subsequently performing atmospheric physics computations at nodal intersections through sophisticated differential equation solutions [
4]. These processes include the motion of the atmosphere, radiative transfer, turbulent mixing, etc., and then describe the physical processes in the atmosphere, oceans, and Earth system using multiple sets of mathematical–physical equations, which are based on the laws of physics, such as conservation of mass, conservation of momentum, and the principles of thermodynamics, and are solved in conjunction with the initial observational data [
5].
In recent years, mesoscale NWP models have become an important direction in NWP research. The main models include the High-Resolution Limited Area Model (HIRLAM) [
6], the Fifth-Generation Mesoscale Model (MM5) [
7], the European Center for Medium-Range Weather Forecasting’s model (ECMWF), and the Weather Research and Forecasting Model (WRF) [
8]. Among them, the WRF, with a higher accuracy than traditional numerical weather prediction models and a higher spatial and temporal resolution, is an important tool for the meteorological and atmospheric research community. It has attracted much attention in numerical prediction studies for renewable energy [
9].
Although the mathematical–physical approach is effective in predicting atmospheric dynamics, it requires significant computational resources and a large amount of data to calibrate. It also relies on accurate and comprehensive initial observations to construct the initial state of the model, and the quality and spatial–temporal resolution of these observations have a significant impact on the accuracy of forecasts [
10].
Statistical models are widely used in the field of renewable energy forecasting. For example, Yatiyana et al. (2018) used autoregressive integrated moving averages (ARIMAs) to model the estimation of wind power in Western Australia [
11]. Wang et al. (2018) designed a multistep ahead-of-the-range wind speed prediction technique based on heteroskedasticity multinomial kernel learning and verified its reliability [
12]. Statistical modeling combined with probabilistic forecasting has great advantages in the interval prediction of renewable energy generation, and a large number of interval prediction methods have been developed, among which quantile regression combined with kernel density estimation is an important research direction. Kernel density estimation is a nonparametric method for evaluating the probability density function of a random variable without any distributional assumptions. The purpose of kernel density estimation is to smooth the contribution of each sample by applying a kernel function of a given width to each data sample [
13], and this method has been widely used for the interval prediction of renewable energy sources due to its flexibility, efficiency, and smoothness. For example, Hwangbo et al. (2019) proposed an interval prediction framework based on a combination of neural network and kernel density estimation methods and applied it to distributed PV power generation prediction, and the simulation results showed that the method can construct more accurate prediction intervals [
14].
Although statistical models are heavily used and have great advantages in renewable energy interval forecasting, statistical models rely on the original distribution of data and require high-quality original data; secondly, the methods of quantile regression and kernel density estimation, which are heavily used in interval forecasting, require a large amount of data for probability density estimation, which is not suitable for medium- to long-term forecasting scenarios because the amount of data becomes small.
Prediction models based on machine learning methods have been more advantageous than mathematical–physical method models and statistical methods for mining data potential information and data feature extraction in big data situations [
15]. Machine learning methods do not need to describe the model with the help of complex mathematical relationships and assumptions, but use a large number of input and output processes capable of simulating the relationship between historical data and the target results, so they are often able to make accurate predictions in the case of big data, with stronger learning capabilities [
16]. These methods occupy an indispensable position in the field of renewable energy prediction. Lahouar et al. (2017) proposed a random forest (RF) method to achieve advanced wind forecasting without parameter tuning and extended the RF with quantile regression forests to construct confidence intervals for prediction, which significantly improved the prediction accuracy of the algorithm [
17]. Demolli et al. (2019) [
18] used five machine learning algorithms, including the least absolute shrinkage selection operator (LASSO), K Nearest Neighbor (KNN), Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost), Random Forest (RF), and Support Vector Regression (SVR), to perform short-term wind power forecasting based on daily wind speed data. The results showed that the use of machine learning algorithms had an excellent performance in wind power forecasting [
18].
Advancements in computational technologies, particularly through GPU-accelerated parallel computing architectures, have revolutionized deep learning implementation by substantially addressing historical computational bottlenecks in parameter optimization and iterative training processes [
19]. Deep learning, as a component of machine learning, has been rapidly developing in the field of renewable energy prediction in recent years. As an important branch of machine learning, a large number of neural network models have been applied in the field of renewable energy prediction, and deep convolutional neural networks [
20], deep recurrent neural networks [
21], and stacked limit learning machines are frequently used for renewable energy prediction [
22]. It is widely recognized that deep learning-based neural networks have demonstrated a superior performance in terms of accuracy, stability, and effectiveness in prediction [
23].
Machine learning and its important branch of deep learning play important roles in the field of renewable energy prediction, but due to the need for a large amount of data, methods currently focus on the short-term and ultra-short-term prediction of renewable energy prediction, which is not necessarily excellent for long-term prediction.
Since renewable energy forecasting is affected by many factors and is characterized by nonlinearity and no smoothness, a single model structure struggles to accurately capture data characteristics, so the forecasting effect is often poor. Combined modeling methods that combine the advantages of multiple models can achieve better prediction results than direct modeling using raw data, so combined models are widely used in the field of renewable energy prediction [
24]. Among them, using data decomposition to construct parallel combinatorial forecasts is the most common practice, and the commonly used data decomposition methods are wavelet decomposition (WD) and empirical modal decomposition (EMD). Liu et al. (2021) addressed the problem of inherent fluctuations and potential information difficult to mine in ultra-short-term forecasting methods for renewable energy, utilized wavelet decomposition (WT) to decompose the raw data into simple primitive sequences, fused them with the Attention mechanism, and constructed an ultra-short-term wind and photovoltaic power forecasting method based on the Self-Attention mechanism with the WT-BiLSTM [
25]. Zheng et al. (2020) used wavelet decomposition to decompose one-dimensional sequences into high-dimensional information and constructed a support vector machine prediction model based on wavelet decomposition [
26]. Luo [
27] et al. (2021), Lv [
28] et al. (2022), and Wu [
29] et al. (2019) built a combined prediction model based on the decomposition of original sequences into different sub-sequences based on the data decomposition method, although as the dimension of the data increased, the complexity of each subsequence decreased.
In the field of long-term renewable energy generation forecasting, the characterization of nonlinear periods has been an important factor affecting model construction and forecasting accuracy. To solve these problems in the long-term forecasting of renewable energy generation, grey forecasting is an excellent solution. Compared with other prediction methods, it does not have strict requirements for data distribution, and at the same time, it can effectively deal with the prediction problems of highly uncertain systems in the case of “small data” through grey information generation and grey information mining techniques [
30].
A large number of grey forecasting theory studies have developed many seasonal grey forecasting models to address the periodical seasonality in long-term renewable energy generation forecasting. These models are optimized mainly considering two aspects, data preprocessing and changing the model structure to optimize the model. In terms of data preprocessing, Wang et al. (2017) used the method of data grouping to seasonally group periodical seasonal data, increase the “quasi-exponentiality” characteristics of the original data, and improve the predictive performance of the grey prediction model [
31]. Based on this idea, a series of optimization models were derived, for example, Chen et al. (2021) proposed a seasonal grey prediction model (AWBO-DGGM (1,1)) by combining the buffer operator and the DGGM (1,1) model and applied it to the prediction of the electricity consumption of industrial enterprises in Zhejiang Province [
32]. Li et al. (2023) proposed a fractional-order cumulative prediction model based on a weighted average weakened buffer operator, which was based on the fractional-order cumulative seasonal grouping grey prediction model (WAWBO-FSGGM (1,1)) for accurate hydroelectric power generation prediction [
33]. Wang et al. (2023) introduced a smoothing coefficient
into the DGGM (1,1) model and used the exponential smoothing coefficient
for time series with different seasonal fluctuation characteristics to construct the ESM-DGGM (1,1) model, which further optimized the DGGM (1,1) [
34]. Zhou et al. (2021) proposed a new DGSTM (1,1) grey seasonality model [
35].
In terms of data preprocessing, another approach is to draw on the parallel combinatorial forecasting method, which uses data decomposition to increase the number of time series while reducing the complexity of the time series, integrating these time series using different forecasting methods [
36]. For example, Wang et al. (2022), based on spectral analysis, decomposed data and built a grey prediction model for the trend term and a Fourier prediction model for the periodic term, and then accumulated the predicted values [
37]. Zhang et al. (2021) constructed a prediction model based on a least squares support vector machine, based on Fourier analysis, to de-fit the multi-periodicity of data and correct the random residual terms in the sequence to improve the prediction accuracy of the model [
38]. Combining the theory of the component composition of time series and spectral analysis to decompose them using the idea of combinatorial forecasting is great progress for the prediction of cyclic seasonal data, and in addition to the integration of different forecasting models for separate sequences, the use of seasonal factors for data reduction is also an important method. For example, Qian et al. (2020) used HP filter decomposition to decompose data into periodical and trend terms for systems with periodical fluctuations and used seasonal factors to reduce the data. The model was able to realize the effective prediction of the evolution trend of systems with “periodical fluctuations”, and achieved a better result in the application of wind power generation prediction [
39]. On this basis, Ran et al. (2023) proposed the EMD-DGM model, further mining the data characteristics of periodical seasonality based on EMD decomposition theory to enhance the predictive ability of the model [
40]. Sui et al. (2021) designed a moving average filter, which not only realized the identification of the seasonal and trend characteristics of seasonal time series, but also extended the seasonal periodical from four to twelve periods [
41].
Structural modifications for periodicity adaptation in nonlinear time series analysis have emerged as a critical strategy in grey system theory. The seminal SGM (1,1) framework was introduced by pioneered seasonal modeling through innovative aggregation operators, establishing a methodological foundation that has since evolved through successive refinements to enhance predictive robustness [
42]. Li et al. (2023) developed a new structurally adaptive fractional time lag grey prediction model (FTDNSGM (1, m)) for nonlinear systems [
43]. He et al. (2022) introduced fractional dynamic weighting coefficients to define a new information preference, satisfying the new information preference principle of cumulative generation operators and establishing a new structure-adaptive new information priority discrete grey prediction model to realize the effective use of system information under “small data” and “poor information” [
44]. Wang et al. (2020) introduced seasonal dummy variables as grey actors into the traditional GM (1,1) model, and proposed a GM (1.1) model with seasonal dummy variables (GMSD (1,1)) [
45]. Zhou et al. (2021) fused dummy variables, a fractional-order cumulative operator, and seasonal features and developed a least-squares support vector regression with a seasonal grey forecasting model (GSLSSVR) [
46]. Qian et al. (2021) added periodicity and nonlinear terms into the model structure to enhance the traditional DGM (1,1) model’s ability to capture nonlinear features and linear development trends, which can achieve adaptability to arbitrary periodic time series [
47]. These two processing ideas have different characteristics, as shown in
Table 1.
1.3. Innovations
In terms of forecasting methods, mathematical–physical models, statistical prediction models, and machine learning models are not suitable for long-term forecasting due to the late development of China’s renewable energy industry and the small amount of data available. The long-term forecasting of China’s renewable energy generation encounters a complex and highly uncertain system with “poor information” and “small data” due to China’s geographic location and many interfering factors due to climate characteristics. The traditional grey prediction model has a natural advantage for the prediction problem of highly uncertain complex systems with “poor information” and “small data” [
48]. However, for the seasonal data characteristics of long-term renewable energy prediction, the traditional grey prediction model is ineffective. A large number of grey optimization models, from the perspectives of data preprocessing and the complexity of the prediction model structure, respectively, can be used to build some powerful seasonal grey prediction models. With these two ideas, however, there are still some limitations. For example, after addressing the model structure complexity, the number of parameters to be estimated increases, which often requires intelligent algorithms to carry out auxiliary calculations, with considerable technical difficulties. Meanwhile, traditional data preprocessing will destroy the information of the original data and reduce the interpretability of the model, which increases the difficulty of promoting the methodological model in practical application scenarios.
Based on the above, the innovations of this paper are as follows:
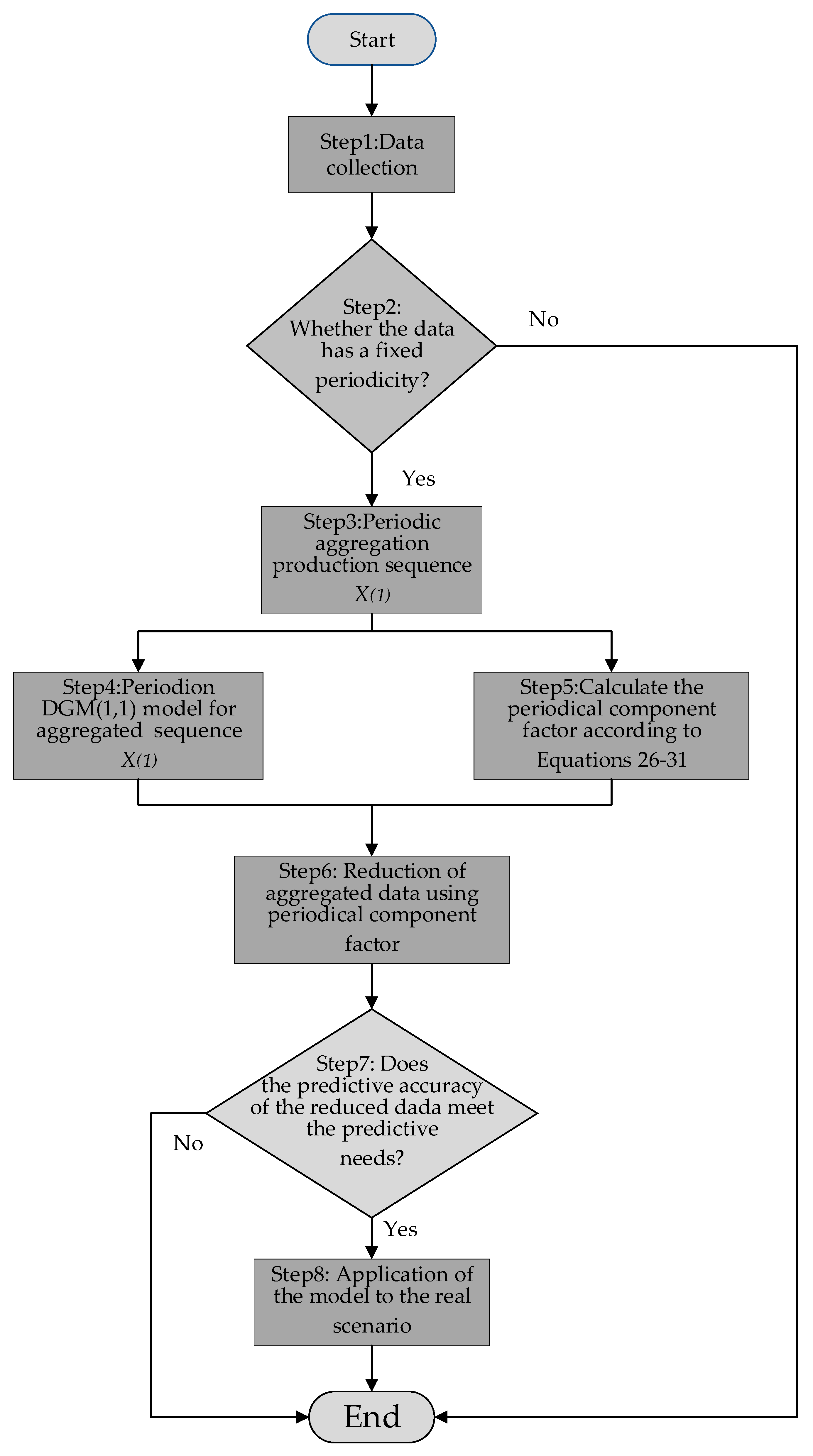
(1) A new seasonal grey prediction model based on periodical aggregation and periodical component factors is proposed. Based on the data-driven perspective, the model improves the existing seasonal grey prediction model by utilizing the grey prediction theory, data preprocessing technology, and seasonal factor theory, and proves the superiority and validity of the newly proposed model through a comparative analysis of two cases.
(2) Based on the classical seasonal grey model, which cannot effectively explore the potential information of seasonal time series, making the model’s interpretability low, the model structure complicated, and technical implementation difficult, the newly proposed model is based on the data preprocessing method of periodical aggregation, which effectively uses the characteristics of periodical seasonal data and constructs a model with a simple structure and strong interpretability of the prediction steps, solving the problems of the existing classical seasonal grey forecasting model to a certain extent.